CT in the Evaluation of the Orbit and the Bony Interorbital Distance
|
|
|
- Miranda Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 265 CT in the Evaluation of the Orbit and the Bony Interorbital Distance Mahmood F. Mafee' Samuel Pruzansky 2 Manuel M. Corrales' Mohan G. Phatak' Galdino E. Valvassori' Glen D Dobben' Vlastimil Capek' The distance between the orbits and their individual dimensions are important in the diagnosis of craniofacial anomalies. Most observers rely on standard radiographs for measuring the bony interorbital distance. Tomography of the skull base and orbital computed tomography (CT) can also be used. This article describes the normal range of the bony interorbital distance and other useful orbital linear and angular measurements as determined from a series of CT scans of the orbits in 400 adults who had CT for other purposes. The normal interorbital distance measured at the posterior border of the frontal processes of the maxilla on nonrotated scans, in the plane of the optic nerve, ranges from 2.29 to 3.21 cm (average, 2.67 cm) in men and 2.29 to 3.20 cm (average, 2.56 cm) in women. The widest interorbital distance lies behind the posterior poles of the globes. This ranges from 3.16 to 4.10 cm (average, 3.37 cm) in men and 2.93 to 3.67 cm (average, 3.20 cm) in women. The eyes are often involved in craniofacial malformations, which includes orbital clefts and orbital hypotelorism and hypertelorism. Measurement of the bony interorbital distance is useful in establishing the severity of the hypertelorism. Surgical treatment of hypertelorism involves translocation of the globes toward the midline by lateral wall osteotomy at a point posterior to the equator of the eye [1]. The degree of hypertelorism and character of the lateral orbital wall determine the type of lateral wall osteotomy [1]. Computed tomography (CT) is very helpful in preoperative evaluation of such patients. The CT scan may also show an encephalocele or a porencephalic cyst as an additional feature of the malformation [2]. This is a report of measurements of the normal orbit with reference to hypertelorism and other anomalies. Materials and Methods Received April 1, 1981 ; accepted after revision August 9, Presented at the annual meeting of the American Roentgen Ray Society, San Francisco, March Deceased. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of Illinois Hospital, Chicago, IL Address reprint requests to M. F. Mafee, Department of Radiology, Eye and Ear Infirmary, 1855 W. Taylor St., Chicago, IL Center for Craniofacial Anomalies, University of Illinois Hospital, Chicago, IL AJNR 7: , March/April /86/ American Society of Neuroradiology Four hundred adults (200 men aged 18-82, average age 52; 200 females aged 17-88, average age 54) were examined with the General Electric CT 7800 scanner (+500 to -500 scale). To obtain uniform images for linear measurements, the window width and level were set at 250 and 50, respectively, for all cases. Data were collected from patients with normal orbits who were studied for suspicion of brain infarction, hearing loss, and brain tumors. None had any underlying craniofacial anomaly or congenital malformations. The patients were Caucasian except for a few who were Oriental. In all instances 5 or 10 mm sections were obtained parallel to the infraorbital-meatal plane. The optic nerve and canal are roughly parallel to this plane. For this study, data were collected only from the nonrotated axial sections in the plane of the optic nerves (fig. 1 A). The horizontal CT sections through the orbits at this level generally show two patterns: (1) a parallel separation of the medial orbital walls and (2) a fusiform or lateral spread of the ethmoidal air cells with the widest separation of the orbital walls occurring posterior to the posterior pole of the globe. The distance between the medial walls of the bony orbits at various points and other linear and angular measurements are illustrated in figures 1 and 2. Several reference points have been used. Anterior pole is applied to the central point of the anterior curvature of the eyeball and posterior pole to the central point of its posterior
2 266 MAFEE ET AL. AJNR :7, March/April 1986 A 8 Fig. 1.-A, Axial CT scan of orbits at level of plane of optic nerves shows outline of globes, lenses, vitreous bodies, level of medial check ligaments (3), medial and lateral rectus muscles, optic nerves, and retroorbital fat compartments. Note nasal bone (1) and frontal process of maxilla (2) on each side. Frontal process of maxilla forms most anterior part of medial wa ll of bony orbit. Lacrimal bone is seen as a thin, increased density immediately posterior to frontal process of maxilla. Lamina papyracea is seen as very thin density hardly distinguishable from medial aspect of medial rectus. Posterior to that is most posterior part of medial wall of bony orbit (4), which is related to anterior part of sphenoid sinus. (Reprinted from [3].) B, Diagram showing different points selected for various measurements presented in table 1. 2A Fig. 2.-A, Axial CT scan of head at level of planum sphenoid ale and anterior roots of lesser wings of sphenoid shows cranial openings (arrows) of optic canals. B, Diagram showing structures in A. A = cranial opening of optic canal; B = anterior root of lesser wing of sphenoid ; C = posterior border of chiasmatic groove; D = planum sphenoidale; E = tuberculum sellae; F = pituitary fossa ; G = middle clinoid; H = dorsum sellae; I = posterior clinoid; J = midportion of cranial opening of optic canal ; K = anterior clinoid; L = anterior border of chiasmatic groove. 28 Fig year-old girl with left microphthalmia. Posteroanterior view of skull. Left orbital plate of frontal bone (vertical arrows), left lesser wing of sphenoid (2), and left maxillary sinus are hypoplastic; superior orbital fissures are asymmetric (1). Note difference between oblique lines (horizontal arrows), which represent cortices of temporal surface of great wings of sphenoid bone. curvature. These points are designated as point A and point P, respectively (fig. 1). A line joining the two poles forms the optic axis (AP). The primary axes of the two eyeballs are nearly parallel. The lacrimal bone and the lamina papyracea cast a thin line of increased density posterior to the frontal process of the maxilla. CT is the best method to evaluate the course and angle of the optic nerves. The optic canal can also be demonstrated. The cranial opening of the optic canal is well demonstrated in figure 2A. The optic canal lies between the two roots of the lesser wing and is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid bone. The anterior root is broad and flat and is continuous with the planum sphenoidale. The posterior root is shorter and thicker and connected to the body of the sphenoid opposite the posterior border of the sulcus chiasmatis. In figure 2, the JJ line is considered the distance between the central optic canals at their cranial openings. With regard to the globe, the AP distance (fig. 1) is considered the anteroposterior diameter and the TT distance is considered the transverse diameter of the eyeball. For the measurement of the transverse diameter of the globe exclusive of the thickness of the lateral and medial rectus muscles, measurements were obtained with the cursor placed at the junction of the scleral ring and images of the rectus muscle. For the measurement of the eyeball diameters, no attempt was made to correlate the values obtained with possible myopia or hypermetropia. Results Our results (table 1) show that the medial orbital walls, in a horizontal section taken at the plane of the optic nerves, tend to be parallel or divergent (fig. 1 A). The narrowest interorbital distance at this section level is at the posterior border of the frontal process of the maxilla (fig. 1), and the widest distance is at or posterior to the posterior poles of the eyeballs. There was a slight difference between the right and left eyeball measurements. Discussion In the diagnosis of craniofacial anomalies, thorough radiographic inspection of the cranial vault, orbits, facial bones, and temporal bones and their interrelationships yields useful diagnostic information [3]. CT is particularly useful in identifying bony and soft-tissue features in these regions. Anatomic and Developmental Considerations Under normal conditions the eye directs orbital growth. During the first year of life, the eye practically doubles in volume and attains more than 50% of its adult volume [4]. By the end of the third year, 75% of adult volume is achieved (similar to neural growth [4]). The shape of the orbital cranial junction is also influenced by development of the brain and skull [5]. When the brain is underdeveloped but the eye is normal, the orbital plate of the frontal bone is usually elevated into the anterior fossa of the skull. In microcephaly the orbits
3 AJNR :7, March/April 1986 ORBITAL MEASUREMENTS BY CT 267 TABLE 1: CT Orbital Measurements in 400 Adults Measurement (cm) Line, Description Minimum Maximum Mean Male Female Male Female Male Female AA, Approximates interpupillary distance. BB, BIOD measured at posterior border of frontal processes of maxillae ee, BIOD measured posterior or at level of orbital equator (useful orbits).. DO, Distance between anterior margin of frontal processes of zygomatic bones at level of plane of optic nerves... EE, Distance between optic nerves where they enter eyeballs FF, BIOD measured at level of posterior poles of eyeballs GG, BIOD measured at its widest part (usually posterior to FF line) HH, BIOD measured at its most posterior part (apex of bony orbit) II, Distance between superior orbital fissures at apex of bony orbit. JJ, Distance between central portion of cranial opening of optic canals. KK, Distance between tips of anterior clinoid processes EI, Length of intraorbital part of optic nerve: Right Left AP, Anteroposterior diameter of eyeball : Right Left TT, Transverse diameter of eyeball: Right Left Angle between optic nerve axes (in degrees) Note.-BIOD = bony interorbital distance. Fig. 4.- ln mandibulofacial dysostosis, orbits often show deficiency of lateral orbital floor, representing orbital cleft. In severe malar hypoplasia, lateral orbital wall is formed by greater wing of sphenoid and zygomatic process of frontal bone. (Courtesy of Samuel Pruzanskyand Paul Tessier.) antimongoloid axis of orbit z ygomatic P""oces 5 i of temperal bone are usually circular and the roofs are highly arched [5]. When the eye is underdeveloped but the brain is normal, the orbital plate of the frontal bone appears hypoplastic and the vertical or calvarial part is usually normal (fig. 3). In coronal suture synostosis, the orbit on the side of fusion is elongated superiorly and laterally imparting a harlequin appearance (plagiocephaly). Correction of the cranial deformity can lead to spontaneous correction of the orbital deformity in some instances [6]. In mandibulofacial dysostosis the orbits may be defective inferolaterally due to malar bone hypoplasia. With tomography the deficiency of the lateral orbital floor (orbital cleft) can be demonstrated [3]. In cases of severe malar hypoplasia the laterall wall of the orbit is formed by the greater wing of the sphenoid and the zygomatic process of the frontal bone (fig. 4). The medial wall of the orbital cavity is extremely thin, except in its most posterior portion, where it is related to the anterior
4 268 MAFEE ET AL. AJNR :7, March/April1986 Fig. 5.-Caldwell (inclined posteroanterior) view of skull. Lamina papyracea of ethmoid is demonstrated by two lines on each side. Horizontal arrows poin t to anterior part of lamina papyracea and lower vertical arrows point to posterior part of it. Upper vertical arrows point to black dots, which indicate points at which usually interorbital distance is measured on radiograph. (Reprinted from 131.) A Fig year-old boy born without a nose and with Left microphthalmus and apparent hypertelorism. A, Left globe slightly smaller than right. Increased soft tissue between medial wall of orbit and globe anteriorly has clinical appearance of hypertelorism. In fact, interorbital bony distance is normal. e, Coronal view. Irregular, thick compact bone in anterior midface with absent nasal structures and maxillary sinuses. B portion of the sphenoid sinus and forms its lateral wall. This orbital wall slopes gently downward and laterally into the floor. This is best seen on the Caldwell view of the skull (fig. 5), where the anterior and posterior parts of the lamina papyracea are well demonstrated. The lacrimal bones, which are the smallest and the most fragile of the cranial bones, are situated at the front of the medial walls of the orbits. Their anterior border articulates with the frontal process of the maxilla, the posterior border with the orbital plate (lamina papyracea) of the ethmoid (fig. 1 A). The value of CT can be appreciated in a patient with severe nasomaxillary hypoplasia who was found clinically to have hypertelorism (fig. 6). CT clearly shows the nasal and maxillary deformity. The bony interorbital distance is normal. Increased soft tissue in the nasoorbital angles has created the appearance of pseudohypertelorism or telecanthus [7]. The bony interorbital distance is an essential measurement in diagnosing orbital hypotelorism or hypertelorism [8-12]. Before CT the principal methods used for such measurements have been based on conventional posteroanterior projection and cephalometric radiography. While such projections may be useful in the study of normal subjects, their utility in pathologic states is questionable. One major problem is that a conventional film is a composite of various structures at different planes; in some patients measurement landmarks are difficult to identify. The best methods to evaluate the bony interorbital distance are base tomography and CT. CT also provides significant information on the orbits, ethmoid, sphenoid sinuses, facial bones, the median and paramedian craniofacial cleft, and central nervous system pathology. The bony interorbital distance was first defined by Cameron (8) in a small number of dried skulls as the maximum distance between the medial walls of the bony orbits measured at the juncture of the crista lacrimalis posterior with the frontolacrimal suture. Currarino and Silverman [9), in their studies of arhinencephaly and trigonocephaly, measured the bony interorbital distance between the medial walls at what was described to be the junction between each medial angular process of the frontal bone with the maxillary and lacrimal bones. In order to provide a statistically more reliable standard, Gerald and Silverman [10] repeated the original work of Currarino and Silverman [9] using the same technical factors, and studied 100 patients in each year of age from birth to 12 years. Hansman [11] presented measurements of the interorbital distance and thickness of the skull based on radiographs of the skull and paranasal sinuses in a large group of healthy subjects. According to him, from "infancy to adulthood, the bony interorbital distance for girls is consistently narrower than for boys. Starting at 1 year 6 months, there is gradual increase in the size of the measurements for both sexes. At about 13 years of age the girl's growth began to level off. Since the boys continue to increase to the age of about 21 years, the measurements in girls fall more markedly below the boys as growth is completed. " The average adult measurement in women is 25 mm and in men 28 mm [11]. CT of the orbit provides along with other information an opportunity to evaluate the distance between the orbits and, if necessary, any other linear or angular measurements. The lacrimal bones and the orbital plates of the ethmoid cast a thin line of increased density on the CT scan and, therefore, the bony interorbital distance can be measured at any desired points. Since orbital hypertelorism and hypotelorism are associated with a variety of other malformations affecting the hard and soft tissues [13), it is essential that appropriate radiographic methods including conventional radiography, cephalometry, tomography, and CT be used. Further study
5 AJNR :7, March/April 1986 ORBITAL MEASUREMENTS BY CT 269 of more cases to determine the normal standards for the bony interorbital distance in infancy and childhood is needed to determine the patterns of growth. The bony interorbital distance in pathologic conditions and the anatomic factors contributing to reduced orbital capacity and exophthalmos and the effect of form on function in Apert and Crouzon syndromes can be effectively evaluated by CT. This problem is being studied in various craniofacial anomalies and will be taken up in a subsequent publication. ACKNOWLEDGMENT We thank Leah M. Freeman for secretarial assistance. REFERENCES 1. Converse JM, McCarthy JG, Wood-Smith D. Reconstructive plastic surgery for orbital hypertelorism. In: Converse JM, Mc Carthy JG, Wood-Smith D, eds. Symposium on diagnosis and treatment of craniofacial anomalies, vol 20. St. Louis: Mosby, 1979: Becker MH. Computed tomography in the evaluation of the craniofacial malformations. In: Converse JM, McCarthy JG, Wood-Smith D, eds. Symposium on diagnosis and treatment of craniofacial anomalies, vol 20. St. Louis: Mosby, 1979: Mafee MF, Valvassori GE. Radiology of the craniofacial anomalies. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 1981 ;14: Tessier P. The definitive plastic surgical treatment of the severe facial deformities of craniofacial dysostosis. Crouzon's and Apert's diseases. Plast Reconstr Surg 1971 ;48 : Campbell JA. Craniofacial anomalies. In: Newton TH, Potts DG, eds. Radiology of the skull and brain, vol 1, book 2. St. Louis: Mosby, 1971 : Pruzansky S. Time: the fourth dimension in syndrome analysis applied to craniofacial malformations. Birth Defects 1977 ;13 : Mustarde JC. Epicanthus and telecanthus. Br J Plast Surg 1963; 16: Cameron J. Interorbital width. New cranial dimension. Its significance in modern and fossil man in lower mammals. Am J Phys Anthropol 1931 ; 1 5: Currarino G, Silverman FN. Orbital hypotelorism, arhinencephaly, and trigoncephaly. Radiology 1960;74 : Gerald BE, Silverman FN. Normal and abnormal interorbital distances with special reference to mongolism. AJR 1956;95 : Hansman CF. Growth of interorbital distance and skull thickness as observed in roentgenographic measurements. Radiology 1966;86: Morin J, Hiu J, Anderson J, Grainger R. A study of growth in the interorbital region. Am J Ophthalmo/1936;56 : Tessier P. Orbital hypertelorism. (1) Successful surgical attempts, material and methods, causes and mechanism. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 1972;6:
An important indication for imaging the anterior skull base
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.C. Hughes M.J. Kaduthodil D.J.A. Connolly P.D. Griffiths Dimensions and Ossification of the Normal Anterior Cranial Fossa in Children BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interpretation of CT of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.C. Hughes M.J. Kaduthodil D.J.A. Connolly P.D. Griffiths Dimensions and Ossification of the Normal Anterior Cranial Fossa in Children BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Interpretation of CT of
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
1 Eyelids. Lacrimal Apparatus. Orbital Region. 3 The Orbit. The Eye
 1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
ofunusual and Occult Clefts of the Palate JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, MD. SIDNEY L. HOROWITZ, D.D.S. MELVIN H. BECKER M.D, New York New York-4:11
 TheUse oftomographyin: the Diagnosis ofunusual and Occult Clefts of the Palate JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, MD. SIDNEY L. HOROWITZ, D.D.S. MELVIN H. BECKER M.D, New York New York-4:11 The ma or1ty of patients
TheUse oftomographyin: the Diagnosis ofunusual and Occult Clefts of the Palate JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, MD. SIDNEY L. HOROWITZ, D.D.S. MELVIN H. BECKER M.D, New York New York-4:11 The ma or1ty of patients
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study
 Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
Relationship of the Optic Nerve to the Posterior Paranasal Sinuses: A CT Anatomic Study Mark C. DeLano, F. Y. Fun, and S. James Zinreich PURPOSE: To delineate the relationship between the optic nerves
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY
 OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
OPERATIVE CORRECTION BY OSTEOTOMY OF RECESSED MALAR MAXILLARY COMPOUND IN A CASE OF OXYCEPHALY By Sir HAROLD GILLIES, C.B.E., F.R.C.S., and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S., R.C.S. From the Plastic
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir. HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi
 Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi
 Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi There are six extrinsic muscles of the eyeball, namely the (S), Medial (M), (I), & Lateral (L) recti, and (SO) and (IO) Obliques. In
Muscles of the Eyeball (Extra Ocular Muscles) Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi There are six extrinsic muscles of the eyeball, namely the (S), Medial (M), (I), & Lateral (L) recti, and (SO) and (IO) Obliques. In
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Boundaries Septum Turbinates & Meati Lamellae Drainage Pathways Variants
 The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Nasal region. cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?
 Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Extraoral Radiology October 10th, 2008
 Extraoral Radiology October 10th, 2008 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 November 8 th, 1895 Extraoral Projections Images can be produced in the dental office X-ray source can be Intraoral
Extraoral Radiology October 10th, 2008 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 November 8 th, 1895 Extraoral Projections Images can be produced in the dental office X-ray source can be Intraoral
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
By JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, M.D., and DAUBERT TELSEY, D.D.S.
 THE TRIPARTITE OSTEOTOMY OF THE MID-FACE FOR ORBITAL EXPANSION AND CORRECTION OF THE DEFORMITY IN CRANIOSTENOSIS By JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, M.D., and DAUBERT TELSEY, D.D.S. Center for Craniofacial Anomalies
THE TRIPARTITE OSTEOTOMY OF THE MID-FACE FOR ORBITAL EXPANSION AND CORRECTION OF THE DEFORMITY IN CRANIOSTENOSIS By JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, M.D., and DAUBERT TELSEY, D.D.S. Center for Craniofacial Anomalies
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
Physical and Refractive Characteristics of the Eye at Birth and During Infancy
 described.' Chapter 3 This chapter is taken from: Isenberg, S. (d.). (1989). The eye in infancy. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers. Physical and Refractive Characteristics of the Eye at Birth and During
described.' Chapter 3 This chapter is taken from: Isenberg, S. (d.). (1989). The eye in infancy. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers. Physical and Refractive Characteristics of the Eye at Birth and During
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit
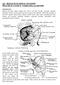 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
Skull. Sphenoid and Ethmoid bones
 Skull. Sphenoid and Ethmoid bones PhD., Dr. David Lendvai Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embriology Semmelweis University, Faculty of Medicine 2018. Skeletal system Structure of the skull Border
Skull. Sphenoid and Ethmoid bones PhD., Dr. David Lendvai Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embriology Semmelweis University, Faculty of Medicine 2018. Skeletal system Structure of the skull Border
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
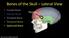 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury
 Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns. CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns
 CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology
CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway and Related Structures
 Pictorial Essay The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway and Related Structures David L. Daniels, Mahmood F. Mafee, Michelle M. Smith, Timothy L. Smith, Thomas P. Naidich, W. Douglas Brown, William E. Bolger,
Pictorial Essay The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway and Related Structures David L. Daniels, Mahmood F. Mafee, Michelle M. Smith, Timothy L. Smith, Thomas P. Naidich, W. Douglas Brown, William E. Bolger,
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
The cribriform plate. ethmoid bone. Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths.
 ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
CT of Maxillofacial Injuries
 CT of Maxillofacial Injuries Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology changes the diagnosis Technologic Evolution
CT of Maxillofacial Injuries Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology changes the diagnosis Technologic Evolution
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal Ostiomeatal Channels and Paranasal Sinuses
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.192 on 12/22/17 from IP address 37.44.202.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.192 on 12/22/17 from IP address 37.44.202.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Orbit Deformities in Craniofacial Neurofibromatosis Type 1
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1678 1682, September 2003 Orbit Deformities in Craniofacial Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Claude Jacquemin, Thomas M. Bosley, and Helena Svedberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The possible
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1678 1682, September 2003 Orbit Deformities in Craniofacial Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Claude Jacquemin, Thomas M. Bosley, and Helena Svedberg BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The possible
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Cephalometric Analysis
 Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball
 Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Lateral Area. Carmen Elena Georgescu1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3. Objectives.
 Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Lateral Area Carmen Elena Georgescu1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary Intraoral examinations are the backbone of dental radiography.
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Lateral Area Carmen Elena Georgescu1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary Intraoral examinations are the backbone of dental radiography.
Reassessment of Sphenoid Dysplasia Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:644 648, April 2002 Reassessment of Sphenoid Dysplasia Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Claude Jacquemin, Thomas M. Bosley, Don Liu, Helena Svedberg, and Amal Buhaliqa
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:644 648, April 2002 Reassessment of Sphenoid Dysplasia Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Claude Jacquemin, Thomas M. Bosley, Don Liu, Helena Svedberg, and Amal Buhaliqa
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Extraoral radiography Introduction: Extraoral radiographs (outside the mouth) are taken when large areas of the skull or jaw must be examined or when
 Extraoral radiography Introduction: Extraoral radiographs (outside the mouth) are taken when large areas of the skull or jaw must be examined or when patients are unable to open their mouths for film placement.
Extraoral radiography Introduction: Extraoral radiographs (outside the mouth) are taken when large areas of the skull or jaw must be examined or when patients are unable to open their mouths for film placement.
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area
 VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
Introduction. patterns of injury. The injury pattern produced vanes with. j the object striking the face.
 Dolan et al. Facial fractures I Introduction Facial injury constitutes a frequent finding among emergency room patients. Schultz and Oldham estimate that 54% of such patients will have significant trauma.
Dolan et al. Facial fractures I Introduction Facial injury constitutes a frequent finding among emergency room patients. Schultz and Oldham estimate that 54% of such patients will have significant trauma.
Anatomy of. External NOSE. By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC
 Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22,
 JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
mistake ;slides in bold but you still have to go back to our slides to see the figure, tables and some scheme
 Khozama jehad : I am doing my best and I am sorry for any unintended mistake ;slides in bold but you still have to go back to our slides to see the figure, tables and some scheme The Orbit, Orbital Contents
Khozama jehad : I am doing my best and I am sorry for any unintended mistake ;slides in bold but you still have to go back to our slides to see the figure, tables and some scheme The Orbit, Orbital Contents
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Orthodontic Morphological Evaluation of Treacher Collins Syndrome
 Cong. Anorn., 39: 243-253,1999 Original Orthodontic Morphological Evaluation of Treacher Collins Syndrome Sachio UMEMURA Department of Orthodontics, Ohu University School of Dentistry, 31-1 Misumido Tomita,
Cong. Anorn., 39: 243-253,1999 Original Orthodontic Morphological Evaluation of Treacher Collins Syndrome Sachio UMEMURA Department of Orthodontics, Ohu University School of Dentistry, 31-1 Misumido Tomita,
Pre- and Postsurgical Facial Growth in Patients. with Crouzon's and Apert's Syndromes
 Pre- and Postsurgical Facial Growth in Patients with Crouzon's and Apert's Syndromes Sven KrRreiBora, D.D.S., Dr. Obpont. HowArRDp Apuss, D.D.S., M.S. Our report deals with 8 patients with Crouzon's and
Pre- and Postsurgical Facial Growth in Patients with Crouzon's and Apert's Syndromes Sven KrRreiBora, D.D.S., Dr. Obpont. HowArRDp Apuss, D.D.S., M.S. Our report deals with 8 patients with Crouzon's and
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Anatomy of the orbit. Lay-out. Imaging technique. 3 x 3. brief overview of the basic anatomy of the orbit and its structures
 Anatomy of the orbit Prof. Pia C Sundgren MD, PhD Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Sweden Lay-out brief overview of the basic anatomy of the orbit and its structures
Anatomy of the orbit Prof. Pia C Sundgren MD, PhD Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Sweden Lay-out brief overview of the basic anatomy of the orbit and its structures
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
