Basilar artery in frontotemporal approach, 9, 9f 10f in intraventricular anatomy, 198f in subtemporal craniotomy, 191f,
|
|
|
- Madison Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FOSSIndex I 11/7/01 2:18 PM Page 203 Index Note: Page numbers followed by f and t represent figures and tables respectively. AComA. See Anterior communicating artery Annulus fibrosus, 124 in anterior approach to cervical spine, 132, 132f Anterior approach, to cervical spine, indications for, 130 pitfalls and pearls in, , 130f surgical technique in, , 131f 133f, 134 Anterior clinoidectomy extradural, 13, 13f 14f intradural, 14f 16f, Anterior commissure, in intraventricular anatomy, 196f, 197f, 199f Anterior communicating artery approach to, 18 21, 18f 21f in frontotemporal approach, 7, 8f Heubner s artery in, 21, 21f 22f surgical considerations in, 22 in supraorbital craniotomy, 186, 186f Anterior inferior cerebellar artery, in subtemporal craniotomy, 192f 193f Anterior medullary velum, 86 Anterior petrosal drilling, in transpetrosal approach, 80 Anterolateral extradural/intradural approach, to cavernous sinus, 47 49, 47f 49f Anterolateral triangle, in cavernous Anteromedial triangle, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 41, 41f, 45t Anteroseptal vein, in intraventricular anatomy, 196, 196f, 197f Apicectomy, partial labyrinthectomy petrous, Arachnoid dissection, in supraorbital craniotomy, , 185f 186f Arteries. See also specific arteries in cavernous sinus anatomy, 40 Basilar artery in frontotemporal approach, 9, 9f 10f in intraventricular anatomy, 198f in subtemporal craniotomy, 191f, 192f, 193f in supraorbital craniotomy, 187f transcavernous approach to, 50, 50f 51f Biopsy pedicle, in transpedicular approach to thoracic spine, 140, 140f sural nerve, Blind sac closure, of external auditory canal, 77 Bone resection, condylar, in extreme lateral approach, 95 98, 95f 98f Brachial plexus, anterior exposure of, anatomy in, , 166f 167f indications for, 166 pitfalls and pearls in, , 167f surgical technique in, , 168f 169f Burr holes in approaches to cavernous sinus, in frontal lobectomy, 111 in frontotemporal approach, 5 in interhemispheric approach, 107 in midline and paramedian suboccipital approach, 87 in supraorbital craniotomy, in transbasal approach, 27 Carotid artery in frontotemporal approach, 7, 8f internal. See Internal carotid artery Carotid artery triangle, in surgical approach to cavernous sinus, 47 49, 47f 49f Carotid cisterns, in supraorbital craniotomy, 185, 185f Carotid endarterectomy, in anterior approach to cervical spine, 133f, 134 Carpal ligament, release of, 160, 160f Carpal tunnel release, anatomy in, 159 indications for, 159 pitfalls and pearls in, , 159f surgical technique in, 160, 160f Cauda equina syndrome, 126 Caudate, in intraventricular anatomy, 194, 195f Cavernous sinus anatomy of, 37 45, 37f 38f arteries, 40 dural walls, 39 geometric construct, middle cranial fossa subregion, 42 43, 42f 43f middle fossa floor, 39 nerves, 39 40, 40f paraclival subregion, 44, 45f parasellar subregion, 41 42, 41f 42f veins, 40 pitfalls and pearls in, 51 in subtemporal craniotomy, 190 surgical approaches to, anterolateral extradural/intradural, 47 49, 47f 49f indications for, surgical technique in, 46 47, 46f transcavernous to basilar artery, 50, 50f 51f triangles of, 45t Cerebellar tonsils, 88 Cerebellopontine angle, retrolabyrinthine approach to, 71 Cerebrospinal fluid drainage in condylar bone resection, 97 in craniotomy, 70 in lateral subocciptital craniotomy, 97 in retrosigmoid craniotomy,
2 FOSSIndex I 10/27/01 10:26 AM Page INDEX Cervical compression, in anterior approach to cervical spine, , 131f 132f Cervical foraminotomy, 136, 136f Cervical laminectomy, , 136f 137f Cervical spine anatomy of, , 124f, 125f anterior approach to, posterior approach to, upper, transoral approach to, Choroid plexus, in intraventricular anatomy, 195f, 196, 196f, 197f, 199f Cisterna magna, 97 Cisternal anatomy, in pineal region, 100 Classic transbasal approach, 28, 28f Clinoidectomy, anterior extradural, 13, 13f 14f intradural, 14f 16f, Compression cervical spine, , 131f 132f nerve. See Decompression Condylar bone resection, in extreme lateral cranial approach, 95 98, 95f 98f Contralateral third nerve, in frontotemporal approach, 9f Corpectomy, C2-C3 level, 128, 129f Corticectomy, in lobectomy frontal, 112, 112f occipital, 114, 114f Costotransversectomy, 142, 142f 143f Cranial approaches anterior communicating artery, to cavernous sinus, cranio-orbital, extreme lateral, frontal lobectomy, frontotemporal, 4 10 interhemispheric, lobectomies frontal, occipital, temporal, for epilepsy, middle fossa, midline and paramedian suboccipital, occipital lobectomy, orbitozygomatic, to posterior third ventricle and pineal region, preauricular subtemporalinfratemporal approach, retrosigmoid, temporal lobectomy, for epilepsy, transbasal, transpetrosal, transphenoidal, transylvian, Cranial nerves in intraventricular anatomy, 198f in middle fossa approach, 64f in subtemporal craniotomy, 191, 191f 193f Cranio-orbital approaches indications for, 11 pitfalls and pearls in, , 11f 12f surgical technique, 12, 12f Craniotomy bifrontal, in transbasal approach, 27, 28f dural closure in, 70 lateral suboccipital, 95 98, 95f 98f minimally invasive subtemporal, supraorbital, retrosigmoid. See Retrosigmoid craniotomy temporal, 61 in transpetrosal approach, 70 Decompression lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, radial nerve, ulnar nerve, Dens resection, in transoral approach to upper cervical spine, 128, 129f Diffusion fluid, 3 Digastric ridge, in mastoidectomy, 69 Discectomy C2-C3 level, 128, 129f lumbar. See Lumbar discectomy Dissection arachnoid, in supraorbital craniotomy, , 185f 186f intradural, 139, 139f Dorsolateral approaches, to thoracic spine, indications for, 141 pitfalls and pearls in, , 141f surgical technique in, , 142f 143f Dural opening in cervical laminectomy, 137, 137f in frontal lobectomy, 111 in frontotemporal approach, 5, 5f 6f in lateral suboccipital craniotomy and condylar bone resection, 96f, in middle fossa approach, 63 64, 63f in midline and paramedian suboccipital approach, 87, 88f in partial labyrinthectomy petrous apicectomy approach, 73 in posterior approach to thoracic spine, 139, 139f approach, 59, 60f presigmoid, in translabyrinthine approach, 76 in subtemporal craniotomy, , 189f 190f in supracerebellar-infratentorial approach, 103, 103f in supraorbital craniotomy, 184, 184f in surgical approach to cavernous sinus, 47 49, 47f 49f in transcochlear approach, in transphenoidal approach, 35, 35f 36f Dural walls, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 39 Elbow, nerve entrapment at, , 164f Embalming, of head specimens, 3 Embalming fluid, 3 Endarterectomy, carotid, in anterior approach to cervical spine, 133f, 134 Endoscopy intraventricular anatomy examination, considerations in, 200 indications for, , 194f technique in, 194, 195f 199f, subtemporal craniotomy, considerations in, 193 indications for, , 189f technique in, , 189f 193f supraorbital craniotomy considerations in, 188 indications for, , 183f technique in, , 183f 188f thoracic sympathectomy, considerations in, 202 indications for, technique in, , 201f 202f transnasal technique, in transphenoidal approach, 32 33, 32f 34f
3 FOSSIndex I 10/27/01 10:26 AM Page 205 INDEX 205 Epilepsy, temporal lobectomy for. See Temporal lobectomy, for epilepsy Eustachian tube, in preauricular approach, 54, 54f Extended transbasal approach, 28 30, 28f 30f External auditory canal blind sac closure of, 77 in transpetrosal approach, 68 Extradural anatomy, in preauricular Extreme lateral approach, to anatomy in, 90 91, 90f 91f indications for, 90 pitfalls and pearls in, 99 92, 92f surgical technique in, 93 98, 93f 98f Facial nerve in mastoidectomy, 69, 69f in middle fossa approach, 63 transposition, in transpetrosal approach, mobilization techniques, Far lateral lumbar discectomy, indications for, 152 pitfalls and pearls in, , 152f surgical technique in, , 152f 153f Fimbria, in intraventricular anatomy, 195f Foramen of Monroe, in intraventricular anatomy, 195f, 196, 196f, 199f Foramen spinosum, in subtemporal craniotomy, 190f Foraminotomy, cervical, 136, 136f Fornix, in intraventricular anatomy, 196f, 197f, 198 Frontal lobectomy anatomy in, 111 indications for, , 111f surgical technique in, , 112f Frontotemporal approach, to, 4 10 indications for, 4 pitfalls and pearls in, , 4f 5f surgical technique, 5, 5f 10f, 7, 9 Gasserian ganglion, in subtemporal craniotomy, 190, 190f 191f Glassock s triangle, in cavernous Greater superficial petrosal nerve in middle fossa cranial approach, 62, 62f Head specimens, preparation of, 3 Heubner s artery, identification of, 21, 21f 22f Hippocampus, in intraventricular anatomy, 195f ICA. See Internal carotid artery Incisions for cranial approaches cavernous sinus, 46 cranio-orbital approach, 11 12, 11f 12f extreme lateral, 92, 92f frontal lobectomy, 111, 111f frontotemporal, 4 5, 4f 5f interhemispheric, 107 middle fossa, 61, 61f midline and paramedian suboccipital, occipital lobectomy, 113, 113f orbitozygomatic, 11 12, 11f 12f preauricular subtemporalinfratemporal, 55, 55f retrosigmoid craniotomy, 82, 82f temporal lobectomy, 116, 116f transbasal, 27 30, 27f 30f transpetrosal, 67, 68f transphenoidal, 32 transylvian, to sylvian fissure, 23 for endoscopic procedures intraventricular anatomy examination, 194, 194f subtemporal craniotomy, 189, 189f supraorbital craniotomy, 183, 183f thoracic sympathectomy, 201 for peripheral nerve procedures brachial plexus exposure, 167, 167f carpal tunnel release, , 159f for lateral femoral cutaneous nerve decompression, 174, 174f radial nerve decompression, 161, 161f sciatic nerve exploration, 176, 176f suprascapular nerve entrapment, 172, 172f sural nerve biopsy, 178, 178f in thoracic outlet syndrome, 170 ulnar nerve decompression and transposition, 163, 163f for spinal approaches anterior cervical, 130, 130f dorsolateral thoracic, 141, 141f lumbar discectomy, 148, 148f posterior cervical, 135, 135f posterior thoracic, 138, 138f transoral, to upper cervical spine, 127, 127f ventrolateral thoracic, 145, 145f Inferior cerebellar arteries, and retrosigmoid craniotomy, 81, 83f 84f Inferior colliculus, in intraventricular anatomy, 199f Inferolateral triangle, in cavernous Inferomedial triangle, in cavernous Infundibulum, in intraventricular anatomy, 197f, 199f Injection, of head specimens, 3 Injection mixture, 3 Interhemispheric approach, to indications for, 107 pitfalls and pearls in, surgical technique in, , 107f 110f Internal auditory canal in middle fossa cranial approach, 62 63, 62f identification and exposure, 63, 63f retrosigmoid craniotomy and, 84 translabyrinthine approach to, 75, 75f in transpetrosal cranial approach, 80 Internal auditory meatus, in subtemporal craniotomy, 192, 192f Internal carotid artery petrous ICA, 54, 54f in supraorbital craniotomy, 186, 186f, 187, 187f Intertransverse muscle, in far lateral lumbar discectomy, 153, 153f Intradural anatomy, in preauricular approach, Intradural dissection, 139, 139f Intradural tumor resection, lumbar spine, 150, 150f Intraventricular anatomy examination, endovascular, indications for, 194
4 FOSSIndex I 10/27/01 11:28 AM Page INDEX Intraventricular anatomy (continued) pitfalls and pearls in, , 194f technique in, 194, 195f 199f, Kawase s triangle in cavernous sinus anatomy, 42, 42f, 45t in middle fossa cranial approach, 63 Laminectomy cervical, , 136f 137f lumbar, Seec Lumbar laminectomy thoracic, , 138f 139f Lateral extracavitary approach, to thoracic spine, 143, 143f Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve decompression, anatomy in, 174 indications for, 174 pitfalls and pearls in, , 174f surgical technique in, 175, 175f Lateral suboccipital craniotomy, in extreme lateral cranial approach, 95 98, 95f 98f Lateral triangle, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 42, 42f, 45t Latissimus dorsi muscle in lumbar spine surgery, 154 in thoracic spine surgery, 145, 145f Lesser superficial petrosal nerve, in preauricular subtemporalinfratemporal Ligaments in carpal tunnel release, 160, 160f spinal column, 124 longitudinal, 155, 155f, 156f upper cervical, , 128f Lilliquist, membrane of, in supraorbital craniotomy, 187 Lobectomy frontal, occipital, temporal, for epilepsy, Longissimus muscle in extreme lateral cranial approach, 90, 91f in far lateral lumbar discectomy, 153f Lumbar discectomy far lateral, , 152f 153f indications for, 148 pitfalls and pearls in, , 148f surgical technique in, , 148f 149f Lumbar laminectomy indications for, 148 pitfalls and pearls in, , 148f surgical technique in, , 150f Lumbar spine anatomy of, 126, 126f retroperitoneal approach to, Mamillary bodies, in intraventricular anatomy, 197f, 198f, 199f Mastoid anthrum, in mastoidectomy, 69, 69f Mastoidectomy radical, in transcochlear approach, 77 in transpetrosal approach, 68 69, 68f 70f Maxillary nerve, in transphenoidal approach, 32 MCA. See Middle cerebral artery Meckel s cave opening in partial labyrinthectomy petrous apicectomy approach, 73, 73f retrosigmoid craniotomy and, 83 Membrane of Lilliquist, in supraorbital craniotomy, 187 Microfil injection, 3 Middle cerebral artery anatomy of, 23 in supraorbital craniotomy, 184f, 185 in transylvian approach, 25, 25f 26f Middle cranial fossa anatomy of, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 42 43, 42f 43f in cavernous sinus anatomy, 39 Middle fossa approach, to indications for, 61 pitfalls and pearls in, 66 positioning and skin incision, 61, 61f surgical technique, 62, 62f 66f, 68f 79f Middle meningeal artery in middle fossa cranial approach, 62 in subtemporal craniotomy, , 189f 191f Midline suboccipital approach, to anatomy in, 86 indications for, surgical technique in, 87 88, 87f 88f Minimally invasive craniotomies, endoscopic subtemporal, supraorbital, MMA. See Middle meningeal artery Multifidus muscle, in far lateral lumbar discectomy, , 152f 153f Muscles. See also specific muscles in far lateral lumbar discectomy, , 152f 153f of spinal column, 124 thoracic spine, 145, 145f Nasal cavity, in transphenoidal approach, 32 Nerve entrapment at elbow, , 164f suprascapular, at wrist, 165, 165f Nerves. See also individual nerves in cavernous sinus anatomy, 39 40, 40f peripheral. See Peripheral nerve approaches Neuroendoscopic procedures for intraventricular anatomy examination, subtemporal craniotomy, supraorbital craniotomy, thoracic sympathectomy, Neurovascular anatomy, in pineal region, , 101f 102f Nucleus pulposus, 124 Occipital lobectomy anatomy in, 113 indications for, 113 pitfalls and pearls in, , 113f surgical technique in, , 113f 114f Occipital-transtentorial approach, to posterior third ventricle and pineal region, , 104f 105f Oculomotor trigone, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 42, 42f Olfactory nerve in frontotemporal approach, 7, 7f in supraorbital craniotomy, 186, 186f Ophthalmic artery, in supraorbital craniotomy, 187f Optic chasm in frontotemporal approach, 7, 8f in transphenoidal approach, 36f Optic nerves in extended transbasal approach, 30, 30f in frontotemporal approach, 7, 8f in transphenoidal approach, 32
5 FOSSIndex I 10/27/01 10:26 AM Page 207 INDEX 207 Optic recess, in intraventricular anatomy, 198, 198f Orbitozygomatic approach, to indications for, 11 pitfalls and pearls in, , 11f 12f surgical technique, 13, 13f Osteotomy in extended transbasal approach, 29, 29f frontotemporal orbitozygomatic, 46, 46f orbital, 12, 12f orbitozygomatic, 13, 13f Paraclival subregion, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 42, 42f Paramedial triangle, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 41, 41f, 45t Paramedian suboccipital approach, to anatomy in, 86 indications for, surgical technique in, 87 88, 87f 88f Parasellar subregion, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 41 42, 41f 42f Paraspinal muscles in cervical foraminotomy, 136, 136f in cervical laminectomy, , 136f in transpedicular thoracic approach, 140 Parkinson s triangle, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 41, 41f, 45t Partial labyrinthectomy petrous apicectomy, 72 73, 72f 73f Partial transcondylar cranial approach, 95, 95f 96f Patient position for cranial approaches cavernous sinus, 46 cranio-orbital, 11 12, 11f 12f extreme lateral, 92, 92f frontal lobectomy, 111, 111f frontotemporal, 4 5, 4f 5f interhemispheric, 107 middle fossa, 61, 61f midline and paramedian suboccipital, occipital lobectomy, 113, 113f orbitozygomatic, 11 12, 11f 12f preauricular subtemporalinfratemporal, 55 retrosigmoid craniotomy, 82, 82f temporal lobectomy, 116, 116f transbasal, 27 30, 27f 30f transpetrosal, 67, 68f transphenoidal, 32 transylvian, to sylvian fissure, 23 for endoscopic procedures intraventricular anatomy examination, 194, 194f subtemporal craniotomy, 189, 189f supraorbital craniotomy, 183, 183f thoracic sympathectomy, 201 for peripheral nerve procedures brachial plexus exposure, 167, 167f carpal tunnel release, , 159f lateral femoral cutaneous nerve decompression, 174, 174f lumbar laminectomy, 148, 148f radial nerve decompression, 161, 161f sciatic nerve exploration, 176, 176f suprascapular nerve entrapment, 172, 172f sural nerve biopsy, 178, 178f in thoracic outlet syndrome, 170 ulnar nerve decompression and transposition, 163, 163f for spinal approaches anterior cervical, 130, 130f dorsolateral thoracic, 141, 141f lumbar discectomy, 148, 148f posterior cervical, 135, 135f posterior thoracic, 138, 138f transoral, to upper cervical spine, 127, 127f ventrolateral thoracic, 145, 145f Pedicle biopsy, in transpedicular thoracic approach, 140, 140f Peripheral nerve approaches brachial plexus exposure, anterior, carpal tunnel release, lateral femoral cutaneous nerve decompression, radial nerve decompression, sciatic nerve exploration, suprascapular nerve entrapment, sural nerve biopsy, thoracic outlet syndrome, ulnar nerve decompression and transposition, Petrous apicectomy, partial labyrinthectomy, Petrous internal carotid artery, in preauricular subtemporalinfratemporal approach, 54, 54f Pineal region anatomy of, , 101f 102f and posterior third ventricle. See Posterior approaches, to via third ventricle and pineal region Pituitary gland, in transphenoidal approach, 35, 36f Pleural opening, in thoracic spine surgery, 146, 146f Porus trigeminus, in subtemporal craniotomy, 191, 191f Posterior approaches to cervical spine, indications for, , 135f surgical considerations in, 137 surgical technique in, , 135f 137f to via third ventricle and pineal region anatomy of, indications for, 100 pitfalls and pearls in, 106 surgical technique, , 103f 106f to thoracic spine, indications for, , 138f surgical considerations in, 140 surgical technique in, , 138f 140f Posterior cerebral artery in intraventricular anatomy, 197f, 198f, 199f in subtemporal craniotomy, 191f, 192, 192f Posterior clinoid process, 50, 50f Posterior commissure, in intraventricular anatomy, 197f Posterior communicating artery, in frontotemporal approach, 7, 9, 9f Posterior fossa closure, in midline and paramedian suboccipital approaches, 88 Posterior medullary velum, 86 Posterior neck dissection, in extreme lateral approach, 93 94, 93f 94f Posterolateral triangle, in cavernous Posteromedial triangle, in cavernous Preauricular subtemporalinfratemporal approach, to, anatomy in, 52, 53f 54f, indications for, 52 pitfalls and pearls in, 60 55, 55f surgical technique in, 55 60, 55f 60f
6 FOSSIndex I 10/27/01 10:26 AM Page INDEX Premedullary cistern, in preauricular approach, Prepontine cistern, in preauricular approach, 55 Presigmoid dural opening, in translabyrinthine approach, 76 Psoas muscle, in lumbar spine surgery, 154, 154f, 155, 155f, 156f Quadratus lumborum muscle, in lumbar spine surgery, 154, 154f, 155, 155f Radial nerve decompression, anatomy in, 161 indications for, 161 pitfalls and pearls in, , 161f surgical technique in, 162, 162f Resection condylar bone, in extreme lateral approach, 95 98, 95f 98f dens, in transoral approach to upper cervical spine, 128, 129f lumbar intradural tumor, 150, 150f Retrocondylar technique, in extreme lateral cranial approach, 95, 95f Retrolabyrinthine approach, transpetrosal, 71, 71f Retroperitoneal approach, to lumbar spine, indications for, 154 pitfalls and pearls in, , 154f surgical technique in, , 154f 156f Retrosigmoid craniotomy anatomy in, 81 indications for, 81 pitfalls and pearls in, 85 82, 82f surgical technique in, 82 85, 83f 85f Ribs in endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy, , 201f 202f in thoracic spine surgery, 146, 146f Sciatic nerve exploration, anatomy in, 176 indications for, 176 pitfalls and pearls in, , 177f 176, 176f surgical technique in, , 177f Semicircular canal, in translabyrinthine cranial approach, 74, 74f Serratus anterior muscle, in thoracic spine surgery, 145, 145f Silicone injection, 3 Skin incisions. See Incisions Specimen preparation, 3 Sphenoid sinus in subtemporal craniotomy, 190, 190f in transphenoidal approach, 32, 33, 35, 333f 34f Spinal column anatomy of, surgical approaches to anterior, to cervical spine, dorsolateral, to thoracic spine, lumbar discectomy, far lateral, lumbar laminectomy, posterior to cervical spine, to thoracic spine, retroperitoneal, to lumbar spine, transoral, to cervical spine, ventrolateral, to thoracic spine, vertebral column anatomy for, Splenius capitis muscle, in extreme lateral cranial approach, 90, 91f Sternocleidomastoid muscle, in extreme lateral cranial approach, 90, 90f Storage, of head specimens, 3 Sublabial technique, in transphenoidal approach, 34 35, 34f 36f Subtemporal craniotomy, minimally invasive, indications for, 189 pitfalls and pearls in, , 189f technique in, , 189f 193f Subtemporal-infratemporal approach, to. See Preauricular subtemporalinfratemporal approach, to Superior cerebellar artery, in subtemporal craniotomy, 191, 191f Superior colliculus, in intraventricular anatomy, 199f Supracerebellar-infratentorial approach, to posterior third ventricle and pineal region, , 103f 104f Supraorbital craniotomy, minimally invasive indications for, 183 pitfalls and pearls in, , 183f technique in, , 183f 188f Suprascapular nerve entrapment, anatomy in, 172 indications for, 172 pitfalls and pearls in, , 172f surgical technique in, , 172f 173f Supratentorial-infratentorial transsinus approach, to posterior third ventricle and pineal region, 105, 105f 106f Sural nerve biopsy, anatomy in, 178 indications for, 178 pitfalls and pearls in, , 178f technique in, 178, 178f Sylvian cisterns, in supraorbital craniotomy, 185, 185f Sylvian fissure anatomy of, 23, 24f approach to, in frontotemporal approach, 7, 7f 9f, 9, 10f in supraorbital craniotomy, 184f, 185 Sympathectomy, endoscopic thoracic, indications for, 201 pitfalls and pearls in, technique in, , 201f 202f Sympathetic chain, in endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy, , 201f 202f Tegmen tympani, in preauricular Temporal craniotomy, in middle fossa cranial approach, 61 Temporal horn, in intraventricular anatomy, 194, 195f Temporal lobectomy, for epilepsy anatomy in, 115, 115f 116f indications for, 115
7 FOSSIndex I 10/27/01 10:26 AM Page 209 INDEX 209 pitfalls and pearls in, 120 positioning and skin incision, 116, 116f surgical technique, , 117f 119f Temporalis muscle in approaches to cavernous sinus, 46f in cranio-orbital approach, 11, 12f Thalamostriate vein, in intraventricular anatomy, 196, 196f, 197f Thalamus, in intraventricular anatomy, 194, 195f, 197f, 199f Thoracic laminectomy, , 138f 139f Thoracic outlet syndrome, indications for, 170 pitfalls and pearls in, surgical technique in, , 170f 171f Thoracic spine anatomy of, , 125f, 126f dorsolateral approaches to, lateral extracavitary approach to, 143, 143f posterior approach to, transpedicular approach to, 140, 140f ventrolateral approach to, Thoracic sympathectomy, endoscopic, indications for, 201 pitfalls and pearls in, technique in, , 201f 202f Tonsils, cerebellar, in midline and paramedian suboccipital approach, 88 Transbasal approach, to, classic, 28, 28f extended, 28 30, 28f 30f indications for, 27 pitfalls and pearls in, , 27f 30f Transcavernous approach, to basilar artery, 50, 50f 51f Transcochlear technique, in transpetrosal approach, 77, 77f 78f Transcondylar approach, to, 96, 96f Transfacetal approach, to, 95, 95f Transjugular approach, to, 97, 97f Translabyrinthine technique, in transpetrosal approach, 74 76, 74f 76f Transnasal technique, in transphenoidal approach, 32 endoscopic, 32 33, 32f 34f Transoral approach, to upper cervical spine, indications for, 127 pitfalls and pearls in, , 127f surgical technique in, , 127f 129f Transpedicular approach, to thoracic spine, 140, 140f Transpetrosal approaches, to indications for, 67 pitfalls and pearls in, 80 67, 68f surgical technique in general, 67 70, 68f 70f specific, 71 80, 71f 79f Transphenoidal approach, to, anatomical considerations in, 32 indications for, 32 pitfalls and pearls in, surgical technique in, 32 35, 32f 36f Transposition facial nerve, ulnar nerve, Transtubercular technique, in extreme lateral approach, 96, 96f Transylvian approach, to sylvian fissure, indications for, 23 pitfalls and pearls in, surgical technique in, 23, 24f 26f, 25 Triangles, in cavernous sinus anatomy, 45t anterolateral, 42, 42f, 45t anteromedial, 41, 41f, 45t Glassock s, 42, 42f, 45t inferolateral, 42, 42f, 45t inferomedial, 42, 42f, 45t Kawase s, 42, 42f, 45t lateral, 42, 42f, 45t paramedial, 41, 41f, 45t Parkinson s, 41, 41f, 45t posterolateral, 42, 42f, 45t posteromedial, 42, 42f, 45t trigeminal, 42, 42f, 45t Tricortical graft, in anterior approach to cervical spine, 133 Trigeminal triangle, in cavernous Tuber cinerium, in intraventricular anatomy, 197f, 198f, 199f Turbinates, in transphenoidal approach, 32 33, 32f 33f Ulnar nerve decompression and transposition, anatomy in, 163 indications for, , 163f surgical technique in, , 164f 165f Upper cerebellar pontine pathology, in retrosigmoid craniotomy, 83 Vein(s) in cavernous sinus anatomy, 40 of Galen, in intraventricular anatomy, 199f in intraventricular anatomy, 196, 196f, 197f, 199f Ventricles, endoscopic examination of, indications for, 194 pitfalls and pearls in, , 194f technique in, 194, 195f 199f, Ventrolateral approach, to thoracic spine, indications for, 145 pitfalls and pearls in, , 145f surgical technique in, , 145f 147f Vertebral artery exposure, in extreme lateral approach, 93 94, 93f 94f Vertebral column, anatomy of, cervical, , 124f, 125f lumbar, 126, 126f thoracic, , 125f, 126f Vessels. See also individual arteries and veins in specimen preparation, 3 Wrist, nerve entrapment at, 165, 165f
8 FOSSIndex I 10/27/01 10:26 AM Page 210
25/06/2010. Scaricato da 1
 Approcci chirurgici al Clivus DIPARTIMENTO DI NEUROCHIRURGIA SECONDA UNIVERSITÀ DI NAPOLI Prof. Aldo Moraci Surgical Anatomy of the Clivus Scaricato da www.sunhope.it 1 Midsagittal Section of the Skull
Approcci chirurgici al Clivus DIPARTIMENTO DI NEUROCHIRURGIA SECONDA UNIVERSITÀ DI NAPOLI Prof. Aldo Moraci Surgical Anatomy of the Clivus Scaricato da www.sunhope.it 1 Midsagittal Section of the Skull
Skull Base Course. Dissection with fresh temporal bones and half heads
 Skull Base Course Dissection with fresh temporal bones and half heads 711 November 2016 Gruppo Otologico Via Emmanueli 42 Piacenza 29122 t +39 0523 754 362 fax +39 0523 453 708 www.gruppootologico.com
Skull Base Course Dissection with fresh temporal bones and half heads 711 November 2016 Gruppo Otologico Via Emmanueli 42 Piacenza 29122 t +39 0523 754 362 fax +39 0523 453 708 www.gruppootologico.com
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Adult - Cerebrovascular. Adult - Cranio-Cervical Junction. Adult - Epilepsy. Adult - Hydrocephalus
 list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
SURGICAL PROCEDURES OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 98100 Hypothermia - when employed, basic fee for any procedure on nervous system... 25 25 BRAIN Astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, glioblastoma or metastatic tumour Craniotomy plus excision 98130 - supratentorial...
98100 Hypothermia - when employed, basic fee for any procedure on nervous system... 25 25 BRAIN Astrocytoma, oligodendroglioma, glioblastoma or metastatic tumour Craniotomy plus excision 98130 - supratentorial...
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
SURGICAL APPROACHES TO FORAMEN MAGNUM LESIONS
 SURGICAL APPROACHES TO FORAMEN MAGNUM LESIONS 1 Surgical anatomy of foramen magnum Ø F M - located in the occipital bone Ø Three parts of occipital bones : 1 Squamous part Contain F M 2 - Basal (clival)
SURGICAL APPROACHES TO FORAMEN MAGNUM LESIONS 1 Surgical anatomy of foramen magnum Ø F M - located in the occipital bone Ø Three parts of occipital bones : 1 Squamous part Contain F M 2 - Basal (clival)
Table of Contents: Section I. Introduction. 1. Assessing Surgical Innovation. Section II. Trauma to the Scalp, Skull, and Brain
 Table of Contents: Section I. Introduction 1. Assessing Surgical Innovation Section II. Trauma to the Scalp, Skull, and Brain 2. Surgical Repair of Major Defects of the Scalp and Skull 3. Perioperative
Table of Contents: Section I. Introduction 1. Assessing Surgical Innovation Section II. Trauma to the Scalp, Skull, and Brain 2. Surgical Repair of Major Defects of the Scalp and Skull 3. Perioperative
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Case Log Mapping Update: April 2018 Review Committee for Neurological Surgery
 Case Log Mapping Update: April 2018 Review Committee for Neurological Surgery The Review Committee has made the following changes to the CPT code mappings: The following previously untracked CPT codes
Case Log Mapping Update: April 2018 Review Committee for Neurological Surgery The Review Committee has made the following changes to the CPT code mappings: The following previously untracked CPT codes
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]
![_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come] _CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]](/thumbs/81/84146690.jpg) 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
Microsurgical anatomy of the transcondylar, supracondylar, and paracondylar extensions of the far-lateral approach
 J Neurosurg 87:555 585, 1997 Microsurgical anatomy of the transcondylar, supracondylar, and paracondylar extensions of the far-lateral approach HUNG T. WEN, M.D., ALBERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D., TOSHIRO KATSUTA,
J Neurosurg 87:555 585, 1997 Microsurgical anatomy of the transcondylar, supracondylar, and paracondylar extensions of the far-lateral approach HUNG T. WEN, M.D., ALBERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D., TOSHIRO KATSUTA,
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes
 Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Longitudinal fissure separates right and left hemispheres.
 L 10 A B O R A T O R Y Brain/Skull CEREBRAL CORTEX (telencephalon) Longitudinal fissure separates right and left hemispheres. Identify the following structures of the frontal lobe: lateral sulcus central
L 10 A B O R A T O R Y Brain/Skull CEREBRAL CORTEX (telencephalon) Longitudinal fissure separates right and left hemispheres. Identify the following structures of the frontal lobe: lateral sulcus central
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
The Back OUTLINE. Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region
 The Back OUTLINE Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com
The Back OUTLINE Vertebral Column (review) Craniovertebral Joints Dorsal Scapular Region(review) Muscles of the Back Suboccipital Region Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
Surgical Anatomy of the Temporal Bone and Measurements of the Skull Base for Transpetrosal Approaches
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 75(1): 33-40, May, 1998 Surgical Anatomy of the Temporal Bone and Measurements of the Skull Base for Transpetrosal Approaches Mustafa BOZBUGA, Adnan OZTURK, Zafer ARI, Kayihan
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 75(1): 33-40, May, 1998 Surgical Anatomy of the Temporal Bone and Measurements of the Skull Base for Transpetrosal Approaches Mustafa BOZBUGA, Adnan OZTURK, Zafer ARI, Kayihan
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Sectional Anatomy Head Practice Problems
 1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Codes for Back and Spinal Procedures
 20930 Allograft for spine surgery only; morselized 20931 Allograft for spine surgery only; structural 20936 Autograft for spine surgery only (includes harvesting the graft); local (eg, ribs, spinous process,
20930 Allograft for spine surgery only; morselized 20931 Allograft for spine surgery only; structural 20936 Autograft for spine surgery only (includes harvesting the graft); local (eg, ribs, spinous process,
DRAFT PROGRAMME SKULL BASE 360 : ENDO/MICRO SKULL BASE COURSE Pre-congress workshop of AOSBS 2018 September 17-20, 2018
 DRAFT PROGRAMME SKULL BASE 360 : ENDO/MICRO SKULL BASE COURSE Pre-congress workshop of AOSBS 2018 September 17-20, 2018 Chairman MH. Huang Show Chwan Memorial Hospital Changhua, Taïwan President Director
DRAFT PROGRAMME SKULL BASE 360 : ENDO/MICRO SKULL BASE COURSE Pre-congress workshop of AOSBS 2018 September 17-20, 2018 Chairman MH. Huang Show Chwan Memorial Hospital Changhua, Taïwan President Director
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord
 1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH
 5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH The retrosigmoid approach provides good access to the cerebellopontine angle. It is by far simpler and faster with much less need for bone removal than other more extensive lateral
5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH The retrosigmoid approach provides good access to the cerebellopontine angle. It is by far simpler and faster with much less need for bone removal than other more extensive lateral
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Intrapetrous Internal Carotid Artery
 James C. Andrews, M.D., Neil A. Martin, M.D., Keith Black, M.D., Vincent F Honrubia, M.D., and Donald P Becker, M.D. Midd le Cranial Fossa Transtemporal Approach to the Intrapetrous Internal Carotid Artery
James C. Andrews, M.D., Neil A. Martin, M.D., Keith Black, M.D., Vincent F Honrubia, M.D., and Donald P Becker, M.D. Midd le Cranial Fossa Transtemporal Approach to the Intrapetrous Internal Carotid Artery
22110 vertebral segment; cervical vertebral segment; thoracic vertebral segment; lumbar
 The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir. HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi
 Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Neurosurgery 56[ONS Suppl 1]:ONS-4 ONS-27, 2005
![Neurosurgery 56[ONS Suppl 1]:ONS-4 ONS-27, 2005 Neurosurgery 56[ONS Suppl 1]:ONS-4 ONS-27, 2005](/thumbs/82/85896933.jpg) ANATOMIC REPORT MICROSURGICAL ANATOMY AND APPROACHES TO THE CAVERNOUS SINUS Alexandre Yasuda, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida Alvaro Campero, M.D. Department
ANATOMIC REPORT MICROSURGICAL ANATOMY AND APPROACHES TO THE CAVERNOUS SINUS Alexandre Yasuda, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida Alvaro Campero, M.D. Department
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
5. COMMON APPROACHES. Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2.
 5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
Despite the apparent recent evolution and modification
 Extended orbitozygomatic approach to the skull base to improve access to the cavernous sinus and optic chiasm ALLISON TERESA PONTIUS, MD, and YADRANKO DUCIC, MD, FRCS(C), FACS, Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas
Extended orbitozygomatic approach to the skull base to improve access to the cavernous sinus and optic chiasm ALLISON TERESA PONTIUS, MD, and YADRANKO DUCIC, MD, FRCS(C), FACS, Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
*in general the blood supply of the nose comes from branches of the internal and external carotid arteries.
 In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
Management of Giant Aneurysm
 Management of Giant Aneurysm Paul P. Huang, M.D. and Jafar J. Jafar, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery New York University Medical Center New York, New York, USA Introduction Giant intracranial aneurysms
Management of Giant Aneurysm Paul P. Huang, M.D. and Jafar J. Jafar, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery New York University Medical Center New York, New York, USA Introduction Giant intracranial aneurysms
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
ROYAL AUSTRALASIAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS. Neurosurgery Fellowship Examination. First Paper Essay Questions hours. Monday 1 September 2008
 Candidate No.: ROYAL AUSTRALASIAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS Neurosurgery Fellowship Examination First Paper Essay Questions - 1.5 hours Monday 1 September 2008 All Questions must be answered and are of equal
Candidate No.: ROYAL AUSTRALASIAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS Neurosurgery Fellowship Examination First Paper Essay Questions - 1.5 hours Monday 1 September 2008 All Questions must be answered and are of equal
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS
 HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Appearance of Normal Cranial Nerves on Steady-State Free Precession
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. EDUCATION EXHIBIT
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. EDUCATION EXHIBIT
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
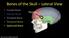 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]
![PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center] PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]](/thumbs/89/98821167.jpg) Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance
 Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance Breast Surgery Excision of lesion or tissue of breast including radical, modified, or quadrant resection, lumpectomy, incisional biopsy,
Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance Breast Surgery Excision of lesion or tissue of breast including radical, modified, or quadrant resection, lumpectomy, incisional biopsy,
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
