FirstRanker.com. [KT 501] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4052
|
|
|
- Clare Shanon Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 [KT 501] AUGUST 2008 Sub. Code : 4052 Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the cavernous sinus under the following headings: situation, extent, boundaries, relations, contents, connections and applied anatomy. 2. Describe the right lung under the following headings: surfaces, borders, impressions, fissures, lobes, hilum and Broncho pulmonary segments. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Rhomboid Fossa. 2. Maxillary Air sinus. 3. Labelled diagram of superolateral Surface of Cerebrum, indicating major Functional Areas. 4. Histology of Retina. 5. Coronary Sinus.. 6. Ansa Cervicalis. 7. Blood supply of Spinal cord. 8. Derivatives of I Branchial Arch. 9. Medial wall of Middle ear. 10. Hyoglossus Muscle - attachments and Relations. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Name the bones meeting at pterion. 2. Indicate the sinuses of the pericardium. 3. Name the terminal branches of internal thoracic Artery. 4. Indicate the Paleocerebellar deep nuclei. 5. Name the muscles attached to the cricoid cartilage. 6. Name two Sensory thalamic nuclei. 7. Name the structures passing through internal acoustic meatus. 8. Name the two parts of orlicularis occuli. 9. Name the Lingual papillae. 10. Indicate the venous sinuses related to the falx cerebri.
2 [KU 501] FEBRUARY 2009 Sub. Code : 4052 Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the tongue under the following headings: Situation and parts, Blood supply, Lymphatic drainage, Histology and development. 2. Describe the interior of right atrium and correlate it with its development. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Ciliary ganglion. 2. Facial artery. 3. Inter peduncular fossa. 4. Mid line structures of the neck. 5. Histology of cornea. 6. Pleural recesses. 7. Development of thyroid gland. 8. Lateral medullary syndrome. 9. Subclavian triangle. 10. T.S. at the level of superior colliculus of mid brain. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. What is ligamentum arteriosum? 2. Significance of pyriform fossa. 3. Name the muscles of mastication. 4. Give the sub divisions of mediastinum. 5. What are Hassal s corpuscles? 6. Name the splanchnic nerves in the thoracic region. 7. What is danger area of face? 8. Give the attachment of supra pleural membrane. 9. What is insula? 10. What is visual stria?
3 [KV 501] AUGUST 2009 Sub. Code : 4052 Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Explain thyroid gland under the following headings: a) Location and parts b) Coverings c) Relations d) Blood supply e) Histology f) Development g) Applied Anatomy. 2. Explain the typical intercostal space. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Development of face. 2. Otic ganglion. 3. Cerebellar peduncles. 4. Right Atrium. 5. Extraocular muscles. 6. Palatine tonsil. 7. Nerve Supply of tongue. 8. Tympanic membrane. 9. Bronchopulmonary segments. 10. Ansacervicalis. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Draw and label the histology of trachea. 2. Name the structures present in the lateral wall of cavernous sinus. 3. Nerve supply of larynx. 4. Parts of corpus callosum. 5. Four derivatives of ectoderm. 6. Enumerate four branches of 1st part of maxillary artery. 7. Structures passing through the foramen ovale. 8. Tributaries of coronary sinus. 9. Name the bones forming the nasal septum. 10. Name muscles of mastication.
4 [KW 501] FEBRUARY 2010 Sub. Code : 4052 Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the superolateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere under the following headings: Sulci and Gyri, functional areas and arterial supply. 2. Describe the arch of aorta under the following headings: Extent, Relations, Branches and microscopic anatomy. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Vocal cord. 2. Hilum of right lung. 3. Styloid apparatus. 4. Histology of parathyroid gland. 5. Development of interatrial septum. 6. Parotid duct. 7. Blood supply of spinal cord. 8. Venous drainage of face. 9. Middle meatus of nose. 10. Carotid sheath. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Name the bones taking part in the formation of nasal septum. 2. Name the structures passing through foramen spinosum. 3. Name any two nerves emerging from medulla oblongata. 4. Name any two structures in relation to mediastinal surface of left lung. 5. Name the parts of lacrimal apparatus. 6. Name the arteries which supply the heart. 7. Name the infrahyoid muscles of the neck. 8. Name the muscles of mastication. 9. Name the terminal branches of facial nerve. 10. Name the unpaired cartilages of the larynx.
5 [KX 501] AUGUST 2010 Sub. Code : 4052 Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the parotid gland under the following headings : a) Location and parts b) Relations c) Covering d) Nerve Supply e) Applied anatomy. 2. Describe in detail congenital anomalies of the Heart. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Development of tongue. 2. Facial artery. 3. Nerve supply of lacrimal gland. 4. Histology of pituitary gland. 5. Atlanto axial joints. 6. Hyoglossus Muscle. 7. Cardiac plexuses. 8. Right coronary artery. 9. Mediastinal surface of left lung. 10. Klinefelter syndrome. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Mention different parts of Diencephalon. 2. Emissary Veins. 3. Lacus lacrimalis. 4. Lymphatic drainage of the face. 5. Horner s Syndrome. 6. Histology of skeletal muscle. 7. Triangle of koch. 8. Barr body. 9. Types of Chromosomes. 10. Bones derived from 1 st pharyngeal arch. *
6 [KY 501] FEBRUARY 2011 Sub. Code : 4052 Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 15 = 30) 1. Describe the cerebellum as: classification, connections, nuclei, blood supply and clinical anatomy. 2. Describe in boundaries, contents and clinical anatomy of Carotid triangle. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Histology of Parotid gland. 2. Histology of Cornea. 3. Development of lung. 4. Internal capsule. 5. Typical intercostal nerve. 6. Cavernous sinus. 7. Connections of basal ganglia. 8. Blood supply of thyroid gland. 9. Lymphatic drainage of tongue. 10. Maxillary air sinus. III. Short Answer Questions : (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Enumerate the muscles of palate. 2. Two features of Naso-pharynx. 3. Congenital anomalies of ventricles of heart. 4. Derivatives of second pharyngeal arch. 5. Arteries supplying the spinal cord. 6. Boundaries of sub-mental triangle. 7. Structures present at hilum of left lung. 8. Name the unpaired dural venous sinuses. 9. Intrinsic muscles of larynx. 10. Waldeyer s ring.
7 [KZ 501] AUGUST 2011 Sub. Code : 4052 Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Maximum: 100 Marks I. Essay Questions : (2 x 10 = 20) 1. Describe in detail about blood supply of brain. 2. Describe submandibular salivary gland under following heading: parts, relations, blood supply, nerve supply, lymphatic drainage and clinical anatomy. II. Write Short notes on : (10 x 5 = 50) 1. Azygos vein 2. Relations of arch of aorta 3. Left coronary artery 4. Histology of cerebral cortex 5. Corpus callosum 6. Horns of lateral ventricle 7. Contents of posterior triangle 8. Extrinsic muscles of tongue 9. Brachiocephalic vein 10. Development of atria. III. Short Answer Questions : (15 x 2 = 30) 1. Interventricular septum 2. Costodiaphragmatic recess 3. Tricuspid valve 4. Oblique fissure of lung 5. Demilunes 6. Falx cerebelli 7. Substantia nigra 8. List special somatic afferent nuclei 9. Functional areas of superior temporal gyrus 10. Waldeyer s ring 11. Middle cervical ganglion 12. Parotid duct 13. Fenestra vestibule 14. Epicranial aponeurosis 15. Derivatives of third aortic arch.
8 [LA 501] FEBRUARY 2012 Sub. Code : 4052 I. Elaborate on : Revised (Non-Semester) Regulations Answer ALL questions in the same order. Maximum: 50 Marks 1. Describe the Thyroid gland under following headings: (1 x 10 = 10) a. Gross features b. Relations c. Blood supply d. Applied anatomy 2. Describe the Right lung under following headings: (1 x 5 = 5) a. Pleura b. Relations of medial surface c. Bronchopulmonary segments d. Applied anatomy. II. Write notes on: (10 x 2 = 20) 1. Pterion 2. Blood supply & nerve supply of scalp 3. 2nd pharyngeal arch 4. Histology of retina 5. Fourth ventricle 6. Name the muscles with nerve supply & action of tongue 7. Digastric triangle 8. Superior mediastinum 9. Down s syndrome 10. Pericardial sinuses. III. Short Answers: (15 x 1 = 15) 1. Parts of corpus callosum 2. Deep nuclei of cerebellum 3. Tentorium cerebelli 4. Name any four branches of external carotid artery 5. Name the components of lacrimal apparatus 6. Name the extraocular muscles of eyeball 7. Development of pituitary gland (in brief) 8. Mention the boundaries of laryngeal inlet 9. Right principal bronchus 10. Pleural diaphragm 11. Moderator band 12. Triangle of Koch 13. Simple squamous epithelium 14. Mention the four features of Tetralogy of Fallot 15. Mention the bones of middle ear cavity.
9 [LB 501] AUGUST 2012 Sub. Code : 4052 (180 Min) Maximum: 100 Marks I. Elaborate on: Pages Time Marks (Max.) (Max.) (Max.) 1. Classify the White matter of cerebrum and describe internal capsule under the following headings: a. Parts and Relations b. Constituent fibres c. Arterial supply d. Applied Anatomy 2. Define Mediastinum. Name its subdivisions. Name the contents of posterior mediastinum and describe oesophagus under the following headings: a. Level of origin b. Parts and Relations c. Level of constrictions d. Microscopic appearance e. Development II. Write notes on: 1. Lateral medullary syndrome Cavernous sinus Pterygo palatine ganglion Carotid triangle Inter atrial septum Pathway of visual reflexes Circle of Willis Intrinsic muscles of larynx Median nasal septum External acoustic meatus III. Short Answers on: 1. Formation and termination of external jugular vein Peculiarities of 1st intercostal nerve Lumbar Puncture Structures lodged in the lateral sulcus of the cerebrum Dangerous area of face Formation and termination of Left superior intercostal vein Suboccipital nerve Ligamentum denticulatum Structures pierced by parotid duct in order Origin and Branches of Middle Meningeal artery
10 [LC 501] FEBRUARY 2013 Sub. Code : 4052 Maximum: 50 Marks I. Elaborate on: (2 x 7.5 = 15) 1. Describe the Spinal cord under the following headings: a. Extent with coverings b. External features and Enlargements c. Cross section at mid thoracic level d. Blood supply e. Applied aspects. 2. Describe the Tongue under the following headings: a. Gross features b. Papillae c. Muscles with action d. Nerve supply e. Lymphatic drainage f. Applied aspects II. Write notes on : (10 x 2.5 = 25) 1. Thoracic duct 2. Pericardium 3. Mediastinal surface of left lung 4. Venous drainage of heart 5. Sagital section of eye ball 6. Paranasal air sinuses (name, Functions, opening, area, applied aspects) 7. Part & Constituent fibres of internal capsule 8. Middle ear cavity 9. Meninges with Meningeal spaces 10. Supero lateral surface of cerebrum III. Short answers on: (10 x 1 = 10) 1. Supra sternal space of Burns 2. Dangerous area of face 3. Structures passing through foreman ovale 4. Boundaries of Laryngeal inlet 5. Branches of ascending & arch of aorta 6. Lumbar puncture 7. Pterion 8. Apex beat 9. Contents of posterior Mediastinum 10. Applied aspects of pleura.
11 [LD 501] AUGUST 2013 Sub. Code : 4052 Maximum: 50 Marks I. Elaborate on: (2 x 7.5 = 15) 1. Describe boundaries and contents of carotid triangle. 2. Describe origin, course, branches of right coronary artery. II. Write notes on: (10 x 2.5 = 25) 1. Parts of corpus callosum 2. Name the extra ocular muscles 3. Facial artery in face 4. Formation of superior vena cava 5. Phrenic nerve 6. Lateral pterygoid muscle 7. Styloid process-structures attached 8. Surfaces, borders of thyroid gland 9. Muscles of tongue 10. Posterior horn of lateral ventricle. III. Short answers on: (10 x 1 = 10) 1. Terminal branches of external carotid artery 2. Arterial supply to pituitary 3. Dangerous area of face 4. Opening of maxillary sinus 5. Auditory tube openings 6. Blood supply to tonsil 7. Nerve supply and action of cricothyroid muscle 8. Attachment of vocalcord 9. Blood supply to lung 10. Terminal branches of internal thoracic artery.
12 [LE 501] FEBRUARY 2014 Sub. Code : 4052 Maximum: 50 Marks I. Elaborate on: (2 x 7.5 = 15) 1. Describe the sulci, gyri and functional areas in superolateral surface of brain with neat labelled diagrams. 2. Describe the extra ocular muscles in detail. II. Write notes on: (10 x 2.5 = 25) 1. Ansa cervicalis 2. Ciliary ganglion 3. Parts, arterial supply of Interventricular septum. 4. Cardiac plexus. 5. Middle ear 6. Origin, Termination and applied anatomy of internal mammary artery. 7. Digastric triangle 8. Third ventricle. 9. Medulla oblongata at mid olivary level. 10. Superior mediastinum III. Short answers on: (10 x 1 = 10) 1. Formation of basal vein 2. Surface marking of apex beat of heart 3. Blood supply of internal capsule. 4. Parts of caudate nucleus. 5. Dangerous area of scalp. 6. Patent ductus arteriosus. 7. Formation and distribution of spinal part of the accessory nerve. 8. Name any four branches of external carotid artery. 9. Define typical intercostal nerve with example. 10. Tributaries of cavernous sinus.
13 [LF 501] AUGUST 2014 Sub. Code : 4052 Maximum: 50 Marks I. Elaborate on: (1 x 10 = 10) 1. Describe the interior of right atrium in detail and add a note about its development and clinical anatomy. II. Write Notes on: (2 x 5 = 10) 1. Lateral wall of nose 2. Midbrain at superior collicular level. III. Short Answers on: (10 x 3 = 30) 1. Orbicularis oculi muscle 2. Blood supply of thyroid gland 3. Azygos vein 4. Pleural recesses 5. Histology of thymus 6. Boundaries and contents of sub occipital triangle 7. Pineal gland 8. Lateral medullary syndrome 9. Lumbar puncture 10. Development of tongue.
14 [LF 501] NOVEMBER 2014 Sub. Code: 4052 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 50 Marks I. Essay: (1 x 10 = 10) 1. Classify the white matter of cerebrum with examples and describe the internal capsule in detail. Add a note on its applied Anatomy. II. Write Notes on: (2 x 5 = 10) 1. Eustachian tube 2. Typical intercostals nerves III. Short Answers on: (10 x 3 = 30) 1. Inferior constrictor of pharynx 2. Blood supply of spinal cord 3. Carotid sheath 4. Left brachiocephalic vein 5. Histology of thyroid gland 6. Parkinsonism 7. Pterygopalatine ganglion 8. Structures present at T 4 level 9. Hilum of right lung 10. Development of pituitary gland.
15 [LG 501] FEBRUARY 2015 Sub.Code :4052 M.B.B.S. DEGREE EXAMINATAION FIRST YEAR PAPER II - ANATOMY - II Time: Three hours Q.P. Code: Answer All Questions Maximum : 50 Marks I. Essay: (1 x 10 = 10) 1. Describe the blood supply of heart. Add a note about its clinical significance. II. Write notes on: (2 x 5 = 10) 1. Lacrimal apparatus 2. Sulci, gyri and functional areas of supero lateral surface of cerebrum. III. Short answers on: (10 x 3 = 30) 1. Falx cerebri 2. Superior laryngeal nerve 3. Histology of cerebellum 4. Muscles of mastication 5. Development of interatrial septum 6. Maxillary sinus 7. Basilar artery 8. Vocal cords 9. Bell s palsy 10. Broncho pulmonary segments ******
16 [LH 501] AUGUST 2015 Sub. Code: 4052 PAPER II ANATOMY - II Q.P. Code: Time : Three Hours Maximum : 50 marks Answer ALL questions I. Elaborate: (1 x 10 = 10) 1. Classify Dural Venous Sinuses. Describe the Cavernous sinus in detail. Add a note on its applied anatomy. II. Write notes on : (2 x 5 = 10) 1. Nucleus, course, distribution and applied anatomy of Hypoglossal nerve 2. Blood supply of Brain III. Short answers on : (10 x 3 = 30) 1. Nasal Septum 2. Floor of 4 th Ventricle 3. Histology of Palatine Tonsil 4. Otic Ganglion 5. Cross sectional diagram of a typical intercostal space 6. Fallot s Tetralogy 7. Corpus Callosum 8. Interior of Right Atrium 9. Boundaries and Contents of Posterior Mediastinum 10. Muscles of Tongue
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701
![February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701](/thumbs/74/69742203.jpg) February 2009 [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks SECTION A (ANATOMY) 1. Describe the uterus under the following heads: a) Situation b) Normal position c) Parts
February 2009 [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks SECTION A (ANATOMY) 1. Describe the uterus under the following heads: a) Situation b) Normal position c) Parts
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI
 IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES NERVOUS SYSTEM TISSUES: HISTOLOGY SLIDES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System. A list of the first 3 digits - 72 terms
 1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1.
 Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1. Classification of internal organs. General plan of tubular organs. 2. The
Module 2 "Splanchnology. Central nervous system and sensory organs. HEART. Vessels and nerves of the head, neck, trunk, limbs" 1. Classification of internal organs. General plan of tubular organs. 2. The
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Brainstem. Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem
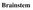 Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Q U E S T I O N A R Y of Anatomy and Histology for students dental medicine
 Q U E S T I O N A R Y of Anatomy and Histology for students dental medicine I. BONES AND JOINTS 1. Bone structure, development and growth. 2. Joints types: fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, bony union
Q U E S T I O N A R Y of Anatomy and Histology for students dental medicine I. BONES AND JOINTS 1. Bone structure, development and growth. 2. Joints types: fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, bony union
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Respiratory System. Ling Shucai
 Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Applied anatomy. Types of ossification & Epiphysis Kinesiology 2
 .General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
.General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
Sectional Anatomy Head Practice Problems
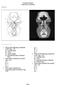 1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves)
 Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of
![function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of](/thumbs/74/71276096.jpg) Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
HEAD & NECK. FACE Muscles, nerve supply - sensory and motor, blood supply, Danger area Level 2: Applied anatomy
 HEAD & COURSE CONTENT COMPETENCIES The first year medical student should be able to understand and describe the gross anatomy of muscles, fascia, vessels, nerves, bones, joints and viscera of the head
HEAD & COURSE CONTENT COMPETENCIES The first year medical student should be able to understand and describe the gross anatomy of muscles, fascia, vessels, nerves, bones, joints and viscera of the head
 Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal
Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal
human anatomy 2016 lecture fifteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector. Section I
 Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Kidney Model (Model 3-13)
 Kidney Model (Model 3-13) Kidney Model Blood Vessels (Model 3-29) Segmental Artery Interlobar Artery Renal Artery Renal Vein Interlobular Artery Interlobular Vein Arcuate Artery Interlobar Vein Arcuate
Kidney Model (Model 3-13) Kidney Model Blood Vessels (Model 3-29) Segmental Artery Interlobar Artery Renal Artery Renal Vein Interlobular Artery Interlobular Vein Arcuate Artery Interlobar Vein Arcuate
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Group D: Central nervous system yellow
 Group D: Central nervous system yellow Central nervous system 1. General structure of nervous system (neuron, glia, synapsis, mediators, receptors) Main points: types of neurons and glial cells, synapses,
Group D: Central nervous system yellow Central nervous system 1. General structure of nervous system (neuron, glia, synapsis, mediators, receptors) Main points: types of neurons and glial cells, synapses,
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
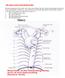 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
Laith Sorour. Facial nerve (vii):
 Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
CHAPTER 24. Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
CHAPTER 24 Respiratory System RESPIRATION INCLUDES Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) Gas exchange between blood and air at alveoli Transport of respiratory
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum. Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes
 Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
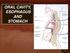 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
HEAD & NECK ANATOMY - MCQ HEAD & NECK ANATOMY
 . ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
. ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying
 Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerve Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor
Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerve Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal
 I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 2009 2010 FIRST YEAR B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2008. Paper. I ANATOMY Paper. I (New Scheme) Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Draw diagrams
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 2009 2010 FIRST YEAR B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2008. Paper. I ANATOMY Paper. I (New Scheme) Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Draw diagrams
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green
 Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
