Blood is carried within a closed transport system that is made up of three types of vessel:
|
|
|
- Lester Stevens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 5 Home A-level Biology Transport Transport in Mammals Biology A-level: Transport Transport in Mammals A recurring theme in biological systems is the surface area to volume ratio. All cells require nutrients and most re need to be removed. With a small organism this demand can be met by simple diffusion over the body surface but larger or very active with a pump to ensure that the supply meets the demand of all cells, even those deep within the body. In mammals, the pump is the heart. Substances are carried in a transport medium of the blood. The blood is con being released out of, or into the blood as it flows through certain vessels called capillaries. Blood vessels Blood is carried within a closed transport system that is made up of three types of vessel: arteries capillaries veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart. Capillaries are the site of the exchange of materials between the blood and tissues. Veins take blood back into
2 Page 2 of 5 Arteries Blood pumped out of the heart is at a very high pressure, so the structure of the arteries must be adapted to this. having very thick walls made up of elastic fibres and smooth muscle. These allow the wall to stretch as blood sur burst or rupture. It also means that as the artery increases in diameter, the pressure is reduced a little. After they 'give', the elastic pressure falls. The artery decreases in diameter thus raising the pressure a little. The lowering of the pressure when it is high, and the raising of it when it is lower produces some smoothing out o obvious though when you feel your neck or wrist that it is by no means complete - you can still feel the pulses of heart. A large artery will split into smaller arterioles that then branch further into many tiny capillaries. Arterioles have w but have a greater proportion of smooth muscle and less elastic tissue. They do not have to withstand as high a ability to contract because of the smooth muscle and regulate the flow of blood to a tissue. Capillaries To work efficiently, the capillaries need to be small enough to be in close proximity with small groups of cells and allow substances to move in and out of the blood.
3 Page 3 of 5 To enable this there are tiny gaps between the cells making up the wall of the capillary. These allow substances of the tissues. The fluid made up of plasma and dissolved substances is called tissue fluid. Tissue fluid Tissue fluid is formed because of the high hydrostatic pressure of the blood at the arteriole end of the capillary th The blood contains plasma proteins giving the blood a relatively high solute potential (and therefore a low water p the blood. Since the hydrostatic pressure has a greater effect than the solute potential at the arteriole end, the ne capillary. No blood cells or large proteins leave as they are too big to fit through the gaps. At the venule end of the capillary, since fluid has been lost, the hydrostatic pressure of the blood is lower and the this, fluid drains back into the blood. At this stage, the useful materials such as amino acids and glucose will have tissue fluid will now contain waste substances such as carbon dioxide and urea. About 90% of the fluid which leaks out of the capillaries seeps back in, the remaining 10% is returned to the bloo called lymph. This system is made up of many blind-ending lymph vessels, which allow tissue fluid to flow into th are large enough to allow proteins, which are too big to get into the capillaries, into the lymph vessels. If tissue flu returned to the blood by the lymphatic system, bloating or oedema is the result. Blood consists of cells bathed in a liquid plasma. When this plasma leaks out of the capillaries, it is called tissue composition to plasma but contains less protein molecules and no red blood cells. White blood cells can escape Lymph is virtually identical in composition to tissue fluid and just has a different name due to its different location This diagram shows the formation of tissue fluid: Veins The capillaries then join to form larger venules which themselves then join to form veins. Since at this stage, the pressure of the blood is low, blood needs to be 'encouraged' to flow back to the heart. To (particularly important if blood is flowing against gravity) there are valves in the veins. Also the veins pass throug muscles are active in contracting and relaxing, the squeezing on the veins moves blood along but due to the valv As the pressure is so much lower in the veins than in the arteries, there is little need for the elastic fibres and sm
4 Page 4 of 5 Previous Principle Return to Principles Next Principle
5 Page 5 of 5
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
CIE Biology A-level Topic 8: Transport in mammals Notes Circulatory systems can either be open, for instance in insects, or closed, like in fish and mammals where the blood is confined to blood vessels
Circulation 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012
 Circulation 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The exchange of substances 3 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and amoeba (below), do not need a circulatory
Circulation 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 The exchange of substances 3 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Single-celled organisms, such as bacteria and amoeba (below), do not need a circulatory
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse
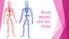 Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
Blood Vessels and Our Pulse Blood Vessels in Your Body All the blood vessels in your body joined together in a straight line would reach from St. John s, Newfoundland, to Victoria, British Columbia, and
 Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Cardiovascular System
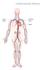 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy. Student Information Page 3A
 Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy Student Information Page 3A Activity Introduction: Once you get home from running around all day, your throat is probably a little dry. You go to your kitchen, get
Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy Student Information Page 3A Activity Introduction: Once you get home from running around all day, your throat is probably a little dry. You go to your kitchen, get
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Circulatory System. The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular
 transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1 1. Moves nutrients to and waste from cells 2. Pathway for disease fighting agents and hormones 3. Control of body temperature homeostasis 2 The Circulatory
TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1 1. Moves nutrients to and waste from cells 2. Pathway for disease fighting agents and hormones 3. Control of body temperature homeostasis 2 The Circulatory
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well
 Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44806 1 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m44806 1 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels
 CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
CIRCULATION Blood and Blood Vessels Blood Vessels The 5 Main Types 1. Arteries 2. Arterioles 3. Capillaries 4. Venules 5. Veins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pgi80ue-amo Arteries: 1) Arteries Function
Circulatory Systems AP Biology
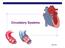 Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
Six main classes of blood vessels (on handout) Wall structure of arteries and veins (on handout) Comparison: Arteries vs. Veins (on handout)
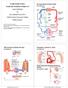 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
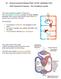 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Collin County Community College
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 6 Blood Vessels 1 Anatomy of Blood Vessels Walls of blood vessels contain 3 distinct layers : Tunica intima innermost layer includes
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 6 Blood Vessels 1 Anatomy of Blood Vessels Walls of blood vessels contain 3 distinct layers : Tunica intima innermost layer includes
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System No cell is further than that carries nutrients. Your circulatory system km of blood vessels. Your heart beats about from the beginning of life until death. During an average lifetime,
The Circulatory System No cell is further than that carries nutrients. Your circulatory system km of blood vessels. Your heart beats about from the beginning of life until death. During an average lifetime,
14-1: The Body s Transport System. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
8 Transport in humans
 Class: Name: ( ) Date: 8 Transport in humans 8.1 The human transport system (Book 1B, p. 8-3) In humans, a transport system is developed to ensure the supply of useful substances to all cells and removal
Class: Name: ( ) Date: 8 Transport in humans 8.1 The human transport system (Book 1B, p. 8-3) In humans, a transport system is developed to ensure the supply of useful substances to all cells and removal
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
: thick middle layer; cardiac muscles : thin inner layer; endothelial lining
 1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
Mr. Ulrich Circulatory Review Name: Regents Biology
 Mr. Ulrich Circulatory Review Name: Regents Biology 1. The muscular nature of the walls of ventricles is most closely associated with their function of A) storing blood from the body B) producing red blood
Mr. Ulrich Circulatory Review Name: Regents Biology 1. The muscular nature of the walls of ventricles is most closely associated with their function of A) storing blood from the body B) producing red blood
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
AP Biology. Circulatory Systems. Exchange of materials. Overcoming limitations of diffusion. Circulatory systems. In circulation
 Circulatory Systems 2008-2009 Exchange of materials nimal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, C ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s easy!
Circulatory Systems 2008-2009 Exchange of materials nimal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, C ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s easy!
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System
 Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS. October 21, 2016
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS October 21, 2016 Review AGENDA Questions Activity Notes HEART HEART = A BIG, WET, MUSCLY PUMP Body temperature ph levels Volume of body fluid REGULATES HEART TRANSPORTS
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS October 21, 2016 Review AGENDA Questions Activity Notes HEART HEART = A BIG, WET, MUSCLY PUMP Body temperature ph levels Volume of body fluid REGULATES HEART TRANSPORTS
Cardiovascular & lymphatic system both are supply fluid flow in to the body. but bothe are deferent type of fluid..
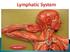 Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
What was the range of the resting heart rates in males after the exercise programme?
 Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of a 6-week exercise programme on the resting heart rate of males and females. The scientists recruited a large group of male volunteers and a large group of female
Q1.Scientists investigated the effect of a 6-week exercise programme on the resting heart rate of males and females. The scientists recruited a large group of male volunteers and a large group of female
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Biology Slide 1 of 36
 Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Circulation. Invertebrates on Land: such as insects, and such as earthworms also do not have a gastrovascular cavity.
 Circulation A. Invertebrates in Water: Organisms that are a cells thick. Diffusion alone is sufficient for single-celled (amoeba and paramecium) and simple, multi-cellular animals such as (hydra, jellies,
Circulation A. Invertebrates in Water: Organisms that are a cells thick. Diffusion alone is sufficient for single-celled (amoeba and paramecium) and simple, multi-cellular animals such as (hydra, jellies,
Blood Vessels. Over view. We have about 60,000 miles of blood vessels!
 Blood Vessels Over view 3 types of blood vessels arteries - carry blood away from heart "branch", "diverge", and "fork" veins - carry blood toward heart "join", "merge", and "converge" capillaries - site
Blood Vessels Over view 3 types of blood vessels arteries - carry blood away from heart "branch", "diverge", and "fork" veins - carry blood toward heart "join", "merge", and "converge" capillaries - site
Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro
 Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro Name Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Progressive Resistance Exercise Progressive resistance exercise
Making Connections Practice Mrs. Fornaro Name Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Progressive Resistance Exercise Progressive resistance exercise
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 3
 Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 3 Fluid Shifts Between Capillaries and Tissue Permeable capillaries allow plasma and solutes to pass into interstitial space interstitial or extracellular
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 3 Fluid Shifts Between Capillaries and Tissue Permeable capillaries allow plasma and solutes to pass into interstitial space interstitial or extracellular
Topic 8 Transport in humans. 1. Blood consists mostly of A. white blood cells B. red blood cells C. blood platelets D. water
 Topic 8 Transport in humans 1. Blood consists mostly of A. white blood cells B. red blood cells C. blood platelets D. water 2. Which of the following is not a correct match? Red blood cell White blood
Topic 8 Transport in humans 1. Blood consists mostly of A. white blood cells B. red blood cells C. blood platelets D. water 2. Which of the following is not a correct match? Red blood cell White blood
CHAPTER 26. Circulation and Gas Exchange
 CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body
 In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
