Wolverine Coronary Cutting Balloon
|
|
|
- Blaze Greer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 < en > Wolverine Coronary MONORAIL OVER-THE-WIRE Microsurgical Dilatation Device Table of Contents Warning...1 device description...1 Contents...1 Quantity Material...1 Intended use/indications for use...1 Contraindications...1 Warnings...1 Precautions...2 Adverse Events...2 Observed Adverse Events...2 Table 1. GRT Major Adverse Events Occurring Within 270 Days (1,238 Patients)...2 Potential Adverse Events...2 Observed Device Malfunctions...2 Clinical Studies...2 Resistant Lesion Registry (RLR)...2 Table 2. Demographics, Risk Factors and Prior Procedures...2 Table 3. Principal Effectiveness and Safety Results of Resistant Lesion Registry (n=29 patients, 30 lesions)...3 Global Randomized Trial (GRT)...3 Table 4. Principal Effectiveness and Safety Results (Intent-to-Treat) All Randomized Lesions Treated (1238 Patients, 1385 Lesions)...3 Table 5. Wolverine Coronary Microsurgical Dilatation Device Compliance...4 How supplied...4 Handling and Storage...4 Operational Instructions...4 Additional Supplies...4 Inspection Prior to Use...4 Wolverine Device Preparation...4 Wolverine Device Positioning...4 Wolverine Device Inflation...4 Wolverine Device Removal...4 References...4 Warranty...5 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Warning Contents supplied STERILE using an ethylene oxide (EO) process. Do not use if sterile barrier is damaged. If damage is found, call your Boston Scientific representative. For single use only. Do not reuse, reprocess or resterilize. Reuse, reprocessing or resterilization may compromise the structural integrity of the device and/or lead to device failure which, in turn, may result in patient injury, illness or death. Reuse, reprocessing or resterilization may also create a risk of contamination of the device and/or cause patient infection or cross-infection, including, but not limited to, the transmission of infectious disease(s) from one patient to another. Contamination of the device may lead to injury, illness or death of the patient. After use, dispose of product and packaging in accordance with hospital, administrative and/or local government policy. Carefully review all instructions prior to use. Observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. device description The Wolverine Over-The-Wire (OTW) Coronary Microsurgical Dilatation Device and the Wolverine Monorail (MR) Coronary Microsurgical Dilatation Device consists of a balloon with 3 or 4 atherotomes (microsurgical blades) mounted longitudinally on its outer surface mm 3.25 mm balloon diameter models contain 3 atherotomes and 3.50 mm 4.00 mm balloon diameter models contain 4 atherotomes. When the device is inflated, the atherotomes score the plaque, creating initiation sites for crack propagation. This process, referred to as atherotomy, allows dilatation of the target lesion with less pressure. The distal section of both devices (and the proximal section of the OTW device) is dual lumen and coaxial. The outer lumen is used for inflation of the balloon, and the inner lumen permits the use of guidewires in (0.36 mm) to facilitate advancement of the device to and through the stenosis to be dilated. The proximal section of the MR device is a single-lumen, stainless steel hypotube with a single luer port hub for inflation/deflation of the balloon. The OTW device has a dual luer port hub: one for inflation/deflation of the balloon, the other for guidewire lumen access. The balloon with atherotomes is designed to provide an inflatable segment of known diameter and length at recommended pressures. A balloon protector is placed over the balloon to maintain a low profile and a mandrel is placed into the inner lumen to protect the patency of the device. The device s tip is tapered to facilitate advancement of the device to and through the stenosis. All shafts have ZGlide TM (hydrophilic) coating. For MR, the ZGlide is located from the guidewire port to the distal tip of the device. For OTW, the ZGlide is located from distal of the proximal marks to the distal tip of the device. The effective catheter length of the MR is 143 cm and the OTW is 142 cm. Marks on the proximal portion of the device shaft (for MR, one at 90 cm and one at 100 cm; for OTW, one at 90 cm and two at 100 cm) indicate the exit of the balloon device tip out of the guide catheter. The device is provided in 6 mm, 10 mm, and 15 mm lengths. The functional atherotome length is the distance between the radiopaque marker bands. These radiopaque marker bands, in conjunction with fluoroscopy, aid in the placement of the cutting balloon segment. A CLIPIT Hypotube Clip is provided with the MR device to aid in handling the device. Contents Quantity Material One (1) Wolverine OTW Device or One (1) Wolverine MR Device One (1) CLIPIT Hypotube Clip (MR Device Only) Intended use/indications for use The Wolverine Device is indicated for dilatation of stenoses in coronary arteries for the purpose of improving myocardial perfusion in those circumstances where a high pressure balloon resistant lesion is encountered. In addition, the target lesion should possess the following characteristics: Discrete (< 15 mm in length), or tubular (10 mm to 20 mm in length) Reference vessel diameter (RVD) of 2.00 mm to 4.00 mm Readily accessible to the device Light to moderate tortuosity of proximal vessel segment Nonangulated lesion segment (< 45 ) Smooth angiographic contour Absence of angiographically visible thrombus and/or calcification Contraindications The Wolverine Device is contraindicated for use in: Delivery through the side cell of a previously placed stent as the deflated could become entangled in the stent. Coronary artery spasm in the absence of a significant stenosis. Warnings Exercise extreme care when treating a lesion distal to a stent. If the guidewire has passed through a stent cell rather than down the axis of the stent, the deflated device could become entangled in the stent. When treating lesions at a bifurcation, the device can be used prior to placing a stent, but should not be taken through the side cell of a stent to treat the side branch of a lesion at a bifurcation. The atherotomy process, because of its mechanism of action, may pose a greater risk of perforation than that observed with conventional Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA). Over sizing increases the risk of perforation. To reduce the potential for vessel damage, the inflated diameter of the device should approximate a 1.1:1 ratio of the diameter of the vessel just proximal and distal to the stenosis. The atherotomy process in patients who are not acceptable candidates for coronary artery bypass surgery requires careful consideration, including possible hemodynamic support during the atherotomy process, as treatment of this patient population carries special risk. When the device is exposed to the vascular system, it should be manipulated while under high-quality fluoroscopic observation. Do not advance or retract the device unless the balloon is fully deflated under vacuum. If resistance is met during manipulation, determine the cause of the resistance before proceeding. Balloon pressure should not exceed the rated burst pressure. The rated burst pressure is based on the results of in vitro testing. At least 99.9% of the balloons (with 95% confidence) will not burst at or below their rated burst pressure. Use of a pressure-monitoring device is recommended to prevent over pressurization. The atherotomy process should only be performed at hospitals where emergency coronary artery bypass graft surgery can be quickly performed in the event of a potentially injurious or life-threatening complication. During preparation and positioning of the device, it is important that all air and fluid are excluded from the inflation lumen of the device until the balloon is in position at the lesion site. Use only the recommended balloon inflation medium (e.g. contrast medium). Never use air or any gaseous medium to inflate the balloon. If resistance is encountered when withdrawing the device through the guide, consider removing the guide and the device as a complete unit.
2 Precautions Prior to performing the procedure, the device should be examined to verify functionality and ensure that its size and shape are suitable for the specific procedure for which it is to be used. The device should be used only by physicians trained in the performance of PTCA. During the procedure, appropriate anticoagulant and coronary vasodilator therapy should be provided to the patient. Anticoagulant therapy should be continued for a period of time after the procedure as determined by the physician. The device is not designed for, and therefore, cannot be used to monitor in vivo arterial pressures. After removal from the guide catheter, system integrity should be verified prior to reinsertion. Use the device prior to the Use By date specified on the package. If difficulty is experienced during balloon inflation, do not continue; remove the device and do not attempt to use it. Select another device. Do not use if sterile barrier is damaged. If damage is found call your Boston Scientific representative. Prior to an angioplasty, the device should be examined to verify functionality and to ensure that its size and shape are suitable for the specific procedure for which it is to be used. Infusion of any medium other than a flush of heparinized normal saline through the guidewire lumen may compromise device performance. Do not attempt to reposition a partially deployed balloon. Attempted repositioning of a partially deployed balloon may result in severe vessel damage. Do not use a guidewire having a diameter greater than in (0.36 mm). Adverse Events Observed Adverse Events The Adverse Events reported in this section were those observed in two clinical investigations: the Resistant Lesion Registry (RLR), which demonstrated the ability of the Cutting Balloon Device to dilate lesions in a series of patients whose lesions could not be dilated with conventional balloon angioplasty; and the Global Randomized Trial (GRT), a multicentered, randomized trial designed to compare the Cutting Balloon Device with conventional angioplasty. Twenty-nine patients were entered into the RLR and a total of 1245 patients were randomized in the GRT; 622 to the Device arm and 623 to the PTCA arm. Seven patients (5 in the Cutting Balloon Device arm and 2 in the PTCA arm) were deregistered after randomization, but before receiving the assigned treatment. Therefore, there were 1238 evaluable patients in the GRT. In the RLR, dissection was the only in-lab complications recorded. Dissections occurred 14 times: six times prior to Device treatment; two times after Cutting Balloon Device treatment; and six times as part of the post- Device adjunctive treatment. One patient death from a cardiac arrest and acute pulmonary edema occurred in the RLR hours post-procedure. This patient was treated for mid-rca lesion with a series of four inflations with a PTCA balloon catheter, followed by a single inflation with the Device. A dissection was noted following use of the Device. Adjunctive treatment included two inflations with a second PTCA balloon catheter followed by placement of a stent. The major adverse events occurring in the GRT are listed in Table 1. There were eight deaths among the patients randomized to the Device arm. Two deaths occurring during the procedure involved perforations. In the first case, the perforation was associated with contrast extravasation and a Grade F dissection which was treated with balloon angioplasty and one stent. Quantitative Coronary Angiography (QCA) reported Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) 3 flow with a 35% residual stenosis and persistent contrast extravasation at the end of the procedure. Tamponade developed and the patient died during surgery. An intramyocardial hematoma was identified. In the second case, the coronary artery ruptured at the Device site and the patient developed ventricular fibrillation. The patient was resuscitated and treated emergently for tamponade, but expired following Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG). In both of these cases, the Device was oversized. The balloon: artery ratio, as determined by QCA, was 1.25:1 and 1.8:1, respectively. A perforation also occurred in the death of another patient who was randomized to the Device arm, but treated with a PTCA balloon because of a failure to cross the lesion with the Device. This patient died 105 days post-procedure due to complications of a CABG performed at that time. One patient died within an hour of the procedure from a presumed re-occlusion. A fifth patient died at 130 days post-procedure from a reported heart attack. Two deaths occurred following exacerbation of a pre-existing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and respiratory failure (20 days), and emergency surgery for an abdominal aortic aneurysm (50 days). The remaining death was reported as the result of respiratory failure caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Perforation was observed in five cases, all in the Device arm. As described above, in two of these cases the patient died acutely. Perforations were treated with PTCA, a stent or both. Table 1. GRT Major Adverse Events Occurring Within 270 Days (1,238 Patients) Adverse Event Device* 2 Conventional Balloon MACE 13.6% (84/617) 15.1% (94/621) Death 1.3% (8/617) 0.3% (2/621) MI 4.7% (29/617) 2.95% (18/621) Q Wave MI 1.5% (9/617) 1.1% (7/621) Non-Q Wave MI Emergent CABG 3.2% (20/617) 1.8% (11/621) 1.0% (6/617) 1.0% (6/621) TLR 11.7% (72/617) 14.8% (92/621) CABG (per pt.) 1.5% (9/617) 2.1% (13/621) PTCA (per pt.) 10.5% (65/617) 12.7% (79/621) Subacute Closure 1.3% (8/617) 1.6% (10/621) Bleeding Complications 0.3% (2/617) 0.0% (0/621) Vascular Complications 0.3% (2/617) 0.2% (1/621) Clinical Perforation 0.8% (5/617) 0.0% (0/621) Difference [95% Ci] -1.5% [-5.4%, 2.4%] 1.0% [0.0%, 2.0%] 1.8% [-0.3%, 3.9%] 0.3% [-0.9%, 1.6%] 1.5% [-0.3%, 3.2%] 0.0% [-2.3%, 1.7%] -3.1% [-6.9%, 0.6%] -0.6% [-2.1%, 0.8%] -2.2% [-5.8%, 1.4%] -0.3% [-1.5%, 3.0%] 0.3% [-1.9%, 0.7%] 0.1% [-1.9%, 1.0%] 0.8% [-0.4%, 2.3%] *Numbers are % (count/sample size). Difference = S CB -S PTCA SE Diff = sqrt [SE CB2 +SE PTCA2 ] CI = Diff ± 1.96*SE Diff Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE); Death, Q Wave MI, emergent CABG, target lesion CABG or TL-PTCA. Target lesion revascularization (TLR) at 9 months: any clinical driven PTCA (TL-PTCA) or bypass surgery (TL-CABG) performed on the target lesion after documentation of recurrent angina and/or evidence of myocardial ischemia by stress testing. Vascular complications: Any vascular complication requiring surgical repair. Potential Adverse Events Potential adverse events include, but are not limited to, the following: Abrupt closure Acute myocardial infarction Angina of unstable angina Arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation Arteriovenous fistula Cardiac tamponade/pericardial effusion Cardiogenic shock Cerebrovascular accident/stroke Coronary aneurysm Coronary artery bypass graft surgery Coronary artery spasm Coronary vessel dissection, perforation, rupture, or injury, possibly requiring surgical repair or intervention Death Drug reactions, including allergic reaction to contrast medium Embolism Hemodynamic compromise Hemorrhage or hematoma Hypo/hypertension Infection Minor vessel trauma Myocardial ischemia Percutaneous re-intervention Pseudoaneurysm (at vascular access site) Pyrogenic reaction Renal failure Respiratory insufficiency Restenosis of the dilated vessel Side branch occlusion Slow flow/no reflow Thrombosis Total occlusion of the coronary artery or bypass graft Transient ischemic attack Vasovagal reaction Ventricular irritability/dysfunction Vessel trauma requiring surgical repair or intervention Volume overload Observed Device Malfunctions There were no Device malfunctions in the RLR. A total of 15 Device malfunctions were recorded in the GRT. Two devices failed to inflate. Thirteen cases of balloon leak or rupture were reported: 9 with the first inflation and 4 with the second inflation. Clinical Studies Resistant Lesion Registry (RLR) The Resistant Lesion Registry (RLR) contains registry data on 30 lesions in 29 patients. All patients were enrolled at a single site between November 1996 and November Study Endpoints The primary endpoint was acute lesion success defined as a reduction in lumen narrowing of at least 20%. The secondary endpoint was procedural success. Procedural success was defined as lesion success, a final residual stenosis of 50 after all devices are used and no major adverse events (MACE, defined as death, CABG, or non-fatal MI). Study Population The RLR patients were selected for treatment on the basis of failed conventional angioplasty, defined as failure to reduce the lumen diameter narrowing by > 20% and the final residual stenosis > 50% with PTCA balloon inflation pressures > 10 atmospheres. The demographics, risk factors and prior history of these patients are shown in Table 2. Table 2. Demographics, Risk Factors and Prior Procedures Demographics: % Male 69% (20/29) Age 65 ± 8.4 Angina Class (CCS) 2.8 ± 0.8 Risk Factors: Diabetes 14% (4/28) Smoking 39% (11/28) HB Pressure 29% (8/28) Hyperlipidemia 48% (13/27) Risk Procedures: MI 33% (9/27) CABG 22% (6/27) PTCA 22% (6/27)
3 Methods Patient data were obtained prospectively on 6 patients under a formal clinical protocol and retrospectively on 23 patients. For both prospective and retrospective patient groups, conventional balloon angioplasty was used as the initial treatment in all but two cases. In these two cases the Cutting Balloon Device was used as the first treatment for dilatation of an unprotected left main, a vessel known to be resistant to PTCA dilatation. Physician discretion was used to further decrease the residual stenosis with additional adjunctive devices following treatment with the Device. Results Of the 29 patients entered into the RLR, balloon resistant lesions were treated in 26 native vessels and 4 saphenous vein grafts (SVGs). Patients were treated with a sequence of devices including the Device. The Cutting Balloon Device was usually used as the second (14 cases) or third (10 cases) device in each treatment sequence. In three cases, the Device failed to cross the lesion on the initial attempt. Successful crossing was achieved with the second attempt (2 cases) following an additional crossing with a PTCA balloon. In the third case there were no further attempts to cross the lesion. In most cases, the Device was inflated once (78%, 25/32); while the number of inflations with the PTCA catheter, prior to the Device, varied from 1 (31%, 14/45), 2 (36%, 16/45), 3 (18%, 8/45), to 4 (16%, 7/45) inflations. Inflation pressures ranged from 8-16 atmospheres for the Device and 4-25 atmospheres for the PTCA catheters. The average inflation pressure for the Device was significantly less than the average pressure used for the PTCA catheters [9.3 ± 1.8 atm (n=32) versus 15.4 ± 3.6 atm (n=45), p < ]. The principal safety and efficacy results of the RLR are shown in Table 3. The primary and secondary endpoints, used for the prospectively enrolled patients, were also applied to the patients enrolled retrospectively. Table 3. Principal Effectiveness and Safety Results of Resistant Lesion Registry (n=29 patients, 30 lesions) Effective Measures: Device %, (n/n), [95% CI] Acute Lesion Success 78% (18/23) [56%, 93%] Procedural Success 74% (17/23) [52%, 90%] % DS - Initial 73% (30) [70%, 77%] Post PTCA 51% (17) [44%, 59%] Post CB 36% (22) [28%, 45%] Final 16% (30) [8%, 23%] Safety Measures: MACE 3% (1/30) [1%, 10%] Dissection, Prior to 20% (6/30) [8%, 39%] Dissection, Device + Adjunctive Use 27% (8/30) [12%, 47%] Global Randomized Trial (GRT) The Global Randomized Trial (GRT) was a multi-centered, randomized trial designed to compare the Device with conventional angioplasty. Patient enrollment in the GRT occurred between June 1994 and November 1996, at 31 centers in the US, Canada, France, Belgium and the Netherlands. Of the 1245 patients enrolled, 622 were assigned to the Device arm and 623 to the PTCA arm. Seven patients (5 in the Device and 2 in the PTCA arm) were deregistered after randomization but before receiving the assigned treatment. Deregistration occurred for the following reasons: resolution of the stenosis between the prior angiogram and the index procedure (3 cases), the presence of calcification requiring atherectomy (1 case), and failing to meet the inclusion criteria (3 cases). Study Endpoints The primary endpoint was angiographic restenosis at 6 months. Secondary endpoints included TLR and MACE at 9 months. A clinical events committee blinded to treatment assignment adjudicated all major clinical events. Study Population Results Patients, between the ages of 25 and 75 years, with atherosclerotic The acute and six months angiographic and clinical results coronary artery disease were eligible for enrollment in the GRT demonstrated that the Device was similar if they were suitable candidates for coronary artery bypass graft to PTCA with respect to Procedure Success (defined as surgery and the target lesions were de novo Type A or B lesions in achievement of < 50% residual diameter stenosis and freedom native arteries without total obstructions or visible thrombus, and from in-hospital major adverse cardiac events [MACE, defined were accessible to the Device. as death, Q wave MI, emergent coronary artery bypass surgery, Methods or repeat target lesion revascularization]), 30-day incidence of MACE, and Angiographic Restenosis (defined as > 50% Patients were prospectively randomized to treatment with either minimum lumen diameter stenosis at follow-up angiography). the Device or PTCA. Access to the target lesion was The principle safety and efficacy results are shown in Table 4. gained through the femoral artery approach. The reference vessel diameter (located just proximal to the target lesion) was measured Individualization of Treatment by quantitative angiography. Avoid use in patients whose lesions possess the following Selection of the Device with the appropriately sized characteristics: reference coronary artery diameter of less balloon diameter was based on the reference vessel diameter. If than 2.0 mm; diffuse (> 20 mm in length); total obstruction necessary, tandem dilatations were allowed for lesion lengths 20 mm. (occlusion); heavy calcification; excessive tortuosity of Over sizing of the balloon was not recommended in the PTCA arm. proximal vessel segment; moderate to extreme angulation of target lesion segment ( 45 ); inaccessible to the device; The protocol allowed for a single inflation of the thrombus present. Device up to 8 atmospheres for a maximum of 90 seconds. Subsequent dilatation(s) with a PTCA balloon were allowed only Appropriate sizing of the Flextome Device if the residual stenosis was > 40%. In the PTCA arm, the inflation is extremely important. Do not exceed a balloon: artery ratio times and pressures were left to the discretion of the investigator. of 1.1:1. Serial inflations with a single balloon, or subsequent inflations Delivery failures are likely to be more frequent with the with increased diameter PTCA balloons were allowed to achieve a Flextome Device than with conventional PTCA. 20% reduction in stenosis and a 50% residual stenosis. Multiple This occurs for two reasons. First, the Flextome violations of the procedural protocol were reported in the Cutting Device has a larger profile than a conventional PTCA catheter Balloon Device arm [33% (212/617) of the Device of the same nominal inflated diameter. Second, the materials of subjects were not treated per protocol]. construction prevent the Flextome Device from being as flexible as a conventional balloon. Clinical follow-up was performed at six weeks, six months and nine months. Baseline quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) was If you intend to use a 15 mm device, but suspect that you may performed pre-procedure, following device use, and after the final have difficulty in reaching the lesion because of tortuosity, treatment in all patients. Follow-up quantitative coronary angiography consider using a 10 mm device with tandem inflations. at 6 months was required in all patients. Anti-coagulation included aspirin 325 mg/day throughout the study. Table 4. Principal Effectiveness and Safety Results (Intent-to-Treat) All Randomized Lesions Treated (1238 Patients, 1385 Lesions) Efficacy Measures (per lesion) Device (N=689) PTCA (N=696) Relative Risk [95% Ci] Difference [95% Ci] Lesion Success 95.5% (642/672) 96.5% (668/692) 0.99 [0.97, 1.01] -1.0 % [-3.1%, 1.1%] Device Success 77.7% (473/609) 77.8% (460/617) 1.00 [0.94, 1.06] -0.1% [-4.8%, 4.5%] Procedure Success 92.9% (566/609) 94.7% (584/617) 0.98 [0.95, 1.01] -1.7% [-4.4%, 1.0%] MLD after Device (mm) Range % DS after Device Range MLD after 6 months (mm) Range % DS after 6 months Range ± 0.52 (672) (0.00, 4.14) 29% ± 14% (672) (-13%, 100%) 1.63 ± 0.62 (551) (0.00, 3.44) 42% ± 19% (551) (-11%, 100%) 2.13 ± 0.53 (692) (0.00, 4.07) 27% ± 13% (692) (-12%, 100%) 1.65 ± 0.61 (559) (0.00, 3.40) 42% ± 19% (559) (-4%, 100%) N/A [-0.14, -0.03] N/A 1.6% [0.1%, 3.0%] N/A [-0.10, 0.05] N/A 0.1% [-2%, 2%] Restenosis Rate at 6 months 31.4% (173/551) 30.4% (170/559) 1.03 [0.87, 1.23] 1.0% [-4.5%, 6.4%] TLR-free at 9 months* 89.3% 86.1% 1.04 [1.00, 1.08] 3.2% [-0.3%, 6.7%] TVR-free at 9 months 88.5% 84.6% 1.05 [1.00, 1.09] 3.9% [0.3%, 7.5%] TVF-free at 9 months 86.9% 84.8% 1.03 [0.98, 1.07] 2.2% [-1.7%, 6.1%] Safety Measures and Other Clinical Events (per patient) (N=617) (N=621) Relative Risk [95% Ci] Difference [95% Ci] MACE 30 days 3.7% (23/617) 2.7% (17/621) 1.36 [0.74, 2.52] 1.0% [-1.0%, 3.0%] MACE > 30 days 10.0% (62/617) 12.9% (80/621) 0.78 [0.57, 1.06] -2.8% [-6.4%, 0.7%] Perforations 0.8% (5/617) 0% (0/621) N/A 0.8% [-0.4%, 2.3%] Vascular Complications 0.3% (2/617) 0.2% (1/621) 2.01 [0.19, 21.11] 0.2% [-0.4%, 0.7%] Numbers are % (count/sample size) or Mean ± 1 SD. CI = Confidence interval. Survivor estimates by Kaplan-Meier method; Standard Error estimates by Greenwood formula. Relative Risk = S CB /S PTCA SE RR = sqrt [(SE CB /S CB2 ) + (SE PTCA /S PTCA )] CI = RR*exp (1.96*SE RR ) Difference = S CB -S PTCA SE Diff = sqrt [SE CB + SE PTCA2 ] CI = Diff ± 1.96*SE DIFF Lesion success: Lesion success was defined as the achievement of a final residual diameter stenosis of < 50% (by QCA core laboratory) using any percutaneous method. Device success: Achievement of a final residual diameter stenosis of < 50% (by QCA core laboratory) in the absence of unplanned coronary stenting, randomized treatment failure or crossover. Procedure success: Achievement of a final residual diameter stenosis of < 50% (by QCA core laboratory) in the absence of: In-Hospital MACE or target lesion revascularization within 7 days after the index procedure. *TLR-free: Survival free from target lesion revascularization at 9 months estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods. TVR-free: Survival free from target vessel lesion revascularization at 9 months estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods. TVF-free: Survival free from target vessels failure (death, Q wave myocardial infarction, or target vessel revascularization) at 9 months estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods. Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE): Death, Q wave MI, emergent CABG, target lesion CABG or TL-PTCA. Primary endpoint: Death, Q wave MI, emergent CABG, target lesion revascularization, or subacute closure within 30 days of the index procedure. Vascular complications: Any vascular complication requiring surgical repair.
4 Table 5. Wolverine Coronary Microsurgical Dilatation Device Compliance Pressure Model Diameter (mm) x Ave. Balloon Diameter (mm) ATM (kpa) 2.00 mm 2.25 mm 2.50 mm 2.75 mm 3.00 mm 3.25 mm 3.50 mm 3.75 mm 4.00 mm 3.0 (304) (405) (507) (608) NOM (709) (811) (912) (1013) (1115) (1216) RBP How supplied Non-pyrogenic Do not use if package is opened or damaged. Do not use if labeling is incomplete or illegible. Handling and Storage Store in a cool, dry, dark place. Operational Instructions Additional Supplies In addition to the Wolverine OTW or Wolverine MR Cutting Balloon Microsurgical Dilatation Device, the following supplies should be prepared for use: Guidewire(s) of appropriate size for advancement of guide catheter Arterial sheath and dilator set (for femoral approach only) in (0.36 mm) x 300 cm guidewire(s) (Wolverine OTW Device) in (0.36 mm) x 185 cm guidewire(s) (Wolverine MR Device) Femoral or brachial guide catheter(s) in the appropriate size and configuration to select the coronary artery - Minimum I.D. of 6 FR guide catheter = in (1.68 mm) (Wolverine OTW Device, and Wolverine MR Device with 3.50 mm 4.00 mm balloon diameters) - Minimum I.D. of 5 FR guide catheter = in (1.42 mm) (Wolverine MR Device with 2.00 mm 3.25 mm balloon diameters) Sterile saline or heparinized sterile saline Radiopaque contrast medium Three-way stopcock or infusion manifold/apparatus Inflation device with manometer 10, 12, or 20 ml (cc) luer-lock Hemostasis valve Guidewire torque device Other supplies and medications per local protocols Inspection Prior to Use All equipment to be used for the procedure, including the Wolverine Device, should be examined carefully to verify functionality. Inspection prior to use should verify that the device and sterile packaging have not been damaged in shipment and that it is ready to be used. Do not use if sterile package is damaged. The device should be prepared and tested following the directions provided below prior to insertion in the body. Note: Do not continue to use the device if damage occurs or sterility is compromised during use. Wolverine Device Preparation Caution: This is a wet negative prep procedure. Customary balloon preparation methods do not apply. These steps must be followed exactly. 1. Sizing the device to the reference artery is extremely important for a successful dilation. Over sizing the balloon increases the risk of perforation. To reduce the potential for vessel damage, the inflated diameter of the device should approximate a ratio of 1.1:1 in relation to the average diameter of the reference coronary artery. 2. Using sterile technique, remove the device in its protective hoop from its package and place onto a sterile field. Do not remove the device from its protective hoop. Do not remove the balloon protector from the device tip. 3. Connect a three-way stopcock to the balloon port. Turn stopcock lever OFF to the balloon. Prepare an inflation device with 5 cc of contrast solution (mixture must be at least 50:50 contrast medium and sterile saline). 4. Attach the inflation device to stopcock. Assure luer connections are properly aligned to avoid stripping the luer thread causing subsequent leakage and use care when connecting the device to avoid damage (e.g., shaft kink). Purge stopcock by flushing 1-2 cc of contrast medium through the middle port. 5. Turn the stopcock lever towards the middle port or open to the balloon and immediately withdraw inflation device plunger to full negative and place the inflation device in a locked position. This will maintain a constant vacuum on the device. Do not allow fluid into the balloon until inflation. This will maintain the folding integrity of the balloon and protect the atherotomes. If fluid has prematurely been introduced into the balloon, do not use the device. If air has been introduced into the balloon, do not use the device. 6. When the device is ready to be inserted into the body, remove the device from its protective hoop. Use care when removing the device to avoid damage (e.g., shaft kink). 7. Using straight force (not a twisting motion), pull the balloon protector distally from the device tip. For Wolverine OTW Devices, the mandrel will slide off with the balloon protector. For Wolverine MR Devices, remove the mandrel distally after removing the balloon protector. Caution: If unusual resistance is felt during removal of the balloon protector or mandrel, do not use the device and replace with another. 8. The Wolverine MR Device may be coiled once and secured using the CLIPIT Clip provided in the device package. Only the proximal shaft should be inserted into the CLIPIT Clip; the clip is not intended for the distal end of the device. Remove the CLIPIT Clip prior to inserting the device into the patient s body. Note: Care should be taken not to kink the shaft of the device upon application or removal of the CLIPIT Clip. 9. Flush the guidewire lumen of the device with heparinized saline. For Wolverine MR Device flush through the distal tip of the device. For Wolverine OTW Device flush through the guidewire port of the device hub. Caution: When handling device, ensure the balloon and blades are not damaged during flushing of the wire lumen. Do not use if any defects are noted. Discard the protective hoop and the balloon protector. 10. Maintain device on a sterile table until ready for use. Wolverine Device Positioning 1. Prepare the vascular access site according to standard practice. 2. Insert a guidewire through the hemostasis valve following the manufacturer s instructions or standard practice. Advance the guidewire carefully into the guide catheter. When complete, withdraw the guidewire introducer, if used Under fluoroscopy, advance the guidewire to the desired vessel, then position the distal wire in the desired location. 4. Confirm the device is fully deflated and under vacuum. Back load the device distal tip onto the guidewire ensuring that the guidewire exits the midsection opening in the Wolverine MR Device or the wire port of the Wolverine OTW Device manifold. When loading or exchanging the device, it is recommended to thoroughly wipe the guidewire clean for better device movement on the guidewire. Guidewire position in the distal portion of the artery must be maintained while loading the balloon onto the guidewire. Note: To avoid kinking, advance the device slowly, in small increments, until the proximal end of the guidewire emerges from the device. 5. Thoroughly aspirate and flush the guide catheter in preparation for introduction of the cutting balloon device. 6. Carefully load the device onto the guidewire and advance through the hemostasis valve using fluoroscopic guidance to the tip of the guide catheter. Caution: Holding the balloon/blade subassembly too tightly or not opening the hemostasis valve enough may result in blade induced damage to the balloon material. If unusual resistance is felt, do not advance the device through the valve. Care should be taken not to over tighten the hemostasis valve around the device shaft as lumen constriction may occur, affecting inflation/deflation of the balloon. 7. Under fluoroscopy, while maintaining guidewire position, advance the device out of the guide catheter and into the selected coronary artery. Marks on the proximal portion of the catheter shaft indicate the exit of the balloon catheter tip out of the guide catheter, and may also be used as guidance. Advance the device and position within the lesion by centering the two radiopaque markers on either end of the lesion. The cutting edge of the atherotomes are located between the radiopaque markers. Confirm that the device is centrally located within the lesion segment before proceeding with the dilatation. Wolverine Device Inflation 1. Under fluoroscopy, slowly inflate the device (1 atm/5 sec) to 6 atm (nominal size). Do not inflate the device above 12 atm (rated burst pressure). Refer to Table 5 or the balloon compliance chart. If difficulty is experienced during balloon inflation, do not continue inflation; deflate and remove the device. 2. When using the device on long lesion segments (those lesions in which the targeted area of dilatation exceeds the length of the Wolverine ), the distal portion of the target lesion should be treated first. Then, dilatation of the proximal lesion segment may be performed. Repeat coronary arteriography after each use to evaluate results. Perform repeat dilatation if needed. Wolverine Device Removal 1. Deflate the device by dialing down on the inflation/ deflation device, then pull a negative vacuum. Maintain vacuum on the device and verify full deflation under fluoroscopy. 2. Repeat coronary arteriography to confirm successful result. 3. Withdraw the device into the guiding catheter. While withdrawing the deflated device and guidewire from the guide catheter through the hemostasis valve, tighten the hemostasis valve. 4. Dispose of the entire device. For Single Use Only. References The physician should consult recent literature on current medical practice on balloon dilatation, such as that published by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association. 1. Management of resistant coronary lesions by the Cutting Balloon Device: Initial experience. Bertrand et al. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn 1997; 41: Device angioplasty for the prevention of restenosis: results of the Device global Randomized Trial. Mauri, et al. Am J Cardiol 2002; 90:
5 Warranty Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) warrants that reasonable care has been used in the design and manufacture of this instrument. This warranty is in lieu of and excludes all other warranties not expressly set forth herein, whether express or implied by operation of law or otherwise, including, but not limited to, any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Handling, storage, cleaning and sterilization of this instrument as well as other factors relating to the patient, diagnosis, treatment, surgical procedures and other matters beyond BSC s control directly affect the instrument and the results obtained from its use. BSC s obligation under this warranty is limited to the repair or replacement of this instrument and BSC shall not be liable for any incidental or consequential loss, damage or expense directly or indirectly arising from the use of this instrument. BSC neither assumes, nor authorizes any other person to assume for it, any other or additional liability or responsibility in connection with this instrument. BSC assumes no liability with respect to instruments reused, reprocessed or resterilized and makes no warranties, express or implied, including but not limited to merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose, with respect to such instruments. EU Authorized EC REP Representative Boston Scientific Limited Ballybrit Business Park Galway IRELAND Australian AUS Sponsor Address Boston Scientific (Australia) Pty Ltd PO Box 332 BOTANY NSW 1455 Australia Free Phone Free Fax Argentina ARG Local Contact Para obtener información de contacto de Boston Scientific Argentina SA, por favor, acceda al link Legal Manufacturer Boston Scientific Corporation 300 Boston Scientific Way Marlborough, MA USA USA Customer Service Do not use if package is damaged. Recyclable Package 2017 Boston Scientific Corporation or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Emerge. PTCA Dilatation Catheter ONLY. monorail. over-the-wire
 90990229-01 Emerge monorail over-the-wire PTCA Dilatation Catheter Table of Contents 2014-09 < EN > warning...1 device description...1 Table 1. Emerge Balloon Coatings...1 Contents...1 Intended use/indications
90990229-01 Emerge monorail over-the-wire PTCA Dilatation Catheter Table of Contents 2014-09 < EN > warning...1 device description...1 Table 1. Emerge Balloon Coatings...1 Contents...1 Intended use/indications
RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter
 AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter Directions for Use 2 AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning Contents
AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter Directions for Use 2 AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning Contents
NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER STERILE. SINGLE USE ONLY. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Non pyrogenic. Do not resterilize. Do not use opened or damaged packages.
Page 1 of 5 NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER STERILE. SINGLE USE ONLY. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Non pyrogenic. Do not resterilize. Do not use opened or damaged packages.
1 Description. 2 Indications. 3 Warnings ASPIRATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
The SplitWire Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty Scoring Device. Instructions for Use
 The SplitWire Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty Scoring Device Instructions for Use Contents Contains one (1) SplitWire device. Sterile. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Radiopaque. For single use
The SplitWire Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty Scoring Device Instructions for Use Contents Contains one (1) SplitWire device. Sterile. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Radiopaque. For single use
PTCA Dilatation Catheter. Instructions for Use
 PTCA Dilatation Catheter Instructions for Use Rx ONLY Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician STERILE. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas Distributed by Medinol
PTCA Dilatation Catheter Instructions for Use Rx ONLY Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician STERILE. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas Distributed by Medinol
PTCA Dilatation Catheter. Instructions for Use
 PTCA Dilatation Catheter Instructions for Use Rx ONLY Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician STERILE. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas Distributed by Medinol
PTCA Dilatation Catheter Instructions for Use Rx ONLY Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician STERILE. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas Distributed by Medinol
ER REBOA Catheter. Instructions for Use
 ER REBOA Catheter Instructions for Use Prytime Medical Devices, Inc. 229 N. Main Street Boerne, TX 78006, USA feedback@prytimemedical.com www.prytimemedical.com US 1 210 340 0116 U.S. and Foreign Patents
ER REBOA Catheter Instructions for Use Prytime Medical Devices, Inc. 229 N. Main Street Boerne, TX 78006, USA feedback@prytimemedical.com www.prytimemedical.com US 1 210 340 0116 U.S. and Foreign Patents
Balloon in Balloon (BIB )
 Balloon in Balloon (BIB ) Stent Placement Catheter INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CAUTION: FEDERAL (USA) LAW RESTRICTS THIS DEVICE TO SALE BY OR ON THE ORDER OF A PHYSICIAN. Read all instructions prior to use. Distributed
Balloon in Balloon (BIB ) Stent Placement Catheter INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CAUTION: FEDERAL (USA) LAW RESTRICTS THIS DEVICE TO SALE BY OR ON THE ORDER OF A PHYSICIAN. Read all instructions prior to use. Distributed
Peripheral Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) Catheter Instructions for Use (IFU)
 Peripheral Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) Catheter Instructions for Use (IFU) For use with the Shockwave Medical, Inc. IVL Generator and Connector Cable Indication for Use The Shockwave Medical IVL System
Peripheral Intravascular Lithotripsy (IVL) Catheter Instructions for Use (IFU) For use with the Shockwave Medical, Inc. IVL Generator and Connector Cable Indication for Use The Shockwave Medical IVL System
Excimer Laser for Coronary Intervention: Case Study RADIAL APPROACH: CORONARY LASER ATHERECTOMY FOR CTO OF THE LAD FOLLOWED BY PTCA NO STENTING
 Excimer Laser for Coronary Intervention: Case Study RADIAL APPROACH: CORONARY LASER ATHERECTOMY FOR CTO OF THE LAD FOLLOWED BY PTCA NO STENTING 1 2013 Spectranetics. All Rights Reserved. Approved for External
Excimer Laser for Coronary Intervention: Case Study RADIAL APPROACH: CORONARY LASER ATHERECTOMY FOR CTO OF THE LAD FOLLOWED BY PTCA NO STENTING 1 2013 Spectranetics. All Rights Reserved. Approved for External
Directions For Use. All directions should be read before use
 Directions For Use All directions should be read before use DEVICE DESCRIPTION: The CLEANER.XT Rotational Thrombectomy System is a percutaneous, 6Fr catheter based system (single piece construction) that
Directions For Use All directions should be read before use DEVICE DESCRIPTION: The CLEANER.XT Rotational Thrombectomy System is a percutaneous, 6Fr catheter based system (single piece construction) that
PTA Balloon Dilatation Catheter
 PTA Balloon Dilatation Catheter March 2016 1/6(3214-0) Catalogue number Serial number Lot number Use by Do not reuse Do not resterilize Do not use if package is damaged Consult instructions for use Keep
PTA Balloon Dilatation Catheter March 2016 1/6(3214-0) Catalogue number Serial number Lot number Use by Do not reuse Do not resterilize Do not use if package is damaged Consult instructions for use Keep
Balloon in Balloon (BIB )
 in (BIB ) Dilatation Catheter INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CAUTION: FEDERAL (USA) LAW RESTRICTS THIS DEVICE TO SALE BY OR ON THE ORDER OF A PHYSICIAN. Read all instructions prior to use. Distributed by: B. Braun
in (BIB ) Dilatation Catheter INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CAUTION: FEDERAL (USA) LAW RESTRICTS THIS DEVICE TO SALE BY OR ON THE ORDER OF A PHYSICIAN. Read all instructions prior to use. Distributed by: B. Braun
Advanced Innovation for Exceptional Performance
 Advanced Innovation for Exceptional Performance longest BALLOON LENGTHS ON THE MARKET Bard Peripheral Vascular Ultraverse 014 300 mm Boston Scientific Coyote 220 mm Cordis SLEEK RX 220 mm Aviator Plus
Advanced Innovation for Exceptional Performance longest BALLOON LENGTHS ON THE MARKET Bard Peripheral Vascular Ultraverse 014 300 mm Boston Scientific Coyote 220 mm Cordis SLEEK RX 220 mm Aviator Plus
DURABLE. CONSISTENT. SAFE. IN.PACT Admiral Drug-Coated Balloon
 DURABLE. CONSISTENT. SAFE. Drug-Coated Balloon THE SCIENCE BEHIND THE OUTCOMES DCB has proven, long-term durable outcomes across multiple clinical trials, as well as across complex patient and lesion types.
DURABLE. CONSISTENT. SAFE. Drug-Coated Balloon THE SCIENCE BEHIND THE OUTCOMES DCB has proven, long-term durable outcomes across multiple clinical trials, as well as across complex patient and lesion types.
Z-MED II BALLOON AORTIC AND PULMONIC VALVULOPLASTY CATHETER. Instructions for Use
 Z-MED II BALLOON AORTIC AND PULMONIC VALVULOPLASTY CATHETER Instructions for Use CAUTION: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Manufactured for: B. Braun Interventional
Z-MED II BALLOON AORTIC AND PULMONIC VALVULOPLASTY CATHETER Instructions for Use CAUTION: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Manufactured for: B. Braun Interventional
Figure 1: Revolution TM Peripheral Atherectomy System Diagram. Table 1: Revolution TM Peripheral Atherectomy System Specifications Minimum Burr
 Instructions For Use All instructions should be read before use CAUTION Investigational Device. Limited by Federal (or United States) law to investigational use. DEVICE DESCRIPTION: The Revolution TM Peripheral
Instructions For Use All instructions should be read before use CAUTION Investigational Device. Limited by Federal (or United States) law to investigational use. DEVICE DESCRIPTION: The Revolution TM Peripheral
Instructions for Use 1
 Instructions for Use 1 Instructions for Use IMPORTANT! Please read before use. Description The Sniper is a dual lumen catheter comprised of an inner guidewire/infusion lumen and an outer, annular lumen
Instructions for Use 1 Instructions for Use IMPORTANT! Please read before use. Description The Sniper is a dual lumen catheter comprised of an inner guidewire/infusion lumen and an outer, annular lumen
PTA Balloon Dilatation Catheter
 PTA Balloon Dilatation Catheter 1/6(3211-0) February 2016 TIS-488-06272017 Catalogue number Serial number Lot number Use by Do not reuse Do not resterilize Do not use if package is damaged Consult instructions
PTA Balloon Dilatation Catheter 1/6(3211-0) February 2016 TIS-488-06272017 Catalogue number Serial number Lot number Use by Do not reuse Do not resterilize Do not use if package is damaged Consult instructions
Radux StandTall Instructions for Use Sheath Extender and Securement Clasp
 Radux StandTall Instructions for Use Sheath Extender and Securement Clasp USA Caution Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a health care professional. Caution The Radux
Radux StandTall Instructions for Use Sheath Extender and Securement Clasp USA Caution Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a health care professional. Caution The Radux
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 PERICARDIUM COVERED STENT (PCS) INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE STERILE - Ethylene Oxide Sterilized. For single use only. Do not re-sterilize. THE CLINICAL TECHNIQUES AND PROCEDURES DESCRIBED HERE DO NOT REPRESENT
PERICARDIUM COVERED STENT (PCS) INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE STERILE - Ethylene Oxide Sterilized. For single use only. Do not re-sterilize. THE CLINICAL TECHNIQUES AND PROCEDURES DESCRIBED HERE DO NOT REPRESENT
Directions For Use. All directions should be read before use. Page 1 of 8
 Directions For Use All directions should be read before use Page 1 of 8 WARNING: For single use only. Do not reuse, reprocess or re-sterilize. Reuse, reprocessing or re-sterilization may compromise the
Directions For Use All directions should be read before use Page 1 of 8 WARNING: For single use only. Do not reuse, reprocess or re-sterilize. Reuse, reprocessing or re-sterilization may compromise the
Instructions for Use Cordis PRECISE PRO Rx Nitinol Stent System
 100000017144.3 100000017144.3 Instructions for Use Cordis PRECISE PRO Rx Nitinol Stent System Figure 1.065" (1.65 mm) OR.078" (1.98 mm) 16 4 13 10 11 15 8 3 14.062" (1.57 mm) OR.065" (1.65 mm).038" (0.97
100000017144.3 100000017144.3 Instructions for Use Cordis PRECISE PRO Rx Nitinol Stent System Figure 1.065" (1.65 mm) OR.078" (1.98 mm) 16 4 13 10 11 15 8 3 14.062" (1.57 mm) OR.065" (1.65 mm).038" (0.97
Cardiva Catalyst III INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Cardiva Catalyst III INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE IFU 2469 Rev. G CAUTION Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. For single use only GRAPHICAL SYMBOLS ON THE CARDIVA
Cardiva Catalyst III INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE IFU 2469 Rev. G CAUTION Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. For single use only GRAPHICAL SYMBOLS ON THE CARDIVA
Innovation by design. Technology that sets a new standard
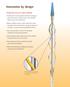 Innovation by design Technology that sets a new standard Flexible nitinol scoring element with three rectangular spiral struts works in tandem with a semi-compliant balloon to score the target lesion Balloon
Innovation by design Technology that sets a new standard Flexible nitinol scoring element with three rectangular spiral struts works in tandem with a semi-compliant balloon to score the target lesion Balloon
REBEL. Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
Assurant Cobalt Iliac BALLOON EXPANDABLE STENT SYSTEM
 Assurant Cobalt Iliac BALLOON EXPANDABLE STENT SYSTEM Innovating for life. CONFORMABILIT Y 6 F S H E AT H C O M PAT I B I L I T Y THE ASSURANT COBALT ILIAC STENT, WITH ITS UNIQUE COBALT CHROMIUM MODULAR
Assurant Cobalt Iliac BALLOON EXPANDABLE STENT SYSTEM Innovating for life. CONFORMABILIT Y 6 F S H E AT H C O M PAT I B I L I T Y THE ASSURANT COBALT ILIAC STENT, WITH ITS UNIQUE COBALT CHROMIUM MODULAR
MICHAEL R. JAFF, DO MASSACHUSETTS, UNITED STATES. Medtronic Further. Together
 DRUG-COATED BALL0ON TREATMENT FOR PATIENTS WITH INTERMITTENT CLAUDICATION: INSIGHTS FROM THE IN.PACT GLOBAL FULL CLINICAL COHORT MICHAEL R. JAFF, DO MASSACHUSETTS, UNITED STATES Medtronic Further. Together
DRUG-COATED BALL0ON TREATMENT FOR PATIENTS WITH INTERMITTENT CLAUDICATION: INSIGHTS FROM THE IN.PACT GLOBAL FULL CLINICAL COHORT MICHAEL R. JAFF, DO MASSACHUSETTS, UNITED STATES Medtronic Further. Together
Express LD Iliac. Premounted Stent System ONLY. over-the-wire
 50455844-01 STERILE - DO NOT RESTERILIZE - SINGLE USE ONLY ONLY 2017-03 < EN > Express LD Iliac over-the-wire Premounted Stent System Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the
50455844-01 STERILE - DO NOT RESTERILIZE - SINGLE USE ONLY ONLY 2017-03 < EN > Express LD Iliac over-the-wire Premounted Stent System Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the
Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
 Page 1 of 5 Reprocessed by Instructions for Use Reprocessed Ultrasound Catheters Reprocessed Device for Single Use Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Page 1 of 5 Reprocessed by Instructions for Use Reprocessed Ultrasound Catheters Reprocessed Device for Single Use Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
CLARIVEIN INFUSION CATHETER
 CLARIVEIN INFUSION CATHETER General Product Description Overview The ClariVein Infusion Catheter (ClariVein -IC) is an infusion catheter system designed to introduce physician-specified medicaments into
CLARIVEIN INFUSION CATHETER General Product Description Overview The ClariVein Infusion Catheter (ClariVein -IC) is an infusion catheter system designed to introduce physician-specified medicaments into
Instructions for Use Reprocessed LASSO Circular Mapping Diagnostic Electrophysiology (EP) Catheter
 Instructions for Use Reprocessed LASSO Circular Mapping Diagnostic Electrophysiology (EP) Catheter Caution: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. DEVICE DESCRIPTION
Instructions for Use Reprocessed LASSO Circular Mapping Diagnostic Electrophysiology (EP) Catheter Caution: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. DEVICE DESCRIPTION
BTK Case Studies Joseph Cardenas, MD AZ Heart & Vascular, Yuma, AZ
 BTK Case Studies Joseph Cardenas, MD AZ Heart & Vascular, Yuma, AZ 1 Case 1 78 yr. old female Rutherford Class II/III lesion 1 block claudicant 2 Pre Treatment Post Treatment Anterior Tibial Artery Occlusion
BTK Case Studies Joseph Cardenas, MD AZ Heart & Vascular, Yuma, AZ 1 Case 1 78 yr. old female Rutherford Class II/III lesion 1 block claudicant 2 Pre Treatment Post Treatment Anterior Tibial Artery Occlusion
7 OVERVIEW OF CLINICAL STUDIES:... 3
 50673276-01 REBEL MONORAIL OVER-THE-WIRE Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System TABLE OF CONTENTS 2018-06 < en > 1 WARNING:... 1 2 DEVICE DESCRIPTION:... 1 Table 2.1 REBEL Stent System Product Description...
50673276-01 REBEL MONORAIL OVER-THE-WIRE Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System TABLE OF CONTENTS 2018-06 < en > 1 WARNING:... 1 2 DEVICE DESCRIPTION:... 1 Table 2.1 REBEL Stent System Product Description...
ROTABLATORTM. Peripheral. Rotational Atherectomy System. Quick Reference Cards
 Peripheral ROTABLATORTM Rotational Atherectomy System Quick Reference Cards Technical Assistance: 1.800.949.6708 Customer Service: 1.888.272.1001 Complaints: 1.800.811.3211 Setup Video: www.bostonscientific.com/rotablatorsetup
Peripheral ROTABLATORTM Rotational Atherectomy System Quick Reference Cards Technical Assistance: 1.800.949.6708 Customer Service: 1.888.272.1001 Complaints: 1.800.811.3211 Setup Video: www.bostonscientific.com/rotablatorsetup
Single Pass MCA Revascularization with Trevo
 Single Pass MCA Revascularization with Trevo By Concentric Medical ProVueTM Retriever Case Reported By Sascha Prothmann, MD Klinikum rechts der Isar, Munich, Germany Images contained herein courtesy of
Single Pass MCA Revascularization with Trevo By Concentric Medical ProVueTM Retriever Case Reported By Sascha Prothmann, MD Klinikum rechts der Isar, Munich, Germany Images contained herein courtesy of
ASAHI Corsair INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 ASAHI Corsair INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SYMBOLS Legal manufacturer Do not use if package is damaged GC Minimum GC I.D. REF Catalogue number Caution, consult accompanying documents Maximum injection pressure
ASAHI Corsair INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SYMBOLS Legal manufacturer Do not use if package is damaged GC Minimum GC I.D. REF Catalogue number Caution, consult accompanying documents Maximum injection pressure
1 Comparison of Warfarin and Aspirin for Symptomatic Intracranial Arterial Stenosis. N Engl J Med 352;13, March 31, 2005
 The risk of ischemic stroke in patients with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease (ICAD) ranges from 7 to 24%. 1,2 Developed specifically for the treatment of ICAD, the Wingspan Stent System and Gateway
The risk of ischemic stroke in patients with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease (ICAD) ranges from 7 to 24%. 1,2 Developed specifically for the treatment of ICAD, the Wingspan Stent System and Gateway
System.
 System www.penumbrainc.com POD System Case Examples 45 cm of POD Packing Coil in 1.5 to 3 mm diameter dilating vessel Bronchial Artery Embolization Dr. Amit Kakkar and Dr. Aksim Rivera, Bronx, NY Inflow:
System www.penumbrainc.com POD System Case Examples 45 cm of POD Packing Coil in 1.5 to 3 mm diameter dilating vessel Bronchial Artery Embolization Dr. Amit Kakkar and Dr. Aksim Rivera, Bronx, NY Inflow:
Lutonix AV Clinical Trial
 Lutonix AV Clinical Trial Long Term Effects of LUTONIX 035 DCB Catheter 18 month Interim Results Scott O. Trerotola, MD Stanley Baum Professor of Radiology Professor of Surgery Associate Chair and Chief,
Lutonix AV Clinical Trial Long Term Effects of LUTONIX 035 DCB Catheter 18 month Interim Results Scott O. Trerotola, MD Stanley Baum Professor of Radiology Professor of Surgery Associate Chair and Chief,
LeMaitre Embolectomy Catheter
 Instructions for Use - English Lemaitre Embolectomy Catheter (Model Numbers 1601-24, e1601-24, 1601-26, e1601-26, 1601-28, e1601-28, 1601-34, e1601-34, 1601-38, e1601-38, 1601-44, e1601-44, 1601-48, e1601-48,
Instructions for Use - English Lemaitre Embolectomy Catheter (Model Numbers 1601-24, e1601-24, 1601-26, e1601-26, 1601-28, e1601-28, 1601-34, e1601-34, 1601-38, e1601-38, 1601-44, e1601-44, 1601-48, e1601-48,
Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter English Instructions for Use. Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter
 Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter English Instructions for Use Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter (Model Numbers 4F-2L-40, 4F-2L-80, 5F-2L-40,
Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter English Instructions for Use Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter Polyurethane Dual Lumen Occlusion Catheter (Model Numbers 4F-2L-40, 4F-2L-80, 5F-2L-40,
SYMBOLOGY. = Manufacturer. = Manufacturing Serial Number. = Manufacturing Lot Number = Catalog Number LOT REF. = Do not resterilize Single Use Only
 damage or expenses directly or indirectly arising from use of this product. This warranty is in lieu of and excludes all other warranties not expressly set forth herein, whether express or implied by operation
damage or expenses directly or indirectly arising from use of this product. This warranty is in lieu of and excludes all other warranties not expressly set forth herein, whether express or implied by operation
Quick Reference Guide
 Quick Reference Guide Indications for Use The AFX Endovascular AAA System is indicated for endovascular treatment in patients with AAA. The devices are indicated for patients with suitable aneurysm morphology
Quick Reference Guide Indications for Use The AFX Endovascular AAA System is indicated for endovascular treatment in patients with AAA. The devices are indicated for patients with suitable aneurysm morphology
Ruby Coil. Large Volume Detachable Coils
 Ruby Coil Ruby Case Examples 38 mm Hepatic Artery Aneurysm Pulmonary AVM 2 Coils Dr. James Benenati Miami Cardiac and Vascular Institute, FL Y90 Embolization Type 2 Endoleak Dr. J Moskovitz Florida Hospital,
Ruby Coil Ruby Case Examples 38 mm Hepatic Artery Aneurysm Pulmonary AVM 2 Coils Dr. James Benenati Miami Cardiac and Vascular Institute, FL Y90 Embolization Type 2 Endoleak Dr. J Moskovitz Florida Hospital,
Azur CX 35 Peripheral Coil System (Detachable) Instructions for Use
 Azur CX 35 Peripheral Coil System (Detachable) Instructions for Use DEVICE DESCRIPTION The Detachable Azur CX 35 Peripheral Coil System (Azur system) consists of a coil implant attached to a delivery system.
Azur CX 35 Peripheral Coil System (Detachable) Instructions for Use DEVICE DESCRIPTION The Detachable Azur CX 35 Peripheral Coil System (Azur system) consists of a coil implant attached to a delivery system.
WallFlex Biliary RX Partially Covered Stent System Prescriptive Information
 Caution/Rx Only: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Intended Use/Indications for Use The WallFlex Biliary RX is indicated for use in the palliative treatment
Caution/Rx Only: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Intended Use/Indications for Use The WallFlex Biliary RX is indicated for use in the palliative treatment
Instructions for Use Reprocessed 3D Diagnostic Ultrasound Catheters
 Reprocessed by Instructions for Use Reprocessed 3D Diagnostic Ultrasound Catheters Reprocessed Device for Single Use Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a
Reprocessed by Instructions for Use Reprocessed 3D Diagnostic Ultrasound Catheters Reprocessed Device for Single Use Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a
DISRUPT CAD. Todd J. Brinton, MD Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Adjunct Professor of Bioengineering Stanford University
 DISRUPT CAD A multicenter, prospective, single-arm study of percutaneous Lithoplasty prior to stent implantation in heavily calcified coronary lesions Todd J. Brinton, MD Clinical Associate Professor of
DISRUPT CAD A multicenter, prospective, single-arm study of percutaneous Lithoplasty prior to stent implantation in heavily calcified coronary lesions Todd J. Brinton, MD Clinical Associate Professor of
Pruitt Irrigation Occlusion Catheter. English Instructions for Use. Pruitt Irrigation Occlusion Catheter
 English Instructions for Use Pruitt Irrigation Occlusion Catheter (Model Numbers 2102-09, e2102-09) Instructions for Use - English Concept Balloon tipped catheters have been used to occlude vessels for
English Instructions for Use Pruitt Irrigation Occlusion Catheter (Model Numbers 2102-09, e2102-09) Instructions for Use - English Concept Balloon tipped catheters have been used to occlude vessels for
Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full thickness woven polyester graft material Fully
 Physician Training Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full thickness woven polyester graft material Fully supported by self-expanding z-stents H&L-B
Physician Training Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full thickness woven polyester graft material Fully supported by self-expanding z-stents H&L-B
DISRUPT PAD. (( Data Summary )) DISRUPT PAD Data Summary SPL Rev. B 2016 Shockwave Medical Inc. All rights reserved.
 DISRUPT PAD (( Data Summary )) DISRUPT PAD Data Summary SPL 60971 Rev. B 1 Summary of the key findings from the DISRUPT PAD Study 99% of femoropopliteal lesions treated were moderately or severely calcified.
DISRUPT PAD (( Data Summary )) DISRUPT PAD Data Summary SPL 60971 Rev. B 1 Summary of the key findings from the DISRUPT PAD Study 99% of femoropopliteal lesions treated were moderately or severely calcified.
TYSHAK DILATATION CATHETER. Instructions for Use CAUTION: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
 TYSHAK DILATATION CATHETER Instructions for Use CAUTION: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Manufactured for: B. Braun Interventional Systems Inc. 824 Twelfth
TYSHAK DILATATION CATHETER Instructions for Use CAUTION: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Manufactured for: B. Braun Interventional Systems Inc. 824 Twelfth
Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Instructions for Use
 Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Instructions for Use GRF-0004-00 Rev. 08 Page 1 of 9 Contents Instructions for Use... 3 Indications for Use... 3 Contraindications... 3 Storage... 4 Warnings... 4 Accessories Provided...
Endorectal Balloon (ERB) Instructions for Use GRF-0004-00 Rev. 08 Page 1 of 9 Contents Instructions for Use... 3 Indications for Use... 3 Contraindications... 3 Storage... 4 Warnings... 4 Accessories Provided...
Sustained Release. Superior Results.
 ELUVIA Drug-Eluting Vascular Stent System Sustained Release. Superior Results. Superiority determined in Post Hoc Superiority Analysis. 12-Month Primary Patency rate of 86.8% in the Eluvia arm (n=309)
ELUVIA Drug-Eluting Vascular Stent System Sustained Release. Superior Results. Superiority determined in Post Hoc Superiority Analysis. 12-Month Primary Patency rate of 86.8% in the Eluvia arm (n=309)
PROMUS Element Experience In AMC
 Promus Element Luncheon Symposium: PROMUS Element Experience In AMC Jung-Min Ahn, MD. University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Heart Institute, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea PROMUS Element Clinical
Promus Element Luncheon Symposium: PROMUS Element Experience In AMC Jung-Min Ahn, MD. University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Heart Institute, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea PROMUS Element Clinical
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial
 Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Effect of Intravascular Ultrasound- Guided vs. Angiography-Guided Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation: the IVUS-XPL Randomized Clinical Trial Myeong-Ki Hong, MD. PhD on behalf of the IVUS-XPL trial investigators
Atherectomy: Jetstream and Directional. George S. Chrysant, M.D.
 Atherectomy: Jetstream and Directional George S. Chrysant, M.D. Disclosures Abbott Vascular: MAB, consultant, proctor Abiomed: consultant Boston Scientific: MAB, consultant, proctor Medicines Company:
Atherectomy: Jetstream and Directional George S. Chrysant, M.D. Disclosures Abbott Vascular: MAB, consultant, proctor Abiomed: consultant Boston Scientific: MAB, consultant, proctor Medicines Company:
Finally, the Control You Need to Deliver Accurate Treatment
 Finally, the Control You Need to Deliver Accurate Treatment LIFESTREAM Covered Stent. has joined BD When you reach for a balloon expandable stent, you require accuracy. The LIFESTREAM Balloon Expandable
Finally, the Control You Need to Deliver Accurate Treatment LIFESTREAM Covered Stent. has joined BD When you reach for a balloon expandable stent, you require accuracy. The LIFESTREAM Balloon Expandable
Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for
 Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
TOBA II 12-Month Results Tack Optimized Balloon Angioplasty
 TOBA II 12-Month Results Tack Optimized Balloon Angioplasty William Gray, MD System Chief, Cardiovascular Division Main Line Health, Philadelphia, PA Dissection: The Primary Mechanism of Angioplasty Lesions
TOBA II 12-Month Results Tack Optimized Balloon Angioplasty William Gray, MD System Chief, Cardiovascular Division Main Line Health, Philadelphia, PA Dissection: The Primary Mechanism of Angioplasty Lesions
Vascu-PICC WITH CUFF PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL VEIN ACCESS CATHETER INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Vascu-PICC WITH CUFF PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL VEIN ACCESS CATHETER INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE INDICATIONS FOR USE: The Vascu-PICC with cuff Peripherally Inserted Central Vein Catheters are designed for
Vascu-PICC WITH CUFF PERIPHERALLY INSERTED CENTRAL VEIN ACCESS CATHETER INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE INDICATIONS FOR USE: The Vascu-PICC with cuff Peripherally Inserted Central Vein Catheters are designed for
OptiCross MHz Peripheral Imaging Catheter
 91080532-01 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. WARNING Contents supplied STERILE using a Radiation process. Do not use if sterile barrier is
91080532-01 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. WARNING Contents supplied STERILE using a Radiation process. Do not use if sterile barrier is
Advisor FL Circular Mapping Catheter, Sensor Enabled D-AVSE-D10-F20, D-AVSE-DF10-F20, D-AVSE-D10-F15, D-AVSE-DF10-F15. Instructions for Use
 Advisor FL Circular Mapping Catheter, Sensor Enabled D-AVSE-D10-F20, D-AVSE-DF10-F20, D-AVSE-D10-F15, D-AVSE-DF10-F15 Instructions for Use For U.S. California Only: Proposition 65, a State of California
Advisor FL Circular Mapping Catheter, Sensor Enabled D-AVSE-D10-F20, D-AVSE-DF10-F20, D-AVSE-D10-F15, D-AVSE-DF10-F15 Instructions for Use For U.S. California Only: Proposition 65, a State of California
Phoenix Atherectomy System Product Overview /LB
 Phoenix Atherectomy System Product Overview Phoenix Atherectomy System- The next generation of atherectomy The first hybrid atherectomy system available Combines the benefits of existing atherectomy systems
Phoenix Atherectomy System Product Overview Phoenix Atherectomy System- The next generation of atherectomy The first hybrid atherectomy system available Combines the benefits of existing atherectomy systems
Per-Q-Cath* PICC Catheters with Excalibur Introducer* System
 Bard Access Systems Per-Q-Cath* PICC and Catheters with Excalibur Introducer* System Instructions For Use Table of Contents Table of Contents Page Contents 1 Product Description, Indications & Contraindications
Bard Access Systems Per-Q-Cath* PICC and Catheters with Excalibur Introducer* System Instructions For Use Table of Contents Table of Contents Page Contents 1 Product Description, Indications & Contraindications
NC EMERGE TM PTCA Dilatation Catheter
 LEARN MORE Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labeling supplied with each device. Information for use only in countries with applicable health
LEARN MORE Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labeling supplied with each device. Information for use only in countries with applicable health
Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System
 Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System Robert F. Riley * and Bill Lombardi University of Washington Medical Center, Division
Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report Solving the Dilemma of Ostial Stenting: A Case Series Illustrating the Flash Ostial System Robert F. Riley * and Bill Lombardi University of Washington Medical Center, Division
NIRxcell CoCr Coronary Stent System
 cordis.com/nirxcell NIRxcell CoCr Coronary Stent System Exceptional Outcomes by Design Exceptionally low TLR rate of 5.1 % at 9 months 1 Superior Deliverability and Crossability 2 Best-in-class Conformability
cordis.com/nirxcell NIRxcell CoCr Coronary Stent System Exceptional Outcomes by Design Exceptionally low TLR rate of 5.1 % at 9 months 1 Superior Deliverability and Crossability 2 Best-in-class Conformability
Talent Abdominal Stent Graft
 Talent Abdominal with THE Xcelerant Hydro Delivery System Expanding the Indications for EVAR Treat More Patients Short Necks The Talent Abdominal is the only FDA-approved device for proximal aortic neck
Talent Abdominal with THE Xcelerant Hydro Delivery System Expanding the Indications for EVAR Treat More Patients Short Necks The Talent Abdominal is the only FDA-approved device for proximal aortic neck
Instructions for Use ANGIOGUARD XP Emboli Capture Guidewire System
 10257072-3 Instructions for Use ANGIOGUARD XP Emboli Capture Guidewire System 1 2 This page has been This page has been 3 CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of
10257072-3 Instructions for Use ANGIOGUARD XP Emboli Capture Guidewire System 1 2 This page has been This page has been 3 CAUTION: Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of
Neuroform EZ Stent System
 Neuroform EZ Stent System Directions for Use 2 Neuroform EZ Stent System 1 cm 1.9 cm 135 cm 185 cm ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning
Neuroform EZ Stent System Directions for Use 2 Neuroform EZ Stent System 1 cm 1.9 cm 135 cm 185 cm ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning
MULTILAYER FLOW MODULATOR (MFM ) FOR PERIPHERAL ANEURYSMS TREATMENT (LOWER LIMBS, VISCERALS AND SUBCLAVIAN)
 0459 MULTILAYER FLOW MODULATOR (MFM ) FOR PERIPHERAL ANEURYSMS TREATMENT (LOWER LIMBS, VISCERALS AND SUBCLAVIAN) WITH ITS ANGIOGRAPHIC CONTROL DELIVERY SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE (I.F.U.) English Français
0459 MULTILAYER FLOW MODULATOR (MFM ) FOR PERIPHERAL ANEURYSMS TREATMENT (LOWER LIMBS, VISCERALS AND SUBCLAVIAN) WITH ITS ANGIOGRAPHIC CONTROL DELIVERY SYSTEM INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE (I.F.U.) English Français
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR:
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR: en English cs Čeština da Dansk nl Nederlands fi Suomi fr Français de Deutsch el Ελληνικά hu Magyar it Italiano lt Lietuvių no Norsk pl Polski pt Português es Español sv Svenska
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR: en English cs Čeština da Dansk nl Nederlands fi Suomi fr Français de Deutsch el Ελληνικά hu Magyar it Italiano lt Lietuvių no Norsk pl Polski pt Português es Español sv Svenska
Instructions for Use Reprocessed Ethicon ENDOPATH XCEL TM Bladeless Trocar with OPTIVIEW Technology
 Reprocessed by Instructions for Use Reprocessed Ethicon ENDOPATH XCEL TM Bladeless Trocar with OPTIVIEW Technology Reprocessed Device for Single Use Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device
Reprocessed by Instructions for Use Reprocessed Ethicon ENDOPATH XCEL TM Bladeless Trocar with OPTIVIEW Technology Reprocessed Device for Single Use Caution: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this device
DESolve NX Trial Clinical and Imaging Results
 DESolve NX Trial Clinical and Imaging Results Alexandre Abizaid, MD, PhD, Instituto Dante Pazzanese, Sao Paulo, Brazil On behalf of the DESolve Nx Trial Investigators Please refer to the TCT2014 App or
DESolve NX Trial Clinical and Imaging Results Alexandre Abizaid, MD, PhD, Instituto Dante Pazzanese, Sao Paulo, Brazil On behalf of the DESolve Nx Trial Investigators Please refer to the TCT2014 App or
Coronary angiography and PCI
 Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
Coronary arteries Coronary angiography and PCI Samo Granda, Franjo Naji Department of Cardiology Clinical department of internal medicine University clinical centre Maribor Coronary arteries Atherosclerosis
Document No. BMB/IFU/40 Rev No. & Date 00 & 15/11/2017 Issue No & Date 01 & 15/11/2017
 Central Venous Catheter Device Description Multi-lumen catheters incorporate separate, non-communicating vascular access lumens within a single catheter body. Minipunctur Access Sets And Trays: Used for
Central Venous Catheter Device Description Multi-lumen catheters incorporate separate, non-communicating vascular access lumens within a single catheter body. Minipunctur Access Sets And Trays: Used for
Are Asian Patients Different? - Updates Of Biomatrix Experience In Regional Settings: BEACON II (3 Yr F up) &
 Are Asian Patients Different? - Updates Of Biomatrix Experience In Regional Settings: BEACON II (3 Yr F up) & Biomatrix TM Single Center Experience (Indonesia)(Final 5 Yr F up) T. Santoso University of
Are Asian Patients Different? - Updates Of Biomatrix Experience In Regional Settings: BEACON II (3 Yr F up) & Biomatrix TM Single Center Experience (Indonesia)(Final 5 Yr F up) T. Santoso University of
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014
 Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Contents Ultra ICE Plus - PI 9 MHz Peripheral Imaging Catheter MDU5 PLUS Sterile Bag 26 gauge needle 10 ml (10 cc) syringe
 50677333-01 Ultra ICE Plus - PI 9 MHz Peripheral Imaging Catheter ONLY 2018-05 < en > Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Carefully read all instructions
50677333-01 Ultra ICE Plus - PI 9 MHz Peripheral Imaging Catheter ONLY 2018-05 < en > Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Carefully read all instructions
AXIOS Stent and Delivery System
 PRESCRIPTIVE INFORMATION AXIOS Stent and Delivery System Warning REFER TO THE DEVICE DIRECTIONS FOR USE FOR COMPLETE INSTRUCTIONS ON DEVICE USE. RX ONLY. CAUTION: FEDERAL LAW (USA) RESTRICTS THIS DEVICE
PRESCRIPTIVE INFORMATION AXIOS Stent and Delivery System Warning REFER TO THE DEVICE DIRECTIONS FOR USE FOR COMPLETE INSTRUCTIONS ON DEVICE USE. RX ONLY. CAUTION: FEDERAL LAW (USA) RESTRICTS THIS DEVICE
CP STENT. Large Diameter, Balloon Expandable Stent
 CP STENT Large, Expandable CP STENT OPTIONS 12mm to Expansion 26mm to Expansion CP Matrix (number of zigs) 1.6 2.2 2.8 3.4 3.9 4.5 5 5.5 6 12 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 CP Details: CP is composed of
CP STENT Large, Expandable CP STENT OPTIONS 12mm to Expansion 26mm to Expansion CP Matrix (number of zigs) 1.6 2.2 2.8 3.4 3.9 4.5 5 5.5 6 12 14 15 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 CP Details: CP is composed of
Pocket Reference Guide For (CTO) Technologies
 to receive our latest news and key activities. Pocket Reference Guide For (CTO) Technologies LinkedIn page Follow us on CORDIS EMEA Table of Contents Essential prescribing information for both FRONTRUNNER
to receive our latest news and key activities. Pocket Reference Guide For (CTO) Technologies LinkedIn page Follow us on CORDIS EMEA Table of Contents Essential prescribing information for both FRONTRUNNER
Contents Ultra ICE Plus 9 MHz Imaging Catheter MDU5 PLUS Sterile Bag 26 gauge needle 10 ml (cc) syringe
 91040401-01 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Carefully read all instructions prior to use. Observe all contraindications, warnings and precautions
91040401-01 ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Carefully read all instructions prior to use. Observe all contraindications, warnings and precautions
Xcela Hybrid PICC with PASV Valve Technology
 Xcela Hybrid PICC with PASV Valve Technology Directions For Use...3 Navilyst Medical, Master DFU Template 8in x 8in Global, 146T0808 Rev/Ver. A, DFU, XCELA HYBRID PICC w/ PASV VALVE TECHNOLOGY, 14600125-01A
Xcela Hybrid PICC with PASV Valve Technology Directions For Use...3 Navilyst Medical, Master DFU Template 8in x 8in Global, 146T0808 Rev/Ver. A, DFU, XCELA HYBRID PICC w/ PASV VALVE TECHNOLOGY, 14600125-01A
JETSTREAM Atherectomy System DELIVERING VERSATILITY TO RESTORE FLOW
 JETSTREAM Atherectomy System DELIVERING VERSATILITY TO RESTORE FLOW DISCOVER THE VALUE OF VERSATILITY Versatility means not having to guess the morphology! Peripheral arterial lesions can present with
JETSTREAM Atherectomy System DELIVERING VERSATILITY TO RESTORE FLOW DISCOVER THE VALUE OF VERSATILITY Versatility means not having to guess the morphology! Peripheral arterial lesions can present with
Cook Medical. Zenith Flex AAA Endovascular Graft with Z-Trak Introduction System Physician Training
 Cook Medical Zenith Flex AAA Endovascular Graft with Z-Trak Introduction System Physician Training Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full-thickness,
Cook Medical Zenith Flex AAA Endovascular Graft with Z-Trak Introduction System Physician Training Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full-thickness,
OCT Guided Atherectomy: Initial Results of the VISION Trial Using the Pantheris Catheter. Patrick Muck, MD
 OCT Guided Atherectomy: Initial Results of the VISION Trial Using the Pantheris Catheter Patrick Muck, MD Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery Good Samaritan Hospital Cincinna
OCT Guided Atherectomy: Initial Results of the VISION Trial Using the Pantheris Catheter Patrick Muck, MD Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery Good Samaritan Hospital Cincinna
Effectiveness of IVUS in Complex Cases
 Effectiveness of IVUS in Complex Cases Satoru Sumituji,M.D. Rinku General Medical Center IVUS is can provide images of the vessel wall and the tissue around the vessel which cannot be viewed by angiography.
Effectiveness of IVUS in Complex Cases Satoru Sumituji,M.D. Rinku General Medical Center IVUS is can provide images of the vessel wall and the tissue around the vessel which cannot be viewed by angiography.
The Role of LUTONIX 035 DCB in AV Fistula Dysfunction Management in our Practice
 The Role of LUTONIX 035 DCB in AV Fistula Dysfunction Management in our Practice Dr Kate Steiner Consultant Interventional Radiologist East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust Disclosure Speaker name: Dr
The Role of LUTONIX 035 DCB in AV Fistula Dysfunction Management in our Practice Dr Kate Steiner Consultant Interventional Radiologist East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust Disclosure Speaker name: Dr
CY2015 Hospital Outpatient: Endovascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments
 CY2015 Hospital Outpatient: Endovascular Procedure APCs Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) CMS finalized the implementation of 25 Comprehensive APC to further
CY2015 Hospital Outpatient: Endovascular Procedure APCs Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) CMS finalized the implementation of 25 Comprehensive APC to further
The Art of. Flow Restoration. Ikazuchi Zero. Semi-Compliant PTCA Balloon OVERVIEW CROSSABILITY LOW PROFILE CASE STUDY CODES
 The Art of Flow Restoration Japan s Recognized PCI Technology For Both Everyday and Complex CTO Cases* Manufactured by Kaneka Corporation, one of Japan s leading providers of interventional devices. Now
The Art of Flow Restoration Japan s Recognized PCI Technology For Both Everyday and Complex CTO Cases* Manufactured by Kaneka Corporation, one of Japan s leading providers of interventional devices. Now
PCI for Chronic Total Occlusions
 PCI for Chronic Total Occlusions Chronic Total Occlusions Why not Medical Treatment? Medical Treatment CTO in 891 pts over 24 years High 10% Mortality Low 2 % 1 year 10 years Puma JA, et al. JACC 1994;23:390A
PCI for Chronic Total Occlusions Chronic Total Occlusions Why not Medical Treatment? Medical Treatment CTO in 891 pts over 24 years High 10% Mortality Low 2 % 1 year 10 years Puma JA, et al. JACC 1994;23:390A
Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft. Device Description Planning and Sizing Deployment Sequence Patient Follow-Up
 Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft Device Description Planning and Sizing Deployment Sequence Patient Follow-Up Device description: Device indications The Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft with Z-Trak Introduction
Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft Device Description Planning and Sizing Deployment Sequence Patient Follow-Up Device description: Device indications The Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft with Z-Trak Introduction
Device Preparation (all steps to be performed per standard interventional technique)
 sertera Biopsy Device Instructions for Use Please read all information carefully. Failure to properly follow the instructions may lead to unintended consequences. Important: This package insert is designed
sertera Biopsy Device Instructions for Use Please read all information carefully. Failure to properly follow the instructions may lead to unintended consequences. Important: This package insert is designed
Absorbable Woven Polyglycolic Acid Mesh Tube (Absorbable Nerve Conduit Tube) INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 2 6
 Absorbable Woven Polyglycolic Acid Mesh Tube (Absorbable Nerve Conduit Tube) INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 2 6 1 0086 SYMBOL DEFINITIONS ENGLISH Do not Reuse Consult Instructions For Use Ethylene Oxide Sterilized
Absorbable Woven Polyglycolic Acid Mesh Tube (Absorbable Nerve Conduit Tube) INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 2 6 1 0086 SYMBOL DEFINITIONS ENGLISH Do not Reuse Consult Instructions For Use Ethylene Oxide Sterilized
