Rapamycin prevents apoptosis of myocardial cells in heart failure rats through up-regulating Akt.
|
|
|
- Linette Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): ISSN X Rapamycin prevents apoptosis of myocardial cells in heart failure rats through up-regulating Akt. Chunxiao Zhang 1,2, Aifen Liu 2, Guohai Su 1,3*, Yudong Chen 2* 1 Shandong University, Jinan, China 2 Department of Cardiology, the Central Hospital of Shengli Oil Field, Dongying, PR China 3 Department of Cardiology, Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, PR China Abstract Objectives: Heart Failure (HF) progression could be prevented by an inhibitor of the mtor and an autophagy enhancer rapamycin. This study aimed to investigate the effect of rapamycin on HF progression and myocardial cells apoptosis. Methods: HF rats were injected with low-, middle-, and high-dose rapamycin. Echocardiography, HE staining, plasma Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP), myocardial cells apoptosis and Akt activation in rapamycin treated rats were detected. Results: HF rats showed reduced cardiac functions, destructive pathological changes in myocardium, enhanced Akt activation and myocardial cells apoptosis. However, rapamycin reversed all the changes in a dose-dependent manner. Cardiac functions were enhanced by rapamycin. Myocardial cells apoptotic percentage, Akt expression, and pathological changes in HF rats myocardium were inhibited by rapamycin administration. Conclusions: Rapamycin protected against myocardial hypertrophy and myocardial cells apoptosis in HF rats in a dose-dependent manner. Keywords: Heart failure, Rapamycin, Akt, Apoptosis. Introduction Heart Failure (HF) is a clinical syndrome with inability of heart pumping blood of which the derived metabolic dysfunction contributes to high rates of disability [1]. Though numerous studies focus on HF, the mechanisms of heart failure are still unclear and the treatment of HF still needs to be improved. The well-known phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor) signaling pathway involves in the regulation of autophagy and apoptosis in mammal cells [2]. PI3K pathway plays an essential role in cell, organ, and body size determination [3]. Despite of Akt s beneficial effects on contractility, prolonged Akt activation could result in contractile dysfunction, including heart failure [4]. The excessive cardiac growth induced by Akt or others, rather than long-term Akt activation itself, is detrimental for the HF or myocardial hypertrophy [4]. On contrary, reports showed that Akt activation inversely preserved cardiac function and prevented injury after transient cardiac ischemia [5]. The overexpressed Akt in mesenchymal stem cells dramatically repaired infarcted myocardium and improved cardiac function [6]. Accepted on August 23, 2017 Rapamycin is a lipophilic, macrolide antibiotic. Rapamycin can effectively attenuate myocytes hypertrophy induced by growth factors in vitro [3]. Moreover, HF progression and the associated long-term Akt activation could be prevented by rapamycin [4,7]. The effect of rapamycin on cell apoptosis is duality too. Rapamycin exhibits apoptotic effect on cancer cells, or protects against apoptotic neuronal death [8,9]. In cancer cells, rapamycin administration induced cancer cell apoptosis and blocked cell proliferation [10-14]. In male germ cells, rapamycin could inhibit chemicals induced apoptosis via impairing ROS-derived dysfunction in mitochondria [15]. In human neuronal SH-SY5Y cells, rapamycin showed neuroprotective against rotenone-induced apoptosis through enhancing autophagy to clear damaged mitochondria [16]. As reported by Shioi et al. rapamycin could attenuate load-induced compensated hypertrophy via an mtor-dependent mechanism [3]. Studies also showed that rapamycin is an inhibitor of the mtor and an autophagy enhancer [7,16-18]. mtor negatively regulates autophagy, and rapamycin could induce autophagy by inactivating mtor [17]. However, the effect of rapamycin on myocardial cells apoptosis in HF progression had not been well reported. Biomed Res 2017 Volume 28 Issue
2 Zhang/Liu/Su/Chen To our best of knowledge, no study focused on mechanism of rapamycin on heart failure as well as the role of AKT in this progress. This study was designed to investigate the effect and mechanism of rapamycin on HF progression. HF rats were injected with rapamycin to evaluated rapamycin s effect on myocardial function, myocardial cells apoptosis, and regulation of Akt. The present study would provide new information on rapamycin protective effect on myocardial cells and in HF progression. Methods and Materials Rat HF model Rat HF model was established as previously described [19,20]. After acclimation for 7 d (under a 12 h light/dark cycle with free access to food and water), 40 male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (280 ± 30 g) received proximal coronary ligation for the induction of chronic myocardial infarction. Rats were standardized feeding for 14 w followed with rapamycin interferences. According to the rapamycin dose, 40 rats model were randomly divided into 4 groups (n=10, for each group), including model group (HF), HF model+1 mg/kg (body weight)/d rapamycin (tail vein injection, low-dose (L) every two weeks), HF model+2.5 mg/kg (body weight)/d (middledose, M) rapamycin and HF model+4.5 mg/kg (body weight)/d rapamycin (high-dose, H). Sham ligated animals (n=10) served as non-failing Controls (CTR). Four weeks after rapamycin interference, animals were anaesthetized and hearts were separated, pieced and prepared immunohistochemistry, and western blot analysis, respectively. Tail vein blood samples were collected for plasma BNP (Brain Natriuretic Peptide) measurement using ELISA kits. All experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care Committee of The Central Hospital of Shengli Oil Field, Dongying, China. Echocardiography The assessment for heart function was performed using twinkling color Doppler ultrasound machine before anaesthetization [21,22]. The Left Ventricular (LV) end diastolic diameter (LVIDd, mm), Left Ventricular end systolic diameter (LVIDs, mm), Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF, %), and Left Ventricular Fractional Shortening (LVFS, %) were recorded or calculated. Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) measurement The plasma BNP level in rat model after 4 w rapamycin interferences were measured according to the ELISA kits [21]. HE staining Immunohistochemistry were performed on the xenograft myocardial tissues. Tissues were fixed, transparent, and embedded. For Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining, 5 µm sections were cut, dehydrated, deparaffinized, and rehydrated. Then sections were stained with HE staining solution (Nanjing Jiancheng Biotechnology Institute). Images were captured using a Olympus microscopy (BX60, Olympus, Japan). TUNNEL assay The apoptosis of myocardial cells was detected using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dutp nick end labeling (TUNNEL) assay (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer s instructions. The apoptotic myocardial cells were stained brown coloration. The average percentage (%) of apoptotic cell number from five arbitrarily selected fields was calculated (under magnification X40) using microscopy (Olympus, Japan). Western blotting analysis Xenograft myocardial tissues from rats were homogenized in ice-cold RIPA buffer, and the supernatants were collected for protein determination. Proteins of 35 µg were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and then transferred to PVDF membrane (Invitrogen Corp., Carlsbad, CA, USA). After blocking with Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA, Sigma, USA), membranes were incubated with primary antibodies against GAPDH (dilution 1: 2000), Akt (dilution 1: 5000) and phosphorylated (p)-akt (dilution 1: 1000, Cell Signal Technology Inc. Danvers, MA, USA) at 4 C overnight. Membranes were then incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h in dark at 37 C. At last, the polypeptide bands were analysed using an Enhanced Chemiluminescence (ECL) detection system. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Data were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) test for difference among groups more than three. P<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Results Rapamycin repairs cardiac function in HF rats Statistical analysis of echocardiography detection showed rapamycin administration significantly prevented HF progression (p<0.05, Table 1). Echocardiography indicators LVIDd (mm) and LVIDs (mm) were significantly increased in HF model (p<0.01), while LVEF (%) and LVFS (%) were dramatically reduced in HF model (p<0.01), as compared to Sham rats. Moreover, the administration of rapamycin into HF model inversed the changes in echocardiography indicators in a dose-dependent manner. Rats received high-dose rapamycin administration showed the lowest LVIDd and LVIDs values and the highest LVEF and LVFS values among the rapamycinadministrated groups (p<0.01). Echocardiography indicators 9648 Biomed Res 2017 Volume 28 Issue 21
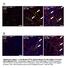
3 Rapamycin prevents apoptosis of myocardial cells in heart failure rats through up-regulating Akt assessment showed rapamycin administration prevented the HF progression. Table 1. Echocardiography indicators in rats (Mean ± SD). Group LVIDd (mm) LVIDs (mm) LVEF (%) LVFS (%) Sham 5.46 ± ± ± ± 1.29 HF model 7.24 ± 0.16 ** 4.09 ± 0.11 ** ± 2.19 ** ± 1.01 ** HF+L 6.98 ± 0.43 **# 3.79 ± 0.24 **# ± 2.21 **# ± 1.57 **# HF+M 6.42 ± 0.11 **#^ 3.33 ± 0.54 *# ± 1.64 **#^ ± 0.89 **##^ HF+H 5.97 ± 0.32 *##^ 3.04 ± 0.19 *##^ ± 2.89 *##^^ ± 1.12 *##^^ LVIDd: Left Ventricular (LV) End Diastolic Diameter; LVIDs: Left Ventricular End Systolic Diameter; LVEF: Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction; LVFS: Left Ventricular Fractional Shortening. *, and ** indicates p<0.05, and p<0.01, vs. Sham, respectively. #, and ## indicates p<0.05, and p<0.01, vs. HF model, respectively. ^, and ^^ indicates p<0.05, and p<0.01, vs. HF+L, respectively. myocardium tissues between the Sham and high-dose rapamycin administrated HF rat (Figure 1). Figure 1. HE staining for pathological changes in myocardium of HF rats. Magnification X200. Rapamycin suppresses pathological changes in myocardium in HF rats Using HE staining, we found the myocardium tissue of HF rats showed pathological changes including disorganization of cardiac myocytes, hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes, and increased intercellular collagen fibers. HF model showed numerous vacuoles of varying sizes and shapes of myocardial cells. However, all the pathological changes could be suppressed by rapamycin administration. Moreover, these rapamycin suppressed the pathological changes in in myocardium of HF rats in a dose-dependent manner. No obvious differences were observed in pathological changes in Figure 2. TUNNEL assay. Percentage (%) of TUNEL positive cell number was calculated as positive cells 100/total number of cells. ** indicates p<0.01, vs. Sham. #, and ## indicates p<0.05, and p<0.01, vs. HF model, respectively. && indicates p<0.01, vs. HF+L model. Magnification X200. Rapamycin inhibits apoptosis of myocardial cells in HF rats We performed the TUNNEL assay to analysis the apoptosis of myocardial cells in HF rats and to evaluate rapamycin s antiapoptotic effect on myocardial cells. Results showed significant apoptotic myocardial cells percentage in HF rats in comparison with that in Sham rats (p<0.01, Figure 2). The Biomed Res 2017 Volume 28 Issue
4 Zhang/Liu/Su/Chen percentage of apoptotic myocardial cells was reduced by rapamycin in a dose-dependent manner. HF rats received highdose rapamycin showed the lowest percentage of apoptotic myocardial cells (Figure 2). Rapamycin reduced plasma BNP level The plasma BNP concentration in rats was detected to evaluate the effect of rapamycin on BNP expression. Results showed that BNP level were significantly upregulated in HF model in comparison with the sham controls (p<0.01, Figure 3). However, the BNP levels in HF model were significantly reduced by rapamycin administration, as compared to the HF model (p<0.05), in a dose-dependent manner. The BNP level in high-dose rapamycin treated rats was lower than low- or middle-dose rapamycin treated rats (p<0.01). We demonstrated that rapamycin administration reduced plasma BNP level in HF rats. Figure 3. BNP ELISA assay. ** indicates p<0.01, vs. Sham. #, and ## indicates p<0.05, and p<0.01, vs. HF model, respectively. & indicates p<0.05, vs. HF+L. Figure 4. Western blot analysis for Akt activation. ** indicates p<0.01, vs. Sham. #, and ## indicates p<0.05, and p<0.01, vs. HF model, respectively. & indicates p<0.05, vs. HF+L. Rapamycin impedes Akt activation As reported long-term Akt activation induces contractile dysfunction [4]. Heart failure progression induced by longterm Akt activation could be prevented by rapamycin [4]. We detected the activation of Akt and found the upregulation of Akt in HF rats (p<0.01, Figure 4). However, the activation of Akt could be inhibited by rapamycin administration in a dosedependent manner. Significant reduction in Akt expression were observed in high-dose rapamycin administrated rats, versus rats treated with low- or middle-dose rapamycin administrated rats (p<0.05, Figure 4). Discussion The present study demonstrated that rapamycin administration to HF rats could prevent HF progression via inhibiting apoptosis of myocardial cells through inactivation of Akt. Studies showed that Akt is a crucial factor in the regulation of autophagy and apoptosis [2]. The chronic activation of Akt could induce feedback inhibition of PI3K [23]. The upregulation of Akt plays a key role in the inhibition of cardiomyocyte apoptosis or autophagy in hypoxia/ reoxygenation or ischaemia/reperfusion injury rat [24,25]. During HF progression, long-term Akt activation induces contractile dysfunction [4]. Heart failure progression induced by long-term Akt activation could be prevented by rapamycin [4,7]. In the present study, we demonstrated the dramatically Akt activation and apoptosis of myocardial cells in HF rats as compared to the normal control. After rapamycin administration, however, the expression of Akt as well as myocardial cells apoptosis was significantly inhibited, in a dose-dependent manner. These demonstrated that rapamycin could inhibit the apoptosis via reducing overexpression of Akt in HF progression. Shioi et al. previously reported that rapamycin attenuated loadinduced compensated hypertrophy via an mtor-p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (p70s6k) protein-dependent mechanism [3]. In further study by McMullen et al. they demonstrated that rapamycin administration blocked S6 phosphorylation and concluded that mtor-p70s6k1 signaling cascade might be the major pathway activated during compensated hypertrophy [26]. In this presents study, we demonstrated that rapamycin alleviated pathological changes including suppressing cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in myocardium. This fact suggested mtor-p70s6k1 signaling cascade might be the major pathway mediated by rapamycin in HF progression. The effect of rapamycin on cell apoptosis is duality. Rapamycin exhibited apoptotic effect and blocked cancer cells proliferation on one hand [8-14]. On the other hand, rapamycin could inhibit chemicals induced excess death or apoptosis via enhancing autophagy [15,16]. In the presents study, we demonstrated that rapamycin protected against HF-derived myocardial cells apoptosis and inhibited Akt activation in HF myocardium. These results showed the rapamycin protective effect against myocardial cells apoptosis in HF rats via inhibiting Akt overexpression Biomed Res 2017 Volume 28 Issue 21
5 Rapamycin prevents apoptosis of myocardial cells in heart failure rats through up-regulating Akt Conclusions We concluded that rapamycin protected against myocardial cells apoptosis in HF rats in a dose-dependent manner. HF rats received rapamycin showed ameliorative heart functions, reduced plasma BNP level and myocardial cells apoptosis in comparison with controls. These demonstrated rapamycin protective effect against HF progression and the therapeutic potential for HF therapy. Acknowledgment There is no Funding. All of the authors have no conflict of interest in this research. Ethics, Consent and Permissions Ethical approval was given by the medical ethics committee of Department of Cardiology, The Central Hospital of Shengli Oil Field. Consent to Publish All of the authors have consented to publish this research. Author s Contribution Each author has made an important scientific contribution to the study and has assisted with the drafting or revising of the manuscript. Interest Conflict All of the authors have no conflict of interest in this research. References 1. Miller MS, VanBuren P, LeWinter MM, Braddock JM, Ades PA, Maughan DW. Chronic heart failure decreases crossbridge kinetics in single skeletal muscle fibres from humans. J Physiol 2010; 588: Hou X, Hu Z, Xu H, Xu J, Zhang S, Zhong Y. Advanced glycation endproducts trigger autophagy in cadiomyocyte via RAGE/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2014; 13: Shioi T, Mcmullen JR, Tarnavski O, Converso K, Sherwood MC, Manning WJ. Rapamycin attenuates loadinduced cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Circulation 2003; 107: Shiojima I, Sato K, Izumiya Y, Schiekofer S, Ito M, Liao R. Disruption of coordinated cardiac hypertrophy and angiogenesis contributes to the transition to heart failure. J Clin Investig 2005; 115: Matsui T, Tao J, del Monte F, Lee KH, Li L, Picard M. Akt activation preserves cardiac function and prevents injury after transient cardiac ischemia in vivo. Circulation 2001; 104: Noiseux N, Gnecchi M, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Zhang L, Solomon SD, Deb A. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing Akt dramatically repair infarcted myocardium and improve cardiac function despite infrequent cellular fusion or differentiation. Mol Ther 2004; 14: McMullen JR, Jennings GL. Differences between pathological and physiological cardiac hypertrophy: novel therapeutic strategies to treat heart failure. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2007; 34: Ding K, Wang H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Xu J, Li T. Rapamycin protects against apoptotic neuronal death and improves neurologic function after traumatic brain injury in mice via modulation of the mtor-p53-bax axis. J Surg Res 2015; 194: Saqcena M, Patel D, Menon D, Mukhopadhyay S, Foster DA. Apoptotic effects of high-dose rapamycin occur in S- phase of the cell cycle. Cell Cycle 2015; 14: Alayev A, Berger SM, Kramer MY, Schwartz NS, Holz MK. The combination of rapamycin and resveratrol blocks autophagy and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 2015; 116: Morad SA, Schmid M, Buchele B, Siehl HU, El Gafaary M, Lunov O. A novel semisynthetic inhibitor of the FRB domain of mammalian target of rapamycin blocks proliferation and triggers apoptosis in chemoresistant prostate cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 2013; 83: Frost P, Berlanger E, Mysore V, Hoang B, Shi Y, Gera J. Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors induces tumor cell apoptosis in vivo primarily by inhibiting VEGF expression and angiogenesis. J Oncol 2013; Wang YD, Su YJ, Li JY, Yao XC, Liang GJ. Rapamycin, an mtor inhibitor, induced apoptosis via independent mitochondrial and death receptor pathway in retinoblastoma Y79 cell. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015; 8: Nekova TS, Dotterweich J, Schütze N, Einsele H, Stuhler G. Small molecule enhancers of rapamycin induce apoptosis in myeloma cells via GSK3A/B preferentially within a protective bone marrow microenvironment. Br J Haematol 2014; 167: He X, Song W, Liu C, Chen S, Hua J. Rapamycin inhibits acroleininduced apoptosis by alleviating ROSdriven mitochondrial dysfunction in male germ cells. Cell Proliferat 2014; 47: Pan T, Rawal P, Wu Y, Xie W, Jankovic J, Le W. Rapamycin protects against rotenone-induced apoptosis through autophagy induction. Neurosci 2009; 164: Ravikumar B, Berger Z, Vacher C, Okane CJ, Rubinsztein DC. Rapamycin pre-treatment protects against apoptosis. Human Mol Gene 2006; 15: Cui Y, Kam K, Sherman D, Janczewski WA, Zheng Y, Feldman JL. Defining prebötzinger complex rhythm- and pattern-generating neural microcircuits in vivo. Neuron 2016; 91: Kumarswamy R, Lyon AR, Volkmann I, Mills AM, Bretthauer J, Pahuja A. SERCA2a gene therapy restores Biomed Res 2017 Volume 28 Issue
6 Zhang/Liu/Su/Chen microrna-1 expression in heart failure via an Akt/ FoxO3A-dependent pathway. Eur Heart J 2012; 33: Lyon AR, Bannister ML, Collins T, Pearce E, Sepehripour AH, Dubb SS. SERCA2a gene transfer decreases SR calcium leak and reduces ventricular arrhythmias in a model of chronic heart failure. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol Wang F, Li D, Chen J, Hu WJ, Liu Y. Heart protective effects of luteolin on rats with doxorubicin-induced heart failure. Latin Am J Pharm 2013; 32: Li S, Guo K, Wu J, Guo Z, Li A. Altered expression of c- kit and nanog in a rat model of Adriamycin-induced chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 2017; 7: Nagoshi T, Matsui T, Aoyama T, Leri A, Anversa P, Li L. PI3K rescues the detrimental effects of chronic Akt activation in the heart during ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Investig 2005; 115: Wang L, Lu Y, Liu X, Wang X. Ghrelin protected neonatal rat cardiomyocyte against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting apoptosis through Akt-mTOR signal. Mol Biol Rep 2017; Fan G, Yu J, Asare PF, Wang L, Zhang H, Zhang B. Danshensu alleviates cardiac ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy and apoptosis via activation of mtor signalling. J Cell Mol Med 2016; 20: McMullen JR, Sherwood MC, Tarnavski O, Zhang L, Dorfman AL, Shioi T. Inhibition of mtor signaling with rapamycin regresses established cardiac hypertrophy induced by pressure overload. Circulation 2004; 109: * Correspondence to Guohai Su Department of Cardiology Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University PR China Department of Cardiology The Central Hospital of Shengli Oil Field PR China 9652 Biomed Res 2017 Volume 28 Issue 21
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate. than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Short-Term Doxorubicin Treatment
 Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
The alleviation of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by lycopene.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7720-7724 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The alleviation of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by lycopene. Zhenjun Liu *, Guangming He, Lili Zhao Intensive Care
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7720-7724 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The alleviation of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by lycopene. Zhenjun Liu *, Guangming He, Lili Zhao Intensive Care
MCD-microRNA. WU Hong-quan, LIU Di-chuan *, TONG Xin, CAI Min, HUANG Jing. (LVIDd) A [ ] (2012)
![MCD-microRNA. WU Hong-quan, LIU Di-chuan *, TONG Xin, CAI Min, HUANG Jing. (LVIDd) A [ ] (2012) MCD-microRNA. WU Hong-quan, LIU Di-chuan *, TONG Xin, CAI Min, HUANG Jing. (LVIDd) A [ ] (2012)](/thumbs/81/83672149.jpg) MCD-microRNA [ ] A (MCD)-microRNA MCD MCD 4 MCD-microRNA HEK293 PCR MCD mrna 28 + 3 ( + + + + + + ) 7 7 ( + ) MCD-microRNA 4 4d 1 28d (LVEF) (FS) (LVIDd)A PCR 1 MCD mrna82% + + + LVEF FS (P 0.05) (P 0.05)
MCD-microRNA [ ] A (MCD)-microRNA MCD MCD 4 MCD-microRNA HEK293 PCR MCD mrna 28 + 3 ( + + + + + + ) 7 7 ( + ) MCD-microRNA 4 4d 1 28d (LVEF) (FS) (LVIDd)A PCR 1 MCD mrna82% + + + LVEF FS (P 0.05) (P 0.05)
A Long-Term and Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor Protects against Myocardial. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
 Supporting Information A Long-Term and Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor Protects against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Xiaotian Sun 1 *, Wenshuo Wang 2, Jing Dai 3, Sheng Jin 4, Jiechun Huang
Supporting Information A Long-Term and Slow-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor Protects against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Xiaotian Sun 1 *, Wenshuo Wang 2, Jing Dai 3, Sheng Jin 4, Jiechun Huang
Full Record.
 第 1 頁, 共 2 頁 Full Record Record 1 of 6 (Set #2) Title: Insulin-like growth factor-1 mediates stretch-induced upregulation of myostatin expression in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes Author(s): Shyu KG, Ko WH,
第 1 頁, 共 2 頁 Full Record Record 1 of 6 (Set #2) Title: Insulin-like growth factor-1 mediates stretch-induced upregulation of myostatin expression in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes Author(s): Shyu KG, Ko WH,
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
European Society of Cardiology Congress DONOR AGE NEGATIVELY INFLUENCES THE CYTOPROTECTIVE PARACRINE EFFECTS EXERTED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS
 European Society of Cardiology Congress 28 Aug - 01 Sep 2009, Stockholm - Sweden DONOR AGE NEGATIVELY INFLUENCES THE CYTOPROTECTIVE PARACRINE EFFECTS EXERTED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS Massimiliano
European Society of Cardiology Congress 28 Aug - 01 Sep 2009, Stockholm - Sweden DONOR AGE NEGATIVELY INFLUENCES THE CYTOPROTECTIVE PARACRINE EFFECTS EXERTED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS Massimiliano
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
The influence and significance of rapamycin on cardiomyocyte autophagy level of early heart failure rat.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (8): 3563-3567 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The influence and significance of rapamycin on cardiomyocyte autophagy level of early heart failure rat. Zhang Shuli *#, Jianhui
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (8): 3563-3567 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The influence and significance of rapamycin on cardiomyocyte autophagy level of early heart failure rat. Zhang Shuli *#, Jianhui
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Pretargeting and Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry-Mediated Endogenous Stem Cell Homing for Heart Repair
 Pretargeting and Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry-Mediated Endogenous Stem Cell Homing for Heart Repair Mouse Model of Myocardial Infarction (MI) All animal work was compliant with the Institutional Animal
Pretargeting and Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry-Mediated Endogenous Stem Cell Homing for Heart Repair Mouse Model of Myocardial Infarction (MI) All animal work was compliant with the Institutional Animal
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): Effect of microrna-21 on PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a signal transduction pathway. ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6135-6139 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of microrna-21 on PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a signal transduction pathway. Ying Han 1*, Wen-Yan Xie 2*, Chang-Sheng Xu 1, Hua-Jun
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6135-6139 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of microrna-21 on PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a signal transduction pathway. Ying Han 1*, Wen-Yan Xie 2*, Chang-Sheng Xu 1, Hua-Jun
International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science
 1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
SOCS3 is involved in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by Ang II.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (10): 4480-4484 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info SOCS3 is involved in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by Ang II. Jian-min Yang 1,2, Bin Chen 2, Hong Li 2, Guo-xin Tong 2,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (10): 4480-4484 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info SOCS3 is involved in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by Ang II. Jian-min Yang 1,2, Bin Chen 2, Hong Li 2, Guo-xin Tong 2,
Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic
 Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Lokesh Makhija, BE, Veda Krishnan, MSc, Rakhshinda Rehman, MTech, Samarpana Chakraborty, MSc, Shuvadeep Maity,
Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Lokesh Makhija, BE, Veda Krishnan, MSc, Rakhshinda Rehman, MTech, Samarpana Chakraborty, MSc, Shuvadeep Maity,
Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men
 Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men 17-01-2013 Dirk J Duncker Experimental Cardiology, Cardiology, Thoraxcenter Cardiovascular Research Institute COEUR Erasmus MC, University Medical
Exercise in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling: of Mice and Men 17-01-2013 Dirk J Duncker Experimental Cardiology, Cardiology, Thoraxcenter Cardiovascular Research Institute COEUR Erasmus MC, University Medical
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Xinfuli Granule improves post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling and myocardial fibrosis in rats by regulating TGF-β/Smads signaling pathway
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2017) 14: 301 307 2017 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Article Open Access Xinfuli Granule improves post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling and
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2017) 14: 301 307 2017 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Article Open Access Xinfuli Granule improves post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling and
Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It?
 MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W. Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 TAC 8W TAC 2W
 A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
A Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Tcf21 MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W B Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg Sham GFP Col 1/3 Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 2W Postn MCM ; R26 mtmg TAC 8W Supplementary
Effect of low temperatures on BAX and BCL2 proteins in rats with spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury
 Effect of low temperatures on BAX and BCL2 proteins in rats with spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury P. Zhu 1 *, M.Y. Zhao 1,2 *, X.H. Li 1 *, Q. Fu 1, Z.F. Zhou 1, C.F. Huang 1, X.S. Zhang 1, H.L.
Effect of low temperatures on BAX and BCL2 proteins in rats with spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury P. Zhu 1 *, M.Y. Zhao 1,2 *, X.H. Li 1 *, Q. Fu 1, Z.F. Zhou 1, C.F. Huang 1, X.S. Zhang 1, H.L.
Effects of sitagliptin on cardiac metabolism in mice
 Effects of sitagliptin on cardiac metabolism in mice M. Lenski, J.-C. Reil, M. Böhm, U. Laufs Saarland University Hospital Department of Internal Medicine III, Cardiology Homburg - Germany Disclosures
Effects of sitagliptin on cardiac metabolism in mice M. Lenski, J.-C. Reil, M. Böhm, U. Laufs Saarland University Hospital Department of Internal Medicine III, Cardiology Homburg - Germany Disclosures
Sean Davidson. The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute University College London, UK
 Key pathways to ischemia-reperfusion injury Sean Davidson The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute University College London, UK Outline What is ischaemia-reperfusion injury? What causes ischaemia-reperfusion
Key pathways to ischemia-reperfusion injury Sean Davidson The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute University College London, UK Outline What is ischaemia-reperfusion injury? What causes ischaemia-reperfusion
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY
 AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats
 Pharmaceutical The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats Objective: To investigate repairing effect
Pharmaceutical The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats Objective: To investigate repairing effect
E. Cervio, P. Danieli, C. Ciuffreda, F. Pisano, M. Roccio, M. Gnecchi. The authors have no financial disclosures to declare
 16 th ISCT Annual Meeting SOLUBLE FACTORS RELEASED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS OF FETAL ORIGIN LEAD TO CARDIOMYOCYTE PROTECTION THROUGH THE INHIBITION OF PRO-APOPTOTIC SIGNALING E. Cervio, P. Danieli,
16 th ISCT Annual Meeting SOLUBLE FACTORS RELEASED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS OF FETAL ORIGIN LEAD TO CARDIOMYOCYTE PROTECTION THROUGH THE INHIBITION OF PRO-APOPTOTIC SIGNALING E. Cervio, P. Danieli,
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Induction of myocardial infarction Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (7 mg/kg). In the supine position, endotracheal intubation was performed.
Supplementary Material Induction of myocardial infarction Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (7 mg/kg). In the supine position, endotracheal intubation was performed.
Mimecan and cardiac extracellular matrix integrity Lucas Van Aelst, MD Department of Internal Medicine, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
 Mimecan and cardiac extracellular matrix integrity Lucas Van Aelst, MD Department of Internal Medicine, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium VIB-Vesalius Research Center, KULeuven, Leuven, Belgium
Mimecan and cardiac extracellular matrix integrity Lucas Van Aelst, MD Department of Internal Medicine, University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Belgium VIB-Vesalius Research Center, KULeuven, Leuven, Belgium
Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning
 Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning J. Li, J.S. Wang, Z.X. Xie, W.Z. Wang, L. Wang, G.Y. Ma, Y.Q.
Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning J. Li, J.S. Wang, Z.X. Xie, W.Z. Wang, L. Wang, G.Y. Ma, Y.Q.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Repair Vascular Damage after Chemotherapy: Past, Present and Future
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Repair Vascular Damage after Chemotherapy: Past, Present and Future Cell Therapy 2014 Las Vegas, NV, USA Sulaiman Al-Hashmi, PhD Sultan Qaboos University Oman What are MSCs? Stem
Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Repair Vascular Damage after Chemotherapy: Past, Present and Future Cell Therapy 2014 Las Vegas, NV, USA Sulaiman Al-Hashmi, PhD Sultan Qaboos University Oman What are MSCs? Stem
Acta Physiologica Sinica
 , 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
, 1999 4, 51 (2), 187 192 187 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 1998204222 1998206203 3 (No139500052) 3 3, 221002 3 3 3 3 3 (, 200031) ( Ito), 28 d (H28, 6 h/ d), Ito (16118 4161 6132 1135 pa/ pf, P < 0105),
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA. Lumen area ( m 2 )
 Elastin Lumen area ( m 2 ) Media to lumen ratio (x1) H.E. Medium thickness ( m) Medium area ( m 2 ) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA A (Bmal1 flox/flox ) (SM-Bmal1 -/- ) B 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 1µm 5 8 4 6 3 2 4 1 2 Supplemental
Elastin Lumen area ( m 2 ) Media to lumen ratio (x1) H.E. Medium thickness ( m) Medium area ( m 2 ) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA A (Bmal1 flox/flox ) (SM-Bmal1 -/- ) B 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 1µm 5 8 4 6 3 2 4 1 2 Supplemental
Deposited on: 25 July 2011
 Morton, E., Macrae, I.M., McCabe, C., Brown, S.M. and White, F. (2006) Identification of the growth arrest and DNA damage protein GADD34 in the normal human heart and demonstration of alterations in expression
Morton, E., Macrae, I.M., McCabe, C., Brown, S.M. and White, F. (2006) Identification of the growth arrest and DNA damage protein GADD34 in the normal human heart and demonstration of alterations in expression
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice.
 Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant molecular mechanism.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Up-Regulation of Phosphorylated ATM/ATR Substrate/Akt Expression by Phenylephrine in Peri-Infarct Myocardium in Rats
 Original Article??? Acta Cardiol Sin 2011;27:182 8 Basic Science Up-Regulation of Phosphorylated ATM/ATR Substrate/Akt Expression by Phenylephrine in Peri-Infarct Myocardium in Rats Yang Mu, 1,2 Gang Li,
Original Article??? Acta Cardiol Sin 2011;27:182 8 Basic Science Up-Regulation of Phosphorylated ATM/ATR Substrate/Akt Expression by Phenylephrine in Peri-Infarct Myocardium in Rats Yang Mu, 1,2 Gang Li,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Probe. Hind III Q,!?R'!! /0!!!!D1"?R'! vector. Homologous recombination
 Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Diastolic Heart Failure. Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012
 Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Diastolic Heart Failure Edwin Tulloch-Reid MBBS FACC Consultant Cardiologist Heart Institute of the Caribbean December 2012 Disclosures Have spoken for Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Sat on a physician advisory
Ethanol vapour induced dilated cardiomyopathy in chick embryos
 Ethanol vapour induced dilated cardiomyopathy in chick embryos Kiran Kamran, 1 Muhammad Yunus Khan, 2 Liaqat Ali Minhas 3 1084 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Objective: To study the effects of ethanol vapour
Ethanol vapour induced dilated cardiomyopathy in chick embryos Kiran Kamran, 1 Muhammad Yunus Khan, 2 Liaqat Ali Minhas 3 1084 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Abstract Objective: To study the effects of ethanol vapour
Paracrine Mechanisms in Adult Stem Cell Signaling and Therapy
 Paracrine Mechanisms in Adult Stem Cell Signaling and Therapy Massimiliano Gnecchi, Zhiping Zhang, Aiguo Ni, Victor J. Dzau Circulation Research 2008 Nov 21;103(11):1204-19 Introduction(1) After AMI all
Paracrine Mechanisms in Adult Stem Cell Signaling and Therapy Massimiliano Gnecchi, Zhiping Zhang, Aiguo Ni, Victor J. Dzau Circulation Research 2008 Nov 21;103(11):1204-19 Introduction(1) After AMI all
Supporting Information. Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell. Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
 Supporting Information Table of contents Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell differentiation and cardioprotection (page 2) Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
Supporting Information Table of contents Calculation of the relative contributions of myocyte proliferation, stem cell differentiation and cardioprotection (page 2) Supporting Information Fig 1 (page 9)
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
The neuroprotective effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin on rat brain injury caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia
 Neurology Asia 2014; 19(4) : 399 403 The neuroprotective effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin on rat brain injury caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia 1,2 Ya-Ning Zhao, 1 Xia Guo, 2 Hong-Yang Wang,
Neurology Asia 2014; 19(4) : 399 403 The neuroprotective effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin on rat brain injury caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia 1,2 Ya-Ning Zhao, 1 Xia Guo, 2 Hong-Yang Wang,
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Effects of norepinephrine on hemodynamics, vascular elasticity, cardiac pump function, and inflammatory factors in patients with septic shock
 838396EJI0010.1177/2058739219838396European Journal of InflammationWang et al. letter2019 Letter to the Editor Effects of norepinephrine on hemodynamics, vascular elasticity, cardiac pump function, and
838396EJI0010.1177/2058739219838396European Journal of InflammationWang et al. letter2019 Letter to the Editor Effects of norepinephrine on hemodynamics, vascular elasticity, cardiac pump function, and
Hearts were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (ph 7.4) overnight, embedded in paraffin, and
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Histology of Heart Hearts were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (ph 7.4) overnight, embedded in paraffin, and serially sectioned into 5-µm slices. Standard hematoxylin
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Histology of Heart Hearts were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (ph 7.4) overnight, embedded in paraffin, and serially sectioned into 5-µm slices. Standard hematoxylin
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
 Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and function in
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ. ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
 ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
ΕΘΝΙΚΟ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΠΟΔΙΣΤΡΙΑΚΟ ΠΑΝΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΙΟ ΑΘΗΝΩΝ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΗ ΣΧΟΛΗ Ά ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ Διευθυντής: Καθηγητής Δημήτριος Τούσουλης ΒΙΟΔΕΙΚΤΕΣ ΣΤΗΝ ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ ΤΟΥΣΟΥΛΗΣ Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
Effect of sphingosine-1-phosphate and myoblast transplantation on rat acute myocardial infarction
 Effect of sphingosine-1-phosphate and myoblast transplantation on rat acute myocardial infarction H. Yu 1, P.L. Chen 2, Y. Zhao 1, X. Gu 3, W. He 1 and Z. Gong 2 1 Key Laboratory of System Biomedicine
Effect of sphingosine-1-phosphate and myoblast transplantation on rat acute myocardial infarction H. Yu 1, P.L. Chen 2, Y. Zhao 1, X. Gu 3, W. He 1 and Z. Gong 2 1 Key Laboratory of System Biomedicine
Cell therapy: enhancing the therapeutic potential of cardiac progenitors for delivery post myocardial infarction. Rita Alonaizan
 Cell therapy: enhancing the therapeutic potential of cardiac progenitors for delivery post myocardial infarction Rita Alonaizan Department of Physiology, Anatomy & Genetics St Catherine s College Supervisor:
Cell therapy: enhancing the therapeutic potential of cardiac progenitors for delivery post myocardial infarction Rita Alonaizan Department of Physiology, Anatomy & Genetics St Catherine s College Supervisor:
InteractionofInflammatoryResponseandSympatheticNervousSystemintheCentralRegulationofChronicHeartFailureinRats
 : I Surgeries and Cardiovascular System Volume 16 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
: I Surgeries and Cardiovascular System Volume 16 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin 2012 Sep ~ 6. http / /www. cnki. net /kcms /detail / R html
 1262 1262 ~ 6 2012-8 - 14 17 19 http / /www. cnki. net /kcms /detail /34. 1086. R. 20120814. 1719. 018. html MG - 63 1 1 2 2 1. 453003 2. 361005 doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1001-1978. 2012. 09. 018 A 1001-1978
1262 1262 ~ 6 2012-8 - 14 17 19 http / /www. cnki. net /kcms /detail /34. 1086. R. 20120814. 1719. 018. html MG - 63 1 1 2 2 1. 453003 2. 361005 doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1001-1978. 2012. 09. 018 A 1001-1978
Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9):
 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9): 691-695 691 Letter to the Editor Protective Effects of Tetramethylpyrazine on Cerebrovascular Regulations in Rats with Chronic Alcoholic Encephalopathy LI Hui 1,, YANG
Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9): 691-695 691 Letter to the Editor Protective Effects of Tetramethylpyrazine on Cerebrovascular Regulations in Rats with Chronic Alcoholic Encephalopathy LI Hui 1,, YANG
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Exendin-4 attenuates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting high mobility group box 1 protein expression
 original article Cardiology Journal 213, Vol. 2, No. 6, pp. 6 64 DOI: 1.563/CJ.213.159 Copyright 213 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Exendin-4 attenuates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting
original article Cardiology Journal 213, Vol. 2, No. 6, pp. 6 64 DOI: 1.563/CJ.213.159 Copyright 213 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Exendin-4 attenuates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting
Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR-2B cells untreated (-) or stimulated (+) for 45 min
 Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR2B cells untreated () or stimulated () for 45 min with 5 ng/ml TGFβ or 10 ng/ml BMP4 were incubated with
Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR2B cells untreated () or stimulated () for 45 min with 5 ng/ml TGFβ or 10 ng/ml BMP4 were incubated with
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography Control (n=4)
 Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
Supplemental Table 1. Echocardiography (n=4) Mlc2v cre/+ ; DNMAML (n=4) LVIDd, mm 3.9±0.3 4.3±0.3 LVIDs, mm 2.6±0.4 2.9±0.2 d, mm 0.72±0.06 0.75±0.1 LVPWd, mm 0.72±0.06 0.77±0.11 FS, % 33±6 33±1 EF, %
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea
 Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Value of echocardiography in chronic dyspnea Jahrestagung Schweizerische Gesellschaft für /Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Pneumologie B. Kaufmann 16.06.2016 Chronic dyspnea Shortness of breath lasting
Mechanical Stress-Dependent Autophagy Components Release via Extracellular
 Supporting Information for Mechanical Stress-Dependent Autophagy Components Release via Extracellular Nanovesicles in Tumor Cells Kaizhe Wang,, Yuhui Wei,, Wenjing Liu,, Lin Liu,, Zhen Guo,, Chunhai Fan,,
Supporting Information for Mechanical Stress-Dependent Autophagy Components Release via Extracellular Nanovesicles in Tumor Cells Kaizhe Wang,, Yuhui Wei,, Wenjing Liu,, Lin Liu,, Zhen Guo,, Chunhai Fan,,
The biological bases of treatment related cardiac and lung toxicity
 The biological bases of treatment related cardiac and lung toxicity Monica Mangoni Cardiopulmonary toxicity of anticancer treatments Chemotherapy TKIs MoAB CARDIAC TOXICITY Radiation effect -------------------------------Early
The biological bases of treatment related cardiac and lung toxicity Monica Mangoni Cardiopulmonary toxicity of anticancer treatments Chemotherapy TKIs MoAB CARDIAC TOXICITY Radiation effect -------------------------------Early
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
Nimbolide inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis through ROS-mediated
 Nimbolide inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis through ROS-mediated apoptosis and inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition Ramadevi Subramani a, Ph.D., Elizabeth Gonzalez b, MS.,
Nimbolide inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis through ROS-mediated apoptosis and inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition Ramadevi Subramani a, Ph.D., Elizabeth Gonzalez b, MS.,
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease. Why Animal Models of Disease? Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison
 In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Ventricular Interactions in the Normal and Failing Heart
 Ventricular Interactions in the Normal and Failing Heart Congenital Cardiac Anesthesia Society 2015 Pressure-volume relations Matched Left ventricle to low hydraulic impedance Maximal stroke work limited
Ventricular Interactions in the Normal and Failing Heart Congenital Cardiac Anesthesia Society 2015 Pressure-volume relations Matched Left ventricle to low hydraulic impedance Maximal stroke work limited
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update
 NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 Overexpression Improves Left Ventricular Remodeling and Function in a Rat Model of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 59, No. 8, 2012 2012 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.09.071
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 59, No. 8, 2012 2012 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.09.071
B-cell. Astrocyte SCI SCI. T-cell
 RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
Diastolic Dysfunction: Hypertension to Hypertrophy to Heart Failure
 Diastolic Dysfunction: Hypertension to Hypertrophy to Heart Failure Dr. Shelley Zieroth FRCPC Assistant Professor, Cardiology, University of Manitoba Director of Cardiac Transplant and Heart Failure Clinics
Diastolic Dysfunction: Hypertension to Hypertrophy to Heart Failure Dr. Shelley Zieroth FRCPC Assistant Professor, Cardiology, University of Manitoba Director of Cardiac Transplant and Heart Failure Clinics
Supplementary Figure 1 Lymphocytes can be tracked for at least 4 weeks after
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lymphocytes can be tracked for at least 4 weeks after photoconversion by using H2B-Dendra2. 4-5 PPs of H2B-Dendra2 BM chimeras were photoconverted and analyzed 7 days (upper panel)
Supplementary Figure 1 Lymphocytes can be tracked for at least 4 weeks after photoconversion by using H2B-Dendra2. 4-5 PPs of H2B-Dendra2 BM chimeras were photoconverted and analyzed 7 days (upper panel)
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Protective role of silymarin in a mouse model of renal Ischemia Reperfusion injury
 Tan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2015) 10:198 DOI 10.1186/s13000-015-0436-4 RESEARCH Open Access Protective role of silymarin in a mouse model of renal Ischemia Reperfusion injury Jian Tan, Jianpeng Hu,
Tan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2015) 10:198 DOI 10.1186/s13000-015-0436-4 RESEARCH Open Access Protective role of silymarin in a mouse model of renal Ischemia Reperfusion injury Jian Tan, Jianpeng Hu,
A MODEL OF GAP JUNCTION CONDUCTANCE AND VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIA
 A MODEL OF GAP JUNCTION CONDUCTANCE AND VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIA X. D. Wu, Y. L. Shen, J. L. Bao, C. M. Cao, W. H. Xu, Q. Xia Department of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou,
A MODEL OF GAP JUNCTION CONDUCTANCE AND VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIA X. D. Wu, Y. L. Shen, J. L. Bao, C. M. Cao, W. H. Xu, Q. Xia Department of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou,
Cardiac Gene Therapy: Beyond the Mouse. David M Kaye Heart Failure Research Group Baker IDI, Melbourne, AUSTRALIA
 Cardiac Gene Therapy: Beyond the Mouse David M Kaye Heart Failure Research Group Baker IDI, Melbourne, AUSTRALIA Presenter Disclosure Information FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE: Equity: Osprey Medical Grants/Research
Cardiac Gene Therapy: Beyond the Mouse David M Kaye Heart Failure Research Group Baker IDI, Melbourne, AUSTRALIA Presenter Disclosure Information FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE: Equity: Osprey Medical Grants/Research
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy se
 A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody to NFkB p65 (v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian))
 Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Muraski et al. 10.1073/pnas.0709135105 SI Text Generation of Transgenic Animals. Pim-WT and Pim-DN cdnas were subcloned NheI/SmaI from pegfp-c1 Pim-1 and pegfp-c1 Pim-DN plasmids
Supporting Information Muraski et al. 10.1073/pnas.0709135105 SI Text Generation of Transgenic Animals. Pim-WT and Pim-DN cdnas were subcloned NheI/SmaI from pegfp-c1 Pim-1 and pegfp-c1 Pim-DN plasmids
MOLECULAR MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ANGIOTENSIN-(1-7)/Mas. Short title: Ang-(1-7)/Mas signaling pathway in cardiomyocytes
 MOLECULAR MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ANGIOTENSIN-(1-7)/Mas SIGNALING PATHWAY IN CARDIOMYOCYTES 1 Marco Fabrício Dias-Peixoto, 1 Robson A.S. Santos, 1 Enéas R.M. Gomes, 1 Márcia N.M. Alves, 1 Pedro W.M. Almeida,
MOLECULAR MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ANGIOTENSIN-(1-7)/Mas SIGNALING PATHWAY IN CARDIOMYOCYTES 1 Marco Fabrício Dias-Peixoto, 1 Robson A.S. Santos, 1 Enéas R.M. Gomes, 1 Márcia N.M. Alves, 1 Pedro W.M. Almeida,
Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk TAC is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2.
 3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
3562-RG-1 Supplementary Figure 1 Fetal gene upregulation by 1-wk is significantly increased in mice lacking RGS2. ANP(Nppa) /BNP(Nppb) A-type and B-type natriuretic peptide; β-mhc (Myh7) beta myosin heavy
Genetic ablation of Acp1 (Lmptp) in mice prevents heart failure
 Genetic ablation of Acp1 (Lmptp) in mice prevents heart failure Coralie Poizat, Ph.D. Director, Cardiovascular Research Program KFSHRC-Riyadh Saudi Heart Failure Working Group Jeddah, 5 December 2015 Cardiovascular
Genetic ablation of Acp1 (Lmptp) in mice prevents heart failure Coralie Poizat, Ph.D. Director, Cardiovascular Research Program KFSHRC-Riyadh Saudi Heart Failure Working Group Jeddah, 5 December 2015 Cardiovascular
