Embryonic Development of the Human Heart
|
|
|
- Anthony Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Embryonic Development of the Human Heart 1. Embryonic development of From formation of the zygote up until the third week of development the embryo s demand for O 2 and nutrients is met by simple diffusion. During the third week of development however, O 2 cannot reach all cells in the embryo by diffusion. So, during the third week the cardiovascular system begins to develop in order to meet this increased demand for O 2 and nutrients. The cardiovascular system begins in the extraembryonic mesoderm of the yolk sac on day 17. Blood islands form in the splanchnopleuric mesoderm of the yolk sac wall. These blood islands begin to anastamose forming the initial vascular network. On day 18, embryonic vasculature begins to form as the blood islands fuse to form a primitive vascular network, extend towards and anastamose with the developing embryonic vasculature establishing a primitive circulatory system. 2. 1
2 Embryonic development of The figure above shows the earliest stages of cardiovascular formation in which blood islands are forming, anastamosing, and growing towards the embryonic disc. 3. Embryonic development of A heart is required to pump blood through this new vascular system and as a result the heart develops in conjunction with the vascular system. The heart is actually derived from the developing vascular system. It begins its development as a pair of vascular elements, the endocardial tubes. The endocardial tubes like all of the vascular system are derived from the splanchnopleuric mesoderm; the endocardial tubes, however, are derived from a special horseshoe shaped region of splanchnopleuric mesoderm called the cardiogenic region. On about day 19 the endocardial tubes begin to develop from the cardiogenic region. The cardiogenic region is located cranial and lateral to the neural plate. Late in the third week, embryonic folding begins to move the endocardial tubes from their cranial and lateral position to a midline position, in what will become the thoracic region. Once the endocardial tubes have reached this midline position they fuse and form a primitive heart tube. 4. 2
3 Embryonic development of Shortly after the primitive heart tube has formed it begins remodeling to attain the adult heart form. Externally, the primitive heart tube develops a series of constrictions and expansions, after which time the heart loops and folds into a characteristic S shape in order to establish the correct spatial relationships needed to accommodate the chambers of the mature heart. Internally, the heart is divided by septae into four separate chambers of the heart. The following presentations show embryonic heart formation externally and internally during the first nine weeks of development. 5. External Development of the Heart This program shows three dimensional clay models of different stages of human embryonic heart development. Each of these models is shown rotating These different models are intended to demonstrate the main events taking place in the external development of the human heart. Directions: By clicking on one of the links listed on page 8 you will gain access to different models of various stages of external heart development. On each presentation set you will find the following four buttons on the top right side of the page. Beginning click this button if you wish to restart the presentation at any point. Previous click this button if you wish to go back to a previous view. This button will also stop rotation of the image. Press Next to resume rotation. Next this button will allow you to progress through the presentation more quickly. If you have paused the program for any reason it will allow you to progress through the program one slide at a time; if double clicked it will restart the programs automatic progression through the slides. End click this button to take you to the last slide in the series. 6. 3
4 External Development of the Heart Other buttons of interest: Spacebar this will progress you through the program one slide at a time if the program has been paused for any reason. Escape button this button takes you out of the any of the presentations on the different stages of heart development and returns you to this page. s button this button will pause the presentation at any time. + button this button will restart the presentation any time it has been paused. 7. External Development of the Heart Day 21 of heart development Day 23 of heart development Day 25 of heart development Day 28 of heart development Day 35 of heart development Adult form of the heart 8. 4
5 Internal Development of the heart This program shows coronal sections of clay models of the human heart. These different models are intended to demonstrate the main events taking place during the internal development of the heart. Directions: By clicking on the link below you will gain access to these different heart models. Once you have done this you will find four buttons in the upper right side of your screen: Beginning this button will return you to the very first slide in the series (week 4). Previous this button will move you to the previous slide in the series. Next this button will advance you through the series of stages one slide at a time. End this slide will take you to the last slide in this series (week 9+). Note: For some of the different stages of heart development there is only one slide ( weeks 4 & 5), all other stages (weeks) there are three different slides. If you are to navigate through this program you must do so one slide at a time (using the Next button, or the space bar). If at any point you wish to quit the program on internal development of heart, simply press the escape button on your keyboard; this will return you to this page. Link to internal development of the heart 9. 5
Development of the Heart *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Organogenesis Part 2. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm
 Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
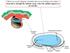 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
Development of the Heart
 Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Embryology of the Heart
 *Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
*Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
Chapter 6. Villous Growth
 Core Curriculum in Perinatal Pathology Chapter 6 Villous Growth Overview of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis Vasculogenesis Extraembryonic Vasculogenesis Angiogenesis Branching angiogenesis Sprouting angiogenesis
Core Curriculum in Perinatal Pathology Chapter 6 Villous Growth Overview of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis Vasculogenesis Extraembryonic Vasculogenesis Angiogenesis Branching angiogenesis Sprouting angiogenesis
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT
 CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT Fahey/Insel/Roth, Fit & Well: Core Concepts and Labs in Physical Fitness and Wellness, Chapter 3 ANATOMY OF THE HEART O The heart is divided into right and left hand side
CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT Fahey/Insel/Roth, Fit & Well: Core Concepts and Labs in Physical Fitness and Wellness, Chapter 3 ANATOMY OF THE HEART O The heart is divided into right and left hand side
W.S. O. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
Development of the heart
 Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
and the beat goes on: developing a heart and vascular system
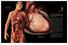 HEARTCHAPTER1.qxp 7/15/05 10:22 AM Page 4 this integrated system of heart, blood, and vessels is known as the cardiovascular system. CHAPTER 1 and the beat goes on: developing a heart and vascular system
HEARTCHAPTER1.qxp 7/15/05 10:22 AM Page 4 this integrated system of heart, blood, and vessels is known as the cardiovascular system. CHAPTER 1 and the beat goes on: developing a heart and vascular system
Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm)
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm) Further Development: Digestive System Foregut, Midgut, Hindgut Heart and Aortic Arches
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm) Further Development: Digestive System Foregut, Midgut, Hindgut Heart and Aortic Arches
The heart & Cardiovascular system
 The heart & Cardiovascular system The heart s continuous pulse create a base for our understanding of rhythms in everyday life. Bonnie Bainbridge Cohen The heart constantly beats throughout our lives never
The heart & Cardiovascular system The heart s continuous pulse create a base for our understanding of rhythms in everyday life. Bonnie Bainbridge Cohen The heart constantly beats throughout our lives never
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I
 6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations.
 6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
Animal Reproduction. Hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. # lectures for cumulative test # 01 book 01
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 05 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture Meetings
Circulatory System: Introduction. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College
 Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month
 Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Operating Instructions. Stryker Rugged Stair-PRO Stair Chair Model 6252 (SWL 35 stone 227 kg 500 lb)
 Operating Instructions Stryker Rugged Stair-PRO Stair Chair Model 6252 (SWL 35 stone 227 kg 500 lb) Component Identification: Operational Daily safety checks: 1) Framework intact 2) Wheels and castors
Operating Instructions Stryker Rugged Stair-PRO Stair Chair Model 6252 (SWL 35 stone 227 kg 500 lb) Component Identification: Operational Daily safety checks: 1) Framework intact 2) Wheels and castors
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology. Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity
 Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos
 S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Introduction Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos Many laboratories that examine sea urchin embryos do
S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Introduction Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos Many laboratories that examine sea urchin embryos do
Formation defects Scoliosis Deformities I 07 1
 What is congenital scoliosis? Congenital scoliosis is a spinal deformity with lateral deviation and rotation of the spinal column, where congenital dysfunctions in embryonal vertebra development cause
What is congenital scoliosis? Congenital scoliosis is a spinal deformity with lateral deviation and rotation of the spinal column, where congenital dysfunctions in embryonal vertebra development cause
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries
 Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Flatworms. Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
The cardiovascular system is composed of a pump the heart and blood
 5 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Dynamics O B J E C T I V E S 1. To understand the relationships among blood flow, pressure gradient, and resistance 2. To define resistance and describe the main factors
5 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Dynamics O B J E C T I V E S 1. To understand the relationships among blood flow, pressure gradient, and resistance 2. To define resistance and describe the main factors
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Spinal Fusion. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla
 Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
Development of Spinal Cord & Vertebral Column Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawi & Prof. Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: q Describe the development of the spinal cord
2/2/2011. Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
PHYSIOEX 3.0 EXERCISE 33B: CARDIOVASCULAR DYNAMICS
 PHYSIOEX 3.0 EXERCISE 33B: CARDIOVASCULAR DYNAMICS Objectives 1. To define the following: blood flow; viscosity; peripheral resistance; systole; diastole; end diastolic volume; end systolic volume; stroke
PHYSIOEX 3.0 EXERCISE 33B: CARDIOVASCULAR DYNAMICS Objectives 1. To define the following: blood flow; viscosity; peripheral resistance; systole; diastole; end diastolic volume; end systolic volume; stroke
- anterior endoderm produces Wnt inhibitors (e.g. Cerberus, Dickkopf, Crescent); prevent Wnts from binding to their receptors
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Gilbert Chapter 15. Lateral Plate Mesoderm and Endoderm December 12, 2006 LATERAL PLATE MESODERM Two bands of lateral plate mesoderm lie peripheral to the intermediate
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Gilbert Chapter 15. Lateral Plate Mesoderm and Endoderm December 12, 2006 LATERAL PLATE MESODERM Two bands of lateral plate mesoderm lie peripheral to the intermediate
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Option A: Neurobiology & Behavior HL BIOLOGY 2 ND EDITION DAMON, MCGONEGAL, TOSTO, AND
 Option A: Neurobiology & Behavior A1: NEURAL DEVELOPMENT USE THE INFO IN THE PRESENTATION TO COMPLETE A1 NOTES GUIDE INFORMATION TAKEN FROM: HL BIOLOGY 2 ND EDITION DAMON, MCGONEGAL, TOSTO, AND WARD BIOLOGY
Option A: Neurobiology & Behavior A1: NEURAL DEVELOPMENT USE THE INFO IN THE PRESENTATION TO COMPLETE A1 NOTES GUIDE INFORMATION TAKEN FROM: HL BIOLOGY 2 ND EDITION DAMON, MCGONEGAL, TOSTO, AND WARD BIOLOGY
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1 1. Moves nutrients to and waste from cells 2. Pathway for disease fighting agents and hormones 3. Control of body temperature homeostasis 2 The Circulatory
TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1 1. Moves nutrients to and waste from cells 2. Pathway for disease fighting agents and hormones 3. Control of body temperature homeostasis 2 The Circulatory
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Introduction to TEE using Heartworks Echocardiography Simulator
 Introduction to TEE using Heartworks Echocardiography Simulator Steven M. Ewer, MD Assistant Professor Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health Version
Introduction to TEE using Heartworks Echocardiography Simulator Steven M. Ewer, MD Assistant Professor Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health Version
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. Repetition: Muscle tissue
 Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease. Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc.
 The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc. Seattle, WA embryology We recognize the VACTERL association and frequency of
The Brain: Prenatal and Postnatal Effects of Congenital Heart Disease Dianna M. E. Bardo, M D Swedish Cherry Hill Radia, Inc. Seattle, WA embryology We recognize the VACTERL association and frequency of
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur
 Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur Anand Sharma, Achal Sharma, R.S. Mittal SMS Medical College, Jaipur, India Abstract: A composite type of SCM is very rare and only a
Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur Anand Sharma, Achal Sharma, R.S. Mittal SMS Medical College, Jaipur, India Abstract: A composite type of SCM is very rare and only a
Colorado Agriscience Curriculum. Unit 3 Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1 Animal Growth and Development
 Colorado Agriscience Curriculum Unit 3 Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1 Animal Growth and Development Periods of Growth There are two separate stages we are concerned with in animal growth and development.
Colorado Agriscience Curriculum Unit 3 Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1 Animal Growth and Development Periods of Growth There are two separate stages we are concerned with in animal growth and development.
Laerdal-SonoSim Procedure Trainer
 EN Laerdal-SonoSim Procedure Trainer User Guide www.laerdal.com Intended Use The Laerdal-SonoSim Procedure Trainer allows learners the ability to perform ultrasound guidance with real-patient data on multiple
EN Laerdal-SonoSim Procedure Trainer User Guide www.laerdal.com Intended Use The Laerdal-SonoSim Procedure Trainer allows learners the ability to perform ultrasound guidance with real-patient data on multiple
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting
 Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
Ontwikkeling; bevruchting http://www.lima.ohiostate.edu/biology/archive/flowers. html Young Lily anther x40. Four pollen sacs and a cross section of the fillament are visible. Diploid (2N chromosomes)
GLOOKO FOR ios MIDS USER GUIDE
 GLOOKO FOR ios MIDS USER GUIDE October 2018 IFU-0001 13 Glooko MIDS is cleared for US only Rx only TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS MOBILE INSULIN DOSING SYSTEM (MIDS)... 2 Intended Use... 2 Warnings...
GLOOKO FOR ios MIDS USER GUIDE October 2018 IFU-0001 13 Glooko MIDS is cleared for US only Rx only TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS MOBILE INSULIN DOSING SYSTEM (MIDS)... 2 Intended Use... 2 Warnings...
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Virtual imaging for teaching cardiac embryology.
 Virtual imaging for teaching cardiac embryology. Jean-Marc Schleich, Jean-Louis Dillenseger To cite this version: Jean-Marc Schleich, Jean-Louis Dillenseger. Virtual imaging for teaching cardiac embryology..
Virtual imaging for teaching cardiac embryology. Jean-Marc Schleich, Jean-Louis Dillenseger To cite this version: Jean-Marc Schleich, Jean-Louis Dillenseger. Virtual imaging for teaching cardiac embryology..
NEXTGEN ALLERGY DEMONSTRATION
 NEXTGEN ALLERGY DEMONSTRATION This demonstration reviews entry of allergies & intolerances in NextGen. This has been prepared for EHR 5.8 & KBM 8.3. Some slides from earlier versions may be used when the
NEXTGEN ALLERGY DEMONSTRATION This demonstration reviews entry of allergies & intolerances in NextGen. This has been prepared for EHR 5.8 & KBM 8.3. Some slides from earlier versions may be used when the
Lecture 9A. Muscle structure. Outline
 Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
The following describes general use of ELIOS device
 General use of the device The following describes general use of ELIOS device 1. Introduction of graphical user interface Presence indicator of SD card Charging indicator General Informations Screen title
General use of the device The following describes general use of ELIOS device 1. Introduction of graphical user interface Presence indicator of SD card Charging indicator General Informations Screen title
Demo Mode. Once you have taken the time to navigate your RPM 2 app in "Demo mode" you should be ready to pair, connect, and try your inserts.
 Demo Mode RPM 2 is supported with a "demonstration (Demo) mode" that easily allows you to navigate the app. Demo mode is intended for navigation purposes only. Data in Demo mode are simply random data
Demo Mode RPM 2 is supported with a "demonstration (Demo) mode" that easily allows you to navigate the app. Demo mode is intended for navigation purposes only. Data in Demo mode are simply random data
Development of the Genital System
 Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
Development of the Genital System Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta The mesonephros develops primitive nephrotomes draining into a mesonephric duct nephrotome mesonephric
KneeAlign System Surgical Technique Guide
 KneeAlign System Surgical Technique Guide Table of Contents Step 1 System Assembly... 1 Step 2 System Assembly... 2 Step 3 System Assembly... 2 Step 4 System Assembly... 2 Step 5 Sensor Pairing... 2 Step
KneeAlign System Surgical Technique Guide Table of Contents Step 1 System Assembly... 1 Step 2 System Assembly... 2 Step 3 System Assembly... 2 Step 4 System Assembly... 2 Step 5 Sensor Pairing... 2 Step
Review Article The Radiological Manifestations of the Aberrant Air Surrounding the Pleura: In the Embryological View
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Pulmonary Medicine Volume 0, Article ID 900, pages doi:0.55/0/900 Review Article he Radiological Manifestations of the Aberrant Air Surrounding the Pleura: In the mbryological
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Pulmonary Medicine Volume 0, Article ID 900, pages doi:0.55/0/900 Review Article he Radiological Manifestations of the Aberrant Air Surrounding the Pleura: In the mbryological
Heart 3: Organogenesis, CHD, prenatal circulation
 Heart 3: Organogenesis, CHD, prenatal circulation Heart development Development of vasculature Pathogenesis of CHD Prenatal circulation and its remodeling after birth David Sedmera Charles University First
Heart 3: Organogenesis, CHD, prenatal circulation Heart development Development of vasculature Pathogenesis of CHD Prenatal circulation and its remodeling after birth David Sedmera Charles University First
Contents. Quick Start Guide
 Quick Start Guide Tip Scan Button Handpiece Docking Station Contents Installation Guide:... 1 Attaching, Detaching & Rotating the Tip:... 2 Patient Environment:... 2 Tip Cleaning & Sterilization:... 3
Quick Start Guide Tip Scan Button Handpiece Docking Station Contents Installation Guide:... 1 Attaching, Detaching & Rotating the Tip:... 2 Patient Environment:... 2 Tip Cleaning & Sterilization:... 3
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE. Thomas Marino, Ph.D.
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
Circulatory System. The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Reproduction. Asexual vs Sexual
 Reproduction Asexual vs Sexual Why is Reproduction Important? The means by which an organism produces offspring Biologically and evolutionarily speaking, reproduction is what has made the continuation
Reproduction Asexual vs Sexual Why is Reproduction Important? The means by which an organism produces offspring Biologically and evolutionarily speaking, reproduction is what has made the continuation
Actiwatch. Clinician Guide
 Actiwatch Clinician Guide 2013 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. and its affiliates. All rights reserved. Overview of Actiwatch The Actiwatch is designed for documenting physical movements associated
Actiwatch Clinician Guide 2013 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. and its affiliates. All rights reserved. Overview of Actiwatch The Actiwatch is designed for documenting physical movements associated
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
The Effects of Hand Strength on Pointing Performance
 Chapter 1 The Effects of Hand Strength on Pointing Performance P. Biswas and P. Robinson 1.1 Introduction Pointing tasks form a significant part of human-computer interaction in graphical user interfaces.
Chapter 1 The Effects of Hand Strength on Pointing Performance P. Biswas and P. Robinson 1.1 Introduction Pointing tasks form a significant part of human-computer interaction in graphical user interfaces.
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut
 Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
Mitosis & Meiosis. Practice Questions. Slide 1 / 68. Slide 2 / 68. Slide 3 / Identify two differences between meiosis and mitosis.
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 68 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 68 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Mitosis & Meiosis. Practice Questions. Slide 1 / 68. Slide 2 / 68. Slide 3 / 68. Slide 4 / 68. Slide 6 / 68. Slide 5 / 68
 Slide 1 / 68 Slide 2 / 68 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of
Slide 1 / 68 Slide 2 / 68 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT
 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
Part 1 Making the initial neuron connection
 To begin, follow your teacher's directions to open the Virtual Neurons software. On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In
To begin, follow your teacher's directions to open the Virtual Neurons software. On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In
Pharyngeal apparatus. - At the third week, it is a 3 layered structure: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. This is called trilaminar disc
 Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
MemRx Orthodontic Appliances
 MemRx Orthodontic Appliances Uses and Instructions The MemRx Fundamentals As the need for faster, more efficient treatment of non-compliant patients increases, orthodontic!technology and materials has
MemRx Orthodontic Appliances Uses and Instructions The MemRx Fundamentals As the need for faster, more efficient treatment of non-compliant patients increases, orthodontic!technology and materials has
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
The Foregut. At first the esophagus is short. but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly
 GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
GI embryology 2 The Foregut At first the esophagus is short but with descent of the heart and lungs it lengthens rapidly The muscular coat, which is formed by surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, is striated
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
SIM 16/17 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system
 SIM 16/17 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British
SIM 16/17 T1.2 Limitations of the human perceptual system Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Acknowledgements: Most of this course is based on the excellent course offered by Prof. Kellogg Booth at the British
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) Lecture-2
 Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) Lecture-2 Functions Transport hemoglobin, which in turn carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. RBCs contain a large quantity of carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme that
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes) Lecture-2 Functions Transport hemoglobin, which in turn carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. RBCs contain a large quantity of carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme that
Heart to Heart! Advance
 Heart to Heart! Lesson Concept Link The structure of the heart enables it to oxygenate and pump blood throughout the body. In the previous lesson, students investigated the structure and function of the
Heart to Heart! Lesson Concept Link The structure of the heart enables it to oxygenate and pump blood throughout the body. In the previous lesson, students investigated the structure and function of the
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
How to use mycontrol App 2.0. Rebecca Herbig, AuD
 Rebecca Herbig, AuD Introduction The mycontrol TM App provides the wearer with a convenient way to control their Bluetooth hearing aids as well as to monitor their hearing performance closely. It is compatible
Rebecca Herbig, AuD Introduction The mycontrol TM App provides the wearer with a convenient way to control their Bluetooth hearing aids as well as to monitor their hearing performance closely. It is compatible
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs. Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #19 Animals II Nematoda, Arthropoda, Echinodermata and Chordata
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #19 Animals II Nematoda, Arthropoda, Echinodermata and Chordata BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #19 Animals II Nematoda, Arthropoda, Echinodermata and Chordata BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer
Ergonomic Equipment Guide
 Ergonomic Equipment Guide Enhancing Wellness Through a Safer, More Efficient Workstation Version 2.3 (12/4/2014) A free resource provided by The Office Spot, who is solely responsible for its content.
Ergonomic Equipment Guide Enhancing Wellness Through a Safer, More Efficient Workstation Version 2.3 (12/4/2014) A free resource provided by The Office Spot, who is solely responsible for its content.
Case Report Embryologic Association of Tornwaldt s Cyst with Cerebral Artery Abnormalities and Infarction: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2012, Article ID 129503, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/129503 Case Report Embryologic Association of Tornwaldt s Cyst with Cerebral Artery Abnormalities and Infarction: A Case
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2012, Article ID 129503, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/129503 Case Report Embryologic Association of Tornwaldt s Cyst with Cerebral Artery Abnormalities and Infarction: A Case
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
