Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm)
|
|
|
- Brianne Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 10 Dr. Stuart Sumida Further Development of the Mesoderm (and Endoderm)
2 Further Development: Digestive System Foregut, Midgut, Hindgut Heart and Aortic Arches Excretory and Reproductive Systems
3 Further Development: Digestive System Foregut, Midgut, Hindgut
4
5 The brain grows at an incredible rate. It grows so fast that it makes the head bend around under the embryo's body. This completes the gut cranially (foregut) and caudally (hindgut) before the middle (midgut).
6 Do your own illustration here:
7 This creates a tri-partite division of the abdominal gut in vertebrates. The subdivision is so FUNDAMENTAL that nervous supply, arterial supply, and venous drainange all organize themselves around it(!!) Foregut Midgut Hindgut Unpaired Abdominal Artery Celiac Artery Anterior Mesenteric Artery Posterior Mesenteric Artery Unpaired Hepatic Portal Vein Splenic Vein Anterior Mesenteric Vein Posterior Mesenteric Vein Sympathetic Nerve Greater Splanchnic Nerve Lesser Splanchnic Nerve Least Splanchnic Nerve Sympathetic Ganglion Celiac Ganglion Anterior Mesenteric Ganglion Posterior Mesenteric Ganglion Parasympathetic Nerve Vagus (X) Vagus (X) Caudal Outflow
8 Early Development of the Stomach Further Development of the Foregut.
9 Continued Development of the Stomach Further Development of the Foregut.
10 Further Development of the Foregut. Rotation of the Foregut
11 Do your own illustration here:
12 Development of diverticula of the foregut
13 Pancreas Development
14 Further Development: Heart and Aortic Arches
15 In amniotes: The first blood vessels of the embryo form inside the embryonic disc even before somites appear. They form near the edge of the yolksac (the primitive condition for macrolecithal amniotes that stored yolk for food).
16 Angiogenetic cell clusters extend in an arc around the head end of the ventral opening of the yolk sac. Initially, this means that the angiogenetic cell clusters (and the blood vessel that forms from them) have the pattern of a "horseshoe" if viewed from a dorsal or ventral perspective.
17 An important point to understand is that the coelom runs up and down either side of the body. At the head end, right underneath the developing pharynx, the coelom on the left communicates with the coelom on the right. Thus, the coelom cuts across the midline here.
18 The brain grows at an incredible rate. It grows so fast that it makes the head bend around under the embryo's body. This is why the heart winds up on the VENTRAL SIDE of the body.
19 Amniote Heart Development
20
21 Aortic Arch Pattern of a Generalized Vertebrate Embryo
22 Draw Generalized View, Ventral Aspect here:
23 Aortic Arch Pattern of a Lungfish
24 Draw Lungfish, Ventral Aspect here:
25 Aortic Arch Pattern of an Amphibian (Lateral Aspect) (in this case a salamander)
26 Aortic Arch Pattern of an Amphibian (Ventral Aspect)
27 Draw Amphibian, Ventral Aspect here:
28 Aortic Arch Pattern of a Reptile (Lateral Aspect)
29 Aortic Arch Pattern of Two Reptiles (Ventral Aspect)
30 Draw Reptile, Ventral Aspect here:
31 Aortic Arch Pattern of a Bird (Lateral Aspect)
32 Draw Bird, Ventral Aspect here:
33 Aortic Arch Pattern of a Mammal (Lateral Aspect)
34 Aortic Arch Pattern of a Mammal (Ventral Aspect)
35 Draw Mammal, Ventral Aspect here:
36
37
38 Aortic Arch Pattern of a Human (Ventral Aspect)
39 Aortic Arch Summary: Arch I: Mostly disappears ( a small part becomes a bit of the maxillary artery).
40 Aortic Arch Summary: Arch II: DISAPPEARS
41 Aortic Arch Summary: Arch III: CAROTID ARCH becomes part of carotid arteries.
42 Aortic Arch Summary: Arch IV: AORTIC ARCH -- Right side disappears. Left side becomes ARCH OF AORTA.
43 Aortic Arch Summary: Arch v: DISAPPEARS
44 Aortic Arch Summary: Arch VI: PULMONARY ARCH Becomes pulmonary artery to lungs.
45 Great Veins of the Thorax 1. Venous blood dumps in the right atrium of the heart. (a) Blood from the cranial region enters via superior vena cava (b) Body blood enters via inferior vena cava 2. Inferior vena cava - passes through the diaphragm after receiving blood from the abdominal gut. 3. Superior vena cave & its 3 tributaries: (a) Azygous vein (b) Right brachiocephalic vein (c) Left brachiocephalic vein
46 Superior Vena Cava Azygous Vein Hemiazygous Vein
47
48 Further Development: Excretory and Reproductive Systems
49
50
51
52
53 Developing
54 Do your own illustration here:
55
56 Development of urogenital organs/relationship TO ADULT MORPHOLOGY MARS Former kidney duct become ductus deferns, epididymous, retains connection to bladder VENUS New tubes fuse at midline to become uterine tubes, uterus, superior 2/3 vagina X X X X X X X X
57 ERECTILE TISSUE IN THE MALE Males have three columns of erectile tissue. Right and left bulbs fuse in the midline to form the CORPORA SPONGIOSUM surrounds the urethra. Urethra emerges out of tip of enlarged genital tubercle the GLANS OF THE PENIS. At its tip is the bulbous dilation that is the GLANS OF THE PENIS. Right and left crura remain independent and form the paired CORPORA CAVERNOSA. Right and left sides are bound to one another by TUNICA ALBUGINEA.
58
59
60 ERECTILE TISSUE IN THE FEMALE Erectile tissue is present, but bulbs do not fuse in midline and do not enlarge as much. They form separate masses of erectile tissue on either side of the vginal opening - the BULBS OF THE VESTIBULE, which become the LABIA MINORA (singular, MINORUM) As a result, the female urethra cannot be enclosed in the midline (as in the corpora spongiosa of the male) The tip end if the midline columns is the CLITORIS. Similarly sensitive to glans of male.
61 Clitoris Labia majorum Labia minorum
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida. Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Embryology of the Heart
 *Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
*Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم
 MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Organizational Overview of Thorax, Abdomen, Pelvis. Introduction to Blood
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 2; Wednesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Organizational Overview of Thorax, Abdomen, Pelvis Introduction to Blood Organizational Overview of Thorax,
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 2; Wednesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Organizational Overview of Thorax, Abdomen, Pelvis Introduction to Blood Organizational Overview of Thorax,
The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
EMBRYOLOGY NOTES. I. Summary of First Three Weeks a. Definitions b. Germ layers. Central Nervous System. III. Gastrointestinal System
 EMBRYOLOGY NOTES I. Summary of First Three Weeks a. Definitions b. Germ layers II. Central Nervous System III. Gastrointestinal System IV. Urogenital System and Homologues V. Cardiovascular System and
EMBRYOLOGY NOTES I. Summary of First Three Weeks a. Definitions b. Germ layers II. Central Nervous System III. Gastrointestinal System IV. Urogenital System and Homologues V. Cardiovascular System and
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the
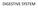 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
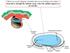 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut
 Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE
 TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels on the basis of their structure and function.
 Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Arteries. Lecture #2
 Arteries Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs and tissues
Arteries Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs and tissues
Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal. Yes, with uterine artery (collateral circulation between abdominal +pelvic source)
 Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
Blood supply to internal female genitalia: uterine Internal iliac Sup. large branch: uterus, inf. Small branch: cervix+ sup. Vagina Yes, cranially with ovarian, caudally with vaginal Medially in base of
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE
 SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
2/2/2011. Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Contents. Pig Dissection. Contents. External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index
 Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Laboratory Exercise 4 Laboratory Examination of the Pig Embryo
 S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Laboratory Exercise 4 Laboratory Examination of the Pig Embryo Introduction With the use of serial cross-sections of chicken embryos, you recently completed
S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Laboratory Exercise 4 Laboratory Examination of the Pig Embryo Introduction With the use of serial cross-sections of chicken embryos, you recently completed
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Organogenesis Part 2. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm
 Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Pelvis MCQs. Block 1. B. Reproductive organs. C. The liver. D. Urinary bladder. 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: E.
 Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
Sheet. April/14 th /2013. Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Muna Abu Hijleh. 1 P a g e
 Sheet Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Muna Abu Hijleh 1 P a g e 29 April/14 th /2013 Superior & Posterior Mediastinum ***Superior mediastinum * is bounded from: -Anterior by manubrium sterni -posterior
Sheet Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Muna Abu Hijleh 1 P a g e 29 April/14 th /2013 Superior & Posterior Mediastinum ***Superior mediastinum * is bounded from: -Anterior by manubrium sterni -posterior
Spleen. Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum. Vessel walls. Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels. Artery elastic tissue
 Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Development of the urogenital system
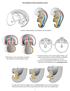 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the Heart
 Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Stimulatory
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries
 Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Development of the heart
 Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Development of the Urinary System
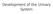 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Pharyngeal apparatus. - At the third week, it is a 3 layered structure: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. This is called trilaminar disc
 Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Embryology of the Gut and Mesenteries, slide 7 This is very similar to a cross-section we looked at when were talking about formation of the diaphragm
 Embryology of the Gut and Mesenteries, slide 2 This is a median sagittal section of a four week embryo, most of you can probably draw it in your sleep. I made a few modifications from some of the earlier
Embryology of the Gut and Mesenteries, slide 2 This is a median sagittal section of a four week embryo, most of you can probably draw it in your sleep. I made a few modifications from some of the earlier
The Female and Male External Genitalia. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
The Female and Male External Genitalia Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Anatomy of the female external genitalia This consists of : The vulva which is made up of: o The clitoris o Vestibular apparatus
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2
 Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2 Last time we talked about embryology of the GIT. We said that the development of the stomach is accompanied with the development of the duodenum and the pancreas. Also we talked
Embryology - GIT - Lecture 2 Last time we talked about embryology of the GIT. We said that the development of the stomach is accompanied with the development of the duodenum and the pancreas. Also we talked
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall
 Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Perineum. done by : zaid al-ghnaneem
 Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ANATOMY. Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks)
 ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
Laboratory Exercise 3 Laboratory Examination of the Chicken Embryo Part II
 Biology 340, Comparative Embryology, Laboratory Exercise 3 Page 16 S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Laboratory Exercise 3 Laboratory Examination of the Chicken Embryo Part II Introduction
Biology 340, Comparative Embryology, Laboratory Exercise 3 Page 16 S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Laboratory Exercise 3 Laboratory Examination of the Chicken Embryo Part II Introduction
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Omran Saeed. Mohammad Al-muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Urinary system development. Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development
 Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
FORMS OF EMBRYONIC PRIMORDIA
 FORMS OF EMBRYONIC PRIMORDIA BY PROF. ANTHONY OBIOMA NWAOPARA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ONDO CITY, ONDO STATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES To recognise the different forms of embryonic primordia. To recognise
FORMS OF EMBRYONIC PRIMORDIA BY PROF. ANTHONY OBIOMA NWAOPARA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ONDO CITY, ONDO STATE LEARNING OBJECTIVES To recognise the different forms of embryonic primordia. To recognise
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
Comparative Anatomy Urogenital System. Note Set 11 Chapter 15
 Comparative Anatomy Urogenital System Note Set 11 Chapter 15 Urogenital System Ducts of excretory and reproductive systems are intimately associated Figure 14.1: Embryonic and evolutionary development
Comparative Anatomy Urogenital System Note Set 11 Chapter 15 Urogenital System Ducts of excretory and reproductive systems are intimately associated Figure 14.1: Embryonic and evolutionary development
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. X Biology II
 Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum. Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes
 Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Superior and Posterior Mediastinum Assoc. Prof. Jenny Hayes WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for the purposes of research or study.
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
