Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors. Implications for adrenal diseases. Gary D.
|
|
|
- Magdalen Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors Implications for adrenal diseases Gary D. Hammer Condensation of the Ventral Intermediate Mesoderm Forms the Urogenital Ridge Mesonephros (embryonic kidney) Coelomic epithelium Adrenogonadal primordium Coelomic Epithelium Species: Mouse Day Gestation: Approx. Human Age: 5-6 weeks View: Transverse Cut 1
2 SF-1 Expression Specifically Marks Developing Steroidogenic Tissues Mesonephros (embryonic kidney) Adrenogonadal primordium Nathan Bingham and Keith Parker Shared SF-1 lineage of adrenal & gonads 2
3 Adrenocortical development Lineage relationship and signaling between 3 structures fetal zone mesenchymal capsule definitive zone definitive zone Adrenocortical development 3
4 Adrenocortical development Defining a fetal zone specific enhancer of SF-1: FAdE Zubair et al. MCB 26: (2006) 4
5 Fetal zone cells give rise to definitive zone cells Zubair et al. MCB 28: (2008) Restricted window in which the FAdE active fetal zone cells can develop into adult adrenal cortex. 5
6 SF-1 expression (FAdE) is shut off and a putative DAdE is activated in fetal zone cells that then become definitive zone cells Does an SF-1 negative state serve as an intermediate during the FadE to DadE switch 6
7 Cells of the SF-1 negative capsule are also derived from the fetal zone cells Mohammed Zubair Do fetal zone cells give rise to 2 independent cell populations? (SF-1 negative capsule and SF-1 positive definitive zone cells)? OR 7
8 Does an SF-1 negative state serve as an intermediate during the FadE to DadE switch? (SF-1 negative capsule give rise to the definitive zone cells)? Emergence of SF-1 positive cells within clusters of SF-1 negative capsular/subcapsular spindle cells SF-1 1 negative capsular/subcapsular subcapsular spindle cells Capsular cells are SF-1 1 negative Cortical cells are defined by SF-1 SF-1 1 positive cortical cells Bielinska et al Endocrinology 144( 9): ,
9 Upstream stimulatory factors (USF1/2) regulates basal SF-1 expression (+1) -123 E box CAAT box GA rich element bhlh -123 E box (+1) USF -123 E box (+1) Harris and Mellon (1998) Mol. Endocrinology 12: POD1: Inhibitor of SF-1 mediated differentiation POD1 -HLH transcription factor -inhibits differentiation -inhibits SF-1 in adrenal cells -localizes to adrenal capsule POD1 USF1 Ebox SF-1 promoter Lu et al, Mech of Devel 73: 23-32,
10 Pod-1(Capsulin, TCF21) is restricted to SF-1 negative capsular cells (Loss of Pod-1 induces SF-1 expression in capsule) 2.0 SF-1 expression Pod1 -/- Pod1 +/- Claudimara Lofti in collaboration with Sue Quaggin Adrenocortical homeostasis - Capsular niche Sf1 positive fetal zone cells (precursor cells) give rise to Sf1 negative capsular stem cells that serve to replenish definitive zone subcapsular progenitor cells 10
11 Adrenocortical homeostasis - Capsular niche Sf1 positive fetal zone cells (precursor cells) give rise to Sf1 negative capsular stem cells that serve to replenish definitive zone subcapsular progenitor cells Adrenocortical homeostasis - Capsular niche Sf1 positive fetal zone cells (precursor cells) give rise to Sf1 negative capsular stem cells that serve to replenish definitive zone subcapsular progenitor cells 11
12 Adrenocortical homeostasis - differentiation of definitive cortex Sf1 positive differentiated definitive cells Adrenocortical homeostasis Capsular niche: stem cells gives rise to subcapsular progenitor cells of definitive cortex Subcapsular progenitors: undifferentiated cells give rise to differentiated cortical cells Understanding how signaling pathways control stem/progenitor cells is critical to our quest to understand and treat adrenal diseases 12
13 subcapsular progenitor cells: transiently amplifying cells Capsule Proliferating cells zg Cortex zf Medulla PCNA zr Brendan Looyenga subcapsular progenitor cells: zona Undifferentiated/Intermedia of rat Mitani et al, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (3): , 324,
14 Capsular/subcapsular implants proliferate and differentiate into functional adrenal tissue H&E SF-1 IHC Felix Beuschlein Adrenal hypoplasia and cancer syndromes: Stem cell diseases? stem cell signaling defects associated with adrenal disease stem cell self renewal Wnt signaling/dax1 (adenomatous polyposis coli syndrome/cahypoplasia) stem cell fate TGF signaling (pediatric low grade ACC fetal blastoma) stem cell niche/fate IGF signaling (Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome ) stem cell apoptosis p53 (Li-Fraumeni syndrome) Understanding how these and other signaling pathways control tissue stem cells is critical to our quest to understand and treat adrenal growth disorders Goal: Identify new genes that can be TARGETS for new therapies Wnt antagonists IGF antagonists 14
15 Binary model of PARACRINE factor regulation of adrenal capsule/subcapsule fate Alex Kim and Isabella Finco PARACRINE factor regulation of transcriptional cascades determine self-renewal (proliferation) and cell fate (differentiation) self renewal paracrine activation IGF Wnt transcription activation Dax-1 Sf-1 SHH fate 15
16 Wnt signaling Capsule as niche Wnt signaling gatekeeper of the non-committed fate of subcapsular progenitor cells progenitor cell proliferative non-steroidogenic Wnt responsive progenitor differentiated cortical cells non-proliferative steroidogenic Wnt non-responsive differentiated cell Keith Parker 16
17 Canonical Wnt signaling emerges under capsule in definitive cortex becoming restricted to subcapsular cells Wnt 2b Wnt 4 adr Dev. Dyn. 222: 26 Endo 143: 4358 Alex Kim Adrenal-restricted ablation of Wnt Signaling X SF-1 CRE partial (recombination in some cells) floxed βcat SF-1 CRE complete (recombination in all cells) 17
18 Newborn complete -catenin null mice exhibit absence of adrenals Complete -catenin null mice exhibit cessation of definitive cortex formation SF-1 WT β-cat SF-1 TH KO β-cat 18
19 Newborn partial -catenin null mice exhibit normal adrenals Aging partial -catenin null mice exhibits late adrenocortical cell loss 19
20 Adrenal stem/progenitor cell depletion: A common mechanism of adrenal failure? β-catenin null mouse IMAGe syndrome Tan et al., Am J Med Genet 2006 normal (mouse) acd mouse AHC, DAX1(NR0B1) mutation Lack & Kozakewich Pathology ofthe Adrenal Gland, 1990 Dax-1 as downstream mediator of Wnt signaling gatekeeper of multipotency of subcapsular progenitor cells progenitor cell proliferative non-steroidogenic Dax-1 positive progenitor differentiated cortical cells non-proliferative steroidogenic Dax-1 negative differentiated cell Larry Jameson 20
21 Dax-1 -paradox Nuclear receptor cloned as gene responsible for X-linked Congenital Adrenal Hypoplasia Dax-1 in vivo Human Loss of Function: Adrenal HYPO function Mouse Loss of Function: Adrenal HYPERfunction Dax-1 in vitro SF-1 CCAAGGTCA Dax-1 SF-1 Dax-1 CCAAGGTCA ta rg e t gene or Young Dax-1 null mice exhibit enhanced ACTH responsiveness 600 Corticosterone (ng/ml) Dax-1 null Wild type minutes Joshua Scheys 21
22 Young Dax-1 null mice exhibit enhanced ACTH responsiveness relative ACTH/CS ratio WT Dax1 null Age (weeks) Young Dax-1 null mice exhibit enhanced ACTH responsiveness BUT Old Dax-1 mice exhibit loss of ACTH responsiveness relative ACTH/CS ratio WT Dax1 null Age (weeks) 22
23 Aging Dax-1 null mice exhibit decreased StAR expression (despite early enhanced steroidogenesis) Relative StAR expression Wild type Dax-1 null Weeks of age Aging Dax-1 null mice exhibit decreased SF-1 expression (perhaps reflective of loss of early subcapsular proliferation) Relative SF-1 expression Wild type Dax-1 null Weeks of age 23
24 Enhanced adrenal proliferation in young Dax-1 null mice is lost over time 20 BrdU/Adrenal Dax1 KO 5 Wt Age (weeks) Aging Dax-1 null mice exhibit features of cytomegalic congenital adrenal hypoplasia (Hyperfunction + variable temporal onset of adrenal failure in pts with Dax-1 mutations) Dax-1 null Wild type stochastic depletion of progenitor cells 24
25 Dax1 expression is enriched in the subcapsular adrenal cortex LacZ Wnt-Gal β-catenin SF-1 Dax-1 β-cat SF-1 Dax-1 Physiologic regulation of Dax-1 Wnt (paracrine - capsule) β-cat SF-1 GR Dax-1 glucocorticoid (endocrine adrenal) Brian Gummow 25
26 Physiologic regulation of Dax-1 Wnt (paracrine - capsule) β-cat SF-1 GR Dax-1 ACTH (endocrine - pituitary) glucocorticoid (endocrine adrenal) Brian Gummow Adrenal-restricted constitutive activation of Wnt Signaling X floxed APC SF-1 CRE 26
27 Young APC null mice exhibit accumulation of β-catenin/dax-1 positive cells at medullary boundary (expansion of undifferentiated progenitors?) WT Apc low KO 9 Weeks 15 Weeks 30 Weeks ABC WT PCNA KO β-actin Young APC null mice exhibit activation of β-catenin target genes commensurate with down-regulation of differentiation genes (expansion of undifferentiated progenitors?)
28 Adrenal-specific KO of APC exhibits increase in adrenal size over time Adrenal weight (mg) KO WT Age (Weeks) Aging APC null mice develop adrenocortical adenomas (dysplasia - adenoma progression?) WT 15 Weeks 30 Weeks 45 Weeks H&E (4x) H&E (10x) Sf1 β-catenin 28
29 Aging APC mice develop adrenocortical carcinoma (adenoma carcinoma progression?) adrenal tumor APC KO adrenal wild type kidney size (mm) Wnt/β-catenin status marks variation in gene expression in human ACC Familial ACC APC Sporadic ACC - β-catenin Tom Giordano 29
30 Wnt/β-catenin activation in ACC predicts worse survival Survival Probability Membranous Nuclear β-catenin membranous β-catenin nuclear years Goal: Utilize upcoming Wnt/β-catenin inhibitors in ACC Wnt/β-catenin status marks variation in gene expression in ACC BUT NOT adrenal adenomas (ACA) -Wnt -Wnt +Wnt -Wnt +Wnt normal ACA ACC 30
31 IGF signaling as candidate that synergizes with Wnt/ -catenin in ACC Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome: Overgrowth syndrome with elevated risk of embryonic tumors (Wilms Tumor, ACC and others) 80% of cases associated with chromosome 11 defect Loss Of Imprinting or (LOI) Loss Of Heterozygosity (LOH) of 11p15.5 = HIGH IGF2 LOI of IGFII locus in stem cells as initiation event in cancer IGF2 is the most up-regulated gene in adrenal cancer (and p57 and H19 are coordinately down-regulated) normal ACA ACC H19 IGF2 p57 31
32 ZAC1 is expressed in stem cells and controls imprinting of IGFII locus Jelininc, P. and Shaw, P. J Pathol 2007; 211: ZAC1 is downregulated in pediatric ACC West, A. N. et al. Cancer Res 2007;67: ZAC1 is expressed in capsular/subcapsular cells IGF2 p57 ZAC1 mouse e14.5 Jelininc, P. and Shaw, P. J Pathol 2007; 211:
33 Cross talk between Wnt and IGF signaling in adrenal stem cell niche IGF Wnt Adrenal IGF2 LOI (constitutive IGF2) Adrenal APC null (constitutive Wnt) Ferdous Barlaskar Aging APC null mice exhibit increased adrenal IGF2 and decreased p57kip2 (only in ACC of aging APC null mice) (not in ACA of young APC null mice) 2 Fold Expression Igf2 p57kip2 0 33
34 IGF2 LOI mice exhibit commensurate increase in IGF2 Relative IGF2 expression 2 1 wt IGF2 LOI Cre- Cre low IGF2 LOI mice exhibit increased β-catenin staining in subcapsular area Cre high β-catenin expression Total Akt p-akt Ser473 wt Total β-catenin Active β-catenin H19 β-actin 34
35 Cross talk between Wnt and IGF signaling Jin, T. et al Cellular Signalling 20(10): PARACRINE factor regulation of transcriptional cascades determine self-renewal (proliferation) and cell fate (differentiation) self renewal paracrine activation IGF Wnt transcription activation Dax-1 Sf-1 SHH fate 35
36 Understanding how signaling pathways control stem/progenitor cells is critical to our quest to understand and treat adrenal diseases 36
What s New in Adrenal Gland Pathology. Marina Scarpelli
 What s New in Adrenal Gland Pathology Marina Scarpelli Background Histological criteria for adrenocortical proliferative lesions Immunohistochemical markers Molecular markers Histological Criteria for
What s New in Adrenal Gland Pathology Marina Scarpelli Background Histological criteria for adrenocortical proliferative lesions Immunohistochemical markers Molecular markers Histological Criteria for
From crypt stem cell to colorectal cancer
 19 3 2007 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 19, No. 3 Jun., 2007 1004-0374(2007)03-0321-05 ( 510405) Wnt Notch BMP R735.35; R730.21 A From crypt stem cell to colorectal cancer WEN Bin*, CHEN Weiwen
19 3 2007 6 Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 19, No. 3 Jun., 2007 1004-0374(2007)03-0321-05 ( 510405) Wnt Notch BMP R735.35; R730.21 A From crypt stem cell to colorectal cancer WEN Bin*, CHEN Weiwen
Effects of Dicer Inactivation in the Developing Mouse Adrenal Cortex and Micro-RNAs in Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Kenneth Thomas Krill
 Effects of Dicer Inactivation in the Developing Mouse Adrenal Cortex and Micro-RNAs in Adrenocortical Carcinoma by Kenneth Thomas Krill A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Effects of Dicer Inactivation in the Developing Mouse Adrenal Cortex and Micro-RNAs in Adrenocortical Carcinoma by Kenneth Thomas Krill A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
The Beauty of the Skin
 The Beauty of the Skin Rose-Anne Romano, Ph.D Assistant Professor Department of Oral Biology School of Dental Medicine State University of New York at Buffalo The Big Question How do approximately 50 trillion
The Beauty of the Skin Rose-Anne Romano, Ph.D Assistant Professor Department of Oral Biology School of Dental Medicine State University of New York at Buffalo The Big Question How do approximately 50 trillion
Adrenocortical zonation, renewal, and remodeling
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Adrenocortical zonation, renewal, and remodeling Marjut Pihlajoki University of Helsinki Julia Dorner Washington
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Adrenocortical zonation, renewal, and remodeling Marjut Pihlajoki University of Helsinki Julia Dorner Washington
Meeting Report. From December 8 to 11, 2012 at Atlanta, GA, U.S.A
 Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
PKA signaling drives reticularis differentiation and sexually dimorphic adrenal cortex renewal
 PKA signaling drives reticularis differentiation and sexually dimorphic adrenal cortex renewal Typhanie Dumontet,, Pierre Val, Antoine Martinez JCI Insight. 2018;3(2):e98394.. Research Article Development
PKA signaling drives reticularis differentiation and sexually dimorphic adrenal cortex renewal Typhanie Dumontet,, Pierre Val, Antoine Martinez JCI Insight. 2018;3(2):e98394.. Research Article Development
CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION
 CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION More than 20 years ago the founding member of the Wnt gene family, Wnt-1/Int1, was discovered as a proto-oncogene activated in mammary gland tumors by the mouse mammary
CHAPTER 6 SUMMARIZING DISCUSSION More than 20 years ago the founding member of the Wnt gene family, Wnt-1/Int1, was discovered as a proto-oncogene activated in mammary gland tumors by the mouse mammary
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
SF-1, DAX-1 AND ACD: MOLECULAR DETERMINANTS OF ADRENOCORTICAL GROWTH AND STEROIDOGENESIS
 ENDOCRINE RESEARCH Vol. 28, No. 4, pp. 601 611, 2002 1 2 3 SF-1, DAX-1 AND ACD: MOLECULAR DETERMINANTS OF ADRENOCORTICAL GROWTH AND STEROIDOGENESIS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 F. Beuschlein, 1, * C. E. Keegan,
ENDOCRINE RESEARCH Vol. 28, No. 4, pp. 601 611, 2002 1 2 3 SF-1, DAX-1 AND ACD: MOLECULAR DETERMINANTS OF ADRENOCORTICAL GROWTH AND STEROIDOGENESIS 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 F. Beuschlein, 1, * C. E. Keegan,
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
Urogenital Development
 2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Summary and Concluding Remarks
 Summary and Concluding Remarks Chapter 6 The intestinal epithelium provides an excellent model system for investigating molecular mechanisms regulating cell lineage establishment, stem cell proliferation,
Summary and Concluding Remarks Chapter 6 The intestinal epithelium provides an excellent model system for investigating molecular mechanisms regulating cell lineage establishment, stem cell proliferation,
IDENTIFYING, MODELING AND TARGETING IGF-II OVEREXPRESSION IN ADRENOCORTICAL CARCINOMA. Ferdous M. Barlaskar
 IDENTIFYING, MODELING AND TARGETING IGF-II OVEREXPRESSION IN ADRENOCORTICAL CARCINOMA by Ferdous M. Barlaskar A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
IDENTIFYING, MODELING AND TARGETING IGF-II OVEREXPRESSION IN ADRENOCORTICAL CARCINOMA by Ferdous M. Barlaskar A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a,
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Tetrapod Limb Development
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
The Wnt/βcatenin signaling pathway
 Wnt signaling is crucial for functioning of the endometrium The Role of Wnt Signaling in Uterus Development (I) and in Homeostasis (II) and Malignancy (III) of the Uterine Endometrium Leen J Blok Erasmus
Wnt signaling is crucial for functioning of the endometrium The Role of Wnt Signaling in Uterus Development (I) and in Homeostasis (II) and Malignancy (III) of the Uterine Endometrium Leen J Blok Erasmus
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Transcriptional control in the murine adrenal cortex and testis
 Transcriptional control in the murine adrenal cortex and testis Anja Schrade Children s Hospital University of Helsinki Finland Doctoral Programme in Biomedicine ACADEMIC DISSERTATION To be presented,
Transcriptional control in the murine adrenal cortex and testis Anja Schrade Children s Hospital University of Helsinki Finland Doctoral Programme in Biomedicine ACADEMIC DISSERTATION To be presented,
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
Sex Differentiation. Course Outline. Topic #! Topic lecture! Silverthorn! Membranes (pre-requisite material)!!
 Sex Differentiation The goal of these lectures is to discuss how a control system is formed. For this, we will use basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual differentiation
Sex Differentiation The goal of these lectures is to discuss how a control system is formed. For this, we will use basic physiology associated with the control of reproduction (from sexual differentiation
Fetal adrenal capsular cells serve as progenitor cells for steroidogenic and stromal adrenocortical cell lineages in M. musculus
 2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd (2013) 140, 4522-4532 doi:10.1242/dev.092775 RESEARCH ARTICLE STEM CELLS AND REGENERATION Fetal adrenal capsular cells serve as progenitor cells for steroidogenic
2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd (2013) 140, 4522-4532 doi:10.1242/dev.092775 RESEARCH ARTICLE STEM CELLS AND REGENERATION Fetal adrenal capsular cells serve as progenitor cells for steroidogenic
Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines
 Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines Dra Martha Robles Flores Department of Biochemistry Facultad de Medicina Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Tissue anatomy of the
Protein Kinase C Modulates Wnt Signaling In Colon Tumoral Cell Lines Dra Martha Robles Flores Department of Biochemistry Facultad de Medicina Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México Tissue anatomy of the
Heart Development. Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells. Robert G. Kelly
 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences Heart Development 19th June 2013 Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells Robert G. Kelly Animal models of heart development
ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences Heart Development 19th June 2013 Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells Robert G. Kelly Animal models of heart development
Haematopoietic stem cells
 Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Review Article Role of Orphan Nuclear Receptor DAX-1/NR0B1 in Development, Physiology, and Disease
 Advances in Biology, Article ID 582749, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/582749 Review Article Role of Orphan Nuclear Receptor DAX-1/NR0B1 in Development, Physiology, and Disease Enzo Lalli 1,2,3
Advances in Biology, Article ID 582749, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/582749 Review Article Role of Orphan Nuclear Receptor DAX-1/NR0B1 in Development, Physiology, and Disease Enzo Lalli 1,2,3
Development of B and T lymphocytes
 Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Development of B and T lymphocytes What will we discuss today? B-cell development T-cell development B- cell development overview Stem cell In periphery Pro-B cell Pre-B cell Immature B cell Mature B cell
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Heart Development. Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy
 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
Recommended reading: Abbas et al. 5th edition, chapters 7 and 10; Janeway and Travers, 5th edition, chapter 7.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai 10/05/05; 11 AM Shiv Pillai T Lymphocyte Development Recommended reading:
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation
 Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Stem Cells and The Endometrium. Director, Division of Reproductive Endocrinology and infertility
 Stem Cells and The Endometrium Hugh S. Taylor, M.D. Director, Division of Reproductive Endocrinology and infertility Nothing to disclose Stem Cells Cells that are capable of both self-renewal and have
Stem Cells and The Endometrium Hugh S. Taylor, M.D. Director, Division of Reproductive Endocrinology and infertility Nothing to disclose Stem Cells Cells that are capable of both self-renewal and have
11 -Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, expression, corticotroph adenomas 68 70
 Subject Index Activin activity decrease, gonadotroph 78 pituitary tumorigenesis, role 99 Adenoma, see also specific cell types angiogenesis, see Angiogenesis clonality, see Clonality, pituitary tumors
Subject Index Activin activity decrease, gonadotroph 78 pituitary tumorigenesis, role 99 Adenoma, see also specific cell types angiogenesis, see Angiogenesis clonality, see Clonality, pituitary tumors
Imprinting. Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821
 Imprinting Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the basic concepts of genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that causes
Imprinting Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the basic concepts of genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that causes
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
11. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15 % of the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is formed in the sides of the embryonic tissue, ventral to the mesonephros
Chapter 14 Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome
 Chapter 14 Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome Michael DeBaun and Jennifer Horst Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) (OMIM 130650) is a disease of prenatal overgrowth, congenital malformations, and predisposition
Chapter 14 Beckwith Wiedemann Syndrome Michael DeBaun and Jennifer Horst Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) (OMIM 130650) is a disease of prenatal overgrowth, congenital malformations, and predisposition
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Hepatogenesis I Liver development
 Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
The Pathological l Basis of Disease
 Endocrine Diseases The Pathological l Basis of Disease - Graduate Course CMM5001 Qiao Li, MD, PhD Faculty of Medicine University of Ottawa qiaoli@uottawa.ca Outline Endocrine System Adrenal Gland Anatomy
Endocrine Diseases The Pathological l Basis of Disease - Graduate Course CMM5001 Qiao Li, MD, PhD Faculty of Medicine University of Ottawa qiaoli@uottawa.ca Outline Endocrine System Adrenal Gland Anatomy
My personal experience at University of Toronto and recent updates of
 My personal experience at University of Toronto and recent updates of Endocrine Pathology Toshitetsu Hayashi M.D. Ph.D. ¹Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Takamatsu Red Cross Hospital, Japan ²Laboratory
My personal experience at University of Toronto and recent updates of Endocrine Pathology Toshitetsu Hayashi M.D. Ph.D. ¹Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Takamatsu Red Cross Hospital, Japan ²Laboratory
Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma. Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD
 Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD Disclosures Genentech, Inc Medical Director, Dermatology (employee) Stock holder Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Fundamental
Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD Disclosures Genentech, Inc Medical Director, Dermatology (employee) Stock holder Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Fundamental
Cancer Stem Cells & Glioblastoma
 Cancer Stem Cells & Glioblastoma JP Hugnot «Brain plasticity, Neural stem cells and Glial tumors» INSERM U1051-UM2 Institut des Neurosciences de Montpellier Montpellier 1-Stem cells and Brain Stem Cells
Cancer Stem Cells & Glioblastoma JP Hugnot «Brain plasticity, Neural stem cells and Glial tumors» INSERM U1051-UM2 Institut des Neurosciences de Montpellier Montpellier 1-Stem cells and Brain Stem Cells
Supplementary Figures. T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ
 Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
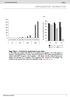 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
Development Supplementary information. Supplementary Figures * * +/+ +/- -/- +/+ +/- -/-
 Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
Regulation of Normal and Neoplastic Steroidogenic Cell Differentiation in the Adrenal Gland and Ovary
 Regulation of Normal and Neoplastic Steroidogenic Cell Differentiation in the Adrenal Gland and Ovary Marjut Pihlajoki Children s Hospital University of Helsinki Finland Pediatric Graduate School ACADEMIC
Regulation of Normal and Neoplastic Steroidogenic Cell Differentiation in the Adrenal Gland and Ovary Marjut Pihlajoki Children s Hospital University of Helsinki Finland Pediatric Graduate School ACADEMIC
THE HIGHS AND LOWS OF ADRENAL GLAND PATHOLOGY
 THE HIGHS AND LOWS OF ADRENAL GLAND PATHOLOGY Symptoms of Adrenal Gland Disorders 2 Depends on whether it is making too much or too little hormone And on what you Google! Symptoms include obesity, skin
THE HIGHS AND LOWS OF ADRENAL GLAND PATHOLOGY Symptoms of Adrenal Gland Disorders 2 Depends on whether it is making too much or too little hormone And on what you Google! Symptoms include obesity, skin
DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT. Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp
 Developmental Anatomy Steven M. Hill, Ph.D. 9/16/13 DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp. 264-273. Objectives:
Developmental Anatomy Steven M. Hill, Ph.D. 9/16/13 DEVELOPMENT OF THE ADRENAL GLAND; TESTES AND MESONEPHRIC DUCT Reading Assignment: The Developing Human, Clinically Oriented Embryology pp. 264-273. Objectives:
Contents. Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX
 Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Wilms' tumour and renal dysplasia: an hypothesis
 J Clin Pathol 1982;35:1069-1073 Wilms' tumour and renal dysplasia: an hypothesis HB MARSDEN, W LAWLER* From the Royal Manchester Children's Hospital, Manchester M27 I HA and the *Department of Pathology,
J Clin Pathol 1982;35:1069-1073 Wilms' tumour and renal dysplasia: an hypothesis HB MARSDEN, W LAWLER* From the Royal Manchester Children's Hospital, Manchester M27 I HA and the *Department of Pathology,
C. elegans Embryonic Development
 Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.
 Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Molecular Characterization of Leukemia Stem Cell Development. Scott A. Armstrong MD, Ph.D.
 Molecular Characterization of Leukemia Stem Cell Development Scott A. Armstrong MD, Ph.D. Normal and Leukemic Hierarchies NORMAL HSC (SRC) Myeloid progenitor LTC-IC CFU AML LSC (SL-IC) Leukemic LTC-IC
Molecular Characterization of Leukemia Stem Cell Development Scott A. Armstrong MD, Ph.D. Normal and Leukemic Hierarchies NORMAL HSC (SRC) Myeloid progenitor LTC-IC CFU AML LSC (SL-IC) Leukemic LTC-IC
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES. Molecular Oncology Michael Lea
 TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting
 Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting mice In Biomedical Science Techniques of transgenic and gene-targeting mice are indispensable for analyses of in vivo functions of particular genes and roles of their
Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting mice In Biomedical Science Techniques of transgenic and gene-targeting mice are indispensable for analyses of in vivo functions of particular genes and roles of their
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
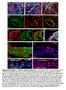 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Not all renal stem cell niches are the same: anatomy of an evolution
 eissn: 2281-0692 Journal of Pediatric and Neonatal Individualized Medicine 2016;5(2):e050225 doi: 10.7363/050225 Received: 2015 Sept 11; revised: 2015 Dec 21; accepted: 2016 Mar 01; published online: 2016
eissn: 2281-0692 Journal of Pediatric and Neonatal Individualized Medicine 2016;5(2):e050225 doi: 10.7363/050225 Received: 2015 Sept 11; revised: 2015 Dec 21; accepted: 2016 Mar 01; published online: 2016
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Urinary System. J. H. Lue. intermediate mesoderm cloaca coelomic epithelium
 Urinary System J. H. Lue Primordium: intermediate mesoderm cloaca coelomic epithelium 1 3w(18d) 3 w 4w (24d) 4w (26d) 2 Intermediate mesoderm 3 Intermediate mesoderm intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge
Urinary System J. H. Lue Primordium: intermediate mesoderm cloaca coelomic epithelium 1 3w(18d) 3 w 4w (24d) 4w (26d) 2 Intermediate mesoderm 3 Intermediate mesoderm intermediate mesoderm urogenital ridge
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is
 Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration. Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research.
 Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Gonadal Developmental Systems Biology
 Spring 2018 Systems Biology of Reproduction Discussion Outline Gonadal Developmental Systems Biology Michael K. Skinner Biol 475/575 CUE 418, 10:35-11:50 am, Tuesday & Thursday February 15, 2018 Week 6
Spring 2018 Systems Biology of Reproduction Discussion Outline Gonadal Developmental Systems Biology Michael K. Skinner Biol 475/575 CUE 418, 10:35-11:50 am, Tuesday & Thursday February 15, 2018 Week 6
Stem Cells. Induced Stem Cells
 Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production
 The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production Thymus Histology Lobulated organ with outer cortex and inner medulla C M Ordered Microenvironments Support T-cell Development CD4-CD8- precursors CD4+CD8+
The Thymus as The Primary Site of T-cell Production Thymus Histology Lobulated organ with outer cortex and inner medulla C M Ordered Microenvironments Support T-cell Development CD4-CD8- precursors CD4+CD8+
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Spermatogenesis. What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis?
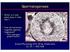 Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
Spermatogenesis What is it and what does it look like? How do hormones regulate spermatogenesis? FSH, androgens, growth factors Animal Physiology (Hill, Wise, Anderson): Ch. 15 435-438 1 Spermatogenesis:
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17)
 Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
Chapter 16: Steroid Hormones (Lecture 17) A) 21 or fewer carbon atoms B) Precursor: 27 carbon cholesterol C) major classes of steroid hormones 1) progestagens a) progesterone- prepares lining of uterus
Sex chromosomes and sex determination
 Sex chromosomes and sex determination History (1) 1940-ties Alfred Jost embryo-surgical experiments on gonads gonadal sex; male gonadal sex presence of testes; female gonadal sex lack of testes. History
Sex chromosomes and sex determination History (1) 1940-ties Alfred Jost embryo-surgical experiments on gonads gonadal sex; male gonadal sex presence of testes; female gonadal sex lack of testes. History
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Altered Mouse Adipose Tissue IGF-1 Expression Influences Glucose Control
 Altered Mouse Adipose Tissue IGF-1 Expression Influences Glucose Control Jan Trost Prof. Gudrun A. Brockmann Humboldt Universität zu Berlin Department of Crop and Animal Sciences Breeding Biology and Molecular
Altered Mouse Adipose Tissue IGF-1 Expression Influences Glucose Control Jan Trost Prof. Gudrun A. Brockmann Humboldt Universität zu Berlin Department of Crop and Animal Sciences Breeding Biology and Molecular
Adrenal Organogenesis and Steroidogenesis
 2 Adrenal Organogenesis and Steroidogenesis Role of Nuclear Receptors Steroidogenic Factor-1, DAX-1, and Estrogen Receptor Meera S. Ramayya Contents Introduction Fetal Adrenal Organogenesis and Steroidogenesis
2 Adrenal Organogenesis and Steroidogenesis Role of Nuclear Receptors Steroidogenic Factor-1, DAX-1, and Estrogen Receptor Meera S. Ramayya Contents Introduction Fetal Adrenal Organogenesis and Steroidogenesis
Urinary system development. Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development
 Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
Urinary system development Male ( ) and Female ( ) Reproductive Systems Development Urogenital system develops from mesodermal uro-genital ridge (intermediate mesoderm) development of male and female genital
CANCER. Inherited Cancer Syndromes. Affects 25% of US population. Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease)
 CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Case Report Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita Presenting as Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
 Case Reports in Endocrinology Volume 2013, Article ID 393584, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/393584 Case Report Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita Presenting as Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Jennifer
Case Reports in Endocrinology Volume 2013, Article ID 393584, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/393584 Case Report Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita Presenting as Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Jennifer
Long-lived keratin 15 + esophageal progenitor cells contribute to homeostasis and regeneration
 Long-lived keratin 15 + esophageal progenitor cells contribute to homeostasis and regeneration Véronique Giroux,, Timothy C. Wang, Anil K. Rustgi J Clin Invest. 2017;127(6):2378-2391. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci88941.
Long-lived keratin 15 + esophageal progenitor cells contribute to homeostasis and regeneration Véronique Giroux,, Timothy C. Wang, Anil K. Rustgi J Clin Invest. 2017;127(6):2378-2391. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci88941.
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics. DNA methylation in prostate cancer
 Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Glioblastoma Multiforme Highly malignant, invasive, difficult-to-treat primary brain tumor" " Frequency: 9,000 cases/year (peak age, 55 65 years)" " Recurrence: rapid growth; size may double every 10 days"
Glioblastoma Multiforme Highly malignant, invasive, difficult-to-treat primary brain tumor" " Frequency: 9,000 cases/year (peak age, 55 65 years)" " Recurrence: rapid growth; size may double every 10 days"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology"
 Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
Animal Science 434 Reproductive Physiology" Embryogenesis of the Pituitary and Sexual Development: Part A Development of the Pituitary Gland" Infundibulum" Brain" Rathke s Pouch" Stomodeum" Germ Cell Migration"
GENERAL SUMMARY Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro
 Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro-gestational hormone, essential for establishment and maintenance of
Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro-gestational hormone, essential for establishment and maintenance of
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
