Structure and f unction of the seminal vesicle in male Bostrichthys sinensis 3
|
|
|
- Jane Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 50 (2) : , 04 A cta Zoologica S inica , , ,,,,,,,, Leydig,,,, PAS,, 17 PGE 2 PGF 2,, [ 50 (2) : , 04 ] Structure and f unction of the seminal vesicle in male Bostrichthys sinensis 3 ZHAN G Qi2Yong 133, HON G Wan2Shu 1, CHEN Shi2Xi 1, MA Xi2Lan 1, N I Zi2Mian 2 1. Department of Oceanography, Xiamen University, Xiamen , Fujian, China 2. Electron Microscope Laboratory, Xiamen University, Xiamen , Fujian, China Abstract The morphological structure and function of the seminal vesicles in male Bost richthys sinensis were studied by means of histology, transmission electron microscope and Enzyme2linked Immunosorbent assay. The results showed that the seminal vesicles, enclosed by capsula, were a pair of accessory glands to the testes. The seminal vesicle was divided in2 to many locule lumina by the connective tissue partition. Both capsula and partition consisted of smooth muscle fibers, blood capillaries, fibroblasts, fibrocytes and interstitial cells. Single epithelial cells, which were columnar, cuboidal or squamous in shape, were arranged along the partition. During the spawning season, rough endoplasmic reticulum, tubular cristae mitochondria and Golgi complex were well developed ; many secretory granules without membranes accumulated to the apical portion of the epithelial cell. The cell organelles degenerated and large vacuoles appeared after the secretory granules were released. The sphincter muscles were not found from the outlet of the seminal vesicles to the sperm ducts. Fibroblasts were characterized by synthesizing and secreting collagen. The morphology of interstitial cells in the seminal vesicle was similar to that of Leydig cells in the testes. At the peak period of spawning, a large number of spermatozoa, which were mixed with the secretion, appeared in proximal, middle and distal parts of the seminal vesicles. The epithelial cells inside the different locules of the seminal vesicle developed asynchronously. The results showed that sperm added to the seminal vesicle fluid could increase sperm motility, prolong sperm longevity, and improve the fertilization rates of sper2 matozoa. Fiber2like secretion of the seminal vesicles showed PAS positive reaction in dark purple2red colour, suggesting that the secretion should be mucopolysaccharide2mucin. The seminal vesicle fluid contained 17 OH2P, PGE 2 and PGF 2 which could induce female broodfish to spawn, indicating this fluid functions as a sex pheromone [ Acta Zoologica Sinica 50 (2) : , 04 ]. Key words Chinese black sleeper, Bost richthys sinensis, Seminal vesicle, Morphological structure, Ultrastructure, Function , (No No ) of China (No and No ) ] 33 (Corresponding author). ν 04 Acta Zoologica Sinica [ This research was funded by grants from National Natural Science Foundation
2 ( Claridae) ( Gobiidae) (Blennidae) (Bagri2 2 dae) ( Tripterygiidae) (Ba2 trachoididae) 211, ( Seminal vesicle) ( Sun2, dararaj, 1958 ; Rastogi, 1969 ; Fishelson, 1991 ; Fishelson et al., 1994 ; Lahnsteiner et al., 1992 ; Scaggiante et al., 1999),,,, ( Bost richthys 5-12 mm, 4-7 mm, sinensis) 4-13 mm, mm ( 1 ; : 1),,, cm, g,,, 43 Bouin,, 6 m, HE PAS Olympus DX % 1,,, J EM2100CX Cayman,, 1 A. B. P : D : SD : BC : Fig11 The seminal veicles of the male Bostrichthys sinen2 sis A. Right lobe. B. Left lobe. P : Proximal part. D : Distal part. SD : Sperm duct. BC : Blood capillary. PGE 2, PGF 2 -, ( 17 2, Diag2 : 2) nostic Systems Laboratories B IO2RAD550 ( n, (: = 6 ), 3) 14-29, 17 OH2P PGE 2 PGF 2, m, m t, P < 0105,, P < 10-17, m, m (: 12, 13), ,, Olympus 2216 m, m,,, m, m m, 95 % m,, 4, m, ( )
3 2 : 271, m, m,, m,, m (: 4, 5, 6),, (: 10), 112 m, 4-8,, (: 14, 15),,,,, (: 16) ( m),, m (: 17),,,,,, ( GSI),, ( SVSI),,,,, (, : 18),,,,,,,,,, 212, (: 5),, PAS (: 8),,,, , m, 1 (: 8),,,,, (:, 9) (: 19, ),,,,,, m,,,, (:, ),,, m, m m,,,, (, : 11),, m m, m, ,, m,,, (: 22),,
4 ,,, 2512, , (6417 %) ; : (1),, (56 %), 95 %,, 2 h 6 min ;,, 90 %, 1 h 47 min (2), 17 2 (17 OH2P), 85 %, PGE 2 PGF 2, 1 h 44 min, 17 OH2P ( ng/ ( 1), ml) ( ng/ ml ), ( P > 0105) ( 2) PGE 2 ( pg/ ml ) PGF 2 HCG L HRH2A 3 ( pg/ ml) 1 Table 1 Sperm motility and sperm longevity of Bostrichthys sinensis Habitat ( %) Sperm motility ( %) Sperm (h : min) Sperm longevity (h : min) + Sperm + seminal vesicle fluid ( %) 3 Sperm motility ( %) (h : min) 3 3 Sperm longevity (h : min) T ( ) S ( %) Wild Cultured % 3 The sperm motility means the percentage of swimming spermatozoa in total number of spermatozoa1 33 The sperm longevity means the duration from the moment of activation to the death of 95 % activated spermatozoa. 2 Table 2 Swimming speed of sperm varies in Bostrichthys sinensis + (h : min) Sperm Sperm + seminal vesicle fluid Habitat Duration after activation (h : min) ( m/ s) ( m/ s) T ( ) S ( %) Swimming speed ( m/ s) Swimming speed ( m/ s) Wild Cultured
5 2 : 273 PGE 2 ( pg/ ml ) PGF 2 ( pg/ ml) ( P < 0105), 17 OH2, Table 3 17 OH2P, PGE 2 and PGF 2 levels of seminal vesicle, testis and ovarian extract in mature Bostrichthys sinensis 17 OH2P Extract (ng/ ml) PGE 2 (pg/ ml) PGF 2 (pg/ ml) Seminal vesicle 6100 Testis Ovary ,,, P PGE 2 PGF 2, Fishelson et al. (1994) 3 ( Clarias gariepinus) 17 OH2P PGE 2 PGF 2, Leydig, Leydig, ( Clarias gariepinus) Leydig, 3 2HSD 3 2HSD (UDPGD),,,, ( Resink et al., 1987,, 1989 ; Schoonen et al., 1986, 1987, 1988 ; Hurk Sundararaj (1958) ( Het2 and Resink, 1992) eropneustes f ossilis),, 17 OH2 Nawar P PGE 2 PGF 2 Ξ, (1959) ( Clarias lazera),,,,, Rastogi (1969) PGE 2 ( M yst us tengara), Fichel2 ( References) son et al. (1994) ( Clarias gariepi2 Fishelson L, Comparative cytology and morphology of seminal nus), vesicles in male gobiid fishes. Japan. J. Ichthyol. 38 (1) : Fishelson L, Vuren J HJ V, Tyran A, Ontogenesis and ultrastruc2, ture of seminal vesicles of the catfish Clarias gariepinus. J. Mor2 phol. 219 : , Hurk RVD, Resink J W, Male reproductive system as sex pheromone producer in teleost fish. J. Exp. Zool. 261 : , ( Seminal vesicle), Lahnsteiner F, Seiwald M, Patzner RA, Ferrero EA, The semi2 nal vesicles of the male grass goby, Zosterisessor ophiocephal us ( Teleostei, Gobiidae). Zoomorphology 111 : Lahnsteiner et al. (1992) Nawar G, Observations on the seminal vesicle of the nile catfish Clarias lazera. Ann. and Mag. Nat. Hist. 11 : ( Zosterisessor ophiocephal us) Rastogi RK, Seminal vesicles and sperm duct of an Indian catfish Myst us tengara (, Ham. ), with particular reference to their season2 al cycle. Acta Anat. 72 : , Resink J W, Hurk RVD, Zoelen RFO GV, Huisman EA, The Ξ,,, 04.. ( ). Hong, WS, Zhao WH, Ma XL, 04. A preliminary study on the induction of spawning by sex pheromones in Bost richthys sinensis. Journal of Fsheries of China ( In press).
6 seminal vesicle as source of sex attracting substances in the African catfish Clarias gariepinus. Aquaculture 63 : Resink, J W, Schoonen WGEJ, Albers PCH, File DM, Notenboom CD, Hurk RVD, Oordt PGWJ, The chemical nature of sex attracting pheromones from the seminal vesicle of the African cat2 fish Clarias gariepinus. Aquaculture 83 : Scaggiante M, Mazzoldi C, Petersen CW, Rasotto MB, Sperm competition and mode of fertilization in the grass goby Zosterisessor ophiocephalus ( Teleostei, Gobiidae). J. Exp. Zool. 283 : Schoonen, WGEJ, Lambert J GD, Steroid metabolism in the seminal vesicles of the African catfish Clarias gariepi nus. (Burchell), during the spawning season, under natural conditions, and kept in ponds. Gen. Comp. Endrocrinol. 61 : Schoonen, WGEJ, Lambert J GD, Gas chromatographic mass spectrometric analysis of steroids and steroid glucuronides in the seminal vesicle fluid of the African catfish Clarias gariepi nus. Gen. Comp. Endrocrinol. 68 : Schoonen WGEJ, Lambert J GD, Oordt PGWJ V, 1988 Quantitative analysis of steroids and steroid glucuronides in the seminal vesicle fluid of feral spawning and feral and cultivated nonspawning African catfish Clarias gariepi nus. Gen. Comp. Endrocrinol. 70 : Sundararaj BI, The seminal vesicles and their seasonal changes in the Indian catfish Heteropneustes. Copeia (4) :
7 2 : (SV) ( T) (U) (UP) 2., ( ) ( ξ ) (CC) ( ) ( ), (CC) (CP) (LL) ( ξ ) ( ), ( ξ ) ( ) ( ), (LL) PAS, (LL) ( ) (S) ( ) ( ξ ) , ( ) ( ξ ) ( Ρ ) (BC) ( T) (SV) ( ) , (LL) (CC) (CP) (S) , , (RER) (M) ( G) (CM) , (LL) ( G) (SG), (CF) (LL) (S) (C) (LL) (LV), (MB) , ( ) ( ξ ) (N) (CF) ( ) , (N) BC : C : CC : CF : CM : CP : G: LL : LV : M : MB : N : RER : S : SD : G: SV : T : U : UP : Explanation of Plates Plate 1. The seminal vesicles (SV), testis ( T), urinary bladder (U) and urogenital papilla (UP) in male Bost richthys sinensis. 2. Transverse section through the seminal vesicle of male Bost richthys si nensis, showing the connective tissue capsula ( ) and partition ( ξ ) Smooth muscle fibers ( ) in the connective tissue capsula (CC) Columnar epithelial cells ( ) in the seminal vesicle, showing the connective tissue capsula (CC), the connective tissue partition (CP), locule lumi2 na (LL) and fibroblast ( ξ ) Cuboidal epithelial cells ( ) in the seminal vesicle, showing the bubble2like secretion ( ξ ) Squamous epithelial cells ( ) Necrotic cells ( ) became detached from the epithelium and accumulated in the locule lumina (LL) The secretion of seminal vesicle showed PAS positive reaction in dark purple2red colour, showing the locule lumina (LL) were filled with the sper2 matozoa ( ) and the secretion (S) The spermatozoa ( ) were enclosed by fiber2like seminal vesicle fluid ( ξ ) The sperm duct, showing epithelial cells ( ), spermatozoa ( ξ ), fibroblasts ( ), blood capillary (BC), testes ( T) and seminal vesicle (SV). Ρ The interstitial cells ( ) in the connective tissue partition of seminal vesicle
8 Plate 12. Longitudinal section through the seminal vesicle of male Bost richthys sinensis, showing the locule lumina (LL), connective tissue capsula ( CC), connective tissue partition (CP) and the secretion (S) Longitudinal section through the seminal vesicle of male Bost richthys si nensis, as showed above Epithelial cell in the seminal vesicle, showing rough endoplasmic reticulum ( RER), tubular cristae mitochondria (M), Golgi complex ( G) and cell membrane (CM) Epithelial cell in seminal vesicle, showing the locule lumina (LL) and Golgi complex ( G) Secretory granules (SG) accumulated to the apical portion of epithelial cell in the seminal vesicle, showing collagenous fiber (CF) in the locule lumi2 na (LL) The secretion (S) and cytoplasm (C) were released to the locule lumina (LL) Large vacuoles appeared in the epithelial cell of seminal vesicle, showing myelin body (MB) Fibroblast in the connective tissue capsula and partition, showing collagen fibrils ( ), collagenous fibers ( ξ ) and nucleus (N) Collagenous fibers (CF) in the locule lumina Fibrocytes ( ) in the connective tissue capsula and partition Interstitial cell in the connective tissue partition of seminal vesicle, showing its nucleus (N) BC : Blood capillary. C : Cytoplasm. CC : Connective tissue capsula. CF : Collagenous fiber. CM : Cell membrane. CP : Connective tissue partition. G: Golgi complex. LL : Locule lumina. LV : Large vacuole. M : Mitochondria. MB : Myelin body. N : Nucleus. RER : Rough endoplasmic reticulum. S : Secretion. SD : Sperm duct. SG: Secretory granule. SV : Seminal vesicle. T : Testis. U : Urinary bladder. UP : Urogenital papilla.
9 : ZHAN G Qi2Yong et al. : Structure and function of the seminal vesicle in male Bost richthys sinensis Plate ( Explanation at the end of the text)
10 : ZHAN G Qi2Yong et al. : Structure and function of the seminal vesicle in male Bost richthys sinensis Plate ( Explanation at the end of the text)
A Histological Study of the Seminal Vesicle of the Armoured Catfish
 Anat. Histol. Embryol. 36, 111 115 (2007) Ó 2006 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2006 Blackwell Publishing Ltd ISSN 0340 2096 Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Sciences and Aquaculture Center,
Anat. Histol. Embryol. 36, 111 115 (2007) Ó 2006 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2006 Blackwell Publishing Ltd ISSN 0340 2096 Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Sciences and Aquaculture Center,
Immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure of the thyroid gland of the grey mullet ( M ugil cephalus) 3
 49 (2) :230 237, 2003 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 33 (, 361005) 1 3 ;, ( TG), ;, 2 3, [ 49 (2) : 230 237, 2003 ] Immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure of the thyroid gland of the grey mullet ( M ugil cephalus)
49 (2) :230 237, 2003 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 33 (, 361005) 1 3 ;, ( TG), ;, 2 3, [ 49 (2) : 230 237, 2003 ] Immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure of the thyroid gland of the grey mullet ( M ugil cephalus)
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
All lecture of practical OSPE file
 All lecture of practical OSPE file Red: questions. Dark red: very important. Black: complete answers. Gray: notes extra. Editing File You should know before the exam: The diagrams in these slides are going
All lecture of practical OSPE file Red: questions. Dark red: very important. Black: complete answers. Gray: notes extra. Editing File You should know before the exam: The diagrams in these slides are going
Journal of Fishery Sciences of China
 10 5 2 0 0 3 1 0 Journal of Fishery Sciences of China Vol. 10 No. 5 Oct. 2003 1 2 1 1 1 1 (1. 361005 ; 2. 361005) : Olympus BH - 2 ( Scylla serrata) 4 : ; ; ; 2 :A ;B A B B A B : ; ; : Q952 :A :1005-8737
10 5 2 0 0 3 1 0 Journal of Fishery Sciences of China Vol. 10 No. 5 Oct. 2003 1 2 1 1 1 1 (1. 361005 ; 2. 361005) : Olympus BH - 2 ( Scylla serrata) 4 : ; ; ; 2 :A ;B A B B A B : ; ; : Q952 :A :1005-8737
5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Glandular epithelium Gland: Is a collection of epithelial cells the secrets a certain product, like: proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. Secretion : A certain material that is produced
5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Glandular epithelium Gland: Is a collection of epithelial cells the secrets a certain product, like: proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. Secretion : A certain material that is produced
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
A. Incorrect! Axons covey messages from the cell body of the neuron. D. Correct! Dendrites convey messages to the cell body of the neuron.
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 14: Animal Form No. 1 of 10 1. The branches of a neuron receiving information from another cell and which transmit the message to the cell body are called? (A) (B) (C) (D)
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 14: Animal Form No. 1 of 10 1. The branches of a neuron receiving information from another cell and which transmit the message to the cell body are called? (A) (B) (C) (D)
CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION
 CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION CHAPTER 2 https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Cellular components of animal & plant cells https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Plant Cells Cell wall Plasma membrane
CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION CHAPTER 2 https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Cellular components of animal & plant cells https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Plant Cells Cell wall Plasma membrane
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
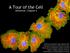 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System. VIBS 289 lab
 Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
I Chowdhury & K P Joy* Department of Zoology, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi , India Received 27 May 1999; revised 23 March 2000
 Indian Journal of xperimental Biology Vol. 38 July 2, pp. 713-719 ffects of administration of testosterone on some biochemical correlates in seminal vesicle of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) during preparatory
Indian Journal of xperimental Biology Vol. 38 July 2, pp. 713-719 ffects of administration of testosterone on some biochemical correlates in seminal vesicle of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) during preparatory
STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION
 STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION IN ANIMALS ANIMAL TISSUES :- Are Classified in to four types 1.Epithelal Tissues 2.Connective Tissues 3.Muscular Tissues 4.Neural Tissues Vikasana - CET 2012 1.Epithelial Tissues
STRUCTURAL ORGANSTAION IN ANIMALS ANIMAL TISSUES :- Are Classified in to four types 1.Epithelal Tissues 2.Connective Tissues 3.Muscular Tissues 4.Neural Tissues Vikasana - CET 2012 1.Epithelial Tissues
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
43 (2) : , 1997 A cta Zoologica S inica
 43 (2) : 119 126, 1997 A cta Zoologica S inica (, 350007) ( ),,,,,,,,,, A B (Deurs et al., 1973 ; Grier, 1973 ; Todd, 1976 ; Gardiner, 1978 ; Poirier et al., 1982 ; Billard, 1986 ;, 1990 ;, 1992 ;, 1996a,
43 (2) : 119 126, 1997 A cta Zoologica S inica (, 350007) ( ),,,,,,,,,, A B (Deurs et al., 1973 ; Grier, 1973 ; Todd, 1976 ; Gardiner, 1978 ; Poirier et al., 1982 ; Billard, 1986 ;, 1990 ;, 1992 ;, 1996a,
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER)
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED INJECTIONS OF CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN ON THE TESTES OF THE LEOPARD FROG (RANA PIPIENS SCHREBER) ROBERT P. McCOURT Department of Zoology and Entomology, The Ohio State University,
AMELOGENESIS. Prof. Shaleen Chandra
 AMELOGENESIS Epithelial Enamel Organ Outer Enamel Epithelium Stellate Reticulum Stratum Intermedium Inner Enamel Epithelium Cervical Loop Life Cycle of Ameloblasts Morphogenic stage Organizing Stage Formative
AMELOGENESIS Epithelial Enamel Organ Outer Enamel Epithelium Stellate Reticulum Stratum Intermedium Inner Enamel Epithelium Cervical Loop Life Cycle of Ameloblasts Morphogenic stage Organizing Stage Formative
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
川北医学院讲稿. Under low power note the testis is enclosed by a strong fibrous. layer of serous epithelium. These fibrous tissue
 川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface
 Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
4. A phospholipid is an example of organization at the level.
 1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland 1. Endocrine Glands 2. Exocrine Glands Endocrine Glands Exocrine Glands
 Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Histology of the Thyroid Gland
 Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Parts (organelles) of the Cell
 Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
human cell Mader s Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapters 1, 3 and 4
 1 The human cell INTRODUCTION All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing
1 The human cell INTRODUCTION All living things are composed of cells, which are the smallest units of life and are so small they can only be viewed through a microscope. Cells are made from pre-existing
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei
 Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
Chapter 7 Nerve tissue 1 Liu Jiamei General description: nerve tissue nerve cells (neurons): show numerous long processes receive the stimulation make contact with each other, conduct the nerve impulse
GENERAL SUMMARY. Observations
 GENERAL SUMMARY Observations The seasonal variation in the gonadosomatic indices (GSI) of male and female confirmed that the spawning season of Lepidocephalus thermalis was from October to November, coinciding
GENERAL SUMMARY Observations The seasonal variation in the gonadosomatic indices (GSI) of male and female confirmed that the spawning season of Lepidocephalus thermalis was from October to November, coinciding
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Efferent Ducts and Epididymis
 increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81
 Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject:- Anatomy, Physiology and Health Education Class:- B.P. Ed. Semester- I Presented By:- Dr. Mahesh Singh Dhapola Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells.
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject:- Anatomy, Physiology and Health Education Class:- B.P. Ed. Semester- I Presented By:- Dr. Mahesh Singh Dhapola Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells.
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
 Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Anatomy PHL 212. Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan. -
 Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh
 Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Anatomy & Physiology Revealed Instructions. 1. From the Module dropdown menu, chose the 12. Digestive system.
 #10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
#10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
Introduction. Materials and methods
 Bangladesh'. Fish. Res., 11(1), 2007: 01-05 BFRI A comparative study on the induced breeding and in vitro fertilization performance by various inducing agents in catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch)
Bangladesh'. Fish. Res., 11(1), 2007: 01-05 BFRI A comparative study on the induced breeding and in vitro fertilization performance by various inducing agents in catfish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch)
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope.
 1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope. Select your answers from the list below. 10x 40x 100x light microscope... x transmission
1 (a) State the maximum magnification that can be achieved by a light microscope and a transmission electron microscope. Select your answers from the list below. 10x 40x 100x light microscope... x transmission
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Microscope Requirements
 SEMEN EVALUATION EQUIPMENT Microscope Requirements Good quality lenses Phase-contrast preferred for % progressive motility evaluations Objectives 10X, 20X*, 40X*, 100X, minimum Heated stage preferred *Preferably
SEMEN EVALUATION EQUIPMENT Microscope Requirements Good quality lenses Phase-contrast preferred for % progressive motility evaluations Objectives 10X, 20X*, 40X*, 100X, minimum Heated stage preferred *Preferably
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
/searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1
 http://www.studiodaily.com/main /searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1 2011-2012 Cytology: science/study of cells To view cells: Light microscopy resolving power: measure of clarity Electron microscopy
http://www.studiodaily.com/main /searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1 2011-2012 Cytology: science/study of cells To view cells: Light microscopy resolving power: measure of clarity Electron microscopy
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
48 (1) : , ( Pochon2Masson, 1983 ; Arsenault, 1984 ; Papathanassiu et al., 1984 ;, 1988 ; Medina et al., 1992 ; Medina, 1994 ;,
 48 (1) :100 106, 2002 A cta Zoologica S inica (, 361005) ( Thenus orientalis),,, :,, 5 6, ( Pochon2Masson, 1983 ; Arsenault 1984 ; Papathanassiu et al., 1984 ;, 1988 ; Medina et al., 1992 ; Medina, 1994
48 (1) :100 106, 2002 A cta Zoologica S inica (, 361005) ( Thenus orientalis),,, :,, 5 6, ( Pochon2Masson, 1983 ; Arsenault 1984 ; Papathanassiu et al., 1984 ;, 1988 ; Medina et al., 1992 ; Medina, 1994
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
By: Brooke Sheppard
 By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
Cells & Tissues. Chapter 3
 Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
A classification of epithelial tissues
 A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
REPRODUCTION The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis.
 1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
