Primary mucinous cystadenoma of the spermatic cord within the inguinal canal
|
|
|
- Brent Flynn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kim et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:139 CASE REPORT Open Access Primary mucinous cystadenoma of the spermatic cord within the inguinal canal Jee-Yeon Kim 1, Young-Taek Lee 2, Hyun-Jeong Kang 3 and Chang-Hun Lee 1* Abstract We report a hitherto not documented case of primary mucinous cystadenoma arising in the spermatic cord within the right inguinal canal of a78-year-old man. The tumor was painless, hard and mobile. A computed tomography scan on the pelvis revealed an oval shaped, low attenuation mass, measuring 5.0x2.5x2.1 cm, that was present adjacent to the vas deferens. Grossly, the excised mass was multicystic mucinous tumor, filled with thick mucoid materials. Microscopically, the cystic wall was irregularly thickened. The cystic epithelium commonly showed short papillae lined by a single layer of columnar to cuboidal mucinous epithelial cells without significant stratification or cytologic atypia. Goblet cells were also frequently present. Immunohistochemically, the neoplastic cells showed positive reaction to carcinoembryonic antigen, cytokeratin 20, CDX2, epithelial membrane antigen, and CD15. However, they were negative for PAX8 and Wilms tumor 1 protein. Pathological diagnosis was a papillary mucinous cystadenoma of the spermatic cord. Although mucinous cystadenoma in this area is extremely rare, it is important that these lesions be recognized clinically and pathologically in order to avoid unnecessary radical surgery. Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: vs/ Keywords: Mucinous cystadenoma, Vas deferens, Spermatic cord Background Primary tumors of the spermatic cord can be of many types, but cystadenoma is especially exceptional. To the best of our knowledge, this is the third report of primary cystadenoma in the spermatic cord since the original report by McCluggage et al. in 1996 [1]. Interestingly, the neoplastic cells of the present case show mucinous character with intestinal differentiation, which is a unique finding distinct from previous two reports [1,2]. The clinicopathological features of this tumor are presented herein with a brief review of the differential diagnosis, pathology and possible histogenesis. Case presentation Clinical summary A 78-year-old man presented with a painless right inguinal swelling that was firstly noticed 3 months ago. The right inguinal mass was hard mobile. Otherwise, * Correspondence: cnlee@pusan.ac.krl 1 Department of Pathology and Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, 1-10 Ami-dong, Seo-gu, Busan , Republic of Korea Full list of author information is available at the end of the article there were no other specific symptoms. During physical examination, spermatic cords could be palpated on both sides. The testis and epididymis appeared normal. Routine blood analysis was all within normal limits. Ultrasound imaging on the right inguinal area showed a lobulated hypoechoic mass, measuring 5.0 cm, without internal vascularity. A computed tomography (CT) scan on the pelvis revealed an oval shaped, low attenuation mass, measuring 5.0x2.5x2.1 cm and showing a well demarcated smooth margin in the right inguinal area (Figure 1). At operation, a white cystic mass was found within the right inguinal canal and adhered to the vas deferens. The tumor was completely excised with an adjacent part of the vas deferens. Pathological findings Gross pathological examination revealed a multicystic mucinous tumor, measuring 4.5 cm in greatest diameter, filled with gelatinous mucoid materials (Figure 2A). Microscopically, the cystic wall was irregularly thickened and fibrotic (Figure 2B). The cystic epithelial lining was frequently detached from the wall, and focally showed 2012 Kim et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
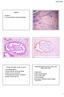
2 Kim et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:139 Page 2 of 6 Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced CT scan on the pelvis. It reveals an oval shaped, low attenuation mass (asterisk), measuring 5.0x2.5x2.1 cm, and showing a well demarcated smooth margin in the right inguinal area. short simple papillae supported on delicate fibrovascular stalks. The epithelium itself consisted of simple mucinous, nonciliated columnar cells with basally located small nuclei. In the most part of the epithelium, the nuclei are arranged in one or two layers. On Masson trichrome stain, the mucinous cystic tumor clearly displayed degenerated but encircling muscular layers which were reminiscent of muscular coat of the vas deferens (Figure 2C). Intraepithelial goblet cells were frequently present. However, neither remarkable papillary tufting Figure 2 Gross and microscopic findings of the cystic inguinal tumor. The tumor is completely excised with an adjacent part of vas deferens. A thick mucin content, taken out of the cystic tumor, is also noted (A). A multicystic mucinous tumor, filled with gelatinous mucoid materials, is microscopically present. The cystic wall, neighboring to vas deferens (asterisk), is irregularly thickened and fibrotic (B, x20). Masson trichrome stain clearly displays degenerated but still encircling muscular layers in the cystic wall of the tumor (C, x40; inlet showing high power view of x200). The cystic epithelial lining shows short papillary formation, and consists of a single layer of bland-looking columnar mucinous epithelial cells with frequent goblet cells (D, x 200).
3 Kim et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:139 Page 3 of 6 nor nuclear atypia was present. Mitoses were rare or absent (Figure 2D). Areas of mucin extravasation into stroma were present, but there was no stromal invasion by tumor cells. These histologic findings were qualifying the tumor as benign mucinous neoplasm. The vas deferens around the tumor was histologically unremarkable. Its lumen was empty. The tumor was close to the vas deferens, but the direct contiguity between both structures was not definitely noted. On the contrary, adense collagenous tissue separated the tumor from adjacent vas deferens tubules. Spermatozoa were present in neither the tumor nor the vas deferens, possibly reflecting senile atrophy of the testicles. Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemically, the neoplastic cells showed diffuse positive staining to carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA; clone II-7; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark), cytokeratin 20 (CK20; clone Ks20.8; Lab Vision Corp., Fremont, CA, USA), CDX2 (clone DAK-CDX2; 1:25, DAKO) and epithelial membrane antigen (EMA; clone E29; Dako). They were also focally positive for CD15 (clone Carb-3; Dako), but negative for PAX8 (clone PAX8R1; Abcam Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA) and Wilms tumor 1 protein (WT-1; clone 6 F-H2; Dako) (Figure 3). Adjacent ductus deferens tubule showed diffuse positive staining to EMA, CD15 and PAX8, but negative reaction to CEA, CK20, CDX2 and WT-1. Pathological diagnosis was a papillary mucinous cystadenoma of the spermatic cord. Follow-up After surgery, the patient has recovered well, and shows no recurrence at 8 months follow-up after local excision of the tumor. Discussion Primary tumors of the spermatic cord are rare. Furthermore, because of the intimate anatomic connection of the spermatic cord with the scrotum and the tunica vaginalis testis, it is often impossible to decide from which of these anatomic compartments these tumors have arisen. From a topographic and surgical standpoint, it would perhaps be more appropriate to simply divide them into those of the scrotum and those of the inguinal canal, without attributing them to a particular anatomic structure [3]. Topographically, the present case was arisen from the spermatic cord within the inguinal canal outside the epididymis. Grossly, the tumor was entirely cystic. Microscopically, the epithelium of the cystic wall consisted of simple mucinous, nonciliated columnar cells with basally located small nuclei. The uniform round to oval nuclei lacked atypia and arranged in one or two layers. Focally, the epithelium showed simple short papillae. Characteristically, there was noted the presence of abundant luminal mucin and intraepithelial goblet cells. The findings were indicative of mucinous cystadenoma with intestinal differentiation. The intestinal differentiation was confirmed from positive reaction of the epithelial cells to CEA, CK20 and CDX2. Only 2 previously reported cases of cystadenoma developed in the spermatic cord of the inguinal region have been so far found in the English literature [1,2]. However, the tumors had serous epithelial lining (of benign or borderline character) which was histologically distinguished from the present case. In addition, serous cystic tumors, two-thirds of which seemed to be a partial manifestation of von Hippel-Lindau s syndrome, have been also described in the head of the epididymis. Approximately, 40% of these epididymic tumors are known to follow bilateral occurrence [4]. And in those cases, the efferent ducts of the epididymis are proposed as the origin of a papillary cystadenoma in the epididymis [5]. Regarding clinical manifestation, there was no evidence of syndromatic pattern and bilaterality in the present case, including his relatives. As a matter of fact, we were not able to establish the tissue of origin of this papillary mucinous cystadenoma with certainty. However, we could make two speculations. Firstly, because the tumor did not show any direct connection with surrounding vas deferens tubules, we consider its origin from mesonephric (or Wolffian) duct anlages on the basis of its location and microscopic appearance. In the present case, neoplastic mucinous cells revealed cytoplasmic positivity to CD15 and EMA which was similar to immunohistochemical pattern of epithelial cells of normal vas deferens. Furthermore, the tumor was encircled by a rather degenerated, thin smooth muscle coat that was identified from Masson trichrome stain. Taken altogether, the features would be reminiscent of mesonephric duct anlage structure. Additionally, the tumor cells showed diffuse positive reaction to CK20, CDX2 and CEA which is characteristic of intestinal epithelial cells, and frequent occurrence of goblet cells in the epithelium. These findings of intestinal differentiation are those not expected in normal vas deferens, but may be related to versatile phenotypic expression frequently seen in mucinous neoplasms elsewhere. We also performed PAX8 immunohistochemical stain to identify if there is a possible evidence of Müllerian differentiation in the tumor. PAX8 is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of nuclear transcription factors and is important in organogenesis of the thyroid, kidney, and Müllerian system. PAX-8 is known to be expressed in a variety of ovarian epithelial tumors [6]. In the present case, however, the tumor cells were negative for PAX8. Thus, the evidence of Müllerian differentiation was not proven in this case. Secondly, the lesion may be resulted from a post-
4 Kim et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:139 Page 4 of 6 Figure 3 Immunohistochemical findings of the tumor. Immunostaining for CEA. The cytoplasm of neoplastic cells shows diffuse strong positive reaction to CEA (A, x 200). Immunostaining for CK20. The tumor cells also exhibit diffuse positive reaction to CK20 (B, x 200). Immunostaining for CDX2. The nuclei of neoplastic epithelial cells display diffuse strong positive reaction to CDX2 (C, x 200). Immunostaining for CD15. The cells are focally positive for CD15 (D, x 200). Immunostaining for PAX8. The cells are negative for PAX8 (E, x 200). Immunostaining for WT-1. The cells are negative for WT-1 (F, x 200). inflammatory cystic dilatation of a segment of the vas deferens, and followed by intestinal metaplasia and mucin production. In this speculation, a peritumoral fibromuscular wall that was histologically seen may be resulted from any sequelae of chronic inflammation. It is well known that the histology of mucinous cystadenoma is commonly found in female ovary. Generally, ovarian mucinous cystadenomas are large, unilateral, multilocular cystic tumors containing mucoid material. Microscopically, they are composed of glands and cysts lined by a single layer of columnar cells with abundant intracellular mucin. Cellular stratification is minimal, and nuclei are basally located with only mild atypia. Papillary formation in ovarian mucinous cystadenoma is unusual, but when it is present, the papillae are simple and short [7]. These epithelial characteristics were very similar to those of the present case. In ovarian mucinous tumors, gastrointestinal differentiation that was noted in our case is known to occur more often in borderline tumors and carcinomas rather than benign mucinous tumors. Ovarian intestinal-type mucinous borderline tumors are usually found as a larger size and consist of cysts and glands lined by atypical epithelium of gastrointestinal type [8]. The epithelium is usually stratified to two or three layers, nuclear atypia is mild to moderate, and mitotic figures vary from few to numerous. The papillae are commonly found, and are typically thin, branching, and complex [8]. As a whole, the lining epithelial cells in the present case were distinguished from ovarian borderline mucinous tumors in a degree of epithelial proliferation, cellular atypia, and papillary formation. Mucinous cystadenocarcinomas that typically show
5 Kim et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:139 Page 5 of 6 definite stromal invasion, more complicated papillary or cribriform epithelial proliferation, and moderate to marked nuclear atypia can be easily ruled out from the present case. Strictly speaking, it is very rare for us to be aware of any primary tumors of the spermatic cord within the inguinal region that could readily be confused microscopically with papillary cystadenomas. However, when we would take consideration of differential diagnosis, benign papillary mesothelioma or multicystic mesothelioma should be considered firstly under the list of differential diagnosis. This rare tumor of the tunica vaginalis usually appears in young men. Grossly, it consists of a hydrocele sac with papillary or adenomatous excrescences and cystic or solid areas. Microscopically, the tumor is comprised mostly of variably sized papillary formations with fibrovascular cores and covered by cuboidal, columnar, or flattened mesothelial cells with large vesicular nuclei and glassy eosinophilic cytoplasm [9,10], whereas the present case consisted of mucinous epithelial lining and was negative for WT-1, a well-known positive marker of mesothelial cells. Papillary serous tumor of benign or low malignant potential may occur in the tunica vaginalis, testis, spermatic cord, and epididymis. These tumors were described identical to its ovarian counterpart [1,11]. The present case is distinguished by its mucinous epithelial character, bland cytology and no epithelial stratification from serous tumors. Among malignant tumors, mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of this area, if ever, could be easily differentiated from mucinous cystadenoma by typical cytologic and structural anaplasia, including papillary, glandular, mucinous, and solid undifferentiated patterns [12]. Lastly, monodermal and highly specialized teratomas such as endodermal variants of mature cystic teratoma should be also considered [13]. Among them, glandular differentiated (adenomatoid) teratomas are composed mainly of mucinous (intestinal-type) epithelium of endodermal derivation. And these teratomas usually have other minor teratomatous components within the tumors. On the contrary, the present case showed no teratomatous tissue elsewhere in the primary lesion. Instead, it revealed distinct smooth muscle layers encircling around the neoplastic epithelium, which could not be expected from endodermal variants of mature cystic teratoma. Judging from histologic features, the present case mucinous papillary cystadenoma is a benign, noninvasive lesion that is speculated with no capacity for distant metastasis or recurrence, although its precise natural biology is poorly understood due to their extreme rarity. Conclusions Although clinical follow up observation is relatively short in the present case, the tumor is most likely speculated to be a benign neoplastic process when we combined histological findings with clinical histories (no definite evidence of recurrence during 8-months follow up, no tumorous lesion identified so far outside inguinal area). Mucinous papillary cystadenoma is an extremely rare neoplastic lesion of the spermatic cord. Clinically, there are no specific symptoms other than palpable mass, and radiologic imaging could give an impression of cystic or metastatic tumor arising in the inguinal region. The desirable treatment of choice is a local complete excision with sparing of the spermatic cord. However, it is important that the nature of these lesions be recognized clinically and pathologically in order to avoid unnecessary radical surgery. Consent Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this Case Report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in Chief of this journal. Abbreviations CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen; CK20: Cytokeratin 20; EMA: Epithelial membrane antigen; WT-1: Wilms tumor 1 protein; CDX2: Drosophila caudaltype homeobox 2; PAX8: Paired box 8. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions JY-KIM carried out the immunohistochemical staining and wrote the most of the manuscript. YT-LEE collected the patient s clinical information. HJ-KANG, DY-PARK, and GY-HUH participated in pathological investigations and the review of related references. CH-LEE also participated in pathological investigations, revised manuscript for important intellectual content and had given final approval of the version to be published. All of the authors have read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements This study was supported by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea ( ). We wish to give a great appreciation to Mr. Jae-Woo Kim for a dedicated technical handling of the immunohistochemical reactions. Author details 1 Department of Pathology and Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, 1-10 Ami-dong, Seo-gu, Busan , Republic of Korea. 2 Department of Surgery, Kwang Hye Hospital, Busan, Republic of Korea. 3 Department of Pathology, Kwang Hye Hospital, Busan, Republic of Korea. Received: 10 July 2012 Accepted: 5 October 2012 Published: 8 October 2012 References 1. McCluggage WG, Shah V, Nott C, Clements B, Wilson B, Hill CM: Cystadenoma of spermatic cord resembling ovarian serous epithelial tumour of low malignant potential: immunohistochemical study suggesting Müllerian differentiation. Histopathology 1996, 28: Geenen RWF, Bevers RFM, Gielis C, Boon TA: Papillary cystadenoma located in the spermatic cord. J Urol 1997, 158: Srigley JR: The paratesticular region: histoanatomic and general considerations. Semin Diagn Pathol 2000, 17: Srigley JR, Hartwick RW: Tumors and cysts of paratesticular region. Pathol Annu 1990, 25:
6 Kim et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:139 Page 6 of 6 5. Torikata C: Papillarycystadenoma of the epididymis. An ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. J Submicrosc CytolPathol 1994, 26: Nonaka D, Chiriboga L, Soslow RA: Expression of pax8 as a useful marker in distinguishing ovarian carcinomas from mammary carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 2008, 32: Bell DA: Mucinous adenofibromas of the ovary. A report of 10 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1991, 15: Rodriguez IM, Prat J: Mucinous tumors of the ovary. A clinicopathologic analysis of 75 borderline tumors (of intestinal type) and carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 2002, 26: Xiao SY, Rizzo P, Carbone M: Benign papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000, 124: Trpkov K, Barr R, Kulaga A, Yilmaz A: Mesothelioma of tunica vaginalis of uncertain malignant potential - an evolving concept: case report and review of the literature. Diagn Pathol 2011, 6: McClure RF, Keeney GL, Sebo TJ, Cheville JC: Serous borderline tumor of the paratestis: a report of seven cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2001, 25: Nistal M, Revestido R, Paniagua R: Bilateral mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the testis and epididymis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1992, 116: Clement PB, Dimmick JE: Endodermal variant of mature cystic teratoma of the ovary: report of a case. Cancer 1979, 43: doi: / Cite this article as: Kim et al.: Primary mucinous cystadenoma of the spermatic cord within the inguinal canal. Diagnostic Pathology :139. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Papillary adenocarcinoma of the rete testis with adjacent hyperplasia: a case report
 CASE REPORT Papillary adenocarcinoma of the rete testis with adjacent hyperplasia: a case report Carolina Polanco 1, Cooley G. Pantazis 2, Rolando Prieto 2, Kenneth A. Iczkowski 1 1. Medical College of
CASE REPORT Papillary adenocarcinoma of the rete testis with adjacent hyperplasia: a case report Carolina Polanco 1, Cooley G. Pantazis 2, Rolando Prieto 2, Kenneth A. Iczkowski 1 1. Medical College of
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon. Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology
 Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney.
 Dr. Fatima AlAl-Hashimi Hashimi,, MD, FRCPath Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney. The most frequently encountered
Dr. Fatima AlAl-Hashimi Hashimi,, MD, FRCPath Salmaniya Medical Complex, Bahrain Various hereditary, acquired and neoplastic conditions can lead to cyst formation in the kidney. The most frequently encountered
of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].
![of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2]. of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].](/thumbs/80/81450506.jpg) - - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
- - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
3/28/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference. Differential Diagnosis:
 GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours. Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh
 Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
Pathology of Ovarian Tumours Dr. Jyothi Ranganathan MD ( Path) AFMC Pune PDCC (Cytopathology) PGI Chandigarh Outline Incidence Risk factors Classification Pathology of tumours Tumour markers Prevention
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory.
 Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma
 Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Rouba Ali-Fehmi, MD Professor of Pathology The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine 50 year old woman with chief complaint of shortness of breath
Neoplasias Quisticas del Páncreas
 SEAP -Aproximación Práctica a la Patología Gastrointestinal- Madrid, 26 de mayo, 2006 Neoplasias Quisticas del Páncreas Gregory Y. Lauwers, M.D. Director, Service Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard
SEAP -Aproximación Práctica a la Patología Gastrointestinal- Madrid, 26 de mayo, 2006 Neoplasias Quisticas del Páncreas Gregory Y. Lauwers, M.D. Director, Service Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID. Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Papillary Cystadenoma of the Fallopian Tube Not Associated with von Hippel-Lindau Disease: A Case Report
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2014; 48: 382-386 BRIEF CASE REPORT Papillary Cystadenoma of the Fallopian Tube Not Associated with von Hippel-Lindau Disease: A Case Report Jae Yeon Seok Myunghee Kang
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2014; 48: 382-386 BRIEF CASE REPORT Papillary Cystadenoma of the Fallopian Tube Not Associated with von Hippel-Lindau Disease: A Case Report Jae Yeon Seok Myunghee Kang
Intraparenchymatous adenomatoid tumor dependent on the rete testis: A case report and review of literature
 Intraparenchymatous adenomatoid tumor dependent on the rete testis: A case report and review of literature A. Jiménez Pacheco, J. L. Martínez Torres, F. Valle Díaz de la Guardia, M. A. Arrabal Polo, and
Intraparenchymatous adenomatoid tumor dependent on the rete testis: A case report and review of literature A. Jiménez Pacheco, J. L. Martínez Torres, F. Valle Díaz de la Guardia, M. A. Arrabal Polo, and
ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY. Jonathan I. Epstein.
 1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual Combination
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 690891, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/690891 Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 690891, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/690891 Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult. by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department
 Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Institute of Pathology First Faculty of Medicine Charles University. Ovary
 Ovary Barrett esophagus ph in vagina between 3.8 and 4.5 ph of stomach varies from 1-2 (hydrochloric acid) up to 4-5 BE probably results from upward migration of columnar cells from gastroesophageal junction
Ovary Barrett esophagus ph in vagina between 3.8 and 4.5 ph of stomach varies from 1-2 (hydrochloric acid) up to 4-5 BE probably results from upward migration of columnar cells from gastroesophageal junction
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens
 How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology. Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford
 Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Renal tumours: the use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Classification of RCC
Renal tumours: use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Dr Lisa Browning John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Renal tumours: the use of immunohistochemistry & molecular pathology Classification of RCC
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast Laura C. Collins, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology Associate Director, Division of Anatomic Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School
Papillary Lesions of the Breast Laura C. Collins, M.D. Associate Professor of Pathology Associate Director, Division of Anatomic Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School
Tinh hoàn
 Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Article begins on next page
 Pseudopapillary Granulosa Cell Tumor: A Case of This Rare Subtype Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50622/story/]
Pseudopapillary Granulosa Cell Tumor: A Case of This Rare Subtype Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50622/story/]
3 cell types in the normal ovary
 Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors (neoplasms) 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal
Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Low-Grade Cribriform Cystadenocarcinoma with Many Psammoma Bodies of the Salivary Gland
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2013; 47: 481-485 CASE STUDY Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Low-Grade Cribriform Cystadenocarcinoma with Many Psammoma Bodies of the Salivary Gland Ji Yun Jeong Dongbin
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2013; 47: 481-485 CASE STUDY Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Low-Grade Cribriform Cystadenocarcinoma with Many Psammoma Bodies of the Salivary Gland Ji Yun Jeong Dongbin
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
The Origin of Pelvic Low-Grade Serous Proliferative Lesions
 The Origin of Pelvic Low-Grade Serous Proliferative Lesions Ovarian Atypical Proliferative (Borderline) Serous Tumors, Noninvasive Implants and Endosalpingiosis Robert J. Kurman, M.D. Kurman RJ, Vang R,
The Origin of Pelvic Low-Grade Serous Proliferative Lesions Ovarian Atypical Proliferative (Borderline) Serous Tumors, Noninvasive Implants and Endosalpingiosis Robert J. Kurman, M.D. Kurman RJ, Vang R,
Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity
 Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
Case Report Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary gland A case report of new entity Vaibhav Bhika Bari 1*, Sandhya Unmesh Bholay 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor Rajiv Gandhi Medical
Case Report Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor with heterologous element: a case report and a review of the literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(3):1176-1181 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1401091 Case Report Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor with heterologous element: a case report and a review of the literature Longwen
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(3):1176-1181 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP1401091 Case Report Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor with heterologous element: a case report and a review of the literature Longwen
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1)
 Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Case Report Müllerian Remnant Cyst as a Cause of Acute Abdomen in a Female Patient with Müllerian Agenesis: Radiologic and Pathologic Findings
 Volume 2016, Article ID 6581387, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6581387 Case Report üllerian Remnant Cyst as a Cause of Acute Abdomen in a Female Patient with üllerian Agenesis: Radiologic and
Volume 2016, Article ID 6581387, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6581387 Case Report üllerian Remnant Cyst as a Cause of Acute Abdomen in a Female Patient with üllerian Agenesis: Radiologic and
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA
 PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA 1 A good H & E helps! ADENOCARCINOMA DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Relatively uniform proliferation
PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA 1 A good H & E helps! ADENOCARCINOMA DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Relatively uniform proliferation
3 cell types in the normal ovary
 Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal cells
Ovarian tumors 3 cell types in the normal ovary Surface (coelomic epithelium) the origin of the great majority of ovarian tumors 90% of malignant ovarian tumors Totipotent germ cells Sex cord-stromal cells
Division of Pathology
 Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis. Diagnostic Studies and Differential Diagnosis. Seble S. Chekol, MD; Chen-Chin Sun, MD
 Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis Diagnostic Studies and Differential Diagnosis N Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis is an extremely rare tumor representing 0.3%
Malignant Mesothelioma of the Tunica Vaginalis Testis Diagnostic Studies and Differential Diagnosis N Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis testis is an extremely rare tumor representing 0.3%
A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally
 A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally Imrana Tanvir, Ghania Ali, Haseeb Ahmed Khan and Ahmed Nasir Hanifi* Dept. of Histopathology, FMH College of Medicine & Dentistry,
A Serous Borderline Tumor of the Fallopian Tube Detected Incidentally Imrana Tanvir, Ghania Ali, Haseeb Ahmed Khan and Ahmed Nasir Hanifi* Dept. of Histopathology, FMH College of Medicine & Dentistry,
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid.
 Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(4):351 355 ORIGINAL PAPER Value of antimesothelioma HBME 1 in the diagnosis of inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions LILIANA MOCANU 1), ANCA
Presenter: Yeh-Han Wang M.D.
 Korea-Taiwan-Japan Joint Meeting for Gynecological Pathology Mini-lecture Female Adnexal Tumor of Probable Wolffian Origin (FATWO) in Taiwan: A Small Case Series and Literature Review Presenter: Yeh-Han
Korea-Taiwan-Japan Joint Meeting for Gynecological Pathology Mini-lecture Female Adnexal Tumor of Probable Wolffian Origin (FATWO) in Taiwan: A Small Case Series and Literature Review Presenter: Yeh-Han
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
BSD 2015 Case 19. Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is:
 BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES
 DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
DIAGNOSTIC SLIDE SEMINAR: PART 1 RENAL TUMOUR BIOPSY CASES Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON Case 1 43 year-old female,
Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma
 http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches
 Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
This peer-reviewed article can be downloaded, printed and distributed freely for any purposes (see copyright notice below).
 Diagnostic Pathology This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma
Diagnostic Pathology This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
40th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK, 2-5 th October 2016
 40th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK, 2-5 th October 2016 EUS FNA of abdominal organs: An approach to reporting and triage for ancillary testing Date and time: Sunday 2 nd October 2016 15.00-16.30
40th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK, 2-5 th October 2016 EUS FNA of abdominal organs: An approach to reporting and triage for ancillary testing Date and time: Sunday 2 nd October 2016 15.00-16.30
Section 1. Biology of gynaecological cancers: our current understanding
 Section 1 Biology of gynaecological cancers: our current understanding Chapter 1 Morphological sub-types of ovarian carcinoma: new developments and pathogenesis W Glenn McCluggage 1 Introduction In most
Section 1 Biology of gynaecological cancers: our current understanding Chapter 1 Morphological sub-types of ovarian carcinoma: new developments and pathogenesis W Glenn McCluggage 1 Introduction In most
04/09/2018. Salivary Gland Pathology in the Molecular Era Old Friends, Old Foes, & New Acquaintances
 Salivary Gland Pathology in the Molecular Era Old Friends, Old Foes, & New Acquaintances Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory
Salivary Gland Pathology in the Molecular Era Old Friends, Old Foes, & New Acquaintances Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory
Pancreatic Cystic Lesions 원자력병원
 Pancreatic Cystic Lesions 원자력병원 박선 후 Lines of cellular differentiation Ductal Acinar Undetermined Ductal adenocarcinoma Serous/ mucinous tumor Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm Acinar cell carcinoma
Pancreatic Cystic Lesions 원자력병원 박선 후 Lines of cellular differentiation Ductal Acinar Undetermined Ductal adenocarcinoma Serous/ mucinous tumor Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm Acinar cell carcinoma
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate
 Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Macro- and microacinar proliferations of the prostate (with emphasis on cancer mimics) Rodolfo Montironi, MD (IT), FRCPath (UK), IFCAP (USA) Polytechnic University of Marche Region (Ancona) School of Medicine,
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT
 Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Case: The patient is a 62 year old woman with a history of renal cell carcinoma that was removed years ago. A 2.4 cm liver mass was found on CT during follow- up. ALT, AST, Alk Phos and bilirubin were
Case Report Multicentric Infarcted Leiomyoadenomatoid Tumor: A Case Report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol (2009) 2, 99-103 www.ijcep.com/ijcep801004 Case Report Multicentric Infarcted Leiomyoadenomatoid Tumor: A Case Report Ran Hong 1, Dong-Youl Choi 1, Sang Joon Choi 2 and Sung-Chul
Int J Clin Exp Pathol (2009) 2, 99-103 www.ijcep.com/ijcep801004 Case Report Multicentric Infarcted Leiomyoadenomatoid Tumor: A Case Report Ran Hong 1, Dong-Youl Choi 1, Sang Joon Choi 2 and Sung-Chul
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update 5/29/2009
 Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
The Repr duct ve System. Function: producing offspring
 The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association
 218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
Bibliography. Serous Tumors of the Ovary. Nomenclature
 Bibliography Serous Tumors of the Ovary Nomenclature 1. Allison KH, Swisher EM, Kerkering KM, et al. Defining an appropriate threshold for the diagnosis of serous borderline tumor of the ovary: when is
Bibliography Serous Tumors of the Ovary Nomenclature 1. Allison KH, Swisher EM, Kerkering KM, et al. Defining an appropriate threshold for the diagnosis of serous borderline tumor of the ovary: when is
Male Genital Cancers in the US in Frequency of Types
 Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
Update on Thyroid FNA The Bethesda System. Shikha Bose M.D. Associate Professor Cedars Sinai Medical Center
 Update on Thyroid FNA The Bethesda System Shikha Bose M.D. Associate Professor Cedars Sinai Medical Center Thyroid Nodules Frequent occurrence Palpable: 4-7% of adults Ultrasound: 10-31% Majority benign
Update on Thyroid FNA The Bethesda System Shikha Bose M.D. Associate Professor Cedars Sinai Medical Center Thyroid Nodules Frequent occurrence Palpable: 4-7% of adults Ultrasound: 10-31% Majority benign
Unknown Slides Conference
 Unknown Slides Conference Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD Weill Medical College of Cornell Univ. The Methodist Hospital, and UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX November 9, 2013 Amman, Jordan 25 th Congress of
Unknown Slides Conference Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD Weill Medical College of Cornell Univ. The Methodist Hospital, and UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX November 9, 2013 Amman, Jordan 25 th Congress of
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017
 Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Case Report Müllerian Serous Cystadenoma of the Scrotum Following Orchiopexy
 Advances in Urology Volume 009, Article ID 610453, 4 pages doi:10.1155/009/610453 Case Report Müllerian Serous Cystadenoma of the Scrotum Following Orchiopexy Sebastian C. J. van der Putte, 1 Johan Toonstra,
Advances in Urology Volume 009, Article ID 610453, 4 pages doi:10.1155/009/610453 Case Report Müllerian Serous Cystadenoma of the Scrotum Following Orchiopexy Sebastian C. J. van der Putte, 1 Johan Toonstra,
Pathology of the Thyroid
 Pathology of the Thyroid Thyroid Carcinoma Arising from Follicular Cells 2015-01-19 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Carcinomas Arising from Follicular Cells Differentiated Carcinoma Papillary
Pathology of the Thyroid Thyroid Carcinoma Arising from Follicular Cells 2015-01-19 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Carcinomas Arising from Follicular Cells Differentiated Carcinoma Papillary
