Safety Evaluation of Modified Si Jun Zi Tang, Assessment of Controlled and Randomized, Acute and Subchronic Mouse Oral Toxicity Studies
|
|
|
- Norah Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Safety Evaluation of Modified Si Jun Zi Tang, Assessment of Controlled and Randomized, Acute and Subchronic Mouse Oral Toxicity Studies Shuang Ma DVM, MS, Aituan Ma DVM, MS, PhD ABSTRACT In order to evaluate the clinical safety of a modification of the classical formula Si Jun Zi Tang (Wei Qi Booster a (WQB)), acute and subchronic mouse oral toxicity tests were conducted. An acute oral 7-day mouse study using 80 Kunming (KM) mice randomly divided into a saline control and 7 dosages of WQB (range g/kg BW) was conducted to determine LD 50. No mortality or adverse effects were observed in any parameter tested which included food consumption, clinical toxicity, body weights, organ/body weight ratios (liver and kidney) and histologic morphology of the liver, spleen, lung, kidney and duodenum. To determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of WQB, g/ kg BW was given twice daily for 7 days. No mortality or adverse effects were observed in any parameter tested in this study which included all parameters evaluated in the LD 50 study along with hematology. In the subchronic oral study, 15 mice were divided into 3 groups with the control group fed normal chow diet and each of the other two groups either receiving normal chow with 1% WQB or levamisole hydrochloride 0.01 g/kg BW (positive control) for 90 days. No mortality or adverse effects were observed in the 1% WQB in any parameter tested which included all parameters evaluated in the acute studies and with clinical chemistry replacing hematology. Results of these preclinical safety studies conducted with WQB at the highest dose tested which is g/kg BW for 7 days and 1% of food consumed for 90 days demonstrated no toxicity. Key words: Si Jun Zi Tang, Wei Qi Booster, LD 50, MTD, pre-clinical safety testing, hematology; biological indexes; immunity indexes, mouse, Chinese herbal medicine ABBREVIATIONS ALT Alanine aminotransferase ALB Albumin AST Aspartate aminotransferase BUN Blood urea nitrogen CHOL Cholesterol Crea Creatinine GLU Glucose HGB Hemoglobin LD 50 Median Lethal Dose 50 LYM Lymphocyte MID Leukocytes (neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil) MTD Maximum tolerated dose RBC Red blood cell TG Triglyceride UA Uric acid WBC White Blood Cell WQB Wei Qi Booster From: College of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, Agricultural University of Hebei, Baoding China (S. Ma, A, Ma) Herbal medicinal products and supplements have increased exponentially over the past three decades and are now used by more than 80% of the worldwide population. 1 With the increased use of these therapeutic agents, the safety of Chinese herbal medicine has drawn more attention recently from both domestic and abroad. 2 Establishing the safety of therapeutic compounds through toxicity studies is an active stage of research for western pharmaceuticals and is a requirement for approval under government regulations that approve the release of new drugs. In these studies, safety data are collected with the main goal to assess a product s safety profile. Studies of a therapeutic agent s toxicity include identification of organs that may be targeted by the compound; as well as any long term adverse effects. These studies should mimic the planned route, duration and schedule of drug administration as closely as possible. 3 These non-clinical studies may include acute toxicity (7 or 14 day studies), subacute (28-day study), subchronic (90 days or greater) and chronic (1 year) studies usually in a rodent species. Body weights, clinical signs of toxicity, food consumption, clinical pathology, histopathology, organ weights and 29
2 behavioral changes are usually evaluated in these studies along with mortality. A brief review of the literature reveals there is some safety testing of Chinese herbal medicines similar to pharmaceuticals being performed with both single herbs and herbal formulas. Safety evaluation of Xiang Gu (Shitake) was performed by Gao et al in a 14-day study in mice containing 3 dose groups along with a saline control. There were no adverse events recorded and a complete blood count and serum biochemical tests of liver and kidney were all within normal range. 4 The median lethal dose (LD 50 ) and the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of a formula containing Huang Lian (Rhizoma coptidis) and Ku Shen (Sophora flavescens) was tested in a mouse model. These animals were given 40 g/kg BW of the test herbs three times a day for 7 days without mortality or adverse effects on body weight, food and water consumption or clinical signs. The LD 50 was determined to be greater than 40g/kg BW and the MTD greater than 120 g/kg BW. The authors concluded that the traditional Chinese medicines had very low toxicity or no toxicity and were safe to use in the clinic. 5 Kim and his group investigated the safety of Ren Shen Bai Du San (Insampaedok-san water extract, ISSE) in mice, when receiving 5g/kg BW once daily for 15 days. Again, no mortality or adverse effects occurred and ISSE was considered safe for consumption. 6 The acute toxicity of the herbal formula Jin Weng Zhi Li Ke Li which contains several herbs including Huang Qi (Astragalus membranaceus) and Jin Yin Hua (Lonicera japanica thunb) was evaluated in mice in a 7-day study. The results showed the LD 50 was greater than 20 g/ kg BW with no adverse effects in study parameters evaluated. 7 In a 13- week subchronic oral toxicity study of Liu Wei Di Huang Tang, the results showed that all data measured which included mortality, clinical signs, body weight changes, food and water consumption, ophthalmologic findings, urinalysis, hematological and biochemical parameters, gross necropsy findings, organ weights, and histological examination of organs, were within normal limits. 8 A modification of the classical formula Si Jun Zi Tang (Wei Qi Booster a ) has been used in multiple species of domestic animals with success to tonify Wei Qi, Qi and Blood, and clear Heat-Toxins. 9,10 This Chinese herbal medicine consists of Dang Shen (Codonopsis pilosula), Huang Qi (Astragalus membranaceus), Wu Yao (Lindera aggregata), Chen Pi (Citrus reticulata), Dang Gui (Angelica sinensis), Xuan Shen (Scrophularia ningpoensis), Bai Hua She She Cao (Hedyotis diffusa) and Ban Zhi Lian (Scutellaria barbata). Numerous pharmacological studies have shown that this group of herbs can enhance body immunity and provide antitumor effects (references?) Liu and his colleagues demonstrated that Huang Qi saponins, one of the main ingredients of Huang Qi (Astragalus membranaceus), inhibits tumor growth in the hepatoma 22 (H 22 ) model and sarcoma 180 (S 180 ) implants in mice. 11 Bai Hua She She Cao (Oldenlandia) has also demonstrated anti-neoplastic effects as well as antiinflammatory properties. 12,13 In addition, the combination of Huang Qi (Astragalus) and Dang Gui (Angelica) has been shown to stimulate erythropoetin production in cultured kidney cells which therapeutically benefits the treatment of anemia. 14 Although WQB has demonstrated numerous benefits when administered to animals both in clinical and pharmacological studies, its safety in non-clinical toxicity testing remains unknown. The objective of the present study was to evaluate the safety of WQB in acute and subchronic oral rodent studies by the collection of data on body and organ weight changes, histologic changes of selected organs and clinical pathology changes (hematology, clinical chemistry) in order to provide guidance for safe use of this Chinese herbal medicine in clinical applications. The aim of these studies was to set an MTD (maximum tolerated dose), and LD 50 (median lethal dose) for WQB and identify any long term adverse effects (subchronic exposure) from oral administration of the compound. The hypothesis for this group of experimental studies was that WQB would demonstrate very low or no toxicity in these studies. MATERIALS AND METHODS Safety assessment of WQB was conducted through a series of 3 safety tests which included 2 acute toxicity tests (LD 50 and MTD) and 1 subchronic assay. The dosage and experimental procedures used in the LD 50 and MTD studies were consistent with the government legislation Evaluation Procedures and Methods on Health Food Safety Toxicology and Preclinical Safety Evaluation and Experiment issued by the Chinese Ministry of Health. 15,16,17 Consistent with the regulatory requirements, calculation of doses for evaluating compound safety in the LD 50 study included multiples of 1.4X for 7 dosages. If no adverse effects occurred at the highest dose level in this study, then the MTD study dose would be set at double the highest LD 50 dose. Dose determination for the subchronic study was based on a previous study conducted with chickens and was set at 1% WQB added into the normal chow for 90 days. 10 All animals for these studies were sourced from the Laboratory Animal Center of Hebel Medical University. The mice were housed in polypropylene cages with cellulose fiber chip bedding at a temperature of 25ºC and 30-40% humidity along with a 14-hour light and 10-hour dark cycle. All animals were given free access to rodent feed and water in glass bottles with rubber stoppers for an adaptive period of 7 days. All animal care and use was in accordance with the guidelines of the Chinese Council for Animal Care. The first acute toxicity test performed was to establish an LD 50 for WQB. This study contained 80, 8-week-old adult mice with an average weight of 30±2 g. After the adaptive period, the mice were randomly 30
3 divided via a random number table into 8 groups with 10 mice in each group. Mice in the control group were gavaged with 0.4 ml normal saline, while mice in groups 1-7 received the same amount of saline mixed with 2.0 g, 2.80 g, 3.92 g, 5.49 g, 7.68 g, g and g WQB/ kg BW twice daily for 7 days respectively. The animals received daily evaluation of food consumption, clinical signs of toxicity and monitoring for mortality. After 1 week of treatment, the mice were humanely euthanized by ketamine/xylazine overdose and blood was collected for hematology. Parameters evaluated included intermediate cells (eosinophil, neutrophil, basophil leukocytes) (MID), lymphocytes (LYM), red blood cells (RBC) and hemoglobin (HGB) with a commercial hematology analyzer b. Final body weights were recorded along with immediate collection of liver, spleen, lung, kidney and duodenum from the control and high dose groups. The organs were weighed and then placed in Bouin s solution for histopathological evaluation. The second acute toxicity test was to establish the MTD for WQB. This is the highest dose of an agent that can be administered without causing excessive toxicity or decreased survival. This study contained ten 8-week-old mice, with an average weight of 30±2 g. It was conducted as part of the LD 50 study, therefore, the control animal group was shared. The 10 study animals received g/kg BW of WQB twice daily for 7 days. All animals were given free access to food and water after gastric infusion. The animals received daily evaluation of food consumption, clinical signs of toxicity and monitoring for mortality. After 1 week of treatment, the mice were humanely euthanized as previously described and blood was collected for hematology (MID, LYM, RBC, HGB) with evaluation performed by a commercial hematology analyzer b. In addition, final body weight and organ weights (liver, kidney) were recorded c. Protocol organs which included liver, spleen, lung, kidney and duodenum were immediately collected and fixed in Bouin s solution for histological evaluation d. Both acute studies were repeated twice to verify results obtained. Subchronic toxicity studies (90-day or 13 weeks) are conducted to evaluate the safety of long-term administration of drugs or other therapeutic products. To evaluate the long-term safety of WQB, a 90-day study was conducted in mice. The study contained 45 healthy 8-week-old mice randomly divided into 3 groups of 15 animals. The control group was fed normal chow diet with each of the other two groups either receiving normal chow combined with 1% WQB or levamisole hydrochloride e 0.01 g/kg BW. Levamisole hydrochloride was used as a positive control due to its confirmed ability to enhance body immunity and used as comparison of immune enhancement that may occur subsequent to dosing with WQB. Mice were weighed every 2 weeks and received daily evaluation for signs of clinical toxicity, food consumption and mortality. After 90 days, the mice were humanely euthanized as previously described and blood was collected for clinical chemistry evaluation. Serum was obtained from the blood samples by centrifugation at 3,000 rpm for 10 min. The level of triglyceride (TG), cholesterol (CHOL), glucose (GLU), uric acid (UA), creatinine (Crea), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), total protein (TP), albumin (ALB) and aspartate transaminase (AST) were measured f. Final body weight and organ weights (liver, kidney) were recorded along with collection of the liver, spleen, lung, kidney and duodenum for histopathologic evaluation. The tissues were fixed in Bouin s solution and processed for histology by dehydration in a graded ethanol series. They were then embedded in paraffin and serial sections (4-5 um in thickness) were stained with a standard hematoxylineosin (H&E) stain for evaluation by light microscopy. Data were expressed as means plus or minus the standard deviation (mean ± SD). Differences between groups were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using SPSS software package for Windows g. In all tests, statistical significance was considered p<0.05 (*) significant, and p<0.01 (**) very significant. RESULTS There was no mortality in the acute studies (MTD, LD 50 ) in any study group over the 7-day observation period. In addition, no meaningful differences were seen in food consumption and clinical signs of toxicity when treated groups were compared to the control group. The ratio of liver and kidney organ weights to final body weight did not show any statistically significant effect in the WQB dose groups of the LD 50 study, including the 30.12g group in the MTD study (p>0.05) (Table 1). In addition, there were no statistically significant findings in any hematology parameter evaluated in either acute study (Table 2). In both acute studies, histological examination of liver sections from the g WQB group in the LD 50 study (Figure 1 B) and the 30.12g WQB group in the MTD study (Figure 1 C) demonstrated normal hepatocellular morphology with no evidence of hepatocyte hypertrophy or cytoplasmic vacuolation (lipidosis) when compared with their control groups (Figure 1 A). Examination of white pulp in the splenic sections demonstrated normal size and normal lymphocyte populations and volume in both the g and g WQB groups (Figure.1 E, Figure.1 F) when compared to the control group (Figure 1 D). Both WQB groups (Figure 1 H, Figure 1 I) had normal lung morphology when compared to controls (Figure 1 G) characterized by normal alveoli with no interstitial fibrosis or hemorrhage. Kidney sections in the treated groups (Figure 1 K/L) were examined for inflammatory infiltrates, glomerular changes, fibrosis, renal tubule cell injury and urothelium cell loss and were not different from the control group (Figure 1 J). Examination of duodenal sections in the g WQB group from the LD 50 study (Figure 1 N) 31
4 Table 1: Acute toxicity studies; Effect of WQB on organ to final body weight ratio of liver and kidney (n=10) Group WQB Dose (g per Liver weight to body Kidney weight to P-value kg BW) weight ratio body weight ratio P-value Control ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± MTD ± ± In all Tables, statistically significant (p<0.05), is denoted with (*) and very significant (p<0.01), with (**); statistics calculated by ANOVA (Tables 1-5). Table 2: Acute toxicity studies; Effect of WQB on hematological parameters (n=10) Group Dose (g per kg BW) MID(%) P-value LYM(%) P-value RBC (10 12 /L) P-value HGB(g/L) P-value Control Group ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± MTD Group ± ± ± ± *(p<0.05) significant; **(p<0.01)very significant and the MTD study (Figure 1 O) when compared with the control group (Figure 1 M) were normal with no villus blunting or crypt hyperplasia. In the subchronic 90-day study, all mice grew well with normal food consumption along with no mortality or signs of clinical toxicity. There was no statistically significant body weight effect (p>0.05) in any of the treatment groups at any study time point. All animals gained weight equally throughout the study (Table 3) when body weights at various study time points were compared to starting weights during week 1. In addition, there was no statistically significant difference in the kidney/body weight ratio when the treatment groups were compared to the control group. A statistically significant difference occurred in the liver/body weight ratios both in the levamisole group (P-value=0.02) and 1% WQB group (P-value=0.05) (Table 4). There were minor increases and decreases in various clinical chemistry parameters when the 1% WQB group was compared to the control group, however, none of the differences were statistically significant (Table 5) and all chemistry values were within the study reference range. Histopathology of protocol organs in the subchronic study included liver, spleen, lung, kidney and duodenum. Liver sections were examined for toxicologic changes such as abnormalities of the artery, vein and bile ducts in the portal triad, hepatocyte hypertrophy, areas of necrosis and numbers of stellate cells and reticulum fibers in the perisinusoidal spaces (Figures 2 A/B). The white and red pulp were evaluated in the splenic sections for volume of 32
5 copyright 2017 by AJTCVM All Rights Reserved Figure 1: Effect of WQB on liver, spleen, lung, kidney and duodenum histologic morphology in acute toxicity studies (n=10) Photomicrographs of liver: A-C; spleen: D-F; lung: G-I; kidney: J-L; duodenum: M-O Control Group: A, D, G, J, M; Dose Group (15.06 g/kg BW): B, E, H, K, N; MTD Group (30.12 g/ kg BW): C, F, I, L, O; Hepatocyte morphology is normal (arrow) in all WQB dosed groups with no evidence of hepatocellular cytoplasmic vacuolation or lipidosis. There is no difference between the volume of white pulp with lymphocyte numbers and germinal centers in the spleen (arrow) when g/kg BW WQB group and MTD group is compared with the control group. Lung histologic morphology in the g/kg BW WQB group and in the MTD group demonstrates normal lung alveoli (arrow), no interstitial fibrosis or hemorrhage when compared to control mice. Kidney glomerular morphology (arrow) along with renal tubular epithelium in g/kg BW WQB group and in MTD group is normal and shows no evidence of hyperplasia, vascular changes or cellular injury when compared to the control group. The duodenum in the g/kg BW WQB group and in MTD group demonstrates normal villous height and cellular morphology (arrow) with no evidence of villus blunting, crypt hyperplasia or dilatation when compared with the control group. Black bar in right corner of photomicrographs represents 100 μm. 33
6 Table 3: Subchronic study; Effect of WQB on body weight (n=15) Time Control group Levamisole group P-value 1%WQB group P-value 1 week 24.14± ± ± weeks 32.58± ± ± weeks 36.06± ± ± weeks 43.85± ± ± weeks 42.90± ± ± weeks 44.57± ± ± weeks 44.21± ± ± *(p<0.05) significant; ** (p<0.01) very significant Table 4: Subchronic Toxicity Study; Effect of WQB on organ to final body weight ratio (n=15) Indexes Control group Levamisole group P-value 1%WQB group P-value Liver weight to body weight ratio 3.17± ±0.04 * ±0.04* 0.05 Kidney weight to body weight ratio 1.24± ± ± *(p<0.05) significant; ** (p<0.01) very significant Table 5: Subchronic Toxicity Study; Effect of WQB on clinical chemistry parameters in mice (n=15) Indexes Control group Levamisole group P-value 1% WQB group P-value CHOL (mmol/l) 3.54± ± ± TG (mmol/l) Crea (umol/l) Glu (mmol/l) AST (U/L) ALT (U/L) TP (g/l) ALB (g/l) BUN (mmol/l) UA (mg/dl) *(p<0.05) significant; ** (p<0.01) very significant 2.10± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±
7 copyright 2017 by AJTCVM All Rights Reserved Figure 2: Effect of 1% WQB in diet on liver, spleen, lung, kidney and duodenum histologic morphology in subchronic toxicity study (n=15) Photomicrographs of: Liver A-B: Spleen C-D; Lung E-F; Kidney G-H; Duodenum I-J. Control Group A, C, E, G, I; 1% WQB Group B, D, F, H, J. The hepatocytes and portal triads (arrow) in 1% WQB and controls demonstrate normal morphology along with rare observation of stellate cells and reticulum fibers in perisinusoidal spaces. Splenic red and white pulp (arrow) in 1% WQB and controls was filled with appropriate numbers of red blood cells and lymphocytes, respectively, with normal germinal centers in the white pulp and no inflammatory infiltrate. The histologic morphology of lung in both 1% WQB and controls was normal with clear alveolar lumens (arrow), no congestion, edema, inflammation or fibrosis noted in any sections. The renal stroma, including glomeruli (arrow) in the 1% WQB group was normal and no inflammatory cells, fibrosis or renal tubule cell loss was noted. The morphology of the intestinal mucosa in the 1% WQB group was normal with no pathological changes of congestion, edema, inflammatory cell infiltration, erosion or ulcers noted. Black bar in right corner of photomicrographs represents 100 μm. 35
8 erythrocytes, size of the germinal centers and increased inflammatory infiltrate of the interstitium (Figures 2 C/D). Lung section morphology included evaluation for edema, inflammation and fibrosis (Figure 2 E/F) while kidney sections were examined for inflammatory infiltrates, fibrosis, renal tubule cell injury and urothelium cell loss (Figure 2 G/H). The villous morphology of duodenal mucosa was assessed for histologic changes such as edema, inflammatory cell infiltrates, erosions and ulcers (Figure 2 I/J). All were found to be within normal limits. DISCUSSION It is a scientific and regulatory requirement that before any potential new human and some veterinary drugs can be administered to patients in a clinic situation, the toxicity of the compounds should be investigated in order to define safe doses. Safety tests, also referred to as preclinical safety testing, are intended to reveal potential toxicity associated with a prospective medicine. Careful consideration of the doses used in preclinical studies is necessary to fulfill the need to identify target organs that may experience excessive toxicity and usually are identified by setting low, intermediate and high doses, plus a control group. This span of doses will usually cover from no effect to adverse effects or until limited by volume or limit dose (highest dose that should be used in the absence of demonstrable toxicity). Establishing the safety of Chinese herbal medicines as they experience increased use in clinic settings is becoming more common. Two examples of Chinese herbal medicines used as veterinary therapeutics after preclinical safety testing demonstrated their oral safety include Di Weng Ke Li composed of Bai Tou Weng (Pulsatillae Radixand) and Huang Lian (Coptidis Rhizoma) for piglets and Hu Pi Su (Quercetin) for use as a feed additive in animal production. These medicines, similar to the present study, had no deleterious effects, including no reduction in body weights when tested at the highest dose level possible. 18,19,20 In the current experimental study, a modification of the classical formula Si Jun Zi Tang (Wei Qi Booster a ), which is a veterinary specific Chinese herbal medicine, was evaluated for oral safety by using both acute and subchronic mouse studies modeled after preclinical safety studies used to evaluate new pharmaceuticals. Safety assessment of WQB was conducted through a series of 3 safety tests which included 2 acute toxicity tests (LD 50 and MTD) and 1 subchronic assay. The dosage and experimental procedures used in the design of these studies were consistent with government legislation Evaluation Procedures and Methods on Health Food Safety Toxicology and Preclinical Safety Evaluation and Experiment issued by the Chinese Ministry of Health. 15,16,17 There was no mortality in the acute studies (LD 50, MTD) over the 7-day observation period or in the subchronic study over its 90-day observation period. In all studies, no meaningful differences were seen in food consumption and clinical signs of toxicity when treated groups were compared to the control group. The ratio of liver and kidney organ weights to body weight did not show any statistically significant effects in any acute study WQB dose group including the very high dose of 30.12g/ kg BW group in the MTD study (p>0.05). Histopathology of all other organs collected in the WQB groups in the acute and subchronic studies were within normal limits for that organ. In addition, both hematology and clinical chemistry parameters were unaffected in animals dosed with WQB in all safety studies. A statistically significant increase occurred when comparing control liver/final body weight ratio and both treatment groups in the subchronic toxicity study. This was considered a non-adverse finding due to the following: there was no histologic abnormalities including hepatocellular hypertrophy, clinical chemistry values were normal and there was no dose response increase in the liver/body weight ratios in the acute studies. Most likely this finding is secondary to one control group animal with a low liver weight (outlier) which caused an artefactual lowering of the group s liver organ weight ratio results. According to the experimental design and statistical basis of drug evaluation, a Chinese herbal medicine can be considered safe if there is no mortality or adverse clinical signs in animals by gavage at a maximum tolerated oral dose of 10 g/kg BW. 21 There was no adverse effect observed at the highest dose level tested (30.12 g/kg BW) in the acute studies to determine LD 50 and MTD. Since the MTD of WQB was 30.12g/kg body weight (3 times higher than 10 g/kg BW), 0.14 g of WQB is considered acutely nontoxic to a 50 g mouse. When considering the recommended therapeutic dose of WQB for different species, 1.0 mg/kg for humans, 1.87 mg/kg for dogs or 9.1 mg/kg for mice given twice daily; the maximum dose tested (30.12g/kg BW) indicates a very large acute margin of safety (approximately 300X depending on species) when using this Chinese herbal medicine. In the subchronic study, when evaluating long term exposure, 1% WQB was added into the normal feed of experimental animals. With the study mice consuming approximately 6-8g of feed per 30-40g BW/day, the study mice received an approximate dose of 2g/kg or 2000 mg/kg BW of WQB per day for 90 days. When considering the recommended therapeutic dose of WQB for different species, the maximum dose found to have no adverse effects (2000 mg/kg BW) again indicates a large chronic exposure margin of safety of approximately 15X (depending on species). Results of this group of safety studies in mice with modified Si Jun Zi Tang (Wei Qi Booster a ) clearly demonstrated no acute or subchronic toxicity to experimental animals in any study. It may be concluded that WQB is a safe Chinese herbal medicine, even at 36
9 the highest dosage (30.12g/kg BW) for one week and also long term usage at 1% of feed or 2000 mg/kg BW. The hypothesis was therefore accepted that WQB would demonstrate no toxicity in experimental animals under the conditions of these studies. In conclusion, these studies provide evidence of the safety of this Chinese herbal medicine and support the basis of its safe use in clinical practice. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund of Agricultural University of Hebei (NO ) Footnotes a. Wei Qi Booster, Dr. Xie s Jing Tang Herbal Inc, Reddick, FL USA b. KM-23vet, Komeic company, Shanghai, China c. Sartorius, Germany d. Huangxing Science and Technology Co. LTD, Beijing, China e. Levamisole hydrochloride, Jinpai Pharmaceutical, Xuzhou, China f. Bio Sino, Beijing, China g. SPSS 13.0 software, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA REFERENCES 1. Rong WH, Zhan ZS, Pu CY et al. Developing current situation of Chinese herbal and some thought. Journal of Bethune Military Medical College 2011; 9: Keysser CH. Preclinical safety testing of new drugs. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1976; 6(2): Ye ZG, Zhang GP. Progress of safety evaluation of traditional Chinese medicines and its strategy in further studies. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae. 2014;20(16): Gao ZZ, Liu RR, Hu YL et al. A randomized and controlled experimental study of the acute and subacute toxicity of lentinan extracted from Xiang Gu (Shitake) in mice. AJTCVM 2014; 9(2): Liu YW, Wang DM, Zhao Y et al. Detection of the toxicity of traditional Chinese medicines used to treat diseases caused by candida albicans. Journal of Pathogen Biology 2010; 5: Kim YJ, Lee MY, Kim OS et al. Acute oral toxicity of Insampaedok-san, a traditional herbal formula in rats and its protective effects against ovalbumin-induced asthma via anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2014; 14: Yi Q, Li Sk, Zhu ZR et al. Experimental studies of the actue and repeated administration toxicity of the jin weng zhi li granules. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine 2015; 2: Ha HY, Lee JK, Lee HY et al. Safety evaluation of yukmijihwang-tang: assessment of acute and subchronic toxicity in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011; doi: /2011/ Patricia B. Acupuncture and Chinese Herbal Therapy for Acute Upper Respiratory Disease in a Geriatric Quarter Horse. AJTCVM 2009;4: Li S. Influence of WQB on the immune response to Newcastle disease vaccine in chickens [D]. Hebei, China, Agricultural University of Hebei 2013; Liu MH, Ren MP, Chen JP et al. Study on antitumor activity of Astragalus saponins. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica 2009; 25: Wang Q. Studies on anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory experiment of fujian hedyotis diffusa willd [D]. Fujian, China, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2013; Mao Y, Xu F, Xu XJ et al. Research progress on chemic constituent and anti-tumor activity of oldenlandia diffusa willd. Modern Preventive Medicine 2015;42: Zuo ZC, Gan M, Cui HM et al. Effects of Chinese herbal compound on the blood physiological parameters and cytokines of myelosuppressive mice. Chinese Veterinary Science 2013;43: Chinese ministry of health. The Evaluation Procedures and Methods on Health Food Safety Toxicology [S] Yuan BJ, Wang ZQ. The preclinical safety evaluation of new drug. Military Medical Science Press [M]1997, Veterinary drug test specification assembly. The Ministry of Agriculture Veterinary Drug Evaluation Committee Office [S] Teo S, Stirling D, Thomas S et al. A 90-day oral gavage toxicity study of D-methylphenidate and D, L-methylphenidate in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicology 2002;179, Fang X. Toxicity test and therapeutic effect of diweng keli on piglet white scour [D]. Jilin, China, Jilin University 2015, Feng XA. Safety Evaluation of Quercetin as a Feed Additive [D]. Heilongjiang, China, Northeast Agricultural Uuiversity, 2013; Liu CX, Sun RY. Experimental design and statistical basis of drug evaluation. Military Medical Science Press [M] 1998;
Nutrition and Foods Safety Agency of the Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, People s Republic of China. Testing Report
 Ministry Health approved Natural Health Products Testing Agency Issued by: Public Health Inspections, Ministry Health (1996) Publication # 53 Nutrition and Foods Safety Agency the Centre for Disease Prevention
Ministry Health approved Natural Health Products Testing Agency Issued by: Public Health Inspections, Ministry Health (1996) Publication # 53 Nutrition and Foods Safety Agency the Centre for Disease Prevention
24 h. P > h. R doi /j. issn
 38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE I
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE II
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10. Function in Formula. Disperse stagnation
 Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
Cytochrome-C (rat, mouse) forward GGAGGCAAGCATAAGACTGG. mouse hexokinase 2 gene, intron 9 reverse GGGAACACAAAAGACCTCTTCTGG
 Supplementary Table 1. The sequences of oligonucleotide primers. Genes Sequence rat actin forward CGAGTACAACCTTCTTGCAG rat actin reverse GAGTCCTTCTGACCCATACC tubulin (rat, mouse) forward TAGCAGAGATCACCAATGCC
Supplementary Table 1. The sequences of oligonucleotide primers. Genes Sequence rat actin forward CGAGTACAACCTTCTTGCAG rat actin reverse GAGTCCTTCTGACCCATACC tubulin (rat, mouse) forward TAGCAGAGATCACCAATGCC
Clinical Observations
 98 Clinical Observations Clinical Observations on 100 Cases of Ulcerative Colitis Treated with the Method of Clearing Away Heat, Expelling Dampness, Promoting Blood Circulation and Healing Ulcer YE Bai,
98 Clinical Observations Clinical Observations on 100 Cases of Ulcerative Colitis Treated with the Method of Clearing Away Heat, Expelling Dampness, Promoting Blood Circulation and Healing Ulcer YE Bai,
Single Herbs III / Quiz I
 Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Root & Branch Bulk Formula List
 An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
Sample received from: Botali International Enterprise Co., Ltd Tianjin Port Free Trade Zone
 Nutrition and Foods Safety Agency of the Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, People s Republic of China Xi Yuan Hospital of China Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Testing Report Sample processing
Nutrition and Foods Safety Agency of the Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, People s Republic of China Xi Yuan Hospital of China Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Testing Report Sample processing
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 )
 4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3*
 A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
Clinical Pathology Data from Cynomolgus Monkeys from China in which Diarrhea Was Observed during Quarantine
 Exp. Anim. 57(2), 139 143, 2008 Note Clinical Pathology Data from Cynomolgus Monkeys from China in which Diarrhea Was Observed during Quarantine Yan-Wei LIU 1, 2), Syusaku SUZUKI 1), Masatoshi KASHIMA
Exp. Anim. 57(2), 139 143, 2008 Note Clinical Pathology Data from Cynomolgus Monkeys from China in which Diarrhea Was Observed during Quarantine Yan-Wei LIU 1, 2), Syusaku SUZUKI 1), Masatoshi KASHIMA
SAFETY ASPECTS OF MIDAZOLAM
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Burak DiK 1, Emre BAHCIVAN 1,2, Hatice ESER 1,3, Kamil UNEY 1
 Burak DiK 1, Emre BAHCIVAN 1,2, Hatice ESER 1,3, Kamil UNEY 1 1 Selcuk University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Pharmacology and Toxicology Department, Konya, TURKEY 2 Kafkas University Faculty of Veterinary
Burak DiK 1, Emre BAHCIVAN 1,2, Hatice ESER 1,3, Kamil UNEY 1 1 Selcuk University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Pharmacology and Toxicology Department, Konya, TURKEY 2 Kafkas University Faculty of Veterinary
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts
 Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase
 Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Supporting Information (SI) for: Renal Clearable Peptide Functionalized NaGdF 4 Nanodots for. High-Efficiency Tracking Orthotopic Colorectal Tumor in
 Supporting Information (SI) for: Renal Clearable Peptide Functionalized NaGdF 4 Nanodots for High-Efficiency Tracking Orthotopic Colorectal Tumor in Mouse Hongda Chen, a,c Xiaodong Li, b Fuyao Liu, a Huimao
Supporting Information (SI) for: Renal Clearable Peptide Functionalized NaGdF 4 Nanodots for High-Efficiency Tracking Orthotopic Colorectal Tumor in Mouse Hongda Chen, a,c Xiaodong Li, b Fuyao Liu, a Huimao
COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY
 CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
CONTRIBUTOR NAME Daniel Heinrich, DVM CONTRIBUTOR EMAIL dheinric@umn.edu COAUTHORS Jed Overmann, DVM, DACVP; Davis Seelig DVM, PhD, DACVP & Matthew Sturos, DVM COMPANY OR UNIVERSITY University of Minnesota
CHRONIC TOXICITY STUDY OF GARBHPAL RAS, AN AYURVEDIC MEDICINE
 Journal of Herbal Medicine and Toxicology 3 (1) 13-17 (2009) ISSN : 0973-63 Original Article CHRONIC TOXICITY STUDY OF GARBHPAL RAS, AN AYURVEDIC MEDICINE D. MISHRA 1, M. SINHA 1, M. KUMAR 2 AND V. KUMAR
Journal of Herbal Medicine and Toxicology 3 (1) 13-17 (2009) ISSN : 0973-63 Original Article CHRONIC TOXICITY STUDY OF GARBHPAL RAS, AN AYURVEDIC MEDICINE D. MISHRA 1, M. SINHA 1, M. KUMAR 2 AND V. KUMAR
Practical approaches for endocrine toxicity in preclinical safety assessment
 Practical approaches for endocrine toxicity in preclinical safety assessment Akira Inomata, D.V.M., Ph.D., D.J.S.T.P. Tsukuba Drug Safety, Global Drug Safety, Biopharmaceutical Assessments Core Function
Practical approaches for endocrine toxicity in preclinical safety assessment Akira Inomata, D.V.M., Ph.D., D.J.S.T.P. Tsukuba Drug Safety, Global Drug Safety, Biopharmaceutical Assessments Core Function
The Herbalist s Corner
 Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding
 Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research
 Research Article ISSN: 2394 7403 International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research Journal home page: www.ijmhpr.com TOXICITY STUDY OF VAIVILANGAM CHOORANAM E. M. Manikgantan* 1 and R. Pattarayan
Research Article ISSN: 2394 7403 International Journal of Medicine and Health Profession Research Journal home page: www.ijmhpr.com TOXICITY STUDY OF VAIVILANGAM CHOORANAM E. M. Manikgantan* 1 and R. Pattarayan
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
Single Herbs II / Quiz II
 1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
Committee for Risk Assessment RAC. Opinion. on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320)
 Committee for Risk Assessment RAC Opinion on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320) EC number: 223-346-6 CAS number: 3846-71-7 and 2-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4,6-ditertpentylphenol
Committee for Risk Assessment RAC Opinion on the specific target organ toxicity of 2-benzotriazol-2-yl-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol (UV- 320) EC number: 223-346-6 CAS number: 3846-71-7 and 2-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4,6-ditertpentylphenol
Single Herbs III / Quiz II
 Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
A 4-year study of Red Yeast Rice extract known as Xuezhikang which lowers cholesterol... Monday, July 27, 2009
 A 4-year study of Red Yeast Rice extract known as Xuezhikang which lowers cholesterol... 1 At a dose of 600 mg twice a day... 2 Reduced coronary events by 37%... 3 Reduced death from coronary heart disease
A 4-year study of Red Yeast Rice extract known as Xuezhikang which lowers cholesterol... 1 At a dose of 600 mg twice a day... 2 Reduced coronary events by 37%... 3 Reduced death from coronary heart disease
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Organochloride pesticides impaired mitochondrial function in hepatocytes and. aggravated disorders of fatty acids metabolism
 Supplementary Materials Organochloride pesticides impaired mitochondrial function in hepatocytes and aggravated disorders of fatty acids metabolism Qian Liu 1,2,3*, Qihan Wang 4*, Cheng Xu 2,3, Wentao
Supplementary Materials Organochloride pesticides impaired mitochondrial function in hepatocytes and aggravated disorders of fatty acids metabolism Qian Liu 1,2,3*, Qihan Wang 4*, Cheng Xu 2,3, Wentao
TWO CASES OF HYPERTHYROIDISM
 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Acupuncture Today, January, 2008 TWO CASES OF HYPERTHYROIDISM Hyperthyroidism is not often seen in the clinic, but Chinese herbal medicine can be very
The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Acupuncture Today, January, 2008 TWO CASES OF HYPERTHYROIDISM Hyperthyroidism is not often seen in the clinic, but Chinese herbal medicine can be very
Understanding Blood Tests
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Your heart pumps the blood in your body through a system of blood vessels. Blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body. It also carries away
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Your heart pumps the blood in your body through a system of blood vessels. Blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body. It also carries away
Screening of QHF formula for effective ingredients from Chinese herbs and its anti-hepatic cell cancer effect in combination with chemotherapy
 Chinese Medical Journal 2008; 121(4):363-368 363 Original article Screening of QHF formula for effective ingredients from Chinese herbs and its anti-hepatic cell cancer effect in combination with chemotherapy
Chinese Medical Journal 2008; 121(4):363-368 363 Original article Screening of QHF formula for effective ingredients from Chinese herbs and its anti-hepatic cell cancer effect in combination with chemotherapy
Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into
 Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
AN EXTRAORDINARY CHINESE HERBAL PRODUCT FINDS ITS WAY TO NORTH AMERICA. Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD
 AN EXTRAORDINARY CHINESE HERBAL PRODUCT FINDS ITS WAY TO NORTH AMERICA Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD Many of China s remarkable herbal products have been exported to the United States for years; Gan Mao Ling,
AN EXTRAORDINARY CHINESE HERBAL PRODUCT FINDS ITS WAY TO NORTH AMERICA Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD Many of China s remarkable herbal products have been exported to the United States for years; Gan Mao Ling,
Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Colon cancer. Stages of cancer. TCM Anti-Cancer Centre Zhao Cheng R.TCMP, R.Ac., Ph.D.
 Colon cancer TCM Anti-Cancer Centre Zhao Cheng R.TCMP, R.Ac., Ph.D. Stages of cancer The staging of a carcinoma has to do with the size of the tumor, and the degree to which it has penetrated. When the
Colon cancer TCM Anti-Cancer Centre Zhao Cheng R.TCMP, R.Ac., Ph.D. Stages of cancer The staging of a carcinoma has to do with the size of the tumor, and the degree to which it has penetrated. When the
Pharmaceutical Drug Development Consulting
 Dr. Julia Eva Diederichs Pharmaceutical Drug Development Consulting Preclinical investigations and animal studies: for comprehensive characterisation what is scientifically possible and meaningful A Case
Dr. Julia Eva Diederichs Pharmaceutical Drug Development Consulting Preclinical investigations and animal studies: for comprehensive characterisation what is scientifically possible and meaningful A Case
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Effect of sulfur-fumigated Rhizoma dioscoreae on organ morphology and function in rats.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (3): 421-425 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of sulfur-fumigated Rhizoma dioscoreae on organ morphology and function in rats. Yihao Jiang *, Daiquan Jiang, Pengfei
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (3): 421-425 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of sulfur-fumigated Rhizoma dioscoreae on organ morphology and function in rats. Yihao Jiang *, Daiquan Jiang, Pengfei
Medicated diet. Tonify the Qi
 Medicated diet Tonify the Qi 1. Ren shen ginseng root Properties: sweet, slightly bitter, slightly warm Channels entered: LU, SP a. Strongly tonifies the basal qi, Tonifies the lung and spleen qi. a. Benefits
Medicated diet Tonify the Qi 1. Ren shen ginseng root Properties: sweet, slightly bitter, slightly warm Channels entered: LU, SP a. Strongly tonifies the basal qi, Tonifies the lung and spleen qi. a. Benefits
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Our ongoing interest in spirit
 Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
Evaluation of VACUETTE CAT Serum Fast Separator Blood Collection Tube for Routine Chemistry Analytes in Comparison to VACUTAINER RST Tube
 Evaluation of VACUETTE CAT Serum Fast Separator Blood Collection Tube for Routine Chemistry Analytes in Comparison to VACUTAINER RST Tube Background: Greiner-Bio-One, Austria has been selling plastic evacuated
Evaluation of VACUETTE CAT Serum Fast Separator Blood Collection Tube for Routine Chemistry Analytes in Comparison to VACUTAINER RST Tube Background: Greiner-Bio-One, Austria has been selling plastic evacuated
Original Article Protective effects of panaxadiolsaponins on liver and kidney injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):12811-12817 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0018697 Original Article Protective effects of panaxadiolsaponins on liver and kidney injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):12811-12817 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0018697 Original Article Protective effects of panaxadiolsaponins on liver and kidney injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic
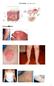 1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
Xiao-Ling Chi, Mei-Jie Shi, Huan-Ming Xiao, Yu-Bao Xie, and Gao-Shu Cai. Correspondence should be addressed to Xiao-Ling Chi;
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
A Tragic Story with A Happy Ending: Patterns of Chinese Herbalism and Laboratory Blood Work
 Page 1 A Tragic Story with A Happy Ending: Patterns of Chinese Herbalism and Laboratory Blood Work By Joseph Thomas, PhD, DiplAc Printed in: Natural Horse Volume 5, Issue 6, 2003 Last summer, my friend
Page 1 A Tragic Story with A Happy Ending: Patterns of Chinese Herbalism and Laboratory Blood Work By Joseph Thomas, PhD, DiplAc Printed in: Natural Horse Volume 5, Issue 6, 2003 Last summer, my friend
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS. Author: Josephine Davis
 DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
Comparative Analgesic and Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Salviae miltiorrhizae Pieces and its Products in Mice
 , 2014, Vol. 1, No. 2,109-114 Available online at http://www.ajethno.com American Journal of Ethnomedicine Comparative Analgesic and Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Salviae miltiorrhizae Pieces and its Products
, 2014, Vol. 1, No. 2,109-114 Available online at http://www.ajethno.com American Journal of Ethnomedicine Comparative Analgesic and Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Salviae miltiorrhizae Pieces and its Products
ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C 18 (100 mm 4.6 mm 3.5 µm) Lichrospher-C 18 (200 mm 4.6 mm 5 µm) Megres5-C 18 (250 mm 4.6 mm 5 µm)
 1 11 Tab. 1 Similarity of 11 batches of Formula Granule of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba /% S1 0904181 0.991 S2 1002065 0.985 S3 1009047 0.998 S4 1101070 0.963 S5 1104052 0.991 S6 1108069 0.975 S7 1110021
1 11 Tab. 1 Similarity of 11 batches of Formula Granule of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba /% S1 0904181 0.991 S2 1002065 0.985 S3 1009047 0.998 S4 1101070 0.963 S5 1104052 0.991 S6 1108069 0.975 S7 1110021
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Geometrical Confinement Directed Albumin-Based
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Geometrical Confinement Directed Albumin-Based
INTRODUCTION TO HERBAL MEDICINE
 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course provides students with an overview of the ideas and concepts they will encounter in their study of Chinese Herbology throughout the Masters program, as well as the basic
COURSE DESCRIPTION This course provides students with an overview of the ideas and concepts they will encounter in their study of Chinese Herbology throughout the Masters program, as well as the basic
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study. of Tetrachloroethylene. in BDF 1 Mice
 Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Tetrachloroethylene in BDF 1 Mice March 1993 Japan Bioassay Laboratory Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Tetrachloroethylene in BDF 1 Mice March 1993 Japan Bioassay Laboratory Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and
Construction of the Vesselcollateral. Guidance for Prevention and Treatment of Vasculopathy. Section 1. China. Clinical Trials.
 Section 1 05 Clinical Trials Construction of the Vesselcollateral Theory and its Guidance for Prevention and Treatment of Vasculopathy China Yiling Wu The Integration of Traditional and Western Medical
Section 1 05 Clinical Trials Construction of the Vesselcollateral Theory and its Guidance for Prevention and Treatment of Vasculopathy China Yiling Wu The Integration of Traditional and Western Medical
Effect of Spirulina-Chinese herbal medicine on quality of eggs and serum biochemical indexes of egg-laying hens
 B- 640 [1-5] Indian J. Anim. Res., rint ISSN:0367-6722 / Online ISSN:0976-0555 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijaronline.in Effect of Spirulina-Chinese herbal medicine
B- 640 [1-5] Indian J. Anim. Res., rint ISSN:0367-6722 / Online ISSN:0976-0555 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com/www.ijaronline.in Effect of Spirulina-Chinese herbal medicine
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma
 Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma WEEK TWO: Class 2 Goals: Students will learn traditional treatment methods - sweating, vomiting, draining downward, harmonizing, warming,
Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma WEEK TWO: Class 2 Goals: Students will learn traditional treatment methods - sweating, vomiting, draining downward, harmonizing, warming,
Acute and subchronic toxicity study of the water extract from Tiliacora triandra (Colebr.) Diels in rats
 Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 30 (5), 611-619, Sep. - Oct. 2008 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Acute and subchronic toxicity study of the water extract from Tiliacora triandra (Colebr.) Diels
Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 30 (5), 611-619, Sep. - Oct. 2008 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Acute and subchronic toxicity study of the water extract from Tiliacora triandra (Colebr.) Diels
Chinese Herbal Patent
 Chinese Herbal Patent Yuxing Liu Ph. D Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin What is Herbal Patent Introduction Advantages of Herbal patent Effective: Convenient: Cheaper: Characters of Herbal Patent
Chinese Herbal Patent Yuxing Liu Ph. D Academy of Oriental Medicine at Austin What is Herbal Patent Introduction Advantages of Herbal patent Effective: Convenient: Cheaper: Characters of Herbal Patent
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Section Two. Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13)
 Section Two Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13) Pungent, warm, SD of wind cold: no sweating, aversion to cold/fever, pain, sp/tense pulse
Section Two Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13) Pungent, warm, SD of wind cold: no sweating, aversion to cold/fever, pain, sp/tense pulse
Ba Wei Di Huang Wan (Rehmannia Eight)
 Ba Wei Di Huang Wan (Rehmannia Eight) Alternate Names Shen Qi Wan Jin Gui Shen Qi Wan (Precious Golden Tonify the Qi Combination) History This formula is a lasting contribution of the master herbalist
Ba Wei Di Huang Wan (Rehmannia Eight) Alternate Names Shen Qi Wan Jin Gui Shen Qi Wan (Precious Golden Tonify the Qi Combination) History This formula is a lasting contribution of the master herbalist
Beijing , China. 4 Department of Surgery, Third Affiliated Hospital of Peking University, Beijing , China. *Corresponding author:
 Title:Eplerenone restores -h blood pressure circadian rhythm and reduces advanced glycation end-products in rhesus macaques with spontaneous hypertensive metabolic syndrome Yan Zhang,,Wen Zheng,, Yuli
Title:Eplerenone restores -h blood pressure circadian rhythm and reduces advanced glycation end-products in rhesus macaques with spontaneous hypertensive metabolic syndrome Yan Zhang,,Wen Zheng,, Yuli
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Low toxicity and accumulation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in mice
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Toxicology Research. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Low toxicity and accumulation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in mice after 270-day consecutive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Toxicology Research. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Low toxicity and accumulation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in mice after 270-day consecutive
Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005)
 Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005) Note: Values and units of measurement listed in these Tables are derived from several resources. Substantial variation exists in the ranges quoted as normal
Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005) Note: Values and units of measurement listed in these Tables are derived from several resources. Substantial variation exists in the ranges quoted as normal
SMALL ANIMAL SOFT TISSUE CASE-BASED EXAMINATION
 SMALL ANIMAL SOFT TISSUE CASE-BASED EXAMINATION CASE-BASED EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS The case-based examination measures surgical principles in case management prior to, during, and after surgery. Information
SMALL ANIMAL SOFT TISSUE CASE-BASED EXAMINATION CASE-BASED EXAMINATION INSTRUCTIONS The case-based examination measures surgical principles in case management prior to, during, and after surgery. Information
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study. of Diphenylamine. in F344 Rats
 Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
Interpretation of the liver hypertrophy in the toxicological evaluation of veterinary medicinal products
 Provisional translation The Food Safety Commission Final decision on September 7, 2017 This English version of the Commission Decision is intended to be reference material to provide convenience for users.
Provisional translation The Food Safety Commission Final decision on September 7, 2017 This English version of the Commission Decision is intended to be reference material to provide convenience for users.
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang. Shi Jue Ming ** Properties: Salty, mild cold LV. Actions: Suppress LV yang, clear eye heat
 C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
Principles of Differentiation and Prescription for Vitiligo in Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on a Literature Investigation
 Received: May 13, 2015 Accepted after revision: October 19, 2015 Published online: December 3, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2296 7362/15/0024 0149$39.50/0 This article is licensed
Received: May 13, 2015 Accepted after revision: October 19, 2015 Published online: December 3, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2296 7362/15/0024 0149$39.50/0 This article is licensed
ROUTINE LAB STUDIES. Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 ROUTINE LAB STUDIES Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a tacrolimus or cyclosporine level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not
ROUTINE LAB STUDIES Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a tacrolimus or cyclosporine level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not
Comparison of VACUETTE Heparin Gel Tubes for Common Chemistry Analytes
 Comparison of VACUETTE Heparin Gel Tubes for Common Chemistry Analytes Background: Greiner-Bio-One, Austria has been selling plastic evacuated tubes (VACUETTE ) for venous blood collection since 9. The
Comparison of VACUETTE Heparin Gel Tubes for Common Chemistry Analytes Background: Greiner-Bio-One, Austria has been selling plastic evacuated tubes (VACUETTE ) for venous blood collection since 9. The
Hepatoprotective effect of a traditional drug, gurgum-7 on carbon- tetrachloride-induced liver damage
 Issues in Biological Sciences and Pharmaceutical Research Vol.4(1),pp.1-5 January 216 Available online at http://www.journalissues.org/ibspr/ http://dx.doi.org/1.15739/ibspr.16.1 Copyright 216 Author(s)
Issues in Biological Sciences and Pharmaceutical Research Vol.4(1),pp.1-5 January 216 Available online at http://www.journalissues.org/ibspr/ http://dx.doi.org/1.15739/ibspr.16.1 Copyright 216 Author(s)
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE
 European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/CVMP/77290/05-FINAL March 2005 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE FLUAZURON SUMMARY REPORT 1. Fluazuron is an insect
European Medicines Agency Veterinary Medicines and Inspections EMEA/CVMP/77290/05-FINAL March 2005 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR VETERINARY USE FLUAZURON SUMMARY REPORT 1. Fluazuron is an insect
Acupuncture Today, July, 2010.
 The Herbalist Corner Acupuncture Today, July, 2010. BROADENING STRATEGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF INSOMNIA Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Successful treatment of insomnia can be an elusive goal, especially
The Herbalist Corner Acupuncture Today, July, 2010. BROADENING STRATEGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF INSOMNIA Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. Successful treatment of insomnia can be an elusive goal, especially
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease
 Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Stability of VACUETTE Lithium Heparin Separator tubes with modified centrifugation conditions
 Stability of VACUETTE Lithium Heparin Separator tubes with modified centrifugation conditions Background: Greiner-Bio-One, Austria has been selling plastic evacuated tubes (VACUETTE ) for venous blood
Stability of VACUETTE Lithium Heparin Separator tubes with modified centrifugation conditions Background: Greiner-Bio-One, Austria has been selling plastic evacuated tubes (VACUETTE ) for venous blood
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease
 Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
SHRIRAM INSTITUTE FOR INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH
 IN RATS SUB CHRONIC ORAL TOXICITY WITH NHH 44 Bt-COTTON SEEDS Report for: UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION DHARWAD-580007 KARNATAKA Guidelines: DBT, Guidelines for Toxicity
IN RATS SUB CHRONIC ORAL TOXICITY WITH NHH 44 Bt-COTTON SEEDS Report for: UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION DHARWAD-580007 KARNATAKA Guidelines: DBT, Guidelines for Toxicity
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
Control Data of Rat
 BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Control Data of BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Rat Taconic Biosciences -1- BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Environmental Conditions and Investigation Items Environmental Conditions (Isolated Barrier
BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Control Data of BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Rat Taconic Biosciences -1- BrlHan:WIST@Tac(GALAS) Environmental Conditions and Investigation Items Environmental Conditions (Isolated Barrier
African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp (2012)
 African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp.16-19 (2012) Effects of Antimalarial Herbal Mixture (Abc 123) on the Liver of Rats *Iliya HA, Wannang NN, Andrew MM, Ibrahim H Department
African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp.16-19 (2012) Effects of Antimalarial Herbal Mixture (Abc 123) on the Liver of Rats *Iliya HA, Wannang NN, Andrew MM, Ibrahim H Department
Acute and Subacute Toxicities of the Ethanol Extract from Alternanthera philoxeroides Griseb.
 Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2005; 32(1-2): 7-14. Original Article Acute and Subacute Toxicities of the Ethanol Extract from Alternanthera philoxeroides Griseb. S. Thanabhorn,
Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2005; 32(1-2): 7-14. Original Article Acute and Subacute Toxicities of the Ethanol Extract from Alternanthera philoxeroides Griseb. S. Thanabhorn,
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Xi Yang, Ri-Bao Wei, Ping Li, Yue Yang, Ting-Yu Su, Yu-Wei Gao, Qing-Ping Li, Xue-Guang Zhang, Xiang-Mei Chen
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9401-9407 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0028098 Original Article Correlation between serum hepatitis B virus DNA replication level and clinicopathology in 235 patients
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9401-9407 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0028098 Original Article Correlation between serum hepatitis B virus DNA replication level and clinicopathology in 235 patients
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS
 Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
e-figure 1. The design of the study.
 e-figure 1. The design of the study. NDM, no diabetes; DM, diabetes; TB, tuberculosis; SN, sputum smear negative; SP, sputum smear positive; AFB, acid fast bacilli. e-figure 2. Representative H&E (A) and
e-figure 1. The design of the study. NDM, no diabetes; DM, diabetes; TB, tuberculosis; SN, sputum smear negative; SP, sputum smear positive; AFB, acid fast bacilli. e-figure 2. Representative H&E (A) and
Rapid Laboratories In House Tests
 Electrolytes CL CL (CHLORIDE) Electrolytes CO2 CO2 (BICARBONATE) Electrolytes K K (POTASSIUM) Electrolytes NA NA (SODIUM) Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) GLU GLU (GLUCOSE) Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) CA CA
Electrolytes CL CL (CHLORIDE) Electrolytes CO2 CO2 (BICARBONATE) Electrolytes K K (POTASSIUM) Electrolytes NA NA (SODIUM) Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) GLU GLU (GLUCOSE) Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) CA CA
no concerns hepatic shunt, high protein diet, kidney failure, metabolic acidosis
 TAKING THE WORK OUT OF INTERPRETING LAB WORK CACVT 2017 SPRING CONFERENCE - GREENWOOD VILLAGE, CO Brandy Helewa, CVT, RVT, VTS (ECC) Penn Foster College - Scranton, PA Knowing what the results on your
TAKING THE WORK OUT OF INTERPRETING LAB WORK CACVT 2017 SPRING CONFERENCE - GREENWOOD VILLAGE, CO Brandy Helewa, CVT, RVT, VTS (ECC) Penn Foster College - Scranton, PA Knowing what the results on your
Effects of Motherwort total alkaloids on prostatitis model of mice. Mingsan Miao, Lin Guo,Shuo Tian
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-05-23 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 926-930, pp 1049-1053 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.926-930.1049 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Effects of Motherwort
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2014-05-23 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 926-930, pp 1049-1053 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.926-930.1049 2014 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Effects of Motherwort
