Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct ISSN APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS. Nalanda College of Pharmacy, Nalgonda, A.P.
|
|
|
- Wesley Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct ISSN Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya S 1 1 Nalanda College of Pharmacy, Nalgonda, A.P. India 2 Chilkur Balaji College of Pharmacy, Hyderabad, A.P., India. ABSTRACT: Much attention have been focused in pharmaceutical research in the area of gastroretensive oral drug delivery. Henceforth a wide spectrum of dosage forms have been developed for drugs which are unstable in alkaline ph, soluble in acidic ph, having a narrow absorption window, site of action specific to stomach. This article provides the entire classification of gastroretensive, formulation considerations for developing gastroretensive, factors affecting gastroretensive, merits and demerits, applications in pharmacy and a comparative diagrammatic representation limelight this article. Those gastroretensive which depend on liberation of carbondioxide show poor patient compliance because of flatulence and belching. INTRODUCTION The oral ingestion is the predominant and most preferable route for drug delivery. Effective oral drug delivery may depend upon the factors such as gastric emptying process, gastrointestinal transit time of dosage form, drug release from the dosage form and site of absorption of drug. Time controlled oral drug delivery offer several advantages over immediate-release dosage forms, including the minimization of fluctuations in drug concentrations in the plasma and at the site of action over prolonged periods of time, resulting in optimized therapeutic concentrations and reduced side effects; a reduction of the total dose administered (while providing similar therapeutic effects) and a reduction of the administration frequency leading to improved patient compliance (Alexander, 2006). The real issue in the development of oral controlled release dosage form is to extend the duration of action of drug from the small intestine. For the successful performance of oral CRDDS the drug should have good absorption throughout the GIT, preferably by passive diffusion (Moes, 1993). International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 589
2 Gastroretentive dosage forms are drug delivery which remain in the stomach for an extended period of time and allow both spatial and time control of drug liberation. Basically gastroretentive swells following ingestion and is retained in the stomach for a number of hours, while it continuously releases the incorporated drug at a controlled rate to preferred absorption sites in the upper intestinal tract. Their application can be advantageous in the case of drugs absorbed mainly from the upper part of GIT or are unstable in the alkaline medium of distal intestinal regions. They can also be used beneficially in the local therapy of the stomach. Drugs that would benefit from GRDDS CNS drugs (for Parkinson disease, epilepsy, Alzheimer and migraine), Anti-viral products (for HIV, herpes and hepatitis) and certain antibiotics, Anti-hypertension drugs, Anti-diabetic agents for Type 2 diabetes, Drugs for local treatment of GI infections and gastric enzyme replacement (N.K. Jain). ADVANTAGES OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Gastroretentive drug delivery have numerous advantages listed below The principle of HBS can be used for any particular medicament or class of medicament. The HBS formulations are not restricted to medicaments, which are principally absorbed from the stomach. Since it has been found that these are equally efficacious with medicaments which are absorbed from the intestine e.g. Chlorpheniramine maleate. The HBS are advantageous for drugs absorbed through the stomach e.g. ferrous salts and for drugs meant for local action in the stomach and treatment of peptic ulcer disease e.g. antacids. The efficacy of the medicaments administered utilizing the sustained release principle of HBS has been found to be independent of the site of absorption of the particular medicaments. Administration of a prolonged release floating dosage form tablet or capsule will result in dissolution of the drug in gastric fluid. After emptying of the stomach contents, the dissolved drug available for absorption in the small intestine. It is therefore expected that a drug will be fully absorbed from the floating dosage form if it remains in solution form even at alkaline ph of the intestine. When there is vigorous intestinal movement and a short transit time as might occur in certain type of diarrhoea, poor absorption is expected under such circumstances it may be advantageous to keep the drug in floating condition in stomach to get a relatively better response. Gastric retention will provide advantages such as the delivery of drugs with narrow absorption windows in the small intestinal region. Many drugs categorized as once-a-day delivery have been demonstrated to have sub optimal absorption due to dependence on the transit time of the dosage form, making traditional extended release development challenging. Therefore, a system designed for longer gastric retention will extend the time within which drug absorption can occur in the small intestine. (Gutierrez et al., 2003).(Figure-1) International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 590
3 Figure. 1: Schematic representation of various gastroretentive formulations Approaches to Gastric Retention Floating Dosage forms Mucoadhesive Raft forming Low density Swelling and Expandable Superporous hydrogels Magnetic Self Unfolding Non-Effervescent 1. Single layer Floating Tablet 2. Bilayer Floating Tablet 3. Alginate beads 4. Hollow microspheres Effervescent High density Gas Generating Volatile liquid/ Vacuum 1. Tablets 2. Capsules 3. Multiple unit type floating pills 4. Floating with ion-exchange resin 1. Intra gastric Gastrointetinal drug delivery 2. Inflatable gastrointestinal drug delivery 3. Intragastric osmotically controlled drug delivery DISADVANTAGES OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM There are certain situations where gastric retention is not desirable. Aspirin and non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs are known to cause gastric lesions and slow release of such drugs in the stomach is unwanted. Thus, drugs that may irritate the stomach lining or are unstable in its acidic environment should not be formulated in gastroretentive.furthermore, other drugs, such as isosorbide dinitrate, that are absorbed equally well throughout the GI tract will not benefit from incorporation into a gastric retention system (Hou et al., 2003). Gastric retention is influenced by many factors such as gastric motility, ph and presence of food. These factors are never constant and hence the buoyancy cannot be predicted exactly or accurately. Gastric emptying of floating forms in supine subjects may occur at random and become highly dependent on the diameter. Therefore, patients should not be dosed with floating forms just before going to bed. High variability in gastric emptying time due to variations in emptying process. Unpredictable bioavailability. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 591
4 Formulation considerations for GRDDS It must be effective retention in the stomach to suit for the clinical demand 1) It must have sufficient drug loading capacity 2) It must be control the drug release profile 3) It must have full degradation and evacuation of the system once the drug release is over 4) It should not have effect on gastric motility including emptying pattern 5) It should not have other local adverse effects (Davis, 2005). Requirements for gastric retention From the discussion of the physiological factors in the stomach it must be noted that to achieve gastric retention, the dosage form must satisfy certain requirements. One of the key issues is that the dosage form must be able to withstand the forces caused by peristaltic waves in the stomach and the constant contractions and grinding and churning mechanisms. To function as a gastric retention device, it must be resist premature gastric emptying. Furthermore, once its purpose has been served, the device should be removed from the stomach with ease. Factors affecting the gastroretentive system Various attempts have been made to retain the dosage form in the stomach as a way of increasing the retention time. These attempts include use of floating dosage forms (gas-generating and swelling or expanding ), mucoadhesive, high-density, modified shape, gastricemptying delaying devices and co-administration of gastric-emptying delaying drugs. Most of these approaches are influenced by a number of factors that affect their bioavailability and efficacy of the gastro retentive system (Sanjay et al., 2003). Density Gastric retention time (GRT) is a function of dosage form buoyancy that is dependent on the density. Size Dosage form units with a diameter of more than 7.5 mm are reported to have an increased GRT compared with those with a diameter of 9.9 mm. Shape of dosage form Tetrahedron and ring shaped devices with a flexural modulus of 48 and 22.5 kilo pounds per square inch (KSI) are reported to have better GRT 90% to 100% retention at 24 hours compared with other shapes. Single or multiple unit formulation Multiple unit formulations show a more predictable release profile and insignificant impairing of performance due to failure of units, allow co-administration of units with different release profiles or containing incompatible substances and permit a larger margin of safety against dosage form failure compared with single unit dosage forms. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 592
5 Fed or unfed state Under fasting conditions, the GI motility is characterized by periods of strong motor activity or the migrating myoelectric complex (MMC) that occurs every 1.5 to 2 hours. The MMC sweeps undigested material from the stomach and, if the timing of administration of the formulation coincides with that of the MMC, the GRT of the unit can be expected to be very short. However, in the fed state, MMC is delayed and GRT is considerably longer. (Caldwell et al., 1998; Murthy et al., 2000). Nature of meal Feeding of indigestible polymers or fatty acid salts can change the motility pattern of the stomach to a fed state, thus decreasing the gastric emptying rate and prolonging drug release. Caloric content GRT can be increased by 4 to10 hours with a meal that is high in proteins and fats (Marvola et al., 1989) (Mojaverian et al., 1988). Frequency of feed The GRT can increase by over 400 minutes when successive meals are given compared with a single meal due to the low frequency of MMC. Gender Mean ambulatory GRT in males (3.4±0.6 hours) is less compared with their age and race matched female counterparts (4.6±1.2 hours), regardless of the weight, height and body surface. Age Elderly people, especially those over 70, have a significantly longer GRT. Posture GRT can vary between supine and upright ambulatory states of the patient. Concomitant drug administration Anticholinergics like atropine and propantheline, opiates like codeine and prokinetic agents like metoclopramide and cisapride can affect floating time. Biological factors Diabetes and Crohn s disease, etc. Figure. 2: Invivo picturisation of various gastro retentive formulations International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 593
6 Approaches to gastric retention Various attempts have been made to retain the dosage form in the stomach as a way of increasing the retention time. These attempts include introducing floating dosage forms (gas generating ) (Deshpande et al., 1997). Swelling and expanding (Urquhart and Theeuwes, 1984; Mamajek, 1980). Mucoadhesive (Lenaerts, 1990; Lehr, 1994). High density (Caldwell et al., 1988). Modified shape (Groning and Heum, 1989; Bechgaard and Ladefoged, 1978).Gastric emptying delaying devices and co-administration of gastric delaying drugs. Among these, the floating dosage forms have been used most commonly. Floating DDS (FDDS), with low density providing sufficient buoyancy to float over the gastric contents, Bioadhesive, enabling the localized retention of the system in the stomach, Swelling and expanding, preventing transit from the gastric sphincter, High density system, remaining in the stomach for longer period of time by sedimenting to the folds of stomach, Superporous hydrogels, and Modified-shaped system A number of other methods like use of passage-delaying agents, magnetically controlled and combination methods like floating-bioadhesive. Floating drug delivery The concept of FDDS was described in the literature as early as FDDS have a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. While the system is floating on the gastric contents the drug is released slowly at the desired rate from the system. This results in an increased GRT and a better control of fluctuations in plasma drug concentration. The device must have sufficient structure to form a cohesive gel barrier, it must maintain an overall specific gravity lower than that of gastric contents ( ) and it should dissolve slowly enough to serve as a drug reservoir. Types of floating drug delivery Based on the mechanism of buoyancy and two distinctly different technologies have been utilized in the development of FDDS. 1) Non- Effervescent FDDS 2) Effervescent FDDS 1) Non-Effervescent FDDS The Non-effervescent FDDS is based on mechanism of swelling of polymer or bioadhesion to mucosal layer in GI tract. The most commonly used excipients in non-effervescent FDDS are gel forming or highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, hydrophilic gums, polysaccharides and matrix forming materials such as polycarbonate, polyacrylate, polymethacrylate, polystyrene as well as bioadhesive polymers such as Chitosan and carbopol. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 594
7 The various types of this system are as: A. Single Layer Floating Tablets They are formulated by intimate mixing of drug with a gel-forming hydrocolloid, which swells in contact with gastric fluid and maintains bulk density of less than unity. They are formulated by intimate mixing of drug with low-density enteric materials such as CAP, HPMC. B. Bi-layer Floating Tablets A bi-layer tablet contain two layer one immediate release layer which releases initial dose from system while the another sustained release layer absorbs gastric fluid, forming an impermeable colloidal gel barrier on its surface, and maintain a bulk density of less than unity and thereby it remains buoyant in the stomach (Oth et al., 1992). C. Alginate Beads Multi-unit floating dosage forms were developed from freeze-dried calcium alginate. Spherical beads of approximately 2.5 mm diameter can be prepared by dropping sodium alginate solution into aqueous solution of calcium chloride, causing precipitation of calcium alginate leading to formation of porous system, which can maintain a floating force for over 12 hours. When compared with solid beads, which gave a short residence time of 1 hour, and these floating beads gave a prolonged residence time of more than 5.5 hours (katayama et al., 1999). D. Hollow Microspheres Hollow microspheres (microballoons), loaded with drug in their outer polymer shells are prepared by a novel emulsion-solvent diffusion method. The ethanol: dichloromethane solution of the drug and an enteric acrylic polymer is poured into an agitated aqueous solution of PVA that is thermally controlled at 40 0 C. The gas phase generated in dispersed polymer droplet by evaporation of dichloromethane forms an internal cavity in microsphere of polymer with drug. The microballoons float continuously over the surface of acidic dissolution media containing surfactant for more than 12 hours in vitro (Kawashima, 1992). 2) Effervescent System Effervescent include use of gas generating agents, carbonates (ex. Sodium bicarbonate) and other organic acid (e.g. citric acid and tartaric acid) present in the formulation to produce carbon dioxide (CO 2) gas, thus reducing the density of the system and making it float on the gastric fluid. An alternative is the incorporation of matrix containing portion of liquid, which produce gas that evaporates at body temperature. These effervescent further classified into two types. 1. Gas generating, 2. Volatile Liquid/Vacuum Containing Systems. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 595
8 1. Gas Generating Systems A. Tablets Floating bilayer tablets with controlled release for furosemide were developed by Ozdemir et al., The low solubility of the drug could be enhanced by using the kneading method, preparing a solid dispersion with β cyclodextrin mixed in a 1:1 ratio (Singh and Brahma, 2000). One layer contained the polymers HPMC K4M, HPMC K100M and CMC (for the control of the drug delivery) and the drug. The second layer contained the effervescent mixture of sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. The in vitro floating studies revealed that the lesser the compression force the shorter is the time of onset of floating, i.e., when the tablets were compressed at 15 MPa, these could begin to float at 20 minutes whereas at a force of 32 MPa the time was prolonged to 45 minutes. Radiographic studies on 6 healthy male volunteers revealed that floating tablets were retained in stomach for 6 hours and further blood analysis studies showed that bioavailability of these tablets was 1.8 times that of the conventional tablets. On measuring the volume of urine the peak diuretic effect seen in the conventional tablets was decreased and prolonged in the case of floating dosage form. B. Floating capsules Floating capsules are prepared by filling with a mixture of sodium alginate and sodium bicarbonate. The were shown to float during in vitro tests as a result of the generation of CO 2 that was trapped in the hydrating gel network on exposure to an acidic environment. C. Multiple unit type floating pills The system consists of sustained release pills as seeds surrounded by double layers. The inner layer consists of effervescent agents while the outer layer is of swellable membrane layer. When the system is immersed in dissolution medium at body temp, it sinks at once and then forms swollen pills like balloons, which float as they have lower density. This lower density is due to generation and entrapment of CO 2 within the system. D. Floating system with Ion-Exchange resins A floating system using ion exchange resin that was loaded with bicarbonate by mixing the beads with 1M sodium bicarbonate solution (Shweta Arora et al., 2005). The loaded beads were then surrounded by a semipermeable membrane to avoid sudden loss of CO 2. Upon coming in contact with gastric contents an exchange of chloride and bicarbonate ions took place that resulted in CO2 generation thereby carrying beads toward the top of gastric contents and producing a floating layer of resin beads. The in vivo behavior of the coated and uncoated beads was monitored using a single channel analyzing study in 12 healthy human volunteers by gamma radio scintigraphy. Studies showed that the gastric residence time was prolonged considerably (24 hours) compared with uncoated beads (1 to 3 hours). International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 596
9 2. Volatile Liquid / Vacuum Containing Systems A. Intra-gastric floating gastrointestinal drug delivery system These can be made to float in the stomach because of floatation chamber, which may be a vacuum or filled with air or a harmless gas, while drug reservoir is encapsulated inside a micro-porous compartment. Table 1: Differentiation between floating and muco adhesive delivery Floating drug delivery system 1. FDDS have a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. 2. Floating of the dosage form can be achieved by two means i.e. either incorporating a gas generating system or volatile liquid/ vacuum system. Examples: Valrelease, Madopar Topalkan HBS, Mucoadhesive drug delivery system 1. The term bioadhesion is defined as adhesion to biological surface i.e. mucus and/or mucosal surface. In instances when the polymeric system interacts with mucus layer only, it is referred as mucoadhesion. 2. Mucoadhesion can be achieved by different mucin-polymer interactions such as Wetting and swelling of the polymer to permit intimate contact with the biological tissue/ interpenetration of bioadhesive polymer chains and entanglement of polymer and mucin chains/ formation of weak chemical bonds/ sufficient polymer mobility to allow spreading/ water transport followed by mucosal dehydration B. Inflatable gastrointestinal delivery In these an inflatable chamber is incorporated, which contains liquid ether that gasifies at body temperature to cause the chamber to inflate in the stomach. These are fabricated by loading the inflatable chamber with a drug reservoir, which can be a drug impregnated polymeric matrix, encapsulated in a gelatin capsule. After oral administration, the capsule dissolves to release the drug reservoir together with the inflatable chamber. The inflatable chamber automatically inflates and retains the drug reservoir compartment in the stomach. The drug continuously released from the reservoir into the gastric fluid. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 597
10 C. Intragastric osmotically controlled drug delivery system It is comprised of an osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery device and an inflatable floating support in a biodegradable capsule. In the stomach, the capsule quickly disintegrates to release the intragastric osmotically controlled drug delivery device. The inflatable support inside forms a deformable hollow polymeric bag that contains a liquid that gasifies at body temperature to inflate the bag. The osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery device consists of two components; drug reservoir compartment and an osmotically active compartment. The drug reservoir compartment is enclosed by a pressure responsive collapsible bag, which is impermeable to vapour and liquid and has a drug delivery orifice. The osmotically active compartment contains an osmotically active salt and is enclosed within a semipermeable housing. In the stomach, the water in the GI fluid is continuously absorbed through the semipermeable membrane into osmotically active compartment to dissolve the osmotically active salt. The osmotic pressure thus created acts on the collapsible bag and in turn forces the drug reservoir compartment to reduce its volume and activate drug release through the delivery orifice. The floating support is also made to contain a bioerodible plug that erodes after a predetermined time to deflate the support. The deflated drug delivery system is then emptied from the stomach. Bioadhesive drug delivery system The term bioadhesion is defined as adhesion to biological surface i.e. mucus and/or mucosal surface. In instances when the polymeric system interacts with mucus layer only, it is referred as mucoadhesion. In order to develop an ideal oral bioadhesive system, it is important to have a through understanding of mucosa, bioadhesive polymers and mucin-polymer interactions in the physiological environment. Intestinal mucosa is composed of high molecular weight glycoproteins hydrated and covering the mucosa with a continuous adherent blanket. Mucin glycoproteins are rich with fucose and sialic acid groups at the terminal ends which provide a net negative charge in the acidic environment. The thickness of the mucin gel layer varies in different regions of the GIT with thickness ranging between μm in stomach to μm in the colon. Cohesion of the mucin gel is dependent upon the glycoprotein concentration. The mucus layer is created biologically to play a number of important functions of protecting the underlying tissues from various diffusing/corrosive elements such as enzymes, acid and other toxic molecules. Also being a visco-elastic gel, it helps in the passage of food over the epithelium, thereby minimizing potential erosive damages. The mucus layer, in addition to providing protection, provides a barrier to drug absorption. Various investigators have proposed different mucin-polymer interactions, such as Wetting and swelling of the polymer to permit intimate contact with the biological tissue Interpenetration of bioadhesive polymer chains and entanglement of polymer and mucin chains. Formation of weak chemical bonds Sufficient polymer mobility to allow spreading Water transport followed by mucosal dehydration (Lehr, 1992; Mortazavi, 1993). International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 598
11 As the mucus layer comes into contact with bioadhesive coated system, various non-specific (Vander Waals, hydrogen bonding and/or hydrophobic interactions) or specific interactions occur between the complimentary structures. However, these interactions last only until the turnover process of mucin and, in order for a bioadhesive system to be successful; it should release its drug contents during this limited adhesion time. Raft-forming Here, a gel-forming solution (e.g. sodium alginate solution containing carbonates or bicarbonates) swells and forms a viscous cohesive gel containing entrapped CO 2 bubbles on contact with gastric fluid. Formulations also typically contain antacids such as aluminium hydroxide or calcium carbonate to reduce gastric acidity. Because raft-forming produce a layer on the top of gastric fluids, they are often used for gastro esophageal reflux treatment as with liquid gaviscon. Low density Gas-generating inevitably have a lag time before floating on the stomach contents, during which the dosage form may undergo premature evacuation through the pyloric sphincter. Low-density (<1 g/cm3) with immediate buoyancy have therefore been developed. They are made of low-density materials, entrapping oil or air. Most are multiple unit, and are also called microballoons because of the low-density core (Sato and Kawashima, 2004). Generally, techniques used to prepare hollow microspheres involve simple solvent evaporation or solvent diffusion methods. Polycarbonate, Eudragit S, cellulose acetate, calcium alginate, agar and low methoxylated pectin are commonly used as polymers. Buoyancy and drug release are dependent on quantity of polymer, the plasticizer polymer ratio and the solvent used. Expandable A dosage form in the stomach will withstand gastric transit if it is bigger than the pyloric sphincter (Caldwell et al., 1988). However, the dosage form must be small enough to be swallowed, and must not cause gastric obstruction either singly or by accumulation. Thus, three configurations are required, a small configuration for oral intake, an expanded gastroretentive form and a final small form enabling evacuation following drug release. Unfoldable are made of biodegradable polymer; the concept is to make a carrier, such as a capsule, incorporating a compressed system, which extends in the stomach. Caldwell et al., 1988 proposed different geometric forms (tetrahedron, ring or planar membrane (4-lobed, disc or 4-limbed cross form) of biodegradable polymer compressed within a capsule. Swellable System Swellable are also retained because of their mechanical properties. The swelling usually results from osmotic absorption of water. The dosage form is small enough to be swallowed, and swells in gastric liquids, the bulk enable gastric retention and maintains the stomach in a fed state, suppressing housekeeper waves. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 599
12 Superporous hydrogels Although these are swellable, they differ sufficiently from the conventional types to warrant separate classification (Chen and park, 2000) with pore size ranging between 10 nm and 10 μm. Absorption of water by conventional hydrogel is very slow process and several hours may be needed to reach an equilibrium state during which premature evacuation of the dosage form may occur. Superporous hydrogel, average pore size > 100 μm, swell to equilibrium size within a minute, due to rapid water uptake by capillary wetting through numerous interconnected open pores. Moreover they swell to a large size (swelling ratio 100 or more) and are intended to have sufficient mechanical strength to withstand pressure by gastric contractions. This is achieved by a co- formulation of a hydrophilic particulate material, Ac-Di- Sol (crosscarmellose sodium). Magnetic system These appear as small gastroretentive capsules containing a magnetic material, whose elimination from the stomach is prevented by the interaction with a sufficiently strong magnet applied to the body surface in the region of the stomach. Despite numerous reports about successful tests, the real applicability of such is doubtful because the desired results can be achieved only provided that the magnet position is selected with very high precision. Probably, the development of new conveniently applied magnetic field sources will improve this concept. Self-unfolding The self-unfolding are capable of mechanically increasing in size relative to the initial dimensions. This increase prevents the system from passing via the pylorus and provides for its prolonged stay in the stomach. A drug can be either contained in a polymeric composition of the gastroretentive system or included as a separate component. Several methods were suggested to provide for the self-unfolding effect. (1) The use of hydrogels swelling in contact with the gastric juice. (2) Osmotic, comprising an osmotic medium in a semipermeable membrane. (3) Systems based on low-boiling liquids converting into a gas at the body temperature. High density Gastric contents have a density close to water (1.004 g /cm 3 ). When the patient is upright small high-density pellets sink to the bottom of the stomach where they become entrapped in the folds of the antrum and withstand the peristaltic waves of the stomach wall. A density close to 2.5 g/cm 3 seems necessary for significant prolongation of gastric residence time and barium sulphate, zinc oxide, iron powder, titanium dioxide are used as excipients. International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 600
13 CONCLUSION Gastroretentive drug delivery have emerged as a current approaches of enhancing bioavailability and controlled delivery of drugs that exhibit an absorption window. Gastroretentive drug delivery approaches comprised mainly of floating, bioadhesive, swelling, magnetic, and high density. These not only provide controlled release of the drug but also present the drug in an absorbable form at the regions of optimal absorbtion. All these drug delivery have their own advantages and drawbacks. To design a successful GRDDS, it is necessary to take into consideration the physicochemical properties of the drug, physiological events in the GIT, formulation strategies, and correct combination of drug and excipients. REFERENCES A.J.Moes (1993). Crit.Rev.Ther.Drug Carrier Syst: Vol.10(2) A.Streubel (2006). Current option in Pharmacology: Vol A.A.Deshpande, N.H.Shah, C.T.Rhodes and W.Malick (1997). Pharm.Res: Vol B.M.Singh and K.H.Kim (2000). J.Control.Rel: Vol C.M.Lehr (1994). Crit.Rev.Ther.Drug Carrier Syst: Vol G.L.Chen and W.H.Hao (1998). Drug Delivery Ind. Pharm: Vol.24(11) G.Sanjay and S.Sharma (2003). Business Briefing Pharmtech. H.Bechgaard and K.Ladefoged (1978). J.Pharm.Pharmcol: Vol H.Katayamma, T.Nishimura, S.Ochi, Y.Tsuruta and Y.Yamazaki (1999). Biol.Pharm.Bull: Vol J.Chen and K.Park (2000). J.Control.Rel: Vol.65(17) J.Guitierrez-rocca, H.Ornidian and K.Shah (2003). Business Briefing Pharmtech: J.Urquhart and F.Theeuwes (1984). US Patent: 4,434,153. K.G.Prathiban, B.S.Kumar, R.Manivannam and D.S.Kumar (2010). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research: Vol.1(5) K.Kavitha, S.K.Yadav and T.T.Mani (2010). Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences: Vol.1(2) L.J.Caldwell, R.C.Gardner and R.C.Cargill (1988). US Patent: 4,735,804. M.Marvola, A.Kannikoski, H.Aito and S.Nykanen (1989). Int.J.Pharm: Vol M.Oth, M. Franz, J.Timmermans and A.Moes (1992). Pharma. Res: Vol N.Ozdemir, S.Ordu and Y.Ozkan (2000). Drug Dev.Ind.Pharm.: Vol.26(8) P.Mojoverian and K.K.H.Chan (1988). Pharm.Res. R.C.Mamajek, E.S.Moyer (1980). US Patent: 4,207,890. R.C.Rowe, P.J.Sheskey and P.J.Weller (2003). Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients: 4 th ed (London). R.Garg and G.D.Gupta (2008). Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: Vol.7(3) R.Groning and G.Heum (1989). Int.J.Pharm: Vol R.J.Dias, S.S.Sakhare and K.K.mali (2009). Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Resarch: Vol.8(4) R.S.R.Murthy and L.H.V.Reddy (2000). Crit.Rev.Ther.Drug Carrier Syst: Vol.19(6) S.Anand and R.K.Kotecha (2010). International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research: Vol.2(2) S.Arora, J.Ali, A.Ahuja, K.K.Roop and B.Sanjula (2005). AAPS PharmSciTech: Vol.6(3) S.H.Shaha, J.K.Patel, K.Pundarikakshudu and N.V.Patel (2009). Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences: Vol.4(1) S.J.Hwang, H.Park and K.Park (1998). Crit.Rev.Ther.Drug Carrier Syst: Vol.15(3) S.N.Brahma (2000). Journal of Controlled Release: Vol S.S.Davis (2005). Drug Discovery Today: Vol S.Y.Hou, V.E.Cowles and B.Berner (2003). Crit.Rev.Ther.Drug Carrier Syst: Vol.20(6) V.F.Patel and N.M.Patel (2006). AAPS PharmSciTech: Vol.7(1) V.M.Lenaerts and R.Gurny (1990). CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. Y.Kawashima, H.Niwa, H.Takeuchi, T.Hino and y.itoh (1992). J.Pharm.Sci: Vol Y.W.Chien (1992). Novel Drug Delivery System: 2 nd edition International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technology Page: 601
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper
 D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use
 Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
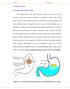 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Review Article
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 4
 (A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
(A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
Physical Pharmacy. Interfacial phenomena. Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department
 Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 73 Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ashwini T *, Shabaraya AR and Vineetha K Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 73 Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ashwini T *, Shabaraya AR and Vineetha K Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College
Topical Preparations
 Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
What is Nanotechnology?
 Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
1 INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Oral Drug Delivery System: 1. Introduction
 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Oral Drug Delivery System: The most widely utilized and preferred route of administration amongst all the routes that have been explored till date, is the oral route for the systemic
1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Oral Drug Delivery System: The most widely utilized and preferred route of administration amongst all the routes that have been explored till date, is the oral route for the systemic
Biopharmaceutics. Lec: 4
 64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
OVERVIEW OF ORAL MUCOSA 1 : A] Structure:
![OVERVIEW OF ORAL MUCOSA 1 : A] Structure: OVERVIEW OF ORAL MUCOSA 1 : A] Structure:](/thumbs/95/123509578.jpg) INTRODUCTION Drug delivery systems that can precisely control the release rate of drug to specific body sites have an enormous potential in the healthcare world. The last two decades in the pharmaceutical
INTRODUCTION Drug delivery systems that can precisely control the release rate of drug to specific body sites have an enormous potential in the healthcare world. The last two decades in the pharmaceutical
Pharmacokinetics Dr. Iman Lec. 3
 Pharmacokinetics r. Iman Lec. 3 Pharmacokinetics A dequate drug doses must be delivered to the target organ to get therapeutic but not toxic levels. So, pharmacokinetic examines the movement of drug over
Pharmacokinetics r. Iman Lec. 3 Pharmacokinetics A dequate drug doses must be delivered to the target organ to get therapeutic but not toxic levels. So, pharmacokinetic examines the movement of drug over
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Large scale production
 Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS OF LEVETIRACETAM
 DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS OF LEVETIRACETAM Dissertation submitted to The Tamilnadu Dr. M.G.R Medical University, Chennai -32 In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the award
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS OF LEVETIRACETAM Dissertation submitted to The Tamilnadu Dr. M.G.R Medical University, Chennai -32 In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the award
Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences
 Srujana G. L.V et al / J Global Trends Pharm Sci, 2016; 7( (2):3065-3073 An Elsevier Indexed Journal ISSN-2230-7346 Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM-
Srujana G. L.V et al / J Global Trends Pharm Sci, 2016; 7( (2):3065-3073 An Elsevier Indexed Journal ISSN-2230-7346 Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM-
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 44 Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Rakshith M*, Viresh KC and Shabaraya AR Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 44 Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Rakshith M*, Viresh KC and Shabaraya AR Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Right time, right place: bioactive delivery systems
 Right time, right place: bioactive delivery systems Zhigao Niu, Alejandra Acevedo-Fani & Ali Rashidinejad Science of Food Team Riddet Institute, Massey University Developing High-Value Foods Food Systems
Right time, right place: bioactive delivery systems Zhigao Niu, Alejandra Acevedo-Fani & Ali Rashidinejad Science of Food Team Riddet Institute, Massey University Developing High-Value Foods Food Systems
Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug
 Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual,
 Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche
 Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
APPLIED CHEMISTRY SURFACE TENSION, SURFACTANTS TYPES OF SURFACTANTS & THEIR USES IN TEXTILE PROCESSING
 APPLIED CHEMISTRY SURFACE TENSION, SURFACTANTS TYPES OF SURFACTANTS & THEIR USES IN TEXTILE PROCESSING Lecture No. 13 & 14 2 Surface Tension This property of liquids arises from the intermolecular forces
APPLIED CHEMISTRY SURFACE TENSION, SURFACTANTS TYPES OF SURFACTANTS & THEIR USES IN TEXTILE PROCESSING Lecture No. 13 & 14 2 Surface Tension This property of liquids arises from the intermolecular forces
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Research & Reviews in. Floating drug delivery systems: A review
 Trade Science Inc. June 2009 Research & s in Volume 3 Issue 1 BioSciences RRBS, 3(1), 2009 [73-83] Floating drug delivery systems: A review P.Sobhita Rani*, Muthu Prasanna P.Surya Prabha K.Praveen Gaddam,
Trade Science Inc. June 2009 Research & s in Volume 3 Issue 1 BioSciences RRBS, 3(1), 2009 [73-83] Floating drug delivery systems: A review P.Sobhita Rani*, Muthu Prasanna P.Surya Prabha K.Praveen Gaddam,
Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides
 Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides John Mitchell John.Mitchell@biopolymersolutions.co.uk Acknowledgements Fundamentals of Hydrocolloid Technology Course (2003-2009) Rob Winwood Colin Melia Steve Harding
Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides John Mitchell John.Mitchell@biopolymersolutions.co.uk Acknowledgements Fundamentals of Hydrocolloid Technology Course (2003-2009) Rob Winwood Colin Melia Steve Harding
Dyspepsia. Dyspepsia covers upper abdominal pain, fullness, early satiety, bloating, and nausea.
 Antacids Hawler medical university Collage of pharmacy/ fourth year /pharmacy practice Sham A. Talat Shareef (B.Sc. Msc. clinical pharmacy) 2017-2018 Sham_talat@yahoo.com Head of Department Of Clinical
Antacids Hawler medical university Collage of pharmacy/ fourth year /pharmacy practice Sham A. Talat Shareef (B.Sc. Msc. clinical pharmacy) 2017-2018 Sham_talat@yahoo.com Head of Department Of Clinical
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy
 On-Line Formulation Training - Anywhere In The World - Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy Belinda Carli Director, Institute of Personal Care Science Image showing absorbance in the outer stratum
On-Line Formulation Training - Anywhere In The World - Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy Belinda Carli Director, Institute of Personal Care Science Image showing absorbance in the outer stratum
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Floating Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 610 : A Review Vinay Kumar Katakam, Jagan Mohan Somagoni, Sunil Reddy, Chandra Mohan Eaga, Bala Ramesha Chary Rallabandi, Madhusudan Rao Yamsani* Centre for Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics, University
610 : A Review Vinay Kumar Katakam, Jagan Mohan Somagoni, Sunil Reddy, Chandra Mohan Eaga, Bala Ramesha Chary Rallabandi, Madhusudan Rao Yamsani* Centre for Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics, University
