Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Digestive System
|
|
|
- Tyrone Emil James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
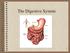
1 Digestive System The digestive system consists of the digestive tract oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and anus and its associated glands salivary glands, liver, and pancreas. Also called the gastrointestinal tract or alimentary canal, its function is to obtain from ingested food the molecules necessary for the maintenance, growth, and energy needs of the body. During digestion proteins, complex carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and fats are broken down into their small molecule subunits that are easily absorbed through the small intestine lining. Most water and electrolytes are absorbed in the large intestine. It consists of a hollow tube of varying diameter, composed of a mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa (or adventitia).
2 Structures within the digestive tract allow the following: 1) ingestion, or introduction of food and liquid into the oral cavity. 2) Mastication, or chewing, which divides solid food into digestible pieces. 3) Motility, muscular movements of materials through the tract. 4) Secretion of lubricating and protective mucus, digestive enzymes, acidic and alkaline fluids, and bile. 5) Hormone release for local control of motility and secretion. 6) Chemical digestion or enzymatic degradation of large macromolecules in food to smaller molecules and their subunits. 7) Absorption of the small molecules and water into the blood and lymph. 8) Elimination of indigestible, unabsorbed components of food. General structure of the digestive tract The digestive tract is a hollow tube with a lumen of variable diameter and a wall made up of four main layers: 1) The mucosa consists of an epithelial lining; an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue rich in blood vessels, lymphatics, lymphocytes, smooth muscle cells, and often containing small glands; and a thin layer of smooth muscle called the muscularis mucosae separating mucosa from submucosa and allowing local movements of the mucosa. The mucosa is also frequently called a mucous membrane. 2) The submucosa contains denser connective tissue with larger blood and lymph vessels and the submucosal (Meissner) plexus of autonomic nerves. It may also contain glands and significant lymphoid tissue. 3) The thick muscularis (or muscularis externa) is composed of smooth muscle cells organized as two or more sublayers. In the internal sublayer (closer to the lumen), the fiber orientation is generally circular; in the external sublayer it is longitudinal. The connective tissue between the muscle sublayers contains blood and lymph vessels, as well as the myenteric (Auerbach) nerve plexus of many autonomic neurons aggregated into small ganglia and interconnected by pre- and postganglionic nerve fibers. This and the submucosal plexus together comprise the enteric nervous system of the digestive tract. Contractions of the muscularis, which mix and propel the luminal contents forward, are generated and coordinated by the myenteric plexus.
3 4) The serosa is a thin layer of loose connective tissue, rich in blood vessels, lymphatics, and adipose tissue, with a simple squamous covering epithelium or mesothelium. In the abdominal cavity, the serosa is continuous with mesenteries, thin membranes covered by mesothelium on both sides that support the intestines. Mesenteries are continuous with the peritoneum, a serous membrane that lines that cavity. In places where the digestive tract is not suspended in a cavity but bound directly to adjacent structures, such as in the esophagus, the serosa is replaced by a thick adventitia, a connective tissue layer that merges with the surrounding tissues and lacks mesothelium. Oral cavity The oral cavity is lined with stratified squamous epithelium, which may be keratinized, partially keratinized, or nonkeratinized depending on the location. The keratinized cell layers resist damage from abrasion and are best developed in the masticatory mucosa on the gingiva (gum) and hard palate. The lamina propria in these regions rests directly on the periosteum of underlying bone. Nonkeratinized squamous epithelium predominates in the lining mucosa over the soft palate, cheeks, the floor of the mouth, and the pharynx, the posterior region of the oral cavity leading to the esophagus. Lining mucosa overlies a thick submucosa containing many minor salivary glands, which secrete continuously to keep the mucosal surface wet, and diffuse lymphoid tissue.
4 Lips Lips, soft pliable anatomical structures that form the mouth margin of most vertebrates, composed of a surface epidermis (skin), connective tissue, and (in typical mammals) a muscle layer. In man the outer skin contains hair, sweat glands, and sebaceous (oil) glands. The edges of the lips are covered with reddish skin, sometimes called the vermilion border, and abundantly provided with sensitive nerve endings. The reddish skin is a transition layer between the outer, hair-bearing tissue and the inner mucous membrane. The interior surface of the lips is lined with a moist mucous membrane. In newborn infants the inner surface is much thicker, with sebaceous glands and minute projections called papillae. Tongue The tongue is a mass of striated muscle covered by mucosa, which manipulates ingested material during mastication and swallowing. The muscle fibers are oriented in all directions, allowing a high level of mobility. Connective tissue between the small fascicles of muscle is penetrated by the lamina propria, which makes the mucous membrane strongly adherent to the muscular core. The lower surface of the tongue is smooth, with typical lining mucosa. The dorsal surface is irregular, having hundreds of small protruding papillae of various types on its anterior two-thirds and the massed lingual tonsils on the posterior third, or root of the tongue. The papillary and tonsillar areas of
5 the lingual surface are separated by a V-shaped groove called the sulcus terminalis. The lingual papillae are elevations of the mucous membrane that assume various forms and functions. There are four types: 1) Filiform papillae are very numerous, have an elongated conical shape, and are heavily keratinized, which gives their surface a gray or whitish appearance. They provide a rough surface that facilitates movement of food during chewing. 2) Fungiform papillae are much less numerous, lightly keratinized, and interspersed among the filiform papillae. They are mushroom-shaped with well vascularized and innervated cores of lamina propria. 3) Foliate papillae consist of several parallel ridges on each side of the tongue, anterior to the sulcus terminalis, but are rudimentary in humans, especially older individuals. 4) Vallate (or circumvallate) papillae are the largest papillae, with diameters of 1 to 3 mm. Eight to twelve vallate papillae are normally aligned just in front of the terminal sulcus.
6 Taste buds Taste buds are ovoid structures within the stratified epithelium on the tongue s surface, which sample the general chemical composition of ingested material. Approximately 250 taste buds are present on the lateral surface of each vallate papilla, with many others present on fungiform and foliate (but not the keratinized filiform) papillae. They are not restricted to papillae and are also widely scattered elsewhere on the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the tongue, where they are also continuously flushed by numerous minor salivary glands. Taste buds detect at least five broad categories of tastants: sodium ions (salty); hydrogen ions from acids (sour); sugars and related compounds (sweet); alkaloids and certain toxins (bitter); and amino acids such as glutamate and aspartate. Teeth In the adult human there are normally 32 permanent teeth, arranged in two bilaterally symmetric arches in the maxillary and mandibular bones. Each tooth has a crown exposed above the gingiva, a constricted neck at the gum, and one or more roots that fit firmly into bony sockets in the jaws called dental alveoli. The crown is covered by very hard, acellular enamel and the roots by a bone-like tissue called cementum. These two coverings meet at the neck of the tooth. The bulk of a tooth is composed of another calcified material, dentin, which surrounds an internal pulp cavity. Dental pulp is highly vascular and well-innervated and consists largely of loose, mesenchymal connective tissue with much ground substance, thin collagen fibers, fibroblasts, and mesenchymal stem cells. The pulp cavity narrows in each root as the root canal, which extends to an opening (apical foramen) at the tip of each root for the blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves of the pulp cavity. The periodontal ligaments are fibrous connective tissue bundles of collagen fibers inserted into both the cementum and the alveolar bone.
7 Esophagus The esophagus is a muscular tube, about 25 cm long in adults, which transports swallowed material from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophageal mucosa has nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, and the submucosa contains small mucus-secreting glands, the esophageal glands, which lubricate and protect the mucosa. Near the stomach the mucosa also contains groups of glands, the esophageal cardiac glands, which secrete additional mucus. Swallowing begins with voluntary muscle action but finishes with involuntary peristalsis. In approximately the upper one-third of the esophagus, the muscularis is exclusively skeletal muscle like that of the tongue. The middle portion of the esophagus has a combination of skeletal and smooth muscle fibers, and in the lower third the muscularis is exclusively smooth muscle. Only the distal 1 to 2 cm of the esophagus, in the peritoneal cavity, is covered by serosa; the rest is enclosed by the loose connective tissue of the adventitia, which blends into the surrounding tissue.
8 Stomach The stomach is a greatly dilated segment of the digestive tract whose main functions are: To continue the digestion of carbohydrates initiated by the amylase of saliva, To add an acidic fluid to the ingested food and mixing its contents into a viscous mass called chyme by the churning activity of the muscularis, To begin digestion of triglycerides by a secreted lipase. To promote the initial digestion of proteins with the enzyme pepsin. Four major regions make up the stomach: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus: - The cardia is a narrow transitional zone, cm wide, between the esophagus and the stomach. - The pylorus is the funnel-shaped region that opens into the small intestine. Both these regions are primarily involved with mucus production and are similar histogically. -The much larger fundus and body regions are identical in microscopic structure and are the sites of gastric glands releasing acidic gastric juice. The mucosa and submucosa of the empty stomach have large, longitudinally directed folds called rugae, which flatten when the stomach fills with food. The wall in all regions of the stomach is made up of all four major layers.
9 The mucosal surface of the stomach is a simple columnar epithelium that invaginates deeply into the lamina propria. The invaginations form millions of gastric pits, each with an opening to the stomach lumen. The surface mucous cells that line the lumen and gastric pits secrete a thick, adherent, and highly viscous mucous layer that is rich in bicarbonate ions and protects the mucosa from both abrasive effects of intraluminal food and the corrosive effects of stomach acid. The gastric glands are lined by epithelium with four major cell types, as well as their pluripotent stem cells that are located in the narrow neck regions of these glands: 1) Mucous neck cells include immature precursors of the surface mucous cells but produce less alkaline mucus while migrating up into the gastric pits. 2) Parietal cells are large cells with many mitochondria and large intracellular canaliculi for production of HCl in the gastric secretion; they also secrete intrinsic factor for vitamin B uptake. 3) Chief (zymogenic) cells, clustered mainly in the lower half of the gastric glands, secrete the protein pepsinogen that is activated by the low ph in the lumen to form the major protease pepsin. 4) Enteroendocrine cells are scattered epithelial cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system, which release peptide hormones to regulate activities of neighboring tissues during food digestion. The mucosa of the stomach cardiac and pyloric regions has branching cardial and pyloric glands that consist almost entirely of columnar mucous cells, lacking parietal and chief cells.
10 Small intestine The small intestine is approximately 7 m long and has three regions: the duodenum (proximal), jejunum (middle), and ileum (distal). Function: The small intestine secretes several hormones; it continues and largely completes the digestion of foodstuffs and absorbs the resulting metabolites. The lining of the small intestine shows a series of permanent circular or semilunar folds (plicae circulares), consisting of mucosa and submucosa, which are best developed in the jejunum. Densely covering the entire mucosa of the small intestine are short (0.5 to 1.5-mm) mucosal outgrowths called villi that project into the lumen. These finger- or leaflike projections are covered by a simple columnar epithelium of absorptive cells called enterocytes, with many interspersed goblet cells. Each villus has a core of loose connective tissue that extends from the lamina propria and contains fibroblasts, smooth muscle fibers, lymphocytes and plasma cells, fenestrated capillaries, and a central lymphatic called a lacteal. Between the villi are the openings of short tubular glands called intestinal glands or crypts (or crypts of Lieberkühn) and the epithelium of each villus is continuous with that of the intervening glands. The epithelium of the intestinal glands includes differentiating cells and pluripotent stem cells for all the cell types of the small intestine include the following:
11 1) Enterocytes, the absorptive cells, are tall columnar cells, each with an oval nucleus located basally: The apical end of each enterocyte displays a prominent ordered region called the striated (or brush) border is seen to be a layer of densely packed microvilli. Each enterocyte has an average of 3000 microvilli. Microvilli, villi, and the plicae circulares all greatly increase the mucosal surface area in contact with nutrients in the lumen, which is an important feature in an organ specialized for nutrient absorption. 2) Goblet cells are interspersed among the absorptive enterocytes. They secrete glycoprotein mucins that are then hydrated to form mucus, whose main : - Function is to protect and lubricate the lining of the intestine. 3) Paneth cells, located in the basal portion of the intestinal crypts below the stem cells, are exocrine cells with large, eosinophilic secretory granules in their apical cytoplasm. Paneth cell granules release lysozyme, phospholipase A2, and hydrophobic peptides called defensins, all of which bind and break down membranes of microorganisms and bacterial cell walls. - Function: paneth cells have an important role in innate immunity and in regulating the microenvironment of the intestinal crypts. 4) Enteroendocrine cells are present in varying numbers throughout the length of the small intestine, secreting various peptide hormones. Many of these are of the open type, in which the constricted apical end of the cell contacts the intestinal lumen and has chemoreceptors similar to those of taste buds, sampling levels of certain nutrients such as sugars to regulate hormone release basally.
12 5) M (microfold) cells are specialized epithelial cells in the mucosa of the ileum overlying the lymphoid follicles of Peyer patches. M cells selectively endocytose antigens and transport them to the underlying lymphocytes and dendritic cells, which then migrate to lymph nodes for an appropriate immune response. Large intestine The large intestine consists of the cecum, colon (ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon), rectum, anal canal, and appendix. The large intestine contains some digestive enzymes received from the small intestine. It houses bacteria that produce vitamin B12 and vitamin K; the former is necessary for hemopoiesis and the latter for coagulation. The large intestine produces abundant mucus, which lubricates its lining and facilitates the passage and elimination of feces. Function: The large intestine functions primarily in the absorption of electrolytes, fluids and gases. Dead bacteria and indigestible remnants of the ingested material are compacted into feces. The mucosa lacks villi and except in the rectum has no major folds. Less than one-third as long as the small intestine, the large intestine has a greater diameter (6-7 cm). The wall of the colon is puckered into a series of large sacs called haustra.the mucosa of the large bowel is penetrated throughout its length by tubular intestinal glands. These and the intestinal lumen are lined by goblet and absorptive cells, with a small number of enteroendocrine cells. The columnar
13 absorptive cells or colonocytes have irregular microvilli and dilated intercellular spaces indicating active fluid absorption. Goblet cells producing lubricating mucus become more numerous along the length of the colon and in the rectum.
14 The distal end of the digestive tract is the anal canal, 3-4 cm long. At the rectoanal junction the simple columnar mucosal lining of the rectum is replaced by stratified squamous epithelium. The mucosa and submucosa of the anal canal form several longitudinal folds, the anal columns, in which the lamina propria and submucosa include sinuses of the rectal venous plexus. Near the anus the circular layer of the rectum s muscularis forms the internal anal sphincter. Defecation involves the action of voluntary muscle comprising the external anal sphincter.
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Dana Alrafaiah. Dareen Abu Shalbak. Mohammad Almuhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
Connective tissue The Digestive System
 Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Esophagus. Transport is achieved by peristaltic contractions and relaxation of the esophageal sphincters (upper and lower)
 GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
GI Histology 2 Esophagus is a muscular tube whose function is to transport foodstuffs from the mouth to the stomach and to prevent the retrograde flow of gastric contents Transport is achieved by peristaltic
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture:
 السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Objectives. Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract
 GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
General functions of digestive system. Ch. 15 The Digestive System. General histology of the wall of the digestive tract. Overview of digestive organs
 Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Digestive System. Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences
 Digestive System Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences Today we will discuss: Histological layers of alimentary canal Oral cavity Lip
Digestive System Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences Today we will discuss: Histological layers of alimentary canal Oral cavity Lip
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE Remember the structures of the digestive system 1
 BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
BELLWORK DEFINE: PERISTALSIS CHYME RUGAE 2.07 Remember the structures of the digestive system 1 STANDARD 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all body systems, and explain how
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Gastrointestinal System!
 Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Week 12 - Outline. Outline. Digestive System I Major Organs. Overview of Digestive System
 Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Outline Week 12 - Digestive System I Major Organs Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Digestive Tract Function GI Tract Structure Regulation of the
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Connective tissue The Digestive System
 Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion?
 Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Dorsum of the tongue. Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types. Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove
 Histology of TONGUE Figure 22.13 Dorsum of the tongue Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types a. filiform papillae,
Histology of TONGUE Figure 22.13 Dorsum of the tongue Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types a. filiform papillae,
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
GI Histology Lab 1. Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji
 GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
the serous membranes lining the peritoneal cavity continuously produce what?
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) - two groups of organs form the digestive system (see Fig. 22-1): 1. digestive tract what is it also called? list the organs that make
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) - two groups of organs form the digestive system (see Fig. 22-1): 1. digestive tract what is it also called? list the organs that make
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Digestive System II - Lower tract Revised
 ANAT D502 Basic Histology Digestive System II - Lower tract Revised 10.12.12 Outline: I. Small intestine II. Enterocyte digestion II. Hepatic portal system IV. Large intestine V. Enteric nervous system
ANAT D502 Basic Histology Digestive System II - Lower tract Revised 10.12.12 Outline: I. Small intestine II. Enterocyte digestion II. Hepatic portal system IV. Large intestine V. Enteric nervous system
The Human Body: Digestive System
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. 1. Digestive System Is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus Carries out digestion which is the process of breaking down food
Directions: Fill in the blanks. 1. Digestive System Is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus Carries out digestion which is the process of breaking down food
Tissues and organs PART 1
 Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function
 Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
Digestion and Absorption. Food:
 Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
الله الر ح م ن الر ح يم مسب
 بسم رلا هللارلا هللا This is the second histology lecture in the GI system. In this lecture, we will discuss the histology of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine so prepare yourself.this sheet
بسم رلا هللارلا هللا This is the second histology lecture in the GI system. In this lecture, we will discuss the histology of the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine so prepare yourself.this sheet
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System 1
 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT KAMPALA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY DAR ES SALAAM TANZANIA Anatomy of the GI Tract The GI tract is essentially a hollow tube connecting the mouth to the anus.
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
Nutrition and the Digestive System
 C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
Overview of the Digestive
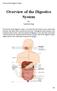 Overview of the Digestive System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although
Overview of the Digestive System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 The Human Digestive System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Define the human digestive
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 The Human Digestive System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Define the human digestive
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
 Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://anatronica.com/anatronica-flashabdominal-cavity.html GI (gastrointestinal) tract = alimentary canal Ingestion Taking in food through
Chapter 16 Adapted from: Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc http://anatronica.com/anatronica-flashabdominal-cavity.html GI (gastrointestinal) tract = alimentary canal Ingestion Taking in food through
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food
 UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
UNIT 2: From Food to Fuel: How the Human Body Utilizes Food Introduction to the Digestive System PART ONE Systems of the Body The Digestive System Also referred to as alimentary system, the gut, gastrointestinal
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove.
 By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
The Digestive system
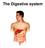 The Digestive system The GI tract (gastrointestinal tract) Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus The accessory digestive organs Supply secretions contributing to the breakdown
The Digestive system The GI tract (gastrointestinal tract) Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus The accessory digestive organs Supply secretions contributing to the breakdown
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
