Chapter 10. An Overview of the Muscle System
|
|
|
- Maurice Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System
2 The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External abdominal oblique Tensor fasciae latae Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Pectoralis minor Coracobrachialis Serratus anterior Brachialis Rectus abdominis Supinator Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor pollicis longus Transverse abdominal Internal abdominal oblique Pronator quadratus Semispinalis capitis Sternocleidomastoid Splenius capitis Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Rhomboideus minor Rhomboideus major Deltoid (cut) Infraspinatus Serratus anterior Triceps brachii (cut) Serratus posterior inferior External abdominal oblique Internal abdominal oblique Erector spinae Flexor carpi ulnaris Extensor digitorum (cut) Gluteus minimus Occipitalis Trapezius Infraspinatus Teres minor Teres major Triceps brachii Latissimus dorsi Extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis External abdominal oblique Extensor digitorum Gluteus medius Extensor carpi ulnaris Gluteus maximus Lateral rotators Adductor longus Sartorius Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Adductors Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Gracilis Adductor magnus Iliotibial band Semimembranosus Biceps femoris Gracilis Semitendinosus Iliotibial band Biceps femoris Gastrocnemius (cut) Fibularis longus Tibialis anterior Extensor digitorum longus Gastrocnemius Soleus Extensor digitorum longus Soleus (cut) Tibialis posterior Flexor digitorum longus Extensor hallucis longus Fibularis longus Calcaneal tendon Gastrocnemius Soleus (a) Anterior view (b) Posterior view
3 Classification of Muscles According to Fascicle Orientation (not a learning objective) fusiform muscles thick in middle and tapered at ends biceps brachii, gastrocnemius parallel muscles have uniform width and parallel fascicles can span longer distances than other shapes rectus abdominis, zygomaticus major triangular (convergent) muscles fan-shaped, broad at origin and tapering to a narrower insertion pectoralis major, temporalis pennate muscles fascicles insert obliquely on a tendon (feather shaped) unipennate, bipennate or multipennate palmar interosseus, rectus femoris and deltoid circular muscles (sphincters) ring around body opening orbicularis oculi, urethral and anal sphincters
4 Fascicle Orientation of Muscles Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Fusiform Parallel Triangular Unipennate Bipennate Multipennate Tendon Circular Belly Pectoralis major Tendon Rectus abdominis Biceps brachii Palmar interosseous Rectus femoris Deltoid Orbicularis oculi strength of a muscle and the direction of its pull are determined partly by the orientation of its fascicles
5 The Functions of Muscles Movement // move from place to place, movement of body parts and body contents in breathing, circulation, feeding and digestion, defecation, urination, and childbirth // role in communication speech, writing, and nonverbal communications Stability // maintain posture by preventing unwanted movements // antigravity muscles resist the pull of gravity and prevent us from falling or slumping over // stabilize joints Control openings and passageways // sphincter muscles = internal muscular rings that control the movement of food, bile, blood, and other materials through tubular structures Heat production by skeletal muscles // 85% of our body heat created by skeletal muscles
6 Characteristics of Muscle Tissue responsiveness (excitability) to chemical signals, stretch and electrical changes across the plasma membrane conductivity local electrical change triggers a wave of excitation that travels along the muscle fiber contractility shortens when stimulated extensibility capable of being stretched between contractions elasticity returns to its original resting length after being stretched
7 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue skeletal cardiac smooth muscle converts the chemical energy of ATP into the mechanical energy of motion
8 How to Identify the Three Different Types of Muscle Striated Voluntary Somatic NS Striated Involuntary ANS No striation Involuntary ANS Note: This lecture will primarily cover skeletal muscle.
9 Connective Tissues of a Muscle Organ Tendon What is the structural relationship between the endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium? Skeletal muscle Muscle fascicle Fascia Nerve Blood vessels Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium Muscle fiber How does the connective tissue's fibers (i.e. collagen fibers) change their orrientation between the tendon and the epimysiumendomysium-perimysium? How does the collagen fibers in the tendon interact with the bone tissue? Muscle fascicle Perimysium Muscle fiber
10 Four Connective Tissues of a Skeletal Muscle 1) Endomysium thin sleeve of loose connective tissue surrounding each muscle fiber allows room for capillaries and nerve fibers to reach each muscle fiber 2) Perimysium slightly thicker layer of connective tissue fascicles bundles of muscle fibers wrapped in perimysium carry larger nerves and blood vessels, and stretch receptors
11 Four Connective Tissues of a Skeletal Muscle 3) Epimysium fibrous sheath surrounding the entire muscle outer surface grades into the fascia inner surface sends projections between fascicles to form perimysium 4) Fascia = sheet of connective tissue that may separate and/or connect neighboring muscles from each other /// also between all other organ systems throughout body Compartment Syndrome /// CNN science reporter, Miles Obrien had his arm amputated 12 hours after a heavy case bruised his arm. Why?
12 Connective Tissues of a Muscle Tendon Fascia Skeletal muscle Muscle fascicle Nerve Blood vessels Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium Muscle fiber Muscle fascicle Perimysium Muscle fiber
13 Connective Tissue in a Muscle Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Perimysium Endomysium Muscle fiber, c.s. Fascicle, c.s. Muscle fiber, l.s. Fascicle, l.s. (c) Victor Eroschenko
14 Muscle Attachments Indirect attachment to bone tendons bridge the gap between muscle fiber's ends and bony attachment the collagen fibers of the endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium continue into the tendon /// these fibers weave themselves into the periosteum and penetrate beyond periosteum into the matrix of bone (weaving into the collagen fibers of the bone matrix very strong structural continuity from muscle into bone /// e.g. biceps brachii, Achilles tendon aponeurosis tendon is a broad, flat sheet (palmar aponeurosis) retinaculum connective tissue band that tendons from separate muscles pass under
15
16 Muscles May Also Be Arranged in Layers
17 Muscle Attachments Some muscles have a more direct (fleshy looking) attachment to bone little separation between muscle and bone muscle seems to immerge (but tendon does exist) directly from bone margins of brachialis, lateral head of triceps brachii Some skeletal muscles do not insert onto the periosteum/bone but attach to the dermis of the skin or to the tendons of another muscle e.g. muscles of facial expression (see next slide)
18
19 Muscle Origins and Insertions Origin bony attachment at stationary end of muscle Belly thicker, middle region of muscle between origin and insertion Insertion bony attachment to mobile end of muscle Origins Scapula Extensors: Triceps brachii Long head Lateral head Insertion Origins Humerus Bellies Flexors: Biceps brachii Brachialis Insertion Radius Ulna
20 Classify Muslces by Their A Function Action the effects produced by a muscle to produce or prevent movement Prime mover (agonist) muscle that produces most of force during a joint action Synergist muscle that aids the prime mover stabilizes the nearby joint modifies the direction of movement
21 Functional Groups of Muscles Antagonist opposes the prime mover relaxes to give prime mover control over an action preventing excessive movement and injury antagonistic pairs muscles that act on opposite sides of a joint Fixator muscle that prevents movement of bone allows other muscles to exert force to produce movement.
22 Muscle Actions Across Elbow Prime mover brachialis Origins Scapula Extensors: Triceps brachii Long head Lateral head Insertion Origins Humerus Bellies Flexors: Biceps brachii Brachialis Insertion Radius Ulna Synergist biceps brachii Antagonist triceps brachii Fixator Rhomboids (muscle that holds scapula firmly in place)
23 Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Muscles Classify By Location of Muscle and Location of Action Intrinsic muscles // entirely contained within a region, such as the hand // both its origin and insertion there Tendon sheath Tendon of flexor digitorum profundus Tendon of flexor digitorum superficialis Lumbricals Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti Abductor digiti minimi Flexor retinaculum Tendons of: Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum superficialis Palmaris longus First dorsal interosseous Adductor pollicis Tendon of flexor pollicis longus Flexor pollicis brevis Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Tendons of: Abductor pollicis longus Flexor carpi radialis Flexor pollicis longus (a) Palmar aspect, superficial
24 Intrinsic VS Extrinsic Muscles Common flexor tendon Flexor digitorum superficialis Extrinsic muscles // act on a designated region, but has its origin elsewhere // e.g. fingers extrinsic muscles in the forearm Flexor pollicis longus (b) Intermediate flexor Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons Flexor digitorum profundus tendons
25 Skeletal Muscle Innervation Key factoids about skeletal muscle innervation skeletal muscles are voluntary skeletal muscle contraction requires a conscious signal from brain knowledge about pathway enables the diagnosis of nerve, spinal cord, and brainstem injuries that effects muscle function general pathway = upper motor neuron (corticospinal and corticobulbar) and lower motor neuron (spinal nerves and cranial nerves) Spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord emerge through intervertebral foramina immediately branch into a posterior and anterior ramus innervate muscles below the neck plexus weblike network of spinal nerves adjacent to the vertebral column Cranial nerves arise from the base of the brain emerge through skull foramina innervate the muscles of the head and neck numbered I to XII
26 Learning Strategy examine models, cadavers, dissected animals, or a photographic atlas to get visual images of the muscle when studying a particular muscle, palpate it on yourself if possible locate origins and insertions of muscles on an articulated skeleton study derivation of each muscle name // usually describes the muscle s location, appearance, origin, insertion or action say the names aloud to yourself or study partner, and spell them correctly
27 Learning Strategy examine models, cadavers, dissected animals, or a photographic atlas to get visual images of the muscle when studying a particular muscle, palpate it on yourself if possible locate origins and insertions of muscles on an articulated skeleton study derivation of each muscle name // usually describes the muscle s location, appearance, origin, insertion or action say the names aloud to yourself or study partner, and spell them correctly
28 Athletic Injuries muscles and tendons are vulnerable to sudden and intense stress proper conditioning and warm-up needed common injuries; compartment syndrome shinsplints pulled hamstrings tennis elbow pulled groin rotator cuff injury treat with rest, ice, compression and elevation /// known as RICE no pain, no gain is a dangerous misconception
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Muscle. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Human Anatomy Unit 2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft organs
Human Anatomy Unit 2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft organs
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping
 Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
Biology 210 Chapter 10 Muscles. Types of Muscle Cells. Types of Muscle Cells
 Biology 210 Chapter 10 Muscles PowerPoint by John McGill Based on notes by Beth Wyatt & PowerPoint by Jack Bagwell Types of Muscle Cells Skeletal (Voluntary, Striated) Muscle these are muscles you control;
Biology 210 Chapter 10 Muscles PowerPoint by John McGill Based on notes by Beth Wyatt & PowerPoint by Jack Bagwell Types of Muscle Cells Skeletal (Voluntary, Striated) Muscle these are muscles you control;
Figure 11-1: The lever-fulcrum principle is illustrated by flexion of the forearm.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Muscle Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Muscle Lecture Test Questions Set 1 Fall 2015 1. Muscle cells exhibit the greatest ability to shrink -- this quality of all protoplasm is: a. voluntary b. involuntary c. fusiform d. contractility e. conductivity
Muscle Lecture Test Questions Set 1 Fall 2015 1. Muscle cells exhibit the greatest ability to shrink -- this quality of all protoplasm is: a. voluntary b. involuntary c. fusiform d. contractility e. conductivity
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege To move the skeleton, the tension created by the contraction of the fibers in most skeletal muscles
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege To move the skeleton, the tension created by the contraction of the fibers in most skeletal muscles
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
10/30/2014 APPEARANCE
 APPEARANCE Striated: has a striped appearance due to the thickness of the protein fibers Smooth: protein fibers (which are arranged the same in striated muscle) is not as thick so you cannot see the pattern
APPEARANCE Striated: has a striped appearance due to the thickness of the protein fibers Smooth: protein fibers (which are arranged the same in striated muscle) is not as thick so you cannot see the pattern
Muscular Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 4 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Muscular Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 4 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Role of muscles Prime mover Synergist Agonist Antagonist Stabilizers Neutralizers Role of muscles Agonist: Muscles producing
Muscular Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 4 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Role of muscles Prime mover Synergist Agonist Antagonist Stabilizers Neutralizers Role of muscles Agonist: Muscles producing
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
The Muscular System. - composed of mostly skeletal muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood and connective tissue
 The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk
 The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Chapter 10. The Muscular System. AP1-Lecture Goodwin College. Introduction. In this chapter we will cover: 4/27/2015
 Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Muscle Tissue. Musculoskeletal System (Part A-3) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-3) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-3) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Chapter 11 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Chapter 11 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM 2 Muscle Tissue - refers to all the contractile tissues of the body; skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Muscular System
1 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Chapter 11 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM 2 Muscle Tissue - refers to all the contractile tissues of the body; skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Muscular System
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
Muscle stations Answers
 Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscular System. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
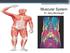 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
Chapter 11: The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Lab Exercise 8. BIOPAC Exercise. Muscle Tissue. Muscles. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Exam 3 Self Quiz. Muscle
 Exam 3 Self Quiz Muscle ***Disclaimer- ALL lectured material is fair game for the exam. The instructor DOES NOT guarantee in any way that these questions will be on the exam. The instructor DOES guarantee
Exam 3 Self Quiz Muscle ***Disclaimer- ALL lectured material is fair game for the exam. The instructor DOES NOT guarantee in any way that these questions will be on the exam. The instructor DOES guarantee
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
The Muscular System OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES. A. Completion
 C H A P T E R 9 The Muscular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe the gross and microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscle. 2. Describe and compare the basic differences
C H A P T E R 9 The Muscular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe the gross and microscopic anatomy of skeletal muscle. 2. Describe and compare the basic differences
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
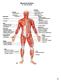 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Muscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Organization
 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Organization AFTER READING THE BOOK, use the following worksheet to link concepts from previous chapters with the concepts of muscle tissue. This worksheet will
Muscular System: Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Organization AFTER READING THE BOOK, use the following worksheet to link concepts from previous chapters with the concepts of muscle tissue. This worksheet will
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER
 ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE
 ERIN C. AMERMAN FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Pundt University of Texas at Tyler MODULE 9.1 OVERVIEW OF SKELETAL S Skeletal muscles are not made of muscle cells
ERIN C. AMERMAN FLORIDA STATE COLLEGE AT JACKSONVILLE Lecture Presentation by Suzanne Pundt University of Texas at Tyler MODULE 9.1 OVERVIEW OF SKELETAL S Skeletal muscles are not made of muscle cells
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
The Muscular System Part A
 10 The Muscular System Part A Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the general function of the body s axial and
10 The Muscular System Part A Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Functional Organization of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the general function of the body s axial and
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
10/4/18. Muscular System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Anatomy. Physiology. Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
 Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction it simply shortens. Lippert
 When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction it simply shortens. Lippert Muscles are attached to bones and to describe the relative points of attachment, we use the terms origin and insertion. Lippert,
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction it simply shortens. Lippert Muscles are attached to bones and to describe the relative points of attachment, we use the terms origin and insertion. Lippert,
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 4.October.2013 Friday
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 4.October.2013 Friday The muscular system consists of all the muscles of the body. The discipline related to the study of muscles is myology. Musculus (muscle) is derived from the
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 4.October.2013 Friday The muscular system consists of all the muscles of the body. The discipline related to the study of muscles is myology. Musculus (muscle) is derived from the
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
The Role of Muscles in Movement
 The Role of Muscles in Movement Muscles can t push, they can only pull as they contract, so most often body movements are the result of the activity of pairs or teams of muscles acting together or against
The Role of Muscles in Movement Muscles can t push, they can only pull as they contract, so most often body movements are the result of the activity of pairs or teams of muscles acting together or against
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46487 1 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m46487 1 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
The Muscular System. Part A
 The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert
 When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
Bell Work. How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive
 Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
7/10/18. Introduction. Muscular System. Anatomy. Physiology. Skeletal Muscle Anatomy. Muscle Fiber
 Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
Introduction Muscular System Chapter 20 Shortening or lengthening of a muscle results from changes in relative positions of one small part of a muscle cell to another To understand contraction, we will
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement Three basic muscle types are found in the body
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement Three basic muscle types are found in the body Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Characteristics
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement Three basic muscle types are found in the body Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Characteristics
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
