The Muscular System. Part A
|
|
|
- Gabriel Merritt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Muscular System Part A 10
2 The Muscular System Part A 10
3 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10
4 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or group of muscles) does, another muscle (or group) undoes
5 Muscle Classification: Functional Groups Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary movement Fixators synergists that immobilize a bone or muscle s origin
6 Naming Skeletal Muscles I call this one Betty
7 Naming Skeletal Muscles Location of muscle bone or body region associated with the muscle Rectus Abdominus
8 Naming Skeletal Muscles Shape of muscle e.g., the deltoid muscle (deltoid = triangle)
9 Naming Skeletal Muscles Relative size e.g., maximus (largest), minimus (smallest), longus (long) Gluteus Maximus
10 Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of fibers e.g., rectus (fibers run straight), transversus, and oblique (fibers run at angles to an imaginary defined axis)
11 Naming Skeletal Muscles Number of origins e.g., biceps (two origins) and triceps (three origins) Triceps Brachii = A long, a lateral and A medial origin
12 Naming Skeletal Muscles Cause this is the occiput Location of attachments named according to point of origin or insertion
13 Naming Skeletal Muscles Action e.g., flexor or extensor, as in the names of muscles that flex or extend, respectively
14 Major Skeletal Muscles: Anterior View The 48 superficial muscles and the diaphragm here are divided into 11 regional areas of the body (definitely know all of these + thenar, hypothenar and extrinsic eye) Head Temporalis Masseter Shoulder Trapezius Deltoid Arm Triceps brachii Biceps brachii Brachialis Forearm Pronator teres Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor digit superficialis Pelvis/thigh Iliopsoas Pectineus Thigh Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Leg Fibularis longus Extensor digitorum longus Tibialis anterior Extensor halluces longus Facial Levator labii sup/inf Levator/depressor anguli oris Epicranius, frontal belly Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major/minor Orbicularis oris Neck Platysma Sternocleidomastoid Thorax Coracobrachialis Subscapularis Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis major Intercostals and diaphragm Abdomen Rectus abdominis Internal oblique Transversus abdominis External oblique Thigh Tensor fasciae latae Sartorius Adductor longus Gracilis Leg Gastrocnemius Soleus
15 Major Skeletal Muscles: Posterior View The 28 superficial muscles here are divided into 7 regional areas of the body (definitely know all of these +, again, thenar, hypothenar and extrinsic eye) Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis Abductor digiti minimi Arm Flexor pollicis brevis Triceps brachii Brachialis Forearm Brachioradialis Extensor carpi radialis longus/brevis Flexor carpi ulnaris Extensor carpi ulnaris Abductor pollicis brevis Extensor digitorum Opponens pollicis Iliotibial tract Leg Gastrocnemius Soleus Fibularis longus Calcaneal (Achilles) tendon Neck Epicranius, occipital belly Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Shoulder Deltoid Infra/supraspinatus Teres major/minor Rhomboid major Latissimus dorsi Hip Thigh Gluteus medius Gluteus maximus Adductor magnus Hamstrings: Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus 89 total
16 Only 165 slides to go in this chapter covering almost every muscle in the body from the smallest eye muscle to the largest thigh muscle. If you haven t started studying yet, tonight would be a very good time.
17 Muscles: Name, O/I, Action, and Innervation Name and description of the muscle be alert to information given in the name (ie, temporalis) Origin and insertion there is always a joint between the origin and insertion Action best learned by acting out a muscle s movement on one s own body (OK, everyone test the fibularis longus right now) Nerve supply name of major nerve that innervates the muscle
18 Muscles of the Scalp Here s the first one. Let s see if you can wrap your head around this one.
19 Muscles of the Scalp Epicranius (occipitofrontalis) bipartite muscle consisting of the: Frontalis & Occipitalis & Galea aponeurotica cranial aponeurosis connecting above muscles These two muscles have alternate actions of pulling the scalp forward and backward
20 Muscles of the Scalp Facial nerve
21 Muscles of the Scalp Epicranius Galea aponeurotica Frontal belly Occipital belly Facial nerve
22
23 Muscles of the Face 11 muscles are involved in lifting the eyebrows, flaring the nostrils, opening and closing the eyes and mouth, and smiling All are innervated by cranial nerve VII (facial nerve) Pretty Face Japanese author Yasuhiro Kano Usually insert in skin (rather than bone), and adjacent muscles often fuse
24 Muscles of the Face Corrugator supercilii Orbicularis oculi Levator labii superioris Zygomaticus minor and major Buccinator Risorius Orbicularis oris Mentalis Depressor labii inferioris Depressor anguli oris Platysma
25 Yes, sorry, you just have to commit them to memory. Here s a sample question from the test The muscles of facial expression are innervated by a) cranial nerve III b) cranial nerve XII c) cranial nerve VII d) cranial nerve V
26
27
28 Muscles of Mastication There are four pairs of muscles involved in mastication (chewing your food) Prime movers temporalis and masseter Grinding movements 2 pterygoids All are innervated by cranial nerve V (trigeminal nerve)
29 Muscles of Mastication All four are Trigeminal nerve, CN V Temporalis Masseter Under masseter
30 Muscles of Mastication Lateral pterygoid Medial pterygoid Masseter pulled away These are Trigeminal nerve, CN V
31 Extrinsic Tongue Muscles Three major muscles that anchor and move the tongue All are innervated by cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal nerve)
32 Extrinsic Tongue Muscles Cranial nerve XII (hypo-glossal nerve) For all the glossus muscles Tongue Genioglossus Mandibular symphysis Geniohyoid Thyroid cartilage Styloid process Styloglossus Hyoglossus Stylohyoid Hyoid bone Thyrohyoid
33
34 But, that s it for the easy innervations: The next bunch have 7 different innervations
35 Muscles of the Anterior Neck and Throat: Suprahyoid Four deep throat muscles Form the floor of the oral cavity Anchor the tongue Elevate the hyoid (suprahyoid, they only pull, so, these must elevate) Move the larynx superiorly during swallowing
36 Muscles of the Anterior Neck and Throat: Suprahyoid Digastric Anterior belly Posterior belly Mylohyoid Stylohyoid Hyoid bone And, a geniohyoid which is deep to the mylohyoid
37 Muscles of the Anterior Neck and Throat: Suprahyoid Hyoid bone Mylohyoid (cut) Geniohyoid
38 But,,,,,,,,
39
40 Muscles of the Anterior Neck and Throat: Infrahyoid Straplike muscles that depress the hyoid and larynx during swallowing and speaking
41 Muscles of the Anterior Neck and Throat: Infrahyoid Thyrohyoid Omohyoid (superior belly) Sternohyoid Sternothyroid Omohyoid (inferior belly) But, again
42
43 Muscles of the Neck: Head Movements
44 Muscles of the Neck: Head Movements Major head flexor is the sternocleidomastoid Lateral head movements are accomplished by the sternocleidomastoid and scalene muscles Head extension is accomplished by the deep splenius muscles and aided by the superficial trapezius
45 Muscles of the Neck: Head Movements 1st cervical vertebra Sternocleidomastoid Base of occipital bone Mastoid process Middle scalene Anterior scalene Posterior scalene (a) Anterior
46 Muscles of the Neck: Head Movements Mastoid process Splenius capitis Spinous processes of the vertebrae Splenius cervicis (b) Posterior
47 Muscles of the Neck: Head Movements Trapezius
48 Muscles of the Neck: Head Movements Flexion and lateral flexion
49 Trunk Movements: Deep Back Muscles
50 Trunk Movements: Deep Back Muscles The prime mover of back extension is the erector spinae Erector spinae, or sacrospinalis, muscles consist of three columns on each side of the vertebrae iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis Lateral bending of the back is accomplished by unilateral contraction of these muscles Other deep back extensors include the semispinalis muscles and the quadratus lumborum
51 Trunk Movements: Deep Back Muscles Mastoid process of temporal bone Longissimus capitis Iliocostalis cervicis Longissimus cervicis Iliocostalis thoracis Longissimus thoracis Spinalis thoracis Erector spinae Iliocostalis lumborum External oblique Iliocostalis Longissimus Spinalis Semispinalis capitis Semispinalis cervicis Semispinalis thoracis Multifidus Quadratus lumborum (d)
52 Trunk Movements: Deep Back Muscles
53 Trunk Movements: Deep Back Muscles
54 Trunk Movements: Short Muscles Four short muscles extend from one vertebra to another These muscles are synergists in extension and rotation of the spine Not in the table Nor this O = origin I = insertion Intertransversarius Rotatores Multifidus Interspinales (e)
55 Muscles of Respiration - Ribs The only thing I could think of was the BBQ ribs and I already did that.
56 Muscles of Respiration The primary function of deep thoracic muscles is to promote movement for breathing External intercostal External intercostals more superficial layer that lifts the rib cage and increases thoracic volume to allow inspiration (a)
57 Muscles of Respiration - Intercostals Internal intercostals deeper layer that aids in forced expiration Internal intercostal
58 Muscles of Respiration - Intercostals Diaphragm most important muscle in inspiration
59 Muscles of Respiration: The Diaphragm Foramen for inferior vena cava Central tendon of diaphragm Xiphoid process of sternum Foramen for esophagus Costal cartilage Diaphragm Foramen for aorta 12th rib Lumbar vertebra Quadratus lumborum Psoas major
60 Muscles of Respiration: The Diaphragm Central tendon of diaphragm Body of thoracic vertebra Aorta Diaphragm (muscular part) Inferior vena cava Esophagus Pericardial sac Pericardium (cut)
61 Muscles of Respiration: Table
62 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall
63 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall
64 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall The abdominal wall is composed of four paired muscles (internal and external obliques, transversus abdominis, and rectus abdominis), their fasciae, and their aponeuroses Fascicles of these muscles run at right and oblique angles to one another, giving the abdominal wall added strength
65 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall - continue In addition to forming the abdominal wall, these muscles: Are involved with lateral flexion and rotation of the trunk Help promote urination, defecation, childbirth, vomiting, coughing, and screaming(sneezing, spitting, tackling, hitting a baseball, throwing, running, driving, getting out of bed, getting into bed )
66 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall Transversus abdominis Internal oblique External oblique Tendinous intersection Rectus abdominis Aponeurosis of the external oblique (a) Inguinal ligament (formed by free inferior border of the external oblique aponeurosis)
67 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall Linea alba Linea alba Not to be confused with. Figure 10.11a
68 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall Jessica Alba
69 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall - continue External oblique IIiac crest Rectus abdominis Internal oblique Pubic tubercle Lumbar fascia Transversus abdominis Lumbar fascia Inguinal ligament (b)
70 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall - continue Transversus abdominis External oblique Aponeuroses (c) Peritoneum Linea alba Again, not. Rectus abdominis Internal oblique Skin
71 Table
72 Extrinsic Shoulder Muscles
73 Extrinsic Shoulder Muscles
74 Extrinsic Shoulder Muscles Muscles of the thorax Anterior: pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, serratus anterior, and subclavius Posterior: latissimus dorsi, trapezius muscles, levator scapulae, and rhomboids These muscles are involved with the movements of the scapula including elevation, depression, rotation, and lateral and medial movements Prime movers of shoulder elevation are the trapezius and levator scapulae
75 Extrinsic Shoulder Muscles Subclavius Clavicle Deltoid Pectoralis major Sternum Subscapularis Pectoralis minor Coracobrachialis Serratus anterior Humerus
76
77 Extrinsic Shoulder Muscles Muscles of the thorax Posterior: latissimus dorsi, trapezius muscles, levator scapulae, and rhomboids These muscles are involved with the movements of the scapula including elevation, depression, rotation, and lateral and medial movements Prime movers of shoulder elevation are the trapezius and levator scapulae
78 Extrinsic Shoulder Muscles Levator scapulae Trapezius Deltoid Rhomboid minor Rhomboid major Supraspinatus Clavicle Spine of scapula Infraspinatus Teres minor Teres major Humerus Latissimus dorsi (c)
79
80 Muscles Crossing the Shoulder Nine muscles cross the shoulder joint and insert into the humerus Prime movers include: Pectoralis major arm flexion Latissimus dorsi and posterior fibers of the deltoid arm extension Middle fibers of the deltoid arm abduction
81 Muscles Crossing the Shoulder Clavicle Deltoid Sternum Pectoralis major Latissimus dorsi (a) Anterior view (b) Posterior view
82
83
84 Muscles Crossing the Shoulder Rotator cuff muscles supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis SITS Function mainly to reinforce the capsule of the shoulder Secondarily act as synergists and fixators
85 Muscles Crossing the Shoulder Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis
86
87 Muscles Crossing the Shoulder The teres major: Act as a synergist Does not contribute to reinforcement of the shoulder joint, not a rotator cuff SITS muscle
88 Muscles Crossing the Shoulder Teres major
89
90 Muscles Crossing the Elbow
91 Muscles Crossing the Elbow Forearm extension The triceps brachii is the prime mover of forearm extension
92 Muscles Crossing the Elbow Triceps brachii: Lateral head Long head
93
94 Muscles Crossing the Elbow Forearm flexion Brachialis and biceps brachii are the chief forearm flexors
95 Muscles Crossing the Shoulder Biceps brachii Long head Short head Biceps brachii Brachialis Brachialis
96
97 Muscles of the Forearm There are a lot of them. Yes, you have to know them.
98 Muscles of the Forearm The two functional forearm muscle groups are: those that cause wrist movement, and those that move the fingers and the thumb These muscles insert via strong ligaments which pass under the flexor and extensor retinacula Most anterior muscles are flexors, and posterior muscles are extensors The pronator teres and pronator quadratus are not flexors, but pronate the forearm The supinator muscle is a synergist with the biceps brachii in supinating the forearm
99 Muscles of the Forearm: Anterior Compartment These muscles are primarily flexors of the wrist and fingers Palmar aponeurosis Flexor retinaculum Flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor carpi ulnaris Palmaris longus Flexor carpi radialis Medial epicondyle of humerus Brachioradialis Pronator teres
100 Table
101 There are some unspecified, as yet unidentified muscles
102 Flexible Politicus Longus
103 Flexible Politicus Longus
104 Mudwater Quadratus
105 Mudwater Quadratus
106 Muscles of the Forearm: Posterior Compartment These muscles are primarily extensors of the wrist and fingers Extensor digitorum Extensor carpi radialis brevis Extensor indicis Extensor digiti minimi Extensor carpi ulnaris Flexor carpi ulnaris Extensor carpi radialis longus (a)
107
108 More undiscovered muscles Extensor Carp Radials Longus and Brevis
109
110 Not this one, but the Extensor digitorum unos
111
112 Not the supinator but the.
113
114 Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand
115 Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand These small muscles: Lie in the palm of the hand (none on the dorsal side) Move the metacarpals and fingers Control precise movements (e.g., threading a needle) Are the main abductors and adductors of the fingers Produce opposition move the thumb toward the little finger
116 Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand Tendons of: Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor digitorum superficialis Third lumbrical Fourth lumbrical Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis Abductor digiti minimi Fibrous sheath Second lumbrical Dorsal interossei First lumbrical Adductor pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Flexor retinaculum Pisiform bone Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons (a) First superficial layer Abductor pollicis longus Tendons of: Palmaris longus Flexor carpi radialis Flexor pollicis longus
117 Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand Flexor digitorum profundus tendon Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon Palmar interossei Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis (cut) Abductor digiti minimi (cut) (b) Second layer Flexor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Dorsal interossei Adductor pollicis Abductor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis longus tendon
118 But. Tendons of: Flexor digitorum profundus Flexor digitorum superficialis Third lumbrical Fourth lumbrical Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis Abductor digiti minimi Pisiform bone Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons (a) First superficial layer Fibrous sheath Second lumbrical Dorsal interossei First lumbrical Adductor pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Flexor retinaculum Abductor pollicis longus Tendons of: Palmaris longus Flexor carpi radialis Flexor pollicis longus
119 And Flexor digitorum profundus tendon Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon Palmar interossei Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis (cut) Abductor digiti minimi (cut) (b) Second layer Flexor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Dorsal interossei Adductor pollicis Abductor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis longus tendon
120 Except for these.know these, for this class, can t guarantee you won t need to know the others later in life Opponens digiti minimi Flexor digiti minimi brevis Abductor digiti minimi Flexor pollicis brevis Abductor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis
121 Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand: Groups There are three groups of intrinsic hand muscles Thenar eminence (ball of the thumb) and Hypothenar eminence (ball of the little finger) each have a flexor, an abductor, and an opponens muscle Midpalm muscles, the lumbricals and interossei, extend the fingers The interossei also abduct and adduct the fingers
122
123
124 Lower Extremity
125
126
127 Eadweard Muybridge Born Died Resting place Occupation Edward James Muggeridge April 9, 1830( ) Kingston upon Thames, England May 8, 1904 (aged 74) Kingston upon Thames Woking Photographer
128 Muscles Crossing Hip and Knee Joints Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh flex the femur at the hip and extend the leg at the knee Posterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh extend the thigh and flex the leg The medial compartment muscles all adduct the thigh These three groups are enclosed by the fascia lata
129 Fascia Lata (latae) not fascia latte
130 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion The most important thigh flexors are the iliopsoas (prime mover), tensor fasciae lata, and rectus femoris
131 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion Iliac crest Psoas major Iliopsoas Iliacus Anterior superior iliac spine Tensor fasciae latae Rectus femoris
132 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion
133 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion The medially located adductor muscles and sartorius assist in thigh flexion If they assist that would make them?????? A) agonists B) synergists C) fixators D) protagonists E) assistorius
134 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion Iliopsoas Psoas major Iliacus Anterior superior iliac spine Tensor fasciae latae Pectineus Sartorius Adductor longus Rectus femoris Adductor magnus
135 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion Adductor brevis Adductor longus Adductor magnus Femur
136 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion
137 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Extension Thigh extension is primarily effected by the hamstring muscles (biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus) Forceful extension is aided by the gluteus maximus
138 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Extension Gluteus maximus Long head Short head Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Hamstrings
139 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Extension
140 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Extension
141 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Medial Rotation ABduction and medial rotation are effected by the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus, and are antagonized by the lateral rotators
142 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Medial Rotation Gluteus medius (cut) Gluteus minimus
143 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Medial Rotation
144 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Lateral Rotation
145 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Lateral Rotation Superior gemellus Obturator internus Inferior gemellus Piriformis Obturator externus Quadratus femoris
146 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Lateral Rotation
147 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Adduction Thigh adduction is the role of five adductor muscles (adductor magnus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, pectineus, and gracilis)
148 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Adduction Pectineus (cut) Adductor longus Adductor magnus Femur
149 Movements of the Thigh at the Hip: Flexion
150 Movements of the Knee Joint
151 Movements of the Knee Joint The sole extensor of the knee is the quadriceps femoris The hamstring muscles flex the knee, and are antagonists to the quadriceps femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius Vastus medialis Rectus femoris tendon (cut) Patella Patellar ligament
152 Movements of the Knee Joint
153 Muscles of the Leg: Movements Various leg muscles produce the following movements at the: Ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion Intertarsal joints inversion and eversion of the foot Toes flexion and extension
154 Muscles of the Anterior Compartment These muscles are the primary toe extensors and ankle dorsiflexors They include the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, and fibularis tertius Tibia Tibialis anterior Extensor digitorum longus Extensor hallucis longus Superior and inferior extensor retinacula
155 Muscles of the Anterior Compartment Tibialis anterior Extensor hallucis longus Extensor digitorum longus
156 Muscles of the Anterior Compartment
157 Muscles of the Lateral Compartment These muscles plantar flex and evert the foot They include the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles Fibularis brevis Fibularis longus
158 Muscles of the Lateral Compartment Fibularis longus Fibularis brevis Tendon of fibularis longus
159 Muscles of the Lateral Compartment
160 Muscles of the Posterior Compartment These muscles primarily flex the foot and the toes They include the gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus Gastrocnemius Medial head Lateral head Tendon of gastrocnemius Calcaneal tendon Medial malleolus
161 Muscles of the Posterior Compartment Soleus Tendon of plantaris Tibialis posterior Fibula Flexor digitorum longus Flexor hallucis longus
162 Muscles of the Posterior Compartment
163 I know that you know that there is no need to know and no time to know everything there is to know, so, no need to know the intrinsic foot muscles. Muscles, end
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk
 The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8
 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Chapter 10. The Muscular System. AP1-Lecture Goodwin College. Introduction. In this chapter we will cover: 4/27/2015
 Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Chapter 11: The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association
 C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp ) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a
 The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8
 Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym!
 Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Bone Practical. Labs Muscle Labs. Final Practical. Divisions of the Muscular System. Quiz format
 Bone Practical Labs 17 + 18 Muscles Wed 7/11 @ 8am 40 50 stations About half axial, half appendicular bones Disarticulated bones: Skulls, partial skulls, vertebrae, ribs, skeletons, arm bones, leg bones,
Bone Practical Labs 17 + 18 Muscles Wed 7/11 @ 8am 40 50 stations About half axial, half appendicular bones Disarticulated bones: Skulls, partial skulls, vertebrae, ribs, skeletons, arm bones, leg bones,
Chapter 10. An Overview of the Muscle System
 Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Module 6 - The Muscular System Introduction to the Muscular System and Muscles of the Head, Neck and Shoulder
 Module 6 - The Muscular System Introduction to the Muscular System and Muscles of the Head, Neck and Shoulder There will be three modules to cover the muscle anatomy of the body. The first module will
Module 6 - The Muscular System Introduction to the Muscular System and Muscles of the Head, Neck and Shoulder There will be three modules to cover the muscle anatomy of the body. The first module will
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Part 1 of 2
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Part 1 of 2 See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline Part 1 of 2 See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Masseter- in front of ear Temporalis Mandible
 Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Muscular System. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER
 ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back
 Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS
 TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Locomotor system - Part 6
 Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY WORKSHEET Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System Background
 ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY WORKSHEET Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System Background Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by dense regular connective tissue in the form of cord-like tendons or membranous
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY WORKSHEET Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System Background Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by dense regular connective tissue in the form of cord-like tendons or membranous
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
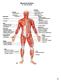 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
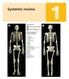 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Muscles of the Cat Review Sheet
 MUSCLES F THE CHEST 1. Pectoralis major clavicle, sternum, costal cartilages greater tubercle of humerus Flexes, adducts and medially rotates arm (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES F
MUSCLES F THE CHEST 1. Pectoralis major clavicle, sternum, costal cartilages greater tubercle of humerus Flexes, adducts and medially rotates arm (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES F
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) The attachment of a muscle s tendon to the stationary bone is called the ; the attachment of the muscle s other tendon to the movable
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) The attachment of a muscle s tendon to the stationary bone is called the ; the attachment of the muscle s other tendon to the movable
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Exam II November 6, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology 141 Exam II November 6, 2014 Name Student Number 1. In regards to the gross anatomy of muscle, which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Perimysium is more superficial than the epimysium
Anatomy and Physiology 141 Exam II November 6, 2014 Name Student Number 1. In regards to the gross anatomy of muscle, which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Perimysium is more superficial than the epimysium
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
Muscles Built on the Maniken
 Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Sports Medicine Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
The Concise Book of Muscles second edition
 The Concise Book of Muscles second edition Chris Jarmey Lotus Publishing Chichester, England North Atlantic Books Berkeley, California Copyright 2003, 2008 by Chris Jarmey. All rights reserved. No portion
The Concise Book of Muscles second edition Chris Jarmey Lotus Publishing Chichester, England North Atlantic Books Berkeley, California Copyright 2003, 2008 by Chris Jarmey. All rights reserved. No portion
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Chapter 6 part 2. Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
