Age distributions per dataset
|
|
|
- Rudolf Dawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Age distributions per dataset MAS LBC OATS PAFIP IDIVAL SHIP NCNG SHIP Trend UCLA NL BP HUBIN STROKEMRI Würzburg Tübingen HMS NESDA OCD VUmc Amsterdam T OCD Fukuoka FBIRN OCD VUmc Amsterdam.T TOP Osaka.T OCD Barcelona OCD London MüNC IMpACT OCD Kunming.T OCD Kyoto.T OCD Kyoto T OCD SU UMCU PAFIP IDIVAL TCD NUIG MCIC CIAM PAFIP IDIVAL OCD India T OCD India.T OCD SNU A OCD Kunming T Meth CT OCD Shangai BIL & GIN Osaka T OCD SNU C OCD SNU B CLiNG BIG.T QTIM BIG T BP Houston NeuroIMAGE OCD Zürich IMAGEN OCD AMC 0 0
3 SupplementaryTableS:DatasetdescriptionandMRimageacquisitiondetails.OntheleftcolumnarethereferencenumbersasusedinTableI,Figures,andSupplementaryMaterialS. Referencenumber Dataset Description Scanner(s) FreeSurferversion Tacquisitiondetails BIG.T BIGT TheBrainImagingGeneticsdatabase,splitbyscannerfieldstrength.A.T(Sonata;Avanto)Siemens. populationbasedsamplefromnijmegen,thenetherlands TheBrainImagingGeneticsdatabase,splitbyscannerfieldstrength.A T(Trio;TimTrio)Siemens. populationbasedsamplefromnijmegen,thenetherlands MRIdatainBIGwereacquiredwitheithera.TeslaSiemensSonataorAvantoscanneroraTeslaSiemensTrioorTimTrio scanner(erlangen,germany).giventhatimageswereacquiredduringseveralsmallerscalestudies,theparametersused wereslightvariationsofastandardtweightedthreedimensionalmagnetizationpreparedrapidgradientechosequence (MPRAGE;.0.0.0mmvoxelsize). MRIdatainBIGwereacquiredwitheithera.TeslaSiemensSonataorAvantoscanneroraTeslaSiemensTrioorTimTrio scanner(erlangen,germany).giventhatimageswereacquiredduringseveralsmallerscalestudies,theparametersused wereslightvariationsofastandardtweightedthreedimensionalmagnetizationpreparedrapidgradientechosequence (MPRAGE;.0.0.0mmvoxelsize). TheBrainimagingoflateralizationstudyatGrouped'Imagerie DTweightedsequence:DFFETFE;TR=ms;TE=.ms;flipangle= ;inversiontime=00ms;turbofieldecho BIL&GIN Neurofonctionnelle,asampleofadultparticipantsenrichedinleft T(Achieva)Philips. factor=;sensefactor=;matrixsize=xxmm;mmisotropicvoxelsize handers(%),frombordeaux,france(mazoyeretal.,) a)tweightedmpragescans:flipangle=,echotime(te)=.ms,repetitiontime(tr)=0ms,slicethickness=mm, matrix=x,numberofslices=. a)t(allegra)siemens();b).t(gyroscan AsubsetofhealthycontrolsfromtheSearchingforEndophenotypes b)tweightedspoiledgradientrecalled(spgr)scans:flipangle=,echotime(te)=ms,repetitiontime(tr)=ms,slice BPHouston Intera)Philips&c).T(GyroscanIntera). ofbipolardisordersstudy(bp) thickness=mm,matrix=x,numberofslices=. Philips c)tweightedsensedscans:flipangle=,echotime(te)=.ms,repetitiontime(tr)=ms,slicethickness=mm, matrix= x, Number of slices =. AsubsetofhealthycontrolsfromCorticalInhibitionandAttentional CIAM T(Allegra)Siemens. TR/TE,/.ms;flipangle,degrees,FOV,mm 0mm mm;andvoxelsize,.mm.0mm.0mm. Modulation:astudyofpsychosis(CIAM)UCT. ATweighted,Dmagnetizationpreparedrapidgradientechosequence(MPRAGE)(TR/TE/TI/FA=0ms/.ms/00 CLiNG AsampleofhealthycontrolsfromClinicalNeuroscienceGöttingen T(TrioTim)Siemens. ms/ ;imagematrix=x;durationminandsec)wasacquiredgeneratingsagittalsliceswithavoxelsizeof mm. a)mpragescan:scanplane=sagittal,tr/te/ti=/./00ms,grappaaccelerationfactor=,flipangle=, HealthysubjectsfromFunctionBiomedicalInformaticsResearch a)t(timtrio)siemens&b)t(discovery resolution= x,fov=0mm,voxelsize=0.x0.x.mm,andnex=. FBIRN. Network(FBIRN) MR0)GE b)irspgrscan:scanplane=sagittal,tr/te/ti=././ms,assetaccelerationfactor=,aflipangle=, resolution= x,fov=0mm,voxelsize=0.x0.x.mm,andnex= ATweighted,magnetizationpreparedrapidgradientechosequence(MPRAGE)(TR/TE/TI/FA=00ms/.0ms/00ms/ ; HMS HealthysubjectsfromtheHomburgMultidiagnosisStudy.T(Sonata)Siemens. imagematrix=x)wasacquiredgeneratingconsecutivesagittalsliceswithavoxelsizeofmm.~min HUBIN AsampleofhealthysubjectsfromHumanBrainInformatics.T(Signa)GE.0 Tweightedimages,usingathreedimensionalspoiledgradientrecalled(SPGR)pulsesequence,wereacquiredwiththe followingparameters;.mmcoronalslices,nogap, flipangle,repetitiontime(tr)=ms,echotime(te)=.0ms, numberofexcitations(nex)=,fieldofview(fov)=cm,acquisitionmatrix=. IMAGEN TheImaginggeneticsconsortium,anEuropeaninternational populationbasedsample(schumannetal.,) T(Achieva)Philips;TBrucker;T(TrioTim) Siemens;T(Verio)Siemens;T(SignaExcite) Brucker/GE&T(SignaHDx)GE. MagneticresonanceimagingdatawereacquiredatEuropeancenters,usingastandardisedTesla,Tweightedgradient echoprotocol(voxelsize=.mmisotropic)basedonthatfromtheadniinitiative ( IMpACT LBC MAS MCIC MethCT TheInternationalMulticentrepersistentADHDGenetics.T(Avanto)Siemens. Allscanshadavoxelsizeof mm,trms,ti=00ms,te.ms,sagittalslices,fieldofviewmm. CollaboraTion:asubsetDutchhealthycontrols Lothianbirthcohortfrom:Scotishsampleofhealthyolder DIRPrepTweightedwholebrainFSPGRvolumeswereacquiredinthecoronalplaneusingaGESignaHorizonHDxt.T subjects(age~0)bornon,aspartofastudyonbrainagingand.t(signahorizonhdx)ge. clinicalmriscannerwithmanufacturersuppliedeightchannelphasedarrayheadcoil;fov=xmm,matrix=x cognition(wardlawetal.,),x.mmthickslices,xx.mmvoxels,tr=ms,te=msandti=00ms. DTweightedstructural(TwTFE turbofieldecho)mri,acquiredcoronallywithrepetitiontimetr=.ms,echotime Sydney'sMemoryandAgingStudy:anepidemiologicalsampleof T(AchievaQuasarDualscanner)Phillips. TE=.ms,flipangle=,matrixsize=,fieldofviewFOV= 0mm,andslicethickness=mmwith europeansubjectshttp:// nogapbetween;yielding mmisotropicvoxels MINDClinicalImagingConsortiumformedbytheMentalIllnessand TR=msforT,TR=msfor.T;TE=.msforT,TE=.msfor.T;FA=forT,FA=for.T;TI=.TSiemens,T(Trio)Siemens&T(Signa) NeuroscienceDiscovery(MIND)InstitutenowtheMindResearch.0 00forT;Bandwidth=forT,Bandwidth=0for.T;0. 0.mmvoxelsize;slicethickness.mm;FOV GE Network(MRN;http//ww.mrn.org) cmmatrix Healthycontrolsfromstudiesonmethamphetamineuse;Universityof Tweighted,DMEMPRAGEsequence:TR=ms;gradedTE=./././.m;flipangle= ;FOV=mm;slice T(MagnetomAllegra)Siemens. CapeTown thickness=mm MüNC TheMünsterNeuroimagingCohort T(GyroscanIntera),Philips. Tweightedimageswereacquiredusingafastgradientechosequence(turbofieldecho),repetitiontime.milliseconds, echotime.milliseconds,flipangle,acquiredoverafieldofviewof(feethead[fh])(anteriorposterior[ap]) (rightleft)andreconstructedtocubicvoxelsof.mm.mm.mm[rl])mm NCNG NESDA NeuroIMAGE TheNorwegianCognitiveNeuroGeneticssample:apopulationbased.T(Sonata)Siemens&.T(Avanto). sampleofeuropeansubjects(espesethetal.,) Siemens AsubsetofhealthycontrolsfromtheNetherlandsStudyofDepression T(Achieva;Intera)Phillips.0 andanxiety. AsampleofeuropeanhealthycontrolsandhealthysiblingsofADHD.T(Sonata),Siemensand.T(Avanto),. patients Siemens ASiemensSonata.Teslascanner(Siemens,Erlangen,Germany)withaconventionalheadcoilwasused.TwoDMPRAGE Tweightedsequences(duration:mins)wererunforallparticipants.Eachvolumeconsistedofsagittalslices (.xxmm),withaninplanevoxelsizeofmm(tr=ms;te=.ms;ti=00ms;flipangle= ;and matrix).#:asiemensavantoscannerwasusedtoacquiretwodmpragetweightedsequences(tr/te/ti/fa=00 ms/.ms/00ms/ ;matrix= ;durationminandspervolume).eachvolumeconsistedofsagittalslices (...mm) ImagingdatawereacquiredattheLeidenUniversityMedicalCenter,AmsterdamMedicalCenter,andUniversityMedical CenterGroningen,equippedwithaSENSE(LeidenUniversityMedicalCenterandUniversityMedicalCenterGroningen)or SENSE(AmsterdamMedicalCenter)channelheadcoil.Foreachsubject,anatomicalimageswereobtainedusingasagittal DlgradientechoTweightedsequence(TR=ms,TE=.ms;matrix=x;voxelsize=xxmm;0slices; duration=.minutes)..tmriscannerswereemployed(siemenssonataandsiemensavanto;siemens,erlangen,germany),usingidentical headcoils(channelphasearrayheadcoil).tweightedwholebrainscan(mprage,slices,acquisitionmatrix x,voxelsize:.0x.0x.0mm;te/tr=./ms,ti=00ms,fa= ;GRAPPAacceleration) ()SequencenameTTFE.Inplaneresolution mm. matrix.slicethickness.mmwithoutgap.numberof slices:.orientation:cortr/te:./.msflipangle:.scanduration:sec.()acquisitionparametersfort OATS OneindividualperfamilyofTheOlderAustralianTwinsStudy.T(Gyroscan)Philips;T(AchievaQuasar Dual)Philips;.T(MagnetomAvanto) Siemens;.T(Sonata)Siemens. weightedstructuralmriscanswere:tr=.ms,te=.ms,flipangle=,matrixsize=x,fov=xx0,and slicethickness=mmwithnogapbetween;yieldingxxmmisotropicvoxels()inplaneresolution= mm,slice thickness=.mm,slicenumber=,tr(repetitiontime)=ms,te(echotime)=.ms,ti(inversiontime)=0ms, flipangle=andnex(numberofexcitations)=.()inplaneresolution= mm,slicethickness=.mm,slicenumber=, TR(Repetitiontime)=ms,TE(Echotime)=.ms,TI(Inversiontime)=0ms,flipangle=andNEX(Numberof Excitations)=. OCDAMC ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD(pedriatric) T(Intera)Philips. T(PhilipsInteraMR)matrixx,slices,voxelsizexx.mm OCDBarcelona ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD.T(SignaExcite)GE. matrixx,slices,voxelsize.x.x.mm OCDFukuoka ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD T(AchievaTX)Philips. T(PhilipsAchievaTX)matrix0x0,TR.ms,TE.ms,TI(inversiontime)0ms,Flipangledegree,FOV0x0,NSA,Sliceticknessmm,numberofslice0,voxelsize.x...mm,scantimes OCDIndia.T Healthycontrols,examinedusingastructuredinterviewtoruleouta psychiatricdiagnosisorneurologicaldisease.t(vison)siemens..t(siemensvision):matrixx,slices,0.x0.xmm OCDIndiaT Healthycontrols,examinedusingastructuredinterviewtoruleouta psychiatricdiagnosisorneurologicaldisease T(Skyra)Siemens. T(SiemensSkyra):matrixX,slices,voxelsize.0X.0X.0mm; OCDKunming.T ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD.T(SignaExcite)GE..T(SignaExcite)GE:matrixx,slices,voxelsize0.x0.x0.mm OCDKunmingT ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD T(Achieva)Philips. T(Achieva)Philips:matrixx,slices,FOV=,voxelsize.x.x0.mm OCDKyoto.T ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD.T(GyroscanIntera)Philips. OCDKyotoT ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD T(Achieva.0TX)Philips. OCDLondon ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD.T(Signa)GEand.T(SignaHDx)GE. OCDShanghai ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD T(Verio)Siemens. OCDSNUA ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD.T(Signa)GE. ThreedimensionalvolumetricacquisitionofaTweightedgradientechosequenceproducedagaplessseriesofcontiguous, thinsagittalsectionswiththefollowingparameters:flipangle, ;acquisitionmatrix, ;fieldofview,cm;section thickness,.mm;voxelsize,0.mm 0.mm.mm;TR,.ms;TE,.ms. ThescanningparametersoftheTweightedthreedimensionalmagnetizationpreparedrapidgradientecho(DMPRAGE) sequenceswereasfollows:flipangle,degrees;acquisitionmatrix,xx0;fieldofview,.cm;sectionthickness,.0mm;voxelsize,.0mmx.0mmx.0mm;tr,.ms;andte,.ms. Sequence:DSPGR,TR:.ms,TE:.ms,FA:º,Orientation:Axial,Matrixsize:xx,Voxelsize:0.x0.x.0;Sequence:DSPGR,TR:.ms,TE:.0ms,FA:º,Orientation:Axial,Matrixsize:xx,Voxelsize:.0x.0x. T(Siemensverio)matrixx,slices,slicetickness.0mm,voxelsizexxmm,TRms,TE.ms,FOV x0,flipangledegree MPRAGEsequencewereacquiredincontiguousaxialslices:TR/TE=0/.ms,fieldofview=cm,flipangle=, matrixx,voxelsize0.x0.x0.0mm. Contiguous.mmsagittalimageswereobtainedwithathreedimensionalTweightedspoiledgradientechosequence OCDSNUB ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD.T(Avanto)Siemens. (echotime=.ms;repetitiontime=.ms;flipangle= ;fieldofview= cm;matrixx;voxelsize 0.x0.x.0mm). HighresolutionTweighted,threedimensionalMPRAGE(TR=0ms;TE=.ms;FOV=0mm;FA= ;matrixx; OCDSNUC ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD T(MagnetomTrio)SIemens. voxelsize.000x0.x0.mm). TweightedMPRAGEsagittalDvolume(TR=ms;TE=.ms;TI=00ms;slices;FOV=x0mm;voxel OCDSU ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD T(MagnetomAllegra)Siemens. size=.x.0x.0mm;slicethickness=mm,flipangle=degrees OCDVUmcAmsterdam.T ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD.T(Sonata)Siemens..T(SiemensSonata)matrixx,slices,voxelsizexx.mm OCDVUmcAmsterdamT ControlsubjectsfromstudiesonOCD T(SignaHDxt)GE. T(SignaHDxt)matrixx,slices,voxelsizex0.x0.mm OCDZurich Healthycontrolsubjects(adolescentsandadults) T(Achieva)Philips. T(PhilipsAchieva)matrix0x0,slices,voxelsizeisotropicxxmm,TR.ms,TE.ms,Flipangledegree TweightedIRFSPGRsagittalDvolume(TR=.ms;TE=.ms;TI=0ms;slices,matrixsize=x, Osaka.T ControlsubjectsfromtheJapaneseOsakacasecontrolstudiesof schizophrenia.t(signa)ge&t(signahdxt)ge. FOV=.0x.0cm,voxelsize=0.x0.x.mm,slicethickness=.mm,flipangle= )TweightedIRFSPGR sagittaldvolume(tr=.ms;te=.ms;ti=0ms;slices,matrixsize=xx,fov=.0x.0cm,voxel size=0.x0.x.0mm,slicethickness=.0mm,flipangle= ) TweightedIRFSPGRsagittalDvolume(TR=.ms;TE=.ms;TI=0ms;slices,matrixsize=x, OsakaT ControlsubjectsfromtheJapaneseOsakacasecontrolstudiesof schizophrenia.t(signa)ge&t(signahdxt)ge. FOV=.0x.0cm,voxelsize=0.x0.x.mm,slicethickness=.mm,flipangle= )TweightedIRFSPGR sagittaldvolume(tr=.ms;te=.ms;ti=0ms;slices,matrixsize=xx,fov=.0x.0cm,voxel size=0.x0.x.0mm,slicethickness=.0mm,flipangle= ) PAFIPIDIVAL Healthycontrolsfromstudiesonschizofrenia.T(Signa)GE.0 Tweightedimages,usingaspoiledgrass(SPGR)sequence,wereacquiredinthecoronalplanewiththefollowing parameters:te=ms,tr=ms,nex=,fa=o,fov=x.cm,slicethickness=.mmandamatrixofx PAFIPIDIVAL Healthycontrolsfromstudiesonschizofrenia T(Achieva)Phillips. SagittalT,TR=00ms;TE=.ms;FA=o;Voxelsize=xxmm;Slicethickness=mm;Matrixsize=x PAFIPIDIVAL Healthycontrolsfromstudiesonschizofrenia.T(Signa)GE.0 QTIM AnaselectsubsetoftwinsingletonsofeuropeandescentfromThe QueenslandTwinImagingstudy. T(Bruker)Medspec. SHIP PopulationbasedsamplefromTheStudyofhealthinPomerania (northeasterngermany).t(avanto)siemens. SHIPT PopulationbasedsamplefromTheStudyofhealthinPomerania (northeasterngermany).t(avanto)siemens. STROKEMRI Healthycontrolsfromanongoingstrokestudy,Oslo T(HDxT)GE. TCD NUIG HealthysubjectsfromTCD(Dublin)andNUIG(Galway) TCD:T(Intera)Philips;NUIG:.T TCD:.NUIG:. (Magnetom),Siemens TOP ControlsubjectsfromTematiskOmrådePsykoser(Thematically OrganizedPsychosisResearch)..T(Sonata)Siemens HealthycontrolsfromtheBipolarGeneticsdataset.ThisNIMHfunded 0 UCLA NLBP studyiscarriedoutattheuniversitymedicalcenterutrecht,the Netherlands,inacollaborationwiththeUniversityofCaliforniaLos. T(Achieva)Philips Angeles UMCU Healthycontrolsfromtwoindependentschizophreniacohorts recruitedattheuniversitymedicalcentreutrecht,thenetherlands..t(achieva)philips Tweightedimages,usingaspoiledgrass(SPGR)sequence,wereacquiredinthecoronalplanewiththefollowing parameters:te=ms,tr=ms,nex=,fa=o,fov=x.cm,slicethickness=.mmandamatrixofx ScanswerecollectedonaTeslaBrukerMedspecscanner(Bruker,Germany).Tweightedstructuralscanswereacquired withacquisitionparameters:tr=0ms,te=.ms,ti=00ms,flipangle=,or0(coronalorsagittal)slices, FOV=0mm,acquisitionvoxelsize.x0.x0.mm. DTweightedMRIsequencewiththefollowingparameters:MPRAGE/axialplane,TR=00ms,TE=.msandFlip angle= andanoriginalresolutionof.0x.0x.0mm DTweightedMRIsequencewiththefollowingparameters:MPRAGE/axialplane,TR=00ms,TE=.msandFlip angle= andanoriginalresolutionof.0x.0x.0mm SagittalTweightedFSPGRsequence(TE:.,TR:.ms,flipangle:degrees,voxelsixe=xx.millimeter,number ofslices:) TCD:TweightedTFEgradientecho(TE(ms).;TR(ms).;Flipangle( );FOV;Matrixx;No.slices; slicethickness(mm)0.;voxelsize(mm)0.x0.x0.);nuig:.t:tweightedmprage(te(ms).;tr(ms); Flipangle( );FOV;Matrixx(kspaceinterpolationfromx);No.slices;slicethickness(mm)0.; Voxelsize(mm)0.x0.x0.) TwosagittalTweightedmagnetizationpreparedrapidgradientecho(MPRAGE)volumeswereacquiredwiththeSiemens tfld_nspulsesequence(te=.ms,tr=ms,ti=00ms,flipangle= ;FOV=cm,voxelsize=.x0.x mm,numberofpartitions=) ThreedimensionalTweightedimageswereacquiredonaTeslaPhilipsAchievascanner(PhilipsHealthcare,Best,the Netherlands),equippedwithanchannelSENSEheadcoil.Fastfieldechoscanswith0contiguoussagittalslices(TE=. ms,tr=ms,flipangle=,fov=0mm,0.x0.x0.0mm³voxels)wereobtained. AThreeDimensionalFastFieldEcho(DFFE)ona.TPhilipsAchievascanner:TE=.ms,TR=ms,flipangle=, FOV=xmm)withcontiguouscoronal.mmslices Würzburg Tübingen DatasetofhealthycontrolsfromastudyonADHD.T(Avanto)Siemens. AhighresolutionTweightedmagnetizationpreparedrapidgradientechoimaging(MPRAGE)DMRIsequencewas obtainedfromeachparticipant(tr:0ms,te:.ms, flipangle,fov:mm,matrix:,voxelsize: mm
4 SupplementalInformationS.Listofdatasets(arrangedalphabetically)onwhichhandednessanalyseswereperformed, correspondingsamplesizesandassessmentmethods. Dataset Left Right handed handed Assessment BIG.T 0 Selfreport BIGT 0 Selfreport BIL&GIN Selfreport CLiNG SelfreportconfirmedbyEdinburghHandednessInventory FBIRN Selfreport HMS SelfreportconfirmedbyEdinburghHandednessInventory HUBIN 0 Selfreport IMAGEN SelfreportconfirmedbyPurduePegboardtest IMpACT Selfreport LBC Writinghand MCIC AnnettScaleofHandPreference MüNC EdinburghHandednessInventory:Athresholdof(outof)itemswasusedto categorizeasleftorrighthanded. NCNG Selfreport NESDA Selfreport NeuroIMAGE Selfreport OCDVUmcAmsterdam.T Selfreport OCDVUmcAmsterdamT Selfreport Osaka.T SelfreportconfirmedbyEdinburghHandednessInventory OsakaT SelfreportconfirmedbyEdinburghHandednessInventory SHIP Selfreport SHIPTrend Selfreport STROKEMRI Selfreport TOP Selfreport UCLA NLBP Selfreport UMCU Selfreport
5 SupplementalInformationS:Leftrightflipchecks Ofspecialimportancewastoassurethecorrectcorrespondencebetweentheleft/rightorientationoftheprocessed imagedataandtheoriginalsubjectspace.incontrasttotheotheraxes(anteroposteriororsuperiorinferior),the correctorientationontheleftrightaxisisnotdirectlyidentifiablefromvisualfeatures,makingitdifficulttoreadily detectanyerroneousimageflipsduringprocessing.suchproblemsaremuchmoreunlikelysincetheadoptionofthe niftiimagingstandard( DICOMformatted)dataisprocessedwithincorrectassumptions(SPMdocumentation,p.; BecausetheENIGMAprotocolstartsaftertheraw(oftenDICOMformatted)datahasbeenconvertedintoanimaging standard(orconvertedbyfreesurferitself),thismeantthatconversionfromthedicomformatwasthemostlikely stepwhereanyerrorcouldhavetakenplace.thiswasassessedusingseveralstrategies,dependingontheavailable informationateachsite.thebil&gin,fbirn,mas,nesdaandoatssampleshadmadeuseofparamagneticfiducial markersonasubsetoftheirsubjects,thuseliminatingorientationambiguity.inqtimandship,subjectswithaknown unilateralbrainabnormalitywereusedtocheckthecorrectorientationoftheimageafterconversion.inbig,cling, HMSandOCDSU,afewexamplesweremanuallycheckedformismatchesbetweentheDICOMandniftiheader information,i.e.acorrectflipfrom'radiological'to'neurological'orientation.finally,wecheckedtheconsistency betweenseveral,commonlyused,dicomtonifticonversiontoolsanddicomimagesgeneratedfromdifferent manufacturers/models(usingexamplesdownloadedfromthemanufacturer'swebsites).theconvertorsusedinthis stepwere:"mri_convert"( MRIConvert"( ( Giventhatthesechecksyieldednoproblems,andthatthedatasetswherenoerrorwasdetectedcomprised0%ofthe totalmetaanalysissample,wewereconfidentthatsuchorientationerrorsmusthavebeenveryunlikely.
6 Supplementary Information S. Plots of the relationship between and subcortical AIs in the BIG T sample. Regression analyses of linear and quadratic relationships revealed only linear effects of with AIs of the nucleus accumbens, caudate nucleus and putamen (as indicated by the dashed lines).
7 N. accumbens AI against Accumbens AI Amygdala AI Amygdala AI against Thalamus AI against Thalamus AI Caudate N. AI against Caudate AI
8 Putamen AI against Putamen AI Globus Pallidus AI against Globus pallidus AI Hippocampus AI against Hippocampus AI
9 Supplementary Information S. Boxplots of AI distributions for each dataset and structure. For each structure, the datasets are ordered top-to-bottom by their median AIs. The identities of the datasets are given by the numbers in the lefthand columns, with reference to Table. The horizontal length of each box represents the nd to rd quartile of the AI distribution (i.e. containing half of subjects in each dataset) and split at the median AI. The vertical width of each dataset's box is proportional to the square root of its sample size. The whiskers show the minimum and maximum values (curtailed in cases where the outer box boundary was reached). The vertical dotted lines indicate the points of perfect symmetry, AI=0.
10 N. accumbens Amygdala Caudate N Globus pallidus Hippocampus Putamen Thalamus
11 Supporting Information S. Meta-analyzed results from testing population-level lateralization (mean AI's 0) separately by sex. A positive Z-score indicates leftward asymmetry in volume (L>R), while a negative Z-score reflects a rightward asymmetry (R>L). Females N z-score Males N z-score Nucleus accumbens -.0 Nucleus accumbens Amygdala 0 -. Amygdala -. Caudate nucleus 0 -. Caudate nucleus -. Globus pallidus. Globus pallidus 0. Hippocampus -. Hippocampus 0 -. Putamen. Putamen 0. Thalamus 0. Thalamus.
12 Phenotype Phenotype Phenotype correlation Phenotype correlation P Genetic correlation Genetic correlation P AI_amygdala AI_accumbens AI_amygdala AI_caudate AI_amygdala AI_hippocampus AI_amygdala AI_pallidum AI_amygdala AI_putamen AI_amygdala AI_thalamus AI_caudate AI_accumbens AI_caudate AI_hippocampus AI_caudate AI_pallidum AI_caudate AI_putamen 0..E AI_caudate AI_thalamus AI_hippocampus AI_accumbens AI_hippocampus AI_pallidum AI_hippocampus AI_putamen AI_hippocampus AI_thalamus 0..E AI_pallidum AI_accumbens AI_pallidum AI_putamen AI_pallidum AI_thalamus -0..E AI_putamen AI_accumbens AI_putamen AI_thalamus -0..E AI_thalamus AI_accumbens Supplementary Information S. Phenotypic and genetic correlations among AIs in the GOBS dataset.
Supplementary Table S3: Instrument for diagnosing Major Depressive Disorder and exclusion criteria by site.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1: ENIGMA - Major Depressive Disorder Working Group Demographics. Age (in years), sex, and patients-control breakdown for participating sites Supplementary Table
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1: ENIGMA - Major Depressive Disorder Working Group Demographics. Age (in years), sex, and patients-control breakdown for participating sites Supplementary Table
Human subcortical brain asymmetries in 15,847 people worldwide reveal effects of age and sex
 Brain Imaging and Behavior (2017) 11:1497 1514 DOI 10.1007/s11682-016-9629-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Human subcortical brain asymmetries in 15,847 people worldwide reveal effects of age and sex Tulio Guadalupe
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2017) 11:1497 1514 DOI 10.1007/s11682-016-9629-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Human subcortical brain asymmetries in 15,847 people worldwide reveal effects of age and sex Tulio Guadalupe
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology
 General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Automated morphometry in adolescents with OCD and controls, using MR images with incomplete brain coverage
 Automated morphometry in adolescents with OCD and controls, using MR images with incomplete brain coverage M.Sc. Thesis Oscar Gustafsson gusgustaos@student.gu.se Supervisors: Göran Starck Maria Ljungberg
Automated morphometry in adolescents with OCD and controls, using MR images with incomplete brain coverage M.Sc. Thesis Oscar Gustafsson gusgustaos@student.gu.se Supervisors: Göran Starck Maria Ljungberg
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol
 MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
Supplementary Table 1. Bipolar, schizophrenia, and controls were analyzed for 362 mtdna SNPs using
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Bipolar, schizophrenia, and controls were analyzed for 362 mtdna SNPs using Affymetrix 6 cel files. The number of cases and controls of European ancestry from
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Bipolar, schizophrenia, and controls were analyzed for 362 mtdna SNPs using Affymetrix 6 cel files. The number of cases and controls of European ancestry from
NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium. NACC Vascular Consortium
 NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
NACC Vascular Consortium NACC Vascular Consortium Participating centers: Oregon Health and Science University ADC Rush University ADC Mount Sinai School of Medicine ADC Boston University ADC In consultation
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
How to interpret scientific & statistical graphs
 How to interpret scientific & statistical graphs Theresa A Scott, MS Department of Biostatistics theresa.scott@vanderbilt.edu http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/theresascott 1 A brief introduction Graphics:
How to interpret scientific & statistical graphs Theresa A Scott, MS Department of Biostatistics theresa.scott@vanderbilt.edu http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/theresascott 1 A brief introduction Graphics:
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES. nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral hemispheres. course 1
 Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline Human Anatomy Module 2 Content module 11 Study subject The olfactory brain. Basal nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral
Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline Human Anatomy Module 2 Content module 11 Study subject The olfactory brain. Basal nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral
Asymmetric Bias in User Guided Segmentations of Brain Structures
 Asymmetric Bias in User Guided Segmentations of Brain Structures Martin Styner a,b, Rachel G Smith b, Michael M Graves b, Matthew W Mosconi b, Sarah Peterson b, Scott White b, Joe Blocher b, Mohammed El-Sayed
Asymmetric Bias in User Guided Segmentations of Brain Structures Martin Styner a,b, Rachel G Smith b, Michael M Graves b, Matthew W Mosconi b, Sarah Peterson b, Scott White b, Joe Blocher b, Mohammed El-Sayed
Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching. Intention and Executive Control
 Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching Intention and Executive Control Yehene E, Meiran N, Soroker N Taskalternationcostwithoutask alternation:measuringintentionality. A behavioral dissociation
Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching Intention and Executive Control Yehene E, Meiran N, Soroker N Taskalternationcostwithoutask alternation:measuringintentionality. A behavioral dissociation
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Hoogman M, Bralten J, Hibar DP, et al. Subcortical
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Hoogman M, Bralten J, Hibar DP, et al. Subcortical
MISTIE Catheter Placement Analysis. Qian Qian Liu
 MISTIE Catheter Placement Analysis Qian Qian Liu Objectives Determine various factors that may affect catheter placement score and percentage clot volume reduction Location of the clots ICH designation
MISTIE Catheter Placement Analysis Qian Qian Liu Objectives Determine various factors that may affect catheter placement score and percentage clot volume reduction Location of the clots ICH designation
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation
 A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation Jun Y. Wang, Randi J. Hagerman, Susan M. Rivera 2012 International Fragile X Conference Center for Mind and Brain Subcortical
A Multimodal Imaging Analysis of Subcortical Gray Matter in Fragile X Premutation Jun Y. Wang, Randi J. Hagerman, Susan M. Rivera 2012 International Fragile X Conference Center for Mind and Brain Subcortical
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Information SI1: Image Exclusion Criteria: Each image segmentation was individually examined by a neuroimaging expert at each site by overlaying the segmentation
Supplementary Information Supplementary Information SI1: Image Exclusion Criteria: Each image segmentation was individually examined by a neuroimaging expert at each site by overlaying the segmentation
Population. Sample. AP Statistics Notes for Chapter 1 Section 1.0 Making Sense of Data. Statistics: Data Analysis:
 Section 1.0 Making Sense of Data Statistics: Data Analysis: Individuals objects described by a set of data Variable any characteristic of an individual Categorical Variable places an individual into one
Section 1.0 Making Sense of Data Statistics: Data Analysis: Individuals objects described by a set of data Variable any characteristic of an individual Categorical Variable places an individual into one
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using Linear Discriminative Analysis and Quadratic Discriminative Analysis
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology (IJIRCST) ISSN: 2347-5552, Volume-2, Issue-6, November-2014 Classification and Statistical Analysis of Auditory FMRI Data Using
Course Calendar - Neuroscience
 2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis I
 Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis I JULY 2011 Afsaneh Yazdani Preface What is Statistics? Preface What is Statistics? Science of: designing studies or experiments, collecting data Summarizing/modeling/analyzing
Introduction to Statistical Data Analysis I JULY 2011 Afsaneh Yazdani Preface What is Statistics? Preface What is Statistics? Science of: designing studies or experiments, collecting data Summarizing/modeling/analyzing
Early Learning vs Early Variability 1.5 r = p = Early Learning r = p = e 005. Early Learning 0.
 The temporal structure of motor variability is dynamically regulated and predicts individual differences in motor learning ability Howard Wu *, Yohsuke Miyamoto *, Luis Nicolas Gonzales-Castro, Bence P.
The temporal structure of motor variability is dynamically regulated and predicts individual differences in motor learning ability Howard Wu *, Yohsuke Miyamoto *, Luis Nicolas Gonzales-Castro, Bence P.
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Course Calendar
 Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Green SA, Hernandez L, Tottenham N, Krasileva K, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M. The neurobiology of sensory overresponsivity in youth with autism spectrum disorders. Published
Supplementary Online Content Green SA, Hernandez L, Tottenham N, Krasileva K, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M. The neurobiology of sensory overresponsivity in youth with autism spectrum disorders. Published
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Van Laere K, Vanhee A, Verschueren J, et al. Value of 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online March
Supplementary Online Content Van Laere K, Vanhee A, Verschueren J, et al. Value of 18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online March
CONTENT SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE E. INSTRUMENTAL VARIABLE ANALYSIS USING DESEASONALISED PLASMA 25-HYDROXYVITAMIN D. 7
 CONTENT FIGURES 3 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE A. NUMBER OF PARTICIPANTS AND EVENTS IN THE OBSERVATIONAL AND GENETIC ANALYSES. 3 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE B. FLOWCHART SHOWING THE SELECTION PROCESS FOR DETERMINING
CONTENT FIGURES 3 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE A. NUMBER OF PARTICIPANTS AND EVENTS IN THE OBSERVATIONAL AND GENETIC ANALYSES. 3 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE B. FLOWCHART SHOWING THE SELECTION PROCESS FOR DETERMINING
Supplementary Information. Combined Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Arterial Spin Labeling as
 Supplementary Information Combined Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Arterial Spin Labeling as Markers of Early Parkinson s disease Xiaobo Wei MD 1, Ronghua Yan MD, Ph.D 2, Zhaoyu Chen MD 1, Ruihui Weng MD
Supplementary Information Combined Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Arterial Spin Labeling as Markers of Early Parkinson s disease Xiaobo Wei MD 1, Ronghua Yan MD, Ph.D 2, Zhaoyu Chen MD 1, Ruihui Weng MD
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate
 Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
QUANTIFYING CEREBRAL CONTRIBUTIONS TO PAIN 1
 QUANTIFYING CEREBRAL CONTRIBUTIONS TO PAIN 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Overview of the SIIPS1 development. The development of the SIIPS1 consisted of individual- and group-level analysis steps. 1) Individual-person
QUANTIFYING CEREBRAL CONTRIBUTIONS TO PAIN 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Overview of the SIIPS1 development. The development of the SIIPS1 consisted of individual- and group-level analysis steps. 1) Individual-person
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Lecture 12: more Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Regression
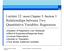 Lecture 12: more Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Regression Equation of Regression Line; Residuals Effect of Explanatory/Response Roles Unusual Observations Sample
Lecture 12: more Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Regression Equation of Regression Line; Residuals Effect of Explanatory/Response Roles Unusual Observations Sample
Classic Evidence: Raine, Buchsbaum and LaCasse, 1997 Brain Abnormalities in Murderers indicated by PET (pg 16-19)
 Classic Evidence: Raine, Buchsbaum and LaCasse, 1997 Brain Abnormalities in Murderers indicated by PET (pg 16-19) Patrick has just been arrested for murder. He confesses to the crime of killing his next
Classic Evidence: Raine, Buchsbaum and LaCasse, 1997 Brain Abnormalities in Murderers indicated by PET (pg 16-19) Patrick has just been arrested for murder. He confesses to the crime of killing his next
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Supplementary Figure 1 A schema illustrating the concept of ASD-ness.
 Supplementary Figure A schema illustrating the concept of ASD-ness. It is proposed here that, at the individual level, the output of the ASD classifier with a good generalization across sites might provide
Supplementary Figure A schema illustrating the concept of ASD-ness. It is proposed here that, at the individual level, the output of the ASD classifier with a good generalization across sites might provide
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
Validation of basal ganglia segmentation on a 3T MRI template
 Validation of basal ganglia segmentation on a 3T MRI template Claire Haegelen, Nicolas Guizard, Pierrick Coupé, Florent Lalys, Pierre Jannin, Xavier Morandi, D. Louis Collins To cite this version: Claire
Validation of basal ganglia segmentation on a 3T MRI template Claire Haegelen, Nicolas Guizard, Pierrick Coupé, Florent Lalys, Pierre Jannin, Xavier Morandi, D. Louis Collins To cite this version: Claire
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Redlich R, Opel N, Grotegerd D, et al. Prediction of individual response to electroconvulsive therapy via machine learning on structural magnetic resonance imaging data. JAMA
Supplementary Online Content Redlich R, Opel N, Grotegerd D, et al. Prediction of individual response to electroconvulsive therapy via machine learning on structural magnetic resonance imaging data. JAMA
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Lecture 6B: more Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Regression
 Lecture 6B: more Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Regression! Equation of Regression Line; Residuals! Effect of Explanatory/Response Roles! Unusual Observations! Sample
Lecture 6B: more Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Regression! Equation of Regression Line; Residuals! Effect of Explanatory/Response Roles! Unusual Observations! Sample
Table of Contents. Plots. Essential Statistics for Nursing Research 1/12/2017
 Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
Essential Statistics for Nursing Research Kristen Carlin, MPH Seattle Nursing Research Workshop January 30, 2017 Table of Contents Plots Descriptive statistics Sample size/power Correlations Hypothesis
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables.
 bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
bivariate analysis: The statistical analysis of the relationship between two variables. cell frequency: The number of cases in a cell of a cross-tabulation (contingency table). chi-square (χ 2 ) test for
Reproducibility is necessary but insufficient for addressing brain science issues.
 1 Reproducibility is necessary but insufficient for addressing brain science issues. GLM promises nothing but the higher amplitude of the experimental trials on the average compared with the control trials.
1 Reproducibility is necessary but insufficient for addressing brain science issues. GLM promises nothing but the higher amplitude of the experimental trials on the average compared with the control trials.
The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia
 Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Before we get started:
 Before we get started: http://arievaluation.org/projects-3/ AEA 2018 R-Commander 1 Antonio Olmos Kai Schramm Priyalathta Govindasamy Antonio.Olmos@du.edu AntonioOlmos@aumhc.org AEA 2018 R-Commander 2 Plan
Before we get started: http://arievaluation.org/projects-3/ AEA 2018 R-Commander 1 Antonio Olmos Kai Schramm Priyalathta Govindasamy Antonio.Olmos@du.edu AntonioOlmos@aumhc.org AEA 2018 R-Commander 2 Plan
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Translational Clinical Science
 Translational Clinical Science Alasdair Vance Head, Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics University of Melbourne Royal Children s Hospital Outline of Presentation 1. Translational Clinical
Translational Clinical Science Alasdair Vance Head, Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics University of Melbourne Royal Children s Hospital Outline of Presentation 1. Translational Clinical
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY DETAILS
 Journal: EJNMMI Research Title: The relationship between endogenous thymidine concentrations and [ 1 F]FLT uptake in a range of preclinical tumour models Authors: Kathrin Heinzmann 1,, Davina J Honess
Journal: EJNMMI Research Title: The relationship between endogenous thymidine concentrations and [ 1 F]FLT uptake in a range of preclinical tumour models Authors: Kathrin Heinzmann 1,, Davina J Honess
A possible mechanism for impaired joint attention in autism
 A possible mechanism for impaired joint attention in autism Justin H G Williams Morven McWhirr Gordon D Waiter Cambridge Sept 10 th 2010 Joint attention in autism Declarative and receptive aspects initiating
A possible mechanism for impaired joint attention in autism Justin H G Williams Morven McWhirr Gordon D Waiter Cambridge Sept 10 th 2010 Joint attention in autism Declarative and receptive aspects initiating
Long-Term Effects of Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation on Force Control in a Patient with Parkinson s Disease-Driven Action Tremor
 Long-Term Effects of Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation on Force Control in a Patient with Parkinson s Disease-Driven Action Tremor Karen L. Francis, PhD* Waneen W. Spirduso, EdD Tim Eakin, PhD Pamela Z.
Long-Term Effects of Thalamic Deep Brain Stimulation on Force Control in a Patient with Parkinson s Disease-Driven Action Tremor Karen L. Francis, PhD* Waneen W. Spirduso, EdD Tim Eakin, PhD Pamela Z.
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
 American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
 Passport control a bit carried away. appreciated the advice forgot to talk to the manager, next thing I know my fmri thankfully, when aroused things back to normal Inattentive impaired children and adolescents:
Passport control a bit carried away. appreciated the advice forgot to talk to the manager, next thing I know my fmri thankfully, when aroused things back to normal Inattentive impaired children and adolescents:
Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines
 Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines Altmann A. 1,2,7 *, Schröter M.S. 1,3 *, Spoormaker V.I. 1, Kiem S.A. 1, Jordan D. 4, Ilg R. 5,6,
Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines Altmann A. 1,2,7 *, Schröter M.S. 1,3 *, Spoormaker V.I. 1, Kiem S.A. 1, Jordan D. 4, Ilg R. 5,6,
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
SpeechEasy: Altered auditory feedback in Adults with Persistent Developmental Stuttering
 SpeechEasy: Altered auditory feedback in Adults with Persistent Developmental Stuttering Anne L. Foundas, M.D., Principal Investigator (PI) Tulane University & Tulane Neuroscience Program Phone: 504-988-2241
SpeechEasy: Altered auditory feedback in Adults with Persistent Developmental Stuttering Anne L. Foundas, M.D., Principal Investigator (PI) Tulane University & Tulane Neuroscience Program Phone: 504-988-2241
Medical Statistics 1. Basic Concepts Farhad Pishgar. Defining the data. Alive after 6 months?
 Medical Statistics 1 Basic Concepts Farhad Pishgar Defining the data Population and samples Except when a full census is taken, we collect data on a sample from a much larger group called the population.
Medical Statistics 1 Basic Concepts Farhad Pishgar Defining the data Population and samples Except when a full census is taken, we collect data on a sample from a much larger group called the population.
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Chapter 1: Exploring Data
 Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
Chapter 1: Exploring Data Key Vocabulary:! individual! variable! frequency table! relative frequency table! distribution! pie chart! bar graph! two-way table! marginal distributions! conditional distributions!
Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Differences in brain structure and function between the sexes has been a topic of
 Introduction Differences in brain structure and function between the sexes has been a topic of scientific inquiry for over 100 years. In particular, this topic has had significant interest in the past
Introduction Differences in brain structure and function between the sexes has been a topic of scientific inquiry for over 100 years. In particular, this topic has had significant interest in the past
Standing strong in the roaring 40s ANZFPS November HOBART. Credit: Tourism Tasmania and Garry Moore
 Standing strong in the roaring 40s ANZFPS November 18-20 2018 HOBART Credit: Tourism Tasmania and Garry Moore Thinking on your feet the interplay between cognition, gait and falls Dr Michele Callisaya
Standing strong in the roaring 40s ANZFPS November 18-20 2018 HOBART Credit: Tourism Tasmania and Garry Moore Thinking on your feet the interplay between cognition, gait and falls Dr Michele Callisaya
2.4.1 STA-O Assessment 2
 2.4.1 STA-O Assessment 2 Work all the problems and determine the correct answers. When you have completed the assessment, open the Assessment 2 activity and input your responses into the online grading
2.4.1 STA-O Assessment 2 Work all the problems and determine the correct answers. When you have completed the assessment, open the Assessment 2 activity and input your responses into the online grading
Supplemental Data. Inclusion/exclusion criteria for major depressive disorder group and healthy control group
 1 Supplemental Data Inclusion/exclusion criteria for major depressive disorder group and healthy control group Additional inclusion criteria for the major depressive disorder group were: age of onset of
1 Supplemental Data Inclusion/exclusion criteria for major depressive disorder group and healthy control group Additional inclusion criteria for the major depressive disorder group were: age of onset of
Role of the ventral striatum in developing anorexia nervosa
 Role of the ventral striatum in developing anorexia nervosa Anne-Katharina Fladung 1 PhD, Ulrike M. E.Schulze 2 MD, Friederike Schöll 1, Kathrin Bauer 1, Georg Grön 1 PhD 1 University of Ulm, Department
Role of the ventral striatum in developing anorexia nervosa Anne-Katharina Fladung 1 PhD, Ulrike M. E.Schulze 2 MD, Friederike Schöll 1, Kathrin Bauer 1, Georg Grön 1 PhD 1 University of Ulm, Department
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation. Jacobs et al.
 Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation Jacobs et al. Supplementary Information Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects
Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation Jacobs et al. Supplementary Information Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Meaning-based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 1.138/s41562-17-28- In the format provided by the authors and unedited. -based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps John M. Henderson 1,2 *
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters DOI: 1.138/s41562-17-28- In the format provided by the authors and unedited. -based guidance of attention in scenes as revealed by meaning maps John M. Henderson 1,2 *
Supplementary Information on TMS/hd-EEG recordings: acquisition and preprocessing
 Supplementary Information on TMS/hd-EEG recordings: acquisition and preprocessing Stability of the coil position was assured by using a software aiming device allowing the stimulation only when the deviation
Supplementary Information on TMS/hd-EEG recordings: acquisition and preprocessing Stability of the coil position was assured by using a software aiming device allowing the stimulation only when the deviation
A WEB-BASED INFRASTRUCTURE FOR MRI- BASED COMPUTER CLASSIFICATION OF NEUROLOGICAL PATIENTS: NEURO-IMAGE
 A WEB-BASED INFRASTRUCTURE FOR MRI- BASED COMPUTER CLASSIFICATION OF NEUROLOGICAL PATIENTS: NEURO-IMAGE F. Chionna 1, A. Cerasa 2, M. Giacovazzo 3, A. Iannella 3, Martini 1, N. Savino 1, V.Giannini 3,
A WEB-BASED INFRASTRUCTURE FOR MRI- BASED COMPUTER CLASSIFICATION OF NEUROLOGICAL PATIENTS: NEURO-IMAGE F. Chionna 1, A. Cerasa 2, M. Giacovazzo 3, A. Iannella 3, Martini 1, N. Savino 1, V.Giannini 3,
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
The hippocampus operates in a threshold manner during spatial source memory Scott D. Slotnick a and Preston P. Thakral b
 Cognitive neuroscience and neuropsychology 265 The hippocampus operates in a threshold manner during spatial source memory Scott D. Slotnick a and Preston P. Thakral b Long-term memory can be based on
Cognitive neuroscience and neuropsychology 265 The hippocampus operates in a threshold manner during spatial source memory Scott D. Slotnick a and Preston P. Thakral b Long-term memory can be based on
4.3 Measures of Variation
 4.3 Measures of Variation! How much variation is there in the data?! Look for the spread of the distribution.! What do we mean by spread? 1 Example Data set:! Weight of contents of regular cola (grams).
4.3 Measures of Variation! How much variation is there in the data?! Look for the spread of the distribution.! What do we mean by spread? 1 Example Data set:! Weight of contents of regular cola (grams).
Incomplete immune response to Coxsackie B viruses. associates with early autoimmunity against insulin
 Incomplete immune response to Coxsackie B viruses associates with early autoimmunity against insulin Michelle P. Ashton 1, Anne Eugster 1, Denise Walther 1, Natalie Daehling 1, Stephanie Riethausen 2,
Incomplete immune response to Coxsackie B viruses associates with early autoimmunity against insulin Michelle P. Ashton 1, Anne Eugster 1, Denise Walther 1, Natalie Daehling 1, Stephanie Riethausen 2,
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
