Review Questions. Know how Aristotle and Plato differed in their ideas of universals and particulars.
|
|
|
- Gabriella Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Questions Chapter 1 What is cognition? What is cognitive psychology? What is the distinction between structure and process? Who was Diogenes of Apollania? What is the transcendental method proposed by Kant? Know how Aristotle and Plato differed in their ideas of universals and particulars. Where did St. Augustine think that cognition/ memory occurred? What was psychophysics? Who was Wilhelm Wundt? What is the introspective method? What is structuralism and who started this movement? Who was Hermann von Ebbinghaus? What is functionalism and who started this movement? What is behaviorism and how did this movement affect cognitive psychology? What events lead to the re-birth of cognitive psychology / science? What are the assumptions of cognitive psychology? Chapter 2 What does the scientific method require of experimental cognition? What is a process model? How do cognitive scientists measure information processing? What are some common guiding analogies for cognitive scientists? What is the Standard Information Processing Approach (Atkinson & Shiffrin, 1968)?
2 What is the problem with the Standard Information Processing Approach? What are some problems with Process Models? Explain Neisser s (1976) New Information Processing Approach. Chapter 3 What types of photoreceptors does the human retina have and how are they distributed? What is contralaterality? How does sensation differ from perception? What is Helmholtz s trichomatic colour perception theory? What is the opponent process theory? What is the order of neural activation in visual sensation? What is the difference between bottom-up and top-down processing? How do visual saccades and fixations differ? What is visual persistence? And what is visual sensory memory? Explain Sperling s (1960) tachistoscope experiment. How does backward masking inform our understanding of iconic memory? What is the format of representation in iconic memory? How do template theories of pattern recognition differ from Feature theories? What is the pandemonium theory? What is the connectionism theory? What is the recognition by components theory? How quickly does pattern recognition copy information from sensory store to working memory? What is prosopagnosia? Apperceptive agnosia? Associative agnosia? What do are the implications of agnosias for cognitive science?
3 Chapter 4 What is explicit and implicit processing and give an example of each. Describe two important factors related to selective attention in Norman s Pertinence Model. Describe Johnston and Heinz s Multimode Model of Attention. How does Kahneman s Capacity theory differ from the early, middle or late section models proposed by Broadbent, Treisman and Norman? What were the main findings of Shiffrin & Schneider s (1977) study on controlled versus automatic search. What are the disadvantages of automaticity? Explain and describe the stroop effect. Describe the procedures, results and implications (including the cost and benefits) of Posner and Snyder s (1975) study on high validity and low validity priming. What is hemi-neglect? How does Logan (1988), in his Instance Theory of Automaticity, explain how something becomes automatic? Chapter 5 According to Sternberg, how do we access info from STM? How did Sternberg determine how long it takes us to scan/search STM? What are the limitations to Sternberg s conclusions? STM can hold a variety of informational codes. Name four codes and provide evidence for each. What are three differences between STM and WM? Explain the serial position curve. What is the effect of distraction, word frequency and rate of presentation on the serial position curve?
4 What is the difference between dissociation and double dissociation? What is release from PI? What is the difference between decay and interference in STM. Chapter 6 What is the key difference between explicit and implicit memory? What types of information are stored in episodic and semantic memory? Describe the mnemonic devices (1) Method of Loci and (2) Peg Word Describe the procedure used by Rundus (1971). What were the results of this experiment? What was Ebbinghaus s major contribution to the study of memory? What are metamemory and metacognition? Outline the Levels of Processing view (Craik & Lockhart). What was a major problem with this view? What was the main finding in Bousfield s (1953) experiment on organization and storage of information in memory? What is the paired-associate learning task? What did Jenkins & Dallenbach do and what were the results of this experiment? Chapter 7 Define semantic memory and give an example of a semantic memory. What were the results of Loftus & Palmer s (1974) experiment? Be able to describe the components in Collins & Quillian s Network model (i.e., what are nodes? Spreading activation? Intersection search?) What is Smith s Feature Comparison Model? (i.e., what are feature lists? Defining features? Characteristic features?) What is the sentence verification task? What is the typicality effect?
5 What is a prototype? Describe priming. (define: prime, probe/target, costs/benefits) Define stimulus onset asynchrony (SOA). What is connectionism? Chapter 8 What are the 7 sins of memory? What is hypermnesia? What is reconstructive memory? How did Ebbinghaus & Bartlett differ in their approach to studying LTM? What were Barlett s major findings of how people recalled material over time? What is a schema? Script? Describe the Bransford & Franks (1971) study on semantic integration. What s the difference between technical accuracy and content accuracy in memory? What is a proposition? How did Sachs study support the validity of propositions?
September 25, Measures of facilitated responding (priming) Lexical decision
 1 Memory I: Basic Findings September 25, 2008 2 3 Major Historical Landmarks Basic Phenomena Hermann Ebbinghaus Uber das Gedächtniss (1885): first major treatise on empirical study of memory Bartlett (1932):
1 Memory I: Basic Findings September 25, 2008 2 3 Major Historical Landmarks Basic Phenomena Hermann Ebbinghaus Uber das Gedächtniss (1885): first major treatise on empirical study of memory Bartlett (1932):
Really Excellent Ideas!
 Course website: http://www2.sfu.ca/psychology/groups/faculty/spalek/teaching/221/index.htm Really Excellent Ideas! keep up with text readings attend lectures/tutorials be on time at start and after break
Course website: http://www2.sfu.ca/psychology/groups/faculty/spalek/teaching/221/index.htm Really Excellent Ideas! keep up with text readings attend lectures/tutorials be on time at start and after break
General Knowledge/Semantic Memory: Chapter 8 1
 General Knowledge/Semantic Memory: Chapter 8 1 Cognitive Psychology (EXP 4680) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. GENERAL KNOWLEDGE AND SEMANTIC MEMORY CHAPTER 8 Background on Semantic Memory o semantic memory includes
General Knowledge/Semantic Memory: Chapter 8 1 Cognitive Psychology (EXP 4680) Christine L. Ruva, Ph.D. GENERAL KNOWLEDGE AND SEMANTIC MEMORY CHAPTER 8 Background on Semantic Memory o semantic memory includes
Exam #4 Study Guide. Chapter 7 Memory
 Exam #4 Study Guide Chapter 7 Memory I. Memory Structural categorizations A. By length of time i. Sensory Store ii. Short Term Memory (working memory) iii. Long Term Memory B. By type of information i.
Exam #4 Study Guide Chapter 7 Memory I. Memory Structural categorizations A. By length of time i. Sensory Store ii. Short Term Memory (working memory) iii. Long Term Memory B. By type of information i.
MEMORY. Announcements. Practice Question 2. Practice Question 1 10/3/2012. Next Quiz available Oct 11
 Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
Memory 2/15/2017. The Three Systems Model of Memory. Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information
 Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
How should you study for Friday's exam?
 How should you study for Friday's exam? re-read textbook? re-read lecture slides? study guide? NO! these are passive. Use active study. Test yourself by Take the practice quizzes in Moodle Create your
How should you study for Friday's exam? re-read textbook? re-read lecture slides? study guide? NO! these are passive. Use active study. Test yourself by Take the practice quizzes in Moodle Create your
CogSysIII Lecture 6: Attention, Memory Organization and Information Presentation
 CogSysIII Lecture 6: Attention, Memory Organization and Information Presentation Human Computer Interaction Ute Schmid Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University last change May 22, 2007 CogSysIII Lecture
CogSysIII Lecture 6: Attention, Memory Organization and Information Presentation Human Computer Interaction Ute Schmid Applied Computer Science, Bamberg University last change May 22, 2007 CogSysIII Lecture
ASHI 712. The Neuroscience of Human Memory. Dr. Olave E. Krigolson LECTURE 2: Short Term Memory and Sleep and Memory
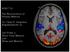 ASHI 712 The Neuroscience of Human Memory Dr. Olave E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca LECTURE 2: Short Term Memory and Sleep and Memory Working / Short Term Memory Sunglasses Chair Dress Earrings Boots Bed
ASHI 712 The Neuroscience of Human Memory Dr. Olave E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca LECTURE 2: Short Term Memory and Sleep and Memory Working / Short Term Memory Sunglasses Chair Dress Earrings Boots Bed
VISUAL MEMORY. Visual Perception
 VISUAL MEMORY Visual Perception Memory is unqiue Other aspects of visual perception Bombard us with stimuli at every instance Memory Helps us to make sense from chain of such instances Slide 2 Two Theories
VISUAL MEMORY Visual Perception Memory is unqiue Other aspects of visual perception Bombard us with stimuli at every instance Memory Helps us to make sense from chain of such instances Slide 2 Two Theories
Identify these objects
 Pattern Recognition The Amazing Flexibility of Human PR. What is PR and What Problems does it Solve? Three Heuristic Distinctions for Understanding PR. Top-down vs. Bottom-up Processing. Semantic Priming.
Pattern Recognition The Amazing Flexibility of Human PR. What is PR and What Problems does it Solve? Three Heuristic Distinctions for Understanding PR. Top-down vs. Bottom-up Processing. Semantic Priming.
Chapter 5 Short-term/Working Memory
 Chapter 5 Short-term/Working Memory Original Information Processing Model rehearsal transfer Sensory Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory input from the world attention retrieval Characterizing Memories
Chapter 5 Short-term/Working Memory Original Information Processing Model rehearsal transfer Sensory Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory input from the world attention retrieval Characterizing Memories
U3A PSYCHOLOGY. How Memory works January 2019
 U3A PSYCHOLOGY How Memory works January 2019 How memory works This session will cover: A definition of memory Different types of memory Some theories of memory Why we forget How to improve your memory?
U3A PSYCHOLOGY How Memory works January 2019 How memory works This session will cover: A definition of memory Different types of memory Some theories of memory Why we forget How to improve your memory?
Sperling conducted experiments on An experiment was conducted by Sperling in the field of visual sensory memory.
 Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
Outline 3/14/2013. Practice question What are the two types of learning we discussed? Example: remembering our ATM PIN. PSYC 120 General Psychology
 Outline 3/14/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 14: Memory 3 processes of memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 Office
Outline 3/14/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 14: Memory 3 processes of memory Encoding Storage Retrieval Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 Office
Introduction and Historical Background. August 22, 2007
 1 Cognitive Bases of Behavior Introduction and Historical Background August 22, 2007 2 Cognitive Psychology Concerned with full range of psychological processes from sensation to knowledge representation
1 Cognitive Bases of Behavior Introduction and Historical Background August 22, 2007 2 Cognitive Psychology Concerned with full range of psychological processes from sensation to knowledge representation
11/14/2017 SUPPORT FOR A MULTI STORE MODEL TEMPORARY MEMORY: SHORT-TERM AND WORKING MEMORY INFORMATION PROCESSING MODEL & THE MODAL MODEL OF MEMORY
 SUPPORT FOR A MULTI STORE MODEL Distinctions between STM and LTM Behavior Biological Neurological TEMPORARY MEMORY: SHORT-TERM AND WORKING MEMORY Learning & Memory Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D. Ebbinghaus no
SUPPORT FOR A MULTI STORE MODEL Distinctions between STM and LTM Behavior Biological Neurological TEMPORARY MEMORY: SHORT-TERM AND WORKING MEMORY Learning & Memory Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D. Ebbinghaus no
1960s Many models of memory proposed. Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)-Modal Model. Sensory Memory. Short-term Memory. Long-term Memory.
 1 1960s Many models of memory proposed Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)-Modal Model Sensory Memory Short-term Memory Long-term Memory 2 Primary Memory Secondary Memory 3 1 4 Sensory Memory Short-Term Memory
1 1960s Many models of memory proposed Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968)-Modal Model Sensory Memory Short-term Memory Long-term Memory 2 Primary Memory Secondary Memory 3 1 4 Sensory Memory Short-Term Memory
Experimental Psychopathology. Lecture 39
 Experimental Psychopathology Lecture 39 1 The Symptoms Are Not the Disease Vocabulary of the Medical Model Symptoms Superficial Manifestations of Underlying Pathology Syndromes Clusters of Symptoms that
Experimental Psychopathology Lecture 39 1 The Symptoms Are Not the Disease Vocabulary of the Medical Model Symptoms Superficial Manifestations of Underlying Pathology Syndromes Clusters of Symptoms that
Lecture 9 Cognitive Processes Part I. Kashif Sajjad Bhatti Assistant Professor IIU, Islamabad
 Lecture 9 Cognitive Processes Part I Kashif Sajjad Bhatti Assistant Professor IIU, Islamabad In the Last Lecture Vision Color Theory 3D Vision Reading Hearing Human Ear Processing Sound Touch (Haptic Perception)
Lecture 9 Cognitive Processes Part I Kashif Sajjad Bhatti Assistant Professor IIU, Islamabad In the Last Lecture Vision Color Theory 3D Vision Reading Hearing Human Ear Processing Sound Touch (Haptic Perception)
Introduction to Long-Term Memory
 Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Cognition. Mid-term 1. Top topics for Mid Term 1. Heads up! Mid-term exam next week
 Cognition Prof. Mike Dillinger Mid-term 1 Heads up! Mid-term exam next week Chapters 2, 3, of the textbook Perception, Attention, Short-term memory The lectures are to help you digest the chapters; exams
Cognition Prof. Mike Dillinger Mid-term 1 Heads up! Mid-term exam next week Chapters 2, 3, of the textbook Perception, Attention, Short-term memory The lectures are to help you digest the chapters; exams
Short-Term and Working Memory. Outline. What is memory? Short-term memory Working memory Working memory and the brain. Chapter 5
 Short-Term and Working Memory Chapter 5 Outline Short-term memory Working memory Working memory and the brain What is memory? The Persistence of Memory -Salvador Dali Intuitions about memory Memory for
Short-Term and Working Memory Chapter 5 Outline Short-term memory Working memory Working memory and the brain What is memory? The Persistence of Memory -Salvador Dali Intuitions about memory Memory for
Cognitive Psychology. Robert J. Sternberg EDITION. Yak University THOIVISOISI * WADSWORTH
 EDITION Cognitive Psychology Robert J. Sternberg Yak University THOIVISOISI * WADSWORTH Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States C H A P T E R 1 Introduction to Cognitive Psychology
EDITION Cognitive Psychology Robert J. Sternberg Yak University THOIVISOISI * WADSWORTH Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States C H A P T E R 1 Introduction to Cognitive Psychology
ATTENTION! Learning Objective Topics. (Specifically Divided and Selective Attention) Chapter 4. Selective Attention
 ATTENTION! (Specifically Divided and Selective Attention) Chapter 4 Learning Objective Topics Selective Attention Visual Tasks Auditory Tasks Early vs. Late Selection Models Visual Search Divided Attention
ATTENTION! (Specifically Divided and Selective Attention) Chapter 4 Learning Objective Topics Selective Attention Visual Tasks Auditory Tasks Early vs. Late Selection Models Visual Search Divided Attention
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015
 Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF EDUCATION AND PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PATHWAYS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016
 EDP07 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF EDUCATION AND PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PATHWAYS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 COGNITIVE AND BIOPSYCHOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES MODULE NO: PSC4003 Date: Wednesday 18 th
EDP07 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF EDUCATION AND PSYCHOLOGY PSYCHOLOGY PATHWAYS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 COGNITIVE AND BIOPSYCHOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES MODULE NO: PSC4003 Date: Wednesday 18 th
CHAPTER 6: Memory model Practice questions at - text book pages 112 to 113
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 6: Memory model Practice questions at - text book pages 112 to 113 1) Which of the following sequences reflects the order in which the human brain processes
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 6: Memory model Practice questions at - text book pages 112 to 113 1) Which of the following sequences reflects the order in which the human brain processes
Memory (1) Visual Sensory Store. Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory
 Memory (1) Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory Visual Sensory Store It appears that our visual system is able to hold a great deal of information but that if we do not attend to this information
Memory (1) Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) Model of Memory Visual Sensory Store It appears that our visual system is able to hold a great deal of information but that if we do not attend to this information
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind
 Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology, 3e by Ronald T. Kellogg Chapter 2. Multiple Choice
 Multiple Choice 1. Which structure is not part of the visual pathway in the brain? a. occipital lobe b. optic chiasm c. lateral geniculate nucleus *d. frontal lobe Answer location: Visual Pathways 2. Which
Multiple Choice 1. Which structure is not part of the visual pathway in the brain? a. occipital lobe b. optic chiasm c. lateral geniculate nucleus *d. frontal lobe Answer location: Visual Pathways 2. Which
Part I History & Conceptualizations
 Part I History & Conceptualizations What is Cognitive Psychology? Formal Definition all processes by which sensory input is transformed, reduced, d elaborated, stored, recovered, and used. d (Neisser,
Part I History & Conceptualizations What is Cognitive Psychology? Formal Definition all processes by which sensory input is transformed, reduced, d elaborated, stored, recovered, and used. d (Neisser,
Consolidating working memory: Enhancing cognitive performance through effective encoding
 Consolidating working memory: Enhancing cognitive performance through effective encoding Donna Bayliss Neurocognitive Development Unit School of Psychology University of Western Australia 1 Consolidation
Consolidating working memory: Enhancing cognitive performance through effective encoding Donna Bayliss Neurocognitive Development Unit School of Psychology University of Western Australia 1 Consolidation
How Many Memory Stores Are There? PDF created with pdffactory trial version
 How Many Memory Stores Are There? Outline The serial position curve The modal model Empirical evidence: manipulations and dissociations The modal model: critique Single-store models Two-store vs. single-store
How Many Memory Stores Are There? Outline The serial position curve The modal model Empirical evidence: manipulations and dissociations The modal model: critique Single-store models Two-store vs. single-store
MUSINGS ON ATTENTION. In a busy world filled with sounds, how do we select what to listen to?
 Part II -Attention MUSINGS ON ATTENTION In a busy world filled with sounds, how do we select what to listen to? How do we find meaningful information within a complex scene? What role does attention play
Part II -Attention MUSINGS ON ATTENTION In a busy world filled with sounds, how do we select what to listen to? How do we find meaningful information within a complex scene? What role does attention play
Templates for Rejection: Configuring Attention to Ignore Task-Irrelevant Features
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2012, Vol. 38, No. 3, 580 584 2012 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/12/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0027885 OBSERVATION Templates
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2012, Vol. 38, No. 3, 580 584 2012 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/12/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0027885 OBSERVATION Templates
A: implicit, unconscious, tacit. The name for cognitive processes of which we lack awareness
 A: implicit, unconscious, tacit The name for cognitive processes of which we lack awareness A: top-down The usually conscious influence of past experience on behavior A: circular reasoning Given 2 premises,
A: implicit, unconscious, tacit The name for cognitive processes of which we lack awareness A: top-down The usually conscious influence of past experience on behavior A: circular reasoning Given 2 premises,
Human cogition. Human Cognition. Optical Illusions. Human cognition. Optical Illusions. Optical Illusions
 Human Cognition Fang Chen Chalmers University of Technology Human cogition Perception and recognition Attention, emotion Learning Reading, speaking, and listening Problem solving, planning, reasoning,
Human Cognition Fang Chen Chalmers University of Technology Human cogition Perception and recognition Attention, emotion Learning Reading, speaking, and listening Problem solving, planning, reasoning,
STRUCTURAL ACCOUNTS OF MEMORY
 STRUCTURAL ACCOUNTS OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
STRUCTURAL ACCOUNTS OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education 2014/2015
Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information:
 EVALUATION OF THE MODAL MODEL OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
EVALUATION OF THE MODAL MODEL OF MEMORY Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept. of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
History of Cognitive Psychology and its Relation to other Fields
 History of Cognitive and its Relation to other Fields Lesson I: Introduction module 02 Introduction.02. 1 Precursors of modern cognitive psychology until 1950 Roots in philosophy Plato, Aristoteles, Descartes,
History of Cognitive and its Relation to other Fields Lesson I: Introduction module 02 Introduction.02. 1 Precursors of modern cognitive psychology until 1950 Roots in philosophy Plato, Aristoteles, Descartes,
AS Module 1. Cognitive & Developmental Psychology. Cognitive Human Memory. The nature and structure of memory Thought to be three types
 AS Module 1 Cognitive & Developmental Psychology Cognitive Human Memory The nature and structure of memory Thought to be three types Sensory memory Short term memory Long term memory Short Term Memory
AS Module 1 Cognitive & Developmental Psychology Cognitive Human Memory The nature and structure of memory Thought to be three types Sensory memory Short term memory Long term memory Short Term Memory
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Chapter 5. Memory Structures and Processes. Chapter 5 Memory Processes
 Chapter 5 Memory Structures and Processes Chapter 5 Memory Processes 1 Memory The Man with the 30 Second Memory Chapter 5 Memory Processes 2 Are Some things Easier (Harder) to remember than others? Chapter
Chapter 5 Memory Structures and Processes Chapter 5 Memory Processes 1 Memory The Man with the 30 Second Memory Chapter 5 Memory Processes 2 Are Some things Easier (Harder) to remember than others? Chapter
Chapter 1. What is Memory?
 + Chapter 1 What is Memory? Reductionism m + Psychological Theories Theories are comparable to maps, helping to: Summarize knowledge in a simple and structured manner Pose new, testable questions that
+ Chapter 1 What is Memory? Reductionism m + Psychological Theories Theories are comparable to maps, helping to: Summarize knowledge in a simple and structured manner Pose new, testable questions that
Chapter 7. Mental Representation
 Chapter 7 Mental Representation Mental Representation Mental representation is a systematic correspondence between some element of a target domain and some element of a modeling (or representation) domain.
Chapter 7 Mental Representation Mental Representation Mental representation is a systematic correspondence between some element of a target domain and some element of a modeling (or representation) domain.
Cognitive Psychology. Mark Rafter Multiple Intelligences
 Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Multiple Intelligences Handouts: Please pick up a copy of today
Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Multiple Intelligences Handouts: Please pick up a copy of today
DEPARTMENT OF ARTS AND EDUCATION COURSE OUTLINE FALL 2015 PY 1040 (C2) BASIC PSYCHOLOGICAL PROCESSES 3 (3-0-0) 45 Hours
 1 DEPARTMENT OF ARTS AND EDUCATION COURSE OUTLINE FALL 2015 PY 1040 (C2) BASIC PSYCHOLOGICAL PROCESSES 3 (3-0-0) 45 Hours INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Bruce Galenza PHONE: 780-539-2994 OFFICE: C-403 EMAIL: bgalenza@gprc.ab.ca
1 DEPARTMENT OF ARTS AND EDUCATION COURSE OUTLINE FALL 2015 PY 1040 (C2) BASIC PSYCHOLOGICAL PROCESSES 3 (3-0-0) 45 Hours INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Bruce Galenza PHONE: 780-539-2994 OFFICE: C-403 EMAIL: bgalenza@gprc.ab.ca
Animal Behavior. Relevant Biological Disciplines. Inspirations => Models
 Animal Behavior Relevant Biological Disciplines Neuroscience: the study of the nervous system s anatomy, physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology Psychology: the study of mind and behavior Ethology:
Animal Behavior Relevant Biological Disciplines Neuroscience: the study of the nervous system s anatomy, physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology Psychology: the study of mind and behavior Ethology:
Optical Illusions 4/5. Optical Illusions 2/5. Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5. Reading. Reading. Fang Chen Spring 2004
 Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
Pattern Recognition. Organization of Lectures. Complexities of Perception
 Pattern Recognition Complexities Constraints Models Organization of Lectures Complexities of perception Constraints on perception Pattern recognition models Template Distinctive-feature Spatial/configural
Pattern Recognition Complexities Constraints Models Organization of Lectures Complexities of perception Constraints on perception Pattern recognition models Template Distinctive-feature Spatial/configural
This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved
 Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
Lecture 2. Social Cognition. September 16th, 2009 : Lecture 2. Social Cognition : Overview (Social) Cognition Basics
 Lecture 2 Social Cognition September 16th, 2009 : Lecture 2 Social Cognition : Overview Lecture 2 Social Cognition Social Cognition : Overview! Thinking about social objects Social Cognition Social Object!
Lecture 2 Social Cognition September 16th, 2009 : Lecture 2 Social Cognition : Overview Lecture 2 Social Cognition Social Cognition : Overview! Thinking about social objects Social Cognition Social Object!
Cortex and Mind Chapter 5. Memory is stored knowledge about the internal and external environments; it includes perceptual and motor knowledge.
 Cortex and Mind Chapter 5 Memory is stored knowledge about the internal and external environments; it includes perceptual and motor knowledge. Review of classical classification of learning and memory
Cortex and Mind Chapter 5 Memory is stored knowledge about the internal and external environments; it includes perceptual and motor knowledge. Review of classical classification of learning and memory
Attention. What is attention? Attention metaphors. Definitions of attention. Chapter 6. Attention as a mental process
 What is attention? Attention Chapter 6 To drive a car you Use effort Sustain attention Orient to several locations Restrict attention Select particular objects Search for particular objects Respond with
What is attention? Attention Chapter 6 To drive a car you Use effort Sustain attention Orient to several locations Restrict attention Select particular objects Search for particular objects Respond with
Midterm Exam 1 NAME: UW ID:
 File = D:\p355\mid1a.p355.spr16.docm 1 John Miyamoto (email: jmiyamot@uw.edu) Psych 355: Introduction to Cognitive Psychology Spring 2016 Course website: https://faculty.washington.edu/jmiyamot/p355/p355-set.htm
File = D:\p355\mid1a.p355.spr16.docm 1 John Miyamoto (email: jmiyamot@uw.edu) Psych 355: Introduction to Cognitive Psychology Spring 2016 Course website: https://faculty.washington.edu/jmiyamot/p355/p355-set.htm
MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL
 MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL ARE OUR LONG TERM MEMORIES PROCESSED AND STORED IN SPECIFIC LOCATIONS? Our memories are flexible and superimposable, a panoramic blackboard with an endless supply
MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL ARE OUR LONG TERM MEMORIES PROCESSED AND STORED IN SPECIFIC LOCATIONS? Our memories are flexible and superimposable, a panoramic blackboard with an endless supply
7. Attention and Memory March 14, :18 PM
 7. Attention and Memory March 14, 2014 7:18 PM Seizures: uncontrolled random firings of groups of neurons that can spread across the brain H.M. s seizures originated in the temporal lobes Removed parts
7. Attention and Memory March 14, 2014 7:18 PM Seizures: uncontrolled random firings of groups of neurons that can spread across the brain H.M. s seizures originated in the temporal lobes Removed parts
the human chapter 1 the human Vision Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term
 chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
the human chapter 1 the human Vision The Eye - physical reception Interpreting the signal (cont) Interpreting the signal
 the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
the human chapter 1 the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
visual, auditory, haptic, movement sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving, skill, error
 chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
chapter 1 the human the human Information i/o visual, auditory, haptic, movement Information stored in memory sensory, short-term, long-term Information processed and applied reasoning, problem solving,
Chapter 1: Cognitive Psychology. Influences: Early. Influences: Structuralism. Introduction. Method 1/1/2015. Concerned with What/How Wilhelm Wundt
 Chapter 1: Cognitive Psychology History, Methods, and Paradigms 1 Introduction Structuralism Behaviorism Individual Differences Influences Early Functionalism Gestalt Cognitive Revolution History, Methods,
Chapter 1: Cognitive Psychology History, Methods, and Paradigms 1 Introduction Structuralism Behaviorism Individual Differences Influences Early Functionalism Gestalt Cognitive Revolution History, Methods,
A Retrieval Theory of Priming in Memory
 Psychological Review Copyright 1988 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 1988, Vol. 95, No. 3, 385--408 0033-295X/88/$00.75 A Retrieval Theory of Priming in Memory Roger Ratcliff and Gail McKoon
Psychological Review Copyright 1988 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 1988, Vol. 95, No. 3, 385--408 0033-295X/88/$00.75 A Retrieval Theory of Priming in Memory Roger Ratcliff and Gail McKoon
Mental Imagery. What is Imagery? What We Can Imagine 3/3/10. What is nature of the images? What is the nature of imagery for the other senses?
 Mental Imagery What is Imagery? What is nature of the images? Exact copy of original images? Represented in terms of meaning? If so, then how does the subjective sensation of an image arise? What is the
Mental Imagery What is Imagery? What is nature of the images? Exact copy of original images? Represented in terms of meaning? If so, then how does the subjective sensation of an image arise? What is the
Perception: Pattern or object recognition. Chapter 3
 Perception: Pattern or object recognition Chapter 3 Perception Sensation vs. perception What are the mechanisms responsible? What is the process? Q: How do we interpret lines and patterns as objects? Q:
Perception: Pattern or object recognition Chapter 3 Perception Sensation vs. perception What are the mechanisms responsible? What is the process? Q: How do we interpret lines and patterns as objects? Q:
Memory. Information Processing Approach
 Memory Information Processing Approach 5 Steps in Information ato Processing 1 Sensory Transduction Data first enters sensory register lasts 1 2secs C O N S O L I D A T I O N 5 Steps in Information ato
Memory Information Processing Approach 5 Steps in Information ato Processing 1 Sensory Transduction Data first enters sensory register lasts 1 2secs C O N S O L I D A T I O N 5 Steps in Information ato
Skills Center Psychology Practice Exam I Psychology The Adaptive Mind by Nairne
 1.) Psychology is defined as a. the scientific investigation of thought processes. b. the understanding of abnormal behavior. c. the scientific study of behavior and mind. d. the study of mental illness
1.) Psychology is defined as a. the scientific investigation of thought processes. b. the understanding of abnormal behavior. c. the scientific study of behavior and mind. d. the study of mental illness
Learning & memory. Phenomenon:
 Learning & memory Phenomenon: 9/11/2001 Where were you on the following day? Your 10th birthday? What did you do? Do you remember when you had an accident? How did it happen? Can you remember a Skill you
Learning & memory Phenomenon: 9/11/2001 Where were you on the following day? Your 10th birthday? What did you do? Do you remember when you had an accident? How did it happen? Can you remember a Skill you
Chapter 3: Information Processing
 SENG 5334: Human Factors Engineering & INDH 5931: Research Topics in IH/Safety Chapter 3: Information Processing By: Magdy Akladios, PhD, PE, CSP, CPE, CSHM 1 A Model of Information Processing Def: A model
SENG 5334: Human Factors Engineering & INDH 5931: Research Topics in IH/Safety Chapter 3: Information Processing By: Magdy Akladios, PhD, PE, CSP, CPE, CSHM 1 A Model of Information Processing Def: A model
Information Processing Mid-February 2007
 Information Processing Mid-February 2007 Information Processing The Information Processing Approach Speed of Processing Attention What Is the Information-Processing Approach? Focuses on ways people process
Information Processing Mid-February 2007 Information Processing The Information Processing Approach Speed of Processing Attention What Is the Information-Processing Approach? Focuses on ways people process
Perceptual Processes II: Attention and Consciousness
 Perceptual Processes II: Attention and Consciousness Chapter 3 1 Attention [Attention] is taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible
Perceptual Processes II: Attention and Consciousness Chapter 3 1 Attention [Attention] is taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible
Introduction and Research Methods
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Research Methods Instruction Tip Have students fill out index cards the first day of class indicating their major, year in school, what grade they expect in the class, why they
Chapter 1 Introduction and Research Methods Instruction Tip Have students fill out index cards the first day of class indicating their major, year in school, what grade they expect in the class, why they
Human Learning and Memory
 Human Learning and Memory This innovative textbook is the first to integrate learning and memory, behavior, and cognition. It focuses on fascinating human research in both memory and learning (while also
Human Learning and Memory This innovative textbook is the first to integrate learning and memory, behavior, and cognition. It focuses on fascinating human research in both memory and learning (while also
2/27/2017. Modal Model of Memory. Executive Attention & Working Memory. Some Questions to Consider (over the next few weeks)
 Executive Attention & Working Memory Memory 1 Some Questions to Consider (over the next few weeks) Why can we remember a telephone number long enough to place a call, but then we forget it almost immediately?
Executive Attention & Working Memory Memory 1 Some Questions to Consider (over the next few weeks) Why can we remember a telephone number long enough to place a call, but then we forget it almost immediately?
AQA A Level Psychology. Topic Companion. Memory. Joseph Sparks & Helen Lakin
 AQA A Level Psychology Topic Companion Memory Joseph Sparks & Helen Lakin AQA A LEVEL Psychology topic companion: MEMORY Page 2 Contents Memory The multi-store model 3 Types of long-term memory 9 The working
AQA A Level Psychology Topic Companion Memory Joseph Sparks & Helen Lakin AQA A LEVEL Psychology topic companion: MEMORY Page 2 Contents Memory The multi-store model 3 Types of long-term memory 9 The working
October 2, Memory II. 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome. 9 Recent/Remote Distinction. 11 Frontal/Executive Contributions to Memory
 1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
Sensation is the conscious experience associated with an environmental stimulus. It is the acquisition of raw information by the body s sense organs
 Sensation is the conscious experience associated with an environmental stimulus. It is the acquisition of raw information by the body s sense organs Perception is the conscious experience of things and
Sensation is the conscious experience associated with an environmental stimulus. It is the acquisition of raw information by the body s sense organs Perception is the conscious experience of things and
in Cognitive Neuroscience
 Finish: History of Cognitive Psychology Then: Physiological Measures. in Cognitive Neuroscience Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 03/29/2018: Lecture 01-4 Note: This Powerpoint
Finish: History of Cognitive Psychology Then: Physiological Measures. in Cognitive Neuroscience Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 03/29/2018: Lecture 01-4 Note: This Powerpoint
Cognitive Psychology. Mark Rafter Information Processing
 Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Photographs: I ll talk about these. Handouts: Please pick up a
Cognitive Psychology Mark Rafter http://www.canyons.edu/faculty/rafterm Roster: Please put a checkmark next to your name or add your name. Photographs: I ll talk about these. Handouts: Please pick up a
Psyc 3705, Cognition--Introduction Sept. 13, 2013
 Cognitive Psychology: Introduction COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY The domain of Cognitive Psychology A brief history of Cognitive Psychology Professor: Dana R. Murphy, Ph.D. Meeting times: Fridays 9 AM to 11:50
Cognitive Psychology: Introduction COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY The domain of Cognitive Psychology A brief history of Cognitive Psychology Professor: Dana R. Murphy, Ph.D. Meeting times: Fridays 9 AM to 11:50
DEPARTMENT OF ARTS AND EDUCATION COURSE OUTLINE WINTER PY1040 (B3): Basic Psychological Processes 3 (3-0-0) 45 Hours for 15 Weeks
 1 DEPARTMENT OF ARTS AND EDUCATION COURSE OUTLINE WINTER 2017 PY1040 (B3): Basic Psychological Processes 3 (3-0-0) 45 Hours for 15 Weeks INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Bruce Galenza PHONE: 780-539-2994 OFFICE: C-403
1 DEPARTMENT OF ARTS AND EDUCATION COURSE OUTLINE WINTER 2017 PY1040 (B3): Basic Psychological Processes 3 (3-0-0) 45 Hours for 15 Weeks INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Bruce Galenza PHONE: 780-539-2994 OFFICE: C-403
Chapter 6. Attention. Attention
 Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Sensory Memory, Short-Term Memory & Working Memory
 Sensory, Short-Term & Working Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/17/2018: Lecture 04-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Sensory, Short-Term & Working Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/17/2018: Lecture 04-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Attentional Blink Paradigm
 Attentional Blink Paradigm ATTENTIONAL BLINK 83 ms stimulus onset asychrony between all stimuli B T D A 3 N P Z F R K M R N Lag 3 Target 1 Target 2 After detection of a target in a rapid stream of visual
Attentional Blink Paradigm ATTENTIONAL BLINK 83 ms stimulus onset asychrony between all stimuli B T D A 3 N P Z F R K M R N Lag 3 Target 1 Target 2 After detection of a target in a rapid stream of visual
The e#ect of temporal uncertainty on measurements: The case of priming e#ects. Rika MIZUNO and Takao MATSUI (Chubu University)
 8 1 2010 33 40 1) The e#ect of temporal uncertainty on measurements: The case of priming e#ects Rika MIZUNO and Takao MATSUI (Chubu University) Previous studies have found that, in experiments that present
8 1 2010 33 40 1) The e#ect of temporal uncertainty on measurements: The case of priming e#ects Rika MIZUNO and Takao MATSUI (Chubu University) Previous studies have found that, in experiments that present
Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk.
 chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
What do we need it for? Attention. Functions of attention. 1. Focusing
 What do we need it for? Attention Processing limitations Finding friend at airport Finite processing resources @ given time Motor limitations Can only move in one direction Pick up finite # of things One
What do we need it for? Attention Processing limitations Finding friend at airport Finite processing resources @ given time Motor limitations Can only move in one direction Pick up finite # of things One
What do we need it for? Attention. Functions of attention. 1. Focusing
 What do we need it for? Attention Processing limitations Finding friend at airport Finite processing resources @ given time Motor limitations Can only move in one direction Pick up finite # of things One
What do we need it for? Attention Processing limitations Finding friend at airport Finite processing resources @ given time Motor limitations Can only move in one direction Pick up finite # of things One
Psych 401: Exam 1 Review. Be familiar with the role of philosophy and physiology in the development of psychology
 Psych 401: Exam 1 Review Below are major points to know for your exam. Exam questions will come from both lecture and the text book (Chapters 1-4). There will likely be an essay question related to the
Psych 401: Exam 1 Review Below are major points to know for your exam. Exam questions will come from both lecture and the text book (Chapters 1-4). There will likely be an essay question related to the
DISSOCIATION BETWEEN DECLARATIVE AND PROCEDURAL MECHANISMS IN LONG-TERM MEMORY
 DISSOCIATION BETWEEN DECLARATIVE AND PROCEDURAL MECHANISMS IN LONG-TERM MEMORY A dissertation submitted to the Kent State University College of Education, Health, and Human Services in partial fulfillment
DISSOCIATION BETWEEN DECLARATIVE AND PROCEDURAL MECHANISMS IN LONG-TERM MEMORY A dissertation submitted to the Kent State University College of Education, Health, and Human Services in partial fulfillment
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues. Outline. Starting Points. Starting Points
 Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
Working Memory: Critical Constructs and Some Current Issues Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Background Maintenance: Modality specificity and buffers Interference resolution: Distraction and
What Effect Do Schemas Have On The Recall Of
 What Effect Do Schemas Have On The Recall Of Memories AIM:Bartlett aimed to investigate the effect of culture on memory. memory ability/ability to recall and have advantageous effects if asked to do a
What Effect Do Schemas Have On The Recall Of Memories AIM:Bartlett aimed to investigate the effect of culture on memory. memory ability/ability to recall and have advantageous effects if asked to do a
Working Memory Load and the Stroop Interference Effect
 Q. Gao, Z. Chen, P. Russell Working Memory Load and the Stroop Interference Effect Quanying Gao, Zhe Chen, & Paul Russell University of Canterbury Although the effect of working memory (WM) load on the
Q. Gao, Z. Chen, P. Russell Working Memory Load and the Stroop Interference Effect Quanying Gao, Zhe Chen, & Paul Russell University of Canterbury Although the effect of working memory (WM) load on the
Competing Frameworks in Perception
 Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception
 Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Cognition. Prof. Mike Dillinger
 Cognition Prof. Mike Dillinger 1 2 Inside LTM What does knowledge/meaning/information look like when it s IN LTM? Mental representation See Chapters 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 in the text [only 6, 8, 9 on exam] 3 Outline
Cognition Prof. Mike Dillinger 1 2 Inside LTM What does knowledge/meaning/information look like when it s IN LTM? Mental representation See Chapters 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 in the text [only 6, 8, 9 on exam] 3 Outline
Brief History of Cognitive Psychology
 Brief History of Cognitive Psychology Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 03/27/2018: Lecture 01-3 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help
Brief History of Cognitive Psychology Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 03/27/2018: Lecture 01-3 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help
Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B
 Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B Cortical Analysis of Visual Context Moshe Bar, Elissa Aminoff. 2003. Neuron, Volume 38, Issue 2, Pages 347 358. Visual objects in context Moshe Bar.
Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B Cortical Analysis of Visual Context Moshe Bar, Elissa Aminoff. 2003. Neuron, Volume 38, Issue 2, Pages 347 358. Visual objects in context Moshe Bar.
The Meaning of the Mask Matters
 PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Report The Meaning of the Mask Matters Evidence of Conceptual Interference in the Attentional Blink Paul E. Dux and Veronika Coltheart Macquarie Centre for Cognitive Science,
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Report The Meaning of the Mask Matters Evidence of Conceptual Interference in the Attentional Blink Paul E. Dux and Veronika Coltheart Macquarie Centre for Cognitive Science,
MEMORY AND INTELLIGENCE IN ALGERIAN SCHOOLED CHILDREN
 PEOPLES DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF ALGERIA MINISTERY OF HIGHER EDUCATION AND SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH UNIVERSITY OF CONSTANTINE FACULTY OF LETTERS & FOREIGN LANGUAGES DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH MEMORY AND INTELLIGENCE
PEOPLES DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF ALGERIA MINISTERY OF HIGHER EDUCATION AND SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH UNIVERSITY OF CONSTANTINE FACULTY OF LETTERS & FOREIGN LANGUAGES DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH MEMORY AND INTELLIGENCE
