CHAPTER 10. The Dynamics of the Personality: SCLT View of Learning THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH. part 2
|
|
|
- Shona Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 10 THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH part 2 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 All behaviour is acquired through learning Important differences between social cognitive views of learning and those of standard behaviourism (Skinner): Skinner: Individuals learn passively on the basis of environmental reinforcement/punishment / SCLT: Individuals are active participants who influence their own learning process (via selfregulation) Skinner: Conditioning is the only form of learning / SCLT: Learning takes place via direct experience, observation, selfregulation Skinner: Learning is always linked to reinforcement by an external agent / SCLT: Learning is linked to direct, vicarious, and selfreinforcement Direct reinforcement/punishment: individual receives reward/punishment for their behaviour from an external agent Vicarious reinforcement/punishment: individual observes another being rewarded/punished for a particular behaviour Self-reinforcement/punishment: an individual rewards/punishes themselves for engaging in a particular behaviour An individual s subjective acceptance of reward and punishment is the most important element in learning Learning through direct experience Behaviour changes as a result of performing a behaviour (i.e.. as a result of being rewarded or punished by someone else for performing the behaviour) Skinner: occurs via operant conditioning or respondent condition SCLT: Observational learning through self-regulation is more important than learning through direct experience
2 Cognitive processes play an important role in learning through direct experience (Skinner would not agree with this) People do not simply produce behaviour they consciously perceive and evaluate the consequences of the behaviour Self-reinforcement is as important (if not more important) than direct (environmental) reinforcement Observational Learning This is the most important form of learning People only learn a few behaviours from direct experience alone Social Learning all learning phenomena in which social and cognitive factors play a role The Model: the person, book, film character etc whose behaviour is being observed The Observer: the person observing the model s behaviour The Reinforcement Agent: the person who rewards or punishes the model s behaviour The behaviour of the observer changes as a result of observing the behaviour of the model Vicarious reinforcement: when the model s behaviour is reinforced and this is observed by the observer, resulting in the observing acquiring the model s behaviour Modelling: the model s behaviour Imitation: when the observer copies the model s behaviour Counter-imitation: when the observer engages in the opposite behaviour to that which they observed the model performing For observational learning to take place: Observer must pay attention to the model s behaviour The observer must retain (remember) the model s behaviour (retention) depends on the observer s attention The observer must reproduce the model s behaviour at some point in the future (reproduction)
3 Factors influencing Observational Learning The nature of the modelled behaviour The nature of the behaviour influences attention, retention, and reproduction of behaviour New, unknown, active, captivating behaviour attracts attention of observers and such behaviour is more easily acquired The characteristics of the model The behaviour of a high status model, or a model that is perceived as similar to the observer, is more likely to be reproduced by the observer than that of a low-status or dissimilar model The characteristics of the observer Motivation, interests, values, self-confidence, opinions, intelligence, and perceptions Personality influences the choice of models, which behaviour will hold the observer s attention, which behaviours will be retained and which behaviours will be reproduced Expectations about the outcome of behaviour strongly influence the reproduction of behaviour The results of the model s behaviour Vicarious outcomes (reinforcement or punishment of model s behaviour) Vicarious rewards usually leads to behaviour imitation Vicarious punishment usually leads to counter-imitation Vicarious consequences highlight factors the observer needs to take into account in planning their behaviour influence the observer s motivation influence observer s emotional reaction and values (in response to the reaction of the model) influence the observer s perceptions of the model and the reinforcing agent
4 Vicarious punishment and reward have a similar effect on the acquisition of new behaviour vicarious reward leads to reproduction of behaviour more often than vicarious punishment Vicarious punishment and reward both lead to the acquisition of new behaviour more than when there are no consequences for the model The observer judges the outcome of model s behaviour to previous experience this relative outcome of the model s behaviour is an important determinant of whether the observer will reproduce a model s behaviour Observers can imitate a model s behaviour indirectly via similar behaviours Self-efficacy Observational learning is influenced by the degree to which an individual has confidence in their ability to reproduce the behaviour Learning through Self-regulation (an individual s ability to regulate their own behaviour, specifically their learning processes) Includes self-reinforcement and self-punishment Two types of self-regulation: Internal Self-regulation: Subjective evaluation of own behaviour External Self-regulation: arranging a situation and the outcome of behaviour so that the individual is able to reward or punish themselves in a concrete way Regarded as the most important form of learning The effect of rewards or punishment from external agents depends on the individual s interpretation The Development of the Personality Development, via the learning of new behaviour (and the modification of existing behaviour), occurs across the entire lifespan Development is an ongoing process of change resulting from the interaction between genetic and environmental factors
5 The Optimal Development of the Personality Views on Psychopathology Optimal development is characterized by: the ability to recognize factors that are relevant to effective functioning in a given situation the ability to succeed in producing behaviour that meets the individual s standards Optimal development is dependent upon the individual s cultural context Pathological behaviour is learnt via observational learning Do not need to look for underlying dynamic causes of psychopathological behaviour A lack of self-efficacy is important for the development of undesirable pathological behaviour Implications and Applications: Interpretation and handling of Aggression 9.1, 9.2, & 9.3 for self-study Aggressive behaviours form part of each individual s behaviour repertoire and are more likely to be repeated if they lead to rewarding consequences New aggressive behaviours can be learnt through observing aggressive models The likelihood of acquired aggressive responses being reproduced depend on factors such as outcome expectancies, self-efficacy perceptions, individual interpretation, self-regulating strategies and values Implications and Applications: Interpretation and handling of Aggression Aggressive responses can be provoked by unpleasant stimuli and by the expectations of rewarding outcomes Persistence in aggressive behaviour is regulated by its results The regulation of aggressive behaviour is a function of the interaction between the individual, the situation, and behaviour (reciprocal determinism)
6 Evaluation of the Theory SCLT is a very popular personality theory Large volumes of research that support its assumptions Criticism: New terms are regularly developed for existing phenomena, making it difficult to develop a simple, logical structure to the theory
CHAPTER 10. Background THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH. part 1. Background. Background. Social Cognitive Learning Theory
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH part 1 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 Social Cognitive Learning Theory Agrees with behaviouristically-oriented theories that behaviour is learnt Differs
CHAPTER 10 THE SOCIAL COGNITIVE LEARNING APPROACH part 1 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 Social Cognitive Learning Theory Agrees with behaviouristically-oriented theories that behaviour is learnt Differs
Bandura s Social Learning & Cognitive Learning Theory
 Bandura s Social Learning & Cognitive Learning Theory Theories of Developmental Psychology By: Razieh Tadayon Nabavi 2011-2012 1 Albert Bandura He was born December 4, 1925 in a small town in northern
Bandura s Social Learning & Cognitive Learning Theory Theories of Developmental Psychology By: Razieh Tadayon Nabavi 2011-2012 1 Albert Bandura He was born December 4, 1925 in a small town in northern
Foundations of Individual Behavior
 Robbins & Judge Organizational Behavior 13th Edition Foundations of Individual Behavior Bob Stretch Southwestern College 2-0 Chapter Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able
Robbins & Judge Organizational Behavior 13th Edition Foundations of Individual Behavior Bob Stretch Southwestern College 2-0 Chapter Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able
Observational Learning. The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224).
 LP 6E observational learning 1 Observational Learning The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224). Observational learning LP 6E observational
LP 6E observational learning 1 Observational Learning The acquisition or changing a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (page 224). Observational learning LP 6E observational
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn?
 Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
Chapter 5: How Do We Learn? Defining Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior or the potential for behavior that results from experience Results from many life experiences, not just structured
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 111
 Dikran J. Martin Psychology 111 Name:. Date:. Lecture Series: Chapter 16 Motivation, Thought, and Behavior: The Social Learning Theories Pages:19 TEXT: Funder, David C., (2000). The Personality Puzzle
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 111 Name:. Date:. Lecture Series: Chapter 16 Motivation, Thought, and Behavior: The Social Learning Theories Pages:19 TEXT: Funder, David C., (2000). The Personality Puzzle
SOCI 323 Social Psychology
 SOCI 323 Social Psychology Session 5 Socialisation: the Humanising Process Lecturer: Dr. Peace Mamle Tetteh, Department of Sociology Contact Information: ptetteh@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of
SOCI 323 Social Psychology Session 5 Socialisation: the Humanising Process Lecturer: Dr. Peace Mamle Tetteh, Department of Sociology Contact Information: ptetteh@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of
Learning Approaches. Classical Conditioning Conditioned Stimulus (CS)... Conditioned Response (CR)... Acquisition... Extinction...
 Reading: H & O Chapters 9, 10, 11 Terms you should know. J. B. Watson Pavlov Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Conditioned Response
Reading: H & O Chapters 9, 10, 11 Terms you should know. J. B. Watson Pavlov Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Conditioned Response
Learning. Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning.
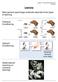 Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
Chapter 10: observational learning 1 Learning Most general psychology textbooks describe three types of learning. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning (or vicarious learning)
Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches
 Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches What is Learning o What Learning Is and Is Not Learning - a relatively permanent influence on behavior, knowledge, and thinking skills that comes about
Chapter 7 Behavior and Social Cognitive Approaches What is Learning o What Learning Is and Is Not Learning - a relatively permanent influence on behavior, knowledge, and thinking skills that comes about
Induction Lesson and Summer Transition
 Induction Lesson and Summer Transition Year 11 starting A Level whats the difference? Induction Lesson and Summer Transition Assignment OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you MUST BE ABLE TO Know what
Induction Lesson and Summer Transition Year 11 starting A Level whats the difference? Induction Lesson and Summer Transition Assignment OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you MUST BE ABLE TO Know what
Learning. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice.
 Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice. What is Learning? Learning is the process that allows us to adapt (be flexible) to the changing conditions
Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience or practice. What is Learning? Learning is the process that allows us to adapt (be flexible) to the changing conditions
Name. True or False: 1. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience. True False
 Chapter 5 Quiz Name Learning (Modules 15, 16, 17) True or False: 1. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience. 2. A stimulus that naturally brings about a particular
Chapter 5 Quiz Name Learning (Modules 15, 16, 17) True or False: 1. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience. 2. A stimulus that naturally brings about a particular
Basic characteristics
 Learning Basic characteristics The belief that the universe is lawful and orderly The occurrence of phenomena as a function of the operation of specific variables Objective observation Controlled experiments
Learning Basic characteristics The belief that the universe is lawful and orderly The occurrence of phenomena as a function of the operation of specific variables Objective observation Controlled experiments
Learning & Language Development
 Learning & Language Development Classical Conditioning An involuntary response when a stimulus that normally causes a particular response is paired with a new, neutral stimulus. After enough pairings,
Learning & Language Development Classical Conditioning An involuntary response when a stimulus that normally causes a particular response is paired with a new, neutral stimulus. After enough pairings,
Topic 4: Learning Theories
 Edexcel Psychology A-level Topic 4: Learning Theories Notes Part 1 The Learning Approach: Behaviourism A01 Introduction and Assumptions: The behaviourist approach is an approach to explaining behaviour
Edexcel Psychology A-level Topic 4: Learning Theories Notes Part 1 The Learning Approach: Behaviourism A01 Introduction and Assumptions: The behaviourist approach is an approach to explaining behaviour
Learning: Some Key Terms
 Learning: Some Key Terms Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Reinforcement: Any event that increases the probability that a response will recur Focus on what can be seen
Learning: Some Key Terms Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Reinforcement: Any event that increases the probability that a response will recur Focus on what can be seen
CHAPTER 15 SKINNER'S OPERANT ANALYSIS 4/18/2008. Operant Conditioning
 CHAPTER 15 SKINNER'S OPERANT ANALYSIS Operant Conditioning Establishment of the linkage or association between a behavior and its consequences. 1 Operant Conditioning Establishment of the linkage or association
CHAPTER 15 SKINNER'S OPERANT ANALYSIS Operant Conditioning Establishment of the linkage or association between a behavior and its consequences. 1 Operant Conditioning Establishment of the linkage or association
Chapter 12: Observational Learning. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 12: Observational Learning Lecture Outline Observational learning Observational learning in Classical conditioning Observational learning in operant conditioning Observational learning in animals
Chapter 12: Observational Learning Lecture Outline Observational learning Observational learning in Classical conditioning Observational learning in operant conditioning Observational learning in animals
Learning Theories - Behaviourism -
 Learning Theories - Behaviourism - Kimberley A. Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/257e-570 Office Hour: Thursdays 2-3pm Office: S302 Outline What is Learning? Classical Conditioning
Learning Theories - Behaviourism - Kimberley A. Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/257e-570 Office Hour: Thursdays 2-3pm Office: S302 Outline What is Learning? Classical Conditioning
NEGOTIATION SEVENTH EDITION
 NEGOTIATION SEVENTH EDITION ROY J. LEWICKI DAVID M. SAUNDERS BRUCE BARRY 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution
NEGOTIATION SEVENTH EDITION ROY J. LEWICKI DAVID M. SAUNDERS BRUCE BARRY 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution
CHAPTER TWELVE. MISCHEL AND BANDURA: Cognitive Social Learning Theory 10/14/08. Personality Psychology. Chapter Overview.
 Personality Psychology Psychology 370 Sheila K. Grant, Ph.D. Professor California State University, Northridge CHAPTER TWELVE MISCHEL AND BANDURA: Cognitive Social Learning Theory Chapter Overview TRAITS
Personality Psychology Psychology 370 Sheila K. Grant, Ph.D. Professor California State University, Northridge CHAPTER TWELVE MISCHEL AND BANDURA: Cognitive Social Learning Theory Chapter Overview TRAITS
Introduction to Attitudes
 Introduction to Attitudes Learning Goals Understand the construct of attitudes Understand how are attitudes formed Attitudes Attitude: Positive or negative reaction to a person, object, or idea Good-bad
Introduction to Attitudes Learning Goals Understand the construct of attitudes Understand how are attitudes formed Attitudes Attitude: Positive or negative reaction to a person, object, or idea Good-bad
Personality. Unit 3: Developmental Psychology
 Personality Unit 3: Developmental Psychology Personality Personality: The consistent, enduring, and unique characteristics of a person. There are many personality theories that provide a way of organizing
Personality Unit 3: Developmental Psychology Personality Personality: The consistent, enduring, and unique characteristics of a person. There are many personality theories that provide a way of organizing
MHR Chapter 5. Motivation: The forces within a person that affect his or her direction, intensity and persistence of voluntary behaviour
 MHR Chapter 5 Motivation: The forces within a person that affect his or her direction, intensity and persistence of voluntary behaviour Employee Engagement: Individual s emotional and cognitive motivation,
MHR Chapter 5 Motivation: The forces within a person that affect his or her direction, intensity and persistence of voluntary behaviour Employee Engagement: Individual s emotional and cognitive motivation,
Slide 3.1. Learning and memory
 Slide 3.1 Learning and memory Slide 3.2 Learning defined Learning is a change in behaviour that is caused by experience. Learning can occur through simple associations between a stimulus and a response
Slide 3.1 Learning and memory Slide 3.2 Learning defined Learning is a change in behaviour that is caused by experience. Learning can occur through simple associations between a stimulus and a response
Innate? Learned? Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Aggression and Violence. What is violence?
 Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
Aggression and Violence Aggression and Violence: Innate or Learned? Howie Fine Birkbeck College ohow many people believe that violence is innate? ohow many believe that violence is a learned behaviour?
Learning = an enduring change in behavior, resulting from experience.
 Chapter 6: Learning Learning = an enduring change in behavior, resulting from experience. Conditioning = a process in which environmental stimuli and behavioral processes become connected Two types of
Chapter 6: Learning Learning = an enduring change in behavior, resulting from experience. Conditioning = a process in which environmental stimuli and behavioral processes become connected Two types of
Developmental Psychology and Learning SOCIAL EDUCATION COURSE Academic year 2014/2015
 Developmental Psychology and Learning SOCIAL EDUCATION COURSE Academic year 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #6 Monday, Oct. 27 th 2014: 19:00/21:00 Friday, Oct. 31 th 2014, 09:00/11:00 LESSON PLAN: HUMAN
Developmental Psychology and Learning SOCIAL EDUCATION COURSE Academic year 2014/2015 EXTENDED SUMMARY Lesson #6 Monday, Oct. 27 th 2014: 19:00/21:00 Friday, Oct. 31 th 2014, 09:00/11:00 LESSON PLAN: HUMAN
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 6 Learning 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 6.1 How Do the Parts of Our Brains Function? 6.1 What Are
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 6 Learning 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 6.1 How Do the Parts of Our Brains Function? 6.1 What Are
Psychological Perspectives. Unit 11
 Psychological Perspectives Unit 11 What is Psychology? What is Psychology?? Psychology is the science of the mind. So what are Psychological Perspectives? Psychological perspectives are ways of investigating
Psychological Perspectives Unit 11 What is Psychology? What is Psychology?? Psychology is the science of the mind. So what are Psychological Perspectives? Psychological perspectives are ways of investigating
Module 30. Learning by Observation
 Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Module 30 Learning by Observation 1 Module 30 Describe the process of observational learning, and explain how some scientists believe it is enabled by mirror neurons. Discuss the impact of prosocial modeling
Operant Conditioning
 Operant Conditioning Classical v. Operant Conditioning Both classical and operant conditioning use acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Classical conditioning
Operant Conditioning Classical v. Operant Conditioning Both classical and operant conditioning use acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Classical conditioning
Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality. Copyright Allyn & Bacon (2009)
 Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality Roots in Gestalt Psychology Human beings seek meaning in their environments We organize the sensations we receive into meaningful perceptions Complex stimuli
Chapter 7: Cognitive Aspects of Personality Roots in Gestalt Psychology Human beings seek meaning in their environments We organize the sensations we receive into meaningful perceptions Complex stimuli
E Cog Sci II -- Plass New York University
 Overview Situated Cognition Theoretical conceptions of human nature can influence what people actually become. 2001-2005, Jan L. Plass 1 Psychological Theory Examples of theories Psychodynamic theory (inner
Overview Situated Cognition Theoretical conceptions of human nature can influence what people actually become. 2001-2005, Jan L. Plass 1 Psychological Theory Examples of theories Psychodynamic theory (inner
Learned Helplessness
 LP 5E 1 Learned Helplessness Dogs were classically conditioned to associate a tone to the pain of an electric shock. In order to do this, the dogs were harnessed and could not avoid electric shocks. It
LP 5E 1 Learned Helplessness Dogs were classically conditioned to associate a tone to the pain of an electric shock. In order to do this, the dogs were harnessed and could not avoid electric shocks. It
CHAPTER 3 The Development of the Personality
 CHAPTER 3 The Development of the Personality THE PSYCHOANALYTICAL THEORY OF SIGMUND FREUD part 2 Dr Hermann Swart Psychosexual Theory: Focuses on the development of the sex drive Progression from one phase
CHAPTER 3 The Development of the Personality THE PSYCHOANALYTICAL THEORY OF SIGMUND FREUD part 2 Dr Hermann Swart Psychosexual Theory: Focuses on the development of the sex drive Progression from one phase
Com 400 Dr. Raz. Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research
 Com 400 Dr. Raz Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research Review Theory an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events Some guiding questions What are different ways to study
Com 400 Dr. Raz Media Effects and Cultural Approaches to Research Review Theory an idea or set of ideas that is intended to explain facts or events Some guiding questions What are different ways to study
The eight steps to resilience at work
 The eight steps to resilience at work Derek Mowbray March 2010 derek.mowbray@orghealth.co.uk www.orghealth.co.uk Introduction Resilience is the personal capacity to cope with adverse events and return
The eight steps to resilience at work Derek Mowbray March 2010 derek.mowbray@orghealth.co.uk www.orghealth.co.uk Introduction Resilience is the personal capacity to cope with adverse events and return
Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience
 Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning, even
Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning, even
Lesson 12. Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior
 Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
Lesson 12 Understanding and Managing Individual Behavior Learning Objectives 1. Identify the focus and goals of individual behavior within organizations. 2. Explain the role that attitudes play in job
Study Unit 3 -Part 2. Consumer Learning SIM University. All rights reserved. Introduction. In this presentation, you will learn:
 Study Unit 3 -Part 2 Consumer Learning Introduction In this presentation, you will learn: Consumer learning process Various theories of learning Consumer Learning in Marketing Consumer learning is the
Study Unit 3 -Part 2 Consumer Learning Introduction In this presentation, you will learn: Consumer learning process Various theories of learning Consumer Learning in Marketing Consumer learning is the
CHAPTER 2 FOUNDATIONS OF INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR
 CHAPTER 2 FOUNDATIONS OF INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR "Intelligence is but one characteristic that people bring with them when they join an organization. In this chapter, we look at how biographical characteristics
CHAPTER 2 FOUNDATIONS OF INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR "Intelligence is but one characteristic that people bring with them when they join an organization. In this chapter, we look at how biographical characteristics
CHAPTER 3. Background THE PSYCHOANALYTICAL THEORY OF SIGMUND FREUD. part 1. The View of the Person. The View of the Person
 CHAPTER 3 THE PSYCHOANALYTICAL THEORY OF SIGMUND FREUD part 1 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 Background First personality theory and (arguably) the most comprehensive Possible contextual influences
CHAPTER 3 THE PSYCHOANALYTICAL THEORY OF SIGMUND FREUD part 1 Dr Hermann Swart hswart@sun.ac.za 1 Background First personality theory and (arguably) the most comprehensive Possible contextual influences
Aggression. Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental. Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz. Biological Theories
 Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental Aggression Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz Biological Theories Environmental Theories 1. Frustration/aggression 2. Theory of aggressive cues Cognitive Associationist
Two Types 1. Hostile 2. Instrumental Aggression Instinct Theory 1. Freud 2. Lorenz Biological Theories Environmental Theories 1. Frustration/aggression 2. Theory of aggressive cues Cognitive Associationist
Classical conditioning or classical learning theory
 Learning theories These theories see criminality as normal learned behaviour. Some behaviour is instinctive and is possessed by an individual at birth; the possession of this is determined by biological
Learning theories These theories see criminality as normal learned behaviour. Some behaviour is instinctive and is possessed by an individual at birth; the possession of this is determined by biological
Title: Bandura s Social Learning Theory & Social Cognitive Learning Theory
 Theories of Developmental Psychology Title: Bandura s Social Learning Theory & Social Cognitive Learning Theory Razieh Tadayon Nabavi 2011-2012 Table of content Father of the Cognitive Theory... 3 Introduction...
Theories of Developmental Psychology Title: Bandura s Social Learning Theory & Social Cognitive Learning Theory Razieh Tadayon Nabavi 2011-2012 Table of content Father of the Cognitive Theory... 3 Introduction...
1. A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher.
 1. A stimulus change that increases the future frequency of behavior that immediately precedes it. 2. In operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified
1. A stimulus change that increases the future frequency of behavior that immediately precedes it. 2. In operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specified
Theories of Learning
 Theories of Learning Learning Classical conditioning Classical conditioning in real life Operant conditioning Operant conditioning in real life Learning and the mind Watson s Extreme Environmentalism Give
Theories of Learning Learning Classical conditioning Classical conditioning in real life Operant conditioning Operant conditioning in real life Learning and the mind Watson s Extreme Environmentalism Give
Module 10b--Operant and Cognitive Approaches
 Module 10b--Operant and Cognitive Approaches Student: 1. Classical conditioning involves behavior and its consequences. 2. According to the law of effect, behavior that is followed by positive consequences
Module 10b--Operant and Cognitive Approaches Student: 1. Classical conditioning involves behavior and its consequences. 2. According to the law of effect, behavior that is followed by positive consequences
3. Behavioral Perspective of Learning
 3. Behavioral Perspective of Learning Behavior: Big Questions Is learning just a change of behavior? Can learning happen without intent? Can new behavior be shaped by manipulating the environment? 3.1
3. Behavioral Perspective of Learning Behavior: Big Questions Is learning just a change of behavior? Can learning happen without intent? Can new behavior be shaped by manipulating the environment? 3.1
Department of Psychology
 PYC2015/201/3/2010 PERSONALITY THEORIES Department of Psychology PAPER CODE: PYC2015 TUTORIAL LETTER: 201/3/2010 2 PERSONALITY THEORIES PYC2015 TUTORIAL LETTER 201/3/2010 Dear Student In this tutorial
PYC2015/201/3/2010 PERSONALITY THEORIES Department of Psychology PAPER CODE: PYC2015 TUTORIAL LETTER: 201/3/2010 2 PERSONALITY THEORIES PYC2015 TUTORIAL LETTER 201/3/2010 Dear Student In this tutorial
Contents. Chapter. A Closer Look at You. Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude. Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You
 Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Contents Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude 1 Section 17.1 Your Personality Personality develops from
Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Chapter 17 A Closer Look at You Contents Section 17.1 Your Personality Section 17.2 Develop a Positive Attitude 1 Section 17.1 Your Personality Personality develops from
Coon/Mitterer Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior, 12e
 Chapter 1 What is psychology? What are its goals? What is critical thinking? How does psychology differ from false explanations of behavior? Why is the scientific method important to psychologists? How
Chapter 1 What is psychology? What are its goals? What is critical thinking? How does psychology differ from false explanations of behavior? Why is the scientific method important to psychologists? How
PSYCHOLOGY GENERAL COURSE
 PSYCHOLOGY GENERAL COURSE Marking key for the Externally set task Sample 2016 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained
PSYCHOLOGY GENERAL COURSE Marking key for the Externally set task Sample 2016 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained
Dikran J. Martin. Psychology 110. Name: Date: Principal Features. "First, the term learning does not apply to (168)
 Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Learning: How We're Changed Pages: 26 by Experience TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition). Boston, MA: Allyn and
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Learning: How We're Changed Pages: 26 by Experience TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition). Boston, MA: Allyn and
c) Redraw the model and place on it relevant attributions for each of the four boxes.
 CHAPTER 6: Attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence, and leadership Practice questions - text book pages 107-108 1) a) Figure 6.21 partly illustrates Weiner s model of attribution. Explain the
CHAPTER 6: Attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence, and leadership Practice questions - text book pages 107-108 1) a) Figure 6.21 partly illustrates Weiner s model of attribution. Explain the
Behavioral EQ MULTI-RATER PROFILE. Prepared for: By: Session: 22 Jul Madeline Bertrand. Sample Organization
 Behavioral EQ MULTI-RATER PROFILE Prepared for: Madeline Bertrand By: Sample Organization Session: Improving Interpersonal Effectiveness 22 Jul 2014 Behavioral EQ, Putting Emotional Intelligence to Work,
Behavioral EQ MULTI-RATER PROFILE Prepared for: Madeline Bertrand By: Sample Organization Session: Improving Interpersonal Effectiveness 22 Jul 2014 Behavioral EQ, Putting Emotional Intelligence to Work,
Discovering Diversity Profile Group Report
 Discovering Diversity Profile Group Report Sample Report (5 People) Friday, June 18, 2010 This report is provided by: Intesi! Resources 14230 N. 20th Way Phoenix, AZ 85022 Phone: 602-482-6422 Toll Free:
Discovering Diversity Profile Group Report Sample Report (5 People) Friday, June 18, 2010 This report is provided by: Intesi! Resources 14230 N. 20th Way Phoenix, AZ 85022 Phone: 602-482-6422 Toll Free:
Organizational Behaviour
 Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Motivational concepts and application The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department
Bachelor of Commerce Programme Organizational Behaviour Individual Behaviour Motivational concepts and application The Da Vinci Institute for Technology Management (Pty) Ltd Registered with the Department
Learning. Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience.
 Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience. Classical Conditioning Learning through Association Ivan Pavlov discovered the form of learning called Classical
Learning Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior acquired through experience. Classical Conditioning Learning through Association Ivan Pavlov discovered the form of learning called Classical
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Developmental Psychology = a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span. Zygote = the fertilized
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Developmental Psychology = a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span. Zygote = the fertilized
Counseling and Psychotherapy Theory. Week 5. Cognitive-Behavioral Approach I : Behavioral Approach
 Counseling and Psychotherapy Theory Week 5. Cognitive-Behavioral Approach I : Behavioral Approach Contents 1 2 3 Major Concepts and Propositions 1 Overview/Classical Conditioning 2 Operant Conditioning
Counseling and Psychotherapy Theory Week 5. Cognitive-Behavioral Approach I : Behavioral Approach Contents 1 2 3 Major Concepts and Propositions 1 Overview/Classical Conditioning 2 Operant Conditioning
Robin Seim. Social Learning Theory
 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 1 Robin Seim Social Learning Theory May 17, 2014 EDUC 532 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 2 The social learning theory was derived by Albert Bandura in attempt to understand why people act
SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 1 Robin Seim Social Learning Theory May 17, 2014 EDUC 532 SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY 2 The social learning theory was derived by Albert Bandura in attempt to understand why people act
acquisition associative learning behaviorism B. F. Skinner biofeedback
 acquisition associative learning in classical conditioning the initial stage when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned
acquisition associative learning in classical conditioning the initial stage when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned
INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVELOPMENT
 INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVELOPMENT UNIT 2 - INDIVIDUALS IN INDUSTRY Organizational Behavior: - Perception, Personality, Learning, stress management, group dynamics and Motivation. ORGANISATIONAL
INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT AND ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVELOPMENT UNIT 2 - INDIVIDUALS IN INDUSTRY Organizational Behavior: - Perception, Personality, Learning, stress management, group dynamics and Motivation. ORGANISATIONAL
acquisition associative learning behaviorism A type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
 acquisition associative learning In classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned
acquisition associative learning In classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned
Learning Theories Reviewed
 Learning Theories Reviewed Applications and Challenges Howie Fine 1 Applications of Classical Conditioning 1 Watson (1921) - Little Albert - demonstrated that classical conditioning accounts for some cases
Learning Theories Reviewed Applications and Challenges Howie Fine 1 Applications of Classical Conditioning 1 Watson (1921) - Little Albert - demonstrated that classical conditioning accounts for some cases
Module One: Booklet #7
 Module One: Booklet #7 Is a relatively permanent change in behaviour that results from experience There are various ways is which people learn (we will look at some learning styles in Module 2) We will
Module One: Booklet #7 Is a relatively permanent change in behaviour that results from experience There are various ways is which people learn (we will look at some learning styles in Module 2) We will
June 16, The retina has two types of light-sensitive receptor cells (or photoreceptors) called rods and cones.
 K K The retina has two types of light-sensitive receptor cells (or photoreceptors) called rods and cones. rods: 75 to 150 million cells which are very sensitive to all levels of light. cones: 6 to 7 million
K K The retina has two types of light-sensitive receptor cells (or photoreceptors) called rods and cones. rods: 75 to 150 million cells which are very sensitive to all levels of light. cones: 6 to 7 million
Conditioning and Learning. Chapter 7
 Conditioning and Learning Chapter 7 Learning is knowledge of skills acquired by instruction or studying. It is a permanent change in behavior due to reinforcement. Reinforcement refers to any event that
Conditioning and Learning Chapter 7 Learning is knowledge of skills acquired by instruction or studying. It is a permanent change in behavior due to reinforcement. Reinforcement refers to any event that
Unit 06 - Overview. Click on the any of the above hyperlinks to go to that section in the presentation.
 Unit 06 - Overview How We Learn and Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning s Applications, and Comparison to Classical Conditioning Biology, Cognition, and Learning Learning By
Unit 06 - Overview How We Learn and Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning s Applications, and Comparison to Classical Conditioning Biology, Cognition, and Learning Learning By
Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING
 Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Site: University of the Philippines Open University: Course: EDS_103_1T_2015-16- Theories of Learning Book: Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Printed by: Reyes
Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Site: University of the Philippines Open University: Course: EDS_103_1T_2015-16- Theories of Learning Book: Module 3.2 SOCIAL THEORIES OF LEARNING Printed by: Reyes
Calm, Alert and Learning. January, 2014
 Calm, Alert and Learning January, 2014 What We Have Learned Self regulation is a framework Co-planning, co-creating, co-teaching, coreflecting, Co-regulation is important before self-regulation, and on-going
Calm, Alert and Learning January, 2014 What We Have Learned Self regulation is a framework Co-planning, co-creating, co-teaching, coreflecting, Co-regulation is important before self-regulation, and on-going
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 6 Learning 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 1 Humans are learning machines! Learning: A change in behavior,
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 6 Learning 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 1 Humans are learning machines! Learning: A change in behavior,
Developmental Psychology
 WJEC Psychology A-level Developmental Psychology Notes Kohlberg, L (1968): The Child As A Moral Philosopher 1 Kohlberg assumed that all moral development occurs in a set series of stages and is motivated
WJEC Psychology A-level Developmental Psychology Notes Kohlberg, L (1968): The Child As A Moral Philosopher 1 Kohlberg assumed that all moral development occurs in a set series of stages and is motivated
External Regulation of Motivation. Motivating Others To Do Uninteresting Activities
 Chapter 5 Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations External Regulation of Motivation Hidden Costs of Rewards Cognitive Evaluation Theory Types of Extrinsic Motivation Incentives Consequences Rewards External
Chapter 5 Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations External Regulation of Motivation Hidden Costs of Rewards Cognitive Evaluation Theory Types of Extrinsic Motivation Incentives Consequences Rewards External
Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior 13 th ed. Introduction: The Psychology of Studying Reflective Learning.
 Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior 13 th ed. Introduction: The Psychology of Studying Reflective Learning I.1 What is the best way to read a textbook? I.2 How can learning in class
Introduction to Psychology: Gateways to Mind and Behavior 13 th ed. Introduction: The Psychology of Studying Reflective Learning I.1 What is the best way to read a textbook? I.2 How can learning in class
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Learning Chapter Module 21 Observational Learning Module 21: Observational Learning
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Learning Chapter Module 21 Observational Learning Module 21: Observational Learning
Chapter 17 Therapy and Change
 Chapter 17 Therapy and Change Section 1 What is Psychotherapy? Psychotherapy is a general term for the several approaches used by mental health professionals to treat psychological disorders. Objectives
Chapter 17 Therapy and Change Section 1 What is Psychotherapy? Psychotherapy is a general term for the several approaches used by mental health professionals to treat psychological disorders. Objectives
Behaviorism. B. F. Skinner
 Behaviorism B. F. Skinner B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) B. F. Skinner (1904-1990) Skinner s life Predetermined, lawful, and orderly A product of past reinforcements 1925: Hamilton College (NY): degree in English,
Behaviorism B. F. Skinner B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) B. F. Skinner (1904-1990) Skinner s life Predetermined, lawful, and orderly A product of past reinforcements 1925: Hamilton College (NY): degree in English,
Myers PSYCHOLOGY. (7th Ed) Chapter 8. Learning. James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University. Worth Publishers
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 8 Learning James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Learning Learning relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience Association
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 8 Learning James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Learning Learning relatively permanent change in an organism s behavior due to experience Association
Associative Learning
 Learning Learning Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Biological Components of Learning Cognitive Components of Learning Behavioral Therapies Associative
Learning Learning Associative Learning Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Biological Components of Learning Cognitive Components of Learning Behavioral Therapies Associative
Chapter 6: Learning The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 6: Learning Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience Distinguishes between changes due to maturation and changes brought about by experience Distinguishes
Chapter 6: Learning Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience Distinguishes between changes due to maturation and changes brought about by experience Distinguishes
cognitive-developmental theory classical conditioning Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Chapter 1
 adaptation accommodation behaviorism assimilation chronosystem case study cognitive-developmental theory classical conditioning control group cohort effect the modification of existing schemes to permit
adaptation accommodation behaviorism assimilation chronosystem case study cognitive-developmental theory classical conditioning control group cohort effect the modification of existing schemes to permit
PSYCHOLOGY. Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow Learning? What s that? A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice. Note that learning is NOT the same as
PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 6 LEARNING PowerPoint Image Slideshow Learning? What s that? A relatively permanent change in behavior brought about by experience or practice. Note that learning is NOT the same as
CHAPTER 15 MOTIVATION
 CHAPTER 15 MOTIVATION Koon Vui Yee 1 Learning Outcomes 15.1 Describe the nature of motivation. 15.2 Describe and differentiate various types of motivation theories under content perspectives. 15.3 Explain
CHAPTER 15 MOTIVATION Koon Vui Yee 1 Learning Outcomes 15.1 Describe the nature of motivation. 15.2 Describe and differentiate various types of motivation theories under content perspectives. 15.3 Explain
Monday, September 8, 14 THEORIES OF
 THEORIES OF Structuralism Wilhelm Wundt Structuralism Structuralism Wilhelm Wundt Discovered basic elements of conscious experience Structuralism Wilhelm Wundt Discovered basic elements of conscious experience
THEORIES OF Structuralism Wilhelm Wundt Structuralism Structuralism Wilhelm Wundt Discovered basic elements of conscious experience Structuralism Wilhelm Wundt Discovered basic elements of conscious experience
Experimental examination of reputation of collective sanctioners
 Experimental examination of reputation of collective sanctioners Rie Mashima (Kumamoto Gakuen University) Nobuyuki Takahashi (Hokkaido University) E-mail: mashima@kumagaku.ac.jp Although sanctioning is
Experimental examination of reputation of collective sanctioners Rie Mashima (Kumamoto Gakuen University) Nobuyuki Takahashi (Hokkaido University) E-mail: mashima@kumagaku.ac.jp Although sanctioning is
The Learning Process. Learning is a Process. Behavioral Learning Theories. Chapter 3 Learning and Memory. How many of these do you remind?
 Chapter 3 Learning and Memory Consumer Behavior Buying, Having, and Being Sixth Edition 3-1 The Learning Process Learning: A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience Incidental Learning:
Chapter 3 Learning and Memory Consumer Behavior Buying, Having, and Being Sixth Edition 3-1 The Learning Process Learning: A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience Incidental Learning:
*Taken from the old syllabus. The new (2019) syllabus may have changes.
 I was a student at an IB school in Australia for my senior schooling. One of the subjects I took was Psychology at Higher Level (HL), and I finished with a 7. I was also getting consistent 7s throughout
I was a student at an IB school in Australia for my senior schooling. One of the subjects I took was Psychology at Higher Level (HL), and I finished with a 7. I was also getting consistent 7s throughout
Introduction to Psychology Social Psychology Quiz
 MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
MULTIPLE CHOICE: 1. We usually adapt our behavior to the demands of the social situation, and in ambiguous situations: A) We take our cues from the behavior of others. B) We will do the same thing that
Bronze statue of Pavlov and one of his dogs located on the grounds of his laboratory at Koltushi Photo taken by Jackie D. Wood, June 2004.
 Ivan Pavlov http://physiologyonline.physiology.org/ cgi/content/full/19/6/326 Bronze statue of Pavlov and one of his dogs located on the grounds of his laboratory at Koltushi Photo taken by Jackie D. Wood,
Ivan Pavlov http://physiologyonline.physiology.org/ cgi/content/full/19/6/326 Bronze statue of Pavlov and one of his dogs located on the grounds of his laboratory at Koltushi Photo taken by Jackie D. Wood,
CHAPTER 7: Achievement motivation, attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence. Practice questions - text book pages
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 7: Achievement motivation, attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence Practice questions - text book pages 111-112 1) Which one of the following best explains achievement
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 7: Achievement motivation, attribution theory, self-efficacy and confidence Practice questions - text book pages 111-112 1) Which one of the following best explains achievement
6/11/2014. Session 2. INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION and EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE. Learning objectives. Learning objectives continued
 Session 2 INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION and EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE The publishers material used in the following activities are used with the express permission of the publisher. Learning objectives 1 Differentiate
Session 2 INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION and EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE The publishers material used in the following activities are used with the express permission of the publisher. Learning objectives 1 Differentiate
SOCIAL STRATIFICATION AND SOCIAL VALUES
 SOCIAL STRATIFICATION AND SOCIAL VALUES Definitions Social stratification is the division of population into two or more layers, each of which is relatively homogeneous and between which there are differences
SOCIAL STRATIFICATION AND SOCIAL VALUES Definitions Social stratification is the division of population into two or more layers, each of which is relatively homogeneous and between which there are differences
Rewards & Education 1
 Rewards & Education 1 B. F. SKINNER OPERANT CONDITIONING OPERANT BEHAVIORS ARE ACTIONS THAT INDIVIDUALS TAKE TO MEET THE DEMANDS OF THEIR ENVIRONMENTS Reinforcement & Punishment Reinforcer Any consequence
Rewards & Education 1 B. F. SKINNER OPERANT CONDITIONING OPERANT BEHAVIORS ARE ACTIONS THAT INDIVIDUALS TAKE TO MEET THE DEMANDS OF THEIR ENVIRONMENTS Reinforcement & Punishment Reinforcer Any consequence
Assessing Readiness To Change
 Assessing Readiness To Change Transtheoretical Model The Transtheoretical Model describes the stages of behavior prior to change. It focuses on the individual s decision making. This model involves the
Assessing Readiness To Change Transtheoretical Model The Transtheoretical Model describes the stages of behavior prior to change. It focuses on the individual s decision making. This model involves the
