E Ebracteate. Without bracts. Eciliate. Without celia. Emarginate. Having a shallow notch at the apex. Glossary
|
|
|
- Roy Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glossary Need help identifying native plants? Here is a few definitions to help you from the Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida by Richard P. Wunderlin A Acaulescent. Without a leafy stem; leaves all clustered in a basal rosette. Acicular. Slender and pointed; needle-shaped. Acuminate. Tapering gradually to a slender pointed apex, the sides of the taper slightly concave. Alternate. Leaves situated one at a node. Also stamens alternate with petals. Apex. The tip. Armed. Having thorns, spines, or prickles. B Bearded. Having a tuft, line, or ring of stiff trichomes a hairlike outgrowth from the epidermis. Bifurcate. Two-folked Bipinnate. Compound leaves divided into segments with each segment again divided into segments. Bristle. A stiff, strong, but slender trichome. C Calyx. The outermost series of the perianth parts of a flower, composed of the sepals. Campanulate. Bell-shaped. Capillary. Hairlike. Carpel. The ovule bearing unit of the flower. Caudate.With a tail-like appendage. Celia. Marginal trichomes. Compound. A leaf with two or more leaflets; an ovary with two or more joined carpels. Conic. Coned-shaped. Cordate. Heart-shaped, with rounded lobes and a sinus at the base. Cotyledon. The primary leaf. Crenate. Toothed with shallow, rounded teeth, scalloped. Cyme. A broad, flat inflorescence in which the ventral flower matures first. D Deciduous. Falling off at the end of the growing season. Dehiscent. Opening regularly by valves, slits at matrity. Dentate. With sharp-pointed teeth, tips pointing outward. Digitate. Palmately compound. Dioecious. Having male and female reproductive structures on different individuals as opposed to monoecious. Distichous. Arranged in two ranks, producing leaves or flowers on opposite sides of the stem in the same plane. E Ebracteate. Without bracts. Eciliate. Without celia. Emarginate. Having a shallow notch at the apex.
2 Entire. A margin without teeth, lobes, or divisions. Epiphytic. Growing on another plant, but not deriving nutrition from it as opposed to parasitic. Erose. With an irregularly eroded or jagged margin. Evergreen. Retaining green leaves in the dormant season Exfoliating. Peeling off in layers. F Falcate. Sickle-shaped. Farina. The mealy coating on a surface. Fascicle. A small close bundle or cluster. Filament. The stalk of the stamen. Filiform. Threadlike. Fimbriate. Unevenly fringed with slender projections along the margin. Flabellate. Fan-shaped. Flexuous. Having a zig-zag form. Floriferous. Having flowers Fruit. A ripened ovary, together with any other structures that ripen with it and form a unit with it. Funnelform. Shaped like a funnel Fusiform. Spindle-shaped, swollen in the middle and tapering toward both ends. G Gemmiparous. Producing small, vegetative buds that detach and grow into a new plant. Glabrate. Nearly glabrous Glabrous. Without trichomes (Hairlike growth) or glands Gland. An area on the surface of an organ or end of the trichome which secretes or contains fluid. Glaucous. Covered with a fine, waxy, whitish or bluish coating that rubs off easily. Glomerate. In dense clusters or heads. Glutinous. Covered with a sticky secretion. Granular. With a surface appearing as if covered with minute grainlike particles. H Hastate. Shaped like an arrowhead. Herbaceous. Lacking persistent woody parts. Hirsute. Having coarse, stiff trichomes. Hyaline. Thin and translucent or transparent. I Imbricate. Overlapping Incised. Deeply, sharply, and irregularly cut. Indumentum. The trichomes collectively. Induplicate. With the margins folded or rolled inward. Indurate. Hardened. Inflated. Bladder-like. Inflorescence. The arrangement of the flowers on an axis Internode. The part of the stem between two nodes. Involucre. A series of bracts surrounding a single or cluster of flowers. K Keel. A sharp or conspicuous, longitudinal, dorsal ridge; the two, often united, lower petals of a papilionaceous Fabaceae (Pea Family) flower.
3 L Lacerate. Torn, or with an irregularly jagged margin. Laciniate. Divided into narrow, pointed segments Lanceolate. Lance-shaped, longer than wide, widest near the base and gradually tapering to the apex. Leaflet. An ultimate unit of a compound leaf. Lenticel. A slightly raised, corky area on the stem and branches of woody plants. Locule. The cavity in an ovary or fruit. Lunate. Crescent-shaped. Lustrous. Shining. M Mealy. Covered with fine granules. Membranaceous. Having a texture that is thin/flexible. Midrib, midvein. The main or central vein. Monoecious. A plant with unisexual flowers on the same individual. Monadrous. Having a single stamen. Monomorphic. Having a single form. Muricate. With minute, spiny projections. N Nectar. A sugar or protein rich secretion which serves as an attractant and food source for animals. Nectary. An organ or tissue that secretes nectar. Node. The place on a stem where a leaf or branch is attached. Nodose. Knobby. O Obcordate. Inverse heart-shaped, deeply lobed at apex and tapering to the base. Oblanceolate. Inverse lance-shaped, broadest at apex and gradually tapering to base. Oblique. Slanting; unequal sided. Obovate. Inverse egg-shaped in outline. Obsolete. Nat apparent, rudimentary. Operculum. A little lid. Opposite. Situated directly across from each other at the same node or level. Ovary. The ovule-bearing part of a carpel which become the fruit. Ovate. Egg-shaped in outline. Ovule. The structure which, after ferilization, becomes the seed. P Palmate. Lobed, divided, or veined in a radiate manner. Pandurate. Fiddle-shapped. Panicle. A compound inflorescence with pedicellate flowers. Papilla. Small, rounded protuberances. Parasite. A plant growing on a deriving nutrition from another living plant to which it is attached. Pedate. A palmately lobed or divided leaf in which the two side lobes are again divided. Pedicel. Stalk of one flower in an inflorescence. Peduncle. Stalk supporting a flower cluster or a solitary flower. Peltate. Shield-shaped; attached to the stalk by the lower surface, usually near the center. Perfect. Flowers containing both functional male and female reproductive structures. Perfoliate. A sessile leaf, leaflet, or bract whose base completely surrounds the stem, so that the stem appears to pass through the leaf.
4 P Perianth. Collectively the calyx and corolla. Pericarp. The wall of a fruit. Personate. A tubular corolla with the lip nearly closed by a palate. Petaloid. Resembling a petal in texture and color. Petiole. The stalk of a leaf. Pinnate. A compound leaf divided once with the leaflets arranged on both sides of the axis. Plumose. Feathery Procumbent. Trailing or lying flat, but not rooting at the nodes. Pubescent. With dense, short, soft, straight trichomes. Pustule. A small, blister-like elevation. Pyriform. Pear-shaped. R Raceme. A simple, elongate, unbranched inflorescence with pedicellate flowers. Rachis. The primary axes of an inflorescence or a pinnately compound Rugose. Wrinkled. leaf. Ray. The branch of an umbel. Reniform. Kidney-shaped. Repent. Creeping. Retuse. With a shallow notch of an otherwise rounded or blunt apex. Revolute. With the margins rolled backward, the edge turned under. Rhombic. Diamond-shaped. Rotund. Circular. Rudimentary. Imperfectly developed andnon-functional. S Scabrous. Rough to the touch. Scandent. Climbing. Seed. A mature ovule. Sepal. One division of the calyx. Septum. A partition. Serrate. Toothed along the margin with sharp, forward-pointing teeth. Sessile. Attached directly by the base, without a stalk. Sinuate. With a strongly wavy margin. Spadix. A spike with small, partially embedded flowers on a thickened fleshly axis in the Araceae, this usually subtended by a spathe. Spathe. A usually large and solitary bract, surrounding an inflorescence. Spike. An unbranched, elongate, inflorescence with sessile or subsessile flowers. Sporangium. A body bearing spores. Spore. In pteridophyters (ferns), the one cell reproductive structure. Stamen. The male organ of the flower. Stellate. Star-shaped; trichomes with branches radiating from the base. Stigma. The upper part of the carpel or style with is receptive to pollen. Stipe. A stalk. Stipel. One of a pair of small stipulelike appendages on the leaflets of compound leaves. Stipule. One of a pair of appendages found at the base of a petiole on many leaves.
5 Stolon. An elongate stem creeping on the surface of the ground. Striate. Marked with fine, more or less parallel lines or ridges. Style. The more or less elongated part of the carpel between the ovary and the stigma. Subulate. Elongate and tapering gradually from the base to apex; awl-shaped. T Taproot. The main central root from which smaller branch roots originate. Ternate. Borne in threes. Testa. Seed coat. Tetragonal. Four-sided. Thyrse. The opening of a tubular calyx or corolla. Thyrsiform, thyrsoid. Resembling a thyrse. Tomentose. With dense, matted, soft hairs. Tomentulose. Diminutive of tomentose. Triandrous. Having three stamens. Trichome. A hairlike outgrowth from the epidermis. Trifoliaolate. A compound leaf with three leaflets. Truncate. With the base or apex transverse straight or nearly so, as if cut off. Tuber. A thickened part of a rhizome. Tuberous. Bearing tubers; thickened like a tuber. Turbinate. Top-shaped; inversely conical. Turgid. Swollen. U Unbel. An inflorescence where pedicels arise from a common point. Unarmed. Lacking thorns, spines, or prickles. Undulate. With a wavy margin or surface. Unisexual. A flower with a functional satem or carpel, but not both. Vein. A strand of fibrovascular tissue visible without magnification. Velutinous. Velvety; densely covered with fine short, soft, spreading trichomes. Venation. The vein pattern. Ventral. Front; the upper side of an organ. Verruca. A wartlike projection. Verrucose, verrucate. Having a warty surface. Verticillate. Arranged in whorls. Villous. Having long, soft, unmatted hairs. Viscid. Sticky. W Whorl. An arrangement of three or more similar structures at a node or another common point. Z Zygomorphic. Having a bilateral symmetry, capable of being divisible by only one plane into equal halves; irregular.
Plant Terminology. Floral Symmetry
 Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Plant Terminology Parts of a Flower Pedicel--the stalk of an individual flower Calyx--outermost whorl of a flower Sepal--one member of the calyx Corolla--second whorl of a flower Petal--one member of the
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. E2-4 Flower Anatomy
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology. Station 1. Whole plant structure. Differences between roots, stems, and leaves:
 Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
Part 1. Vegetative and Inflorescence Morphology Station 1. Whole plant structure Differences between roots, stems, and leaves: Often, the most important differences between roots, stems, and leaves are
IB 168 Plant Systematics
 IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
IB 168 Plant Systematics Laboratory 14: Rosidae Part 2 Today we will continue looking at the Rosid clade. The families in today s lab are all members of the Eurosid I clade; next time we will finish looking
Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 12, Issue 4 (February, 1912)
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 12, Issue 4 (February, 1912) 1912-02 The Mallows of Ohio Linnell, Mary
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 12, Issue 4 (February, 1912) 1912-02 The Mallows of Ohio Linnell, Mary
GLOSSARY Achene Acidic Soil Actinomorphic Acute Acuminate Aggregate Alkaline Soil Alpine Plants Alternate Leaves Annual Anther Apetalous Apocarpous
 GLOSSARY Achene A dry indehiscent fruit with a single seed, as in strawberry. Acidic Soil Soil with high concentrations of hydrogen ions and low concentrations of mineral salts; as opposed to alkaline.
GLOSSARY Achene A dry indehiscent fruit with a single seed, as in strawberry. Acidic Soil Soil with high concentrations of hydrogen ions and low concentrations of mineral salts; as opposed to alkaline.
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure. Name
 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5 83.3 82.1 81.0 79.8 Flower Morphology Name You are already familiar
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12
 BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
BIOLOGY 460/560 PLANT PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS ^!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! REQUIRED MATERIAL LAB EXAM
BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12
 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ATTENTION STUDENTS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! BIOLOGY 363 VASCULAR PLANTS LABORATORY #12 ! ANGIOSPERM FLOWER MORPHOLOGY & ANATOMY !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Flower Morphology. Flower Structure
 wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
wrong 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 right 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 score 100 98.8 97.6 96.4 95.2 94.0 92.9 91.7 90.5 89.3 88.1 86.9 85.7 84.5
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds
 The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
The Flower, Pollination, and Seeds Class 9 th Chapters 6,7,8 1 The Flower A complete or a perfect flower, has all the four Whorls. If, even one whorl is missing, it is an Incomplete Flower. The fourth
Review of the previous lecture
 Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
Review of the previous lecture Phylogeny Phylogenetic trees ingroup; outgroup; sister relationship; most recent common ancestor; monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups; Character homology;
Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits
 BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 9: Take-Home Exercise on Flowers and Fruits In this take-home lab, you will use information from your textbook, a Supplement PDF (Suppl.)
The Flower - what is it? 1/31/18. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants. Magnoliophyta - Flowering Plants
 - what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
- what is it? Floral structure will be examined in lab next Mon/Tues save space in your notes! Introduction to Angiosperms "angio-" = vessel; so "angiosperm" means "vessel for the seed [seed encased in
Flower Shapes and their function. Describing Flower Shapes
 Flower Shapes and their function Describing Flower Shapes Flower Shapes As with leaf shapes and the arrangement of flowers, these descriptions can only give you a general idea of the shapes of flowers.
Flower Shapes and their function Describing Flower Shapes Flower Shapes As with leaf shapes and the arrangement of flowers, these descriptions can only give you a general idea of the shapes of flowers.
LABORATORY 2: Flowers
 LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA
 SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
SUPPORTING MATERIAL CHARACTER TABLES FOR FAMILIES OF THE NON-ARBOREAL, SPRING-FLOWERING FLORA OF THE EASTERN PIEDMONT OF NORTH CAROLINA A multi-access key (MAK) is a data set in which each taxon is evaluated
Plants Provision for Life. Chapter 2 7 th Grade
 Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Plants Provision for Life Chapter 2 7 th Grade Lesson 2.1- Structure of Flowers Pistil- female reproductive structure Stigma- sticky top part. Traps pollen. Style- slender tube connecting stigma and ovary.
Parts of a Flower. Stamen = Pistil = Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel. anther + filament
 Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Flowers 1/25/2017 1 Parts of a Flower Stamen = anther + filament Pistil = stigma + style + ovary Petals (corolla) Sepals (calyx) Perianth = calyx + corolla Receptacle Peduncle / Pedicel 1/25/2017 Flowers
Botany Physiology. Due Date Code Period Earned Points
 Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
Name Botany Physiology C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points Bot Phys 4W1 Flowers (divide by 6.5) Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 1. (4 points) The female reproductive organs are the
ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme of
 ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
ON AN ABNORMALITY IN PURPUREA By VIOLET L. ANDERSON. DIGITALIS Quain Student of Botany, University College, London. (With 6 figures in the text.) ACURIOUS malformation in one of the flowers on a raceme
ANACARDIACEAE CASHEW (SUMAC) FAMILY
 ANACARDIACEAE CASHEW (SUMAC) FAMILY Plant: vines (usually woody), shrubs, or small trees Stem: woody, particularly with age, often with milky or resinous juice (resin ducts in bark) Root: Leaves: simple
ANACARDIACEAE CASHEW (SUMAC) FAMILY Plant: vines (usually woody), shrubs, or small trees Stem: woody, particularly with age, often with milky or resinous juice (resin ducts in bark) Root: Leaves: simple
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 5. Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology: The study of various external features of the organism is known as morphology. Adaptation: Any alteration in the structure or function
Reproduction in plants
 Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Reproduction in plants No individual organism can live forever, but reproduction makes sure that organisms do not become extinct. Organisms reproduce sexually or asexually and some organisms, such as angiosperms
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals
 Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Class XI Biology Chapter 5 Structural organization in plants and animals Answer 1. Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in plants, namely the tap root system and fibrous root system. e
Glossary of Botanical Terms
 Glossary of Botanical Terms Adventitious Aerating/Knee root Aerial roots Aerial stem Androdioecious Andromonoecious Anther Apical/Terminal Arborescent Aril Ascending Asymmetric Bark Basal Berry Bipinnate
Glossary of Botanical Terms Adventitious Aerating/Knee root Aerial roots Aerial stem Androdioecious Andromonoecious Anther Apical/Terminal Arborescent Aril Ascending Asymmetric Bark Basal Berry Bipinnate
3/18/2012. Chapter 36. Flower Parts. Flower Parts. Reproduction in Angiosperms
 Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Chapter 36 Reproduction in Angiosperms Bryophytes >450mya 360 mya Fig. 27-4, p. 584 Lily Flower Flower Parts Sepals cover and protect flower parts in bud Collectively calyx Petals Can attract animal pollinators
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants
 Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Reproduction and Development in Flowering Plants Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants The flower functions in sexual reproduction of plants and precedes the development of seeds and fruits. Flowers
Anacardiaceae cashew family
 Anacardiaceae cashew family Mostly tropical, the family includes nearly 600 species; four species are native to Nova Scotia. Leaflets are pinnately or palmately compound. Typical are small, regular flowers,
Anacardiaceae cashew family Mostly tropical, the family includes nearly 600 species; four species are native to Nova Scotia. Leaflets are pinnately or palmately compound. Typical are small, regular flowers,
Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/22/10
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Class XI Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants Biology
 Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
Question 1: What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees Primarily, there are two types of root systems found in
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction
 NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
NOTES: CH 38 Plant Reproduction *Modifications in reproduction were key adaptations enabling plants to spread into a variety of terrestrial habitats. * Water has been replaced by wind and animals as a
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES
 USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
Flowering Plant Reproduction
 Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
Lab Exercise Flowering Plant Reproduction Objectives - To be able to identify the parts of a flower - Be able to distinguish between dicots and monocots based on flower morphology - Become familiar with
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the:
 1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
1. What is meant by modification of root? What type of modification of root is found in the: (a) Banyan tree (b) Turnip (c) Mangrove trees (a) Banyan tree - prop roots (b) Turnip - storage roots (c) Mangrove
NCERT. Requirement: Specimens of pea/lentil plant with tendrils, Cactus/Argemone, Pitcher Plant/Utricularia, bulbs of onion/garlic/crocus.
 Exercise 9 46 Aim: To study the modifications of leaf. Principle: Leaf is the most important vegetative organ of the plant. It is a lateral appendage borne at nodes of stem and is associated with photosynthesis,
Exercise 9 46 Aim: To study the modifications of leaf. Principle: Leaf is the most important vegetative organ of the plant. It is a lateral appendage borne at nodes of stem and is associated with photosynthesis,
ffisffi AIDGA IIou: to use thi^s 4VE.?ntr Equ prncnt BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To At-t-
 ffisffi BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To Att The FSC (Field Studies Council) is an independent educational charity committed to raising awareness about the natural world. The organisation works
ffisffi BnrrucrNG ENvTnoNMENTAL UNpTRSTANDTNG To Att The FSC (Field Studies Council) is an independent educational charity committed to raising awareness about the natural world. The organisation works
Reproductive Development and Structure
 Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
Reproductive Development and Structure Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction takes place with slight variations in different groups of plants. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]
![W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.]](/thumbs/89/98832613.jpg) W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
W. B. Turrill, 253 OBSERVATIONS ON THE PERIANTH IN RANUNCULUS AURICOMUS AND ANEMONE CORONARIA. BY W. B. TUKRILL, B.SC. [WITH THREE FIGUKHS IN THK I EXT.] 'T^HE origin of the perianth in the Angiosperms
A Dry, single-seeded, indehiscent fruit, as in sunflower. Producing the spore-bearing structure at the apex of the main stem.
 Achene Acrocarpous Alternate Annual Anterior Appressed Aquatic Avian Awn Axillary Badland Bajada Banner Callous Capsule A Dry, single-seeded, indehiscent fruit, as in sunflower. Producing the spore-bearing
Achene Acrocarpous Alternate Annual Anterior Appressed Aquatic Avian Awn Axillary Badland Bajada Banner Callous Capsule A Dry, single-seeded, indehiscent fruit, as in sunflower. Producing the spore-bearing
 In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
ARNICA (WHOLE PLANT) FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ARNICA MONTANA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS
 ARNICA (WHOLE PLANT) FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ARNICA MONTANA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Arnica montana ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Whole, fresh, blooming plant Arnica montana L.
ARNICA (WHOLE PLANT) FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS ARNICA MONTANA FOR HOMOEOPATHIC PREPARATIONS Arnica montana ad praeparationes homoeopathicas DEFINITION Whole, fresh, blooming plant Arnica montana L.
Key to Families of Vascular Plants Key to Groups
 Key to Families of Vascular Plants Key to Groups APPENDIX 1 1. Plants never bearing seeds, but reproducing by spores (FERNS AND FERN ALLIES; /MONILOPHYTA).......................................................KEY
Key to Families of Vascular Plants Key to Groups APPENDIX 1 1. Plants never bearing seeds, but reproducing by spores (FERNS AND FERN ALLIES; /MONILOPHYTA).......................................................KEY
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Kingdom Plantae, Part II - Gymnosperms and Angiosperms I. Introduction Reproduction in the seed plants (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms) has been greatly influenced by the requirements of a terrestrial existence.
Safety Dissection tools are very sharp. Use appropriately and do not leave unattended in the presence of children.
 Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plant Dissection Consider the lilies, how they grow: they labour not, neither do they spin. But I say to you, not even Solomon in all his glory was clothed like one of these. Luke 12:27 Introduction In
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Understand the evolutionary relationships between plants and algae. Know the features that distinguish plants from algae. Understand the
plant reproduction Alternation of Generations chapter 38
 Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Alternation of Generations Haploid (n) plant reproduction chapter 38 Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) ARCHEGONIUM ANTHERIDIUM Sperm Mature Sorus Sporangium sporophyte
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Angiosperms. The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species.
 Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
PREFACE. Best of luck to all the aspirants!
 PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
PREFACE Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution and taxonomy. It provides detailed
Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus terrestris L.
 ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
ISSN 2278-4136 ZDB-Number: 2668735-5 IC Journal No: 8192 Volume 1 Issue 5 Online Available at www.phytojournal.com Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Pharmacognostical Studies on Flower of Tribulus
Operation Flower Dissection
 Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
Operation Flower Dissection Classroom Activity: K-4 Time: One to two 50-minute class periods Overview: In this activity, students will observe the similarities and differences between flowers of different
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S.
 POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC C CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL? EMBRYO SAC OVULE L.S. POLYGONUM EMBRYO SAC? CHALAZAL END ANTIPODAL CELL CENTRAL
A guide to eucalypt species identification
 A guide to eucalypt species identification Peter White There are approximately 900 currently recognized species of Eucalyptus, Corymbia and Angophora. On a handful, there can be characters that are so
A guide to eucalypt species identification Peter White There are approximately 900 currently recognized species of Eucalyptus, Corymbia and Angophora. On a handful, there can be characters that are so
plant reproduction chapter 40 Alternation of Generations
 Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
Alternation of Generations plant reproduction chapter 40 Haploid (n) Diploid (2n) Sporangium Spore dispersal Spore (n) Young Mature (n) Archegonium Antheridium Sperm Sporangium Mature sporophyte (2n) New
ANGIOSPERM L.S. POLLEN GRAIN
 ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
ANGIOSPERM 2 L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM T 2 CELLS L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL G L.S. POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL > L.S. GENERATIVE CELL POLLEN GRAIN ANGIOSPERM TUBE CELL GENERATIVE CELL
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from
 Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Flowers, Fruit and Seeds Notes Flower Structure and Reproduction Taken from http://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/flower_coloring.html Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are
Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Pollination: Flower to Fruit Vocabulary: anther, cross pollination, filament, fruit, nectar, ovary, ovule, pedicel, petal, pistil, pollen, pollen tube, pollination, receptacle,
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION?
 LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
LABORATORY EXERCISE # 18 HOW ARE SEED PLANTS ADAPTED FOR NUTRITION AND REPRODUCTION? INTRODUCTION As plants evolved into land-dwelling organisms, the action of getting the gametes together for sexual reproduction
Nyla Phillips-Martin 2013 mscraftynyla.blogspot.com
 1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
1 Here are exciting ways to teach your students about the parts of a flower and the function of each part. It includes: A DIY craft activity for assembling the flower parts together to make a complete
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage about reproduction in flowering plants and then complete it by filling the spaces with the most appropriate word or words. The male reproductive organs
Sporocarp of Marsilea. Dr.Sukanya Baruah Chaliha. Asst. Professor Dept of Botany Class-3 rd Sem(Major) MDKG College,Dibrugarh.
 Sporocarp of Marsilea Dr.Sukanya Baruah Chaliha. Asst. Professor Dept of Botany Class-3 rd Sem(Major) MDKG College,Dibrugarh. External Morphology Soft and green when young but turns dark brown and hard
Sporocarp of Marsilea Dr.Sukanya Baruah Chaliha. Asst. Professor Dept of Botany Class-3 rd Sem(Major) MDKG College,Dibrugarh. External Morphology Soft and green when young but turns dark brown and hard
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS
 BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
BIOLOGY 210 Lab #9 Page 72 ANGIOSPERMS Angiosperm (Flowering Plant) Reproduction Raven 6 th, p. 495-515; 7 th, p. 434-451 A. Introduction You studied the morphology and anatomy of the stems, roots, and
SOME time ago, in the pages of this journal. Miss Saunders described
 [359] FLORAL ANATOMY OF RIVINA HUMILIS L., AND THE THEORY OF CARPEL POLYMORPHISM BY A. C. JOSHI AND V. S. Benares Hindu University, India (With 6 figures in the text) RAO SOME time ago, in the pages of
[359] FLORAL ANATOMY OF RIVINA HUMILIS L., AND THE THEORY OF CARPEL POLYMORPHISM BY A. C. JOSHI AND V. S. Benares Hindu University, India (With 6 figures in the text) RAO SOME time ago, in the pages of
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
Modes of Reproduction Very Short answer Questions 1. What is the dominant phase in the life cycle of an angiosperm? A: Sporophyte phase (diploid phase). 2. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the two
The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida
 Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Kingdom Plantae The plant kingdom is in the domain Eukarya and in the supergroup Archaeplastida The closest living relative of plants are in the green algae are charophytes. At one time the had a common
Name Date of Data Collection. Class Period Lab Days/Period Teacher. Construction of a Dichotomous Classification Key
 Construction of a Dichotomous Classification Key New York State Learning Standards Annotation: MST 1, 1.1 a-b, 1.2a, 1.3a-b, 1.4a, 2.2a, 3.1a; MST 4 1.1a, 1.2a, 2.2a, 3.1a, 3.1h, 5.1a-b, 6.1a-b, 6.2a-b,
Construction of a Dichotomous Classification Key New York State Learning Standards Annotation: MST 1, 1.1 a-b, 1.2a, 1.3a-b, 1.4a, 2.2a, 3.1a; MST 4 1.1a, 1.2a, 2.2a, 3.1a, 3.1h, 5.1a-b, 6.1a-b, 6.2a-b,
Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations
 ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
ABSTRACT Floral Structures - Analysis and Critical Observations 24.1 Vinod kumar Flower is the most important structure of a plant which is responsible for the sexual reproduction of the plant. Understanding
Peony Flower Anatomy I
 Peony Flower Anatomy I Don Hollingsworth, APS Director Maryville, Missouri What Makes a Peony Flower Luxurious? Rich luxury of the flowers explains why peonies are wanted, why loved and why known in history
Peony Flower Anatomy I Don Hollingsworth, APS Director Maryville, Missouri What Makes a Peony Flower Luxurious? Rich luxury of the flowers explains why peonies are wanted, why loved and why known in history
UNIT VII. Inflorescences. Types of inflorescenes
 UNIT VII Inflorescences Types of inflorescenes Some species of plants produce solitary flowers. Solitary flowers are are borne singly and separate from one another. Solitary Flowers Saucer Magnolia solitary
UNIT VII Inflorescences Types of inflorescenes Some species of plants produce solitary flowers. Solitary flowers are are borne singly and separate from one another. Solitary Flowers Saucer Magnolia solitary
Plant Life Cycles. Plant life cycles alternate between. producing gametes. Life cycle phases look different among various
 Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Plant Life Cycles Plant life cycles alternate between two cycles: Producing spores and producing gametes A two phase life cycle is called alternation of generations Diploid phase Haploid phase Alternates
Original content Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
TEACHER RESOURCE NOTES Skills Practice Lab Dissecting Flowers Teacher Notes TIME REQUIRED One 45-minute period SKILLS ACQUIRED Collecting data Experimenting Identifying patterns Inferring Interpreting
Teaching A2 Biology Practical Skills Appendix 2
 Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
Practical 10 - T(a)(d) The structure of wind pollinated flowers and fruit. This practical focuses on recording accurately Biological drawings. You will be developing other assessed skills throughout the
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION
 UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
UNIT 4. REPRODUCTION ACTIVITIES: 1. What is the life cycle? Explain the main stages in a living being s life cycle 2. What is reproduction? 3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
Chapter 38 Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology Concept 38.1 Pollination enables gametes to come together within a flower Diploid (2n) sporophytes produce spores by meiosis; these grow into haploid
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS WITH SEEDS
 There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
There are several stages in the process of sexual reproduction in plants with seeds (spermatophytes): gamete formation, pollintation, fertilisation, seed and fruit formation, seed disemination and seed
Mastery. Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis. Chapter Content CHAPTER 3 LESSON 1. Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions.
 Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Chapter Content Mastery Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Directions: Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. LESSON 1 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Meiosis II
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land
 Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Plants II Reproduction: Adaptations to Life on Land Objectives: Be able to describe/illustrate the evolutionary relationships of embryophytes. Be able to map major events in the evolution of plant reproduction
Flowering plants can be pollinated by wind or animals.
 Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Wed 4/5 Activities Learning Target Class Activities *attached below (scroll down)* Website: my.hrw.com Username: bio678 Password:a4s5s Describe the reproductive organs and fertilization of flowering plants.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Four main events must occur in order for sexual reproduction to take place. 1. The organism must be developed and mature sexually. 2. Gametogenesis; production of
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction
 Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
Chapter 31: Plant Reproduction Plants and Pollinators Pollen had evolved by 390 million years ago Sperm packed inside a nutritious package Transferred first by wind currents Later transferred by insects
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
 1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
1 Stamen Anther Filament Stigma Carpel Style Ovary Petal Sepal Ovule 2 A B Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels C A + B gene activity B + C gene activity C gene activity Carpel Petal (a) A schematic diagram of
Glossary. The living component or part of the biosphere. An animal's body takes on the same temperature as that of their environment.
 Abiotic component Adventitious roots Amnion Angiosperms Arachnids Arthropods Atmosphere Autotrophic Biodiversity Biosphere Biotic component Coldblooded Contraceptives Crosspollination Crustacea Dicotyledons
Abiotic component Adventitious roots Amnion Angiosperms Arachnids Arthropods Atmosphere Autotrophic Biodiversity Biosphere Biotic component Coldblooded Contraceptives Crosspollination Crustacea Dicotyledons
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers
 WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
WHMF121 Session Eleven Flowers Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Todays Topic - Flowers o Anatomy of a flower Various types of flowers o Inflorescences Various types of inflorescences
Angiosperm Reproduction
 Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Name Angiosperm Reproduction Today you will examine closely the reproductive aspects of the Anthophyta (aka Magnoliophyta aka Angiosperms) to finish your phylogenetic study of reproduction and evolution
Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae. Today 4 families
 Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae Today 4 families Rosaceae (rose family) Overview World: 110 genera, 3000 spp. CA: 37 genera, 147 spp. Rosa Malus fusca Prunus ilicifolia (drupe) Rubus fruticosus
Rosaceae Cucurbitaceae Malvaceae Rhamnaceae Today 4 families Rosaceae (rose family) Overview World: 110 genera, 3000 spp. CA: 37 genera, 147 spp. Rosa Malus fusca Prunus ilicifolia (drupe) Rubus fruticosus
Liriodendron tulipifera - yellow poplar
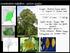 Liriodendron tulipifera - yellow poplar Lauraceae - laurel familiy Umbellularia californica - California bay Sassafras albidum - sassafras Phylogeny of angiosperms! Basal angiosperm! Amborella! Nymphaeales!
Liriodendron tulipifera - yellow poplar Lauraceae - laurel familiy Umbellularia californica - California bay Sassafras albidum - sassafras Phylogeny of angiosperms! Basal angiosperm! Amborella! Nymphaeales!
BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant
 BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant 1 mark Questions 1. Name the modification of leaf for climbing 2. Name the underground part of the flowering plant? 3. What is the direct elongation
BIOLOGY I PUC UNIT 05: Morphology of Flowering plant 1 mark Questions 1. Name the modification of leaf for climbing 2. Name the underground part of the flowering plant? 3. What is the direct elongation
L[Jly, i88 BOTANICAL GAZETTE. IJndescribed plants fromi Guatelmala. IV.
 i88 BOTANICAL GAZETTE L[Jly, IJndescribed plants fromi Guatelmala IV JOHN DONNELL, SMITH (WITH PLATE XI) (Gonzalea thyrsoidea-pilose: leaves except veins glabi-ate, oblong (8-9 inches), each end acuminate,
i88 BOTANICAL GAZETTE L[Jly, IJndescribed plants fromi Guatelmala IV JOHN DONNELL, SMITH (WITH PLATE XI) (Gonzalea thyrsoidea-pilose: leaves except veins glabi-ate, oblong (8-9 inches), each end acuminate,
Chapter 17. Part 1 Plants. Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land. Lecture by Dr. Prince
 Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land Part 1 Plants Lecture by Dr. Prince Plants and Fungi A Beneficial Partnership Plants and fungi colonized land together Mycorrhizae, mutually beneficial
Chapter 17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land Part 1 Plants Lecture by Dr. Prince Plants and Fungi A Beneficial Partnership Plants and fungi colonized land together Mycorrhizae, mutually beneficial
We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower.
 5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
5 th level CS We will learn to label the parts of a plant and flower. We will learn that plants produce flowers which have male and female organs. We will learn that seeds are formed when pollen from the
Plant Reproduction. In a nutshell
 Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
Plant Reproduction In a nutshell 2007-2008 Plant Diversity mosses ferns conifers flowering plants Bryophytes non-vascular land plants Pteridophytes seedless vascular plants Gymnosperm pollen & naked seeds
[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS
![[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS [396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS](/thumbs/84/89173932.jpg) [396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS I BY S. B. KAUSIK, M.SC. Central College, Bangalore With 5 figures in the text N the following study, a description is given of five cases of abnormalities
[396] MORPHOLOGY OF ABNORMAL FLOWERS IN SOME ANGIOSPERMS I BY S. B. KAUSIK, M.SC. Central College, Bangalore With 5 figures in the text N the following study, a description is given of five cases of abnormalities
CHAPTER 5 MORPHOLOGY OF FLOWERING PLANTS 5.1 THE ROOT
 5.1 The Root 5.2 The Stem 5.3 The Leaf 5.4 The Inflorescence 5.5 The Flower 5.6 The Fruit 5.7 The Seed 5.8 Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant 5.9 Description of Some Important Families
5.1 The Root 5.2 The Stem 5.3 The Leaf 5.4 The Inflorescence 5.5 The Flower 5.6 The Fruit 5.7 The Seed 5.8 Semi-technical Description of a Typical Flowering Plant 5.9 Description of Some Important Families
Introduction. Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
Introduction It has been said that an oak is an acorn s way of making more acorns. In a Darwinian view of life, the fitness of an organism is measured only by its ability to replace itself with healthy,
DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L.
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L. BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, Bedford College, Regent's Park, London, N.W.i {Received 4 January 1959) (With Plates 3
DEVELOPMENT OF THE INFLORESCENCE AND SPIKELETS OF ANTHOXANTHUM ODORATUM L. BY B. C. SHARMAN Department of Botany, Bedford College, Regent's Park, London, N.W.i {Received 4 January 1959) (With Plates 3
11. BREDIA Blume, Mus. Bot. 1:
 Tashiroea Matsumura. 11. BREDIA Blume, Mus. Bot. 1: 24. 1849. 野海棠属 ye hai tang shu Herbs or shrublets, erect or creeping to ascending. Stems terete or 4-sided. Leaves petiolate; leaf blade secondary veins
Tashiroea Matsumura. 11. BREDIA Blume, Mus. Bot. 1: 24. 1849. 野海棠属 ye hai tang shu Herbs or shrublets, erect or creeping to ascending. Stems terete or 4-sided. Leaves petiolate; leaf blade secondary veins
Parts of a flower. ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil. petal sepal. petal. ovary PERIANTH. receptacle. peduncle
 THE FLOWER Parts of a flower ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil petal sepal petal PERIANTH peduncle ovary receptacle Parts of a flower Capsicum annuum floral bud Arrangement of floral leaves Brassica napus
THE FLOWER Parts of a flower ANDROECIUM stamen GYNOECIUM pistil petal sepal petal PERIANTH peduncle ovary receptacle Parts of a flower Capsicum annuum floral bud Arrangement of floral leaves Brassica napus
