Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles
|
|
|
- Shanon Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa, Joshua H. Siegle, Jason T. Ritt, Jonathan T. Ting, Guoping Feng and Christopher I. Moore Supplementary Information Materials and Methods: VGAT-ChR2-YFP transgenic mice BAC transgenic mice were generated as previously described (Zhao et al., 2010). Briefly, A BAC clone containing the VGAT gene (RP23-392P11) was obtained from the Children s Hospital Oakland Research Institute. Humanized ChR2 containing the H134R mutation was fused to EYFP and inserted into the ATG codon in exon I of the VGAT gene through homologous recombination (Lee et al., 2001). The expression of the VGAT gene in the BAC clone was disrupted to avoid overexpression of VGAT in the BAC transgenic mice. Transgenic mice were generated by the injection of modified BAC DNA constructs into fertilized oocytes, using standard pronuclear injection techniques (Feng et al., 2004). Fertilized eggs were collected from the mating between C57BL/6J and CBA F1 hybrids. Founder mice were crossed to C57BL/6J to establish the transgenic line. Detailed characterization of this line of mice will be described elsewhere. VGAT-ChR2 mice were maintained in a heterozygous state. Neonatal mice were genotyped using the forward primer ACCCTTCTGTCCTTTTCTCC and reverse primer GCAAGGTAGAGCATAGAGGG. Mice 6-8 weeks old were used for drive implantation surgery as discussed below. All research involving mice have been conducted according to the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines. All procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Brain Processing and Confocal Microscopy For histological experiments, mice were given a terminal dose of ketamine/xylazine anesthesia. Mice were perfused with ice-cold 1% phosphate buffered saline, followed by 4% paraformaldehyde. Brains were harvested and placed in 40% sucrose solution for 24 hours, after which coronal brain sections of 40 μm were cut using a freezing microtome and processed as free-floating sections. Mouse GAD67 antibody 1:1000 (Millipore, Temeluca, CA) followed by secondary staining with goat-anti-mouse antibody conjugated to Alexa 546 (Millipore, Temeluca, CA) was used for staining of GABAergic cells. Confocal microscopy was performed on a Nikon (Tokyo, Japan) PCM 2000 controlled by the Compix (Cranberry Township, PA) software package. Image analysis was performed using the public domain NIH Image J program (available at For the low magnification image of TRN, a 10x objective was used. Higher-power images of thalamus and neocortex were collected with a 40x 1
2 Plan Fluor objective. Laser power, gain, and black level were modulated to remove fluorophore bleed-though between channels. These parameters were kept constant for experiments requiring quantitative comparison among TRN, VPm and SI. Statistical comparisons between groups were done using a Student s t-test. Implant design, printing and loading Dual-site implants, with openings spaced to target ventral posteriomedial thalamus (VPm) and primary somatosensory cortex (SI), were designed in 3D CAD software (SolidWorks, Concord, MA) and stereolithographically printed in Accura 55 plastic (American Precision Prototyping, Tulsa, OK). Each implant was loaded with five thalamic and three cortical 20 micron tungsten stereotrodes (California Fine Wire Company, Grover Beach, CA), which were pinned to a custom-designed electrode interface board (EIB) (Sunstone Circuits, Mulino, OR). Two EEG wires and one ground wire (A-M systems, Carlsborg, WA), were also affixed to the EIB. An optical fiber targeting TRN (Doric Lenses, Quebec, Canada) was glued to the EIB. Animal Surgery Mice 6-8 weeks old were anesthetized with 1% isofluorane and placed in a stereotaxic frame. For each animal, five stainless-steel screws were implanted in the skull to provide EEG contacts (two prefrontal sites), ground (cerebellar), and mechanical support for the drive. A ~2.0 x 1.5mm craniotomy was drilled with a center coordinate of (M/L 2.5mm, A/P 1.7mm). The implant was attached to a custom-designed stereotaxic arm and lowered to the craniotomy. Thalamic stereotrodes were lowered to the following stereotaxic coordinates (M/L 1.9mm, A/P 1.7mm, D/V -3.5mm) which positioned the fiber optic at approximately the following coordinates (M/L 2mm, A/P 1.7mm, D/V -3.25mm) and neocortical stereotrodes at (M/L 3.25mm, A/P 1.7mm, D/V -0.5mm). Electrophysiological Recording Following recovery, each animal was connected to 16-channel preamplifier headstage (Neuralynx, Bozeman, MT). All data were recorded using a Neuralynx Cheetah 32 recording system. Signals from each stereotrode were amplified, filtered between 0.1 and 9 khz and digitized at approximately 30 khz. Local field potentials were collected from a single channel on each stereotrode. The LFP and EEG traces were amplified and filtered between 1 and 100 Hz. Signals were referenced to the cerebellar ground screw in most cases. When referencing to the ground screw produced significant noise, one of the EEG channels was used as a reference. For state analysis, EEG (filtered between 1-50 Hz) and EMG (Filtered between Hz) recordings were performed as has been described previously (Halassa et al., 2009) (Fig. 2). Video Recording Mice were recorded using a Sony HDR-XR150 camera at 30 Hz frame rate. Visual inspection of frames was used to label the animal s state as active vs. quiet (Fig. 2). Optogenetic Stimulation 2
3 A fiber optic patch cord (Doric Lenses) delivered light from a 473 nm laser (Opto Engine, Midvale, UT) to the fiber optic connector on the implant. Prior to connecting to the implant, laser power was measured and titrated to 15 mw using a neutral density filter (Thorlabs, Newton, NJ). Power at the tip of the implanted fiber was ~50% of this value, based on measurements prior to surgery. Thus, there was 7-8 mw of power at the fiber tip, or mw/mm 2 for a 200-micron fiber. An analog stimulus generator (Grass Technologies, Warwick, RI) was used to shape laser pulses of 20 msec duration and Hz frequency. Data Analysis All data were analyzed in Matlab (Mathworks, Natick, MA) using a combination of customwritten software and routines derived from the Chronux toolbox ( Clustering was performed offline using the MClust toolbox ( based on spike amplitudes and energies on the two electrodes of each stereotrode. Units were separated by hand, and crosscorrelation and autocorrelation analyses were used to confirm unit separation. Firing rate was calculated by computing the number of spikes over a 1 s window. Bursts were defined as spike sequences from a single unit with an interspike interval of less than 4 msec preceded by a period of non-spiking of more than 100 msec (Bezdudnaya et al., 2006). Spectrograms were generated using the Chronux toolbox. State-dependent analysis was based on visually detected changes in animal activity and thalamic firing rates. For Figure 2D, one session from each animal was used in which there were clear transitions between high and low activity. Evoked spindle power in each condition was normalized by the total pre-stimulus spindle power. For Figure S6, percentiles were calculated for the firing rate of each cluster, averaged for each recording session, and subsequently normalized by the maximum firing rate of that cluster for that session. This approach allowed for averaging of all clusters across all sessions. Spindles were scored visually for all sessions by an observer blind to the state analysis. 3
4 Supplementary Figures Figure S1: Enriched expression of ChR2-YFP in TRN (A) Low magnification single confocal section of VGAT-ChR2 mouse thalamus showing selective expression of ChR2 (green, YFP fluorescence) in TRN demarcated by GAD67-positive cell bodies (red). (B) Higher magnification confocal section of (A), showing colocalization of ChR2 and GAD67 staining at the cell membrane (white arrow in Merge). (C) Lack of labeling of cell bodies by either ChR2 or GAD67 in VPm thalamus and the process-like expression of ChR2, presumably from TRN axons (D) Cortical GAD67-positive neurons also expressed the ChR2-YFP construct. Exposure was several fold higher (compare to B for clarity). (E) Fluorescence in these brain regions showed significantly higher expression of ChR2 in TRN compared to SI and VPm (TRN vs. VPm, **, p<1.6x10-8 ; TRN vs. SI, **, p<5.2x10-8 ; VPm vs. SI, #, p< Error bars are SEM). 4
5 Figure S2: Brief optical stimulation in VGAT-ChR2 mice drives TRN cell firing Top: A TRN unit (Left) waveform isolated from a stereotrode in a freely behaving mouse, compared to (Right) a TC unit isolated from a separate stereotrode in VPm. Middle: Raster plot showing direct optical drive of the TRN. Note initial drive followed by rebound burst, likely reflecting recruitment of intra-trn feedforward inhibition. Bottom: The time-matched PSTH of TRN unit optical drive. 5
6 Figure S3: TRN drive does not alter firing rate but alters burst rate of TC neurons (Left) Individual TC neuron s firing rate (open circles) plotted before and after stimulation showed no change. (Right) In contrast, burst rate increased in 8 out of the 11 neurons recorded. Figure S4: Optical stimulation results in a wide-range of burst probability across recorded TC cells Histogram of burst probability showing that TC cells exhibited a wide range of burst responses following optical stimulation of TRN. Note that six out of the nine cells show burst probability > 20%. 6
7 Figure S5: Spontaneous neocortical spindles can occur in the absence of clear thalamic spindles during natural sleep Representative examples of three sleep spindles occurring in the cortical LFP in the absence of similar activity in thalamic recordings. 7
8 Figure S6: Spindle induction is most likely under conditions of low firing in TC cells (A) Example of unit firing during a session with noticeable variations in firing rate. Trials in which spindles were induced are highlighted by pink lines. The time of laser stimulation is demarcated by a blue vertical line. Note that during high ongoing firing rate epochs, no spindles were induced. (B) Normalized spindle probability of all cells as a measure of firing rate. There was a significant negative correlation between rate, where trials were binned into deciles, and normalized spindle probability (R = , p<0.04, N= 3 animals. Error bars are SEM). 8
9 Figure S7: Spindle induction is largely limited to NREM sleep (A) A representative polysomnography recording session from one mouse, showing state identification by EEG/EMG, as described previously (Halassa et al., 2009). Red asterisk denotes induced spindles during this session. W denotes awake epochs; N NREM-sleep; and, R REM-sleep. (B) Representative traces of EEG, top and EMG, bottom of the three states, NREM sleep, REM sleep and Wakefulness. Gray square highlights the one second post optical stimulation showing spindle induction in NREM sleep but not REM or wakefulness. Quantification across all sessions 9
10 in all animals shows that spindles are highly limited to NREM sleep (~19.56% induction, vs. 1.27% in wakefulness and 0% in REM; p <0.0001). Supplementary References 1. Bezdudnaya, T., et al., (2006)Thalamic burst mode and inattention in the awake LGNd. Neuron 49, Feng, G., et al., (2004). Generation of transgenic mice. Methods Mol. Med. 9, Halassa, M.M., et al., (2009). Astrocytic modulation of sleep homeostasis and cognitive consequences of sleep loss. Neuron 61, Lee EC, et al., (2001) A highly efficient Escherichia coli-based chromosome engineering system adapted for recombinogenic targeting and subcloning of BAC DNA. Genomics 73: Zhao S., et al., (2010) Fluorescent Labeling of Newborn Dentate Granule Cells in GAD67- GFP Transgenic Mice: A Genetic Tool for the Study of Adult Neurogenesis. PLoS One, 5(9). pii: e
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 September 19.
 Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state
 Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Thalamic control of cortical states
 Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplemental Information. In Vivo Optogenetic Stimulation. of Neocortical Excitatory Neurons. Drives Brain-State-Dependent Inhibition
 Current Biology, Volume 21 Supplemental Information In Vivo Optogenetic Stimulation of Neocortical Excitatory Neurons Drives Brain-State-Dependent Inhibition Celine Mateo, Michael Avermann, Luc J. Gentet,
Current Biology, Volume 21 Supplemental Information In Vivo Optogenetic Stimulation of Neocortical Excitatory Neurons Drives Brain-State-Dependent Inhibition Celine Mateo, Michael Avermann, Luc J. Gentet,
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state
 Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man
 Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man D. GRAHAM SLAUGHTER, M.D., BLAINE S. NASHOLD, Jn., M.D., AND GEORGE G. SOMJEN, M.D. The Division of Neurosurgery, and the
Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man D. GRAHAM SLAUGHTER, M.D., BLAINE S. NASHOLD, Jn., M.D., AND GEORGE G. SOMJEN, M.D. The Division of Neurosurgery, and the
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Supplemental Figure 1
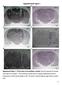 A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience
 How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c
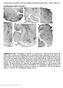 Coherent gamma oscillations couple the amygdala and striatum during learning. Popescu, Popa, Pare SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c LG LP LD R LA BL OT BM HF V HF VP RE VP CL PC d PU e 2 mm R f CP HF 2 mm GP
Coherent gamma oscillations couple the amygdala and striatum during learning. Popescu, Popa, Pare SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c LG LP LD R LA BL OT BM HF V HF VP RE VP CL PC d PU e 2 mm R f CP HF 2 mm GP
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5)
 Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS
 37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG
 Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Awake-behaving recordings in mice during fear conditioning. Eric H. Chang, Ph.D. Goldsmith Postdoctoral Fellow
 Awake-behaving recordings in mice during fear conditioning Eric H. Chang, Ph.D. Goldsmith Postdoctoral Fellow Weill Cornell Medical College Burke Cornell Medical Research Institute White Plains, NY Noldus
Awake-behaving recordings in mice during fear conditioning Eric H. Chang, Ph.D. Goldsmith Postdoctoral Fellow Weill Cornell Medical College Burke Cornell Medical Research Institute White Plains, NY Noldus
Fast modulation of visual perception by basal forebrain cholinergic neurons
 Fast modulation of visual perception by basal forebrain cholinergic neurons The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Fast modulation of visual perception by basal forebrain cholinergic neurons The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits
 Neuron, Volume 66 Supplemental Information Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits Yusuf Tufail, Alexei Matyushov, Nathan Baldwin, Monica L. Tauchmann, Joseph Georges, Anna Yoshihiro,
Neuron, Volume 66 Supplemental Information Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits Yusuf Tufail, Alexei Matyushov, Nathan Baldwin, Monica L. Tauchmann, Joseph Georges, Anna Yoshihiro,
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition. Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT
 Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rett Syndrome Mutation MeCP2 T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4084
 Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
A toolbox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing
 A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001
 Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Movement Initiation Signals in Mouse Whisker Motor Cortex
 Article Movement Initiation Signals in Mouse Whisker Motor Cortex Highlights d Optogenetic excitation (inactivation) of wm1 evokes (inhibits) whisking d d d Layer-specific neuronal activity in wm1 encodes
Article Movement Initiation Signals in Mouse Whisker Motor Cortex Highlights d Optogenetic excitation (inactivation) of wm1 evokes (inhibits) whisking d d d Layer-specific neuronal activity in wm1 encodes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals
 Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
-51mV 30s 3mV. n=14 n=4 p=0.4. Depolarization (mv) 3
 Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplemental Information. Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila. Supplemental Inventory
 1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11239 Introduction The first Supplementary Figure shows additional regions of fmri activation evoked by the task. The second, sixth, and eighth shows an alternative way of analyzing reaction
doi:10.1038/nature11239 Introduction The first Supplementary Figure shows additional regions of fmri activation evoked by the task. The second, sixth, and eighth shows an alternative way of analyzing reaction
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Rapid blue-light mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells
 Nature Methods Rapid blue-light mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells Matthew J Kennedy, Robert M Hughes, Leslie A Peteya, Joel W Schwartz, Michael D Ehlers & Chandra L Tucker Supplementary
Nature Methods Rapid blue-light mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells Matthew J Kennedy, Robert M Hughes, Leslie A Peteya, Joel W Schwartz, Michael D Ehlers & Chandra L Tucker Supplementary
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
LETTER. Thalamic amplification of cortical connectivity sustains attentional control
 LETTER doi:1.138/nature2273 Thalamic amplification of cortical connectivity sustains attentional control L. Ian Schmitt 1, Ralf D. Wimmer 1, Miho Nakajima 1, Michael Happ 1, Sima Mofakham 1 & Michael M.
LETTER doi:1.138/nature2273 Thalamic amplification of cortical connectivity sustains attentional control L. Ian Schmitt 1, Ralf D. Wimmer 1, Miho Nakajima 1, Michael Happ 1, Sima Mofakham 1 & Michael M.
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche
 Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Closed-loop optogenetic control of thalamus as a new tool to interrupt seizures after cortical injury Jeanne T. Paz, Thomas J. Davidson, Eric S. Frechette, Bruno Delord, Isael Parada,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Closed-loop optogenetic control of thalamus as a new tool to interrupt seizures after cortical injury Jeanne T. Paz, Thomas J. Davidson, Eric S. Frechette, Bruno Delord, Isael Parada,
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Dynamic Partitioning of a GPI-Anchored Protein in Glycosphingolipid-Rich Microdomains Imaged by Single-Quantum Dot Tracking
 Additional data for Dynamic Partitioning of a GPI-Anchored Protein in Glycosphingolipid-Rich Microdomains Imaged by Single-Quantum Dot Tracking Fabien Pinaud 1,3, Xavier Michalet 1,3, Gopal Iyer 1, Emmanuel
Additional data for Dynamic Partitioning of a GPI-Anchored Protein in Glycosphingolipid-Rich Microdomains Imaged by Single-Quantum Dot Tracking Fabien Pinaud 1,3, Xavier Michalet 1,3, Gopal Iyer 1, Emmanuel
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity
 An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity Naiyan Chen, Hiroki Sugihara, & Mriganka Sur Nature America, nc. All rights reserved. Cholinergic modulation of cortex
An acetylcholine-activated microcircuit drives temporal dynamics of cortical activity Naiyan Chen, Hiroki Sugihara, & Mriganka Sur Nature America, nc. All rights reserved. Cholinergic modulation of cortex
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers
 Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Supplemental Information. Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking. Activity in Early Visual Cortex. Supplemental Information Inventory:
 Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
Neural Recording Methods
 Neural Recording Methods Types of neural recording 1. evoked potentials 2. extracellular, one neuron at a time 3. extracellular, many neurons at a time 4. intracellular (sharp or patch), one neuron at
Neural Recording Methods Types of neural recording 1. evoked potentials 2. extracellular, one neuron at a time 3. extracellular, many neurons at a time 4. intracellular (sharp or patch), one neuron at
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature22324 Effects of photoinhibition on licking Photoinhibition of ALM or thalamus caused only small changes in lick early rates, no response rates, and licking latency. ALM photoinhibition
doi:10.1038/nature22324 Effects of photoinhibition on licking Photoinhibition of ALM or thalamus caused only small changes in lick early rates, no response rates, and licking latency. ALM photoinhibition
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supporting information
 Supporting information Buckley CL, Toyoizumi T (2018) A theory of how active behavior stabilises neural activity: Neural gain modulation by closed-loop environmental feedback. PLoS Comput Biol 14(1): e1005926.
Supporting information Buckley CL, Toyoizumi T (2018) A theory of how active behavior stabilises neural activity: Neural gain modulation by closed-loop environmental feedback. PLoS Comput Biol 14(1): e1005926.
A Corticostriatal Path Targeting Striosomes Controls Decision Making under Conflict
 Cell Supplemental Information A Corticostriatal Path Targeting Striosomes Controls Decision Making under Conflict Alexander Friedman, Daigo Homma, Leif G. Gibb, Ken-ichi Amemori, Samuel J. Rubin, Adam
Cell Supplemental Information A Corticostriatal Path Targeting Striosomes Controls Decision Making under Conflict Alexander Friedman, Daigo Homma, Leif G. Gibb, Ken-ichi Amemori, Samuel J. Rubin, Adam
Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Activity Dependent Changes At the Developing Neuromuscular Junction
 Activity Dependent Changes At the Developing Neuromuscular Junction (slides 16, 17 and 18 have been slightly modified for clarity) MCP Lecture 2-3 9.013/7.68 04 Neuromuscular Junction Development 1. Muscle
Activity Dependent Changes At the Developing Neuromuscular Junction (slides 16, 17 and 18 have been slightly modified for clarity) MCP Lecture 2-3 9.013/7.68 04 Neuromuscular Junction Development 1. Muscle
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
Place-selective firing contributes to the reverse-order reactivation of CA1 pyramidal cells during sharp waves in open-field exploration
 European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 26, pp. 704 716, 2007 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05684.x Place-selective firing contributes to the reverse-order reactivation of CA1 pyramidal cells during sharp
European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 26, pp. 704 716, 2007 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05684.x Place-selective firing contributes to the reverse-order reactivation of CA1 pyramidal cells during sharp
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
