Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5)
|
|
|
- Raymond Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae Kim 3, Eunha Baeg 1, Yong Ho Kim 3,4, Seong-Gi Kim 1, 4, and Minah Suh 1, 4 * Supplementary Table S1 Flexibility of glass, 1% agarose, PDMS, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and silicone. Flexibility was determined by measuring a break point when the elongation was forced. PDMS and silicone have spring-like characteristics and are easily stretchable. 1 1 C Heo et al.,
2 Supplementary Fig. S1 Physical hydrophobic property of glass, 1% agarose, PDMS, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and silicone. (A) Contact angles and wettability of materials. (B) The contact angle represents an angle between a tangential line of liquid (red line) and solid surface where the liquid is located (yellow line) and is independent of drop volume. Wettability is high when the contact angle is close to zero and is low when the material is hydrophobic. Supplementary Fig. S2 Light absorption curve of glass, agarose (1%), PDMS, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and silicone. The light absorbance value of each material is plotted in every 1 nm over nm wavelengths. 2 2 C Heo et al.,
3 Supplementary Fig. S3 Biocompatibility of PDMS and other materials. SHSY5Y cells were cultured for 24 h over the materials, including PET, 1% agarose, silicone, PDMS, and glass, placed in the culture dish. (A) The cell viabilities of all tested materials except for agarose were high (>95%, error bar: mean ± SD), thus indicating high biocompatibility. (B) After 24 h of culture, the cells were attached to and grew on both the control case (culture dish) and the glass and were slightly attached to PET, whereas the cells were rarely attached to agarose (Agar), silicone, and PDMS (Scale bar: 100 μm). Blurry images of PET and silicone are due to the materials alone rather than to the presence of cells. Supplementary Fig. S4 Overall surgical procedures for the chronic PDMS cranial window in a rat. (A) A schematic for a large rectangular (9 mm x 4 mm) skull craniotomy. (B-F) Visualization of each step of the cranial window surgical procedure. At each step, the skin (B), skull (C), and dura (D) were carefully removed. (E) A rectangular shape of the PDMS (black dot-lined) was placed over the exposed brain tissue area and glued over the intact skull. (F) A white-coloured resin was applied to secure the edge of the PDMS and cover the exposed skull area. 3 3 C Heo et al.,
4 Supplementary Fig. S5 Examples of rat s cranial window conditions post-pdms implantation. Generally after 2 weeks, animals exhibited normal activities in their own home cages. Three examples are shown the apparent cortical vasculature at 1, 2, and 5 weeks through a large scale PDMS cranial window. The window size was as described in Supplementary Fig C Heo et al.,
5 Supplementary Fig. S6 Effectiveness of PDMS in enhancing the optical (A-B) and physiological (C- E) condition in acute open skull experiments. (A-B) Images of a brain (A) without and (B) with a PDMS cover was captured after full craniotomy for both hemispheres of the rat brain. Brain with a PDMS cover exhibited less light scattering noise than brains without (B) a PDMS cover. (C) A comparison image of a square skull piece (right) after craniotomy and a tailored square PDMS (white-dotted box). (D-E) In general, when a bone-flap is removed from the region of interest during cranial window surgery, the brain tissue rapidly bulges through the open skull because of the greater intracranial brain pressure. When the duramater is maintained following skull opening, the exposed brain bulges after approximately 10 min (D, left). With full duratomy, brain tissue herniation can be observed even after 10 s (E, left). In contrast, the application of the PDMS cover prevents brain tissue herniation, even though the opened area is large (D and E, right), thus suggesting that the PDMS application might provide effective conditions for studying normal brain physiological function in vivo. 5 5 C Heo et al.,
6 Supplementary Fig. S7 Effectiveness of PDMS for enhancing imaging quality in a thinned skull experiment. (A) A side-view schematic diagram of PDMS implantation over the thinned skull. (B) The large area of thinned-skull brain images without and with PDMS. An image with PDMS cover shows cortical vessels more clearly than an image without PDMS. The thickness of PDMS is ~150 μm. Supplementary Fig. S8 Immunohistochemical images for microglial cells (Iba1), astrocytes (GFAP) and nuclei (DAPI) of a rat with the PDMS cranial window implantation for 10 weeks (right column) versus an age-matched normal rat (left column). Images were captured from three different locations (a, b, c) at the cranial window. There were no clear differences in histological analysis of microglial 6 6 C Heo et al.,
7 cells and astrocytes of animals with and without the PDMS chronic cranial window. Supplementary Fig. S9 Treatment of a clear cyanoacrylate bond to the penetration points of PDMS. In penetration experiments, to avoid potential CSF leakage, a clear cyanoacrylate bond was applied immediately after the electrode was removed (A). After another 5 weeks (B), no signs of breakage of PDMS or CSF leakage were observed (B). Supplementary Fig. S10 Two-photon microscopic images for vessels and microglial cells of a Cx3Cr1 GFP+/- Tg mouse with a PDMS chronic cranial window. Vessels were visualized after injection of dextran-rhodamine (70000 molecular weight). XYZ 3D images were obtained from a mouse at 7 weeks (A) and 15 weeks (B) post-pdms cranial window implantation surgery. XY-plane images are shown at three different depths. 7 7 C Heo et al.,
8 Supplementary Fig. S11 Immunohistochemical analysis of cortical tissue under the PDMS cranial window at 1, 3, and 10 weeks post-imaplantation surgery. (A) Cortical microglial cells in coronally sectioned Cx3Cr1 GFP+/- Tg mouse brain slices were imaged by confocal microscope. Magnified images of the boxed sections in Ipsi are shown to the right. Other immunohistochemical study was examined for cortical vessels (Glut1), astrocytes (GFAP) and nuclei (DAPI) (B) or microglial cells (Iba1), astrocytes (GFAP) and nuclei (DAPI) (C). The images were captured from both contralateral and ipsilateral sides. Contra: Contralateral hemisphere; Ipsi: Ipsilateral hemisphere. 8 8 C Heo et al.,
9 Supplementary Fig. S12 (A) The target position on PDMS window of the mouse was marked in a dotted circle. A glass micropipette filled with Cy3-labeled hydrogel dye is directly inserted into the target site and removed. Two black arrows represent the edge of the micropipette in the insert image at Day 0. After the removal of the micropipette, the injection site s edges are slightly noticeable under the surgical microscope with 60 x magnification but became invisible at 5 days post-injection. (B) The sign of injecting positon at the surface of the PDMS window can be found by the 2p confocal microscope (marked by two white arrows, at z-depth 1 µm). The Cy3-labeled hydrogel (red) is imaged in depth profile and distributed approximately from 30 to 130 µm in Z- depth in the cortical tissue. The Cy3-labeled hydrogel dye was presented in 3D volume image after 20 days post-injection. 9 9 C Heo et al.,
10 Supplementary Videos (5) Available in the seperate uploaded video files. Supplementary Video S1. Video of rat behaviour at 7 weeks post-pdms implantation. A single animal was housed in it s own home cage after cranial window implantation surgery. The animal exhibited normal grooming, drinking, feeding, and sleeping behavior. Supplementary Video S2. Direct insertion of a multi-channel electrode into the cortex through PDMS window. A soft electrode was inserted through a small slit made by an insulin syringe needle (sma ll needle size with 0.33 μm in diameter: 29 gauge) in the PDMS cranial window. The electrode was removed without creating any CSF leakage. Supplementary Video S3. Video of mouse behaviour at 25 weeks post-pdms implantation surgery. Supplementary Video S4. Video of the cortical blood flow after the administration of dextran-rhodamine into Cx3Cr1 GFP+/- Tg mice. Video was captured using fluorescence (green) microscopy at 25 weeks post PDMS implantation surgery. The green highlighted spots on the cortical surface represent Cx3Cr1 GFP-positive microglia cells. Supplementary Video S5. Locomotion video of an awake mouse during two-photon imaging C Heo et al.,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Specimen. Humeral Head. Femoral Head. Objective. Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1
 A B Specimen Humeral Head 2 1 µm 76 µm Femoral Head Objective Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1 A Femoral Head Global Cell Density Superficial Cell Density Cell Number at 1 µm Nuclei /.1
A B Specimen Humeral Head 2 1 µm 76 µm Femoral Head Objective Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1 A Femoral Head Global Cell Density Superficial Cell Density Cell Number at 1 µm Nuclei /.1
Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation
 Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the. development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation Dimitrios Davalos, Jae Kyu Ryu, Mario Merlini, Kim
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation Dimitrios Davalos, Jae Kyu Ryu, Mario Merlini, Kim
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo
 Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Microtubule Teardrop Patterns
 Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
Supporting Information Microtubule Teardrop Patterns Kosuke Okeyoshi 1, Ryuzo Kawamura 1, Ryo Yoshida 2, and Yoshihito Osada 1 * 1 RIKEN Advanced Science Institute, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience
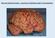 How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization
 Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Current density profiles for backside-plating configuration cells and the cycle stability curve with and without carbon coating. Current density profiles of
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1. Current density profiles for backside-plating configuration cells and the cycle stability curve with and without carbon coating. Current density profiles of
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram of BBB and brain chips.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplementary Movie Caption
 Supplementary Movie Caption 1. Movie S1. Ultrasound-induced blood focusing in vitro (Fig.2b). 2. Movie S2. Acoustic canalization of blood flow in the gap between two capillaries (Fig. 2d). 3. Movie S3.
Supplementary Movie Caption 1. Movie S1. Ultrasound-induced blood focusing in vitro (Fig.2b). 2. Movie S2. Acoustic canalization of blood flow in the gap between two capillaries (Fig. 2d). 3. Movie S3.
Structural and Optical Properties of Single- and Few-Layer Magnetic
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Structural and Optical Properties of Single- and Few-Layer Magnetic Semiconductor CrPS 4 Jinhwan Lee 1, Taeg Yeoung Ko 2, Jung Hwa Kim 3, Hunyoung Bark 4, Byunggil Kang 4, Soon-Gil
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Structural and Optical Properties of Single- and Few-Layer Magnetic Semiconductor CrPS 4 Jinhwan Lee 1, Taeg Yeoung Ko 2, Jung Hwa Kim 3, Hunyoung Bark 4, Byunggil Kang 4, Soon-Gil
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Multiphoton Imaging of Neuronal Activity in vivo in Behavioral Paradigms
 Multiphoton Imaging of Neuronal Activity in vivo in Behavioral Paradigms 2 Outline Surgical preparation Experimental apparatus Synchronization of behavioral trials with imaging Off axis imaging 3 Multiphoton
Multiphoton Imaging of Neuronal Activity in vivo in Behavioral Paradigms 2 Outline Surgical preparation Experimental apparatus Synchronization of behavioral trials with imaging Off axis imaging 3 Multiphoton
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 7: Biomedical Applications
 Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 7: Biomedical Applications Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Computational Medical Imaging Analysis Chapter 7: Biomedical Applications Jun Zhang Laboratory for Computational Medical Imaging & Data Analysis Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington,
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo. SI Figures and Legend
 Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 05505, Republic of Korea.
 Nanoparticle-Assisted Transcutaneous Delivery of a Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3-Inhibiting Peptide Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation Jin Yong Kim 1,5, Jinhyo Ahn 3,4, Jinjoo
Nanoparticle-Assisted Transcutaneous Delivery of a Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3-Inhibiting Peptide Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation Jin Yong Kim 1,5, Jinhyo Ahn 3,4, Jinjoo
Manza Cup HA SURGICAL TECHNIQUE.
 1 PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING. Preoperative assessment of the appropriate size and position of the acetabular component will provide intraoperative guidance for acetabular reaming. To determine the acetabluar
1 PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING. Preoperative assessment of the appropriate size and position of the acetabular component will provide intraoperative guidance for acetabular reaming. To determine the acetabluar
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1:
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration.
 Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
LECTURE 13. Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry
 LECTURE 13 Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry Goniometer circle - centered at the sample, with the x-ray source and detector on the circumference of the circle. Focusing
LECTURE 13 Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry Goniometer circle - centered at the sample, with the x-ray source and detector on the circumference of the circle. Focusing
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information An efficient broadband and omnidirectional light-harvesting scheme employing the hierarchical structure based on ZnO nanorod/si 3 N 4 -coated Si microgroove on 5-inch single crystalline
Supporting Information An efficient broadband and omnidirectional light-harvesting scheme employing the hierarchical structure based on ZnO nanorod/si 3 N 4 -coated Si microgroove on 5-inch single crystalline
Supplementary Fig. 1 Atomic force microscopy topography images Two-dimensional atomic force microscopy images (with an area of 1 m 1 m) of Cu and
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Atomic force microscopy topography images Two-dimensional atomic force microscopy images (with an area of 1 m 1 m) of Cu and Cu(O = 5.0%) films deposited on 20-nm-thick ZnO films during
Supplementary Fig. 1 Atomic force microscopy topography images Two-dimensional atomic force microscopy images (with an area of 1 m 1 m) of Cu and Cu(O = 5.0%) films deposited on 20-nm-thick ZnO films during
High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart.
 High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart. Daniel Aston, Rebecca A. Capel, Kerrie L. Ford, Helen C. Christian,
High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart. Daniel Aston, Rebecca A. Capel, Kerrie L. Ford, Helen C. Christian,
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Pt 8 mm. 12 mm ITO ~ Figure S1. Top view of the Pt-IDA electrode on the glass slide with 50-µm and 50-µm
 Supplementary data A 50 μm Pt 8 mm 12 mm B ITO 50 μm ~ +V 100 nm ~ -V Figure S1. Top view of the Pt-IDA electrode on the glass slide with 50-µm and 50-µm gap distance (A). Side view of the design for the
Supplementary data A 50 μm Pt 8 mm 12 mm B ITO 50 μm ~ +V 100 nm ~ -V Figure S1. Top view of the Pt-IDA electrode on the glass slide with 50-µm and 50-µm gap distance (A). Side view of the design for the
Terahertz reflectometry imaging for low and high grade gliomas
 Terahertz reflectometry imaging for low and high grade gliomas Young Bin Ji 1,9, Seung Jae Oh 1,9, Seok-Gu Kang 2,9, Jung Heo 3,9, Sang-Hoon Kim 1,4, Yuna Choi 1, Seungri Song 3, Hye Young Son 5, Se Hoon
Terahertz reflectometry imaging for low and high grade gliomas Young Bin Ji 1,9, Seung Jae Oh 1,9, Seok-Gu Kang 2,9, Jung Heo 3,9, Sang-Hoon Kim 1,4, Yuna Choi 1, Seungri Song 3, Hye Young Son 5, Se Hoon
Effect of Propecia on the Hair Follicle in Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and Video Imaging Study
 Effect of Propecia on the Hair Follicle in Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and Video Imaging Study Investigators: Department of Dermatology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Effect of Propecia on the Hair Follicle in Male Androgenetic Alopecia: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and Video Imaging Study Investigators: Department of Dermatology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma.
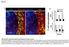 Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Fig S1 CD4 Fibronectin EpCM CD8 CD4 and CD8 T cells show a similar accumulation in the tumor stroma. Fluorescently-labeled CD4 (CMFD, green) and CD8 (Hoechst, yellow) T cells were added to a human lung
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment
 Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Three-Dimensional Quantitative Co-Mapping of Pulmonary Morphology and. Nanoparticle Distribution with Cellular Resolution in Nondissected Murine
 Three-Dimensional Quantitative Co-Mapping of Pulmonary Morphology and Nanoparticle Distribution with Cellular Resolution in Nondissected Murine Lungs Lin Yang,,, Annette Feuchtinger, Winfried Möller,,
Three-Dimensional Quantitative Co-Mapping of Pulmonary Morphology and Nanoparticle Distribution with Cellular Resolution in Nondissected Murine Lungs Lin Yang,,, Annette Feuchtinger, Winfried Möller,,
bio-mof-1 DMASM Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM.
 bio-mof-1 Transmittance bio-mof-1 DMASM DMASMI 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM. Intensity (a.u.) bio-mof-1 DMASM as
bio-mof-1 Transmittance bio-mof-1 DMASM DMASMI 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure S1 FTIR spectra of bio-mof-1, DMASMI, and bio-mof-1 DMASM. Intensity (a.u.) bio-mof-1 DMASM as
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
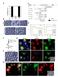 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Patient Information Publications Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health
 Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Katherine Gibson-Corley DVM, PhD, DACVP. Pathology Grand Rounds March 27, 2014
 Katherine Gibson-Corley DVM, PhD, DACVP Pathology Grand Rounds March 27, 2014 Outline Introduction to spinal cord stimulation (SCS) Current SCS devices The Iowa-Patch TM (I-Patch) Post-surgical pathologies
Katherine Gibson-Corley DVM, PhD, DACVP Pathology Grand Rounds March 27, 2014 Outline Introduction to spinal cord stimulation (SCS) Current SCS devices The Iowa-Patch TM (I-Patch) Post-surgical pathologies
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of face patches (a) Sagittal slice showing the location of fmri-identified face patches in one monkey targeted for recording; dark black line indicates electrode. Stereotactic
Integra B: Camino OLM Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Kit SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra 110-4B: Camino OLM Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Kit SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Surgical Technique Th OLM ICP Kit was developed in cooperation with Richard C. Ostrup, M.D., Thomas G. Luerssen, M.D.
Integra 110-4B: Camino OLM Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Kit SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Surgical Technique Th OLM ICP Kit was developed in cooperation with Richard C. Ostrup, M.D., Thomas G. Luerssen, M.D.
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
PHENOTYPIC DYNAMICS OF MICROGLIAL AND MONOCYTE-DERIVED CELLS IN GLIOBLASTOMA-BEARING MICE.
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, TABLES AND VIDEOS PHENOTYPIC DYNAMICS OF MICROGLIAL AND MONOCYTE-DERIVED CELLS IN GLIOBLASTOMA-BEARING MICE. Clément Ricard 1,2,3,4, Aurélie Tchoghandjian 2,4, Hervé Luche 5, Pierre
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, TABLES AND VIDEOS PHENOTYPIC DYNAMICS OF MICROGLIAL AND MONOCYTE-DERIVED CELLS IN GLIOBLASTOMA-BEARING MICE. Clément Ricard 1,2,3,4, Aurélie Tchoghandjian 2,4, Hervé Luche 5, Pierre
cylinder transition in vitro. (A) Still images of time-lapse recording of blastocyst attaching to
 Supplementary information, Figure S1. DVE specification during blastocyst-to-egg cylinder transition in vitro. (A) Still images of time-lapse recording of blastocyst attaching to the substrate with first
Supplementary information, Figure S1. DVE specification during blastocyst-to-egg cylinder transition in vitro. (A) Still images of time-lapse recording of blastocyst attaching to the substrate with first
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
McWilliams et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
5. COMMON APPROACHES. Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2.
 5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
Supplemental Information. Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo
 Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
WIELAND Dental Digital Support CAM handling abutment bridges
 D E N T A L WIELAND Dental Digital Support CAM handling abutment bridges Table of contents 1. Handling in the CAM system... 1 1.1 Importing digital restoration files into the CAM system... 1 1.2 Setting
D E N T A L WIELAND Dental Digital Support CAM handling abutment bridges Table of contents 1. Handling in the CAM system... 1 1.1 Importing digital restoration files into the CAM system... 1 1.2 Setting
APPLICATION SPECIFIC PROTOCOL ANGIOGENESIS... 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS... 1 MONOLAYER FORMATION... 2 OPTION 1: APPLICATION OF ANGIOGENIC STIMULI...
 APPLICATION SPECIFIC PROTOCOL ANGIOGENESIS AIM 3D Cell Culture Chips offer a new perspective in studying angiogenesis by allowing the growth of new vascular sprouts in a 3D matrix from a pre-existing endothelial
APPLICATION SPECIFIC PROTOCOL ANGIOGENESIS AIM 3D Cell Culture Chips offer a new perspective in studying angiogenesis by allowing the growth of new vascular sprouts in a 3D matrix from a pre-existing endothelial
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in. primate lateral prefrontal cortex
 Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Title. Author(s)Ono, Daisuke; Honma, Ken-Ichi; Honma, Sato. CitationScientific reports, 5: Issue Date Doc URL
 Title Circadian and ultradian rhythms of clock gene expres Author(s)Ono, Daisuke; Honma, Ken-Ichi; Honma, Sato CitationScientific reports, 5: 31 Issue Date 215-7-21 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/59574
Title Circadian and ultradian rhythms of clock gene expres Author(s)Ono, Daisuke; Honma, Ken-Ichi; Honma, Sato CitationScientific reports, 5: 31 Issue Date 215-7-21 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/59574
Raman Spectroscopy and imaging to explore skin and hair. What is the Raman scattering effect?
 Diapositive 1 1 Raman Spectroscopy and imaging to explore skin and hair Sir C.V. Raman Nobel price in physics in 193 1 µm Diapositive 2 What is the Raman scattering effect? Incident monochromatic beam
Diapositive 1 1 Raman Spectroscopy and imaging to explore skin and hair Sir C.V. Raman Nobel price in physics in 193 1 µm Diapositive 2 What is the Raman scattering effect? Incident monochromatic beam
Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH).
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. EL spectral characteristics. (a)
 Supplementary Figure 1. EL spectral characteristics. (a) Angular dependence of normalized light intensity at 540 nm according to ZnO layers; Lambertian emission pattern (black square), ZnO-F (red circle),
Supplementary Figure 1. EL spectral characteristics. (a) Angular dependence of normalized light intensity at 540 nm according to ZnO layers; Lambertian emission pattern (black square), ZnO-F (red circle),
Monitoring Tumor Therapy
 Monitoring Tumor Therapy Zenalux Biomedical, Inc. The Zenascope was used to monitor the physiological response to a vascular disrupting agent in mouse tumors. Changes in hemoglobin concentration, hemoglobin
Monitoring Tumor Therapy Zenalux Biomedical, Inc. The Zenascope was used to monitor the physiological response to a vascular disrupting agent in mouse tumors. Changes in hemoglobin concentration, hemoglobin
