Supplemental Information. Sleep Drive Is Encoded by Neural. Plastic Changes in a Dedicated Circuit. Sha Liu, Qili Liu, Masashi Tabuchi, and Mark N.
|
|
|
- Bernice Walsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell, Volume 165 Supplemental Information Sleep Drive Is Encoded by Neural Plastic Changes in a Dedicated Circuit Sha Liu, Qili Liu, Masashi Tabuchi, and Mark N. Wu
2 Supplemental Experimental Procedures Fly Strains Flies were maintained on standard food containing molasses, cornmeal, and yeast at room temperature. UAS-IVS-Syn21-GFP-p10, UAS-myrGCaMP5, CaLexA (LexAop-CD2::GFP; UASmLexA-VP16-NFAT, LexAop-CD8::GFP-2A-CD8::GFP), LexAop2-TNT::HA, UAS-IP3R-RNAi1 UAS-IP3R-RNAi2, UAS-EGFP-L10a, UAS-dsNR1 and UAS-dsNR2 flies, were obtained from Drs. Gerald Rubin, Troy Littleton, Jing Wang, Chi-hon Lee, Jean-Rene Martin, Rob Jackson, and Chia-Lin Wu. UAS-CD4-tdTomato (#35837), UAS-TNT (#28838), STaR (UAS-FLP, brp(frt.stop)v5-2a-lexa-vp16, #55751), UAS-GCaMP6s (#42746), and the Rubin Janelia Farm Gal4 lines were obtained from the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center. The R58H05- DBD and R30G03-AD transgenic lines were generated using standard techniques (Rainbow Transgenics), after subcloning their respective enhancer regions into pbpzpgal4dbduw or pbpp65adzpuw. Female flies were used for all experiments. Additional Sleep Methods For UAS-dTrpA1 experiments, flies were raised at 22 C and 1 day of baseline sleep was recorded at 22 C. Flies were then shifted to 29 C for 12 hrs during the night (ZT12-ZT24), in order to activate the neurons. Arousal threshold was measured at the indicated time by providing stimuli of different intensity and duration using mechanical stimulation. For mechanical stimulation, a vortexer mounting plate and multi-tube vortexer (Trikinetics) were used to apply 0.1g-, 0.5g- or 1.2g-force for 1 sec to the flies. Flies that were inactive for 5 min before a stimulus and exhibited beam crossings within 3 min after the mechanical stimulus were identified as aroused. Sleep propensity was measured by examining the % flies falling asleep within 5 minutes after being aroused, and also assessing sleep latency after flies were aroused. Sleep latency after arousal was defined as the time from arousal to the first sleep bout. Data from flies that were aroused by moderate stimuli (0.5g mechanical stimulation) were analyzed.
3 Immunostaining Immunostaining of whole-mount brains was performed as previously described (Liu et al., 2014). Brains were fixed in 4% PFA for ~40 mins. After washing in PBST (PBS+0.3% Triton X- 100), brain samples were incubated with rabbit anti-gfp (Invitrogen) at 1:1000, mouse anti-gfp (Invitrogen) at 1:500, mouse anti-v5 (Invitrogen) at 1:400, mouse nc82 (Development Studies Hybridoma Bank) at 1:50, rabbit anti-dnr2 (Wu et al., 2007) at 1:1000 at 4 C for 72 hours. The following secondary antibodies were used: Alexa 488 anti-rabbit (Invitrogen, 1:1000), Alexa 488 anti-mouse (Invitrogen, 1:500), Alexa 568 anti-rabbit (Invitrogen, 1:1000) and Alexa 568 antimouse (Invitrogen, 1:500). Brain samples were incubated with secondary antibodies overnight at 4 C. Images were obtained on a Zeiss LSM700 confocal microscopy with 1 µm thick sections under 25x or 63x magnification. Nomenclature The sleep-drive neurons identified in this study, which innervate the most anterior ring of the EB, have recently been referred to as R2 (Lin et al., 2013) and EB A (Wolff et al., 2015) ring neurons. It should be noted that other ring neurons have also previously been named R2 neurons, such as the neurons in the C42 driver (Renn et al., 1999) or the EB1 driver (Young and Armstrong, 2010), which are distinct from the ring neurons in this study. Driver Screen 505 Rubin/Janelia Farm Gal4 drivers were manually selected and obtained from the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center. The criteria for selection were a sparse expression pattern in the brain, and weak or absent expression in the thoracic ganglia. These drivers were crossed to UAS-dTrpA1 flies. At least 8 female flies for each Rubin-Gal4>UAS-dTrpA1 genotype were assessed in the primary screen. To calculate Sleep during neural activation, the sleep amount for each Gal4 driver during dtrpa1 activation at 29 C was measured (ZT12-ZT24) and subtracted from the averaged sleep amount during the same period from all drivers (sleep mean ), and then divided by sleep mean. For Sleep after neural activation, the difference between daytime sleep amount (ZT0-12) after dtrpa1 activation and daytime sleep amount (ZT0-12) of the previous day before dtrpa1 activation (sleep difference ) was calculated. To calculate Sleep after neural activation, sleep difference for each driver was subtracted from the
4 mean sleep difference for all drivers (sleep meandifference ), and then divided by sleep meandifference. Thus, Sleep after neural activation considers both the sleep from all drivers and withingenotype changes, while Sleep before neural activation only considers sleep from all drivers. Scatterplot of Sleep during neural activation vs Sleep after neural activation of all 505 drivers was plotted, and a linear regression analysis was performed by a least squares approach using Prism 5 (Graphpad). To identify drivers that induced sleep after dtrpa1 activation without sleep loss during activation, we selected those drivers with the largest residual values (2.5%) that also exhibited a Sleep during neural activation value 0 (the 8 magenta dots in Figure 1A). Brain registration and averaging High-resolution images of the 8 drivers denoted by magenta in Figure 1A were downloaded from Fly Light ( (Jenett et al., 2012). Using IGSRegistrationTools (Jefferis et al., 2007), a standard reference brain was generated by averaging 17 co-registered nc82 stained brains (randomly selected, and not among in the 505 drivers) from the Fly Light image database. Images of the 8 drivers were registered using IGSRegistrationTools to this standard reference brain using the nc82 channel. Anti-GFP signal from the 8 registered brains were averaged using a MATLAB-based program to generate a heat map. Video measurement of behavior R69F08-Gal4>UAS-dTrpA1 were loaded into DAM (Trikinetics) locomotor tubes. After 12 hours dtrpa1 activation at 29 C from ZT12-ZT24, 2 hr video recordings were made from ZT0 to ZT2 using a Logitech Pro 9000 web camera. The time individual animals spent moving and grooming were manually scored. Feeding behavior was scored when flies were immobile on the food. Functional connectivity measurements R69F08-Gal4>UAS-P2X2; R72G06-LexA>LexAop-GCaMP6s and control flies (UAS-P2X2; R72G06-LexA>LexAop-GCaMP6s) were used to perform functional connectivity experiments as previously described (Yao et al., 2012). In brief, fly brains were dissected in the Adulthemolymph like saline (AHLS) containing 2mM Ca 2+, 108mM NaCl, 5mM KCl, 8.2mM MgCl 2, 2mM CaCl 2, 4mM NaHCO 3, 1mM NaH 2 PO 4, 5mM HEPES, 10mM Sucrose, 5mM Trehalose,
5 ph 7.5. Then, brains were transferred to a custom-made chamber with AHLS. Brains were allowed to settle in the AHLS for ~5 mins for optimum baseline fluorescence stabilization. Perfusion flow was established over the brain with a gravity-fed perfusion system (Warner instrument VC-6). Brains were imaged by a Zeiss AX10 fluorescence microscope under 40x objective lens. Regions of interest (ROIs) were selected over the cell body region of ExFl2 neurons. GCaMP signals were recorded at 2 Hz for 5 min. 5 mm ATP was delivered during the second minute to the brains by switching perfusion flow from AHLS to AHLS with 5mM ATP. The average intensity of the ROIs from the first 30 sec of the recording were used as the F 0. ΔF/F 0 of each frame were calculated by (F n -F 0 )/F 0, where F n is the raw intensity of ROIs of each frame. Electrophysiological recordings Brains were removed and dissected in a Drosophila physiological saline solution (101 mm NaCl, 3 mm KCl, 1 mm CaCl 2, 4 mm MgCl 2, 1.25mM NaH 2 PO 4, 20.7 mm NaHCO 3, and 5 mm glucose; ph 7.2), which was pre-bubbled with 95% O 2 and 5% CO 2. To better visualize the recording site, the glial sheath surrounding the brain was focally and carefully removed after treating with an enzymatic cocktail, collagenase (0.5 mg/ml) and dispase (1.5 mg/ml), at 22 C for 3-4 min and cleaning with a small stream of saline pressure-ejected from a large diameter pipette using a 1 ml syringe. In addition, prior to recording, cell surfaces were cleaned with saline pressure-ejected from a small diameter pipette, using a 1 ml syringe connected to the pipette holder. The preparation was immobilized on the bottom of a recording chamber using a custom-made platinum anchor. The recording chamber was placed on an X-Y stage platform (PP ; Scientifica, UK), and the cell bodies of R2 neurons were visualized with GFP fluorescence on a fixed-stage upright microscope (BX51WI; Olympus, Japan) and viewed with a 40 water immersion objective lens (LUMPlanFl, NA: 0.8, Olympus). As the recording electrode approached the R2 neurons, visualization was achieved by IR-DIC optics. Whole-cell recordings using the perforated patch configuration of the patch-clamp technique were performed at ZT0-ZT2 (+/- 12 hr sleep deprivation) or ZT13-ZT15. Patchpipettes (8-10 MΩ) for perforated patch clamp were fashioned from borosilicate glass capillary (without filament) by using a Flaming-Brown puller (P-1000; Sutter Instrument), and further polished with a MF200 microforge (WPI) prior to filling internal pipette solution (102 mm
6 potassium gluconate, mm CaCl 2, 0.94 mm EGTA, 8.5 mm HEPES, 4 mm Mg-ATP, 0.5mM Na-GTP, 17 mm NaCl; ph7.2). To prepare for the perforated patch recording procedure, β-escin was prepared as a 50- mm stock solution in water (stored up to 2 weeks at 20 C) and was added fresh into the internal pipette solution to a final concentration of 50 μm. As β-escin is light-sensitive, filling syringes were covered with aluminum foil. During the filling process, pipette tips were dipped briefly for 1 sec or less into a small container with β-escin-free internal pipette solution, and then were back-filled with the β-escin-containing solution from the filling syringe. Air bubbles were removed by gentle tapping. β-escin pipette solutions remained stable for several hrs after mixing in the filling syringe, with no evidence of precipitate formation. Recordings were acquired with an Axopatch 200B amplifier (Molecular Devices) or a Model 2400 amplifier with 100 MΩ headstage (A-M systems), and sampled with Digidata 1440A interface (Molecular Devices). These devices were controlled on a computer using pclamp 10 software (Molecular Devices). The signals were sampled at 20 khz and low-pass filtered at 2 khz. Junction potentials were nullified prior to high-resistance (GΩ) seal formation. After establishing a GΩ seal, perforated patches were allowed to develop spontaneously over time (usually ~1 8 min) without any suction pulse applied in the pipette. After breakthrough became evident, as determined by the gradual development of a large capacitance transient in the seal test window of pclamp 10 software, access resistance monitoring was initiated employing the membrane test function. After that point, access resistance was monitored continuously during the final completion of perforation process, until it reached a minimal steady state (access resistance stably < 40 MΩ). Cells showing evidence of mechanical breakthrough, as assessed by the abrupt generation of a large capacitance transient (versus the more progressive, gradual one generated by chemical perforation), were excluded. In addition, cells were also excluded if inflowing cytosolic GFP florescence into the pipette was visually detected during or after recording. One neuron per brain was recorded. During the recording, the bath solution was continuously perfused with saline by means of a gravity-driven system. For identification of bursts in a spike strain, the following criteria were used: burst onset, ISI < 80 ms; burst offset, ISI > 160 ms (Grace and Bunney, 1984). Electrophysiological analysis was performed in Igor software (WaveMetrics), MATLAB (MathWorks), and Clampfit (Molecular devices).
7 TRAP purification of translating RNAs Approximately 250 R2-Split-Gal4, UAS-EGFP-L10a homozygous flies were mechanically sleep deprived for 24 hours. After sleep deprivation the heads were collected and stored at -80 C for TRAP purification. The TRAP experiments were essentially performed following a previously described protocol in Drosophila (Jackson et al., 2015). In our experiments, we used a highaffinity GFP-nanobody GFP-Trap (Allele Biotechnology) for immunoprecipitation of EGFP labeled ribosomes. RNA was extracted from the GFP-Trap beads using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen). qpcr cdna was synthesized using SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System (Invitrogen). qpcr was performed using SYBR PCR master mix (Applied Biosystems) as previously described (Liu et al., 2012). Statistical analysis Statistical analyses were performed with Prism 5 (GraphPad). For comparisons of two groups of normally distributed data, Student s t tests were performed. For multiple comparisons, one-way ANOVAs followed by Tukey s post hoc test were performed. For non-normally distributed data, Mann-Whitney test were performed. For multiple comparisons of non-normally distributed data, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn s post hoc test were performed. Supplemental References Grace, A.A. and Bunney, B.S. (1984). The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: burst firing. J. Neurosci. 4, Jackson, F.R., Ng, F.S., Sengupta, S., You, S., and Huang, Y. (2015). Glial cell regulation of rhythmic behavior. Methods Enzymol. 552, Jefferis, G.S.X.E., Potter, C.J., Chan, A.I., Marin, E.C., Rohlfing, T., Maurer, C.R., and Luo, L.Q. (2007). Comprehensive maps of Drosophila higher offactory centers: Spatially segregated fruit and pheromone representation. Cell 128,
8 Lin, C.Y., Chuang, C.C., Hua, T.E., Chen, C.C., Dickson, B.J., Greenspan, R.J., and Chiang, A.S. (2013). A comprehensive wiring diagram of the protocerebral bridge for visual information processing in the Drosophila brain. Cell Rep. 3, Liu, S., Lamaze, A., Liu, Q., Tabuchi, M., Yang, Y., Fowler, M., Bharadwaj, R., Zhang, J., Bedont, J., Blackshaw, S., et al. (2014). WIDE AWAKE mediates the circadian timing of sleep onset. Neuron 82, Renn, S.C., Armstrong, J.D., Yang, M., Wang, Z., An, X., Kaiser, K., and Taghert, P.H. (1999). Genetic analysis of the Drosophila ellipsoid body neuropil: organization and development of the central complex. J. Neurobiol. 41, Wolff, T., Iyer, N.A., and Rubin, G.M. (2015). Neuroarchitecture and neuroanatomy of the Drosophila central complex: A GAL4-based dissection of protocerebral bridge neurons and circuits. J. Comp. Neurol. 523, Yao, Z., Macara, A.M., Lelito, K.R., Minosyan, T.Y., and Shafer, O.T. (2012). Analysis of functional neuronal connectivity in the Drosophila brain. J. Neurophysiol. 108, Young, J.M., and Armstrong, J.D. (2010). Structure of the adult central complex in Drosophila: organization of distinct neuronal subsets. J. Comp. Neurol. 518,
Supplemental Information. Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila. Supplemental Inventory
 1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
R1 Neural Circuitry on Ellipsoid Body Promotes Sleep in Drosophila Melanogaster. Senior Thesis. Presented to
 R1 Neural Circuitry on Ellipsoid Body Promotes Sleep in Drosophila Melanogaster Senior Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the School of Arts and Sciences Brandeis University Undergraduate Program in Neuroscience
R1 Neural Circuitry on Ellipsoid Body Promotes Sleep in Drosophila Melanogaster Senior Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the School of Arts and Sciences Brandeis University Undergraduate Program in Neuroscience
Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila
 Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila Angelique Lamaze 1, Arzu Öztürk-Çolak 2, Robin Fischer 3, Nicolai Peschel 3, Kyunghee Koh 2 and James E.C. Jepson 1* 1 UCL Institute
Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila Angelique Lamaze 1, Arzu Öztürk-Çolak 2, Robin Fischer 3, Nicolai Peschel 3, Kyunghee Koh 2 and James E.C. Jepson 1* 1 UCL Institute
50mM D-Glucose. Percentage PI. L-Glucose
 Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response
 A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states.
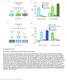 Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 THE PHARMACOLOGICAL DISTINCTION OF GABA A RECEPTOR
B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 GABAA Cell Line Specification Sheet B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH CHO α 1 β 2 γ 2 Cells Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 THE PHARMACOLOGICAL DISTINCTION OF GABA A RECEPTOR
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
A Drosophila model for alcohol reward. Supplemental Material
 Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
Prolonged Synaptic Integration in Perirhinal Cortical Neurons
 RAPID COMMUNICATION Prolonged Synaptic Integration in Perirhinal Cortical Neurons JOHN M. BEGGS, 1 JAMES R. MOYER, JR., 1 JOHN P. MCGANN, 2 AND THOMAS H. BROWN 1 3 1 Department of Psychology, 2 Interdepartmental
RAPID COMMUNICATION Prolonged Synaptic Integration in Perirhinal Cortical Neurons JOHN M. BEGGS, 1 JAMES R. MOYER, JR., 1 JOHN P. MCGANN, 2 AND THOMAS H. BROWN 1 3 1 Department of Psychology, 2 Interdepartmental
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
In vivo whole-cell recording with high success rate in anaesthetized and awake mammalian brains
 Wang et al. Molecular Brain (2016) 9:86 DOI 10.1186/s13041-016-0266-7 METHODOLOGY In vivo whole-cell recording with high success rate in anaesthetized and awake mammalian brains Yao Wang, Yu-zhang Liu,
Wang et al. Molecular Brain (2016) 9:86 DOI 10.1186/s13041-016-0266-7 METHODOLOGY In vivo whole-cell recording with high success rate in anaesthetized and awake mammalian brains Yao Wang, Yu-zhang Liu,
Supplemental Information. Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body. Output Synapses Are Cholinergic
 Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
BILAYER CHANNEL RECONSTITUTION
 (1) 1% Agar Salt Bridge 1.0 g Agar 3.75g KCl in 100ml distilled water, store at 4 o C. BILAYER CHANNEL RECONSTITUTION (2) Cs solution: (Cesium Methanesulfonate) 1) 50 mm Cs + solution 0.209 MOPS, 10mM
(1) 1% Agar Salt Bridge 1.0 g Agar 3.75g KCl in 100ml distilled water, store at 4 o C. BILAYER CHANNEL RECONSTITUTION (2) Cs solution: (Cesium Methanesulfonate) 1) 50 mm Cs + solution 0.209 MOPS, 10mM
Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche
 Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1: Electrophysiological recordings from Drosophila olfactory receptor neurons and projection neurons.
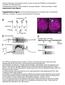 Sensory Processing in the Drosophila Antennal Lobe Increases the Reliability and Separability of Ensemble Odor Representations Vikas Bhandawat, Shawn R. Olsen, Nathan W. Gouwens, Michelle L. Schlief, and
Sensory Processing in the Drosophila Antennal Lobe Increases the Reliability and Separability of Ensemble Odor Representations Vikas Bhandawat, Shawn R. Olsen, Nathan W. Gouwens, Michelle L. Schlief, and
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Supplementary Methods. the ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex (VLO) and basolateral amygdala (BLA). AAV8-CaMKII-HAhM
 Supplementary Materials, Zimmermann et al. Supplementary Methods Surgery. AAV5-CaMKII-HA-hM 4 D(Gi)-IRES-mCitrine or AAV5-CaMKII-GFP was infused into the ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex (VLO) and basolateral
Supplementary Materials, Zimmermann et al. Supplementary Methods Surgery. AAV5-CaMKII-HA-hM 4 D(Gi)-IRES-mCitrine or AAV5-CaMKII-GFP was infused into the ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex (VLO) and basolateral
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/331/6017/599/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Action-Potential Modulation During Axonal Conduction Takuya Sasaki, Norio Matsuki, Yuji Ikegaya* *To whom correspondence
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/331/6017/599/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Action-Potential Modulation During Axonal Conduction Takuya Sasaki, Norio Matsuki, Yuji Ikegaya* *To whom correspondence
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of. parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala
 Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium Martin C, Coolen N, Wu YZ, Thévenot G, Touqui L, PrulièreEscabasse V, Papon JF, Coste
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium Martin C, Coolen N, Wu YZ, Thévenot G, Touqui L, PrulièreEscabasse V, Papon JF, Coste
Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab)
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
Circadian Factor BMAL1 in Histaminergic Neurons Regulates Sleep Architecture
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Circadian Factor BMAL1 in Histaminergic Neurons Regulates Sleep Architecture Xiao Yu, Anna Zecharia, Zhe Zhang, Qianzi Yang, Raquel Yustos, Polona Jager,
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Circadian Factor BMAL1 in Histaminergic Neurons Regulates Sleep Architecture Xiao Yu, Anna Zecharia, Zhe Zhang, Qianzi Yang, Raquel Yustos, Polona Jager,
Why am I working in a Drosophila lab? Dr. Stefan Pulver, Brandeis University
 Why am I working in a Drosophila lab? Dr. Stefan Pulver, Brandeis University !Short life span The advantages of Drosophila as a model organism in neurocience!genetic manipulations are relatively easy!forward
Why am I working in a Drosophila lab? Dr. Stefan Pulver, Brandeis University !Short life span The advantages of Drosophila as a model organism in neurocience!genetic manipulations are relatively easy!forward
Arnaud Ruiz, Emilie Campanac, Ricardo Scott, Dmitri A. Rusakov, Dimitri M. Kullmann
 Presynaptic GABA A receptors enhance transmission and LTP induction at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses Arnaud Ruiz, Emilie Campanac, Ricardo Scott, Dmitri A. Rusakov, Dimitri M. Kullmann Supplementary
Presynaptic GABA A receptors enhance transmission and LTP induction at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses Arnaud Ruiz, Emilie Campanac, Ricardo Scott, Dmitri A. Rusakov, Dimitri M. Kullmann Supplementary
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Drugs, Drug Targets and You: Patch Clamping
 Drugs, Drug Targets and You: Patch Clamping Introduction To elucidate how an ion channel operates, one needs to examine the factors that influence its opening and closing as well as measure the resulting
Drugs, Drug Targets and You: Patch Clamping Introduction To elucidate how an ion channel operates, one needs to examine the factors that influence its opening and closing as well as measure the resulting
The control of spiking by synaptic input in striatal and pallidal neurons
 The control of spiking by synaptic input in striatal and pallidal neurons Dieter Jaeger Department of Biology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322 Key words: Abstract: rat, slice, whole cell, dynamic current
The control of spiking by synaptic input in striatal and pallidal neurons Dieter Jaeger Department of Biology, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322 Key words: Abstract: rat, slice, whole cell, dynamic current
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Development Supplementary information
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Mosaic clonal analysis GSC and SP clones were induced with the FLP/FRT-mediated mitotic recombination technique (Xu and Rubin, 1993) in files with following genotypes:
Supplemental Materials and Methods Mosaic clonal analysis GSC and SP clones were induced with the FLP/FRT-mediated mitotic recombination technique (Xu and Rubin, 1993) in files with following genotypes:
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience
 How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
How we study the brain: a survey of methods used in neuroscience Preparing living neurons for recording Large identifiable neurons in a leech Rohon-Beard neurons in a frog spinal cord Living slice of a
Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation.
 ` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
Supplemental Information. In Vivo Optogenetic Stimulation. of Neocortical Excitatory Neurons. Drives Brain-State-Dependent Inhibition
 Current Biology, Volume 21 Supplemental Information In Vivo Optogenetic Stimulation of Neocortical Excitatory Neurons Drives Brain-State-Dependent Inhibition Celine Mateo, Michael Avermann, Luc J. Gentet,
Current Biology, Volume 21 Supplemental Information In Vivo Optogenetic Stimulation of Neocortical Excitatory Neurons Drives Brain-State-Dependent Inhibition Celine Mateo, Michael Avermann, Luc J. Gentet,
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
RNA-interference knockdown of Drosophila pigment dispersing factor in neuronal subsets: The anatomical basis of a neuropeptide s circadian functions
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 RNA-interference knockdown of Drosophila pigment dispersing factor in neuronal subsets: The anatomical basis
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 RNA-interference knockdown of Drosophila pigment dispersing factor in neuronal subsets: The anatomical basis
Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Microinsemination schedule. 1. Preparation of mediums
 Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Masumi Hirabayashi Section of Mammalian Transgenesis, Center for Genetic Analysis of Behavior, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, National
Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Masumi Hirabayashi Section of Mammalian Transgenesis, Center for Genetic Analysis of Behavior, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, National
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70
 Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70 Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70 Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Age-Related Reduction of Recovery Sleep and Arousal Threshold in Drosophila
 pii: sp-00707-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.5665/sleep.6032 BASIC SCIENCE Age-Related Reduction of Recovery Sleep and Arousal Threshold in Drosophila Julie Vienne, PhD 1 ; Ryanne Spann 2 ; Fang Guo, PhD 1 ;
pii: sp-00707-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.5665/sleep.6032 BASIC SCIENCE Age-Related Reduction of Recovery Sleep and Arousal Threshold in Drosophila Julie Vienne, PhD 1 ; Ryanne Spann 2 ; Fang Guo, PhD 1 ;
Division of Hypothalamic Research, Departments of Internal Medicine and
 1 5-HT 2C Rs Expressed by Pro-opiomelanocortin Neurons Regulate Insulin Sensitivity in Liver Yong Xu 1, 3*, Eric D. Berglund 1*, Jong-Woo Sohn 1, William L. Holland 2, Jen-Chieh Chuang 1, Makoto Fukuda
1 5-HT 2C Rs Expressed by Pro-opiomelanocortin Neurons Regulate Insulin Sensitivity in Liver Yong Xu 1, 3*, Eric D. Berglund 1*, Jong-Woo Sohn 1, William L. Holland 2, Jen-Chieh Chuang 1, Makoto Fukuda
Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation
 Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit
 ab136955 Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the sensitive and accurate measurement of Glucose uptake in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab136955 Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the sensitive and accurate measurement of Glucose uptake in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Biol110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 1-4 Friday April 13, 2012 (Start promptly; work fast; the protocols take ~4 h)
 Biol110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 1-4 Friday April 13, 2012 (Start promptly; work fast; the protocols take ~4 h) A. Microscopic Examination of the Plasma Membrane and Its Properties
Biol110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 1-4 Friday April 13, 2012 (Start promptly; work fast; the protocols take ~4 h) A. Microscopic Examination of the Plasma Membrane and Its Properties
Whole Mount Drosophila Embryo In Situ Hybridization with RNA probes 2/5/2001 Leslie Vosshall
 Whole Mount Drosophila Embryo In Situ Hybridization with RNA probes 2/5/2001 Leslie Vosshall DAY ONE All incubations are done at room temperature unless otherwise noted. All solutions and all containers
Whole Mount Drosophila Embryo In Situ Hybridization with RNA probes 2/5/2001 Leslie Vosshall DAY ONE All incubations are done at room temperature unless otherwise noted. All solutions and all containers
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development
 Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate. bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic
 COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
Supplemental Information. Wakefulness Is Governed by GABA and Histamine Cotransmission. Neuron, Volume 87
 Neuron, Volume 87 Supplemental Information Wakefulness Is Governed by GABA and Histamine Cotransmission Xiao Yu, Zhiwen Ye, Catriona M. Houston, Anna Y. Zecharia, Ying Ma, Zhe Zhang, David S. Uygun, Susan
Neuron, Volume 87 Supplemental Information Wakefulness Is Governed by GABA and Histamine Cotransmission Xiao Yu, Zhiwen Ye, Catriona M. Houston, Anna Y. Zecharia, Ying Ma, Zhe Zhang, David S. Uygun, Susan
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA)
 Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA) Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA) Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set
 Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Mouse C-Peptide ELISA Kit
 Mouse C-Peptide ELISA Kit Cat.No: DEIA4507 Lot. No. (See product label) Size 96T Intended Use The Mouse C-Peptide ELISA kit is for the quantitative determination of c-peptide in mouse serum, plasma, and
Mouse C-Peptide ELISA Kit Cat.No: DEIA4507 Lot. No. (See product label) Size 96T Intended Use The Mouse C-Peptide ELISA kit is for the quantitative determination of c-peptide in mouse serum, plasma, and
Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris
 ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
ZOOLOGICAL SCIENCE 21: 131 138 (2004) 2004 Zoological Society of Japan Correlation between Membrane Potential Responses and Tentacle Movement in the Dinoflagellate Noctiluca miliaris Kazunori Oami* Institute
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Arginine-rich peptides destabilize the plasma membrane, consistent with a pore formation translocation mechanism of cell penetrating peptides
 Supplementary materials for: Arginine-rich peptides destabilize the plasma membrane, consistent with a pore formation translocation mechanism of cell penetrating peptides H. D. Herce 1,2, A. E. Garcia
Supplementary materials for: Arginine-rich peptides destabilize the plasma membrane, consistent with a pore formation translocation mechanism of cell penetrating peptides H. D. Herce 1,2, A. E. Garcia
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013
 NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
NS200: In vitro electrophysiology section September 11th, 2013 Quynh Anh Nguyen, 4 th Year Nicoll Lab quynhanh.nguyen@ucsf.edu N276 Genentech Hall, Mission Bay Outline Part I: Theory Review of circuit
Supporting Information File S2
 Pulli et al. Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Biological Samples Page 1 of 6 Supporting Information File S2 Step-by-Step Protocol Reagents: Sucrose (Sigma, S3089) CaCl 2 (Sigma, C5770) Heparin Sodium
Pulli et al. Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Biological Samples Page 1 of 6 Supporting Information File S2 Step-by-Step Protocol Reagents: Sucrose (Sigma, S3089) CaCl 2 (Sigma, C5770) Heparin Sodium
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
SI Materials and methods
 SI Materials and methods Cell culture and transfection. Primary cultures of neonatal cardiac myocytes were prepared as described previously 1. Hearts were removed from rat pups at postnatal day 1 (P1).
SI Materials and methods Cell culture and transfection. Primary cultures of neonatal cardiac myocytes were prepared as described previously 1. Hearts were removed from rat pups at postnatal day 1 (P1).
--- Chapter Cambrian Y. Liu, Cheng Xiao, Scott E. Fraser, Henry A. Lester, David S. Koos
 55 --- Chapter 3 --- Electrophysiological characterization of Grueneberg ganglion olfactory neurons: spontaneous firing, sodium conductance, and hyperpolarization-activated currents Cambrian Y. Liu, Cheng
55 --- Chapter 3 --- Electrophysiological characterization of Grueneberg ganglion olfactory neurons: spontaneous firing, sodium conductance, and hyperpolarization-activated currents Cambrian Y. Liu, Cheng
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Supplementary Movie Caption
 Supplementary Movie Caption 1. Movie S1. Ultrasound-induced blood focusing in vitro (Fig.2b). 2. Movie S2. Acoustic canalization of blood flow in the gap between two capillaries (Fig. 2d). 3. Movie S3.
Supplementary Movie Caption 1. Movie S1. Ultrasound-induced blood focusing in vitro (Fig.2b). 2. Movie S2. Acoustic canalization of blood flow in the gap between two capillaries (Fig. 2d). 3. Movie S3.
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice. The time course of locomotor activity for WT (a, b) or D2R
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice. The time course of locomotor activity for WT (a, b) or D2R
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment
 Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5)
 Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL
 Supporting Online Material Dishinger, J. F., Reid, K. R., Kennedy, R. T. SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Quantitative Sampling of Biphasic and Pulsatile Insulin Release from Pancreatic Islets with High Throughput
Supporting Online Material Dishinger, J. F., Reid, K. R., Kennedy, R. T. SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Quantitative Sampling of Biphasic and Pulsatile Insulin Release from Pancreatic Islets with High Throughput
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr)
 Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
