PARTS OF THE BODY, THE SKELETON AND INTERNAL ORGANS (DELI TELESA, OKOSTJE IN NOTRANJI ORGANI)
|
|
|
- Ralf Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Naslov učne enote (teme) PARTS OF THE BODY, THE SKELETON AND INTERNAL ORGANS (DELI TELESA, OKOSTJE IN NOTRANJI ORGANI) Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
2 Izobraževalni program Zdravstvena nega Ime modula Jezik stroke Naslov učnih tem ali kompetenc, ki jih obravnava učno gradivo Deli telesa, okostje in notranji organi ter oddelki in specialisti v bolnišnici Naslov enote učnega gradiva; to ni ena učna ura DELI TELESA, OKOSTJE IN NOTRANJI ORGANI POVZETEK Gradivo Deli telesa, okostje in notranji organi opisuje: angleško besedišče za poimenovanje delov telesa, kosti ter notranjih organov. Opisuje tudi naloge notranjih organov. Dodan je tudi slovarček nekaterih besed povezanih z obravnavano tematiko. KLJUČNE BESEDE: body, skeleton, bones, internal organs, function AVTOR: Barbara Cesar Recenzent: Lektor: Datum: junij 2009 CILJI: POIMENOVANJE DELOV TELESA, KOSTI, NOTRANJIH ORGANOV V ANGLEŠČINI; FUNKCIJE NOTRANJIH ORGANOV IN KOSTI; To delo je ponujeno pod Creative Commons Priznanje avtorstva-nekomercialno- Deljenje pod enakimi pogoji 2.5 Slovenija licenco. Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
3 Parts of the body 1. ear 2. cheek 3. jaw 4. neck 5. shoulder 6. armpit 7. upper arm 8. elbow 9. waist, loin 10. forearm 11. buttock, hip 12. wrist 13. hand 14. thumb 15. finger 16. thigh 17. calf 18. leg 19. foot (pl. feet) 20. toes 21. hair 22. forehead 23. nose 24. chin 25. Adam s apple 26. chest / thorax 27. nipple 28. breast 29. stomach / tummy / belly (abdomen) 30. navel / belly button 31. hip 32. palm 33. groin 34. genitals 35. knee 36. shin 37. ankle 38. big toe 39. sole 40. heel * backside and bum (infl.) = bottom belly (infl.) = stomach Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
4 The face Label the diagram using the words on the right. 1. temple 2. eyebrow 3. iris 4. nostril 5. nose 6. Adam s apple 7. cheek 8. forehead 9. hair 10. ear 11. ear lobe 12. neck 13. jaw 14. eyelashes 15. lip 16. chin 17. mouth The hand Label the diagram using the words on the right. 1. wrist 2. middle finger 3. ring finger 4. little finger / pinky 5. knuckle 6. thumb 7. nail 8. palm 9. index finger Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
5 Revision of body parts Look at the picture on the right and complete the following sentences. Pay attention to the words in bold type and translate them. He has a pain in his (1). / He s got a ache. He has a stiff (2). He has a scratch on his (3). He has a rash on his (4). He has a graze on his (5). He has a pain in his (6). / He s got a ache. His (7) is swollen. His (8) hurts. He has a scar on his (9). His (10) aches. He has a sprained (11). He has a sore (12). He has a bruise on his (13). He has a sting on his (14). He has a pain in his (15). He has cuts on his (16). He has a swelling in his (17). His (18) ache. He has a blister on his (19). Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
6 The skeleton A/ Label the diagram using the words from the right. 1. breastbone 2. collarbone 3. jaw bone 4. kneecap 5. rib 6. shinbone / tibia 7. shoulder blade 8. skull 9. spine / backbone 10. thigh bone / femur B/ Find the following bones in the above diagram. 1. cheekbone 2. vertebrae 3. humerus 4. radius 5. ulna 6. hip bone 7. pelvis 8. coccyx 9. fibula Internal organs Label the diagram using the words from the left. 1. brain 2. stomach 3. appendix 4. lungs 5. heart 6. pharynx 7. liver 8. bladder Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
7 The function of the organs Match the beginnings of the sentences on the left with the endings on the right. 1. The heart a. circulates around the body supplying oxygen to the cells. 2. Blood b. supports the back and protects the spinal cord. 3. Veins c. are where two bones are connected together by ligaments. 4. Arteries d. carry blood from all parts of the body to the heart. The blood is darker because it is full of carbon dioxide (CO2). 5. The skeleton e. pumps blood around the body through the arteries. 6. The spine f. carry blood from the heart to all parts of the body. The blood is brighter because it is full of oxygen (O2). 7. Joints g. supports the body, gives us shape and protects the internal organs. Do the same with the following sentences. 8. Muscles h. protects our body, regulates body temperature and enables us to sweat. 9. The liver i. is a bag which collects urine before it is passed out of the body through the urethra. 10. The kidneys j. that we breathe in passes through the windpipe into the lungs. 11. The bladder k. are attached to bones by tendons. 12. The skin l. is the organ in a woman s body where a baby grows and develops. 13. The air m. clean blood by separating waste liquid from it. 14. The womb n. helps to clean the blood and produces bile. Quick quiz Answer the following questions about parts of the body. 1. What is the name of the bone that protects our brain? 2. How do we call backs of the joints on our hands? 3. Another name for eye socket is. 4. It grows on our head. 5. What is the name of our breathing organs? 6. What is the name of the organ where food goes after it is eaten? 7. How do we call the first part of the small intestine, just below the stomach? 8. What is the name of the major artery? 9. The main part of the body, without the head and limbs is called. 10. The name of an organ that produces a chemical substance that the body needs. 11. What is the name of the cell in the nervous system which transmits impulses? 12. A type of a nerve ending (it starts with the letter r). 13. What is the name of the substance which stores energy? 14. How do we call fibres that take impulses from one part of the body to another? 15. The name of the major detoxicating organ? Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
8 Word bank bile a bitter greenish-brown liquid produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder. It helps the body to digest food. blood the red liquid which is pumped around the body from the heart through the arteries. Blood carries oxygen, hormones and nutrients. It consists of plasma which contains red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. bone marrow the soft red substance inside the bones. breathe (v.) to take air into the lungs (inhale) through the nose or mouth and let it out (exhale) again. (n.) breath bronchial tube one of the tubes in the chest through which air goes into the lungs. circulation the movement of blood around the body. circulatory system the system which moves blood around the body. It consists of the heart, the blood and the blood vessels. clotting the process by which blood becomes thick and stops flowing. digestion the process by which the food is broken down into simple soluble substances that the body can absorb and use for growth and energy. faeces / fi:si: z/ solid waste from the body = excrement. humerus the bone connecting the shoulder to the elbow. kidney the organ which cleans the blood by removing waste products. It also controls the level of water in the blood. The waste passes into the bladder in the liquid form of urine, which is then passed out of the body. larynx the organ in the throat which contains vocal cords. limb an arm or a leg. liver the organ which changes toxins such as alcohol into less harmful substances. It also produces bile, urea and cholesterol. The liver controls the level of glucose and amino acids in the blood and stores important vitamins and minerals. lung the organ in the chest which fills with air during breathing. Blood that flows into the lungs takes oxygen from the air breathed into the alveoli, puts in carbon dioxide which is then breathed out as a waste product. platelet a small piece of a cell in the blood which helps the blood to clot. radius the larger outer bone in the forearm. receptor a nerve in a sense organ (e.g. the skin or the nose) which sends messages to the central nervous system. spinal cord the nerve tissue in the spine going from the bottom of the brain to the bottom of the back. It is a part of the central nervous system. tendon strong tissue which connects a muscle to a bone. ulna the longer of the two bones connecting the wrist to the elbow. ureter a tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder. urethra the tube that carries urine out of the body. Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
9 MEDPREDMETNO POVEZOVANJE Povezava z biologijo/anatomijo: Izdelava slovarja strokovnih izrazov. Povezava s strokovno terminologijo (latinščino): Primerjava besedišča, ugotavljanje katere latinske besede se uporabljajo v angleščini za opisovanje delov telesa, kosti in organov. Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
10 VIRI: Glendinning, E. H., Howard R.(2007). Professional English in Use. Medicine. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press. Gough, C. (2001). English Vocabulary Organiser. LPT. Kelly, K. (2004). Macmillan Vocabulary Practice Series. Science. Macmillan. Oxford Student's Dictionary of English. (2001). Oxford, OUP. Pohl, A. (2002). Test Your Professional English. Medical. Penguin Books. Visual Encyclopedia. (1998). Dorling Kindersley. Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
11 Naslov učne enote (teme) WARDS, DEPARTMENTS AND SPECIALISTS IN HOSPITAL (ODDELKI IN SPECIALISTI V BOLNIŠNICI) Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
12 Izobraževalni program Zdravstvena nega Ime modula Jezik stroke Naslov učnih tem ali kompetenc, ki jih obravnava učno gradivo Oddelki in specialisti v bolnišnici Naslov enote učnega gradiva; to ni ena učna ura ODDELKI IN SPECIALISTI V BOLNIŠNICI POVZETEK Gradivo Oddelki in specialisti v bolnišnici opisuje: angleško besedišče za poimenovanje oddelkov in specialistov v bolnišnici ter opis dela, ki ga opravljajo posamezni specialisti. KLJUČNE BESEDE: ward, department, specialist, hospital, work AVTOR: Barbara Cesar Recenzent: Lektor: Datum: junij 2009 CIP Kataložni zapis o publikaciji (poskrbi koordinator) CILJI: ANGLEŠKO POIMENOVANJE ODDELKOV IN SPECIALISTOV V BOLNIŠNICI; DELO SPECIALISTOV V BOLNIŠNICI; To delo je ponujeno pod Creative Commons Priznanje avtorstva-nekomercialno- Deljenje pod enakimi pogoji 2.5 Slovenija licenco. Učno gradivo je nastalo v okviru projekta Munus 2. Njegovo izdajo je omogočilo sofinanciranje Evropskega socialnega sklada Evropske unije in Ministrstva za šolstvo in šport.
13 Where do you work? A: Where do you work? B: I work at General Hospital Novo mesto, in a surgical ward. And you where do you work? Some Wards and Departments Translate the following wards and departments into Slovene. Surgical Ward Department of Internal Medicine Orthopaedic Ward Gynaecological Ward Maternity Ward Paediatric Ward Dermatological Ward E.N.T. Ward Intensive Care Unit X-ray Department Operating Theatre (BrE) / Operating Room (AmE) Accident and Emergency Department / Casualty and Emergency Department Central Sterile Supply Department Dispensary Laboratory Occupational Therapy Department Physiotherapy Department Psychiatric Ward Department of Infectious Diseases and Fever Conditions Dialysis Centre Department of Renal Diseases Department of Traumatology Department of Vascular Diseases Department of Lung Diseases Department of Heart Diseases Department of Urology Department of Neurology
14 Specialist What he does Speciality pathologist performs autopsies on dead people pathology cardiologist treats diseases of the heart cardiology gynaecologist treats women s diseases gynaecology obstetrician helps women deliver babies / giving birth obstetrics paediatrician treats children s diseases paediatrics dermatologist treats skin diseases dermatology neurologist treats diseases of the nervous system neurology urologist treats diseases of the urinary tract urology surgeon performs operations surgery psychiatrist treats mental diseases psychiatry psychologist studies the human mind psychology radiologist studies the use of radioactivity in making medical examinations radiology roentgenologist takes and studies x-ray pictures roentgenology ophthalmologist treats eye diseases ophthalmology orthopaedist treats deformities in bones and muscles orthopaedics histologist studies organic tissues histology cytologist studies biological cells cytology haematologist studies blood haematology geriatrician treats and takes care of old people geriatrics anaesthetist gives/administers anaesthetics at operations anaesthesiology physician / GP specializes in medicine medicine
15 VIRI: Dobrajc, F. (2002). English for Nurses. Student's Book. Ljubljana. DZS. Gough, C. (2001). English Vocabulary Organiser. LPT. Oxford Student's Dictionary of English. (2001). Oxford, OUP. Pohl, A. (2002). Test Your Professional English. Medical. Penguin Books.
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
To find more products like this, visit: Remedia's Store
 A Teaching Resource From 2016 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The purchase of this product entitles the individual teacher to reproduce copies for classroom use. The reproduction
A Teaching Resource From 2016 Copyright by Remedia Publications, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The purchase of this product entitles the individual teacher to reproduce copies for classroom use. The reproduction
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body
 1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION
 Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
STATE OF CALIFORNIA DWC DISTRICT OFFICE DOCUMENT COVER SHEET
 STATE OF CALIFORNIA DWC DISTRICT OFFICE DOCUMENT COVER SHEET Is this a new case? Yes No Companion Cases Exist Walkthrough Yes No More than 15 Companion Cases Date:(MM/DD/YYYY) SSN: Case Number 1 (If, use
STATE OF CALIFORNIA DWC DISTRICT OFFICE DOCUMENT COVER SHEET Is this a new case? Yes No Companion Cases Exist Walkthrough Yes No More than 15 Companion Cases Date:(MM/DD/YYYY) SSN: Case Number 1 (If, use
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
Unterrichtsmaterialien in digitaler und in gedruckter Form. Auszug aus: Cross Curriculum Creativity - Biology - Book 1: The Human Body
 Unterrichtsmaterialien in digitaler und in gedruckter Form Auszug aus: Cross Curriculum Creativity - Biology - Book 1: The Human Body Das komplette Material finden Sie hier: School-Scout.de Contents Contents
Unterrichtsmaterialien in digitaler und in gedruckter Form Auszug aus: Cross Curriculum Creativity - Biology - Book 1: The Human Body Das komplette Material finden Sie hier: School-Scout.de Contents Contents
GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS
 GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS PROCEDURES craniotomy: making a surgical incision through the cranium (the part of the skull that encloses the brain); usually done to relieve pressure around the brain.
GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS PROCEDURES craniotomy: making a surgical incision through the cranium (the part of the skull that encloses the brain); usually done to relieve pressure around the brain.
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
Human Body. Bones, Joints and Muscles
 Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
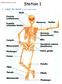 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1
 Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1 1. Unscramble the body systems in the box then write below the correct picture. osnreuv peodctuievrr otorolmoc gitdeevsi teyrocxer 2. Draw and label the organs. A. Kidneys B.
Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1 1. Unscramble the body systems in the box then write below the correct picture. osnreuv peodctuievrr otorolmoc gitdeevsi teyrocxer 2. Draw and label the organs. A. Kidneys B.
PAIN POINT CHECKLIST THE ULTIMATE TO MAXIMISE COMPENSATION FROM YOUR CLAIM
 THE ULTIMATE PAIN POINT CHECKLIST TO MAXIMISE COMPENSATION FROM YOUR CLAIM A visual checklist for personal injury claimants that allows users to comprehensively list and discuss their injuries with their
THE ULTIMATE PAIN POINT CHECKLIST TO MAXIMISE COMPENSATION FROM YOUR CLAIM A visual checklist for personal injury claimants that allows users to comprehensively list and discuss their injuries with their
October. Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives
 October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY
 UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY 1.1.- KNOWING YOUR BODY The first thing we need to do before starting the P.E. class, it s to make sure that we really now our own body. But not only its parts, but also how does
UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY 1.1.- KNOWING YOUR BODY The first thing we need to do before starting the P.E. class, it s to make sure that we really now our own body. But not only its parts, but also how does
HEALTH. Doctors. Level: Materials Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None. Technology Needed:
 HEALTH Doctors Level: Materials Needed: Technology Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None Santa Ana College, School of Continuing Education Parts of the Body Directions: Write
HEALTH Doctors Level: Materials Needed: Technology Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None Santa Ana College, School of Continuing Education Parts of the Body Directions: Write
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male
 http://www.spongelab.com/register/index.cfm Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male The Digestive System 1. How is the digestive system described? Esophagus 2. The esophagus leads from the to the. 3.
http://www.spongelab.com/register/index.cfm Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male The Digestive System 1. How is the digestive system described? Esophagus 2. The esophagus leads from the to the. 3.
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
list of speciality types
 Descriptions of Speciality Types GENERAL PRACTITIONER GENERAL PRACTITIONER GP or family practitioner (FP) Family doctor A medical practitioner whose practice is not limited to any specific branch of medicine
Descriptions of Speciality Types GENERAL PRACTITIONER GENERAL PRACTITIONER GP or family practitioner (FP) Family doctor A medical practitioner whose practice is not limited to any specific branch of medicine
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS. PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Lab Report Sheet. Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did)
 Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems
 Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
EMTB Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Drill
 Session Reference: 1 EMTB Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Drill Instructor Guide Topic: Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Level of Instruction: 3 Time Required: 3 hours Materials: References: Chalkboard
Session Reference: 1 EMTB Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Drill Instructor Guide Topic: Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Level of Instruction: 3 Time Required: 3 hours Materials: References: Chalkboard
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. A collection of the same type of cells working together to perform a function.
 Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
A&P 1. Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities. Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL Phone: (630) Fax: (630)
 319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: HUMAN ANATOMY I The smallest unit part of any living
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: HUMAN ANATOMY I The smallest unit part of any living
ACUPUNCTURE POINTS STIMULATION WITH ACUPUNCTURE PEN A GENERAL GUIDE TO PAIN RELIEF
 ACUPUNCTURE POINTS STIMULATION WITH ACUPUNCTURE PEN A GENERAL GUIDE TO PAIN RELIEF What is Acupuncture? Acupuncture dates back over three thousand years, but only recently has it begun to gain recognition
ACUPUNCTURE POINTS STIMULATION WITH ACUPUNCTURE PEN A GENERAL GUIDE TO PAIN RELIEF What is Acupuncture? Acupuncture dates back over three thousand years, but only recently has it begun to gain recognition
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
Airway Management From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 82 Questions
 Airway Management From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 82 Questions 1. What color will cyanotic skin be? p. 119 *A.) Blue B.) Red C.) Yellow D.) Green 2. Which is the primary path for air to enter
Airway Management From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 82 Questions 1. What color will cyanotic skin be? p. 119 *A.) Blue B.) Red C.) Yellow D.) Green 2. Which is the primary path for air to enter
Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? How do our bodies digest food, remove wastes and send messages? Let s think together? Why do we need food? How could food
Unit 3 Lesson 5 How Do Our Bodies Digest Food, Remove Wastes, and Send Messages? How do our bodies digest food, remove wastes and send messages? Let s think together? Why do we need food? How could food
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique. Systems Shuffle. By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side
 Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique Systems Shuffle By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to
Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique Systems Shuffle By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
Chapter 8. Bellringer. Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System
 Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Transplantable Organs
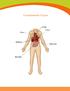 Transplantable Organs Liver Kidneys Pancreas Intestine Organ Information Heart The body s hardest working muscle, the heart beats 70 times each minute as it pumps blood throughout the body. Some conditions
Transplantable Organs Liver Kidneys Pancreas Intestine Organ Information Heart The body s hardest working muscle, the heart beats 70 times each minute as it pumps blood throughout the body. Some conditions
INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODY ANSWER KEY
 PRE-VISIT CLASSROOM ACTIVITY - MEET THE HUMAN BODY Use the guided reading activity and matching worksheet as an in-class activity to introduce your students to the basic functions of the body systems and
PRE-VISIT CLASSROOM ACTIVITY - MEET THE HUMAN BODY Use the guided reading activity and matching worksheet as an in-class activity to introduce your students to the basic functions of the body systems and
MCAS Biology: Human Systems Review
 MCAS Biology: Human Systems Review This booklet is designed to introduce or review the human biology concepts tested on the MCAS exam. Since this unit comes at the end of the year, it is often a rushed
MCAS Biology: Human Systems Review This booklet is designed to introduce or review the human biology concepts tested on the MCAS exam. Since this unit comes at the end of the year, it is often a rushed
Getting The Body Out of Distress
 Getting The Body Out of Distress 18 Exercises 22 min - 22 min I am a Woman - Creative, Sacred, Invincible This moves the energy in every part of the body systematically. This kriya can bring great change.
Getting The Body Out of Distress 18 Exercises 22 min - 22 min I am a Woman - Creative, Sacred, Invincible This moves the energy in every part of the body systematically. This kriya can bring great change.
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science. Mr. Diaz
 Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
A. Incorrect! The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the shoulder, arm, hand, pelvis, leg and foot.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Body Systems Unit End Project
 Body Systems Unit End Project Digestive System Your Assignment Create a model of the digestive system using the top diagram on p 130 in your text book. Use Pipe Cleaners and paper to label the following
Body Systems Unit End Project Digestive System Your Assignment Create a model of the digestive system using the top diagram on p 130 in your text book. Use Pipe Cleaners and paper to label the following
What is the skeletal system?
 .^ ^)\ Djn' ^ /r n_'i & 1^ MW What is the skeletal system? W?c"';'Wi?''l''. 'C'tW;«
.^ ^)\ Djn' ^ /r n_'i & 1^ MW What is the skeletal system? W?c"';'Wi?''l''. 'C'tW;«
The Hard Stuff! All About Bones
 The Hard Stuff! All About Bones A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Book Word Count: 1,353 LEVELED BOOK R The Hard Stuff! All About Bones R U X Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands
The Hard Stuff! All About Bones A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Book Word Count: 1,353 LEVELED BOOK R The Hard Stuff! All About Bones R U X Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
What type of tissue is this
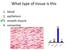 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
S7L Which of these is an important part of the nervous system? A. spinal cord B. stomach C. veins D. muscles
 S7L-4 1. Which of these is an important part of the nervous system? A. spinal cord B. stomach C. veins D. muscles 2. To prevent disease, the human body naturally produces A. enzymes. B. antibodies. C.
S7L-4 1. Which of these is an important part of the nervous system? A. spinal cord B. stomach C. veins D. muscles 2. To prevent disease, the human body naturally produces A. enzymes. B. antibodies. C.
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
BODY SYSTEMS BODY CAVITIES THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Movements BODY CAVITIES. Pediatric Considerations In Respiratory System
 BODY SYSTEMS A body system is a group of organs and other structures work together to carry out specific functions. The following systems work together to carry out a function needed for life: Respiratory
BODY SYSTEMS A body system is a group of organs and other structures work together to carry out specific functions. The following systems work together to carry out a function needed for life: Respiratory
