ATTN: Potential Agents RE: UNKNOWN ORGANISM
|
|
|
- Neal Bennett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ATTN: Potential Agents RE: UNKNOWN ORGANISM We have been receiving a number of unexplainable readings from our scanners off the coast of Bermuda (coordinates are lattitude, ' longitude). We believe there is an organism trapped below the surface on the ocean floor. It is your job to run the correct analyses in order to conclude what this thing is and if it is a threat. We have included all of the data scans. This is a level 3 classified mission. Form a team of scientists to investigate the anomaly that was detected off the coast of Bermuda. You are to find the cause of the anomaly, classify any potential life forms you find, and determine if the anomaly poses any threat. We have provided live scans and images of the area that will aid you in these tasks. Once you have completed your mission, you are to present your findings to your teacher, who is an undercover Agent of S.H.I.E.L.D. with level 5 classified clearance. Your teacher will then relay the infor-mation directly to S.H.I.E.L.D.. Good luck. The world is depending on you.
2 CELL ANALYSIS MISSION OVERVIEW_ We have been receiving a number of unexplainable readings from our scanners off the coast of Bermuda (coordinates are lattitude, longitude). We believe there is an organism trapped below the surface on the ocean floor. It is your job to run the correct analyses in order to conclude what this thing is and if it is a threat. We have included all of the data scans on this document. This is a level 3 classified mission. MISSION BRIEF_ Our scanners were able to collect a few cell cross sections from the area, an animal skin cell, a plant cell, and a cell of the new unknown organism. Compare the new cell to the animal and plant cells in order to gain a better understanding of the organism. When you have completed your analysis, present your findings to your teacher and enter them into the S.H.I.E.L.D. database.
3 CELL ANALYSIS ANIMAL CELL CELL MEMBRANE - a semi-permeable membrane surrounding the cell allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. CYTOPLASM - the gel-like material distributed throughout the cell in which the organelles are located. MITOCHONDRION - The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. RIBOSOME - RNA rich organelle where protein synthesis occurs. VACUOLE - fluid-filled cavities inside a cell. In plants, it is large and contains the water of the cell. In animals, the vacuole is much smaller and is also involved in waste disposal. LYSOSOME - Contains powerful digestive enzymes that digest food, organelles, and bacteria. NUCLEUS - Spherical body surrounded by a membrane which dictates the function of the cell through protein synthesis. Contains the DNA of the cell (in chromosomes).
4 CELL ANALYSIS PLANT CELL CELL MEMBRANE - a semi-permeable membrane surrounding the cell allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. CYTOPLASM - the gel-like material distributed throughout the cell in which the organelles are located. MITOCHONDRION - The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. VACUOLE - fluid-filled cavities inside a cell. In plants, it is large and contains the water of the cell. In animals, the vacuole is much smaller and is also involved in waste disposal. CHLOROPLAST - Creates energy for plant cells through photosynthesis. Not present in animal cells. CELL WALL - a somewhat rigid wall providing structural support that surrounds plant cells. Not present in animal cells. NUCLEUS - Spherical body surrounded by a membrane which dictates the function of the cell through protein synthesis. Contains the DNA of the cell (in chromosomes).
5 CELL ANALYSIS ANOMALY CELL
6 S.H.I.E.L.D. Report: Re: Unknown cell Our scanners were able to collect a few cell cross sections from the area, an animal skin cell, a plant cell, and a skin cell of the new unknown organism. Compare the new cell to the animal and plant cells in order to gain a better understanding of the organism. When you have completed your analysis, present your findings to your teacher and enter them into the S.H.I.E.L.D. database. 1. Label the unknown cell. 2. What similarities does the new skin cell share with the plant cell? Describe any differences. 3. What similarities does the new cell share with the animal cell? Describe any differences.
7 ATTN: Potential Agents RE: UNKNOWN ORGANISM We have been receiving a number of unexplainable readings from our scanners off the coast of Bermuda (coordinates are lattitude, ' longitude). We believe there is an organism trapped below the surface on the ocean floor. It is your job to run the correct analyses in order to conclude what this thing is and if it is a threat. We have included all of the data scans. This is a level 3 classified mission. Form a team of scientists to investigate the anomaly that was detected off the coast of Bermuda. You are to find the cause of the anomaly, classify any potential life forms you find, and determine if the anomaly poses any threat. We have provided live scans and images of the area that will aid you in these tasks. Once you have completed your mission, you are to present your findings to your teacher, who is an undercover Agent of S.H.I.E.L.D. with level 5 classified clearance. Your teacher will then relay the infor-mation directly to S.H.I.E.L.D.. Good luck. The world is depending on you.
8 DNA ANALYSIS MISSION OVERVIEW_ We have been receiving a number of unexplainable readings from our scanners off the coast of Bermuda (coordinates are lattitude, longitude). We believe there is an organism trapped below the surface on the ocean floor. It is your job to run the correct analyses in order to conclude what this thing is and if it is a threat. We have included all of the data scans on this document. This is a level 3 classified mission. MISSION BRIEF_ Our advanced scanners were able to collect a few cell cross sections of the unknown organism. We ran a further analysis of the cell s nucleus and were able to get some information about the organism s DNA structure. We have also provided a scan of human DNA structure. To gain a better understanding of the organism, compare the new unknown cell s DNA to that of a human and enter your findings into the S.H.I.E.L.D. database.
9 DNA ANALYSIS HUMAN CHROMOSOMES
10 DNA ANALYSIS HUMAN DNA
11 DNA ANALYSIS ANOMALY CHROMOSOMES
12 DNA ANALYSIS ANOMALY DNA
13 S.H.I.E.L.D. Report: Re: Brain analysis 1. Label the unknown DNA. 2. What similarities does the unknown DNA share with human DNA? Describe any differences that exist.
14 ATTN: Potential Agents RE: UNKNOWN ORGANISM We have been receiving a number of unexplainable readings from our scanners off the coast of Bermuda (coordinates are lattitude, ' longitude). We believe there is an organism trapped below the surface on the ocean floor. It is your job to run the correct analyses in order to conclude what this thing is and if it is a threat. We have included all of the data scans. This is a level 3 classified mission. Form a team of scientists to investigate the anomaly that was detected off the coast of Bermuda. You are to find the cause of the anomaly, classify any potential life forms you find, and determine if the anomaly poses any threat. We have provided live scans and images of the area that will aid you in these tasks. Once you have completed your mission, you are to present your findings to your teacher, who is an undercover Agent of S.H.I.E.L.D. with level 5 classified clearance. Your teacher will then relay the infor-mation directly to S.H.I.E.L.D.. Good luck. The world is depending on you.
15 BRAIN ANALYSIS MISSION OVERVIEW_ We have been receiving a number of unexplainable readings from our scanners off the coast of Bermuda (coordinates are lattitude, longitude). We believe there is an organism trapped below the surface on the ocean floor. It is your job to run the correct analyses in order to conclude what this thing is and if it is a threat. We have included all of the data scans on this document. This is a level 3 classified mission. MISSION BRIEF_ While the anomaly appeared to show no signs of brain activity, we sent a weak, controlled electrical pulse to its location at the bottom of the sea and received a response. Normally, it would require taking the subject s brain and putting it through an fmri machine but with our S.H.I.E.L.D. satellite, we ve been able to get an accurate fmri scan of this anomaly s brain. An fmri allows us to track brain activity, which may help us determine the behavioral patterns of this being and its species. In other words, we can see whether it is friendly or hostile. Our initial scans indicate that there are a number of similarities between the anomaly s brain and the modern human brain. However, there also appear to be some stark differences. We ve provided you with three documents that should help you find out more about this creature. An annotated chart of the human brain An fmri scan of an adult human brain at rest ½ ½ A S.H.I.E.L.D. Satellite fmri scan of the anomaly s brain We need you to analyze the three documents, compare and contrast the similarities/differences, and make postulations about the creature s behavioral patterns. When you complete your task, input the findings into the S.H.I.E.L.D. search engine to find any known references.
16 BRAIN ANALYSIS PREFRONTAL CORTEX PERSONALITY EXPRESSION MODERATION OF EMOTIONS AND AGGRESSIVE BEHAVIOR DECISION-MAKING SOCIAL BEHAVIORS SENSORY AREA AUDITORY VISUAL OLFACTORY (SMELL) TACTILE (TOUCH) - THIS INCLUDES THERMORECEPTORS (TEMPERATURE) AND PAIN RECEPTORS LIMBIC SYSTEM STORING AND PROCESSING OF NEW MEMORIES INTO LONG-TERM EMOTIONAL REACTIONS
17 BRAIN ANALYSIS HUMAN BRAIN This is an fmri scan of a human brain at rest, which means the person is awake but stationary. Areas of the brain that are highlighted in yellow indicates that that part of the brain is currently displaying increased activity.
18 BRAIN ANALYSIS ANOMALY BRAIN
19 S.H.I.E.L.D. Report: Re: Brain analysis 1. From the brain scans, what similarities do you see in the shape of the human brain compared to the shape of the unknown brain? a. What differences do you see in the shape of the two brains? 2. From the brain scans, what similarities do you see in the activity of a normal human brain compared to the activity of the unknown brain? a. What differences do you see in the activity of the two brains? 3. Based on your observations from the four previous questions (1-2a.), what postulations can you make about the unknown creature based on the brain scans? a. Prefrontal Cortex: b. Limbic System: c. Currently, based on your research, do you believe that the unknown creature is friendly or hostile? Explain.
centriole cytoskeleton plays a role in cell division centriole protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
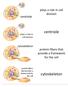 centriole plays a role in cell division plays a role in cell division centriole cytoskeleton protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
centriole plays a role in cell division plays a role in cell division centriole cytoskeleton protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
Cell Processes Review
 1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Name Class Date. What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
By: Brooke Sheppard
 By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
Topic 1: Living Things
 Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
3UNIT. Photosynthesis and. Cellular Respiration. Unit PreQuiz? General Outcomes. Unit 3 Contents. Focussing Questions
 3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
3UNIT Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration General Outcomes In this unit, you will relate photosynthesis to the storage of energy in organic compounds explain the role of cellular respiration in releasing
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Aim 19: Cellular Respiration
 1. During the process of cellular respiration, energy is released from A) carbon dioxide B) oxygen atoms C) water molecules D) chemical bonds 2. The energy used to obtain, transfer, and transport materials
1. During the process of cellular respiration, energy is released from A) carbon dioxide B) oxygen atoms C) water molecules D) chemical bonds 2. The energy used to obtain, transfer, and transport materials
Cell Structure and Function. Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells
 Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells. A typical animal cell THE CELL MEMBRANE FIRST STOP
 WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CELL THEORY- EQ: What are the 3 facts of the cell theory? - pp191. EQ- Which Scientists are connected to cell discovery?
 UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
Cell Organelles and their Functions. Chapter 4 Section 2
 Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
St. Brigid Catholic Academy AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells:
 Name: St. Brigid Catholic Academy Date: Science AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells: Below are two types of cells. What similarities
Name: St. Brigid Catholic Academy Date: Science AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells: Below are two types of cells. What similarities
(A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids. A. Incorrect! Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have cell membranes.
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Looking Inside Cells
 Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell.
 Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Biology. Cell Structure Quiz
 Word List chloroplast chromosome DNA endoplasmic reticulum golgi body lysosome organelle ribosome vesicle A cell has many parts, called, each one of which has a special function. The encloses the cell.
Word List chloroplast chromosome DNA endoplasmic reticulum golgi body lysosome organelle ribosome vesicle A cell has many parts, called, each one of which has a special function. The encloses the cell.
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems. Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells
 IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
NUCLEOLUS CELL MEMBRANE MITOCHONDRIA CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST NUCLEAR MEMBRANE VACOULE NUCLEUS ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD
 CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
Journey to the World of Cells
 Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Bellringer. Objectives. Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Vocabulary. Cell Wall. Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell.
 Bellringer Objectives Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell. Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. Plant cells and animal cells have many cell parts in common. But they also
Bellringer Objectives Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell. Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. Plant cells and animal cells have many cell parts in common. But they also
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers
 Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
B.4B Cellular Processes
 B.4B Cellular Processes Picture Vocabulary homeostasis The process of maintaining a constant state of balance cell membrane Cell part surrounding the cytoplasm and is also a barrier between the inside
B.4B Cellular Processes Picture Vocabulary homeostasis The process of maintaining a constant state of balance cell membrane Cell part surrounding the cytoplasm and is also a barrier between the inside
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7
 Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Cellular Boundaries. Cell Organelles. The Nucleus and Cell Control. Cell Membrane. Cell Wall. Nucleus 10/11/2012. Cell Membrane Cell Wall
 Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided.
 Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key. Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions
 Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Smart cell lesson (1).notebook February 02, 2015
 Cells 1 TEKS Related to the Lesson (12) Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The
Cells 1 TEKS Related to the Lesson (12) Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The
C) amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the animal B) rate of respiration of the animal
 Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION
 CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION CHAPTER 2 https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Cellular components of animal & plant cells https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Plant Cells Cell wall Plasma membrane
CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION CHAPTER 2 https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Cellular components of animal & plant cells https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Plant Cells Cell wall Plasma membrane
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE
 CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Draw and Complete the Chart.
 Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Parts (organelles) of the Cell
 Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Cytology II Study of Cells
 Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cellular Structure and Function
 7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
Lysosome ( lie-so-so-m ) Golgi body ( goal-gee ) Vacuole ( vack-u-ol )
 Chapter 31: Page 304 So far, you have looked at four organelles that you can find in both plant and animal cells: the nucleus, ribosomes, ER, and mitochondria. Every eukaryotic cell uses these small structures
Chapter 31: Page 304 So far, you have looked at four organelles that you can find in both plant and animal cells: the nucleus, ribosomes, ER, and mitochondria. Every eukaryotic cell uses these small structures
Cell Structure and Function
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
 Name Date Period Cells Alive Webquest Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and
Name Date Period Cells Alive Webquest Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Directions: Use Aim # 7-13 (Unit 2) to complete this study guide. Part I. Aim # 7 Inorganic and Organic Molecules. Building Blocks (monomers)
 Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 2 Biochemistry and The Cell Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 2 Important Topics: Aim # 7: Inorganic and Organic Molecules Aim # 8: Organic Macromolecules
Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 2 Biochemistry and The Cell Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 2 Important Topics: Aim # 7: Inorganic and Organic Molecules Aim # 8: Organic Macromolecules
Organelles Defined. Class Copy CELL STUDY NOTES Class Copy
 Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Overview of Cell Structures
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Euakryotic cells are generally one to one hundred times bigger than prokaryotic cells
 Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Cell Basics. Basic Unit of Life. Prokaryotic. Eukaryotic. Plant Cell. Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Bacteria. Very Complex.
 Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function
 Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Biology 30 Mr. Oosterom Development of the Cell Theory People have known about the existence of cells for approximately 300 yrs Early microscopes allowed scientists to
Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Biology 30 Mr. Oosterom Development of the Cell Theory People have known about the existence of cells for approximately 300 yrs Early microscopes allowed scientists to
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions. Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18
 Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18 1. Which of the following would be least affected by defective receptor proteins on a cell membrane? a. Homeostasis b. Muscle activity
Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18 1. Which of the following would be least affected by defective receptor proteins on a cell membrane? a. Homeostasis b. Muscle activity
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
