MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Miles Hoover
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams or 1) illustrations, have a preference for a modality known as: A) visual. kinesthetic. auditory. tactile. Answer: A 2) Sierra says she learns more from reading the textbook for class than from listening to lecture. She is 2) most likely a(n): A) visual learner. tactile learner. auditory learner. kinesthetic learner. Answer: A 3) Jesse felt comfortable using the microscope after listening to directions from his lab professor. His 3) learning style preference must be: A) tactile learner. auditory learner. kinesthetic learner. visual learner. Answer: B 1
2 4) What does the SQ3R method stand for? 4) A) share, quiz, query, question, and read search, quiet, research, read, and remember sort, query, read, recite, and review survey, question, read, recite, and review Answer: D 5) Why should a student use the SQ3R method? 5) A) The SQ3R method provides a student with a strategy for taking notes during lecture class. The SQ3R method provides a student with ways to improve time management skills. The SQ3R method provides a plan for a student to improve textbook reading skills. The SQ3R method provides a student with a strategy for improving test taking skills. 6) What is a good way to manage time in preparation for your anatomy and physiology class? 6) A) I should stay up all night the night before the test to maximize what is stored in short-term memory. I make a schedule and budget my time. I should delay studying until the day or two before the test to best remember the material. I study only on the weekends when I have many hours of free time. Answer: B 2
3 7) What learning modality is engaged when students participate in study groups? 7) A) visual learner kinesthetic learner tactile learner auditory learner Answer: B 8) What is a good strategy for class or laboratory preparation? 8) A) Avoid reading before class as you may get confused. Only read after you have attended class or laboratory. Focus on reading your materials on the weekends when you have hours to spend. Read and prepare notes before attending your class or laboratory. Answer: D 9) How could you use the Learning Outcomes in this book to help you study? 9) A) Rewrite each Learning Outcome in your notes. Read through the Learning Outcomes after you have completed a section. Recite the Learning Outcomes until you have them memorized. Write down the answers to the Learning Outcomes. Answer: D 3
4 10) What results when anabolism occurs more than catabolism in an organism? 10) A) movement excretion growth irritability 11) What is the smallest level of structural organization in the human body? 11) A) tissue level cellular level chemical level organ level 12) Which of the following is the most complex structural level of organization? 12) A) tissue level organ level cellular level chemical level Answer: B 13) Which of the following is the correct sequence, from simplest to most complex, in the levels of 13) structural organization of the human body? A) cellular level, chemical level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level cellular level, tissue level, chemical level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level chemical level, tissue level, cellular level, organ system level, organ level, organismal level 4
5 14) In laboratory, you will study the overall structure and shape of the femur bone without the aid of a 14) microscope. This is a study known as: A) microscopic anatomy. gross anatomy. systemic anatomy. regional anatomy. Answer: B 15) In laboratory, you will study tissues. This area of study is known as: 15) A) cytology. gross anatomy. physiology. histology. Answer: D 16) Which organ system supports the body and protects internal organs? 16) A) skeletal system endocrine system digestive system muscular system Answer: A 17) Which organ system includes blood vessels and the heart? 17) A) cardiovascular system respiratory system lymphatic system endocrine system Answer: A 5
6 18) Which two organ systems include the pancreas as a component? 18) A) endocrine and lymphatic systems respiratory and cardiovascular systems digestive and urinary systems digestive and endocrine systems Answer: D 19) What is a major function of the respiratory system? 19) A) produce vitamin D and retain water return excess tissue fluid to the cardiovascular system digest food and absorb nutrients into the blood deliver oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body Answer: D 20) When we imagine a person exhibiting the anatomical position, the palms of the hands are assumed 20) to be facing: A) to the side. forward. down. backward. Answer: B 21) A person who is standing facing forward with hands at the sides, palms facing forward, is in the: 21) A) anatomical position. supine position. frontal position. sagittal position. Answer: A 6
7 22) A person in the anatomical position is visualized to be: 22) A) laying down on his or her back. sitting down. standing upright. laying down on the stomach. 23) Which directional term indicates the front side of the body? 23) A) superior (cranial) posterior (dorsal) anterior (ventral) medial 24) A directional term that means the same as posterior is: 24) A) anterior. ventral. sagittal. dorsal. Answer: D 25) Body parts that are described as medial are considered to be: 25) A) closer to the midline of the body. toward the head. closer to the point of origin. toward the front. Answer: A 7
8 26) Select the appropriate directional term to complete this sentence: The mouth is to the 26) nose. A) posterior (dorsal) distal inferior (caudal) superior (cranial) 27) Select the appropriate directional term to complete this sentence: The skeletal muscles are 27) to the skin. A) deep posterior inferior (caudal) superficial Answer: D 28) In the anatomical position, the palms are on the: 28) A) posterior (dorsal) surface. anterior (ventral) surface. superior (cranial) surface. lateral surface. Answer: B 29) The point of the shoulder is also known as the: 29) A) antebrachial region. brachial region. digital region. acromial region. Answer: D 8
9 30) James sustained a cut to his mental region, also known as his: 30) A) chin. cheek. mouth. nose. Answer: A 31) The vertebral region is superior to the: 31) A) occipital region. sacral region. cephalic region. cervical region. Answer: B 32) The hand is also known as the: 32) A) pedal region. acromial region. manual region. plantar region. 33) A plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts is known as a: 33) A) midsagittal (median) plane. frontal (coronal) plane. sagittal plane. transverse (horizontal, or cross) plane. Answer: D 9
10 34) Dr. Mitchell performs open heart surgery. The incision he makes through the sternal region of his 34) patient divides the thoracic cavity into equal left and right parts. This incision must be made along a: A) frontal (coronal) plane. transverse (horizontal) plane. midsagittal (median) plane. sagittal plane. 35) What are the two subcavities of the dorsal body cavity? 35) A) pleural and pericardial cavities thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities cranial and vertebral (spinal) cavities abdominal and pelvic cavities 36) What major organs are housed in the thoracic cavity? 36) A) brain and spinal cord stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas urinary bladder, reproductive organs lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea Answer: D 37) What separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity? 37) A) diaphragm pericardium pleura mediastinum Answer: A 10
11 38) The thoracic cavity is situated superior to the abdominopelvic cavity and separated by the 38) diaphragm. Therefore, the diaphragm creates a: A) parasagittal plane. transverse (horizontal) plane, or cross section. frontal (coronal) plane. midsagittal (median) plane. Answer: B 39) What smaller cavity within the thoracic cavity houses the heart, great blood vessels, esophagus, 39) and trachea? A) abdominal cavity peritoneal cavity mediastinum diaphragm 40) Which regions of the abdominopelvic cavity are situated medially? 40) A) right and left hypochondriac regions, and the epigastric region right and left lumbar regions and the umbilical region epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric regions right hypochondriac, right lumbar, and right iliac (inguinal) regions 11
12 41) 41) Select the letter that represents the left iliac (inguinal) region. A) A B C D 42) Which region of the abdominopelvic cavity lies between the right and left lumbar regions? 42) A) hypogastric region epigastric region umbilical region right lumbar region 12
13 43) Serous membranes line certain cavities within the: 43) A) ventral cavities. dorsal cavities. cranial cavity. vertebral (spinal) cavity. Answer: A 44) What is deep to the visceral pericardium? 44) A) pericardial cavity visceral peritoneum parietal pericardium heart muscle Answer: D 45) What would a needle travel through as it enters the right lung? 45) A) visceral pericardium, serous fluid, parietal pericardium, right lung parietal pleura, serous fluid, right lung, visceral pleura parietal pleura, serous fluid, visceral pleura, right lung visceral pleura, serous fluid, parietal pleura, right lung 46) What organ(s) is/are covered by the pleura? 46) A) digestive organs lungs brain and spinal cord heart Answer: B 13
14 47) The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment is termed: 47) A) effector control. homeostasis. integration. positive feedback. Answer: B 48) What part of a feedback loop causes physiological responses to return the variable to the normal 48) homeostatic range? A) receptor (sensor) stimulus control center effector Answer: D 49) A cell or organ that responds to the directions of the control center in a negative feedback loop is 49) termed a(n): A) regulator. stimulus. receptor. effector. Answer: D 14
15 50) When you go outside on a hot summer day, your body temperature heats up above the normal 50) range. Receptors in your brain detect the change in body temperature. The brain activates nerve cells that send messages to sweat glands, causing the body temperature to fall as the sweat evaporates from the skin. What part of this feedback loop is the stimulus? A) nerve cells sweat glands increased body temperature brain 51) When you go outside on a hot summer day, your body temperature heats up above the normal 51) range. Receptors in your brain detect the change in body temperature. The brain activates nerve cells that send messages to sweat glands, causing the body temperature to fall as the sweat evaporates from the skin. What part of this feedback loop is the effector? A) sweat glands increased body temperature nerve cells brain Answer: A 52) How does the effector restore homeostasis in a negative feedback loop? 52) A) The effector opposes the initial stimulus and shuts off when conditions return to the normal range. The effector increases and reinforces the initial stimulus. The effector amplifies the response, but does not continue indefinitely. The effector causes a rapid change in a variable. Answer: A 15
16 53) A mother breastfeeds her infant. As long as the baby suckles his mother's breast, the mother's 53) mammary glands produce milk. Suckling, the stimulus, increases milk production, the response. This scenario is best described as: A) a positive feedback loop. anatomical position. a negative feedback loop. principle of complementarity of structure and function. Answer: A 54) The type of feedback that increases or enhances the effects of the variable is: 54) A) responsive. positive. neutral. negative. Answer: B 55) Which of the following best summarizes the principle of complementarity of structure and 55) function? A) maintenance of a stable internal environment form follows function structure drives function function follows structure Answer: B 16
17 56) Which of the following illustrates a gradient? 56) A) maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment more of something exists in one area than another and the two areas are connected equilibrium or balance between two unconnected areas equal amounts of something exist in areas that are connected Answer: B 57) Blood pressure in arteries is higher than the blood pressure in capillaries. Blood flows from arteries 57) to capillaries due to the presence of a: A) pressure gradient. positive feedback loop. homeostatic imbalance. negative feedback loop. Answer: A 58) What are the two major methods by which cells communicate to coordinate their functions? 58) A) temperature gradients and pressure gradients positive feedback loops and negative feedback loops effectors and responses chemical messengers and/or electrical signals Answer: D 17
18 59) A nerve cell releases chemical messengers to trigger changes in a nearby muscle cell. This is 59) example of a core principle known as: A) feedback loops. gradients. cell-cell communication. principle of complementarity of structure and function. 60) What is NOT one of the four core principles related to homeostasis? 60) A) gradients feedback loops metabolism cell-cell communication TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 61) When studying, you should actively read the textbook by taking notes and making diagrams. 61) Answer: True False 62) You should wait to read the textbook until you have heard the material presented in lecture or 62) laboratory. Answer: True False 63) The smallest level of organization in the human body is the cellular level. 63) Answer: True False 18
19 64) The endocrine system is responsible for generating heat. 64) Answer: True False 65) Patients are always examined while they are standing in the anatomical position. 65) Answer: True False 66) The crural region is posterior (dorsal) to the sural region. 66) Answer: True False 67) The transverse (horizontal plane or cross section) plane divides the body into anterior and 67) posterior parts. Answer: True False 68) Serous fluid lubricates around organs and reduces friction as the organ moves against adjacent 68) structures. Answer: True False 69) Negative feedback loops produce responses in the opposite direction of the initial stimulus while 69) positive feedback loops produce responses in the same direction of the initial stimulus. Answer: True False 70) According to the principle of complementarity of structure and function, structure and function are 70) related only at the cellular level. Answer: True False 19
20 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Match the following with the correct regional anatomical term. 71) Identify the thoracic region. 71) Answer: B 72) Identify the vertebral region. 72) 20
21 73) Identify the cephalic region. 73) Answer: A 74) Identify the popliteal region. 74) Answer: E 75) Identify the gluteal region. 75) Answer: D 21
22 Match the following with the correct body cavity or subdivision. 76) Identify the thoracic cavity. 76) Answer: A 77) Identify the abdominopelvic cavity. 77) Answer: B 78) Identify the cavity where the left lung is housed. 78) 22
23 79) Identify the mediastinum. 79) Answer: D 80) Identify the cavity that houses the heart. 80) Answer: E ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 81) Gillian prefers to study alone. She mostly draws diagrams from the textbook or makes charts and tables to organize her thoughts as she reads. Determine and discuss her learning style. Answer: Gillian prefers a visual/nonverbal learning style. A visual/nonverbal learner usually best understands concepts through the use of diagrams, illustrations, and other visual media without text. Visual/nonverbal learners may experience more success in studying alone than in study groups. 82) Describe the SQ3R method for reading a textbook. Answer: The SQ3R method stands for survey, questions, read, recite, and review. First, you should survey the chapter by skimming the material and figures. Next, form questions about the content in the chapter that you can answer as you read. Actively read by taking notes and drawing diagrams. As you read, recite the material by speaking aloud. The final step is to review what you have read. You may choose to answer questions in the book, write summaries, or discuss topics aloud with study partners. 83) Define metabolism. Answer: Metabolism includes the wide range of chemical processes carried out by living organisms. Metabolism includes both "building" processes in which smaller chemicals are combined to form larger ones, and "breaking down" processes in which larger chemicals are broken down into smaller ones. 84) Explain how gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy differ. Answer: The field of gross anatomy examines structures, including organs and organ systems that can be seen with the unaided eye. The field of microscopic anatomy examines structures that require a microscope to be seen. 23
24 85) Describe anatomical position. Answer: In anatomical position, the body is standing upright, feet are shoulder width apart, upper limbs are at the sides of the trunk, and the head and palms are facing forward. 86) Instead of using the directional terms superior and inferior to describe positions on the upper and lower limbs, what directional terms are used? Define these terms. Answer: Instead of using superior and inferior for the limbs, the terms proximal and distal are used. Proximal refers to something being closer to the point of origin (the trunk) while distal refers to something being farther away from the point of origin. Structures nearer the trunk are proximal while structures farther away are distal. 87) Peggy is having surgery on the right carpal region. A 3 cm incision will be made deep to the skin and muscle, but will be superficial to the bone. Explain to her where her surgery will occur. Answer: Peggy will have surgery on the wrist, or carpal, region of her right hand. The 3 cm incision will penetrate through the skin and muscle, but will not go as deep into her wrist as the bone. 88) During lab dissections, Kelly's instructor directs the students to make a midsagittal cut into their specimen. However, Kelly's lab partner thought she heard the instructor say that a cut along the median plane was to be made. Explain what type of cut should be made into the specimen. Answer: A midsagittal plane of section is also known as a median plane of section. Both divide the body or body part into equal left and right parts. Kelly and her lab partner should make a cut so that their specimen is divided into equal left and right parts. 89) A female patient presents at the emergency room with pain in the right lower quadrant. Which organs might be involved? Answer: The appendix, the right ovary, the first part of the large intestine, or the last part of the small intestine may be the source of pain in this female patient. 90) List the four quadrants and nine regions of the abdominopelvic cavity. Answer: The four quadrants are the right upper quadrant, right lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, and left lower quadrant. The nine regions are the right hypochondriac region, epigastric region, left hypochondriac region, right lumbar region, umbilical region, left lumbar region, right iliac (inguinal) region, hypogastric region, and left iliac (inguinal) region. 24
25 91) Explain where the pericardial cavity is situated in relation to the pericardial membranes. Answer: The pericardial cavity is situated between the visceral pericardium (attached to the heart muscle) and the outer parietal pericardium. 92) Define homeostasis and homeostatic imbalance. Answer: Homeostasis is maintenance of the body's internal environment. Disturbances in homeostasis, known as homeostatic imbalances, can result in disease or death if uncorrected. 93) List and describe the components of a feedback loop. Answer: The components of a feedback loop are the stimulus, receptor (sensor), control center, and effector/response. A stimulus is a regulated variable outside its normal range. A receptor (sensor) is a cellular structure that picks up information and sends it to a control center. The control center is often cells in the brain or an endocrine organ (gland). The control center compares the current value to its set point and determines that it's out of range. The control center sends signals to effectors. Effectors are cells or organs that cause physiological responses that return the variable to the normal homeostatic range. 94) Discuss the role of effector in both the negative and positive feedback loops. Answer: In a negative feedback loop, the effector activity opposes the initial stimulus and shuts off when conditions return to the normal range. However, in a positive feedback loop, the effector's activity actually increases positive feedback reinforces the initial stimulus using a loop of increasing output that amplifies the response. A positive feedback loop therefore causes a rapid change in a variable. 95) List the four core principles that relate to homeostasis. Answer: The four core principles that relate to homeostasis are: 1) feedback loops 2) the relationship of structure and function 3) gradients 4) cell-cell communication 96) Summarize the principle of complementarity of structure and function. Answer: The principle of complementarity can be summarized as form follows function. In other words, the form of a structure is always such that it best suits its function. 25
26 97) Discuss why anatomical position is used. Answer: Anatomical position provides accurate communication among scientists and health care professionals since it prevents experimental and medical errors. Anatomical position also provides a common frame of reference from which all body parts and regions are described. 98) Explain how the popliteal and patellar regions differ. Answer: The popliteal region refers to the posterior (dorsal) side of the knee while the patellar region refers to the anterior (ventral) side of the knee. We may say that the popliteal region is posterior to the patellar region. 99) Jose is having back surgery. Discuss the specific type of section the surgeon should use to make a cut along his vertebral region. Answer: The vertebral region is situated along the body's midline. To operate on this region, the surgeon should make a cut along the midsagittal, or medial, plane on Jose's posterior (dorsal) body surface. The midsagittal plane divides the body into equal left and right parts. 100) Pleurisy is the inflammation of the serous membranes surrounding the lungs. With pleurisy, the inflamed membranes may secrete more serous fluid than normal. Predict the effects of excess serous fluid on serous membrane function. Answer: Serous fluid is an extremely thin, slippery, watery layer situated between the visceral and parietal pleura. This fluid is produced by the cells of the membrane to lubricate around the organs and reduce friction as the lungs move against adjacent structures. Excess fluid around the lungs puts pressure on the lungs and can impair the lubricating function of the serous membranes, making it harder for these membranes to reduce friction. 101) Explain how scratching a chaffing label on a shirt is an example of a negative feedback loop. Answer: An irritation to the skin from a chaffing shirt label is a stimulus detected by a receptor (or sensor). The receptor sends this information to a control center, the brain, where it is determined that the skin irritation is out of normal range. The control center sends signals to effectors that cause physiological responses to return the variable to normal homeostatic range. Scratching, the response, stops the chaffing by moving the label off the skin, and thus removes the stimulus. 26
27 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 1) A 2) A 3) B 4) D 5) C 6) B 7) B 8) D 9) D 10) C 11) C 12) B 13) C 14) B 15) D 27
28 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 16) A 17) A 18) D 19) D 20) B 21) A 22) C 23) C 24) D 25) A 26) C 27) D 28) B 29) D 30) A 28
29 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 31) B 32) C 33) D 34) C 35) C 36) D 37) A 38) B 39) C 40) C 41) C 42) C 43) A 44) D 45) C 29
30 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 46) B 47) B 48) D 49) D 50) C 51) A 52) A 53) A 54) B 55) B 56) B 57) A 58) D 59) C 60) C 30
31 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 61) TRUE 62) FALSE 63) FALSE 64) TRUE 65) FALSE 66) FALSE 67) FALSE 68) TRUE 69) TRUE 70) FALSE 71) B 72) C 73) A 74) E 75) D 31
32 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 76) A 77) B 78) C 79) D 80) E 81) Gillian prefers a visual/nonverbal learning style. A visual/nonverbal learner usually best understands concepts through the use of diagrams, illustrations, and other visual media without text. Visual/nonverbal learners may experience more success in studying alone than in study groups. 82) The SQ3R method stands for survey, questions, read, recite, and review. First, you should survey the chapter by skimming the material and figures. Next, form questions about the content in the chapter that you can answer as you read. Actively read by taking notes and drawing diagrams. As you read, recite the material by speaking aloud. The final step is to review what you have read. You may choose to answer questions in the book, write summaries, or discuss topics aloud with study partners. 83) Metabolism includes the wide range of chemical processes carried out by living organisms. Metabolism includes both "building" processes in which smaller chemicals are combined to form larger ones, and "breaking down" processes in which larger chemicals are broken down into smaller ones. 84) The field of gross anatomy examines structures, including organs and organ systems that can be seen with the unaided eye. The field of microscopic anatomy examines structures that require a microscope to be seen. 85) In anatomical position, the body is standing upright, feet are shoulder width apart, upper limbs are at the sides of the trunk, and the head and palms are facing forward. 86) Instead of using superior and inferior for the limbs, the terms proximal and distal are used. Proximal refers to something being closer to the point of origin (the trunk) while distal refers to something being farther away from the point of origin. Structures nearer the trunk are proximal while structures farther away are distal. 32
33 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 87) Peggy will have surgery on the wrist, or carpal, region of her right hand. The 3 cm incision will penetrate through the skin and muscle, but will not go as deep into her wrist as the bone. 88) A midsagittal plane of section is also known as a median plane of section. Both divide the body or body part into equal left and right parts. Kelly and her lab partner should make a cut so that their specimen is divided into equal left and right parts. 89) The appendix, the right ovary, the first part of the large intestine, or the last part of the small intestine may be the source of pain in this female patient. 90) The four quadrants are the right upper quadrant, right lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, and left lower quadrant. The nine regions are the right hypochondriac region, epigastric region, left hypochondriac region, right lumbar region, umbilical region, left lumbar region, right iliac (inguinal) region, hypogastric region, and left iliac (inguinal) region. 91) The pericardial cavity is situated between the visceral pericardium (attached to the heart muscle) and the outer parietal pericardium. 92) Homeostasis is maintenance of the body's internal environment. Disturbances in homeostasis, known as homeostatic imbalances, can result in disease or death if uncorrected. 93) The components of a feedback loop are the stimulus, receptor (sensor), control center, and effector/response. A stimulus is a regulated variable outside its normal range. A receptor (sensor) is a cellular structure that picks up information and sends it to a control center. The control center is often cells in the brain or an endocrine organ (gland). The control center compares the current value to its set point and determines that it's out of range. The control center sends signals to effectors. Effectors are cells or organs that cause physiological responses that return the variable to the normal homeostatic range. 94) In a negative feedback loop, the effector activity opposes the initial stimulus and shuts off when conditions return to the normal range. However, in a positive feedback loop, the effector's activity actually increases positive feedback reinforces the initial stimulus using a loop of increasing output that amplifies the response. A positive feedback loop therefore causes a rapid change in a variable. 95) The four core principles that relate to homeostasis are: 1) feedback loops 2) the relationship of structure and function 3) gradients 4) cell-cell communication 33
34 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 96) The principle of complementarity can be summarized as form follows function. In other words, the form of a structure is always such that it best suits its function. 97) Anatomical position provides accurate communication among scientists and health care professionals since it prevents experimental and medical errors. Anatomical position also provides a common frame of reference from which all body parts and regions are described. 98) The popliteal region refers to the posterior (dorsal) side of the knee while the patellar region refers to the anterior (ventral) side of the knee. We may say that the popliteal region is posterior to the patellar region. 99) The vertebral region is situated along the body's midline. To operate on this region, the surgeon should make a cut along the midsagittal, or medial, plane on Jose's posterior (dorsal) body surface. The midsagittal plane divides the body into equal left and right parts. 100) Serous fluid is an extremely thin, slippery, watery layer situated between the visceral and parietal pleura. This fluid is produced by the cells of the membrane to lubricate around the organs and reduce friction as the lungs move against adjacent structures. Excess fluid around the lungs puts pressure on the lungs and can impair the lubricating function of the serous membranes, making it harder for these membranes to reduce friction. 101) An irritation to the skin from a chaffing shirt label is a stimulus detected by a receptor (or sensor). The receptor sends this information to a control center, the brain, where it is determined that the skin irritation is out of normal range. The control center sends signals to effectors that cause physiological responses to return the variable to normal homeostatic range. Scratching, the response, stops the chaffing by moving the label off the skin, and thus removes the stimulus. 34
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide
 Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Organization of the Body Chapter 1. Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden
 Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
**Confirm accuracy of above with your instructor.** Revised 8/22/2017 1
 AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
The Language of Anatomy
 The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units
 hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
 Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
The Human Body: An Orientation
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13
 CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Figure 1.2. Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5) Umbilical region. Answer: C. 6) Right hypochondriac. Answer: B
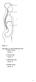 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: ext. 6049
 Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Chapter 1. An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
8/27/2017. The Human Body: An Orientation. Homeostasis BODY SYSTEMS WORK TOGETHER TO MAINTIN HOMEOSTASIS. Chapter 1 Part B
 Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed.
 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth, and the hottest on record, with temperatures
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth, and the hottest on record, with temperatures
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology
 is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Introductions. Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1. Contact Info. Syllabus Highlights. Course Website. Course Website. Instructor: Joel Dahms
 Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
Introductions. Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1. Contact Info. Syllabus Highlights. Course Website. Course Website. Instructor: Joel Dahms
 Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter 1. Figure 1.1. Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. Answer: C. 2) Cranial cavity. Answer: A
 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later)
 Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
Chapter 1 Introduction and Organization
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Organization 1. Anatomy and physiology is the relationship of the structure and function of the human body. a. Architect Louis Henry Sullivan coined the phrase Form follows function.
Chapter 1 Introduction and Organization 1. Anatomy and physiology is the relationship of the structure and function of the human body. a. Architect Louis Henry Sullivan coined the phrase Form follows function.
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Chapter 1. Figure 1.1. Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. Answer: C. 2) Cranial cavity. Answer: A
 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Then think about these: Check your Packet- three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last?
 Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
Date Lab Pd. Lecture Notes (57)
 Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
A&P Key Terms 01 Human Body Anatomy & Physiology
 Cover Page A&P Key Terms 01 Human Body Anatomy & Physiology Author: OpenStax College Published 2015 About Us Powered by QuizOver.com The Leading Online Quiz & Exam Creator Create, Share and Discover Quizzes
Cover Page A&P Key Terms 01 Human Body Anatomy & Physiology Author: OpenStax College Published 2015 About Us Powered by QuizOver.com The Leading Online Quiz & Exam Creator Create, Share and Discover Quizzes
Station 2: Torso Model Practical
 Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities
 Page1 Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities Objectives Understand the purpose of the scientific method and describe the six steps involved List and describe the sections
Page1 Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities Objectives Understand the purpose of the scientific method and describe the six steps involved List and describe the sections
Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms
 1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B
 Human Anatomy & Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B 1) Thoracic cavity.
Human Anatomy & Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B 1) Thoracic cavity.
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology professor edit
 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology professor edit PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body You must be
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology professor edit PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body You must be
