Millest räägime? Miks tekib Parkinsoni tõbi? kiire meeldetuletus taastusravi meeskonnale. Parkinsoni tõve avastamislugu
|
|
|
- Herbert Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Millest räägime? Miks tekib Parkinsoni tõbi? kiire meeldetuletus taastusravi meeskonnale. Egle Seppo Taastusarst AS Keila Taastusravikeskus Ajaloost Epidemioloogiast Anatoomiast Etiopatogeneesist Sümptomaatikast Diagnoosimisest Parkinsoni tõve avastamislugu sajand BC papüürus ürikud Egiptusest 10 sajand BC India Ayurveda meditsiin Kampa vata 175. AD kirjeldas Claudius Galenus rahuoleku treemor, kehatüve ebalus, halvatus 1817 James Parkinson Essay on the Shaking Palsy 1872 Jean-Martin Charcot Parkinsoni tõbi Revolutsioon Parkinsoni tõve ajaloos 1897 Edouard Brissaud subthalamuse või pedunculus cerebri isheemiline kahjustus? 1912 Frederic Lewy patoloogilised muutused ajus Lewy kehakesed 1919 Konstantin Tretiakoff substantia nigra publitseeris Rolf Hassler 1950 Arvid Carlsson dopamiini roll haiguse tekkes -> Nobeli preemia 1994 Alice Lazzarini meeskonnaga määratles haiguse geneetilise komponendi 1
2 Mõned faktid ravi ajaloost Kuulsaid parkinsonihaigeid Mucuna viljad Ajurveda meditsiinis 19.sajandil antikolinergilised alkaloidid 1911 sünteesiti Levodopa Casimir Funk i poolt 1967 Levodopa kliinilises praktikas 1939 esimesed kirurgilised katsetused 1980ndate lõpp aju süvastimulatsioon -> FDA poolt kliinilisse katsetusse 1997 Kuulsaid parkinsonihaigeid Parkinsoni tõve epidemioloogia 2. enamlevinud neurodegeneratiivne haigus 1% > 60 aastaste elanikkonnast 7-10 milj. inimest kogu maailmas WHO -> tõsine tervishoiuprobleem vananevas ühiskonnas Europiidne rass enam Levimus / , indoeuroopas / Eestis 152/ ; 16.6/ aastas Neuroanatoomia 2
3 Neuroanatoomia - basaalganglionid Neuroanatoomia 3
4 Neurotransmitterid Neurotransmitter Funktsioon Sekretsiooni koht Atsetüülkoliin Pidurdav/erutav CNS/PNS Biogeensed amiinid Noradrenaliin/Adrenaliin Erutav/pidurdav CNS/PNS Dopamiin Pidurdav/erutav CNS/PNS Serotoniin Pidurdav CNS Aminohapped GABA Pidurdav CNS Gly Pidurdav CNS Glu Erutav CNS Asp Erutav CNS Neuropeptiidid VIP, SubstantsP, enkefaliinid Pidurdav/erutav CNS/PNS C₈H₁₁NO₂ Dopamiin Dopamiin Peaaju närvilõpmed Väljaspool närvisüsteemi Veresoonkond vasodilataator -> vasopressoorne ja inotroopne efekt (positiivne kronotroopne ja inotroopne toime) Hingamiselundkond Neerud - diureesi Kõhunääre väheneb insuliini produktsioon Seedetrakt aeglustab soole motoorikat Immuunsüsteem - Ly ak ivsust Mida dopamiin teeb peaajus? Motoorika kontroll Kognitsioon Motivatsioon Õppimisvõime Uni Käitumine Sarrustusvõime Meeleolu Tähelepanu Dopamiini süntees 4
5 Kuidas tekib liigutus? erutav pidurdav LCS ja RS tract Peamised neurotransmitterid Pidurdavad (GABA, Dopamiin) Erutavad (Glutamaat, Dopamiin) Indirect Putamen Direct Pidurdus: Vähenenud pidurdus = tugevam vastusreaktsioon Suurenenud pidurdus = nõrgem vastusreaktsioon Erutus: Vähenenud erutus = nõrgem vastusreaktsioon Suurenenud erutus = tugevam vastusreaktsioon GP ext Nucl.Subth. SNpars comp Basal ganglia GP int Mot.Thalamus vlppn dppn erutav pidurdav Putamen Indirect SNpars comp GP ext Nucl.Subth. Basal ganglia Direct GP int LCS ja RS tract Mot.Thalamus vlppn dppn Pidurduse tulemusel: Thalamus vlppn Põhjus Ajukoore motoorsete keskuste erutuvuse Retikulospinaaltrakti aktiivsuse muutus, LMN Tulemus Vähenenud tahtelised liigutused: bradükineesia ja akineesia Lihasrigiidsus posturaalsetes ja jäsemelihastes dppn ülekanne RF Kõnnimustri häirumine Parkinsonitõve riskifaktorid Vanus Perekondlik anamnees Sugu Rass Tööstusmürgid(MPTP) ja pestitsiidid (Serotone, benomüül) Eluanamnees (peatrauma, isiksuse omadused?, emotsionaalne stress?) B-vitamiini, foolhappe puudus? Häirunud östrogeenide produktsioon? Parkinsonitõve etioloogilised faktorid Pärilikkus α-synuclein/sncaprotein/park1 4.krom; AD PARKIN/PARK2-6.krom; AR PINK1/PARK6 1.krom; AR LRRK2/PARK8 12.krom; AD DJ-1/PARK7-1.krom; AR Glycocerebrosidas 1.krom; AD UCH-L1/PARK5(ubikvitiin proteolüütilise süsteemi ensüüm) vähenenud ensüümi aktiivsus; 4.krom Omi/HtrA2(apoptoosi inhibiitor) Nurr1(dopaminergilise tasakaalu säilitamine)- 2.krom mtdna polymerasγ/polg1 15.krom "Etiology and Pathogenesis of PD"; Neurol.Clin 27(2009)
6 Henchcliffe C and Beal MF (2008) Mitochondrial biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis Nat Clin Pract Neurol /ncpneuro0924 Parkinsonitõve patogenees Parkinsoni tõve sümptomaatika UK Parkinsonitõve Seltsi Ajupanga Diagnoosikriteeriumid (UK PDS BB) Parkinsonistliku sündroomi diagnoos Välistavad kriteeriumid Toetavad kriteeriumid Henchcliffe C and Beal MF (2008) Mitochondrial biology and oxidative stress in Parkinson disease pathogenesis Nat Clin Pract Neurol /ncpneuro0924 Parkinsoni tõve Eesti ravijuhend 2008 EFNS/MDS-ES recommendations for the diagnosis of Parkinson s disease 2012 Parkinsonistliku sündroomi diagnoos: Bradükineesia ja vähemalt üks järgnevatest: Lihasrigiidsus 4-6Hz rahutreemor Posturaalne ebastabiilsus, mis ei ole põhjustatud primaarse nägemis-, vestibulaarse, tserebellaarse ega propriotseptiivse funktsiooni häirest 6
7 Välistavad kriteeriumid: Korduvad insuldid anamneesis parkinsonismi süvenemisega Korduvad peatraumad anamneesis Entsefaliit anamneesis Oculogyric crisis ( ) Neuroleptikumravi sümptomite tekkimise ajal >1 sugulane sama haigusega ( ) Püsiv remissioon Püsiv ühepoolne haaratus 3 aastat peale haiguse algust Supranukleaarne halvatus Tserebellaarsed nähud Varajane autonoomse NS haaratus Varane raske dementsus Babinski refleks Tuumor või hüdrotseefalus CT-uuringul Puudulik vastus L-dopa suurtele annustele (malabsorptsiooni puudumisel) Toksiliste ainete toime (MPTP) ( ) EFNS/MDS-ES Toetavad kriteeriumid: Kindla Parkinsonitõve diagnoosiks nõutav 3 või enama kriteeriumi esinemine: Ühepoolne haiguse algus Esineb rahutreemor Progresseeruv kulg Püsiv sümptomite asümmeetria (väljendunum kehapoolel, kus tekkisid esmassümptomid) ( ) Levodopa hea toimeefekt (70-100%) Rasked levodopast tingitud düskineesiad Levodopa toimeefekt >5 aasta ( ) Haiguse kliiniline kulg >10 aasta ( ) Hüposmia ( ) Visuaalsed hallutsinatsioonid ( ) ( )( ) EFNS/MDS-ES Parkinsoni tõve diagnostikast Kliiniline diagnostika B tase Geneetiline diagnostika B tase Autonoomse funktsiooni testid vähene tõendus Olfaktoorne test Atüüpiline ja sekundaarne parkinsonism A tase Retsessiivne parkinsonitõbi A-tase Ravimtest ei ole soovitatud parkinsonihaiguse differentsiaaldiagnostikaks Neurofüsioloogilised testid vähe tõenduspõhiseid uuringuid Neuropsühholoogilised testid A tase Neuroradioloogilised uuringud TCS A tase MRI A, B ja C tase SPECT A tase PET vähene tõendus 7
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective. Dr John Coyle
 Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
Parkinsoni tõve Eesti ravijuhend
 Parkinsoni tõve Eesti ravijuhend Koostajad: Pille Taba Toomas Asser Ülle Krikmann Tiiu Tomberg Malle Paris Tiina Tammik Tiiu Paju Ene Olt Eve Kanarik Margus Ennok Krista Ankru Heleri Kivil Ene Taurafeldt
Parkinsoni tõve Eesti ravijuhend Koostajad: Pille Taba Toomas Asser Ülle Krikmann Tiiu Tomberg Malle Paris Tiina Tammik Tiiu Paju Ene Olt Eve Kanarik Margus Ennok Krista Ankru Heleri Kivil Ene Taurafeldt
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview
 Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease. SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease
 Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Infektsioonhaigused 21. sajandil
 Infektsioonhaigused 21. sajandil Irja Lutsar Eesti Arstide Päevad 04. 04. 2014 Infektsioonhaigused läbi aegade: Inglismaa ja Wales Infektsioonhaigused 20.sajandil Läkaköha Eestis Difteeria Eestis Mida
Infektsioonhaigused 21. sajandil Irja Lutsar Eesti Arstide Päevad 04. 04. 2014 Infektsioonhaigused läbi aegade: Inglismaa ja Wales Infektsioonhaigused 20.sajandil Läkaköha Eestis Difteeria Eestis Mida
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease
 Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Extrapyramidal Motor System. Basal Ganglia or Striatum. Basal Ganglia or Striatum 3/3/2010
 Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
Extrapyramidal Motor System Basal Ganglia or Striatum Descending extrapyramidal paths receive input from other parts of motor system: From the cerebellum From the basal ganglia or corpus striatum Caudate
UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S DISEASE
 UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S DISEASE WHAT IS PARKINSON S DISEASE? A progressive disease of the nervous system marked by tremor, muscular rigidity, and slow, imprecise movement, chiefly affecting middleaged
UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S DISEASE WHAT IS PARKINSON S DISEASE? A progressive disease of the nervous system marked by tremor, muscular rigidity, and slow, imprecise movement, chiefly affecting middleaged
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Malattia di Parkinson: patogenesi molecolare e nuove strategie terapeutiche
 LA NEUROSONOLOGIA NELLE PATOLOGIE DEGENERATIVE E VASCOLARI CEREBRALI San Benedetto del Tronto 6-8 novembre 2017 Malattia di Parkinson: patogenesi molecolare e nuove strategie terapeutiche Giuseppe De Michele
LA NEUROSONOLOGIA NELLE PATOLOGIE DEGENERATIVE E VASCOLARI CEREBRALI San Benedetto del Tronto 6-8 novembre 2017 Malattia di Parkinson: patogenesi molecolare e nuove strategie terapeutiche Giuseppe De Michele
Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson s disease
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
Clinical guidelines for Estonian physisians for the management of Parkinson s disease
 Parkinsoni tõve ravijuhend Eesti arstidele Pille Taba 1, Toomas Asser 1, Rein Zupping 2, Sulev Haldre 1, Siiri-Merike Lüüs 1 1 TÜK Närvikliinik 2 Mustamäe Haigla Võtmesõnad Parkinsoni tõbi, diagnoosikriteeriumid,
Parkinsoni tõve ravijuhend Eesti arstidele Pille Taba 1, Toomas Asser 1, Rein Zupping 2, Sulev Haldre 1, Siiri-Merike Lüüs 1 1 TÜK Närvikliinik 2 Mustamäe Haigla Võtmesõnad Parkinsoni tõbi, diagnoosikriteeriumid,
Clostridium difficile diagnostika. Paul Naaber
 Clostridium difficile diagnostika Paul Naaber Paul Naaber 08.12.2011 Sissejuhatus Grampositiivne anaeroob Moodustab eoseid Virulentsusfaktorid Toksiin A ja B olulised haiguse tekkes binary toxin tähtsus
Clostridium difficile diagnostika Paul Naaber Paul Naaber 08.12.2011 Sissejuhatus Grampositiivne anaeroob Moodustab eoseid Virulentsusfaktorid Toksiin A ja B olulised haiguse tekkes binary toxin tähtsus
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Parkinson's Disease. Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology
 Parkinson's Disease Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology 18 February 2002 Parkinson Disease Neurological disease affecting over four million patients
Parkinson's Disease Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology 18 February 2002 Parkinson Disease Neurological disease affecting over four million patients
Overview. Overview. Parkinson s disease. Secondary Parkinsonism. Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits
 Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Mari-Liis Ilmoja SA Tallinna Lastehaigla
 Mari-Liis Ilmoja SA Tallinna Lastehaigla 22.05.2015 24,165 anaesthesias 724 adverse events; 31:1000 53% respiratory Risk factors: infancy, higher ASA status, ENT surgery Perioperative anaesthetic morbidity
Mari-Liis Ilmoja SA Tallinna Lastehaigla 22.05.2015 24,165 anaesthesias 724 adverse events; 31:1000 53% respiratory Risk factors: infancy, higher ASA status, ENT surgery Perioperative anaesthetic morbidity
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Basal ganglia motor circuit
 Parkinson s Disease Basal ganglia motor circuit 1 Direct pathway (gas pedal) 2 Indirect pathway (brake) To release or augment the tonic inhibition of GPi on thalamus Direct pathway There is a tonic inhibition
Parkinson s Disease Basal ganglia motor circuit 1 Direct pathway (gas pedal) 2 Indirect pathway (brake) To release or augment the tonic inhibition of GPi on thalamus Direct pathway There is a tonic inhibition
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders
 Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Understanding Dystonia
 Understanding Dystonia Sand Sharks Anthony Richardsen, Lindsey Rathbun, Evan Harrington, Chris Erzen The Essentials What, Why, How What is Dystonia? Dystonias are movement disorders often characterized
Understanding Dystonia Sand Sharks Anthony Richardsen, Lindsey Rathbun, Evan Harrington, Chris Erzen The Essentials What, Why, How What is Dystonia? Dystonias are movement disorders often characterized
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve
 Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
Ch. 45 Continues (Have You Read Ch. 45 yet?) u Central Nervous System Synapses - Synaptic functions of neurons - Information transmission via nerve impulses - Impulse may be blocked in its transmission
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
FDG-PET e parkinsonismi
 Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity. Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS
 Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
Parkinson s Disease. Prevalence. Mark S. Baron, M.D. Cardinal Features. Clinical Characteristics. Not Just a Movement Disorder
 Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT. Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof
 PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof Definition Clinical symptoms: Pathogenesis: Etiology: Neurodegenerative syndrome with chronic,
PARKINSON S DISEASE: current aspects of ETIOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS and TREATMENT Dilek Ince Gunal, MD Assoc. Prof Definition Clinical symptoms: Pathogenesis: Etiology: Neurodegenerative syndrome with chronic,
Genetic Parkinson s studying the few to treat the many
 Edinburgh Talk 01.12.12 Genetic Parkinson s studying the few to treat the many Miratul Muqit, Wellcome Trust Intermediate Fellow, Honorary Consultant Neurologist, MRC Protein Phosphorylation Unit, University
Edinburgh Talk 01.12.12 Genetic Parkinson s studying the few to treat the many Miratul Muqit, Wellcome Trust Intermediate Fellow, Honorary Consultant Neurologist, MRC Protein Phosphorylation Unit, University
Summary and Conclusion
 Parkinson s disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system primarily affecting the motor system of the body and is also known as Shaking palsy (Bendick, 2002). Parkinson's disease is the second
Parkinson s disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system primarily affecting the motor system of the body and is also known as Shaking palsy (Bendick, 2002). Parkinson's disease is the second
Äge neerupuudulikkus etioloogia ja patogenees. Äge neerukahjustus (ÄNK)( ÄNK olulisus kliinilises praktikas. ÄNK olulisus kliinilises praktikas
 Äge neerupuudulikkus etioloogia ja patogenees. Mai Rosenberg, TÜ, T, Sisekliinik Krooniline neeruhaigus (KNH) globaalne probleem Äge neerukahjustus (ÄNK)( Äge neerukahjustus (ÄNK)( ÄNK olulisus kliinilises
Äge neerupuudulikkus etioloogia ja patogenees. Mai Rosenberg, TÜ, T, Sisekliinik Krooniline neeruhaigus (KNH) globaalne probleem Äge neerukahjustus (ÄNK)( Äge neerukahjustus (ÄNK)( ÄNK olulisus kliinilises
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
Parkinson disease: Parkinson Disease
 Surgical Surgical treatment treatment for for Parkinson disease: Parkinson Disease the Present and the Future the Present and the Future Olga Klepitskaya, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Co-Director,
Surgical Surgical treatment treatment for for Parkinson disease: Parkinson Disease the Present and the Future the Present and the Future Olga Klepitskaya, MD Associate Professor of Neurology Co-Director,
A Parkinson s Disease and related disorders
 A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging. Dr. Olav E. Krigolson Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE
 ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging Dr. Olav E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE The Basal Ganglia Primary motor cortex Execution of movement
ASHI691: Why We Fall Apart: The Neuroscience and Neurophysiology of Aging Dr. Olav E. Krigolson krigolson@uvic.ca Lecture 5: PARKINSONS DISEASE The Basal Ganglia Primary motor cortex Execution of movement
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Parkinson s Disease: The Mystery, the Myth and the Magic
 Parkinson s Disease: The Mystery, the Myth and the Magic THE MYSTERY Despite its prominence in contemporary literature and the text book symptoms, diagnosis and standard of care treatments, there s a lot
Parkinson s Disease: The Mystery, the Myth and the Magic THE MYSTERY Despite its prominence in contemporary literature and the text book symptoms, diagnosis and standard of care treatments, there s a lot
UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S AND THE POWER OF INTENT. Samantha Elandary, MA, CCC-SLP Founder & Chief Executive Officer Parkinson Voice Project
 UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S AND THE POWER OF INTENT Samantha Elandary, MA, CCC-SLP Founder & Chief Executive Officer Parkinson Voice Project What is Parkinson s? TOOLS FOR MANAGING PARKINSON S! Medications!
UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S AND THE POWER OF INTENT Samantha Elandary, MA, CCC-SLP Founder & Chief Executive Officer Parkinson Voice Project What is Parkinson s? TOOLS FOR MANAGING PARKINSON S! Medications!
The Parkinson s You Can t See
 The Parkinson s You Can t See We principally see the motor phenomena of Parkinson's disease, but is there an early stage without visible features? Might this provide a window for disease-modifying therapy?
The Parkinson s You Can t See We principally see the motor phenomena of Parkinson's disease, but is there an early stage without visible features? Might this provide a window for disease-modifying therapy?
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease
 Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease FABIO G. TEIXEIRA,MIGUEL M.CARVALHO KRISHNA M. PANCHALINGAM ANA J.RODRIGUES
Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease FABIO G. TEIXEIRA,MIGUEL M.CARVALHO KRISHNA M. PANCHALINGAM ANA J.RODRIGUES
Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers
 Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers 2018 Movement Disorders Half Day Symposium Elise Anderson MD Medical Co-Director, PBSI Movement Disorders 6/28/2018 1 Disclosures GE Speaker,
Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers 2018 Movement Disorders Half Day Symposium Elise Anderson MD Medical Co-Director, PBSI Movement Disorders 6/28/2018 1 Disclosures GE Speaker,
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy"
 Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Origins. Update on Parkinson s Disease
 Update on Parkinson s Disease Melinda Burnett, MD Origins First described in 1817 by James Parkinson: Involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action and even when supported;
Update on Parkinson s Disease Melinda Burnett, MD Origins First described in 1817 by James Parkinson: Involuntary tremulous motion, with lessened muscular power, in parts not in action and even when supported;
From the brain to intelligent systems: The attenuation of sensation of self-generated movement
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU Institute of Computer Science Computer Science Curriculum Kristjan-Julius Laak From the brain to intelligent systems: The attenuation of sensation of self-generated movement Master
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU Institute of Computer Science Computer Science Curriculum Kristjan-Julius Laak From the brain to intelligent systems: The attenuation of sensation of self-generated movement Master
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Haigusjuht. Helen Kikerpill II a arst-resident radioloogia
 Haigusjuht Helen Kikerpill II a arst-resident radioloogia 21.04.2011 Kliinilised andmed: valu paremas puusas [Manaster et al] 21.04.2011 MRT uuring lülisamba nimmeosast Olulist spinaalkanali ahenemist
Haigusjuht Helen Kikerpill II a arst-resident radioloogia 21.04.2011 Kliinilised andmed: valu paremas puusas [Manaster et al] 21.04.2011 MRT uuring lülisamba nimmeosast Olulist spinaalkanali ahenemist
10/13/2017. Disclosures. Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders. Deep Brain Stimulation: Objectives.
 Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
Deep Brain Stimulation in the Treatment of Movement Disorders Disclosures None Eleanor K Orehek, M.D. Movement Disorders Specialist Noran Neurological Clinic 1 2 Objectives To provide an overview of deep
May 9, Q Financial Results
 May 9, 2017 Q1 2017 Financial Results Agenda Today s Speakers Paul Cox, Senior Director, Investor Relations Jeff Jonas, M.D., Chief Executive Officer Steve Kanes, M.D., Ph.D., Chief Medical Officer Kimi
May 9, 2017 Q1 2017 Financial Results Agenda Today s Speakers Paul Cox, Senior Director, Investor Relations Jeff Jonas, M.D., Chief Executive Officer Steve Kanes, M.D., Ph.D., Chief Medical Officer Kimi
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE ABSTRACT
 Review Article Allied Science International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE DR. M.P.SANTHOSH KUMAR M.D.S. Reader, Department of
Review Article Allied Science International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE DR. M.P.SANTHOSH KUMAR M.D.S. Reader, Department of
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors
 Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 1: Dopamine and Norepinephrine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Overview of Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors Criteria for defining a
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 1: Dopamine and Norepinephrine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Overview of Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors Criteria for defining a
responsiveness HMPAO SPECT in Parkinson's disease before and after levodopa: correlation with dopaminergic (SSmTc HMPAO) as a tracer in 21 patients
 18 1ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:18-185 Department of Neurology H S Markus A J Lees Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London,
18 1ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:18-185 Department of Neurology H S Markus A J Lees Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London,
The Biology of Parkinson s Disease and its treatments
 The Biology of Parkinson s Disease and its treatments Paola Sacchetti, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Director MS Neuroscience Department of Biology University of Hartford, CT psacchett@hartford.edu (860)768-5926
The Biology of Parkinson s Disease and its treatments Paola Sacchetti, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Director MS Neuroscience Department of Biology University of Hartford, CT psacchett@hartford.edu (860)768-5926
Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies. Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai
 Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai 1 Scope Modality of treatment Pathophysiology of PD and dopamine metabolism Drugs Are there
Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai 1 Scope Modality of treatment Pathophysiology of PD and dopamine metabolism Drugs Are there
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications. Dr. Stuart Inglis
 Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
Chapter 8. Parkinsonism. M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University.
 Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
M. Carranza M. R. Snyder J. Davenport Shaw T. A. Zesiewicz. Parkinson s Disease. A Guide to Medical Treatment
 M. Carranza M. R. Snyder J. Davenport Shaw T. A. Zesiewicz Parkinson s Disease A Guide to Medical Treatment SEEd srl. All rights reserved Piazza Carlo Emanuele II, 19 10123 Torino, Italy Tel. 011.566.02.58
M. Carranza M. R. Snyder J. Davenport Shaw T. A. Zesiewicz Parkinson s Disease A Guide to Medical Treatment SEEd srl. All rights reserved Piazza Carlo Emanuele II, 19 10123 Torino, Italy Tel. 011.566.02.58
ÕLAVALU FUNKTSONAALNE DIAGNOSTIKA
 ÕLAVALU FUNKTSONAALNE DIAGNOSTIKA Dr.TOOMAS TEIN SA TÜK Traumatoloogia-ortopeedia kliinik Erakliinik MEDEX 2012 Õlaliigese valu Õlavalu esineb 7 34 % rahvastikust (21 % > 70 a.) 40 50 % läheb perearsti
ÕLAVALU FUNKTSONAALNE DIAGNOSTIKA Dr.TOOMAS TEIN SA TÜK Traumatoloogia-ortopeedia kliinik Erakliinik MEDEX 2012 Õlaliigese valu Õlavalu esineb 7 34 % rahvastikust (21 % > 70 a.) 40 50 % läheb perearsti
Getting involved in Parkinson s disease
 Getting involved in Parkinson s disease DEVELOPING AND EXPLOITING C. ELEGANS MODEL FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Supported by the PD society Anton Gartner, Ph.D. University of Dundee MSI/WTB Complex Gene Regulation
Getting involved in Parkinson s disease DEVELOPING AND EXPLOITING C. ELEGANS MODEL FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Supported by the PD society Anton Gartner, Ph.D. University of Dundee MSI/WTB Complex Gene Regulation
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
La neurosonologia. Ecografia cerebrale e nuove applicazioni nelle malattie neurodegenerative. Nelle patologie degenerative e vascolari cerebrali
 La neurosonologia Nelle patologie degenerative e vascolari cerebrali Andrea Pilotto Ecografia cerebrale e nuove applicazioni nelle malattie neurodegenerative Prof. Daniela Berg Department of Neurodegeneration
La neurosonologia Nelle patologie degenerative e vascolari cerebrali Andrea Pilotto Ecografia cerebrale e nuove applicazioni nelle malattie neurodegenerative Prof. Daniela Berg Department of Neurodegeneration
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
Biomedical Technology Research Center 2011 Workshop San Francisco, CA
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Parts of the motor circuits
 MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
MOVEMENT DISORDERS Parts of the motor circuits cortical centers: there are centers in all the cortical lobes subcortical centers: caudate nucleus putamen pallidum subthalamical nucleus (Luys) nucleus ruber
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
This is a free sample of content from Parkinson's Disease. Click here for more information or to buy the book.
 A AADC. See Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase AAV. See Adeno-associated virus Acetylcholine (ACh), functional imaging, 174 175 ACh. See Acetylcholine Adaptive immune system central nervous system, 381
A AADC. See Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase AAV. See Adeno-associated virus Acetylcholine (ACh), functional imaging, 174 175 ACh. See Acetylcholine Adaptive immune system central nervous system, 381
PARKINSON S DISEASE. Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons 5/11/16 CARDINAL FEATURES OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Parkinson s disease
 5/11/16 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease Prevalence increases with age (starts 40s60s) Seen in all ethnic groups, M:F about 1.5:1 Second most common neurodegenerative disease Genetics role greater
5/11/16 PARKINSON S DISEASE Parkinson s disease Prevalence increases with age (starts 40s60s) Seen in all ethnic groups, M:F about 1.5:1 Second most common neurodegenerative disease Genetics role greater
Täiskasvanute astma käsitlus esmatasandil Tõendusmaterjali kokkuvõte
 Täiskasvanute astma käsitlus esmatasandil Tõendusmaterjali kokkuvõte Kliinilineküsimusnr 8 1. Kliinilise küsimusetekst: Kas astma diagnoosiga püsiravi vajavatele patsientidele tuleks ravi tiitrimisel (step-up)
Täiskasvanute astma käsitlus esmatasandil Tõendusmaterjali kokkuvõte Kliinilineküsimusnr 8 1. Kliinilise küsimusetekst: Kas astma diagnoosiga püsiravi vajavatele patsientidele tuleks ravi tiitrimisel (step-up)
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Connections of basal ganglia
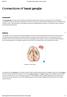 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Parkinson s Disease. Sirilak yimcharoen
 Parkinson s Disease Sirilak yimcharoen EPIDEMIOLOGY ~1% of people over 55 years Age range 35 85 years peak age of onset is in the early 60s ~5% of cases characterized by an earlier age of onset (typically
Parkinson s Disease Sirilak yimcharoen EPIDEMIOLOGY ~1% of people over 55 years Age range 35 85 years peak age of onset is in the early 60s ~5% of cases characterized by an earlier age of onset (typically
PPMI Imaging Core Update
 PPMI Imaging Core Update John Seibyl, MD 7 May 2013 PPMI Imaging Core Update 1. PPMI status update: enrollment, demographics, compliance 2. DAT analyses -baseline and initial progression data -phantom
PPMI Imaging Core Update John Seibyl, MD 7 May 2013 PPMI Imaging Core Update 1. PPMI status update: enrollment, demographics, compliance 2. DAT analyses -baseline and initial progression data -phantom
Non-Genetic Ataxia Susan L. Perlman, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Director, Ataxia Clinic
 Non-Genetic Ataxia Susan L. Perlman, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Director, Ataxia Clinic Is Anything Non-Genetic? 1,212,000 references in PubMed under genetics
Non-Genetic Ataxia Susan L. Perlman, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Director, Ataxia Clinic Is Anything Non-Genetic? 1,212,000 references in PubMed under genetics
Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes
 Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes Poster No.: C-0851 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Onu, L. Badea,
Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes Poster No.: C-0851 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Onu, L. Badea,
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection
 Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
Deep Brain Stimulation: Patient selection Halim Fadil, MD Movement Disorders Neurologist Kane Hall Barry Neurology Bedford/Keller, TX 1991: Thalamic (Vim) DBS for tremor Benabid AL, et al. Lancet. 1991;337(8738):403-406.
Terminoloogia. Psühhoos. Klassifikatsioon: Klassifikatsioon:
 PSÜHHOOSI TERMINOLOOGIA, ETIOPATOGENEES JA KLIINILINE PILT. Dr. Evelin Eding PERH Psühhiaatriakliiniku vanemarst. Pärnu 30.11.2007 Terminoloogia Psühhoos psüühikahäire, mille puhul mõtlemine, tundeelu,
PSÜHHOOSI TERMINOLOOGIA, ETIOPATOGENEES JA KLIINILINE PILT. Dr. Evelin Eding PERH Psühhiaatriakliiniku vanemarst. Pärnu 30.11.2007 Terminoloogia Psühhoos psüühikahäire, mille puhul mõtlemine, tundeelu,
