The Relationship Between Vital Energy and the Human Brain and the Autonomic Nervous System
|
|
|
- Angela Nelson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DISCLAIMER The information contained within this document does not constitute medical advice or diagnosis and is intended for education and information purposes only. It was current at the time of publication and every effort is made to keep the document up to date. The information contained herein includes both psychological and non psychological interventions. The delivery of psychological services requires a medical referral whilst non psychological services do not. Each person is an individual and has a unique psychological profile, biochemistry, developmental and social history. As such, advice will not be given over the internet and recommendations and interventions within this website cannot be taken as a substitute for a thorough medical or allied health professional assessment or diagnosis.
2 The Relationship Between Vital Energy and the Human Brain and the Autonomic Nervous System Article QUICK LINKS : Introduction / Composition of the CSF / The Human Brain / Frontal Lobes (or Prefrontal Cortex) / The Cingulate system / Temporal Lobes / Brain Stem / Cerebellum / Limbic System / The Human Nervous System / Further Reading Suggestions / References INTRODUCTION Physicians originally regarded the healing principles as an art and creative work of service to humanity and the "idea" of "healing" pervades all cultures. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity". According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, "while the level of disease or infirmity can be assessed by mortality, disability and morbidity statistics, the presence of positive wellbeing is more difficult to measure". At this time in history we are at the cross roads of a paradigm shift in the way that we view the world around us. In Western society we are moving away from the century old allopathic model of medicine of anaesthetising pain or cutting it out, and reaching toward a more integrative approach to healing, of 'functional medicine' through balancing lifestyle, good nutrition, spirituality and vital energy necessary for good health. Prevention is indeed better than the cure. Biological, mechanical and chemical processes are no longer absolutely repeatable in double blind studies. The notion of spirit, energy transfer and quantum physics renders the scientific model as we know it increasingly obsolete. The very idea of creative consciousness in healing was for a time, lost in the science of our times, which is largely materially based and "of course minds trained to material concepts only can not be expected to function well at altitudes of penetration, comparison, and compassion". The central theme of 'life' was lost in our search for countless external details in matter only. The general practice of today is grossly physical rather than 'atomic' in its principle and application. This means that many modern physicians work mainly with symptomatics - treating usually just the symptoms and NOT the underlying cause. Scientific focus on the implications of chemistry and 'curing' symptoms appears to have blinded us to another vital component of our being. The idea of energy fields in action through physiological functions, according to the finer lines of force and mind energy patterns, is not yet generally accepted. 2 / 21
3 For true healing to take place, it must be applied from a dedicated, integrative and spiritual approach in tandem with the patient's own efforts and in full knowledge of the scientific discoveries of our times. Keith Thomas once said "ALL THAT IS CURRENTLY KNOWN IS NOT ALL THAT WILL EVER BE KNOWN". Current paradigms will be slow to change, but shift does happen!! Witness the Ptolemaic Earth at the center of our universe and how it finally gave way to Copernican theory. Witness also David Bohm's current theory of "Implicate Order" in light of the non-linear physics of "Chaos Theory", Or Rupert Sheldrake's theories of "Morphic Resonance". In protecting the prevailing paradigms, science and medicine, like all institutions move ever so slowly, so as purportedly 'not to make mistakes'. As a consequence, genuinely new and important ideas can tend to be subjected to intense and unprecedented scrutiny, or alternatively they are reviled, and rejected out of hand. And older philosophies such as vitalism which respects the individual's inherent rights to functional integrity are lost in the archives. In nature, each individual pattern is sustained by the whole through its latent powers of attraction within its own electro-magnetic energy field, which is reliant upon its seed pattern keynote. This keynote is the central core of its creative energy field as an individual, separate being, endowed with consciousness and awareness and potential for growth. The philosophy and study of the body as a manifestation of consciousness now provides a physical foundation for psychology and psychiatry through the concepts of cellular memory. The core of man lies in the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the cerebrospinal tract. In fact, Randolph Stone, DO DC, once said that "the human soul swims in a sea of cerebrospinal fluid". This is interesting, as there is also an ancient Chinese concept of 'Sui-Hai-ku' - which means "Brain Sea". The allegory is apt as the sea ebbs and flows, is subject to electrical storms, is salty and full of myths, phantasms and beasts. The brain as it lies suspended in CSF is like a sea creature, passively waiting in the depths, pumping and billowing, processing and waiting. It knows. 3 The Eastern idea of the chakras as centres of energy in the human body has long been substantiated through simple anatomy and the correlation to major nerve plexuses within the body and emanating from the spinal column or cord. 3 / 21
4 4 / 21
5 This core essence and the currents of the energy fields within us and around us, provide for us that within which we move and have our being as a living human entity in harmony and health or disharmony and disease. Ancient writings, particularly the Vedas (6,000 BC), tell us that the core of man follows a twin serpentine pathway describing the flow of kundalini or vital energy around the spinal column. (viz. The Caduceus or Staff of Hermes). Modern anatomical and physiological investigation now confirms this ancient representation in the spiral flow of cerebrospinal fluid within the membrane known as the dura mater, and the intricacy of the serpentine crossover or decussation 8, of spinothalmic tracts or afferent and efferent pathways of the spinal cord itself. Brain, Ventricles, Spinal Cord and Meninges in sagittal section 5 / 21
6 Candace Pert, a neuroscientist, biochemist and researcher into the body / mind connection, tells us in her book 'Molecules of Emotion', that molecules called neuropeptides are the chemical carriers of our essence, and that the memories and patterns of man are locked into the cellular and perhaps even molecular makeup of his physical being. 5 Bodyworkers have long known that relaxing chronically tight muscles, or activating certain trigger or reflex points can actually trigger remembrance of traumatic incidents in our lives that we had thought that we had put behind us and all but forgotten. Coupled with guided imagery, this phenomenon has developed into a therapeutic technique that has become known as Somatoemotional Release. 10 Modern anatomy shows us that cerebrospinal fluid has many functions and is significantly more complex than generally thought of. The whole of the bodily processes are dependent upon this innocuous fluid. Anatomical texts tell us that CSF is a clear and colourless, slightly viscous fluid. 8 The Classic Collector's Edition of Gray's Anatomy describes it as being "a clear, limpid fluid, having a saltish taste and a slightly alkaline reaction". The same text says of it's 'chief function' as "probably to afford mechanical protection to the nervous centres, and to prevent the effects of concussions communicated from without". As we shall see, mechanical protection is only one of the CSF functions, but the main problem here is that the observation is of dissected corpses, and not of the living man. In a living person, the CSF is actually quite viscous and in fact, yellowish in colour. Ask any emergency worker who has attended cases of traumatic head injury and witnessed the flow of living CSF. COMPOSITION OF THE CSF CSF differs from plasma and blood. It is primarily different in its electrolyte composition and the fact that it is relatively protein free. The blood / brain barrier is designed to feed the CNS only the end product elements refined from the metabolism of food. Formed in the mid-brain in a structure known as the choroid plexus, CSF is classified as a secretion rather than a simple filtrate. CSF volume in the body is some 150 ml, which is reabsorbed as rapidly as it is formed, approximately 20m/hr or about 480 ml per day. 8 It has a specific gravity of 1.007, with a ph of It is primarily composed of the following elements: Glucose: The brain is quite greedy when it comes to glucose, consuming between %. The brain will sacrifice a lot of body function to keep its glucose levels consistent. Glucose levels in cerebrospinal fluid are usually between between mmol/l. Monocarboxyllic Acid Amino Acids: These are transported across the blood/brain barrier by one of three carriers according to their status - acidic, neutral or basic (alkaline). There is competition for carrier molecules, hence dietary supplementation can influence which amino acids cross. Tryptophan for example competes with 5 other neutral acids and is the precursor for synthesis in the brain of the neurotransmitter serotonin. 6 / 21
7 Nucleic Acids: These include specific carriers for adenine and nucleosides. Choline: (amine) Hormones: Vitamins: The B group are especially prevalent Electrolytes: The brain electrolyte balance is in delicately maintained homeostasis. This is acheived through junctions, gradients and other transport mechanisms. The CSF is in free equillibrium with cerebral interstitial fluid, the unwavering composition of which is vital to the maintenance of the functional integrity of the brain. Sodium (Na+) is the most abundant ion in CSF, ECF and plasma, accounting for 95%of the cation of these fluids. Other CSF electrolytes are K+, Ca++, Mg++, and Cl- as well as HCO3- (bicarbonate ion). It also contains some lymphoycytes (- from 0-10 lymphocytes per mm3) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) at g/L. The electrical nature of CSF is well known. The ions facilitate the rhythmic electrical activity and the generation and delivery of the action potential in the central nervous system. This activity is basic to neurological and therefore - all function. Even slight changes in the ionic composition of CSF could seriously disrupt production of postsynaptic potentials and action potentials. Cerebrospinal fluid contributes to homeostasis in three main ways. 1. Mechanical Protection: The fluid serves as a shock absorbing medium to protect the delicate tissue of the brain and spinal cord that would otherwise cause them to crash against the bony walls of the cranial and vertebral cavities. The fluid buoys the brain so that it 'floats' in the cranial cavity. 2. Chemical Protection: CSF provides an optimal chemical environment for accurate neuronal signalling. 3. Circulation: CSF is a medium of exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and nervous tissue. 7 / 21
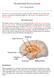
8 THE HUMAN BRAIN The human brain sits at the top of our living caduceus, controlling bodily functions in near perfect homeostasis. As the body's command centre, it is jealously guarded, 'floating' in a nourishing and protective sea of Cerebro Spinal Fluid (CSF), bounded by the meninges - the dura mater (which means literally - 'Strong Mother'), the sub-arachnoid space and the pia mater, and of course the hard casing of the human skull. Nevertheless, even a slight blow to the head from any angle can potentially cause substantial damage to the delicate nerve fibres and neural networks that form our functional and thinking patterns. Obtaining a general understanding of the brain and its functions is important to understanding the rehabilitation process in any presenting difficulty. It is very important, however, to understand that rehabilitation concerns the whole person not just the 'affected part'. The identification of an individual problem simply gives the therapist areas in which to focus treatment plans designed to work toward the rehabilitation/rebalancing of the whole person. Each problem area affects other areas. Resolving one problem often has a major impact on other problems. For example, re-establishing postural balance and eliminating dizziness greatly enhances concentration and attention, which allows for improved cognition and problem solving. The Basic Divisions of the Human Brain 8 / 21
9 Diagrammatic Sagittal Detail Dysfunction or injury to the brain may occur in a specific location, or may be diffuse (many different locations). Difficulties resulting from brain dysfunction include: Visual illusions - inaccurately seeing objects. Word blindness - inability to recognize words. Difficulty in recognizing drawn objects. Inability to recognize the movement of an object (Movement Agnosia). Difficulties with reading and writing. Short term memory difficulties Personality changes and / or emotional liability FRONTAL LOBES (or Prefrontal cortex) Located at forehead above eyes. The frontal lobes receive input from various neocortical regions including the dorsomedial thalamic nucleus, and the parietal association cortex. The prefrontal orbital cortex, however, receives fibres from the pars magnocellularis of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, and from the mesencephallic recticular formation as well as from limbic structures. In this way the prefrontal cortex appears to receive information about all sensory modalities and also about motivational and emotional states of the individual. There are strong efferent connections to the motor and pre motor cortex, the basal ganglia and the caudate nucleus. Orbital-prefrontal regions send fibres into the hypothalamus, subthalamus, septum, mesencephalon and the pons / 21
10 Functions associated with the frontal lobes: Conscious thought Concentration Perseverance Judgement Attention span Impulse control - self monitoring and supervision Problem Solving Organisation Critical thinking Forward thinking Ability to feel and express emotions Empathy 10 / 21
11 Decreased activity in the prefrontal cortex is a finding often cited in people who have cognitive difficulty, such as in schizophrenia or major depression. Abnormal frontal activity is a major factor in ADD and ADHD. The prefrontal cortex is involved in mediating concentration, impulse control and critical thinking. THE CINGULATE SYSTEM At the top of the brain, in the middle of the frontal lobes is an area of the brain termed the "cingulate gyrus". It is the part of the brain which allows you to shift your attention from thing to thing, to move from idea to idea, to see the options in life. Feelings of safety and security have also been attributed to this part of the brain. The term that possibly best relates to this part of the brain is 'cognitive flexibility'. Functions of the Cingulate System: Allows shifting of attention Helps the mind move from idea to idea Allows the mind to see options Cognitive flexibility (helps you go with the flow) Adaptability Ability to cooperate Increased activity in the top, middle portions of the frontal lobes is frequently cited as a finding in obsessive-compulsive disorder, a condition where people become "stuck" on certain thoughts or behaviours. Aggressive people often become "stuck" on real or imagined injustices and think about them over and over. Oppositional, and addictive behaviours are also evident. Chronic pain, eating disorders and road rage appear to accompany cingulate dysfunction. 11 / 21
12 TEMPORAL LOBES Located at sides of head above ears, the temporal lobes form the wings of the soul of our living caduceus. FUNCTIONS The dominant side is usually the left hand side and governs: Hearing ability Understanding and processing language Memory acquisition - particularly long term memory Some visual perceptions Categorisation of objects. The non dominant side or right side governs: Recognition of facial expressions Decoding vocal intonation Rhythm Music Visual learning OBSERVED PROBLEMS Difficulty in recognizing faces (Prosopagnosia). Difficulty in understanding spoken words (Wernicke's Aphasia). Disturbance with selective attention to what we see and hear. Difficulty with identification of, and verbalization about objects. Short-term memory loss. Interference with long-term memory and amnesia Increased or decreased interest in sexual behaviour. Inability to categorise objects (Categorisation). Right lobe damage can cause persistent talking. Increased aggressive behaviour. Dark or violent thoughts Religious or moral preoccupation Social skill troubles Emotional instability 12 / 21
13 Hypergraphia (excessive writing) Periods of spaciness or confusion Seizures BRAIN STEM Located deep in the brain, leads to spinal cord. Often referred to as The 'Reptilian' or 'Primitive' Brain. The majority of the cranial nerves exit from the brain stem at the pons. FUNCTIONS Breathing Heart Rate Swallowing Reflexes to seeing and hearing (Startle Response). Controls sweating, blood pressure, digestion, temperature (Autonomic Nervous System). Affects level of alertness. Ability to sleep. Sense of balance (Vestibular Function). OBSERVED PROBLEMS Decreased vital capacity in breathing, important for speech. Swallowing food and water (Dysphagia). Difficulty with organisation/perception of the environment. Problems with balance and movement. Dizziness and nausea (Vertigo). Sleeping difficulties (Insomnia, sleep apnoea). 13 / 21
14 CEREBELLUM Located at the base of the skull, and attached to the rear of the brain stem. It is sometimes referred to as The Little Brain. FUNCTIONS Coordination of voluntary movement Balance and equilibrium Some memory for reflex motor acts. OBSERVED PROBLEMS Loss of ability to coordinate fine movements. Loss of ability to walk. Inability to reach out and grab objects. Tremors. Dizziness (Vertigo). Slurred Speech (Scanning Speech). Inability to make rapid movements. LIMBIC SYSTEM Is a group of cellular structures located between the brainstem and the cortex. It is often referred to as the mammalian brain. FUNCTIONS Maintaining homeostasis - body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, blood sugar levels. Controls appetite and sleep cycles Strongly linked to emotional reactions that have to do with survival. Sets the emotional tone of the mind Filters external events to internal states (creates emotional colouring) Ear marks events as internally important Stores highly charged emotional memories Modulates motivation Promotes bonding Directly processes the sense of smell (which is another reason why aromatherapy can be so effective) Modulates libido 14 / 21
15 The limbic system has two key components: the hypothalamus (below the thalamus) and the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus regulates eating, drinking, sleeping, waking, body temperature, balance and many other functions. Through a combination of electrical and chemical messages, it directs the pituitary gland - the master gland of the body. OBSERVED PROBLEMS Moodiness, irritability and clinical depression Increased negative thinking Negative perceptions of events Decreased motivation Appetite and sleep problems Increased or decreased sexual responsiveness Social isolation The human brain has evolved over time, and from the archaeological records, it has demonstrated spectacular growth in the past few million years. This growth, presumably in consciousness as well as size and capacity for creativity, allowed us to change the environment in which we live and our ability to make those changes is increasing. The problem lies in the fact that our ability to create always leaps ahead of our ability to adapt. Thus we are locked in a cycle of adapting to unprecedented situations. 15 / 21
16 If there are too many changes in our lives, our ability to adapt may be taxed to the limit, and we may become ill. In our modern society, the number of 'changes' that we experience is far greater than we were designed for, our current environment is, for many people beyond their biological limits. But just how does stress cause disease? The emergency reaction, which is a primitive survival mechanism, is under the direct control of the brain. It stimulates the heart to beat faster and directs peripheral blood vessels to clamp down, thus increasing blood pressure. The principle neurotransmitters (chemical carriers of messages between nerve connections) that accomplish this are epinepherine (adrenaline) and norepinepherine (noradrenaline). This brings us to / 21
17 THE HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM The central nervous system (CNS) is representative of the staff of our living caduceus. The sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic (PNS) systems, like the cerebrospinal pathway, are representative of the twin serpentine pathway of kundalini energy, activating the chakric centres or nerve plexuses as it rises up the spinal cord in sushumna to the brain centres (hence the practice of Kundalini Yoga). Human nervous system physiology is generally divided into the central nervous system (CNS), comprising the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which comprises nervous tissue outside the CNS, including the cranial and spinal nerves. 1 The peripheral nervous system is further divided into the somatic system, concerned with muscular activities, and the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls visceral structures (glands and organs of the body). Finally, the ANS is sub-divided into the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), the innervation mechanisms dominate when the individual is at rest, and the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), which is dominate in situations requiring mobilisation of energy. The following schematic drawing explains these divisions somewhat, but is imperfect due to the fact that there are some parts of the ANS which are under the control of the CNS. For example, the hypothalamus and medulla are important in control of ANS functions, so the autonomic nervous system in fact has its nuclei within the central nervous system. 17 / 21
18 IMAGE MISSING The ANS in Western medicine is believed to be exclusively motor in its function. That is, it sends out impulses to various organs and systems in the body so that the body functions automatically without the conscious control of the owner of the body. 10 In the East and the Orient, practices such as yoga, tai-chi, qi-gong, breathwork and meditation (all techniques of self-directing vital energy) have been used to beneficially influence the autonomic nervous system (ANS) for centuries. It was not until the advent of biofeedback (Especially the pioneering work of Drs. Elmer and Alyce Green), that Western science demonstrated that this could be so. More importantly, biofeedback training in combination with diet and specific exercises, has been clinically demonstrated to bring the ANS under the conscious control of its owner, enhancing stability, balance, flexibility and adaptability are the corner stones of optimal function and homeostasis. The significance of this is easily recognised in the divisions of the human populace in terms of behaviour. Classifications of 'Type A' and 'Type B' in this regard is well known. Type A persons are generally have an exaggerated reaction to the stresses of daily life. These individuals are coronary prone, and have been described as fast-paced, impatient, and irritable; they tend to be deeply involved in their work, and deny failure, fatigue and illness. Type A's tend to try to get more and more done in less time. Type A individuals are twice as likely to develop heart disease than Type B's, who may be as successful, but tend to be calmer, better organised, less 'time urgent', concerned more with quality than quantity, and generally less prone to frustration. Type A's tend to be more SNS hypertonic, and type B's are more PNS. As mentioned, the ANS is divided into two systems - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) ganglia are located most often near the spine, its roots lying in the thoracic and lumbar regions. Hence it is sometimes referred to as the thoracolumbar division. The parasympathetic ganglia are usually located near the organs that they innervate, send impulses to, or otherwise essentially control. Its nerve roots exit the CNS from the brain stem, and the lower or sacral end of the spinal cord. The PNS is sometimes referred to as the craniosacral division. The sympathetic part of the nervous system is the one which takes care of emergency responses. Flight or Fight. The SNS is called to arms on a daily basis. Sometimes, this is done without the SNS being allowed to express the energy that it has procured for the perceived excessive demand. This situation when repeated over and over, results in an elevated baseline of activity and the result of this sympathetic hyperactivity is chronic stress, which in turn leads to all kinds of stress related health problems. (Ulcers of the stomach and / or bowel, high blood pressure, hardening of the arteries, high cholesterol, coronary artery 18 / 21
19 disease, chest pains and stroke to name a few). The SNS then, expends our vital energy. On the other side of the coin we have the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), who's job it is to balance and restore energy reserves to safe levels. The 'spending habits' of your sympathetic nervous system vary with your personality. If you are chronically angry, fearful, guilty etc., the chances are that your sympathetic nervous system is in chronic hyperalert. If you tend to be complacent, secure, happy, and accepting, your SNS baseline will be lower, and the easier it is for your PNS to rebalance your energy levels. Clearly then, any technique which can lower stress levels is going to be beneficial to your health. The autonomic nervous system as already mentioned, influences internal organs and organ systems. When stimulated, the sympathetic nerves 1. Increase heart rate 2. Increase blood flow to heart muscle 3. Increase blood flow to skeletal muscle 4. Increase skeletal muscle strength and performance 5. Reduce blood flow to the skin 6. Reduce blood flow to all internal organs 7. Reduce conscious thought processes in the higher brain centres 8. Shut down digestive processes 9. Shut down peristalsis 10.Shut down kidney function 11.Open the bronchi 12.Raise blood sugar It is important to note that all processes that are not necessary in the immediate moment for the perceived activity are shut down - including healing which is in process! Parasympathetic nervous system responses are almost the exact opposite of the SNS. When activated, the PNS nerves slow heart rate, lower blood pressure, open the blood vessels to the skin and internal organs. The PNS has little influence over skeletal muscle, however, it does influence smooth muscle, and thus provides positive stimulation of the gastrointestinal system, enhancing peristalsis, digestion and elimination. 19 / 21
20 Most glands in the body secrete their hormones when the PNS goes into action. The adrenal glands however, which aid the SNS in it's 'flight or fight' response, are slowed by the PNS. PNS activity favours anabolic activity - that is, it favours the absorption of nutrients and calories, and their conversion into stored energy and/or the formation of protein building blocks. SNS activity depletes these energy reserves and this in turn depletes our immune system. Indirectly, the ANS divisions (sympathetic and parasympathetic) are very much involved in our responses to emotions such as fear, anger, rage, panic, pleasure, etc. In actuality, these emotions are triggered by higher brain centres which send messages to the ANS control centres, dictating in turn many of the bodily functions and responses. The responses then produce additional sensory input, which then contributes to a continuation of the emotional response. The emotional response then has potential to escalate unless the higher brain centres are able to intervene. Thus it is easy to see the delicate balance and how easy it is for us to become locked into a thought pattern against our conscious volition. Equally, it is easy to see how the cycle may be broken through the use of vital energy techniques and other training such as biofeedback. The human brain is marvellous in its resilience and capacity for adaptation. The concept of brain "plasticity" is transforming neuroscience. Michael M. Merzenich, (University of California, San Francisco Medical Centre), asserts that "the brain was constructed to change". "The plasticity of the living matter of our nervous system is the reason we do a thing with difficulty the first time, but soon do it more and more easily and finally with sufficient practice, do it semi-mechanically or automatically. The brain is built for change and functions in the environment in which it grows. The brain of every individual is continuously shaping its own processing and performance capabilities. Our capabilities reflect not just WHAT we ve learned- but also how our brain has evolved TO learn. By its very nature, the brain s self-organising process is time based" (Menzenah14). Given this plasticity, is it not possible then for the brain to heal itself too, given appropriate stimulation? FURTHER READING SUGGESTIONS Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) & Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Brain Injury QEEG and Neurofeedback - diagnostic and training modalities for the enhancement of CNS functioning in ADHD and other disorders For more information or to make an appointment please contact us on (02) during business hours. 20 / 21
21 REFERENCES 1. Andreassi, J.L., Psychophysiology, Human Behaviour & Physiological Response, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, New Jersey. 2. Burger, B., Esoteric Anatomy, 1998, North Atlantic Book, Berkley, California. 3. Cohen, D., (DC), An Introduction to Craniosacral Therapy - Anatomy, Function, and Treatment, 1995, North Atlantic Books, Berkley, CA, USA. 4. Ornstein, R. and Thompson, R.F., The Amazing Brain, 1984, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 5. Pert, Candace B.(Phd), Molecules of Emotion , Scribner - New York, USA. 6. Stone, R., (DO, DC), Polarity Therapy - Vol I, , CRCS Publications, Somertown, TN, USA. 7. Stone, R., (DO, DC), Polarity Therapy - Vol II, , CRCS Publications, Somertown, TN, USA. 8. Tortora, G.J.(MA.BS), and Grabowski, S.R.(Phd), Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 1993, Harper Collins Publishers, New York, USA. 9. Upledger, J., (DO,DC, F.A.A.O.), Vredevoogd, J.D., (M.F.A.), Caraniosacral Therapy, 1983, Eastland Press, Seattle, Washington. 10.Upledger, J., (DO,O.M.M.), A Brain is Born, 1996, North Atlantic Books, Berkeley, California. 11.Niedermeyer, E.(M.D.), Frontal Lobe Functions and Dysfunctions, Clinical EEG Electroenchalography, Vol. 29, No.2, April Krebs, C., (Dr.), A Revolutionary Way of Thinking, 1998, Hill of Content Publishing, Melbourne, Australia. 13.Amen, D.G., (MD), Healing ADD, 2001, G.P. Putnam's Sons, New York, NY 14.Merzenich, M.M. (2001): "Brain Plasticity". Paper delivered at the International Society for Neuronal Regulation Annual Conference, Monterey, CA. See also the article "The Mutable Brain" by Marguerite Holloway in Scientific American, September 2003, / 21
The Human Brain INTRODUCTION
 DISCLAIMER The information contained within this document does not constitute medical advice or diagnosis and is intended for education and information purposes only. It was current at the time of publication
DISCLAIMER The information contained within this document does not constitute medical advice or diagnosis and is intended for education and information purposes only. It was current at the time of publication
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system
 Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
The Emotional Nervous System
 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Nervous System and Special Senses HEALTH SCIENCE
 Nervous System and Special Senses HEALTH SCIENCE Bellwork!! What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-time-test/ State Standards 8) Outline
Nervous System and Special Senses HEALTH SCIENCE Bellwork!! What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-time-test/ State Standards 8) Outline
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Instructor s Review for Final Exams. The Nervous System
 Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
8.3 The Central Nervous System. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Nervous System. Dentalelle Tutoring. 1
 Nervous System Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com 1 Basics The nervous system along with the endocrine (hormonal) system works to control all activities within the human body. It does this by communicating
Nervous System Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com 1 Basics The nervous system along with the endocrine (hormonal) system works to control all activities within the human body. It does this by communicating
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
The Nervous System An overview
 Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, WORKBOOK - Biology WORKBOOK. Student:
 WORKBOOK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Teacher: Student: Biology Iva Kubištová.. School year:../ This material was prepared with using http://biologygmh.com/ Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nervous system, Senses,
WORKBOOK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Teacher: Student: Biology Iva Kubištová.. School year:../ This material was prepared with using http://biologygmh.com/ Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nervous system, Senses,
A Healthy Brain. An Injured Brain
 A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Amani Nofal. -Loai Alzghoul
 -1 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Amani Nofal -Loai Alzghoul 1 P a g e Today we will start talking about the physiology of the nervous system and we will mainly focus on the Central Nervous System. Introduction:
-1 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Amani Nofal -Loai Alzghoul 1 P a g e Today we will start talking about the physiology of the nervous system and we will mainly focus on the Central Nervous System. Introduction:
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
2. When a neuron receives signals, an abrupt, temporary the inside becomes more positive in the polarity is generated (an action potential).
 Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Chapter 8. The Nervous System
 Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
E) A, B, and C Answer: D Topic: Concept 49.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Neurotransmitter: dopamine. Physiology of additive drugs. Dopamine and reward. Neurotransmitter: dopamine
 Physiology of additive drugs Cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and opiates influence the neurotransmitter dopamine. Neurotransmitter: dopamine Dopamine - a neurotransmitter associated with several functions,
Physiology of additive drugs Cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and opiates influence the neurotransmitter dopamine. Neurotransmitter: dopamine Dopamine - a neurotransmitter associated with several functions,
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1).
 1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424. By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi
 Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424 By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions, mental activities,
Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424 By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions, mental activities,
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
The Human Brain: Anatomy, Functions, and Injury
 The Human Brain: Anatomy, Functions, and Injury Main Menu Brain Anatomy Brain Functions Injury Mechanisms Brain Anatomy Menu Skull Anatomy Interior Skull Surface Blood Vessels of the Brain Arteries of
The Human Brain: Anatomy, Functions, and Injury Main Menu Brain Anatomy Brain Functions Injury Mechanisms Brain Anatomy Menu Skull Anatomy Interior Skull Surface Blood Vessels of the Brain Arteries of
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
