Interferon- induction and related signaling pathways in human hepatocyte cell lines
|
|
|
- Adam Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 81 1, *, 2, *, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2 1. /, ; 2. ( ), : ( IFN- ), IFN-, ( HBV), 3 PH5CH8 Huh7 HepG2, IFN- ( NDV) - poly( I C), IFN-, Huh7 HepG2, PH5CH8 NDV poly( I C) IFN- 3 IFN-,, PH5CH8, Huh7 HepG2 HBV, IFN : ; ; ; Interferon- induction and related signaling pathways in human hepatocyte cell lines CHEN Hui 1, *, WU Min 2, *, YU Shi-Yan 1, 2, CHEN Jie-Liang 1, 2, YUAN Zheng-Hong 1, 2 1. Key Laboratory of Medical Molecular Virology, Ministry of Education and Health, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai , China; 2. Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center Affiliated to Fudan University, Shanghai , China Abstract: Interferon- plays an important role in innate immunity against viral infection. Hepatocytes, as hepatitis viruses-harboring cells, are reported to possess the potential to inductively express interferon-. However, a practical in vitro cell model for investigating the interplay between hepatitis B virus and host cells is rarely reported. Here, we determined the inductive expression of interferon- by interferon- agonists ( Newcastle disease virus, NDV) and poly ( I C) in immortalized primary hepatic cell line, PH5CH8, and hepatocarcinoma cell lines, Huh-7 and HepG2. The data demonstrated that inductive expression of interferon- in PH5CH8 cells was significantly higher than that in Huh7 or HepG2 cells. In addition, the expression level of key molecules critical for interferon- induction was investigated to clarify the underlying mechanism. The results showed that the background expression level was fairly low in Huh7 and HepG2 cell lines, compared to that in PH5CH8 cells. It is suggested that PH5CH8 cells possess intact potential to produce interferon- and reconstitution of a selective interferon-deficient hepatic cell line might be achieved via introduction of related molecules critical for interferon induction. Key words:hepatocyte; Interferon- ; Induction signaling pathway; Interferon- agonists : 973 ( 2005 CB522902), ( EYF162002) :, zhyuan@ shaphc. org Corresponding author: YUAN Zheng-Hong, zhyuan@ shaphc. org * : ( hepatitis B virus, HBV) ( hepatitis C virus, HCV) [ 1],, [ 2, 3 ]
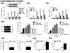
2 Journal of Microbes and Infection, June 2009, Vol. 4, No. 2 ( interferon-, IFN- ) ( interferon-, IFN- ), [ 4] ( ), HCV [ 5], NS3/ 4A IFN- TIR ( Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-, TRIF) [ 6] 1( interferon- promoter stimulator 1, IPS-1) [ 7 ] ; HBV Toll ( Toll-like receptor, TLR) [ 8], 1 ( signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, STAT1) [ 9] ;,, Huh7 HepG2 2, 2, Huh7 TLR , HepG2 TLR , [ 10 ],,, PH5CH8 1 HCV, prsv-tag ( SV40 T ) G418 [ 1 1], TLR3 A ( retinoic acid-inducible gene-, RIG- ) 5( melanoma differentiation-associated gene- 5, MDA-5) [ 12], IFN- ( Newcastle disease virus, NDV) - ; poly ( I C) < PH5CH8 Huh7 HepG2, ( polymerase chain reaction, PCR) ( enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA) IFN-,, IFN-, % CO 2, 3d 1, PH5CH8 Okayama Nobuyuki Kato, 2 mmol /L 100 g/l ( Toyobo ) 10 mg/l ( Gibco ) 5 mg/l ( Gibco ) mol/l ( Gibco ) 0. 1 mol /L ( Gibco ) 5 mg/l ( Gibco ) 100 g/l ( Gibco ) 2% ( Gibco ) 10 mg/l ( Gibco ) 200 mg/l ( Sigma ) 500 g/l ( Gibco ) DMEM( Gibco ) F-12( Gibco ) ( 1 1) [ 13 ] ; Huh7 HepG2, 10% u/l 100 mg/l DMEM 1. 2 pifn- -Luc IFN- pgl3-luc, McGill Rongtuan Lin ( firefly luciferase, Fluc) prl-tk ( Renilla luciferase, Rluc),, Promega 1. 3 NDV poly( I C) NDV ( NDV PSF 48 h,,, NDV ) 100 HAU/ml ; poly( I C) ( Sigma ) 50 mg/l, 1. 4 RNA PCR 200 l TRIzol ( MRC ) RNase/DNase EP 1/5
3 83 5 min, g 15 min, g 10 min % 300 l, g 10 min,, 10 min 25 l DEPC ddh 2 O, 10 u DNase ( RNase-free) ( TaKaRa ), min DNA, 30 u ( Toyobo ) cdna, 2 l 10 pmol/l ( 1) PCR ( 25 l) PCR GAPDH, PCR 3 1 PCR Tab 1. Primers used for real-time PCR Primers Forward ( 5 3 ) Reverse ( 5 3 ) IFN- GATTCATCTAGCACTGGCTGG CTTCAGGTAATGCAGAATCC IRF7 TGGTCCTGCTGAAGCTGGAA GATGTCGTCATAGAGGCTGTTGG MxA CCACTGGACTGACGACTTGA GAGGGCTGAAAATCCCTTTC ISG56 TAGCCAACATGTCCTCACAGAC TCTTCTACCACTGGTTTCATGC GAPDH GGTATCGTGGAAGGACTCATGA ATGCCAGTGGCTTCCCGTTCAGC , 90% Fugene 6( Roche ) 25 ng pifn- -Luc 10 ng prl-tk,36 h NDV poly( I C), 16 h 200 l 1 Passive Lysis Luciferase Assay System ( Promega ) Lumat LB9507 Fluc Rluc, 10 s, Fluc Rluc ELISA , 90% NDV poly( I C), 16 h, IFN- ( FUJIREBIO ) ELISA OD ( 450 nm), IFN-, IU/ml cm, 48 h, 2 SDS Loading, 10 min 10 l 10% - ( sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE) ( 10 ma, 3 h) ( 300 ma, 60 min) 0. 2 m ( Schleicher & Schuell ), 5% -20 ( phosphate buffered saline with0. 5% Tween-20, PBST) ; 3 h, 4, 1 PBST 10 min, 3, C ( horse radish peroxidase, HRP), 2 h, 1 PBST 10 min, 3, Western Lightning ( PerkinElmer ), ( Kodak ) -actin( Sigma ) CST , 3 t, P < IFN- NDV poly( I C) IFN-, TLR3 RIG- IFN- [ 14 ] IFN-, NDV PH5CH8 Huh7 HepG2, poly ( I C) PH5CH8 Huh7 ( ), 6 h TRIzol RNA, PCR, IFN-, PH5CH8 NDV, IFN , Huh7 HepG
4 Journal of Microbes and Infection, June 2009, Vol. 4, No ( 1A B) ; poly( I C) PH5CH8 IFN- mrna Huh7 ( 1C), 7 ( interferon regulator factor 7, IRF7) [ 15 ], NDV PH5CH8 Huh7 IRF7 mrna,, PH5CH8 NDV IRF7, Huh7 ( 1D) 2. 2 IFN- IFN-, PH5CH8 Huh7 HepG2 IFN-, TLR MyD88 TRIF, RIG- IPS-1, 2( tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2, TRAF2) TRAF3 TRAF6, 1 1 ( interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1, IRAK1) IRAK4, PH5CH8, Huh7 HepG2 TRIF IRAK1 TRAF3 TRAF6, MyD88 IRAK4 ( 2) A: PH5CH8, Huh7, HepG2 cells in 24-well plates were challenged with 100 HAU/ml NDV for 6 h. Total RNA was isolated and analyzed for IFN- mrna by real-time RT-PCR. All samples were normalized using GAPDH ( housekeeping gene) expression. B: Fold induction of IFN- mrna was calculated by dividing normalized RNA levels of stimulated cells with that of mock-treated cells based on A. C: PH5CH8 and Huh7 cells in 24 -well plates were added with 50 mg /L poly( I C) for 6 h. IFN- mrna was then quantified as that described in A. D: IRF7 mrna of NDV ( 100 HAU/ml, 6 h) - treated PH5CH8 or Huh7 cells was quantified as that described in A. Data ( means SE) were from three independent experiments. * P < IFN- Fig 1. Comparison of NDV- and poly( I C) - induced IFN- production in three cell lines 2. 3 IFN- IFN- c-jun/ 2( activating transcription factor 2, ATF2) B( nuclear factor B, NF- B) IRF3 [ 16], PH5CH8 Huh7 HepG2 ( mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK) / 1( activator protein 1, AP1) I B ( NF- B inhibitor kinases, IKKs) /NF- B
5 85 TANK ( TANK-binding kinase 1, TBK1) / IRF3 IFN-, 3, PH5CH8 NF- B IKK IKK IKK TBK1/IRF3 TBK1 Huh7 HepG2, MAPK/ AP-1 ( 3) PH5CH8, Huh7, or HepG2 cells ( cultured in 10 cm dishes) were lysated in 2 SDS Loading Buffer, separated in 10 % SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against indicated genes ( -actin as loading control). 2 IFN- Fig 2. Comparison of IFN- induction-associated upstream adaptor and kinase expression in three cell lines PH5CH8, Huh7, or HepG2 cells ( cultured in 10 cm dishes) were lysated in 2 SDS Loading Buffer, separated in 10 % SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against indicated genes ( GAPDH as loading control). 3 IFN- Fig 3. Comparison of three signaling pathways critical for IFN- induction in three cell lines 2. 4 PH5CH8 IFN- PH5CH8 IFN-, ELISA PH5CH8 NDV poly( I C) IFN-, NDV poly( I C) PH5CH8 IFN- ( 4A), IFN- ( 4B) MxA ISG56 2 IFN- [ 1 7], IFN-,, NDV 16 h, PCR MxA ISG56 mrna,, NDV PH5CH8 MxA( 4C) ISG56( 4D) PH5CH8 IFN- 3, [ 18 ], HBV,, [ 19 ] Huh7 HepG2 HBV, 2 HBV, [ 20 ] IFN- NDV poly( I C), HepG2 IFN-, Huh7 IFN-, PH5CH8 IFN- mrna, NDV poly( I C) ; ( MxA ISG56 IRF7),, TLR RIG-I
6 Journal of Microbes and Infection, June 2009, Vol. 4, No. 2 A: PH5CH8 cells in 24-wells plates were treated with either NDV( 100 HAU/ml) or poly( I C) ( 50 mg/ ml) for 16 h. Supernant was then collected for ELISA. B: PH5CH8 cells in 24-well plates were co-transfected with pifn- -Luc ( 25 ng) and prl-tk ( 10 ng) for 36 h before treated with NDV( 100 HAU/ml) for 16 h. IFN- promoter activity was represented as the ratio of FLuc to RLuc. MxA ( C) or ISG56 ( D) mrna of NDV ( 100 HAU/ml, 16 h) -treated PH5 CH8 cells was quantified as previously described. Data ( means SE) were from three independent experiments. 4 PH5CH8 IFN- Fig 4. Levels of induced IFN-,IFN- promoter activity and inducible gene expression in primary hepatic cell line PH5CH8 [ 21], Huh7 HepG2 IFN-, Huh7 HepG2 PH5CH8 IFN-, PH5CH8, Huh7 HepG2, IFN- [ 16 ], PH5CH8, Huh7 HepG2 IKK/NF- B TBK1/IRF3, RIG- Huh7 IFN- ( ), Li TLR3 Huh7 poly ( I C) ISGs [ 12 ], Huh7 HepG2,, TLR3 HEK293 TLR3 IFN- [ 22], Huh7 HepG2, PH5CH8 ;, IFN-,, [ 1] Nascimbeni M, Rehermann B. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection [ J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2005, 5( 3) : [ 2] Gao B, Jeong WI, Tian Z. Liver: An organ with predominant innate immunity [ J]. Hepatology, 2008, 47( 2) : [ 3] Racanelli V, Rehermann B. The liver as an immunological organ [ J]. Hepatology, 2006, 43 ( 2 Suppl 1) : S54-S62
7 87 [ 4] Takeuchi O, Akira S. Innate immunity to virus infection [ J]. Immunol Rev, 2009, 227( 1) : [ 5] Naka K, Dansako H, Kobayashi N, et al. Hepatitis C virus NS5B delays cell cycle progression by inducing interferon-beta via Toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway without replicating viral genomes [ J]. Virology, 2006, 346( 2) : [ 6] Li K, Foy E, Ferreon JC, et al. Immune evasion by hepatitis C virus NS3 /4A protease-mediated cleavage of the Toll-like receptor 3 adaptor protein TRIF [ J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102( 8) : [ 7] Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, et al. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus [ J]. Nature, 2005, 437 ( 7062) : [ 8] Wu J, Meng Z, Jiang M, et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses Toll-like receptor-mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells [ J]. Hepatology, 2009, 49( 4) : [ 9] Christen V, Duong F, Bernsmeier C, et al. Inhibition of alpha interferon signaling by hepatitis B virus [ J]. J Virol, 2007, 81( 1) : [ 10] Preiss S, Thompson A, Chen X, et al. Characterization of the innate immune signalling pathways in hepatocyte cell lines [ J]. J Viral Hepat, 2008, 15( 12) : [ 11] Ikeda M, Sugiyama K, Mizutani T, et al. Human hepatocyte clonal cell lines that support persistent replication of hepatitis C virus [ J]. Virus Res, 1998, 56( 2) : [ 12] Li K, Chen Z, kato N, et al. Distinct poly( I-C) and virus-activated signaling pathways leading to interferonbeta production in hepatocytes [ J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280( 17) : [ 13] Noguchi M, Hirohashi S. Cell lines from non-neoplastic liver and hepatocellular carcinoma tissue from a single patient [ J]. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim, 1996, 32 ( 3) : [ 14] Jefferies C, Fitzgerald K. Interferon gene regulation: not all roads lead to Tolls [ J]. Trends Mol Med, 2005, 11 ( 9) : [ 15] Sato M, Suemori H, Hata N, et al. Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN- / gene induction [ J]. Immunity, 2000, 13( 4) : [ 16] Edwards MR, Slater L, Johnston SL. Signalling pathways mediating type I interferon gene expression [ J]. Microbes Infect, 2007, 9( 11) : [ 17] Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Type I interferons in host defense [ J]. Immunity, 2006, 25( 3) : [ 18] Haller O, Kochs G, Weber F. The interferon response circuit: induction and suppression by pathogenic viruses [ J]. Virology, 2006, 344( 1) : [ 19] Iannacone M, Sitia G, Ruggeri ZM, et al. HBV pathogenesis in animal models: Recent advances on the role of platelets [ J]. J Hepatol, 2007, 46( 4) : [ 20] Keskinen P, Nyqvist M, Sareneva T, et al. Impaired antiviral response in human hepatoma cells [ J]. Virology, 1999, 263( 2) : [ 21] Kawai T, Akira S. Innate immune recognition of viral infection [ J]. Nat Immunol, 2006, 7( 2) : [ 22] Yamamoto M, Sato S, Mori K, et al. Cutting edge: a novel Toll/ IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter that preferentially activates the IFN-beta promoter in the Tolllike receptor signaling [ J]. J Immunol, 2002, 169 ( 12) : ( : )
1. TLR. TLR Toll-like receptors. Toll Toll-like receptor, TLR TLR TLR TLR. type I TLR TLR. Toll
 54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
Regulation of cell signaling cascades by influenza A virus
 The Second International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 08) Lijiang, China, October 31 November 3, 2008 Copyright 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 389 394 Regulation of cell signaling cascades
The Second International Symposium on Optimization and Systems Biology (OSB 08) Lijiang, China, October 31 November 3, 2008 Copyright 2008 ORSC & APORC, pp. 389 394 Regulation of cell signaling cascades
Distinct Poly(I-C) and Virus-activated Signaling Pathways Leading to Interferon- Production in Hepatocytes*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 280, No. 17, Issue of April 29, pp. 16739 16747, 2005 2005 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Distinct Poly(I-C)
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 280, No. 17, Issue of April 29, pp. 16739 16747, 2005 2005 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Distinct Poly(I-C)
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai , PR China. Downloaded from by IP:
 Journal of General Virology (2010), 91, 2080 2090 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.020552-0 Hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibits RIG-I- and Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta interferon induction in human hepatocytes
Journal of General Virology (2010), 91, 2080 2090 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.020552-0 Hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibits RIG-I- and Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta interferon induction in human hepatocytes
HCV. Viperin protein inhibits hepatitis C virus replication partially through disturbing the association of nonstructural proteins with lipid rafts
 2009 12 4 4 Journal of Microbes and Infection, December 2009, Vol. 4, No. 4 203 Viperin 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2 1., 200032; 2. /, 200032 :, ( HCV), ( PCR) HCV RNA, HCV,, Viperin HCV, HCV Viperin HCV RNA, Viperin
2009 12 4 4 Journal of Microbes and Infection, December 2009, Vol. 4, No. 4 203 Viperin 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2 1., 200032; 2. /, 200032 :, ( HCV), ( PCR) HCV RNA, HCV,, Viperin HCV, HCV Viperin HCV RNA, Viperin
Hepatitis C Virus and Cytokine Responses
 Hepatitis C Virus and Cytokine Responses Eui-Cheol Shin, M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory of Immunology & Infectious Diseases (LIID), Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering (GSMSE), KAIST Daejeon, Korea
Hepatitis C Virus and Cytokine Responses Eui-Cheol Shin, M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory of Immunology & Infectious Diseases (LIID), Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering (GSMSE), KAIST Daejeon, Korea
IFN TLR TLR TLR. Toll-like receptor TLR. IFN Retinoic acid inducible gene-i RIG-I RIG-I RNA RIG-I RIG-I RIG-I
 58 2 pp.97-104 2008 1. RNA RIG-I 1 2 3 RIG-I RIG-I RNA RNA IFN RIG-I RNA RIG-I RNA RNA RIG-I RNA RIG-I 1 2 Toll-like receptor TLR I 606-8507 53 TEL : 075-751-4031 FAX : 075-751-4031 E-mail: sgo@virus.kyoto-u.ac.jp
58 2 pp.97-104 2008 1. RNA RIG-I 1 2 3 RIG-I RIG-I RNA RNA IFN RIG-I RNA RIG-I RNA RNA RIG-I RNA RIG-I 1 2 Toll-like receptor TLR I 606-8507 53 TEL : 075-751-4031 FAX : 075-751-4031 E-mail: sgo@virus.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Nature Immunology doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Raf-1 inhibition does not affect TLR4-induced type I IFN responses.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Raf-1 inhibition does not affect TLR4-induced type I IFN responses. Real-time PCR analyses of IFNB, ISG15, TRIM5, TRIM22 and APOBEC3G mrna in modcs 6 h after stimulation with TLR4
Supplementary Figure 1 Raf-1 inhibition does not affect TLR4-induced type I IFN responses. Real-time PCR analyses of IFNB, ISG15, TRIM5, TRIM22 and APOBEC3G mrna in modcs 6 h after stimulation with TLR4
Oncostatin M synergistically inhibits HCV RNA replication in combination with interferon-a
 FEBS Letters 583 (2009) 1434 1438 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Oncostatin M synergistically inhibits HCV RNA replication in combination with interferon-a Masanori Ikeda *, Kyoko Mori, Yasuo Ariumi,
FEBS Letters 583 (2009) 1434 1438 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Oncostatin M synergistically inhibits HCV RNA replication in combination with interferon-a Masanori Ikeda *, Kyoko Mori, Yasuo Ariumi,
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Hepatic Expression of HCV RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Triggers Innate Immune Signaling and Cytokine Production
 Short Article Hepatic Expression of HCV RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Triggers Innate Immune Signaling and Cytokine Production Guann-Yi Yu,,,, Guobin He, Chia-Yang Li, Martin Tang, Sergei Grivennikov, Wan-Ting
Short Article Hepatic Expression of HCV RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Triggers Innate Immune Signaling and Cytokine Production Guann-Yi Yu,,,, Guobin He, Chia-Yang Li, Martin Tang, Sergei Grivennikov, Wan-Ting
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/366/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Viral entry route determines how human plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce type I interferons Daniela Bruni, Maxime
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/366/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Viral entry route determines how human plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce type I interferons Daniela Bruni, Maxime
Although it has been recognized as a leading cause of
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:1710 1718 Antiviral Suppression vs Restoration of RIG-I Signaling by Hepatitis C Protease and Polymerase Inhibitors YUQIONG LIANG,*, HISASHI ISHIDA,*, OLIVER LENZ, TSE I LIN,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2008;135:1710 1718 Antiviral Suppression vs Restoration of RIG-I Signaling by Hepatitis C Protease and Polymerase Inhibitors YUQIONG LIANG,*, HISASHI ISHIDA,*, OLIVER LENZ, TSE I LIN,
LETTERS. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses
 doi:10.1038/nature04734 Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses Hiroki Kato 1,3 *, Osamu Takeuchi 1,3 *, Shintaro Sato 3, Mitsutoshi Yoneyama 4, Masahiro Yamamoto
doi:10.1038/nature04734 Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses Hiroki Kato 1,3 *, Osamu Takeuchi 1,3 *, Shintaro Sato 3, Mitsutoshi Yoneyama 4, Masahiro Yamamoto
Role of Innate Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Infection Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D.
 Role of Innate Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Infection Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D. Biology Lead Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Toronto General Hospital Research Institute University Health Network (UHN) HBV
Role of Innate Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Infection Adam J. Gehring, Ph.D. Biology Lead Toronto Centre for Liver Disease Toronto General Hospital Research Institute University Health Network (UHN) HBV
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Hiromichi Dansako 1,2, Daisuke Yamane 1, Christoph Welsch 1, David R. McGivern 1, Fengyu Hu 1, Nobuyuki Kato 2, Stanley M. Lemon 1 * Abstract
 Class A Scavenger Receptor 1 (MSR1) Restricts Hepatitis C Virus Replication by Mediating Toll-like Receptor 3 Recognition of Viral RNAs Produced in Neighboring Cells Hiromichi Dansako 1,2, Daisuke Yamane
Class A Scavenger Receptor 1 (MSR1) Restricts Hepatitis C Virus Replication by Mediating Toll-like Receptor 3 Recognition of Viral RNAs Produced in Neighboring Cells Hiromichi Dansako 1,2, Daisuke Yamane
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Medicine and Health Sciences Commons
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 Induction of IFN-beta and the innate antiviral response in myeloid cells occurs through an IPS-1-dependent
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 Induction of IFN-beta and the innate antiviral response in myeloid cells occurs through an IPS-1-dependent
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors inhibits hepatitis B virus replication
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/17-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:1.3748/wjg.v18.i22.285 World J Gastroenterol 212 June 14; 18(22): 285-2858 ISSN 17-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-284 (online) 212 Baishideng.
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/17-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:1.3748/wjg.v18.i22.285 World J Gastroenterol 212 June 14; 18(22): 285-2858 ISSN 17-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-284 (online) 212 Baishideng.
A preliminary report on the influence of baseline cellular immunity to the therapeutic responses of peg-interferon
 146 2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 e 2a 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 1., 200025; 2., 200032 : ( CHB) ( IFN), IFN IFN, e ( HBeAg) CHB 19, 14, IFN- 2a 180 g, 1, 48,
146 2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 e 2a 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 1., 200025; 2., 200032 : ( CHB) ( IFN), IFN IFN, e ( HBeAg) CHB 19, 14, IFN- 2a 180 g, 1, 48,
West Nile Virus-Induced Interferon Production Is Mediated by the Double-Stranded RNA-Dependent Protein Kinase PKR
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2007, p. 11148 11158 Vol. 81, No. 20 0022-538X/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00446-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. West Nile Virus-Induced
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2007, p. 11148 11158 Vol. 81, No. 20 0022-538X/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00446-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. West Nile Virus-Induced
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay
 Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
(polymerase chain reaction,pcr)
 134 2008 9 3 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection September 2008 Vol 3 No. 3 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 ( HBV) (HCV) DNA RNA (PCR) HBV HCV DNA Klenow ( DNA) ( RNA) BLAST HBV HCV 1 10 6 / ml 15 % 1 10 4 / ml PCR ;
134 2008 9 3 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection September 2008 Vol 3 No. 3 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 ( HBV) (HCV) DNA RNA (PCR) HBV HCV DNA Klenow ( DNA) ( RNA) BLAST HBV HCV 1 10 6 / ml 15 % 1 10 4 / ml PCR ;
Inarigivir ACHIEVE Trial Results and HBV Clinical Program Update. August 2, 2018
 Inarigivir ACHIEVE Trial Results and HBV Clinical Program Update August 2, 2018 FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENT This presentation includes forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities
Inarigivir ACHIEVE Trial Results and HBV Clinical Program Update August 2, 2018 FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENT This presentation includes forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities
Hepatitis C Virus Reveals a Novel Early Control in Acute Immune Response
 Hepatitis C Virus Reveals a Novel Early Control in Acute Immune Response Noëlla Arnaud 1, Stéphanie Dabo 1, Daisuke Akazawa 2, Masayoshi Fukasawa 3, Fumiko Shinkai-Ouchi 3, Jacques Hugon 4, Takaji Wakita
Hepatitis C Virus Reveals a Novel Early Control in Acute Immune Response Noëlla Arnaud 1, Stéphanie Dabo 1, Daisuke Akazawa 2, Masayoshi Fukasawa 3, Fumiko Shinkai-Ouchi 3, Jacques Hugon 4, Takaji Wakita
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity
 Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Involvement of FKBP6 in hepatitis C virus replication
 Supplementary Information Involvement of FKBP6 in hepatitis C virus replication Hirotake Kasai 1,*, Kunihiro Kawakami 2,*, Hiromasa Yokoe 3, Kentaro Yoshimura 4, Masanori Matsuda 5, Jun Yasumoto 1, Shinya
Supplementary Information Involvement of FKBP6 in hepatitis C virus replication Hirotake Kasai 1,*, Kunihiro Kawakami 2,*, Hiromasa Yokoe 3, Kentaro Yoshimura 4, Masanori Matsuda 5, Jun Yasumoto 1, Shinya
Identification of Host Cytosolic Sensors and Bacterial Factors Regulating the Type I Interferon Response to Legionella pneumophila
 Identification of Host Cytosolic Sensors and Bacterial Factors Regulating the Type I Interferon Response to Legionella pneumophila Kathryn M. Monroe, Sarah M. McWhirter, Russell E. Vance* Division of Immunology
Identification of Host Cytosolic Sensors and Bacterial Factors Regulating the Type I Interferon Response to Legionella pneumophila Kathryn M. Monroe, Sarah M. McWhirter, Russell E. Vance* Division of Immunology
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
The current recommended therapy for chronic
 SPECIAL ARTICLE Mechanisms of Action of Interferon and Ribavirin in Chronic Hepatitis C: Summary of a Workshop Raymond T. Chung, 1 Michael Gale Jr, 2 Stephen J. Polyak, 2 Stanley M. Lemon, 3 T. Jake Liang,
SPECIAL ARTICLE Mechanisms of Action of Interferon and Ribavirin in Chronic Hepatitis C: Summary of a Workshop Raymond T. Chung, 1 Michael Gale Jr, 2 Stephen J. Polyak, 2 Stanley M. Lemon, 3 T. Jake Liang,
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Correspondence should be addressed to Shilin Li; and Limin Chen; limin chen
 Mediators of Inflammation Volume 25, Article ID 58989, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/25/58989 Research Article Vitamin D Potentiates the Inhibitory Effect of MicroRNA-3a in Hepatitis C Virus Replication
Mediators of Inflammation Volume 25, Article ID 58989, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/25/58989 Research Article Vitamin D Potentiates the Inhibitory Effect of MicroRNA-3a in Hepatitis C Virus Replication
Dissociation of a MAVS/IPS-1/VISA/Cardif-IKKε Molecular Complex from the Mitochondrial Outer Membrane by Hepatitis C Virus NS3-4A Proteolytic Cleavage
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2006, p. 6072 6083 Vol. 80, No. 12 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02495-05 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Dissociation of a MAVS/IPS-1/VISA/Cardif-IKKε
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2006, p. 6072 6083 Vol. 80, No. 12 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02495-05 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Dissociation of a MAVS/IPS-1/VISA/Cardif-IKKε
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
The hepatitis B viral X protein activates NF-jB signaling pathway through the up-regulation of TBK1
 FEBS Letters 584 (2010) 525 530 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org The hepatitis B viral X protein activates NF-jB signaling pathway through the up-regulation of TBK1 Hye Rim Kim, Sae Hee Lee, Guhung
FEBS Letters 584 (2010) 525 530 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org The hepatitis B viral X protein activates NF-jB signaling pathway through the up-regulation of TBK1 Hye Rim Kim, Sae Hee Lee, Guhung
Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p.
 Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with. unipartite and bipartite structure. Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2
 Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
10th International Rotavirus Symposium Bangkok, Thailand
 Rotavirus Host Range Restriction and Innate Immunity: Mechanisms of Vaccine Attenuation Harry Greenberg MD Stanford University 10th International Rotavirus Symposium Bangkok, Thailand 09/19/12 B dsrna
Rotavirus Host Range Restriction and Innate Immunity: Mechanisms of Vaccine Attenuation Harry Greenberg MD Stanford University 10th International Rotavirus Symposium Bangkok, Thailand 09/19/12 B dsrna
Hepatitis B virus upregulates the expression of kinesin family member 4A
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 3503-3507, 2015 Hepatitis B virus upregulates the expression of kinesin family member 4A CHENG LIANG ZHU 1, DUO ZHI CHENG 2, FANG LIU 3, XIAO HONG YAN 3, KAI LANG WU 3, FU
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 3503-3507, 2015 Hepatitis B virus upregulates the expression of kinesin family member 4A CHENG LIANG ZHU 1, DUO ZHI CHENG 2, FANG LIU 3, XIAO HONG YAN 3, KAI LANG WU 3, FU
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 3: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Introduction to Toll-like
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 3: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Introduction to Toll-like
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Natural small molecule FMHM inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by promoting TRAF6 degradation via K48-linked polyubiquitination Ke-Wu Zeng 1, Li-Xi Liao 1,
Supporting Information Natural small molecule FMHM inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by promoting TRAF6 degradation via K48-linked polyubiquitination Ke-Wu Zeng 1, Li-Xi Liao 1,
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
General concepts of antiviral immunity. source: wikipedia
 General concepts of antiviral immunity source: wikipedia Antiviral defense mechanisms - the birth of immunity Evolution of antiviral defense 4 Principles of innate and adaptive defense mechanisms R/M System
General concepts of antiviral immunity source: wikipedia Antiviral defense mechanisms - the birth of immunity Evolution of antiviral defense 4 Principles of innate and adaptive defense mechanisms R/M System
Type-I interferon (IFN-a/b) is a critical first line
 Major Vault Protein: A Virus-Induced Host Factor Against Viral Replication Through the Induction of Type-I Interferon Shi Liu, Qian Hao, Nanfang Peng, Xin Yue, Yu Wang, Yanni Chen, Jianguo Wu, and Ying
Major Vault Protein: A Virus-Induced Host Factor Against Viral Replication Through the Induction of Type-I Interferon Shi Liu, Qian Hao, Nanfang Peng, Xin Yue, Yu Wang, Yanni Chen, Jianguo Wu, and Ying
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Silver staining and immunoblotting of the purified TAK1 kinase complex. The TAK1 kinase complex was purified through tandem affinity methods (Protein A and FLAG), and aliquots of the purified
Figure S1. Silver staining and immunoblotting of the purified TAK1 kinase complex. The TAK1 kinase complex was purified through tandem affinity methods (Protein A and FLAG), and aliquots of the purified
Viral dynamics and Resistance Implications for HCV drug development
 Viral dynamics and Resistance Implications for HCV drug development Robert T. Schooley, M.D. University of California, San Diego June 23, 2011 SVR Rate Priorities in HCV Therapeutics 100 90 80 70 60 50
Viral dynamics and Resistance Implications for HCV drug development Robert T. Schooley, M.D. University of California, San Diego June 23, 2011 SVR Rate Priorities in HCV Therapeutics 100 90 80 70 60 50
Advances in gene encoding proteins of human herpesvirus 6
 2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 165 6 1, 2 1., 241000; 2., 210029 : 6 ( HHV-6) DNA, HHV-6 80 100, ( IE) DNA DNA HHV-6 : 6 ; ; Advances in gene encoding proteins
2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 165 6 1, 2 1., 241000; 2., 210029 : 6 ( HHV-6) DNA, HHV-6 80 100, ( IE) DNA DNA HHV-6 : 6 ; ; Advances in gene encoding proteins
Action and Mechanism of Epstein Barr virus Latent Membrane Protein1. induced Immortalization of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts *
 21 1 21 1 16-20 2006 1 VIROLOGICA SINICA January 2006 EB 1 MEF * ** 410078 Action and Mechanism of Epstein Barr virus Latent Membrane Protein1 induced Immortalization of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts * HE
21 1 21 1 16-20 2006 1 VIROLOGICA SINICA January 2006 EB 1 MEF * ** 410078 Action and Mechanism of Epstein Barr virus Latent Membrane Protein1 induced Immortalization of Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts * HE
Influence of Host Cell Defence during Influenza Vaccine Production in MDCK Cells
 Vaccine Technology III, 07 June 2010 Puerto Vallarta/Mexico Influence of Host Cell Defence during Influenza Vaccine Production in MDCK Cells T. Frensing 1, C. Seitz 1, B. Heynisch 2 and U. Reichl 1/2 1
Vaccine Technology III, 07 June 2010 Puerto Vallarta/Mexico Influence of Host Cell Defence during Influenza Vaccine Production in MDCK Cells T. Frensing 1, C. Seitz 1, B. Heynisch 2 and U. Reichl 1/2 1
NLRC5 Negatively Regulates the NF-kB and Type I Interferon Signaling Pathways
 NLRC5 Negatively Regulates the NF-kB and Type I Interferon Signaling Pathways Jun Cui, 1,2,5 Liang Zhu, 1,3,5 Xiaojun Xia, 1,5 Helen Y. Wang, 1 Xavier Legras, 1 Jun Hong, 1 Jiabing Ji, 1 Pingping Shen,
NLRC5 Negatively Regulates the NF-kB and Type I Interferon Signaling Pathways Jun Cui, 1,2,5 Liang Zhu, 1,3,5 Xiaojun Xia, 1,5 Helen Y. Wang, 1 Xavier Legras, 1 Jun Hong, 1 Jiabing Ji, 1 Pingping Shen,
Alcoholic hepatitis is a drug-induced disorder
 Alcoholic hepatitis is a drug-induced disorder Gyongyi Szabo, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School Source: 2 Sobernation.com Clinical Progression of ALD Mortality Acute
Alcoholic hepatitis is a drug-induced disorder Gyongyi Szabo, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School Source: 2 Sobernation.com Clinical Progression of ALD Mortality Acute
ISG15 sirna # Ctrl sirna+ifn+wt. Virus titer (Pfu/ml) hours post infection. d USP18 sirna #2 IFN
 a ISG15 sirna Ctrl #1 #2 ISG15 conjugates IB: ISG15 Virus titer (Pfu/ml) b ISG15 sirna #2 10 7 Ctrl sirna+ifn+wt Ctrl sirna+ifn+67 10 6 ISG15 sirna+ifn+wt ISG15 sirna+ifn+67 10 5 10 4 10 3 Free ISG15 10
a ISG15 sirna Ctrl #1 #2 ISG15 conjugates IB: ISG15 Virus titer (Pfu/ml) b ISG15 sirna #2 10 7 Ctrl sirna+ifn+wt Ctrl sirna+ifn+67 10 6 ISG15 sirna+ifn+wt ISG15 sirna+ifn+67 10 5 10 4 10 3 Free ISG15 10
GB Virus B Disrupts RIG-I Signaling by NS3/4A-Mediated Cleavage of the Adaptor Protein MAVS
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2007, p. 964 976 Vol. 81, No. 2 0022-538X/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02076-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. GB Virus B Disrupts RIG-I
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2007, p. 964 976 Vol. 81, No. 2 0022-538X/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02076-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. GB Virus B Disrupts RIG-I
The Coxsackievirus B 3C pro Protease Cleaves MAVS and TRIF to Attenuate Host Type I Interferon and Apoptotic Signaling
 The Coxsackievirus B 3C pro Protease Cleaves MAVS and TRIF to Attenuate Host Type I Interferon and Apoptotic Signaling Amitava Mukherjee 1, Stefanie A. Morosky 2, Elizabeth Delorme-Axford 1, Naomi Dybdahl-Sissoko
The Coxsackievirus B 3C pro Protease Cleaves MAVS and TRIF to Attenuate Host Type I Interferon and Apoptotic Signaling Amitava Mukherjee 1, Stefanie A. Morosky 2, Elizabeth Delorme-Axford 1, Naomi Dybdahl-Sissoko
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, DDX3X and IKK-α Mediates Multiple Functions in
 Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granule, and Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection Véronique Pène, Qisheng Li#, Catherine Sodroski, Ching-Sheng Hsu, T. Jake Liang# Liver Diseases Branch,
Therapeutic Efficacy of a TLR7 Agonist for HBV Chronic Infection in Chimpanzees
 Therapeutic Efficacy of a TLR7 Agonist for HBV Chronic Infection in Chimpanzees Robert Lanford 1, Bernadette Guerra 1, Deborah Chavez 1, Vida L. Hodara 1, Xubin Zheng 2, Grushenka Wolfgang 3, Daniel B.
Therapeutic Efficacy of a TLR7 Agonist for HBV Chronic Infection in Chimpanzees Robert Lanford 1, Bernadette Guerra 1, Deborah Chavez 1, Vida L. Hodara 1, Xubin Zheng 2, Grushenka Wolfgang 3, Daniel B.
The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections
 REVIEW Andrea K. PERRY et al The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections Andrea K. PERRY 1*, Gang CHEN 2,*, Dahai ZHENG 2,*, Hong TANG 2, Genhong CHENG 1,2,** 1 Department of
REVIEW Andrea K. PERRY et al The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections Andrea K. PERRY 1*, Gang CHEN 2,*, Dahai ZHENG 2,*, Hong TANG 2, Genhong CHENG 1,2,** 1 Department of
Viral Evolution and Interferon Resistance of Hepatitis C Virus RNA Replication in a Cell Culture Model
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 11591 11604 Vol. 78, No. 21 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.21.11591 11604.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Viral
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2004, p. 11591 11604 Vol. 78, No. 21 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.21.11591 11604.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Viral
Review New insights into how HBV manipulates the innate immune response to establish acute and persistent infection
 Antiviral Therapy 2013; 18:1 15 (doi: 10.3851/IMP2542) Review New insights into how HBV manipulates the innate immune response to establish acute and persistent infection Peter Revill 1 *, Zhenghong Yuan
Antiviral Therapy 2013; 18:1 15 (doi: 10.3851/IMP2542) Review New insights into how HBV manipulates the innate immune response to establish acute and persistent infection Peter Revill 1 *, Zhenghong Yuan
The role of Hepatitis C Virus in hepatocarcinogenesis
 The role of Hepatitis C Virus in hepatocarcinogenesis Laura Beretta Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center l8 Incidence and mortality of the five most common cancers worldwide, 2000 Incidence Lung Breast
The role of Hepatitis C Virus in hepatocarcinogenesis Laura Beretta Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center l8 Incidence and mortality of the five most common cancers worldwide, 2000 Incidence Lung Breast
Slides are the property of the author and AASLD. Permission is required from both AASLD and the author for reuse.
 Inarigivir Demonstrates Potent Dose Dependent Anti-Viral Activity in HBV Treatment-Naïve Patients: Role of HBeAg Status and Baseline HBsAg in Anti-Viral Response MF Yuen, M. Elkhashab, CY Chen, YF Chen,
Inarigivir Demonstrates Potent Dose Dependent Anti-Viral Activity in HBV Treatment-Naïve Patients: Role of HBeAg Status and Baseline HBsAg in Anti-Viral Response MF Yuen, M. Elkhashab, CY Chen, YF Chen,
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
NOTES. The Naturally Attenuated Kunjin Strain of West Nile Virus Shows Enhanced Sensitivity to the Host Type I Interferon Response
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2011, p. 5664 5668 Vol. 85, No. 11 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00232-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES The Naturally Attenuated
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2011, p. 5664 5668 Vol. 85, No. 11 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00232-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES The Naturally Attenuated
The Early Interferon Response to Rotavirus Is Regulated by PKR and Depends on MAVS/IPS-1, RIG-I, MDA-5, and IRF3
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 3717 3732 Vol. 85, No. 8 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.02634-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Early Interferon Response
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 3717 3732 Vol. 85, No. 8 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.02634-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Early Interferon Response
Isorce Nathalie, Testoni B., Luangsay S., Locatelli M., Zannetti C., Henry T., Hasan U., Zoulim F., Durantel D.
 Activité antivirale de différents interférons (IFNs) et cytokines proinflammatoires dans des modèles pertinents d hépatocytes infectés par le virus de l hépatite B (HBV) Isorce Nathalie, Testoni B., Luangsay
Activité antivirale de différents interférons (IFNs) et cytokines proinflammatoires dans des modèles pertinents d hépatocytes infectés par le virus de l hépatite B (HBV) Isorce Nathalie, Testoni B., Luangsay
Apoptosis in chronic hepatitis C
 Apoptosis in chronic hepatitis C Dr med. Anna Parfieniuk-Kowerda Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology Medical University of Bialystok Poland APOPTOSIS Apoptosis - type I programmed cell death
Apoptosis in chronic hepatitis C Dr med. Anna Parfieniuk-Kowerda Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology Medical University of Bialystok Poland APOPTOSIS Apoptosis - type I programmed cell death
Multiple Anti-Interferon Actions of the Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2007, p. 7011 7021 Vol. 81, No. 13 0022-538X/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02581-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Multiple Anti-Interferon
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, July 2007, p. 7011 7021 Vol. 81, No. 13 0022-538X/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02581-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Multiple Anti-Interferon
NgAgo-gDNA system efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus replication through accelerating decay of pregenomic RNA
 Accepted Manuscript NgAgo-gDNA system efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus replication through accelerating decay of pregenomic RNA Zhuanchang Wu, Siyu Tan, Leiqi Xu, Lifen Gao, Haizhen Zhu, Chunhong
Accepted Manuscript NgAgo-gDNA system efficiently suppresses hepatitis B virus replication through accelerating decay of pregenomic RNA Zhuanchang Wu, Siyu Tan, Leiqi Xu, Lifen Gao, Haizhen Zhu, Chunhong
Elimination of Hepatitis C Virus from Hepatocytes by a Selective Activation of Therapeutic Molecules
 Elimination of Hepatitis C Virus from Hepatocytes by a Selective Activation of Therapeutic Molecules Xiaoyu Wen 1., Takayuki Abe 1., Hiroshi Kukihara 1, Shuhei Taguwa 1, Yoshio Mori 1, Hideki Tani 1, Nobuyuki
Elimination of Hepatitis C Virus from Hepatocytes by a Selective Activation of Therapeutic Molecules Xiaoyu Wen 1., Takayuki Abe 1., Hiroshi Kukihara 1, Shuhei Taguwa 1, Yoshio Mori 1, Hideki Tani 1, Nobuyuki
The Chimpanzee Model Of HCV: Antiviral Therapy
 The Chimpanzee Model Of HCV: Antiviral Therapy Antiviral Therapies in Chimpanzees PEG IFN + Ribavirin STAT C with DAA Protease Inhibitors Nucleoside analogues Polymerase Inhibitors NS5A Inhibitors Immunomodulators
The Chimpanzee Model Of HCV: Antiviral Therapy Antiviral Therapies in Chimpanzees PEG IFN + Ribavirin STAT C with DAA Protease Inhibitors Nucleoside analogues Polymerase Inhibitors NS5A Inhibitors Immunomodulators
VIRUSES AND CANCER Michael Lea
 VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
The Immune Response of Prolactin and the Induction of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) in Iraqi Patients Infected with Hepatitis C Virus.
 1 The Immune Response of Prolactin and the Induction of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) in Iraqi Patients Infected with Hepatitis C Virus. Prof. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin (MRSC, Ph.D, Post Doctorate) Department
1 The Immune Response of Prolactin and the Induction of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) in Iraqi Patients Infected with Hepatitis C Virus. Prof. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin (MRSC, Ph.D, Post Doctorate) Department
Treatment Options in HCV Relapsers and Nonresponders. Raymond T. Chung, M.D.
 Session IV Treatment Options in HCV Relapsers and Nonresponders Raymond T. Chung, M.D. Director of Hepatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Session IV Treatment Options in HCV Relapsers and Nonresponders Raymond T. Chung, M.D. Director of Hepatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
AG Kaderali Bioinformatics / Mathematical Modeling of Infection
 AG Kaderali Bioinformatics / Mathematical Modeling of Infection Prof. Dr. Lars Kaderali Hiddensee, October 27, 2015 Institut für Bioinformatik Research Overview Experimental Data High-Throughput Screening
AG Kaderali Bioinformatics / Mathematical Modeling of Infection Prof. Dr. Lars Kaderali Hiddensee, October 27, 2015 Institut für Bioinformatik Research Overview Experimental Data High-Throughput Screening
Ebola Virus VP35 Protein Binds Double-Stranded RNA and Inhibits Alpha/Beta Interferon Production Induced by RIG-I Signaling
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2006, p. 5168 5178 Vol. 80, No. 11 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02199-05 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Ebola Virus VP35 Protein
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2006, p. 5168 5178 Vol. 80, No. 11 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02199-05 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Ebola Virus VP35 Protein
The Journal of Experimental Medicine
 Differential Requirement for TANK-binding Kinase-1 in Type I Interferon Responses to Toll-like Receptor Activation and Viral Infection Andrea K. Perry, 1 Edward K. Chow, 2 Julia B. Goodnough, 1 Wen-Chen
Differential Requirement for TANK-binding Kinase-1 in Type I Interferon Responses to Toll-like Receptor Activation and Viral Infection Andrea K. Perry, 1 Edward K. Chow, 2 Julia B. Goodnough, 1 Wen-Chen
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Therapeutic strategies for immune reconstitution in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
 30 1, 1, 2, 3 1. ( ), 201508; 2., 200040; 3., 200032 : ( AIDS) ( HIV) 20 90,,,,,, AIDS, CD4 + T ( CTL), HIV, : ; ; Therapeutic strategies for immune reconstitution in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
30 1, 1, 2, 3 1. ( ), 201508; 2., 200040; 3., 200032 : ( AIDS) ( HIV) 20 90,,,,,, AIDS, CD4 + T ( CTL), HIV, : ; ; Therapeutic strategies for immune reconstitution in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/406/ra126/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The microrna mir-485 targets host and influenza virus transcripts to regulate antiviral immunity and restrict viral
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/406/ra126/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The microrna mir-485 targets host and influenza virus transcripts to regulate antiviral immunity and restrict viral
IRF7 in the Australian Black Flying Fox, Pteropus alecto: Evidence for a Unique Expression Pattern and Functional Conservation
 IRF7 in the Australian Black Flying Fox, Pteropus alecto: Evidence for a Unique Expression Pattern and Functional Conservation Peng Zhou 1, Chris Cowled 1, Ashley Mansell 2, Paul Monaghan 1, Diane Green
IRF7 in the Australian Black Flying Fox, Pteropus alecto: Evidence for a Unique Expression Pattern and Functional Conservation Peng Zhou 1, Chris Cowled 1, Ashley Mansell 2, Paul Monaghan 1, Diane Green
Significance of Hepatitis C. The Evolving Burden of Hepatitis C. The Bad News... The Good News... Chronic Hepatitis C Can be Cured
 Journée scientifique de l'arl Yverdon, 24 mars 2011 Darius Moradpour Service de Gastroentérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Université de Lausanne Significance of Hepatitis
Journée scientifique de l'arl Yverdon, 24 mars 2011 Darius Moradpour Service de Gastroentérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Université de Lausanne Significance of Hepatitis
