Occupational HIV exposures are crisis situations demanding immediate, decisive action. Henderson, 2001
|
|
|
- Melvin Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Post-Exposure Care: A Balancing Act Alice C. Thornton, MD Southeast AIDS Training & Education Center Kentucky Local Performance Site University of Kentucky October 24, 2009 Objectives Review the goals of post-exposure care Describe the three phases of blood borne pathogen exposure management Discuss ways to prevent transmission Provide information/counseling Avoid unnecessary PEP/minimize toxicity it Determine whether transmission has occurred 1
2 Occupational HIV exposures are crisis situations demanding immediate, decisive action. Henderson, 2001 What is an exposure?.a percutaneous injury or contact of mucous membrane or non-intact skin. with blood, tissue or other body fluids that are potentially infectious. MMWR,
3 What is NOT an Exposure? BBP transmission does not occur Through intact skin Via inhalation Beltrami, 2000 Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Use of therapeutic agents to prevent infection following exposure Types of exposures include percutaneous (needlestick), splash, bite, sexual PEP commonly considered for exposures to HIV and Hepatitis B Behrens,
4 HCP: 24 yo ED nurse Case Number #1 Patient spit in her eye while she was trying to start an IV Source patient: 33 yo male, thought to be infected with HIV What are the next steps? Phases in Managing BBP Exposures Phase One First Aid Triage Crisis Management Phase Two Exposure Risk Assessment Source Patient Evaluation PEP Decision Initiating Treatment Beltrami, 2000 Phase Three Post-Exposure Follow-up Source Patient Follow-up ARV Toxicity Monitoring 4
5 First aid Triage Phase 1: Immediate Care Crisis Management First Aid: Treat Exposure Site Soap and water to wash exposed areas Flush exposed mucous membranes with water Flush exposed eyes with water or saline solution Do NOT apply caustic agents or inject antiseptics or disinfectants into the wound 5
6 Triage Goal: evaluation immediately after exposure Refer to qualified provider Employee health department Emergency department Urgent Care Occupational medicine clinic Crisis Management Acute emotional upset is the norm for exposed HCP Education and supportive counseling are key Reassure without being dismissive Be an advocate Refer for mental health evaluation if symptoms are severe or persistent 6
7 Phases in Managing BBP Exposures Phase One First Aid Triage Crisis Management Phase Two Exposure Risk Assessment Source Patient Evaluation PEP Decision Initiating Treatment Phase Three Post-Exposure Follow-up Source Patient Follow-up ARV Toxicity Monitoring Phase 2: Determining Risk Assessment of the Exposure Assessment of the Source PEP Decision PEP Selection Treatment Initiation 7
8 Assessment of the Exposure General Principles HIV, HBV and HCV do not spontaneously penetrate intact skin Airborne transmission of these viruses does not occur Beltrami,
9 Defining Risk -Per-exposure exposure Estimates HIV Percutaneous 0.3% Mucocutaneous 0.09% HCV Percutaneous 1.8% HBV Percutaneous eag+ 22% to 31% eag-1.5-6% MMWR, 2005 MMWR, 2001 Exposure Risk Assessment Type of Exposure Substance Exposure Source 9
10 Types of Exposure Percutaneous injury Mucous membrane exposure Non-intact skin exposure Bites resulting in blood exposure to either person involved Needlestick Defining Risk Less severe ( Solid needle and superficial injury) More severe (L Large-bore hollow needle, deep puncture, visible blood on device, or needle exposed to artery or vein) Mucous membrane and nonintact skin Small volume ( a few drops) Large volume ( major blood splash) MMWR 2001, MMWR
11 Risk Factors for Seroconversion Following Needlesticks CDC-sponsored case-control control study 33 cases, 665 controls with needlesticks from confirmed HIV+ SPs Zidovudine (AZT) monotherapy as PEP Odds of HIV transmission ss was reduced by 81% in HCW that took AZT Cardo 1997 Risk Factors for Seroconversion Risk Factor Odds Ratio* 95% CI Deep injury Visibly bloody device Device in artery/vein Terminally ill SP AZT PEP *p<0.01 for all Cardo
12 Viral load Glove use Other Likely Risk Factors 50% decrease in volume of blood transmitted 1 Hollow bore vs solid bore Large diameter needles weakly associated with increased risk (p = 0.08) 2 Drying conditions Tenfold drop in infectivity every 9 hours 3 1. Mast Cardo Resnick JAMA 1986 Substance 12
13 Infectious Material Blood and blood products, breast milk, vaginal secretions, semen Occupational transmission of HIV: health care and laboratory workers Other body fluids if BLOODY Saliva (only implicated through oral sex) Feces, nasal secretions, saliva, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomitus are not considered potentially infectious unless they are visibly bloody. The risk for transmission of HIV infection from these fluids and materials is low. MMWR Possible: Cerebrospinal fluid, exudates, serosal fluids, amniotic fluid Environmental Concerns Titer of HIV is reduced by 90 to 99 % within several hours after drying and diminishes with time HBV is resistant to drying and has been found to be stable on environmental surfaces for up to 7 days HCV rapid degradation of serum at room temp (data lacking) Beltrami
14 Assessment Determine infectious status of the source patient Determine susceptibility of the exposed person Determine Infectious Status of the Source Presence of HBs AG Presence of HCV AB Presence of HIV AB Unknown sources Evaluate likelihood of exposure Setting in which exposure occurred 14
15 Source Assessment: Laboratory Testing Do not delay PEP while awaiting source patient laboratory results. The decision i to start PEP is based on the clinical risk assessment. Consider testing options: Rapid vs standard HIV antibody test kit Antibody testing vs direct virus assay No option to test discarded needles Source Assessment: Laboratory Testing Rapid ELISA should be considered A negative result allays anxiety and prevents overuse of PEP. All positive tests must be confirmed with a Western Blot or Immunofluoresence assay. 15
16 Source Patient Factors Influence HIV Transmission Risk If source is HIV+ : Viral Load Stage of disease If HIV status in unknown: Risk behavior history Signs/symptoms suggestive of primary HIV infection Prior testing/ History of exposure If source is unknown: Community prevalence Susceptibility of Exposed Person Hepatitis B vaccine status? HBV immune status? Anti-HCV and ALT HIV antibody 16
17 Case #1 Continued Saliva was visibly bloody The patient had been in a fight and had an injured mouth Eye was rinsed immediately Source patient has never taken antiretrovirals, has a CD4 count of about 500 and a viral load of 20,000 copies/ml last time it was checked. She is 8 weeks pregnant Stratifying Risk Splash to mucous membrane or non-intact skin Length and volume of exposure contribute to risk Bite exposures Bite victim not at risk unless blood in saliva Biter has sustained blood to mucous membrane exposure 17
18 Stratifying Risk - Source Assessment If source is HIV+ What is viral load/stage of disease? If HIV status is unknown What is history of risk factors? Any symptoms of primary HIV infection? What is history of testing? If source is unknown What is prevalence where exposure occurred? How long has sharp been environmentally exposed? PEP Decision 18
19 Window of Opportunity Rhesus macaque model: Intravaginal exposure to SIV At 24 hours, SIV detected in vaginal dendritic cells By 48 hours, SIV detected in regional lymph nodes By 5 days, SIV detected in peripheral blood The time to disseminated infection provides a window for intervention Spira, 1996 Evidence from ACTG 076 Randomized controlled trial to assess ability of AZT to reduce perinatal transmission in humans Risk of vertical transmission reduced from 22.6 % in placebo treated controls to 7.6% in treatment arm (AZT alone) Reduction of 67% Reduction in viral load only partially explained reduction in transmission Connor,
20 Effectiveness of PEP: Animal Models Duration of treatment makes a difference Macaques PMPA (Tenofovir) Protection from transmission: 100% in those treated 28 days 50% in those treated 10 days 0% in those treated 3 days Tsai, 1995 Effectiveness of PEP: Animal Models Delay in treatment is detrimental Macaques Protection from transmission 100% that received PEP within 24 hour 50% that received PEP within 48 hours 25% that received PEP within 72 hours Tsai
21 PEP for HIV - General Principles Most exposures do not result in transmission of HIV, so risk ik and db benefit must be weighed ihd carefully. Consider risk of exposure and source. Consider factors in the health care worker concurrent illness or medication pregnancy or breastfeeding Timing of PEP 1-2 hours 24 hours 72 hours 1 week (or more?) 21
22 What are the Downsides to PEP? Tolerability of HIV PEP in Health Care Workers rcent of HCWs Pe Incidence of Common Side Effects Nausea Fatigue Headache Vomiting Diarrhea Myalgias Wang,
23 PEP likely beneficial High risk exposure Known positive source High risk source No delay to rx Choice of drugs minimizes toxicity Side effects may outweigh benefits Low risk exposure Low risk source Found needle Delay (>72 hrs) Drug interactions/coexisting medical conditions. Pregnancy??? Behrens, 2006 How Many Drugs to Use? Two drug PEP regimens improve tolerability and therefore chances of completing full 4 weeks Three (or more) drug PEP regimens provide potentially greater antiviral activity Guidelines recommend more drugs for higher risk exposures 23
24 How Many Drugs to Use? Assess risk for HIV infection: Type of exposure Less severe: solid needle or superficial injury More severe: large-bore hollow needle, deep puncture, visible blood on device, needle used in patient s artery or vein Infection status of source Class 1: asymptomatic HIV infection or known low viral load (<1500 copies RNA/mL) Class 2: symptomatic HIV, AIDS, acute seroconversion, or known high viral load Basic 2-Drug Regimens Two NRTIs Simple dosing, fewer side effects Preferred basic regimens: zidovudine (AZT) OR tenofovir (TDF) plus lamivudine (3TC) OR emtricitabine (FTC) Alternative basic regimens: stavudine (d4t) OR didanosine (ddi) plus lamivudine (3TC) OR emtricitabine (FTC) MMWR
25 Expanded PEP Regimens Expanded 3-drug PEP regimens: Preferred: Lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra) + basic 2-drug regimen Alternative: Atazanavir* ± ritonavir Fosamprenavir ± ritonavir + basic 2-drug regimen Indinavir** ± ritonavir Saquinavir + ritonavir Nelfinavir Efavirenz*** *If atazanavir is coadministered with tenofovir, ritonavir must be included in the PEP regimen. **Avoid in late pregnancy.***teratogenic; avoid in pregnancy Antiretroviral agents generally NOT recommended for PEP: Nevirapine Delavirdine Abacavir Zalcitabine Didanosine + stavudine Antiretroviral agents to be used for PEP only with expert consultation: Enfuvirtide Other newer agents: Intelence and Isentress 25
26 PEP for Percutaneous Injuries Exposure Type Less severe Infection Status of Source HIV+, class 1 HIV+, class 2 Recommend basic 2-drug PEP Recommend expanded 3-drug PEP More severe Recommend Recommend expanded 3-drug expanded 3-drug PEP PEP PEP for Percutaneous Injuries Exposure Type Infection Status of Source Unknown HIV status* Unknown source Less severe More severe Generally, no PEP warranted; consider basic 2- drug PEP if source has HIV risk factors As above Generally, no PEP warranted; consider basic 2-drug PEP if exposure to HIV- infected persons is likely l As above *If PEP is given and source is later determined to be HIV-negative, PEP should be discontinued. 26
27 PEP for Percutaneous Injuries Exposure Type Less severe Infection Status of Source HIV-negative No PEP More severe No PEP PEP for Mucous Membrane and Nonintact Skin Exposures Exposure Type Infection Status of Source HIV+, class 1 HIV+, class 2 Less severe Consider basic 2- drug PEP Recommend basic 2- drug PEP More severe Recommend basic 2-drug PEP Recommend expanded 3-drug PEP 27
28 Exposure Type Less severe More severe PEP for Mucous Membrane and Nonintact Skin Exposures (continued) Infection Status of Source Unknown HIV status* Unknown source Generally, no PEP warranted Generally, no PEP warranted; consider basic 2-drug PEP if source has HIV risk factors Generally, no PEP warranted Generally, no PEP warranted; consider basic 2-drug PEP if exposure to HIV- infected persons is likely *If source is determined to be HIV-negative after PEP is initiated, discontinue PEP. PEP for Mucous Membrane and Nonintact Skin Exposures (continued) Exposure Type Less severe More severe Infection Status of Source HIV-negative No PEP No PEP 28
29 PEP in Pregnancy Most antiretrovirals class B or C Antiretroviral i lp Pregnancy Registry has not detected d increased teratogenic risk for ARVs in general, nor specifically for AZT and 3TC, in the first trimester 1 Avoid efavirenz (anancephaly in monkeys), amprenavir (ossification defects in rabbits), and indinavir in late term (hyperbilirubinemia) Theoretically higher risk of vertical transmission with primary HIV infection 1. Garcia, 2001 Case continued You jointly decide on AZT/3TC/lopinavir/norvir i / i What are the next steps? How long will she stay on therapy? 29
30 HBV PEP Prevalence of chronic hepatitis B infection in U.S. relatively l low Most health-care workers vaccinated against hepatitis B Hepatitis B PEP: immunization + HBIG (hepatitis B Immune Globulin) HBIG effective up to one week following exposure Grady GF et al. JID 1978;138: HBV Documented vaccine responder SAb>10 IU/ml now SAb<10 IU/ml now (nonresponder) Fully vaccinated, but documented nonresponder Fully vaccinated, but response not documented 30
31 Post-Exposure Prophylaxis for Hepatitis B Vaccination & AB Response status of HCW Unvaccinated Source HbsAg + HBIG x 1 and start HB vaccine series Treatment Source HbsAG - Start Vaccine Source of unknown or not available Start HB series Previously vaccinated Responder Nonresponder No tx HBIG x1 and start vaccine/hbig x2 No tx No tx If know high risk, tx as if Ag + AB Unknown Test HCW and then follow above No tx Same as above Hepatitis C Exposure Average risk of seroconversion from percutaneous exposure 18% 1.8% Same risk factors as for HIV thought to apply Gamma globulin not recommended Early recognition and treatment of chronic HCV infection may substantially ti improve odds of eradication MMWR,
32 Phases in Managing BBP Exposures Phase One First Aid Triage Crisis Management Phase Two Exposure Risk Assessment Source Patient Evaluation PEP Decision Initiating Treatment Phase Three Post-Exposure Follow-up Source Patient Follow-up ARV Toxicity Monitoring Phase Three Post-Exposure Follow-up Source Patient Follow-up ARV Toxicity Monitoring 32
33 Follow-up of health-care personnel (HCP) exposed to known or suspected HIV-positive sources Advise to use precautions (e.g., avoid blood or tissue donations, breastfeeding, or pregnancy) to prevent secondary transmission, i especially during the first 6 12 weeks post-exposure. Exposures for which PEP is prescribed: need for monitoring possible drug interactions the need for adherence to PEP regimens Consider re-evaluation of exposed HCP 72 hours postexposure, especially after additional information about the exposure or SP becomes available. MMWR 2005 Post-Exposure Follow-Up HIV Antibody Testing: Baseline, 6 wks, 3 mon, 6 mon Consider 12 month for co-exposures to HIV/HCV HIV testing (PCR) if exposed person develops illness compatible with acute retroviral syndrome HCV Antibody Testing & ALT: Baseline, 6 wks, 3 mos, 6 mos Confirm positives HCV RNA testing Consider at 4-6 weeks if earlier diagnosis needed Unlike HIV, most patients are not symptomatic with acute HCV infection HBV testing as clinically indicated 33
34 Time to Seroconversion HIV HBV SAg HBV SAB IgM IgG HCV 4 weeks 4-7 weeks 6-12 weeks 8-24 weeks weeks Expert Consultation Delayed Exposure Unknown Source Known or Suspected Pregnancy HIV Resistance Toxicities 34
35 Conclusion Vaccinations for HBV should be standard Don t forget barriers Prophylaxis does work National Clinicians Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Hotline (PEPline) 888 / HIV / hours/day
36 References Behrens C, Liss H, Post-Exposure Prophylaxis: an evidence-based reviewnorthwest AIDS Education & Training i Center University i of Washington (Slide Set),2006 Glynn M, National HIV Prevention Conference; June 2005;Atlanta. Abstract T1- B B1101.html. Hall HI, Estimation of HIV incidence in the United States. JAMA. 2008;300: Margolis HS.Prevention of hepatitis B virus transmission i by immunization: An economic analysis of current recommendations. JAMA 1995;274(15): Armstrong GL,Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through Ann Int Med 2006;144(10): References CDC (2006, December) Surveillance of occupationally acquired HIV/AIDS in healthcare personnel, as of December 2006 (modified 20 th September 2007) CDC. Surveillance for Acute Viral Hepatitis- US, 2006 MMWR, March : 57 Henderson..Emerg Infect Dis 2001; 7:254-8 CDC. Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational exposures to HIV and Recommendations for Postexposure Prophylaxis. MMWR, Sept 30: 2005 Beltrami,E. Risk and Management of Blood-Borne Infections in Health Care Workers. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. July 2000; CDC. Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational exposures to HIV and Recommendations for Postexposure Prophylaxis. MMWR, June 2001; 50 (RR!):1-42 Cardo DM. A Case Control Study of HIV Seroconversion in Health Care W k ft P t E NEJM
37 References Mast ST et al. JID 1993;168(6): Cardo DM et al. NEJM 1997;337: Resnick L et al, JAMA 1986;255(14): Spira AI, J Exp Med 1996;183: Connoer EM, Reduction of maternal-fetal transmission of HIV Type 1 with Zidovudine treatment. NEJM 1994;331: Tsai CC, et al. Prevention of SIV in macaques by -9-(2- phosphonylmethoxpropyl) adenine. Science 1995;270: Tsai CC, Journal of Virology.1998;72: Wang SA. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2000;231: Garcia et al. ICAAC, December 2001, Abstract 1325 All Pictures are from Microsoft Clipart 37
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
 Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors
 Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors Case Presentation 27 yo nurse presents to Urgent Care for a needlestick 2 days ago from a diabetic lancet. Source patient (SP): 35 yo male known
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors Case Presentation 27 yo nurse presents to Urgent Care for a needlestick 2 days ago from a diabetic lancet. Source patient (SP): 35 yo male known
One of your office personnel
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury
 43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011
 Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011 Occupational Health Services at The Summit Rita M. Lopez, APRN-BC, MSN 751-4189 rlopez@krmc.org OBJECTIVES DEFINE Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure WHO must
Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011 Occupational Health Services at The Summit Rita M. Lopez, APRN-BC, MSN 751-4189 rlopez@krmc.org OBJECTIVES DEFINE Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure WHO must
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Sue Sebazco, Arlington, Texas A Webber Training Teleclass
 Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
HIV and PEP. LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED
 HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
HIV prophylaxis for health care providers. Dr. A. K. M. Humayon Kabir Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital
 HIV prophylaxis for health care providers. Dr. A. K. M. Humayon Kabir Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital HIV continues to be a major global public health issue, Approximately
HIV prophylaxis for health care providers. Dr. A. K. M. Humayon Kabir Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital HIV continues to be a major global public health issue, Approximately
Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
 Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Occupational exposure Occupational exposure refers to exposure to potential blood-borne infections (HIV, HBV and HCV) that may occur in healthcare settings during performance
Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Occupational exposure Occupational exposure refers to exposure to potential blood-borne infections (HIV, HBV and HCV) that may occur in healthcare settings during performance
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post-Exposure Chemophrophylaxis
 Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV
 Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties An exposure that might place health
Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties An exposure that might place health
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS
 STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
Antonio E. Urbina, M.D. Associate Medical Director Center for Comprehensive Care, West 17 th Street Clinic St. Luke s Roosevelt Hospital DISCLOSURES
 PROPHYLAXISFOLLOWINGHIV, HEPB ANDC EXPOSURES: WHAT SNEW Antonio E. Urbina, M.D. Associate Medical Director Center for Comprehensive Care, West 17 th Street Clinic St. Luke s Roosevelt Hospital DISCLOSURES
PROPHYLAXISFOLLOWINGHIV, HEPB ANDC EXPOSURES: WHAT SNEW Antonio E. Urbina, M.D. Associate Medical Director Center for Comprehensive Care, West 17 th Street Clinic St. Luke s Roosevelt Hospital DISCLOSURES
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure. Marsh Gelbart 2010
 HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
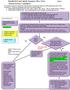 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Non-occupational HIV Post Exposure Prophylaxis (npep)
 Mountain West AIDS Education and Training Center Non-occupational HIV Post Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Robert Harrington, M.D. This presentation is intended for educational use only, and does not in any
Mountain West AIDS Education and Training Center Non-occupational HIV Post Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Robert Harrington, M.D. This presentation is intended for educational use only, and does not in any
HIV, HBV, AND HCV POSTEXPOSURE MANAGEMENT FOR HEALTHCARE WORKERS. Weerawat Manosuthi Bamrasnaradura Infectious Diseases Institute
 HIV, HBV, AND HCV POSTEXPOSURE MANAGEMENT FOR HEALTHCARE WORKERS Weerawat Manosuthi Bamrasnaradura Infectious Diseases Institute Outline Case scenario of HIV postexposure prophylaxis Risks of and how to
HIV, HBV, AND HCV POSTEXPOSURE MANAGEMENT FOR HEALTHCARE WORKERS Weerawat Manosuthi Bamrasnaradura Infectious Diseases Institute Outline Case scenario of HIV postexposure prophylaxis Risks of and how to
Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women. Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School
 Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School Obstetric Complications and HIV Obstetric complications are not increased in
Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School Obstetric Complications and HIV Obstetric complications are not increased in
Occupational and Non- Occupational HIV Post-exposure Prophylaxis
 Occupational and Non- Occupational HIV Post-exposure Prophylaxis Amy V. Kindrick, MD, MPH National Clinicians Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Hotline (PEPline) University of California, San Francisco San Francisco
Occupational and Non- Occupational HIV Post-exposure Prophylaxis Amy V. Kindrick, MD, MPH National Clinicians Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Hotline (PEPline) University of California, San Francisco San Francisco
HIV Update Objectives. Epidemiology. Epidemiology, Transmission and Natural History. Transmission Risk by Exposure. Transmission 9/29/2014
 Objectives HIV Update 2014 Jay Sizemore, MD, MPH Medical Director Chattanooga CARES Assistant Professor UTCOM Chattanooga 2October 2014 Review HIV epidemiology and screening/testing guidelines Discuss
Objectives HIV Update 2014 Jay Sizemore, MD, MPH Medical Director Chattanooga CARES Assistant Professor UTCOM Chattanooga 2October 2014 Review HIV epidemiology and screening/testing guidelines Discuss
/AIDS HIV/ HIV Overview. Nelson L. Michael, MD, PhD Division of Retrovirology Walter Reed Army Institute of Research US Military HIV Research Program
 /AIDS HIV/ HIV Overview Nelson L. Michael, MD, PhD Division of Retrovirology Walter Reed Army Institute of Research US Military HIV Research Program www.hivresearch.org 1 WRAIR Tropical Medicine Course
/AIDS HIV/ HIV Overview Nelson L. Michael, MD, PhD Division of Retrovirology Walter Reed Army Institute of Research US Military HIV Research Program www.hivresearch.org 1 WRAIR Tropical Medicine Course
3/23/2016. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures
 This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
Standard Precautions and HIV Postexposure Prophylaxis in the Health Care Setting
 HIV Curriculum for the Health Professional Standard Precautions and HIV Postexposure Prophylaxis in the Health Care Setting Nancy R. Calles, MSN, RN, PNP, ACRN, MPH Andreea C. Cazacu, MD Objectives 1.
HIV Curriculum for the Health Professional Standard Precautions and HIV Postexposure Prophylaxis in the Health Care Setting Nancy R. Calles, MSN, RN, PNP, ACRN, MPH Andreea C. Cazacu, MD Objectives 1.
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING
 ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Management
 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep)
 Projeto Praça Onze Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Mauro Schechter Principal Investigator, Projeto Praça Onze Professor of Infectious Diseases Universidade
Projeto Praça Onze Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Mauro Schechter Principal Investigator, Projeto Praça Onze Professor of Infectious Diseases Universidade
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
Revised April WGH ER #5 Hospital Rd. Whitehorse Phone: (867) Outside of Whitehorse: Local Community Health Centre/Clinic/ER
 Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
HIV Overview. Mary Marovich, MD, DTMH Division of Retrovirology Walter Reed Army Ins?tute of Research US Military HIV Research Program
 HIV Overview Mary Marovich, MD, DTMH Division of Retrovirology Walter Reed Army Ins?tute of Research US Military HIV Research Program www.hivresearch.org 1 Outline HIV Virology, Transmission, and Pathogenesis
HIV Overview Mary Marovich, MD, DTMH Division of Retrovirology Walter Reed Army Ins?tute of Research US Military HIV Research Program www.hivresearch.org 1 Outline HIV Virology, Transmission, and Pathogenesis
POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS, PRE-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS, & TREATMENT OF HIV
 POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS, PRE-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS, & TREATMENT OF HIV DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none
POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS, PRE-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS, & TREATMENT OF HIV DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none
0.14 ( 0.053%) UNAIDS 10% (94) ( ) (73-94/6 ) 8,920
 0.14 UNAIDS 0.053% 2 250 60 10% 94 73 20 73-94/6 8,920 12 43 Public Health Service Task Force Recommendations 5-10% for Use of Antiretroviral Drugs in 10-20% Pregnant HIV-1-Infected Women for Maternal
0.14 UNAIDS 0.053% 2 250 60 10% 94 73 20 73-94/6 8,920 12 43 Public Health Service Task Force Recommendations 5-10% for Use of Antiretroviral Drugs in 10-20% Pregnant HIV-1-Infected Women for Maternal
Decision Analysis Example
 Decision Analysis Example after Occupational Exposure to Infection after Needlestick Injury Direct inoculation into blood vessels Cutaneous dendritic (Langerhans) cells Delay from injury to infection Initial
Decision Analysis Example after Occupational Exposure to Infection after Needlestick Injury Direct inoculation into blood vessels Cutaneous dendritic (Langerhans) cells Delay from injury to infection Initial
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens
 Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Prophylaxis
 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials. All employees of
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials. All employees of
Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting
 Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
El Paso - Ambulatory Clinic Policy and Procedure
 Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions
 Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions For employees sent to the Emergency Department after hours to be evaluated for needle stick / body fluid exposure 1. Floor or unit Charge RN
Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions For employees sent to the Emergency Department after hours to be evaluated for needle stick / body fluid exposure 1. Floor or unit Charge RN
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc.
 Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP)
 Postexposure Prophylaxis Against Human Immunodeficiency Virus MICHAEL A. TOLLE, MD, MPH, and HEIDI L. SCHWARZWALD, MD, MPH, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas Family physicians often encounter
Postexposure Prophylaxis Against Human Immunodeficiency Virus MICHAEL A. TOLLE, MD, MPH, and HEIDI L. SCHWARZWALD, MD, MPH, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas Family physicians often encounter
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
HIV Management Update 2015
 9/30/15 HIV Management Update 2015 Larry Pineda, PharmD, PhC, BCPS Visiting Assistant Professor Pharmacy Practice and Administrative Science ljpineda@salud.unm.edu Pharmacist Learning Objectives Describe
9/30/15 HIV Management Update 2015 Larry Pineda, PharmD, PhC, BCPS Visiting Assistant Professor Pharmacy Practice and Administrative Science ljpineda@salud.unm.edu Pharmacist Learning Objectives Describe
FAMILY HIV CENTER NJ CARES SANE
 HIV, Hepatitis B & C Postexposure Prophylaxis for Sexual Assault Victims Update for Case Managers Susan Burrows-Clark, RN, MSN, CNS, C. 10/17/11 Antiretroviral Postexposure Prophylaxis After Sexual, Injection-Drug
HIV, Hepatitis B & C Postexposure Prophylaxis for Sexual Assault Victims Update for Case Managers Susan Burrows-Clark, RN, MSN, CNS, C. 10/17/11 Antiretroviral Postexposure Prophylaxis After Sexual, Injection-Drug
Occupational Postexposure Prophylaxis
 National HIV Curriculum PDF created July 1, 2018, 11:59 pm Occupational Postexposure Prophylaxis This is a PDF version of the following document: Section 5: Prevention of HIV Topic 3: Occupational Postexposure
National HIV Curriculum PDF created July 1, 2018, 11:59 pm Occupational Postexposure Prophylaxis This is a PDF version of the following document: Section 5: Prevention of HIV Topic 3: Occupational Postexposure
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM
 Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations. Viral Hepatitis Language. Types of Viral Hepatitis 7/1/2013
 Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis. Laila AL Dabal MD FRCP MSc Infectious Diseases Unit Dubai Health Authority 15 March 2018
 Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis Laila AL Dabal MD FRCP MSc Infectious Diseases Unit Dubai Health Authority 15 March 2018 Indications for Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis: occupational and non-occupational
Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis Laila AL Dabal MD FRCP MSc Infectious Diseases Unit Dubai Health Authority 15 March 2018 Indications for Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis: occupational and non-occupational
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of Transmission for School Staff
 CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update JHS Annual Mandatory Education
 2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
ART and Prevention: What do we know?
 ART and Prevention: What do we know? Biomedical Issues Trip Gulick, MD, MPH Chief, Division of Infectious Diseases Professor of Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College New York City ART for Prevention:
ART and Prevention: What do we know? Biomedical Issues Trip Gulick, MD, MPH Chief, Division of Infectious Diseases Professor of Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College New York City ART for Prevention:
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions
 Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS. Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care. Peter L. Havens, MD, and the Committee on Pediatric AIDS
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care Peter L. Havens, MD, and the Committee on Pediatric AIDS Postexposure Prophylaxis in Children and Adolescents
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care Peter L. Havens, MD, and the Committee on Pediatric AIDS Postexposure Prophylaxis in Children and Adolescents
HIV in the Workplace
 OEM012_CH24.qxp 8/6/08 12:00 PM Page 441 24 HIV in the Workplace Alan L. Williams and Richard J. Thomas* Over 25 years have elapsed since the first cases of what would become known as the acquired immune
OEM012_CH24.qxp 8/6/08 12:00 PM Page 441 24 HIV in the Workplace Alan L. Williams and Richard J. Thomas* Over 25 years have elapsed since the first cases of what would become known as the acquired immune
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training
 Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training OSHA 29 CFR 1910.1030 Protects workers exposed to blood or other potentially infectious diseases Who are at Risk? Workers in many different
determine need but regimen does not change based on risk factor ED medicine attending meets
 HIV PEP Guidelines after Sexual Assault Harborview Medical Center January 2015 Initial risk assessment and discussion with patient about risk and PEP is by clinician who does exam (SANE, Ob-Gyn resident,
HIV PEP Guidelines after Sexual Assault Harborview Medical Center January 2015 Initial risk assessment and discussion with patient about risk and PEP is by clinician who does exam (SANE, Ob-Gyn resident,
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview
 Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of transmission for school staff. for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood
 BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of transmission for school staff for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood MASSACHUSETTS DIVISION OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY Robert Prezioso,
BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of transmission for school staff for staff not directly responsible for providing care or cleaning up blood MASSACHUSETTS DIVISION OF OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY Robert Prezioso,
Overview of HIV. LTC Paige Waterman
 Overview of HIV LTC Paige Waterman Outline Background and Epidemiology HIV Virology, Transmission, and Pathogenesis Acute HIV infection HIV Diagnostics Management of Health Care Personnel Exposed to HIV
Overview of HIV LTC Paige Waterman Outline Background and Epidemiology HIV Virology, Transmission, and Pathogenesis Acute HIV infection HIV Diagnostics Management of Health Care Personnel Exposed to HIV
An International Antiviral Society-USA
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA University of Arizona, Phoenix dougco@email.arizona. edu A look at new guidelines for HIV treatment and prevention Start antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible after HIV
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA University of Arizona, Phoenix dougco@email.arizona. edu A look at new guidelines for HIV treatment and prevention Start antiretroviral therapy as soon as possible after HIV
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK)
 POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational Exposures to HIV and Recommendations for Postexposure Prophylaxis
 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Recommendations and Reports September 30, 2005 / Vol. 54 / No. RR-9 Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational Exposures to HIV
Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report Recommendations and Reports September 30, 2005 / Vol. 54 / No. RR-9 Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational Exposures to HIV
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
Clinical management of non-occupational and occupational exposure to blood borne pathogens. - A Pocket Reference -
 Pocket P.E.P. Clinical management of non-occupational and occupational eposure to blood borne pathogens Development Team: Deborah Yoong, PharmD 1 1, 2, 3 Kevin Gough, MD, MEd 1 Positive Care Clinic, Toronto,
Pocket P.E.P. Clinical management of non-occupational and occupational eposure to blood borne pathogens Development Team: Deborah Yoong, PharmD 1 1, 2, 3 Kevin Gough, MD, MEd 1 Positive Care Clinic, Toronto,
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard. An Overview
 The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens. Montclair Kimberley Academy 1
 Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Zika Virus in Pregnancy What Midwives Need To Know
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Zika Virus in Pregnancy What Midwives Need To Know Margaret A. Lampe, RN, MPH Pregnancy and Birth Defects Surveillance Team Zika Virus Emergency Response U.S.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Zika Virus in Pregnancy What Midwives Need To Know Margaret A. Lampe, RN, MPH Pregnancy and Birth Defects Surveillance Team Zika Virus Emergency Response U.S.
Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed?
 Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed? UMAYYA MUSHARRAFIEH,MD AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF BEIRUT MEDICAL CENTER JUNE 14, 2013 Health care workers who use or may be exposed to needles are at increased
Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed? UMAYYA MUSHARRAFIEH,MD AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF BEIRUT MEDICAL CENTER JUNE 14, 2013 Health care workers who use or may be exposed to needles are at increased
Overview of HIV WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course
 Overview of HIV WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Acknowledgments - Dr. Christina Polyak - Dr. Julie Ake Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are
Overview of HIV WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Acknowledgments - Dr. Christina Polyak - Dr. Julie Ake Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are
For. Correctional. Officers. Your. Health Risks. in Correctional Settings. Facts. About HIV
 For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
INDIAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL ADVANCEMENTS
 INDIAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL ADVANCEMENTS Journal homepage: www.nacd.in CASE REPORT Prophylaxis Following Occupational Exposure To HIV Manika 1, Shashikant M C 2, Shailaja S 3 Sr. Lecturer 1 & 3 Dept of Oral
INDIAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL ADVANCEMENTS Journal homepage: www.nacd.in CASE REPORT Prophylaxis Following Occupational Exposure To HIV Manika 1, Shashikant M C 2, Shailaja S 3 Sr. Lecturer 1 & 3 Dept of Oral
Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis).
 LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
Prof.Pavitra Ganguly M.S., FMAS, FIAGES Prof & HOD Surgery HIMSR & HAHC Hospital Jamia Hamdard,Delhi
 Prof.Pavitra Ganguly M.S., FMAS, FIAGES Prof & HOD Surgery HIMSR & HAHC Hospital Jamia Hamdard,Delhi Universal precaution are control guidelines designed to protect workers from exposure to Diseases spread
Prof.Pavitra Ganguly M.S., FMAS, FIAGES Prof & HOD Surgery HIMSR & HAHC Hospital Jamia Hamdard,Delhi Universal precaution are control guidelines designed to protect workers from exposure to Diseases spread
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training.
 You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV. Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya.
 TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya. Nevada Hepatitis C Outbreak Tied to Las Vegas Clinic. Thousands Now At Risk for Hepatitis,
TRANSMISSION OF BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS: HIV,HBV,HCV Dr Daniel Kimani HIV Prevention Medical Transmission CDC, Kenya. Nevada Hepatitis C Outbreak Tied to Las Vegas Clinic. Thousands Now At Risk for Hepatitis,
Bloodborne Pathogens. By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases
 Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
Blood Borne Pathogens. Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N.
 Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Blood Borne Pathogens
 Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Module 1: HIV epidemiology, transmission and prevention
 Session 2 Module goals Module 1 Participants will be able to: -offer an insight into the epidemiological situation in the country and worldwide -present the HIV transmission modes and the broad approaches
Session 2 Module goals Module 1 Participants will be able to: -offer an insight into the epidemiological situation in the country and worldwide -present the HIV transmission modes and the broad approaches
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools
 Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
HIV / AIDS Course. A 3 CEU Hour Course, copyright 2010 by Harvey Kaltsas, A.P., D.I.M., Dipl.Ac. (NCCAOM) Take the Test
 HIV / AIDS Course A 3 CEU Hour Course, copyright 2010 by Harvey Kaltsas, A.P., D.I.M., Dipl.Ac. (NCCAOM) 1 This course educates about modes of HIV/AIDS transmission, infection control procedures, clinical
HIV / AIDS Course A 3 CEU Hour Course, copyright 2010 by Harvey Kaltsas, A.P., D.I.M., Dipl.Ac. (NCCAOM) 1 This course educates about modes of HIV/AIDS transmission, infection control procedures, clinical
Infectious Disease Control Oi Orientation. Providence Health & Services
 Infectious Disease Control Oi Orientation ti Providence Health & Services Infection Control Who is at risk of infection & why? Exposures and Outcomes What tools do we use to reduce risk? Surveillance Analysis
Infectious Disease Control Oi Orientation ti Providence Health & Services Infection Control Who is at risk of infection & why? Exposures and Outcomes What tools do we use to reduce risk? Surveillance Analysis
