Chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 expressions and clinical significance in bladder cancer
|
|
|
- Buck Gabriel Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 expressions and clinical significance in bladder cancer D.L. Yang, M.M. Xin, J.S. Wang, H.Y. Xu, Q. Huo, Z.R. Tang and H.F. Wang Department of Urology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Yunnan Institute of Urology, Kunming, China Corresponding author: H.F. Wang Genet. Mol. Res. 14 (4): (2015) Received August 14, 2015 Accepted October 7, 2015 Published December 21, 2015 DOI ABSTRACT. It is well known that chemokine receptors and their ligands play important roles in mediating the invasion and metastasis of malignant tumors. This aim of this study was to investigate the expression and clinical significance of chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 in bladder tumor tissues. Cancerous and adjacent normal bladder tissues were collected from 42 patients. The expressions of CXCR4 and CXCL12 proteins were then detected by immunohistochemistry, and the expressions of CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrnas were detected by RT-PCR. Bladder cancer tissues showed higher positive expressions of CXCR4 and CXCL12 than those in normal bladder mucosal tissues (z = 7.332, 6.758, P < 0.001). Positive expressions of CXCR4 and CXCL12 were related to the differentiation degree and invasive depth of cancer tissues (z = , P < 0.05), but not to patient gender or age (z = , P > 0.05). The expression of CXCR4 was positively correlated to CXCL12 expression in bladder cancer tissues (r = 0.661, P < 0.05). RT- PCR revealed that CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrnas were not expressed in normal tissues. Moreover, with increased depth of invasion, CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrna expressions gradually increased in bladder cancer tissues
2 D.L. Yang et al and showed significant intergroup differences (F = , , P < 0.01). Taken together, these results indicate that the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 play important roles in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer. Key words: Bladder cancer; Bladder tumor tissue; CXCR4; SDF-1; CXCL12 INTRODUCTION Bladder cancer is a major urogenital cancer, and is characterized by high progression and recurrence rates. In China, bladder tumors are the most common among all urogenital cancer tumor types and their incidence is on the rise (Raghavan, 2012). According to numerous studies on the invasive mechanisms of tumor metastasis, chemokine receptors and their ligands play important roles in mediating the invasion and metastasis of malignant tumors (Dobner et al., 2012; Domanska et al., 2013). In the current study, we targeted the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12, and investigated their protein and gene expressions using the immunohistochemistry (IHC) methods and reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), respectively, in cancerous and normal bladder tissues, and analyzed their clinical significance. MATERIAL AND METHODS Specimens Forty-two patients (35 males and 8 females) aged years (median 67 years) undergoing operation between July 2010 and June 2011 were enrolled in this study. Postoperatively, all patients were pathologically diagnosed with bladder cancer. No patient received preoperative radiotherapy or chemotherapy. Additionally, normal mucosal bladder tissues (pathological sections confirmed no proliferative or tumor-induced changes) 5 cm above cancer tissues were collected from each patient as controls. Each specimen was processed in duplicate, one was fixed in 4% formaldehyde and one immediately stored at -80 C until further analysis. Reagents Rabbit anti-human CXCR4 and anti-sdf-1 (CXCL12) monoclonal antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA). Astreptavidin peroxidase (S-P) immunohistochemical staining kit and DAB color kit were purchased from Fuzhou Maxim Biotech (Fujian, China). TRIzol Reagent for RNA extraction and the M-MLV First-Strand Synthesis Kit for RT-PCR were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). A Premix Taq kit for amplification of target genes with RT-PCR and DNA markers were purchased from TaKaRa Biotechnology (Dalian, China). CXCR4, CXCL12, and GAPDH (internal control) primers were synthesized by Shanghai Invitrogen (China). All other reagents were purchased from Sigma (US) or Amresco (US), or were produced in China at analytical grade. CXCR4 and CXCL12 protein expression in cancerous and normal bladder tissues detected by the IHC S-P method The resected bladder cancer tissues and normal bladder tissues were aseptically collected.
3 CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions in bladder cancer After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde and paraffin embedding, serial sections approximately 4 μm thick were obtained and mounted onto glass slides, followed by air drying and heating in an oven at 65 C for 2 h. Then, after dewaxing by xylene and hydration by gradient ethanol, 0.3% H 2 O 2 (v/v) was used to inhibit endogenous peroxidase. The sections were then immersed in 10% citrate antigen repair solution and heated in a pressure cooker for 90 s. After cooling, the tissue antigens were repaired, and 3% H 2 O 2 (v/v) was used to inhibit endogenous peroxidase. The sections were then blocked with normal goat serum, and the anti-cxcr4 (working diluted 1:100) and anti-sdf-1 (1:50) antibodies were separately added, and refrigerated overnight at 4 C. The next day, the sections were sufficiently washed (5 min x 3) with phosphate buffer solution (PBS), dripped with a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody working solution, and incubated at 37 C for 15 min. The sections were then washed (5 min x 3) with PBS, dripped with a streptomycin- H 2 O 2 working solution, and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. Then after washing (5 min x 3) with PBS, the sections were colored with a freshly prepared DAB color solution according to manufacturer instructions, re-dyed and clarified with hematoxylin, and sealed with a neutral resin before observation under light microscopy. In negative controls, PBS was used in lieu of the primary antibody. CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrna expression detected by RT-PCR Approximately 100 mg of the cold-stored specimens was collected and ground to a powder. RNA was extracted by adding 1 ml TRIzol Reagent. Absorptions of RNA at 260 and 280 nm were determined by ultraviolet spectrometry, and RNA concentration and purity were calculated. cdna was synthesized by reverse transcription according to the M-MLV First-Strand Synthesis Kit instructions. The cdna was then used as a template for PCR amplification of CXCR4 and CXCL12 transcripts, and GAPDH served as the internal control. PCR primers were as follows for CXCR4: 5'-CTCCTCTTTGTCATCACGCTTCC-3' (forward), 5'-GGATGAGGACACTGCTGTAGAG-3' (reverse); CXCR12: 5'-CTCAACACTCCAAACTGTGCCC-3' (forward), 5'-CTCCAGGTACTCCTGAATCCAC-3' (reverse); and GAPDH: 5'-AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTTG-3' (forward), 5'-AGGGGCCATCCACAGT CTTC-3' (reverse). Amplified fragment lengths for CXCR4, CXCL12, and GAPDH were 126, 104, and 258 bp, respectively. Reactions included pre-denaturation at 94 C for 3 min; followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 94 C for 30 s, renaturation at 55 C for 30 s, and extension at 72 C for 60 s; and a final extension at 72 C for 5 min. After amplification, 5 μl of the products was collected for electrophoresis on a 1.5% agarose gel (containing ethidium bromide) followed by visualization and quantification with a gel imaging system. CXCR4 and CXCL12 protein expression detected by western blot For cell fractionation, approximately 100 mg of bladder tissues was homogenized in liquid nitrogen and the homogenate was extracted in 2 ml homogenization buffer. The crude extract was cleared of debris by centrifugation (4000 g, 40 min, 4 C). The microsomal fraction was separated from the soluble fraction by ultracentrifugation (100,000 g, 30 min, 4 C). The pellet was washed three times in homogenization buffer supplemented with 0.05% Triton X-100 and resuspended in 50 μl SDS-PAGE sample buffer. The soluble fraction was mixed with SDS-PAGE sample buffer (ratio: 2:1 v/v). For SDS-PAGE, 18 μl soluble fraction and 10 μl microsomal fraction were loaded. CXCR4 and CXCL12 protein were detected in 100 μg protein, according to procedures described by Calogero et al. (2001) and Baron et al. (2006), and GAPDH was used as a loading control.
4 D.L. Yang et al Examination of IHC results After positive staining, CXCR4 and CXCL12 appeared as light brown granules in the membrane and/or cytoplasm. Three fields of view obtained from a high power objective (400X) were selected for each section for analysis. A similar number of total cells was counted for each sample, and according to the percentage of positive cells, the IHC results were classified into: negative (-) (5%), weak positive (+) (5-25%), medium positive (++) (25-50%), and strong positive (+++) ( 50%). Analysis of RT-PCR results Band optical densities (BODs) of amplified CXCR4 and CXCL12 fragments obtained from the gel electrophoresis imaging system, were compared with the corresponding GAPDH BODs as the internal control. The Image J software (developed by US National Institutes of Health) was used for optical density analysis. Statistical analysis Data were statistically processed with SPSS 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Grade data were compared by nonparametric statistical rank and Mann-Whitney tests. Correlations were examined by Spearman tests. Measurements were compared by ANOVA, completely and randomly designed variance analysis. Inspection level is α = P < 0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS Protein expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in bladder tumor tissues and normal bladder tissues Positive expressions of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in bladder cancer tissue were significantly higher than those in normal bladder tissue (z = , P < 0.001) (summarized in Figure 1 and Table 1). Clinical significance of CXCR4 and CXCL12 protein expressions in bladder tumor tissues A statistical association between the protein expression of CXCR4/CXCL12 and bladder cancer was observed, while only trends towards statistical associations were observed between CXCR4/CXCL12 protein expression and the degree of differentiation (z = 2.828, P < 0.05) and depth of invasion (z = 4.594, P < 0.01) (Table 2). CXCR4/CXCL12 protein expression was found to be strongly associated with the progression and invasion of bladder cancer. No statistical associations between CXCR4/CXCL12 expression levels and the other clinical parameters analyzed were found (summarized in Table 2). Correlation between the degree of expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in bladder tumor tissues The expressions of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in bladder cancer tissue were positively correlated (r = 0.661, P < 0.05) (summarized in Table 3).
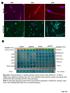
5 CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions in bladder cancer Figure 1. Immunohistochemical staining for CXCR4 and CXCL12. A. Expression of CXCR4 in bladder tumor tissues (S-P method, 400X). B. Normal bladder tissues do not express CXCR4 (S-P method, 400X). C. Expression of CXCL12 in bladder tumor tissues (S-P method, 400X). D. Normal bladder tissues do not express CXCL12 (S-P method, 400X). Table 1. Comparison of CXCR4 and CXCL12 expression between normal bladder tissues and bladder cancer tissues (cases). Group N CXCR4 CXCL Bladder tumor tissues Normal bladder tissues Table 2. Relationship between CXCR4/CXCL12 protein expressions and clinical parameters (cases). Clinical parameter N CXCR4 CXCL z P value z P value Gender Male > >0.05 Female Age (years) > >0.05 > Depth of invasion Ta+T < <0.01 T2+T Degree of differentiation Medium to high < <0.05 Low
6 D.L. Yang et al Table 3. Correlation between CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions in bladder tumor tissues (cases). CXCR4 CXCL12 Total Total CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrna expression in cancerous and normal bladder tissues Semiquantitative mrna analysis revealed that CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrnas were expressed in varying amounts in cancerous tissues, but not in normal tissues (Figure 2). With regard to different stages of bladder cancer, CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrna expressions were the highest in T 2 T 3 stage (15 cases), followed by T 1 stage (11 cases), and T a stage (16 cases), with significant intergroup differences (F = , , P < 0.01). Figure 2. Semiquantitative mrna analysis (GAPDH, 258 bp; CXCR4, 126 bp; CXCL12, 104 bp). The expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrnas are seen in bladder tumor tissues, but not in normal bladder tissues. Lanes 4, 5, 6, 11, 12, and 13 are normal (N) bladder tissues, and lanes 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, and 9 are bladder tumor (T) tissues with different degrees of malignancy. CXCR4 and CXCL12 protein levels in cancerous and normal bladder tissues Western blot analysis revealed that CXCR4 and CXCL12 proteins were expressed in varying amounts in cancerous tissues, but not in normal tissues (Figure 3). With regard to different stages of bladder tumor, CXCR4 and CXCL12 protein expressions were the highest in T 2 T 3 stage (15 cases), followed by T 1 stage (11 cases) and T a stage (16 cases), with significant intergroup differences (F = , , P = 0.000, 0.000, P < 0.01). Figure 3. Western blot analysis. The expressions of CXCR4 and CXCL12 proteins are seen in bladder tumor (T) tissues, but not in normal (N) bladder tissues. Lanes 2, 4, and 6 are normal bladder tissues, and lanes 1, 3, and 5 are bladder cancer tissues with different degrees of malignancy.
7 CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions in bladder cancer DISCUSSION Chemokines (relative molecular weight 7-14 kda) act as chemoattractants for immune cell chemotaxis, such as neutrophils and lymphocytes, and can be produced by various cells. According to the number and position of intramolecular specific cysteines, chemokines can be divided into four sub-families: CXC, CC, C, and CX3C, and likewise, their corresponding receptors can be divided into four types: CXCR, CCR, CR, and CX3CR (Horuk, 2001). CXCR4 is a seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor that contains 352 highly conserved amino acids. CXCR4 is also expressed in several types of tumor cells. Its specific ligand CXCL12, also known as stromal cellderived factor 1 (SDF-1) or pre-b cell stimulating factor (PBSF), belongs to the CXC chemokine family. CXCL12 and CXCR4 show high affinity for one another and can be specifically combined to form the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis, which is the molecular basis of their biological functions and is closely related to the invasion and metastasis of malignant tumors (Roland et al., 2003; Yasumoto et al., 2011). The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis functions as a regulatory element for leukergy, and can have many effects on the extracellular matrix and on tumor cells (Domanska et al., 2013). The activation of chemokine signals can result in various intracellular changes, including the activation of RAS/MAPK (mitogen activated protein kinase) signal transduction pathways, the polymerization of intracellular actins, the rearrangement of the cytoskeleton, the formation of pseudopods, the movements of cells, and consequently can increase tumor cell invasiveness (Luo et al., 2006). There have been many reports on CXCR4 expression in cells from various tumors, such as those from breast, lung, pancreas, colon, ovary, and prostate cancers (Balkwill, 2004; Toyozawa et al., 2012; Dai et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2013), as well as reports on CXCL12 expression in tumor cells, such as those from the primary foci in lymph and neuroglia tumors, and from cancers of the ovary and pancreas (Lira and Furtado, 2012). Studies on bladder cancer have shown that CXCR4 was expressed in bladder tumor cells, but not in normal bladder mucosa, and was more highly expressed in infiltrative tumors than in superficial tumors (Retz et al., 2005). Furthermore, CXCR4 mrna expression was upregulated in infiltrative and advanced bladder cancer tissues, whereas it was low in superficial bladder cancer (Balkwill, 2004). However, no previous report has definitively confirmed the expression of CXCL12 in bladder tumor tissues, or the correlation between the expression levels of CXCR4 and CXCL12. In the current study, IHC analysis revealed that CXCR4 and CXCL12 were more expressed in tumor-invaded bladder tissues than in normal tissues, indicating that CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 are associated with the occurrence of bladder cancer. Association analyses of the degree of CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions in bladder tumor tissues to clinical pathological features revealed that CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions were associated with the invasive depth and differentiation degree of bladder tumors, but not to the gender or age of patients, indicating the important roles of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in the development, invasion, and metastasis of bladder cancer. Further correlation analysis revealed that the expression of CXCR4 was significantly positively correlated with CXCL12 expression, indicating a synergistic effect and potential interdependence between CXCR4 and CXCL12 in bladder cancer. RT-PCR results show that CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrnas were not expressed in normal bladder tissues. The results further demonstrate that CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrnas were expressed in all bladder cancer tumor tissues, the expressions were lower in early-stage cancer tissues and that they were increased with increased invasive depth. These results suggest that during the progression and invasion of bladder cancer, the expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 mrnas
8 D.L. Yang et al are increased, which may also indicate that bladder cancer cells with high CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions are more invasive. All results herein show that the high CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions are closely related to the development, invasion, and metastasis of bladder cancer, and suggest that bladder tumor cells with high CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions are highly invasive. Therefore, the invasive depth, degree of metastasis, and prognosis may be evaluated by CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions in bladder cancer tissues. In vitro studies showed that blocking CXCR4 expression could impact the functions of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis and repress the growth of bladder tumor cells (Wang et al., 2011). In vivo studies also showed that blocking CXCR4 expression could repress the growth of bladder tumor cells, which provides a potential molecular target for prevention and treatment of bladder cancer. Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Research supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (# ), the Yunnan Provincial Department of Education Fund (#2014Z072) and the Joint Project of Science and Technology, Department of Yunnan and Kunming Medical University (#2014FZ031). REFERENCES Balkwill F (2004). The significance of cancer cell expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Semin. Cancer Biol. 14: Baron V, Adamson ED, Calogero A, Ragona G, et al. (2006). The transcription factor Egr1 is a direct regulator of multiple tumor suppressors including TGFbeta1, PTEN, p53, and fibronectin. Cancer Gene Ther. 13: Calogero A, Arcella A, De Gregorio G, Porcellini A, et al. (2001). The early growth response gene EGR-1 behaves as a suppressor gene that is down-regulated independent of ARF/Mdm2 but not p53 alterations in fresh human gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 7: Dai X, Mao Z, Huang J, Xie S, et al. (2013). The CXCL12/CXCR4 autocrine loop increases the metastatic potential of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro. Oncol. Lett. 5: Dobner BC, Riechardt AI, Joussen AM, Englert S, et al. (2012). Expression of haematogenous and lymphogenous chemokine receptors and their ligands on uveal melanoma in association with liver metastasis. Acta Ophthalmol. 90: e638-e644. Domanska UM, Kruizinga RC, Nagengast WB, Timmer-Bosscha H, et al. (2013). A review on CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in oncology: No place to hide. Eur. J. Cancer 49: Horuk R (2001). Chemokine receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 12: Lira SA and Furtado GC (2012). The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Immunol. Res. 54: Luo C, Pan H, Mines M, Watson K, et al. (2006). CXCL12 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin, which plays a role in CXC chemokine receptor 4-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and chemotaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 281: Raghavan D (2012). Introduction: bladder cancer. Semin. Oncol. 39: 523. Retz MM, Sidhu SS, Blaveri E, Kerr SC, et al. (2005). CXCR4 expression reflects tumor progression and regulates motility of bladder cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 114: Roland J, Murphy BJ, Ahr B, Robert-Hebmann V, et al. (2003). Role of the intracellular domains of CXCR4 in SDF-1-mediated signaling. Blood 101: Toyozawa S, Kaminaka C, Furukawa F, Nakamura Y, et al. (2012). Chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a novel marker for the progression of cutaneous malignant melanomas. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 45: Wang H, Yang D, Wang K and Wang J (2011). Expression and potential role of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in human bladder carcinoma cell lines with different metastatic ability. Mol. Med. Rep. 4:
9 CXCR4 and CXCL12 expressions in bladder cancer Yasumoto K, Yamada T, Kawashima A, Wang W, et al. (2011). The EGFR ligands amphiregulin and heparin-binding egf-like growth factor promote peritoneal carcinomatosis in CXCR4-expressing gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 17: Zhang Y, Guo Q, Zhao H, Zhao D, et al. (2013). Expression of CXCR4 is an independent prognostic factor for overall survival and progression-free survival in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Med. Oncol. 30: 341.
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
The expression and significance of tumor associated macrophages and CXCR4 in non-small cell lung cancer
 JBUON 2018; 23(2): 398-402 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE The expression and significance of tumor associated macrophages and
JBUON 2018; 23(2): 398-402 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE The expression and significance of tumor associated macrophages and
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk in a Chinese Han population
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Cytochrome C (10 M) Z-VAD-fmk. Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Z-VAD-fmk
 A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Expression of CXCL12/CXCR4 and its correlation to prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 28:2, 154-158; February 2009]; 2009 Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center Clinical Research Paper Expression of CXCL12/CXCR4 and its correlation to prognosis in esophageal squamous
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 28:2, 154-158; February 2009]; 2009 Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center Clinical Research Paper Expression of CXCL12/CXCR4 and its correlation to prognosis in esophageal squamous
Expression profile of tumor suppressor gene RASSF1 in lacrimal gland carcinoma
 Expression profile of tumor suppressor gene RASSF1 in lacrimal gland carcinoma C.H. Zeng, B. Guo, J. Chen, W.M. He and Q.L. Luo Ophthalmology Department of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Sichuan,
Expression profile of tumor suppressor gene RASSF1 in lacrimal gland carcinoma C.H. Zeng, B. Guo, J. Chen, W.M. He and Q.L. Luo Ophthalmology Department of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Sichuan,
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
 Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells *
 Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4 Related Products..
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model
 CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor
 Figures Part of introduction Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor supressor gene deletion in the induction of thyroid carcinoma. ( by James A Fagin, M.D.)
Figures Part of introduction Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor supressor gene deletion in the induction of thyroid carcinoma. ( by James A Fagin, M.D.)
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
ExpressArt FFPE Clear RNAready kit
 Features and Example Results General problems with FFPE samples Formalin-fixation of tissues results in severe RNA fragmentation, as well as in RNA RNA, RNA-DNA and RNA protein cross-linking, which impairs
Features and Example Results General problems with FFPE samples Formalin-fixation of tissues results in severe RNA fragmentation, as well as in RNA RNA, RNA-DNA and RNA protein cross-linking, which impairs
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
Expression and Significance of GRP78 and HER-2 in Colorectal Cancer
 Expression and Significance of GRP78 and HER-2 in Colorectal Cancer Qiu-xia Ji 1, Li-li Wang 2, Lin Li 3, Xiaoming Xing 2 1 Department of Pathology, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China 2 Department of Pathology,
Expression and Significance of GRP78 and HER-2 in Colorectal Cancer Qiu-xia Ji 1, Li-li Wang 2, Lin Li 3, Xiaoming Xing 2 1 Department of Pathology, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China 2 Department of Pathology,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the clinical features of HBsAg-positive liver cancer
 JBUON 2017; 22(4): 942-946 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the
JBUON 2017; 22(4): 942-946 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Assay Kit
 Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Product Manual. Omni-Array Sense Strand mrna Amplification Kit, 2 ng to 100 ng Version Catalog No.: Reactions
 Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Expression and clinical significance of Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 in breast cancer
 Expression and clinical significance of Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 in breast cancer L. Zhang*, W.P. Yang*, L.Y. Wu, X. Zhu and C.Y. Wei Department of Breast Surgery, Affiliated Tumor
Expression and clinical significance of Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 in breast cancer L. Zhang*, W.P. Yang*, L.Y. Wu, X. Zhu and C.Y. Wei Department of Breast Surgery, Affiliated Tumor
Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
Original Article Human cervical cancer oncogene-1 over expression in colon cancer and its clinical significance
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1):939-943 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003891 Original Article Human cervical cancer oncogene-1 over expression in colon cancer and its clinical significance Kai Meng
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(1):939-943 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003891 Original Article Human cervical cancer oncogene-1 over expression in colon cancer and its clinical significance Kai Meng
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Clinical Study Correlation of Plasma MMP-1 and TIMP-1 Levels and the Colonic Mucosa Expressions in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis
 Mediators of Inflammation Volume 2009, Article ID 275072, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2009/275072 Clinical Study Correlation of Plasma MMP-1 and TIMP-1 Levels and the Colonic Mucosa Expressions in Patients with
Mediators of Inflammation Volume 2009, Article ID 275072, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2009/275072 Clinical Study Correlation of Plasma MMP-1 and TIMP-1 Levels and the Colonic Mucosa Expressions in Patients with
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian cancer
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Function and clinical significance of SUMOylation in type I endometrial carcinoma
 Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-017-0245-5 December 2017, Vol. 3, No. 6, P P ORIGINAL ARTICLE Function and clinical significance of SUMOylation in type I endometrial carcinoma Xin
Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-017-0245-5 December 2017, Vol. 3, No. 6, P P ORIGINAL ARTICLE Function and clinical significance of SUMOylation in type I endometrial carcinoma Xin
Anti-PD-L1 antibody [28-8] ab205921
![Anti-PD-L1 antibody [28-8] ab205921 Anti-PD-L1 antibody [28-8] ab205921](/thumbs/84/91196262.jpg) Anti-PD-L1 antibody [28-8] ab205921 2 Abreviews 16 References 15 Images Overview Product name Anti-PD-L1 antibody [28-8] Description Tested applications Species reactivity Immunogen Rabbit monoclonal [28-8]
Anti-PD-L1 antibody [28-8] ab205921 2 Abreviews 16 References 15 Images Overview Product name Anti-PD-L1 antibody [28-8] Description Tested applications Species reactivity Immunogen Rabbit monoclonal [28-8]
HER2 status assessment in breast cancer. Marc van de Vijver Academic Medical Centre (AMC), Amsterdam
 HER2 status assessment in breast cancer Marc van de Vijver Academic Medical Centre (AMC), Amsterdam 13e Bossche Mamma Congres 17 th June 2015 Modern cancer therapies are based on sophisticated molecular
HER2 status assessment in breast cancer Marc van de Vijver Academic Medical Centre (AMC), Amsterdam 13e Bossche Mamma Congres 17 th June 2015 Modern cancer therapies are based on sophisticated molecular
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Validation Report: VERSA Mini PCR Workstation Reverse Transcription of Avian Flu RNA and Amplification of cdna & Detection of H5N1
 I. Objectives Validation Report: VERSA Mini PCR Workstation Reverse Transcription of Avian Flu RNA and Amplification of cdna & Detection of H5N1 1. To ensure stability of RNA (highly thermolabile and degradatively
I. Objectives Validation Report: VERSA Mini PCR Workstation Reverse Transcription of Avian Flu RNA and Amplification of cdna & Detection of H5N1 1. To ensure stability of RNA (highly thermolabile and degradatively
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Original Article Clinical significance of SOX2 and snail expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9569-9574 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0027666 Original Article Clinical significance of SOX2 and snail expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Na Miao 1*,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9569-9574 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0027666 Original Article Clinical significance of SOX2 and snail expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Na Miao 1*,
Shangqiu Medical College, Shangqiu, China 2. Corresponding author: M.Z. Zhang
 Comparison of the expression of human equilibrative nucleotide transporter 1 (hent1) and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 (RRM1) genes in seven non-hodgkin lymphoma cell lines H.B. Zhao 1,2, X.F. Zhang
Comparison of the expression of human equilibrative nucleotide transporter 1 (hent1) and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 (RRM1) genes in seven non-hodgkin lymphoma cell lines H.B. Zhao 1,2, X.F. Zhang
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population
 Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma
 Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Appendix 1. A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for
 Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Roles of the AIB1 protein in the proliferation and transformation of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Roles of the AIB1 protein in the proliferation and transformation of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma L. Li 1 *, P. Wei 2 *, M.-H. Zhang 1, W. Zhang 2, Y. Ma 1, X. Fang 1, C.-L. Hao 1 and Z.-H.
Roles of the AIB1 protein in the proliferation and transformation of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma L. Li 1 *, P. Wei 2 *, M.-H. Zhang 1, W. Zhang 2, Y. Ma 1, X. Fang 1, C.-L. Hao 1 and Z.-H.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit User Manual (v5)
 Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry
 Nat Met, April 2014 Nat Med, April 2014 Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry Journal Club Timo Böge Overview Introduction Conventional Immunohistochemistry
Nat Met, April 2014 Nat Med, April 2014 Next-Generation Immunohistochemistry: Multiplex tissue imaging with mass cytometry Journal Club Timo Böge Overview Introduction Conventional Immunohistochemistry
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Overexpressing exogenous S100A13 gene and its effect on proliferation of human thyroid cancer cell line TT
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 130-5; 130-134; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Overexpressing exogenous S100A13 gene and its effect on proliferation of
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 130-5; 130-134; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Overexpressing exogenous S100A13 gene and its effect on proliferation of
DNA Methylation of Tumor Suppressor and Metastasis Suppressor Genes in Circulating Tumor Cells and corresponding Circulating Tumor DNA
 DNA Methylation of Tumor Suppressor and Metastasis Suppressor Genes in Circulating Tumor Cells and corresponding Circulating Tumor DNA Maria Chimonidou 1, Areti Strati 1, Nikos Malamos 2, Vasilis Georgoulias
DNA Methylation of Tumor Suppressor and Metastasis Suppressor Genes in Circulating Tumor Cells and corresponding Circulating Tumor DNA Maria Chimonidou 1, Areti Strati 1, Nikos Malamos 2, Vasilis Georgoulias
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set
 Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast cancer cells
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION. Expression and Clinical Significance of STAT3, P-STAT3, and VEGF-C in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Xue Zhao, Xian Sun, Xiao-li Li*
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.6.2873 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Expression and Clinical Significance of STAT3, P-STAT3, and VEGF-C in Small Cell Lung Cancer Xue Zhao, Xian Sun, Xiao-li Li* Abstract
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.6.2873 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Expression and Clinical Significance of STAT3, P-STAT3, and VEGF-C in Small Cell Lung Cancer Xue Zhao, Xian Sun, Xiao-li Li* Abstract
Expression and Clinical Significance of REGγ in Gastric Cancer Tissue and Variously Differentiated Gastric Cancer Cell Lines
 208 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2009) 6: 208-213 DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0208-6 Expression and Clinical Significance of REGγ in Gastric Cancer Tissue and Variously Differentiated Gastric Cancer Cell Lines Jia
208 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2009) 6: 208-213 DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0208-6 Expression and Clinical Significance of REGγ in Gastric Cancer Tissue and Variously Differentiated Gastric Cancer Cell Lines Jia
Expressions of PS-2, CA153 and VEGF and clinical significance in patients with breast cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (22): 9920-9925 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Expressions of PS-2, CA153 and VEGF and clinical significance in patients with breast cancer. Li Zhixiang, Qian Jun *, Li
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (22): 9920-9925 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Expressions of PS-2, CA153 and VEGF and clinical significance in patients with breast cancer. Li Zhixiang, Qian Jun *, Li
The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors
 Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Product Datasheet. DARC Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg. Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5
 Product Datasheet DARC Antibody NB100-2421 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nb100-2421
Product Datasheet DARC Antibody NB100-2421 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nb100-2421
Research Article Correlation and Significance of Urinary Soluble Fas and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Bladder Urothelial Cancer
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 383509, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/383509 Research Article Correlation and Significance of Urinary Soluble Fas and Vascular
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 383509, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/383509 Research Article Correlation and Significance of Urinary Soluble Fas and Vascular
