MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: , 2014
|
|
|
- Alban Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: , 2014 MicroRNA-193b is a regulator of amyloid precursor protein in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid derived exosomal microrna-193b is a biomarker of Alzheimer's disease CHEN-GENG LIU, JING SONG, YUE-QI ZHANG and PEI-CHANG WANG Department of Clinical Laboratory, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing , P.R. China Received November 23, 2013; Accepted June 24, 2014 DOI: /mmr Abstract. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) has an important function in the generation of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In our previous study, mir 193b was found to be downregulated in the hippocampi of 9 month old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice using microrna (mir) array. In the present study, bioinformatic analyses showed that mir 193b was a mir that was predicted to potentially target the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of APP. Subsequently, the function of mir 193b on APP was studied. The levels of mir 193b, exosomal mir 193b, Aβ, tau, p tau, HCY and APOE in samples from APP/PS1 double transgenic mice, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia of Alzheimer type (DAT) patients, were measured. The results indicated that overexpression of mir 193b could repress the mrna and protein expression of APP. The mir 193b inhibitor oligonucleotide induced upregulation of APP. Binding sites of mir 193b in the 3' UTR of APP were identified by luciferase assay. MCI and DAT patients had lower exosomal mir 193b, but not total mir 193b, in the blood as compared with the controls. DAT patients had lower exosomal mir 193b levels in blood as compared with the MCI group. A decreased exosomal mir 193b expression level was additionally observed in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) of DAT patients. Negative correlations were found between exosomal mir 193b and Aβ42 in the CSF of DAT patients. In conclusion, these findings showed that mir 193b may function in the development of AD and exosomal mir 193b has potential as a novel, non-invasive, blood based biomarker of MCI and DAT patients. Introduction Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a prominent neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive loss of memory and other Correspondence to: Professor Pei-Chang Wang, Department of Clinical Laboratory, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, No. 45 Changchun Road, Beijing , P.R. China peichangwang@yahoo.com.cn Key words: Alzheimer's disease, amyloid precursor protein, microrna cognitive functions. Despite considerable progress in genetics and cell biology, numerous questions remain regarding the mechanisms of neurodegeneration and the molecular and pathological components. Extracellular amyloid β (Aβ), which is derived from the larger amyloid precursor protein (APP), is considered to be responsible for the death of neurons and dementia in Alzheimer's disease. An increased expression of APP may increase the risk of AD (1,2). APP levels can be regulated at the genomic, transcriptional or translational level, and in the rate of degradation. Genetic variants in the APP promoter increase APP transcription by 2 3 fold and have been reported to increase the risk of AD (2). APP can be processed by a group of secretases where α secretase produces soluble fragments, whereas β and γ secretase generate Aβ from APP (3). Previous research has suggested that Aβ regulates neuronal and synaptic activity, and accumulation of Aβ in the brain causes a combination of aberrant network activity and synaptic depression (4). MicroRNAs (mirs) are endogenous, short, noncoding RNAs. Mature mirs are single-stranded RNA molecules of ~20 25 nucleotides which act as important post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression by binding with their target mrnas. They are additionally essential for normal neuronal function and survival (3,4). Several mirs have been shown to be important in neuropathology by downregulating AD related proteins, including APP and BACE 1. It has been demonstrated that mir 16, 101, 106a/b, 147 and 160a could function as APP suppressors (5 8). Several cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) or blood-based markers, such as Aβ, tau and phosphorylated tau (p tau) are proposed biomarkers for predicting future cognitive decline in healthy individuals, and the progression to dementia in patients who are cognitively impaired (9 11). Previous studies have shown that APP and BACE 1 are novel markers of AD (12 14). However, there is still an urgent requirement for additional biomarkers that can detect AD in the pre-dementia phase (9 14). Alterations to the regulation of mirs in the blood and CSF may indicate progression in AD (15,16). Exosomes are membrane vesicles with a size of nm that are released from numerous cell types of the body (17). Recent studies have shown that, in addition to functional proteins, exosomes carry mrna as well as mirs (18). In functional terms, exosomes are considered to represent a novel mechanism of intercellular communication. This may be due to the uptake of exosomes by
2 2396 LIU et al: MICROrna-193B WAS A REGULATOR OF app AND EXOSOMAL MICROrna-193B WAS A BIOMARKER OF ad target cells or by triggering cell signaling through membrane receptors (17 19). In a previous study, we found that mir 193b was decreased in the hippocampi of 9 month old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice by mir array. In the present study, bioinformatic analyses showed that mir 193b may potentially target the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of APP and the effects of mir 193b on the expression of APP were studied. Blood and CSF derived exosomal mir 193b was detected in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice, and patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia of Alzheimer type (DAT). Materials and methods Study population. The design of the present study was approved by the ethics committee of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University (Beijing, China), and the written informed consents were obtained from all participants. A total of 43 MCI (23 females, 20 males, mean age 63.8±6.1) and 51 DAT patients (28 females, 23 males, mean age 64.2±6.5) were selected for this study. The CSF was drawn within 2 h following collection of blood (n=7). Age and gender matched control subjects were included in the experimental design. Samples were stored at 80 C until required for further analysis. The expression levels of Aβ, tau and p tau in the plasma and CSF of the subjects were determined by ELISA kit from Cusabio (Wuhan, China). The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University (Beijing, China). Written informed consent was obtained from the patients' family. APP/PS1 double transgenic and wild-type mice. The 3, 6 and 9 month old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice on a C57BL/6J genetic background were purchased from the Institute of Laboratory Animal Science, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Comparative Medical Center (Beijing, China). All the animal protocols were approved by Ethics Committee of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University (Beijing, China). The non transgenic mice were used as wild-type (WT) controls. Blood was taken by removing the eyeballs and CSF like fluid was collected as previously described (20). The hippocampi were isolated as described for mir 193b quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr) detection (n=5). The samples were stored in liquid nitrogen until analysis. Cell culture and mir transfections. SH SY5Y and HEK293 cell lines were purchased from Shanghai Institute of Cell Biology, China. Cells were grown in antibiotic free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 37 C with 5% CO 2. SH SY5Y cells were transfected with 100 nm (final concentration) mir 193b mimic oligonucleotide, mir 193b inhibitor oligonucleotide or a non-specific control small interfering RNA sirna) (GenePharma) using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen Life Sciences, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Reporter vectors and DNA constructs. Reporter vectors containing the putative mir 193b target site from the APP 3' UTR was synthesized with double stranded oligos perfectly complementary to putative mir 193b target site and oligos in which the seed regions were mutated (21). The APP oligos had the sequence (seed region bolded) as follows: 5' CCCAAGCTTTCACATA GCCCCTTAGCCATTTAAGCTTGGG 3'; 3' GGGT TCGAAAGTGTATCGGGGAATCGGTAAATTCGAACC 5'. The mutant APP target oligos had nucleotides 3 6 of the seed region mutated (italicized): 5' CCCAAGCTTTCAC ATAGCCCCTTAACTAGTTAAGCTTGGG 3'; 3' GGGTTC GAAAGTGTATCGGGGAATTGATCAATTCGAACCC 5'. HEK 293 cells were plated in 24 well plates. The following day, cells were transfected with a mir mimic oligonucleotide, reporter vectors bearing either the mir target sequence or the mir seed region mutant target sequence, and one tenth of the molar volume of prl SV40, a Renilla luciferase control vector. Arrest In transfection reagent (Open Biosystems Inc; GE healthcare, Fairfield, CT, USA) was used; any differences in transfection efficiency were accounted for by measuring Renilla luciferase activity. Following 48 h posttransfection, cells were lysed using 100 µl of GLB (Glo Lysis Buffer, Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured using a dual luciferase reporter assay kit (Promega), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to the Renilla luciferase activity. Isolation of RNA and APP mrna qpcr analysis. Total RNA from harvested cells was isolated using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen Life Sciences) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Isolated RNA was reverse transcribed using the PrimeScript RT reagent (Takara Bio, Inc., Shiga, Japan). The mrna expressions of APP was determined using SYBR Green qpcr (Takara Bio, Inc) using a LightCycler 480 System (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). GAPDH was used to normalize the target genes. The PCR primer sequences were as follows: APP, forward, 5' TTGCGAAACTCATCTTCACTGG 3', reverse 5' CAGTGGGCAACACACAAACTCTAC 3'; GAPDH, forward, 5' GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC 3', reverse 5' TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA 3'. The number of samples in each group was five. Western blots. Western blotting was performed as previously described (22). Cells were homogenized in extraction buffer, then incubated at 0 C for 15 min and centrifuged at 2,000 x g for 10 min at 4 C. Aliquots of the supernatants were used for the measurement of the total protein content. Samples were boiled for 5 min in loading buffer and then the proteins (30 µg per well) were separated by 10% SDS PAGE (Bio Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Proteins in the gel were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Pall Corporation, New York, NY, USA). Membranes were incubated with anti APP (diluted 1:500; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), and anti GAPDH (diluted 1:400, Abcam) at room temperature for 1.5 h, respectively. Membranes were then washed and incubated with anti IgG antibody linked to horseradish peroxidase at room temperature for 1 h. The membranes were then incubated with substrate for peroxidase and enhanced chemiluminescence (KPL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) for 1 min and exposed immediately to X ray film for 1 5 min. Films were
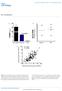
3 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: , then revealed in the conventional manner. The amount of each protein was measured by densitometric analysis and standardized relative to GAPDH. The number of samples in each group was five. Isolation of exosomes. The exosomes were isolated using the Total Exosome Isolation kit (Invitrogen Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, the serum was centrifuged at 2,000 x g for 30 min to remove cells and debris. Following this, 400 µl clarified serum was transferred to a new tube and 0.4 volumes of the Total Exosome Isolation reagent was added. The serum/reagent solution was mixed and then incubated at 4 C for 30 min. After incubation, the samples were centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 10 min at room temperature. The supernatant was discarded and the pellet, containing the exosomes, at the bottom of the tube was resuspended in 200 µl phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Isolation of RNA and mir 193b qpcr analysis. Total RNA in 350 µl CSF, or 200 µl serum samples was extracted using a spin column method with an mirneasy Serum/Plasma kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Exosomal RNA was isolated and purified using a Total Exosome RNA Isolation kit (Invitrogen Life Technologies). The RNA isolated from the CSF was 530 1,500 ng/ml, 2,100 4,700 ng/ml from serum, ng/ml from the exosome. Total RNA in hippocampus tissue from the animal models and cultured cells was extracted using a spin column method using the mirneasy kit (Qiagen). MiRs were reverse transcribed into cdna using the miscript II RT kit (Qiagen) in a 10 µl reaction system. MiR 193b were determined by a TaqMan qpcr method (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), using U6 RNA as an endogenous control. Statistical analyses. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 13.0 for Windows (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). For normally distributed data, results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. The differences between groups were assessed by t tests and analyzed using the Mann Whitney U test. Correlations were determined by computing the Spearman rank correlation coefficient. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Figure 1. Seed region of mir-193b in the 3'-UTRs of APP. APP, amyloid precursor protein; mir, microrna. A B C Figure 2. Effect of mir-193b and mir-193b inhibitor on the (A) mrna and (B and C) protein expression of APP in SH-SY5Y cells. N, negative controls; NC, non-specific control. * P<0.05 as compared with the NC group. Error bars represent the standard deviation. APP, amyloid precursor protein; mir, microrna. Results Bioinformatics retrieval. A total of 34 mirs were found to be putative targets on the 3' UTR of APP. MiR 193b was a mir that may target the 3' UTRs of APP (Fig. 1). MiR 193b represses the mrna and protein expression of APP. As shown in Fig. 2, the mrna and protein expressions of APP were significantly decreased by mirna 193b in SH SY5Y cells (P<0.05). The mir 193b inhibitor oligonucleotide induced a significant upregulation of mrna and protein expression of APP as compared with the nonspecific control groups, respectively (P<0.05). By TaqMan qpcr, a ~55% downregulation of endogenous mir 193b was observed (data not shown). Figure 3. Identification of the mir-193b binding site on the 3'-UTRs of amyloid precursor protein was identified. * P<0.05 as compared with the NC group. NC, non-specific control. 3'UTR, 3' untranslated region.
4 2398 LIU et al: MICROrna-193B WAS A REGULATOR OF app AND EXOSOMAL MICROrna-193B WAS A BIOMARKER OF ad Figure 5. (A) Expression levels of mir-193b in the serum from patients with MCI and DAT. (B) The levels of mir-193b in CSF from patients with DAT. (C) The levels of exosomal mir-193b in the serum from patients with MCI and DAT. (D) The levels of exosomal mir-193b in CSF from patients with DAT. * P<0.05 as compared with the control group; # P<0.05 as compared with the MCI group. Error bars represent the standard deviation. MCI, mild cognitive impairment; DAT, dementia of Alzheimer type; CSF, cerebral spinal fluid; mir, microrna. Figure 4. Levels of mir-193b in (A) hippocampus, (B) CSF and (C) serum of amyloid precursor protein/ps1 transgenic mice. (D and E) The levels of exosomal mir-193b in the CSF and serum of APP/PS1 transgenic mice. * P<0.05 as compared with the WT group. # P<0.05 as compared with the 3-month-old transgenic group. Error bars represent the standard deviation. WT, wild type; mir, microrna; CSF, cerebral spinal fluid. APP 3' UTR is a mir 193b target. Over expression of mir 193b significantly reduces fluorescence from APP reporter vectors in HEK293 cells (P<0.05). These reductions were not observed when mutations were made to the 3'UTR seed regions of APP or BACE 1 were generated (Fig. 3).
5 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: , Exosomal mir 193b decreases in CSF like fluid and serum of transgenic mice. The levels of mir 193b were significantly downregulated in the hippocampi of 3, 6 and 9 month APP/PS1 transgenic mice as compared with the WT mice (P<0.05). The levels of exosomal mir 193b were significantly downregulated in the CSF like fluid and the serum of 3, 6 and 9 month APP/PS1 transgenic mice, as compared with the WT mice (P<0.05). Levels of exosomal mir 193b in the CSF like fluid and serum of 6 and 9 month transgenic mice were significantly lower than that of the 3 month transgenic mice, respectively (P<0.05; Fig. 4). Exosomal mir 193b decreases in the CSF, serum and plasma of AD patients. Compared with the control groups, patients with MCI and DAT had lower levels of exosomal mir 193b in the serum and plasma (P<0.05). Patients with DAT had lower exosomal mir 193b levels in their serum and plasma compared with the MCI groups (P<0.05). It was additionally found that exosomal mir 193b was decreased in the CSF of patients with DAT as compared with the control group (n=7; P<0.05; Fig. 5). The level of exosomal mir 193b was lower in the CSF compared with serum from a given individual (P<0.05; data not shown). There was no correlation between exosomal mirna 193b levels and the CSF and serum from a given individual (data not shown). When the cutoff value was set as the mean concentration two standard deviations of the controls, the positive rates of exosomal mir 193b were 71.43% (5/7) and 58.82% (30/51) in the CSF and serum of patients with DAT respectively, and 58.14% (25/43) in the serum of patients with MCI. Exosomal mir 193b is negatively correlated with Aβ42 in the CSF but not in the serum. A weak, but significant, negative correlation was found between the levels of exosomal mir 193b and Aβ42 in the CSF of patients with DAT (r = 0.442, P<0.05), as well as the control group (r = 0.503, P<0.05). MiR 193b and exosomal mir 193b had no correlation with HCY, ApoE, tau and p tau in the serum and CSF (data not shown). Discussion The potential benefit in the analysis of mir in the diagnosis and treatment of numerous diseases, including cancer, infection and neurodegenerative disease has been previously evaluated by numerous researchers (6,23,24). The expression profiles of mirs are known to be altered in several regions of the AD brain, however the cause or consequence in the pathology of the disease is unknown. There has been no data to suggest a direct genetic link between mirs or mir recognition elements and neurodegenerative disease (6,9,10,23,24). High expression of APP correlating with accelerated accumulation of Aβ in the brain is a feature of AD. Previous research has demonstrated mir 106a/b, 147, 160a, 520c and 655 function as APP suppressors (5 8). In the present study, it was shown that mir 193b could repress the expression of APP by binding its 3' UTR and decay its mrna. The deregulated mir 193b may play a role in the development of AD and the downregulating effects of mir 193b on APP may represent a study direction for AD therapy by mir. Previous studies have demonstrated that mirs are stably expressed in various bodily fluids, and their unique expression patterns can serve as fingerprints of various diseases, including AD (25). The CSF is in direct contact with the extracellular space of the brain and can reflect biochemical changes that occur in the latter. The CSF is therefore the optimal source of AD biomarkers. CSF, however, is not an appropriate sample for screening and routine testing due to its invasive process of sample collection. From this perspective, blood based biomarkers for AD screening and routine testing would be more suitable (26). Circulating mirs can derive from many sources, including cell death and lysed cells, which are passive secretions, as well as active secretion from cells by exosomes and microvesicles. Although endogenous plasma mirnas exist in a form that is resistant to plasma RNase activity and other conditions such as extreme ph, the exosomes may provide additional protection, which allows data to be obtained that reflects the accurate expression level of mir actively secreted from cells. The mirs can also be transported by other carriers such as high and low density lipoprotein, both of which are highly abundant in plasma and cannot be generated by brain (27). The total small RNAs isolated from body fluid may contain more non brain derived mirs than that from exosomes. Furthermore, exosomes are actively secreted from cells, which can help to eliminate the interference from passively secreted mirs. APP/PS 1 double transgenic mice contained insoluble amyloid peptides at the age of 6 9 months, concomitant with the formation of amyloid plaques (28). In the present study, it was shown that the level of mir 193b was decreased in the hippocampi of 3 month transgenic mice, which suggested that the change of mir 193b is earlier than the formation of amyloid plaques. The detection of exosomal mir 193b in the CSF like fluid and plasma of 3, 6 and 9 month transgenic mice demonstrated that exosomal mir 193b was a potential AD biomarker, especially for the earlier stages of the disease. This conjecture was further confirmed by clinical detection, which showed that exosomal mir 193b levels in patients with MCI were higher as compared with the control group and lower as compared with the CSF and plasma samples from patients in the DAT group. Although exosomes can be released by numerous organs, the expression of mir 193b in the exosomes from CSF was ~73% of the endogenous control, which indicated that it was abundant, and the exosomal mir 193b levels in the CSF were correlated. Furthermore, exosome mediated secretion pathways exist in the blood brain barrier (29,30). It is hypothesized that decreased secretion of exosomal mir 193b may lead to the decreased level of exosomal mir 193b in the plasma. In conclusion, these findings showed that mir 193b may function in the development of AD and exosomal mir 193b has potential as a novel, noninvasive blood based biomarkers of patients with MCI and DAT. Acknowledgements This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (no ) and Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (no ). The authors would like to thank Dr Shuang Meng of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing, People's Republic of China for the vector construction and fluorescence detection.
6 2400 LIU et al: MICROrna-193B WAS A REGULATOR OF app AND EXOSOMAL MICROrna-193B WAS A BIOMARKER OF ad References 1. Lewczuk P, Kamrowski Kruck H, Peters O, et al: Soluble amyloid precursor proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid as novel potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease: a multicenter study. Mol Psychiatry 15: , Weiner MW: Dementia in 2012: Further insights into Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Nat Rev Neurol 2: 65 66, Singer O, Marr RA, Rockenstein E, et al: Targeting BACE1 with sirnas ameliorates Alzheimer disease neuropathology in a transgenic model. Nat Neurosci 8: , Tan L, Yu JT, Hu N and Tan L: Non coding RNAs in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol 47: , Junn E and Mouradian MM: MicroRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases and their therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther 133: , Delay C, Mandemakers W and Hébert SS: MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's disease, Neurobiol Dis 46: , Hébert SS and De Strooper B: Alterations of the microrna network cause neurodegenerative disease. Trends Neurosci 32: , Long JM and Lahiri DK: MicroRNA 101 downregulates Alzheimer's amyloid β precursor protein levels in human cell cultures and is differentially expressed. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404: , Delay C, Calon F, Mathews P and Hébert SS: Alzheimer specific variants in the 3'UTR of Amyloid precursor protein affect microrna function. Mol Neurodegener 6: 70, Hébert SS, Papadopoulou AS, Smith P, et al: Genetic ablation of Dicer in adult forebrain neurons results in abnormal tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet 19: , Blennow K, Hampel H, Weiner M and Zetterberg H: Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6: , Rembach A, Faux NG, Watt AD, et al: AIBL research group, Changes in plasma amyloid beta in a longitudinal study of aging and Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 10: 53 61, Lewczuk P, Kamrowski Kruck H, Peters O, et al: Soluble amyloid precursor proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid as novel potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease: a multicenter study. Mol Psychiatry 15: , Zetterberg H, Andreasson U, Hansson O, et al: Elevated cerebrospinal fluid BACE1 activity in incipient Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 65: , Wang WX, Huang Q, Hu Y, Stromberg AJ and Nelson PT: Patterns of microrna expression in normal and early Alzheimer's disease human temporal cortex: white matter versus gray matter. Acta Neuropathol 2: , Schonrock N, Ke YD, Humphreys D, et al: Neuronal microrna deregulation in response to Alzheimer's disease amyloid beta. PLoS One 5: e11070, Hosseini HM, Fooladi AA, Nourani MR and Ghanezadeh F: The role of exosomes in infectious diseases. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 1: 29 37, Pant S, Hilton H and Burczynski ME: The multifaceted exosome: biogenesis, role in normal and aberrant cellular function, and frontiers for pharmacological and biomarker opportunities. Biochem Pharmacol 11: , Boon RA and Vickers KC: Intercellular transport of micrornas. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33: , Wei PC, Tsai CH, Chiu PS and Lai SC: Matrix metalloproteinase 12 leads to elastin degradation in BALB/c mice with eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Int J Parasitol 41: , Wang WX, Rajeev BW and Stromberg AJ: The expression of microrna mir 107 decreases early in Alzheimer's disease and may accelerate disease progression through regulation of beta site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1. J Neurosci 5: , Liu CG, Xu KQ, Xu X, et al: 17Beta oestradiol regulates the expression of Na + /K + ATPase beta1 subunit, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ ATPase and carbonic anhydrase iv in H9C2 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34: , Dassow H and Aigner A: MicroRNAs (mirnas) in colorectal cancer: from aberrant expression towards therapy. Curr Pharm Des 19: , Eulalio A, Schulte L and Vogel J: The mammalian microrna response to bacterial infections. RNA Biol 9: , Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR and Wyman SK: Circulating micrornas as stable blood based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: , Giedraitis V, Sundelöf J, Irizarry MC, et al: The normal equilibrium between CSF and plasma amyloid beta levels is disrupted in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 427: , Vickers KC, Palmisano BT, Shoucri BM, Shamburek RD and Remaley AT: MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol 4: , van Leuven F: Single and multiple transgenic mice as models for Alzheimer's disease, Prog. Neurobiol 61: , Ceruti S, Colombo L, Magni G, et al: Oxygen glucose deprivation increases the enzymatic activity and the microvesicle mediated release of ectonucleotidases in the cells composing the blood brain barrier. Neurochem Int 59: , Ma R, Jiang T and Kang X: Circulating micrornas in cancer: origin, function and application. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31: 38, 2012.
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models. Yu Wu
 Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
Selective filtering defect at the axon initial segment in Alzheimer s disease mouse models Yu Wu Alzheimer s Disease (AD) Mouse models: APP/PS1, PS1δE9, APPswe, hps1 Wirths, O. et al, Acta neuropathologica
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet. Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509
 Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast cancer cells
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits
 Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Human Neurology 3-Plex A
 Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit
 Datasheet EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Datasheet EXO-DNAc Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652
 Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Exosome DNA Extraction Kits
 Exosome DNA Extraction Kits Summary Section 5 Introduction 40 EXO-DNAc 41 EXO-DNA 43 Introduction Genomic DNA Extractiom Kits Ordering informations Products can be purchased directly in our on-line shop:
Exosome DNA Extraction Kits Summary Section 5 Introduction 40 EXO-DNAc 41 EXO-DNA 43 Introduction Genomic DNA Extractiom Kits Ordering informations Products can be purchased directly in our on-line shop:
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Biomarkers for Alzheimer s disease
 Biomarkers for Alzheimer s Disease Henrik Zetterberg, MD, PhD Professor of Neurochemistry The Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg 1 Alzheimer s disease 2 Neuropathological criteria for Alzheimer
Biomarkers for Alzheimer s Disease Henrik Zetterberg, MD, PhD Professor of Neurochemistry The Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg 1 Alzheimer s disease 2 Neuropathological criteria for Alzheimer
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
EXOSOMES & MICROVESICLES
 The Sample Preparation Experts EXOSOMES & MICROVESICLES The New Standard in Exosome Purification and RNA Isolation Best-in-Class, Pure & Simple Exosome Purification, Fractionation of Exosomal Free & Circulating
The Sample Preparation Experts EXOSOMES & MICROVESICLES The New Standard in Exosome Purification and RNA Isolation Best-in-Class, Pure & Simple Exosome Purification, Fractionation of Exosomal Free & Circulating
EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit
 Datasheet EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
Datasheet EXO-DNA Circulating and EV-associated DNA extraction kit This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product.
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
Emerging CSF and serum biomarkers in atypical dementia. Laksanun Cheewakriengkrai, MD. Phramongkutklao Hospital March 7 th, 2018
 Emerging CSF and serum biomarkers in atypical dementia Laksanun Cheewakriengkrai, MD. Phramongkutklao Hospital March 7 th, 2018 Biomarkers A characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as
Emerging CSF and serum biomarkers in atypical dementia Laksanun Cheewakriengkrai, MD. Phramongkutklao Hospital March 7 th, 2018 Biomarkers A characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: , 2019
 326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting
 MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression
 1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Products for cfdna and mirna isolation. Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma
 MACHEREY-NAGEL Products for cfdna and mirna isolation Bioanalysis Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma n Flexible solutions for small and large blood plasma volumes n Highly efficient recovery
MACHEREY-NAGEL Products for cfdna and mirna isolation Bioanalysis Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma n Flexible solutions for small and large blood plasma volumes n Highly efficient recovery
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro
 Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA/cfRNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. R1072 Highlights High-quality cell-free DNA and RNA are easily and robustly purified from up to 3 ml of plasma, serum, or other biological
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA/cfRNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. R1072 Highlights High-quality cell-free DNA and RNA are easily and robustly purified from up to 3 ml of plasma, serum, or other biological
ABIOpure TM Viral (version 2.0)
 ABIOpure TM Viral (version 2.0) DNA/RNA Extraction Handbook Cat No: M561VT50 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Table of Contents Contents Page Kit Components 3 Precautions 3 Stability & Storage 4 General Description
ABIOpure TM Viral (version 2.0) DNA/RNA Extraction Handbook Cat No: M561VT50 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Table of Contents Contents Page Kit Components 3 Precautions 3 Stability & Storage 4 General Description
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
 Molecules 2014, 19, 1568-1575; doi:10.3390/molecules19021568 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
Molecules 2014, 19, 1568-1575; doi:10.3390/molecules19021568 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues. suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by
 Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit
 Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit Cat #:DP022MD/ DP022MD-50 Size:10/50 reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a rapid, simple
Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit Cat #:DP022MD/ DP022MD-50 Size:10/50 reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a rapid, simple
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes
 A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
MicroRNA Biomarkers Released by Platelet Activation. Jie Wang. A thesis. submitted in partial fulfillment of the. requirements for the degree of
 MicroRNA Biomarkers Released by Platelet Activation Jie Wang A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Laboratory Medicine University of Washington 2013
MicroRNA Biomarkers Released by Platelet Activation Jie Wang A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Laboratory Medicine University of Washington 2013
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002
![Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002](/thumbs/79/80181612.jpg) Data Sheet PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 DESCRIPTION: The PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit is designed for screening and profiling purposes. PCSK9 is known to function
Data Sheet PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 DESCRIPTION: The PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit is designed for screening and profiling purposes. PCSK9 is known to function
Analyses of Intravesicular Exosomal Proteins Using a Nano-Plasmonic System
 Supporting Information Analyses of Intravesicular Exosomal Proteins Using a Nano-Plasmonic System Jongmin Park 1, Hyungsoon Im 1.2, Seonki Hong 1, Cesar M. Castro 1,3, Ralph Weissleder 1,4, Hakho Lee 1,2
Supporting Information Analyses of Intravesicular Exosomal Proteins Using a Nano-Plasmonic System Jongmin Park 1, Hyungsoon Im 1.2, Seonki Hong 1, Cesar M. Castro 1,3, Ralph Weissleder 1,4, Hakho Lee 1,2
EXO-Prep One step Exosome isolation Reagent
 Datasheet EXO-Prep One step Exosome isolation Reagent This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product. Do not use this
Datasheet EXO-Prep One step Exosome isolation Reagent This product is for research use only. It is highly recommended to read this users guide in its entirety prior to using this product. Do not use this
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A
 MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Original Article Plasma long noncoding RNA 51A as a stable biomarker of Alzheimer s disease
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4694-4699 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047807 Original Article Plasma long noncoding RNA 51A as a stable biomarker of Alzheimer s disease Yanyao Deng 1,2, Le Xiao
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4694-4699 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047807 Original Article Plasma long noncoding RNA 51A as a stable biomarker of Alzheimer s disease Yanyao Deng 1,2, Le Xiao
ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits
 ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits Cat # EQ806A-1, EQ806TC-1, EQ808A-1 User Manual Storage: Please see individual components Version 2 8/14/2018 A limited-use label license covers this
ExoQuick Exosome Isolation and RNA Purification Kits Cat # EQ806A-1, EQ806TC-1, EQ808A-1 User Manual Storage: Please see individual components Version 2 8/14/2018 A limited-use label license covers this
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN No Treatment. EZN-3920, 2 μm. Time, h
 Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer
 Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Defining the Role of Notch Signaling in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation. Honors Research Thesis
 Defining the Role of Notch Signaling in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation Honors Research Thesis Presented in Fulfillment of the Requirements for graduation with research distinction at The Ohio
Defining the Role of Notch Signaling in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation Honors Research Thesis Presented in Fulfillment of the Requirements for graduation with research distinction at The Ohio
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Cell Lysis Buffer. Catalog number: AR0103
 Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT) and NQO1-null (NQO1-/-) mice.
 competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of
 Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Instructions for Use. RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit /2017 EN
 Instructions for Use RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 01/2017 EN RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 For research use only! (RUO) 163003 INS-163000-EN-S02 96 01 2017 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstr.
Instructions for Use RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 01/2017 EN RealStar Influenza S&T RT-PCR Kit 3.0 For research use only! (RUO) 163003 INS-163000-EN-S02 96 01 2017 altona Diagnostics GmbH Mörkenstr.
Instructions. Fuse-It-mRNA easy. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4 Related Products..
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway
 Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
