Changes in the Number of Double-Strand DNA Breaks in Chinese Hamster V79 Cells Exposed to γ-radiation with Different Dose Rates
|
|
|
- Miranda Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, ; doi: /ijms Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN Changes in the Number of Double-Strand DNA Breaks in Chinese Hamster V79 Cells Exposed to γ-radiation with Different Dose Rates Konstantin V. Kotenko, Andrey Y. Bushmanov, Ivan V. Ozerov, Denis V. Guryev, Natalya A. Anchishkina, Nadezhda M. Smetanina, Ekaterina Y. Arkhangelskaya, Natalya Y. Vorobyeva and Andreyan N. Osipov * State Research Center Burnasyan Federal Medical Biophysical Center of Federal Medical Biological Agency (SRC-FMBC), 46, Zhivopisnaya Str, Moscow , Russia; s: fmbc-fmba@bk.ru (K.V.K.); radclin@yandex.ru (A.Y.B.); varnivey@gmail.com (I.V.O.); denis.guryev@gmail.com (D.V.G.); nanchishkina@gmail.com (N.A.A.); smetaninanm@gmail.com (N.M.S.); ek.arkhangelskaya@gmail.com (E.Y.A.); nuv.rad@mail.ru (N.Y.V.) These authors contributed equally to this work. * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; andreyan.osipov@gmail.com; Tel.: ; Fax: Received: 5 June 2013; in revised form: 15 June 2013 / Accepted: 19 June 2013 / Published: 1 July 2013 Abstract: A comparative investigation of the induction of double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) in the Chinese hamster V79 cells by γ-radiation at dose rates of 1, 10 and 400 mgy/min (doses ranged from 0.36 to 4.32 Gy) was performed. The acute radiation exposure at a dose rate of 400 mgy/min resulted in the linear dose-dependent increase of the γ-h2ax foci formation. The dose-response curve for the acute exposure was well described by a linear function y = x, where y is an average number of γ-h2ax foci per a cell and x is the absorbed dose (Gy). The dose rate reduction down to 10 mgy/min lead to a decreased number of γ-h2ax foci, as well as to a change of the dose-response relationship. Thus, the foci number up to 1.44 Gy increased and reached the plateau area between 1.44 and 4.32 Gy. There was only a slight increase of the γ-h2ax foci number (up to 7) in cells after the protracted exposure (up to 72 h) to ionizing radiation at a dose rate of 1 mgy/min. Similar effects of the varying dose rates were obtained when DNA damage was assessed using the comet assay. In general, our results
2 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, show that the reduction of the radiation dose rate resulted in a significant decrease of DSBs per cell per an absorbed dose. Keywords: DNA double-strand breaks; γ-н2ах foci; γ-radiation; dose rate effect; V79 cells 1. Introduction The majority of cellular DNA lesions caused by ionizing radiation (IR) significantly differ from those caused by endogenous sources in their physical and chemical properties [1]. The most important features of radiation-induced DNA lesions are their complexity and clustering [2]. The radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are the most crucial for the cell fate. Thus, DSBs are assumed to be a basic trigger for the main processes of cellular response to the radiation exposure [3]. Being quite a slow process, repair of DSBs may be inefficient and may result in serious cytogenetic lesions, cell death, the tumor suppressor genes inactivation or an activation of certain oncogenes [4,5]. The principal mechanisms of DSBs induction and repair after an acute and short-term exposure to IR at different doses have been well studied [6 9]. However, in environmental conditions, living organisms are continuously exposed to low dose rate IR. Unfortunately, the reports describe the induction and repair of DSBs after chronic exposure to IR in mammalian cells are contradictory. Thereby, there is still no clear understanding as to whether the mechanisms of the induction and repair of DSBs under chronic IR exposures are similar to those described for acute exposures in the same dose region. The goal of this study was to measure and compare the formation of DSBs in Chinese hamster V79 cells after the exposure to γ-radiation at various dose rates. The immunocytochemical analysis of the phosphorylated Н2АX-histone (γ-н2ах) foci was performed to estimate the cellular DNA DSBs formation. ATM, ATR and DNA-PK, are the major kinases that phosphorylate H2AX following DSB [10]. As a result, dynamic microstructures (foci) with thousands of γ-н2ах molecules are formed at each DSB [11]. One γ-н2ах focus is considered to be associated with one DSB [12]. In addition, we used the neutral version of the single cell gel-electrophoresis method (comet assay) to estimate the double-stranded DNA fragmentation [13]. 2. Results and Discussion Figure 1 shows the formation of γ-н2ах foci per cell nucleus after acute (400 mgy/min) and protracted (1 and 10 mgy/min) irradiation with doses ranging between 0.12 and 4.32 Gy. The γ-н2ах foci measurement was carried out 30 min after the acute exposure to IR. The resulting dose response curve for γ-h2ax formation was linear (Figure 1) and was well described by the function у = x (R 2 = 0.99) where y is an average number of γ-н2ах foci per cell nucleus and х is an absorbed dose (Gy). Assuming that a single focus is associated with a single DNA double-strand break, our results indicate that the acute exposure of V79 cells to IR induced approximately 20 DNA DSBs per cell per Gy. The results obtained are consistent with the literature data on DSB induction in mammalian cells by sparsely IR [14]. However, it is worth mentioning that the actual number of DSBs
3 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, per cell produced by 1 Gy of IR may be higher than the observed number of foci; two or more closely located DSBs may be processed by DNA repair machinery and be joined into a single larger focus that can be taken into account as a single DSB. Figure 1. The yield of γ-н2ах foci in Chinese hamster V79 cells exposed to γ-rays at high (400 mgy/min), medium (10 mgy/min) and low (1 mgy/min) dose rates. Here we demonstrate that the exposure to IR at a lower dose rate (10 mgy/min) leads to a reduced number of γ-н2ах foci per cell nucleus. The foci number increases at the dose of 1.44 Gy and reaches plateau at doses ranged from 1.44 to 4.32 Gy (Figure 1). The dose-response curve obtained shows the result of two simultaneously occurring processes in cells exposed at a low dose rate: DSBs induction and their repair. In fact, mammalian cells use two major pathways to repair DNA DSBs, which are non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) [15]. Hereby, the most of DSBs (approximately 75%) are repaired by the relatively fast NHEJ pathway [16]. The number of radiation-induced DSBs was found to decrease two-fold during 30 min following the exposure [17]. In case of the prolonged irradiation at the same dose rate, there was a certain balance between DSBs formation and their repair (approximately 12 DSBs per cell per h) and the plateau effect appeared. Interesting results on cells exposed to IR at the dose rate of 1 mgy/min have been obtained. There was only a slight increase of the γ-h2ax foci number (up to 7) during all irradiation time (up to 72 h) (Figure 1). Recently, Japanese researchers reported similar results obtained on human fibroblasts exposed to IR at doses up to 5 Gy with a dose rate of 0.3 mgy/min. There was no increase in the level of the phosphorylated p53 protein and the γ-h2ax foci number was only slightly elevated in comparison with control values [18]. However, there is no consensus on the mechanisms of this phenomenon in the literature. It has been reported that the ATM-kinase activation in cultured mammalian cells exposed to IR at a dose rate of 1.5 mgy/min (up to 6 Gy) is reduced [19]. The authors explained the effect of the significantly lower number of γ-н2ах foci (corresponding to the radiation dose) in cells exposed to IR at a low dose rate by the failure to activate ATM-associated
4 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, repair pathways. However, there is some evidence that the phosphorylation of H2AX-histone in cells irradiated at a low dose rate is an ATM-independent process [20]. Moreover, the accumulation of unrepaired breaks should increase the chromatin fragmentation level. To confirm this hypothesis we have estimated the DNA fragmentation level induced by DSBs using the neutral version of comet assay. These results are shown in Figure 2. The changes in the DNA fragmentation level in V79 cells irradiated with different dose rates are found to correlate with the yield of γ-h2ax foci. Moreover, the reduced dose rate of IR resulted in a significant decrease of the DNA fragmentation level (Figure 2). Figure 2. Changes in the DNA fragmentation level in Chinese hamster V79 cells exposed to γ-rays at high (400 mgy/min), medium (10 mgy/min) and low (1 mgy/min) dose rates. Thereby, we propose that an effective DSBs repair and H2AX-histone dephosphorylation take place in normal mammalian cells (without DNA repair deficiency) exposed to low dose and low dose rate sparsely IR. This speculation is based on the results of the comparative study on the cells exposed to IR with different dose rates. As shown earlier in TERT-immortalized human fibroblast, the cytogenetic lesions frequency as well as an elimination of cells irradiated at a low dose rate (0.3 mgy/min) were significantly lower than those in cells irradiated at a high dose rate (2000 mgy/min) [21]. Similar effects were observed in the animal model experiments [22 24]. According to the calculations made by Vilenchik and Knudson, the yield of endogenously-induced DSBs in proliferating human fibroblasts is the same as for the cells irradiated at a dose rate of 5 mgy/min (~8 DSBs/cell/h) [25]. Thus, radiation-induced DSBs can be repaired easily in cells exposed to IR at a dose rate of 1 mgy/min. Our data confirms this conclusion, however there are still some questions to be answered: (1) are the processes of both the endogenous and low-dose radiation-induced DSBs repair are similar and what are the distinctions between them? (2) Might the DNA microdeletions formed by the NHEJ repair pathway lead to the genome instability and the oncological transformation of cells? Our further studies are aimed to find the answers.
5 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, Experimental Section 3.1. Cell Line and Culture Technique Chinese hamster V79 lung fibroblasts obtained from the American Type Culture Collection were maintained with twice weekly subculture in DMEM supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 mg/ml penicillin/streptomycin and 1% L-glutamine. They were grown at 37 C in the presence of 5% CO Cell Irradiation Exponentially growing cells in concentration of cells per milliliter of medium were plated down into T-25 flasks and maintained at 37 C in the presence of 5% CO 2 for 24 h prior to irradiation. Irradiation with Co 60 rays was performed in the specially designed facility for cell culture irradiation (guided temperature conditions with the presence of 5% CO 2 ) with measured dose rates of 0.1, 1, 10 and 400 mgy/min. The total absorbed doses were 0.36, 1.44, 2.88 and 4.32 Gy. The IR exposure times of 0.9, 3.6, 7.2, 10.8 min at the dose rate of 400 mgy/min, 0.6, 2.4, 4.8, 7.2 h at the dose rate of 10 mgy/min and 6, 24, 48 and 72 h at the dose rate of 1 mgy/min were chosen respectively Immunocytochemistry for γ-н2ах To analyze γ-н2ах foci, the method previously described was used [26]. Shortly, cells grown on coverslips were fixed for 20 min in 2% freshly prepared paraformaldehyde, rinsed by tris-buffer and permeabilized in cool ( 20 C) methanol for 1 min. Then cells were transferred into tris-buffer containing 4% FBS and 0.1% Triton X-100 for 20 min. Slides were incubated with monoclonal antibodies against γ-h2ax (Anti-phospho-Histone H2AX Rabbit Monoclonal, Merck-Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) at 4 C over night. Then cells were rinsed and incubated with fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibodies (Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L), FITC conjugate, Merck-Millipore) at room temperature for 1 h. DNA was stained with DAPI (0.5 µg/ml, 5 min). The visualization and further analysis of images were performed using fluorescent microscope Ахioscop-40 FL (Саrl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with the high-resolution camera АxioCamMRс 5 (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) and AxioVision 4.8 software (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The foci were typically scored manually in a blinded manner. One hundred cells per slide were analyzed DNA Comet Assay The level of DNA fragmentation as a result of DSBs formation was estimated by a modified neutral version of the comet assay. [13]. According to the method, the number of DSBs was proportional to the extent of DNA migrated away from the nucleus during electrophoresis of agarose-immobilized single cells. Briefly, 10 μl of cell suspension ( cells/ml) was mixed with 100 μl of 0.5% low melting agarose (Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO, USA) in PBS (ph 7.4) at 37 C and 75 μl was layered on top of the microscope slides pre-coated with 1% normal agarose (Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO, USA). The slides were covered by coverslips and incubated for 5 min at 4 C. After
6 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, removing coverslips and following a 2 h lysis (2.5 M NaCl, 100 mm EDTA, 10 mm Tris-HCl, ph 10.0, 1% Triton X-100, 10% DMSO) at 4 C, the slides were incubated 20 min in TBE buffer (89 mm Tris base ph 8.0, 89 mm boric acid, 2 mm EDTA) at 4 C. The electrophoresis was carried out in TBE buffer at 1.5 V/cm and 4 C for 20 min. The slides were then fixed (70% ethanol for 5 min) and dried. Fluorescent dye SYBRGreen I was utilized to visualize DNA. Analysis of comets was performed using the Ахioscop-40 FL microscope (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with the high-resolution digital camera АxioCamMRс 5 (Carl Zeiss) and AxioVision 4.8 software (Carl Zeiss). Images were analyzed using the specially designed СASP software (СASPlab, Wroclaw, Poland) Statistics Statistical errors were calculated as the standard error. All the experiments were performed at least three times and the data was presented as the mean value ± standard error in each case. 4. Conclusions The present study of the radiation-induced DSBs level in Chinese hamster V79 cells exposed to IR at various dose rates showed a significant decrease in the DSBs level per IR dose in cells irradiated at a lower dose rate compared to a higher dose rate. Evidently, current findings support the threshold hypothesis on the biological effects of IR. The dose rate appeared to be an essential factor in cellular response to IR determining biological effects induction and realization, probably more important than the absorbed dose. It is therefore advisable to consider the dose rate factor in the radiological protection standards. Acknowledgments The studies were partially supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research grant # a. We thank Dmitry Klokov for English proofreading of the manuscript. The authors also acknowledge the anonymous reviewers and editor for constructive comments. Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. References 1. Jeggo, P.A.; Lobrich, M. Contribution of DNA repair and cell cycle checkpoint arrest to the maintenance of genomic stability. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2006, 5, Sutherland, B.M.; Bennett, P.V.; Sidorkina, O.; Laval, J. Clustered damages and total lesions induced in DNA by ionizing radiation: Oxidized bases and strand breaks. Biochemistry 2000, 39, Goodarzi, A.A.; Jeggo, P.; Lobrich, M. The influence of heterochromatin on DNA double strand break repair: Getting the strong, silent type to relax. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2010, 9,
7 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, Halazonetis, T.D.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Bartek, J. An oncogene-induced DNA damage model for cancer development. Science 2008, 319, Mladenov, E.; Magin, S.; Soni, A.; Iliakis, G. DNA double-strand break repair as determinant of cellular radiosensitivity to killing and target in radiation therapy. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, Grudzenski, S.; Raths, A.; Conrad, S.; Rube, C.E.; Lobrich, M. Inducible response required for repair of low-dose radiation damage in human fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, Mosconi, M.; Giesen, U.; Langner, F.; Mielke, C.; Dalla Rosa, I.; Dirks, W.G. 53BP1 and MDC1 foci formation in HT-1080 cells for low- and high-let microbeam irradiations. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2011, 50, Mladenov, E.; Iliakis, G. Induction and repair of DNA double strand breaks: The increasing spectrum of non-homologous end joining pathways. Mutat. Res. 2011, 711, Alloni, D.; Campa, A.; Friedland, W.; Mariotti, L.; Ottolenghi, A. Track structure, radiation quality and initial radiobiological events: Considerations based on the PARTRAC code experience. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2012, 88, Lobrich, M.; Shibata, A.; Beucher, A.; Fisher, A.; Ensminger, M.; Goodarzi, A.A.; Barton, O.; Jeggo, P.A. Gammah2ax foci analysis for monitoring DNA double-strand break repair: Strengths, limitations and optimization. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, Paull, T.T.; Rogakou, E.P.; Yamazaki, V.; Kirchgessner, C.U.; Gellert, M.; Bonner, W.M. A critical role for histone H2AX in recruitment of repair factors to nuclear foci after DNA damage. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, Sharma, A.; Singh, K.; Almasan, A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation: A marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, Wojewodzka, M.; Buraczewska, I.; Kruszewski, M. A modified neutral comet assay: Elimination of lysis at high temperature and validation of the assay with anti-single-stranded DNA antibody. Mutat. Res. 2002, 518, Asaithamby, A.; Chen, D.J. Cellular responses to DNA double-strand breaks after low-dose gamma-irradiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, Goodarzi, A.A.; Jeggo, P.A. The repair and signaling responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Adv. Genet. 2013, 82, Mao, Z.; Bozzella, M.; Seluanov, A.; Gorbunova, V. DNA repair by nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination during cell cycle in human cells. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, Taleei, R.; Nikjoo, H. The Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks: I. A mathematical model. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, Ishizaki, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Yasui, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Tachibana, A. No induction of p53 phosphorylation and few focus formation of phosphorylated H2AX suggest efficient repair of DNA damage during chronic low-dose-rate irradiation in human cells. J. Radiat. Res. 2004, 45, Collis, S.J.; Schwaninger, J.M.; Ntambi, A.J.; Keller, T.W.; Nelson, W.G.; Dillehay, L.E.; Deweese, T.L. Evasion of early cellular response mechanisms following low level radiation-induced DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279,
8 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, Sugihara, T.; Murano, H.; Tanaka, K. Increased gamma-h2a.x intensity in response to chronic medium-dose-rate gamma-ray irradiation. PLoS One 2012, 7, e Nakamura, H.; Fukami, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Tachibana, A.; Nakatsugawa, S.; Hamaguchi, M.; Ishizaki, K. Cytotoxic and mutagenic effects of chronic low-dose-rate irradiation on TERT-immortalized human cells. Radiat. Res. 2005, 163, Osipov, A.N.; Klokov, D.Y.; Elakov, A.L.; Rozanova, O.M.; Zaichkina, S.I.; Aptikaeva, G.F.; Akhmadieva, A. Comparison in vivo study of genotoxic action of high- versus very low dose-rate gamma-irradiation. Nonlinearity Biol. Toxicol. Med. 2004, 2, Tanaka, K.; Kohda, A.; Toyokawa, T.; Ichinohe, K.; Oghiso, Y. Chromosome aberration frequencies and chromosome instability in mice after long-term exposure to low-dose-rate gamma-irradiation. Mutat. Res. 2008, 657, Tanaka, K.; Kohda, A.; Satoh, K.; Toyokawa, T.; Ichinohe, K.; Ohtaki, M.; Oghiso, Y. Dose-rate effectiveness for unstable-type chromosome aberrations detected in mice after continuous irradiation with low-dose-rate gamma rays. Radiat. Res. 2009, 171, Vilenchik, M.M.; Knudson, A.G. Endogenous DNA double-strand breaks: Production, fidelity of repair, and induction of cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, Banath, J.P.; Klokov, D.; MacPhail, S.H.; Banuelos, C.A.; Olive, P.L. Residual gammah2ax foci as an indication of lethal DNA lesions. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (
Cell Damage. Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence
 Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence Patents: CN 2702421, EP 2208068, TR 201308237, 200880115751 The Platform Motorized, inverse fluorescence microscope
Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence Patents: CN 2702421, EP 2208068, TR 201308237, 200880115751 The Platform Motorized, inverse fluorescence microscope
Modelling of Biological Processes
 Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci METODI DDR foci formation in irradiated (2 Gy) cells fixed 2 h later IRIF IRradiation Induced Focus Laser micro-irradiation DDR
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci METODI DDR foci formation in irradiated (2 Gy) cells fixed 2 h later IRIF IRradiation Induced Focus Laser micro-irradiation DDR
Evaluation of DNA damage induced by proton and lithium beams in murine melanoma cells
 Evaluation of DNA damage induced by proton and lithium beams in murine melanoma cells IL Ibañez *1,2, C Bracalente 1, M Edreira 1, MA Palmieri 3, B Molinari 1,2, L Policastro 1,2, A Kreiner 1,2,4, A Burlón
Evaluation of DNA damage induced by proton and lithium beams in murine melanoma cells IL Ibañez *1,2, C Bracalente 1, M Edreira 1, MA Palmieri 3, B Molinari 1,2, L Policastro 1,2, A Kreiner 1,2,4, A Burlón
DNA damage in subpopulations of human lymphocytes irradiated with doses in the range of 0 1 Gy of X-radiation
 NUKLEONIKA 2008;53(4):145 149 ORIGINAL PAPER DNA damage in subpopulations of human lymphocytes irradiated with doses in the range of 0 1 Gy of X-radiation Maria Wojewódzka, Eugeniusz K. Machaj, Aneta Goździk,
NUKLEONIKA 2008;53(4):145 149 ORIGINAL PAPER DNA damage in subpopulations of human lymphocytes irradiated with doses in the range of 0 1 Gy of X-radiation Maria Wojewódzka, Eugeniusz K. Machaj, Aneta Goździk,
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs. Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica
 Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Effects of targeted phosphorylation site mutations in the DNA-PKcs phosphorylation domain on low and high LET radiation sensitivity
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1621-1627, 2015 Effects of targeted phosphorylation site mutations in the DNA-PKcs phosphorylation domain on low and high LET radiation sensitivity IAN M. CARTWRIGHT 1, JUSTIN J. BELL
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1621-1627, 2015 Effects of targeted phosphorylation site mutations in the DNA-PKcs phosphorylation domain on low and high LET radiation sensitivity IAN M. CARTWRIGHT 1, JUSTIN J. BELL
Factors determining DNA double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase.
 Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
The mutagenic and carcinogenic effects of sparsely ionizing
 Radiation dose-rate effects, endogenous DNA damage, and signaling resonance Michael M. Vilenchik* and Alfred G. Knudson *The Sally Balin Medical Center, 110 Chesley Drive, Media, PA 19063; and Division
Radiation dose-rate effects, endogenous DNA damage, and signaling resonance Michael M. Vilenchik* and Alfred G. Knudson *The Sally Balin Medical Center, 110 Chesley Drive, Media, PA 19063; and Division
Cellular Stress Response Induced by Low Dose Gamma Radiation
 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (2): 139 144 (2014) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Research Article Cellular
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (2): 139 144 (2014) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Research Article Cellular
Original Article Blood-based DNA methylation of DNA repair genes in the non-homologous end-joining (NEHJ) pathway in patient with glioma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(8):9463-9467 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0011215 Original Article Blood-based DNA methylation of DNA repair genes in the non-homologous end-joining (NEHJ) pathway in
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(8):9463-9467 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0011215 Original Article Blood-based DNA methylation of DNA repair genes in the non-homologous end-joining (NEHJ) pathway in
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
Residual gh2ax foci as an indication of lethal DNA lesions
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Residual gh2ax foci as an indication of lethal DNA lesions Judit P Banáth 1, Dmitry Klokov 1,2, Susan H MacPhail 1, C Adriana Banuelos 1, Peggy L Olive 1* Abstract Background:
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Residual gh2ax foci as an indication of lethal DNA lesions Judit P Banáth 1, Dmitry Klokov 1,2, Susan H MacPhail 1, C Adriana Banuelos 1, Peggy L Olive 1* Abstract Background:
STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V.
 STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V. Sotnik, T. V. Azizova, and S. V. Osovets Southern Urals Biophysics Institute, Ozyorskoe shosse 19, Ozyorsk, 456780, Russia ABSTRACT The research objective
STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V. Sotnik, T. V. Azizova, and S. V. Osovets Southern Urals Biophysics Institute, Ozyorskoe shosse 19, Ozyorsk, 456780, Russia ABSTRACT The research objective
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells
 The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells Piroska Virág The Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. I. Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania Low dose radiation effects on the
The effects of computed tomography derived low doses on human peripheral blood cells Piroska Virág The Oncology Institute Prof. Dr. I. Chiricuta, Cluj-Napoca, Romania Low dose radiation effects on the
Chapter 2. Aims & Objectives
 2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
Evasion of Early Cellular Response Mechanisms following Low Level Radiation-induced DNA Damage*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 279, No. 48, Issue of November 26, pp. 49624 49632, 2004 2004 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Evasion of
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 279, No. 48, Issue of November 26, pp. 49624 49632, 2004 2004 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Evasion of
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting
 BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
NON-PROBLEMATIC RISKS FROM LOW- DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED DNA DAMAGE CLUSTERS
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 6 Issue 1 Article 4 3-2008 NON-PROBLEMATIC RISKS FROM LOW- DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED DNA DAMAGE CLUSTERS Daniel P Hayes New York City Department of Health &
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 6 Issue 1 Article 4 3-2008 NON-PROBLEMATIC RISKS FROM LOW- DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED DNA DAMAGE CLUSTERS Daniel P Hayes New York City Department of Health &
Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration between LNS INFN and Vinca Institute of Nuclear Sciences
 ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons
 Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Modelling the induction of cell death and chromosome damage by therapeutic protons M.P. Carante 1,2 and F. Ballarini 1,2, * 1 University of Pavia, Physics Department, Pavia, Italy 2 INFN, Sezione di Pavia,
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Genome Instability is Breathtaking
 Genome Instability is Breathtaking Effects of Alpha Radiation exposure on DNA at a molecular level and consequences to cell health Dr. Aaron Goodarzi A.Goodarzi@ucalgary.ca Radiation what do you think
Genome Instability is Breathtaking Effects of Alpha Radiation exposure on DNA at a molecular level and consequences to cell health Dr. Aaron Goodarzi A.Goodarzi@ucalgary.ca Radiation what do you think
Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Medical Physics in the Baltic States 2017 Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose Tadas DIDVALIS 1, 2,, Paulius RUZGYS 1, Saulius ŠATKAUSKAS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE Medical Physics in the Baltic States 2017 Cell Viability, DNA Damage And Relative Mitotic Arrest Dependence On Radiation Dose Tadas DIDVALIS 1, 2,, Paulius RUZGYS 1, Saulius ŠATKAUSKAS
C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than. O-Beam
 1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
1 C-Beam Induces More Chromosomal Damage In Chemo-Radio-Resistant Cells Than 16 O-Beam Utpal Ghosh 1, Regina Lichti Binz, Ratan Sadhukhan, Asitikantha Sarma 3, Subrata Kumar Dey 4,Martin Hauer-Jensen,
Lecture -2- Environmental Biotechnology
 Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Mugimane Manjanatha, Ph.D
 Genotoxicity of Doxorubicin in F344 Rats by Combining the Comet Assay, Peripheral Blood Micronucleus Test, and Pathway-Focused Gene Expression Profiling Mugimane Manjanatha, Ph.D FDA/NCTR/DGMT DISCLAIMER
Genotoxicity of Doxorubicin in F344 Rats by Combining the Comet Assay, Peripheral Blood Micronucleus Test, and Pathway-Focused Gene Expression Profiling Mugimane Manjanatha, Ph.D FDA/NCTR/DGMT DISCLAIMER
LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY
 LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
Ginkgo biloba leaf extract induces DNA damage by inhibiting topoisomerase II activity in human hepatic cells
 Ginkgo biloba leaf extract induces DNA damage by inhibiting topoisomerase II activity in human hepatic cells Zhuhong Zhang 1, Si Chen 2, Hu Mei 3, Jiekun Xuan 2, Xiaoqing Guo 1, Letha Couch 2, Vasily N.
Ginkgo biloba leaf extract induces DNA damage by inhibiting topoisomerase II activity in human hepatic cells Zhuhong Zhang 1, Si Chen 2, Hu Mei 3, Jiekun Xuan 2, Xiaoqing Guo 1, Letha Couch 2, Vasily N.
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition
 Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Advances in biological dosimetry
 Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements
 Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements Kevin M. Prise Centre for Cancer Research & Cell Biology, Queen s University Belfast Outline Definition of bystander
Bystander responses and low dose exposure: Current evidence and future research requirements Kevin M. Prise Centre for Cancer Research & Cell Biology, Queen s University Belfast Outline Definition of bystander
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model
 Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Radiation induced DNA double strand breaks undergoing PET/CT examinations.
 Radiation induced DNA double strand breaks undergoing PET/CT examinations. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. S. May, M. Brand, T. Löwe, M. Sommer, C. Engert, U.
Radiation induced DNA double strand breaks undergoing PET/CT examinations. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. S. May, M. Brand, T. Löwe, M. Sommer, C. Engert, U.
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
Supplementary Figure 1
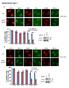 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE
 COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Assessment of Individual Radiosensitivity in Human Lymphocytes using Micronucleus and Microgel Electrophoresis Comet Assays
 Assessment of Individual Radiosensitivity in Human Lymphocytes using Micronucleus and Microgel Electrophoresis Comet Assays Di Giorgio, M.; Sardi, M.; Busto, E.; Vallerga, M.B.; Taja, M.R. and Mairal,
Assessment of Individual Radiosensitivity in Human Lymphocytes using Micronucleus and Microgel Electrophoresis Comet Assays Di Giorgio, M.; Sardi, M.; Busto, E.; Vallerga, M.B.; Taja, M.R. and Mairal,
Adriamycin induces H2AX phosphorylation in human spermatozoa
 Asian J Androl 2008; 10 (5):749 757 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00400.x. Original Article. Adriamycin induces H2AX phosphorylation in human spermatozoa Zhong-Xiang Li 1,*, Ting-Ting Wang 1, Yan-Ting
Asian J Androl 2008; 10 (5):749 757 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00400.x. Original Article. Adriamycin induces H2AX phosphorylation in human spermatozoa Zhong-Xiang Li 1,*, Ting-Ting Wang 1, Yan-Ting
Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
Effect of Ku80 on the radiosensitization of cisplatin in the cervical carcinoma cell line HeLa
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 15: 147-154, 2018 Effect of Ku80 on the radiosensitization of cisplatin in the cervical carcinoma cell line HeLa LIANG ZHUANG 1, FEI LIU 1, PING PENG 1, HUIHUA XIONG 1, HONG QIU 1, XIUGEN
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 15: 147-154, 2018 Effect of Ku80 on the radiosensitization of cisplatin in the cervical carcinoma cell line HeLa LIANG ZHUANG 1, FEI LIU 1, PING PENG 1, HUIHUA XIONG 1, HONG QIU 1, XIUGEN
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3
 Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Comparison of the effects of bleomycin and ionizing radiation in two sublines of murine lymphoma L5178Y
 NUKLEONIKA 2001;46(3):81 86 ORIGINAL PAPER Comparison of the effects of bleomycin and ionizing radiation in two sublines of murine lymphoma L5178Y Marcin Kruszewski, Jolanta Zaim, Iwona Gràdzka, Irena
NUKLEONIKA 2001;46(3):81 86 ORIGINAL PAPER Comparison of the effects of bleomycin and ionizing radiation in two sublines of murine lymphoma L5178Y Marcin Kruszewski, Jolanta Zaim, Iwona Gràdzka, Irena
TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK
 Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
The Comet and TUNEL Assays
 Sperm DNA: organization, protection and vulnerability from basic science to clinical application Methods to assess the status of the sperm DNA: The Comet and TUNEL Assays Lars Björndahl Centre for Andrology
Sperm DNA: organization, protection and vulnerability from basic science to clinical application Methods to assess the status of the sperm DNA: The Comet and TUNEL Assays Lars Björndahl Centre for Andrology
Decay of γ-h2ax foci correlates with potentially lethal damage repair in prostate cancer cells
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 29: 2175-2180, 2013 Decay of γ-h2ax foci correlates with potentially lethal damage repair in prostate cancer cells BREGJE VAN OORSCHOT 1, SUZANNE E. HOVINGH 1, HANS RODERMOND 1, AHMED
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 29: 2175-2180, 2013 Decay of γ-h2ax foci correlates with potentially lethal damage repair in prostate cancer cells BREGJE VAN OORSCHOT 1, SUZANNE E. HOVINGH 1, HANS RODERMOND 1, AHMED
Figure S1. B % of Phosphorylation 32H. 32ss
 Figure S1 8H 32ss 32H 32Hc % of Phosphorylation 3 32H 2 1 32ss 1 2 3 4 Extract (μg) C % of Phosphorylation 18 12 6-32H 32Hc 8H 32ss Dbait Figure S1. List of the Dbait molecules and activation of DN-PK
Figure S1 8H 32ss 32H 32Hc % of Phosphorylation 3 32H 2 1 32ss 1 2 3 4 Extract (μg) C % of Phosphorylation 18 12 6-32H 32Hc 8H 32ss Dbait Figure S1. List of the Dbait molecules and activation of DN-PK
Radiobiological Effects of Alpha-Particles from Astatine-211
 Radiobiological Effects of Alpha-Particles from Astatine-211 From DNA Damage to Cell Death Kristina Claesson Department of Oncology Institute of Clinical Sciences The Sahlgrenska Academy at University
Radiobiological Effects of Alpha-Particles from Astatine-211 From DNA Damage to Cell Death Kristina Claesson Department of Oncology Institute of Clinical Sciences The Sahlgrenska Academy at University
Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy
 Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy Radiology and Physical Medicine María Trinidad Rueda Cáceres Radiotherapy Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy One of the standard treatment options for various malignant
Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy Radiology and Physical Medicine María Trinidad Rueda Cáceres Radiotherapy Importance of ATM in Radiotherapy One of the standard treatment options for various malignant
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
What is radiation quality?
 What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
What is radiation quality? Dudley T Goodhead Medical Research Council, UK DoReMi Radiation Quality workshop Brussels. 9-10 July 2013 What is radiation quality? Let s start at the very beginning. A very
Computational Systems Biology Modeling of DNA-damage Stress Pathways for Assessing Mutation Rates at Low Doses
 Computational Systems Biology Modeling of DNA-damage Stress Pathways for Assessing Mutation Rates at Low Doses Rebecca Clewell Society of Toxicology March 25, 2015 Exposure & Consumer Use Assessment High-content
Computational Systems Biology Modeling of DNA-damage Stress Pathways for Assessing Mutation Rates at Low Doses Rebecca Clewell Society of Toxicology March 25, 2015 Exposure & Consumer Use Assessment High-content
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology
 Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
Use of online cell counting for micronucleus and neurite outgrowth assays on IN Cell Analyzer 2000
 GE Healthcare Application note 28-9673-96 AA IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Use of online cell counting for micronucleus and neurite outgrowth assays on IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Key words: IN Cell Analyzer online
GE Healthcare Application note 28-9673-96 AA IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Use of online cell counting for micronucleus and neurite outgrowth assays on IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Key words: IN Cell Analyzer online
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology
 The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
The In-flux of Nuclear Science to Radiobiology G. Taucher-Scholz, G. Kraft (GSI) 1 B. Michael (Gray Lab) 2 M. Belli (INFN) 3 1 GSI, Biophysik, Planckstr. 1, 64291 Darmstadt, Germany 2 Gray Lab.,Cancer
Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest)
 Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest) Carsten Herskind Dept. of Radiation Oncology. Universitätsmedizin Mannheim Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg
Tumor cell reassortment within the cell cycle (including checkpoints and cell-cycle arrest) Carsten Herskind Dept. of Radiation Oncology. Universitätsmedizin Mannheim Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Genotoxic effects of 60 Co γ-rays on Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells
 NUKLEONIKA 2008;53(4):161 165 ORIGINAL PAPER Genotoxic effects of 60 Co γ-rays on Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells Tiberius Dicu, Ioana Brie, Piroska Virag, Eva Fischer, Maria Perde, Vasile Foriş, Valentin
NUKLEONIKA 2008;53(4):161 165 ORIGINAL PAPER Genotoxic effects of 60 Co γ-rays on Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells Tiberius Dicu, Ioana Brie, Piroska Virag, Eva Fischer, Maria Perde, Vasile Foriş, Valentin
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells
 The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1
 RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes
 A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM
 STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
STUDY OF MUTATION PROCESSES IN BONE MARROW AND BLOOD CELLS AFTER SEPARATE AND COMBINED EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL γ-irradiation OF ORGANISM L.N. Nikolaevich Institute of Radiobiology of National Academy of
DNA repair pathway choice at various conditions immediately post irradiation
 DNA repair pathway choice at various conditions immediately post irradiation Min Liu, Jilin University Hongyan Wang, affiliation Solah Lee, Emory University Bailong Liu, Jilin University Lihua Dong, Jilin
DNA repair pathway choice at various conditions immediately post irradiation Min Liu, Jilin University Hongyan Wang, affiliation Solah Lee, Emory University Bailong Liu, Jilin University Lihua Dong, Jilin
Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples:
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo. Günter Speit
 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo Günter Speit Universität Ulm Institut für Humangenetik D-89069 Ulm (Germany) guenter.speit@uni-ulm.de CEFIC-2012 Günter Speit 1 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde
Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo Günter Speit Universität Ulm Institut für Humangenetik D-89069 Ulm (Germany) guenter.speit@uni-ulm.de CEFIC-2012 Günter Speit 1 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde
DNA double-strand break repair of parental chromatin in ooplasm and origin of de novo mutations. Peter de Boer
 DNA double-strand break repair of parental chromatin in ooplasm and origin of de novo mutations Peter de Boer Department of Obst.& Gynaecology, Div. Reproductive Medicine Radboud University Nijmegen Medical
DNA double-strand break repair of parental chromatin in ooplasm and origin of de novo mutations Peter de Boer Department of Obst.& Gynaecology, Div. Reproductive Medicine Radboud University Nijmegen Medical
us.com AGING 2017, Vol. 9, No. 11
 www.aging us.com AGING 2017, Vol. 9, No. 11 Research Paper Residual γh2ax foci induced by low dose x ray radiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells do not cause accelerated senescence in the progeny
www.aging us.com AGING 2017, Vol. 9, No. 11 Research Paper Residual γh2ax foci induced by low dose x ray radiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells do not cause accelerated senescence in the progeny
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage
 Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
FISH and PNA-FISH. FISH and PNA-FISH. Stochastic effect. Radiation and cancer. 1) chromosome 2) FISH 3) PNA-FISH. Chromosome translocations.
 BIODOSIMETRY IN THE 21 st CENTURY Training Meeting HICARE in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency Hiroshima, Japan, June 10-14, 2013. FISH and FISH and Satoshi Tashiro Research Institute
BIODOSIMETRY IN THE 21 st CENTURY Training Meeting HICARE in collaboration with the International Atomic Energy Agency Hiroshima, Japan, June 10-14, 2013. FISH and FISH and Satoshi Tashiro Research Institute
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
IMMUNOLOGIC REACTIVITY IN HUMAN BREAST CANCER AGAINST CULTURED HUMAN BREAST TUMOR CELLS
 22 IMMUNOLOGIC REACTIVITY IN HUMAN BREAST CANCER AGAINST CULTURED HUMAN BREAST TUMOR CELLS Michael P. Lerner*, J. H. Anglin, Peggy L. Munson, Peggy J. Riggs, Nancy E. Manning, and Robert E. Nordquist Departments
22 IMMUNOLOGIC REACTIVITY IN HUMAN BREAST CANCER AGAINST CULTURED HUMAN BREAST TUMOR CELLS Michael P. Lerner*, J. H. Anglin, Peggy L. Munson, Peggy J. Riggs, Nancy E. Manning, and Robert E. Nordquist Departments
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein
![2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein](/thumbs/86/94743397.jpg) Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [Krause, Mechthild] On: 4 November 2009 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 916558483] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and
This article was downloaded by: [Krause, Mechthild] On: 4 November 2009 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 916558483] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and
Research Article Role of Topoisomerase IIβ in DNA Damage Response following IR and Etoposide
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Journal of Nucleic Acids Volume 21, Article ID 71589, 8 pages doi:1.461/21/71589 Research Article Role of Topoisomerase IIβ in DNA Damage Response following IR and Etoposide
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Journal of Nucleic Acids Volume 21, Article ID 71589, 8 pages doi:1.461/21/71589 Research Article Role of Topoisomerase IIβ in DNA Damage Response following IR and Etoposide
Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 17, 40-46 (2004) Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1 SHU-ZHENG LIU 2, SHUN-ZI JIN, AND XIAO-DONG LIU Department of Radiation Biology, Jilin University
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 17, 40-46 (2004) Radiation-induced Bystander Effect in Immune Response 1 SHU-ZHENG LIU 2, SHUN-ZI JIN, AND XIAO-DONG LIU Department of Radiation Biology, Jilin University
INDUCTION AND REJOINING OF DNA DOUBLE STRAND BREAKS ASSESSED BY H2AX PHOSPHORYLATION IN MELANOMA CELLS IRRADIATED WITH PROTON AND LITHIUM BEAMS
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.070 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 74, No. 4, pp. 1226 1235, 2009 Copyright Ó 2009 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/09/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.070 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 74, No. 4, pp. 1226 1235, 2009 Copyright Ó 2009 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/09/$ see front
Supplementary material. Supplementary Figure legends
 Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
Genome Integrity in Mammalian Oocytes
 Genome Integrity in Mammalian Oocytes ESHRE Workshop on mammalian folliculogenesis and oogenesis April 19 21 Stresa Italy 2003 Workshop Lisbon Genome Integrity Structure is chromatin in open or closed
Genome Integrity in Mammalian Oocytes ESHRE Workshop on mammalian folliculogenesis and oogenesis April 19 21 Stresa Italy 2003 Workshop Lisbon Genome Integrity Structure is chromatin in open or closed
Human lymphocytes responses to low and high doses of Iodine-131. Antonina Cebulska-Wasilewska
 Human lymphocytes responses to low and high doses of Iodine-131 Antonina Cebulska-Wasilewska The H. Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Krakow, Poland 13-16.05.2013.
Human lymphocytes responses to low and high doses of Iodine-131 Antonina Cebulska-Wasilewska The H. Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences Krakow, Poland 13-16.05.2013.
William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc.
 Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Radiobiologcal Research at the JINR Accelerators
 Radiobiologcal Research at the JINR Accelerators Е. А. Krasavin Laboratory of Radiation Biology Академик Н.М.Сисакян Академик В.В.Парин Академик О.Г.Газенко β What fundamental problems were solved by the
Radiobiologcal Research at the JINR Accelerators Е. А. Krasavin Laboratory of Radiation Biology Академик Н.М.Сисакян Академик В.В.Парин Академик О.Г.Газенко β What fundamental problems were solved by the
The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation
 The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Edouard Azzam New Jersey Medical School Newark, USA Two phenomena have been recently implicated
The Impact of Bystander Effects and Adaptive Responses in the Health Risks of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Edouard Azzam New Jersey Medical School Newark, USA Two phenomena have been recently implicated
Accumulation of DNA double strand breaks. in normal tissues after fractionated low dose irradiation
 Aus der Klinik für Strahlentherapie und Radioonkologie Direktor: Prof. Dr. Ch. Rübe UniversitätskliniKum des Saarlandes Accumulation of DNA double strand breaks in normal tissues after fractionated low
Aus der Klinik für Strahlentherapie und Radioonkologie Direktor: Prof. Dr. Ch. Rübe UniversitätskliniKum des Saarlandes Accumulation of DNA double strand breaks in normal tissues after fractionated low
