MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Poppy Stokes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A nanometer would be a suitable unit of measurement for which of the following? 1) A) eukaryotic cells B) molecules and atoms C) cellular organelles and viruses D) bacterial colonies E) prokaryotic cells 2) The numerical aperture of a lens refers to its 2) A) thickness. B) ability to gather light. C) resolution distance. D) curvature. E) working distance. 3) Empty magnification results from increasing magnification without increasing the 3) A) wavelength. B) resolution. C) refraction. D) curvature of the lens. E) focal point. 4) The total magnification of a compound microscope is calculated using the magnification of which of the following? A) the objective and the condenser lense B) the objective and the ocular lenses C) the objective lens and the prism D) the condenser lens and the diaphragm E) the condenser and the ocular lenses 4) 5) If you were trying to visualize flagella without staining, which microscope would you use? 5) A) fluorescent B) phase-contrast C) confocal D) dark-field E) bright-field 6) Why does immersion oil improve resolution? 6) A) It allows light to travel at a uniform speed on its way to the lens. B) It decreases the working distance. C) It increases the numerical aperture. D) Both A and C are correct. E) A, B, and C are correct. 1
2 7) Cilia and flagella can be visualized using which of the following types of microscopes? 7) A) darkfield microscopes B) phase-contrast microscopes C) Nomarski microscopes D) All of the above are correct. E) None of the above is correct. 8) Which of the following types of microscopes is capable of generating a three-dimensional image of a specimen? A) scanning electron B) confocal C) differential interference contrast D) Both B and C are correct. E) A, B, and C are correct. 8) 9) All of the following are associated with an electron microscope EXCEPT: 9) A) magnetic fields. B) a fluorescent screen. C) a prism. D) an electron beam. E) a vacuum. 10) All of the following are types of light microscopes EXCEPT: 10) A) phase-contrast. B) confocal. C) bright-field. D) fluorescent. E) scanning tunneling. 11) Which of the following microscopes is capable of more than 100,000,000X magnification? 11) A) scanning electron microscopes B) scanning tunneling microscopes C) transmission electron microscopes D) bright-field microscopes E) differential interference contrast microscopes 12) If a microbiology lab technician left the crystal violet out of the Gram stain procedure, what would be the result? A) Gram-positive cells would be colorless and Gram-negative cells would be pink. B) Gram-positive cells would be purple and Gram-negative cells would be colorless. C) All cells would be pink. D) Gram-positive cells would be pink and Gram-negative cells would be purple. E) All cells would be purple. 12) 13) All of the following are common to both the Gram stain and the acid-fast stain EXCEPT: 13) A) primary stain. B) a decolorizing agent and a mordant. C) a decolorizing agent. D) a mordant. E) counterstain. 2
3 14) A patient suffering from tuberculosis could be diagnosed by use of the stain. 14) A) Gram B) flagellar C) endospore D) acid-fast E) capsule 15) Which of the following staining procedures uses heat to drive the stain into the cell? 15) A) endospore stain B) acid-fast stain C) capsule stain D) Both A and B are correct. E) A, B, and C are correct. 16) Carbolfuchsin is used in which of the following staining procedures? 16) A) flagellar stain B) Gram stain C) endospore stain D) capsule stain E) acid-fast stain 17) All of the following are components of electron microscopy stains EXCEPT: 17) A) tungsten. B) uranium. C) lead. D) eosin. E) osmium. 18) The kingdoms included in the Linnaean system are: 18) A) Animalia and Prokaryotae. B) Fungi and Protista. C) Protista and Plantae. D) Animalia and Plantae. E) Prokaryotae and Protista. 19) The rules of naming organisms are called 19) A) nomenclature. B) classification. C) identification. D) binomials. E) taxonomy. 20) All of the following are kingdoms proposed by Robert Whitaker EXCEPT: 20) A) Plantae. B) Protista. C) Animalia. D) Archaea. E) Fungi. 21) All of the following are characteristics of a genus name EXCEPT: 21) A) it is either underlined or in italics. B) it is always capitalized. C) it is one of two names used to identify an organism. D) it is written before the specific epithet. E) it is usually an adjective. 3
4 22) Carl Woese proposed the concept of the domain based on differences among which of the following cellular molecules? A) ribosomal RNA B) membrane lipids C) DNA D) proteins E) transfer RNA 23) Which of the following classification methods involves the use of antibodies to recognize different strains of a particular microbe? A) biochemical tests B) physical characteristics C) phage typing D) analysis of nucleic acids E) serological tests 22) 23) 24) A cell's GC ratio is associated with which of the following classification methods? 24) A) physical characteristics B) analysis of nucleic acids C) serological tests D) phage typing E) biochemical tests 25) The size of most cells is measured in 25) A) micrometers. B) meters. C) centimeters. D) nanometers. E) millimeters. 26) Why is visible light relatively limited in its usefulness for microscopy? 26) A) It does not produce enough contrast in specimens. B) It is not powerful enough to penetrate some specimens. C) Its wavelength is too long to enable high resolution of images. D) Both A and B are correct. E) A, B, and C are correct. 27) The refraction of radiation as it passes through a lens creates which of the following? 27) A) resolution distance B) magnification C) immunofluorescence D) resolving power E) contrast 28) All of the following types of microscopes are limited to magnification of about 2000X EXCEPT: 28) A) a dark-field microscope. B) a scanning tunneling microscope. C) a phase-contrast microscope. D) a fluorescent microscope. E) a differential interference contrast microscope. 4
5 29) A structure that appears in a transmission electron micrograph but which is not actually present in the specimen is known as a(n) A) antigen. B) refraction. C) mordant. D) biofilm. E) artifact. 29) 30) Which of the following is NOT true of transmission electron microscopy? 30) A) Glass lenses are used. B) Stains can be applied to improve contrast. C) The sample is placed in a vacuum. D) Electrons are the source of illumination. E) Thin segments must be used. 31) Basic dyes are more commonly used than acidic dyes because 31) A) they are positively charged. B) they bind specifically to the lipid membrane of the cell. C) they fluoresce under UV light. D) they are best used for electron microscopy. E) they work best at a low ph. 32) All of the following are associated with smear preparation EXCEPT: 32) A) fixation using heat. B) agglutination of the specimen. C) killing the microbes in the specimen. D) spreading the specimen onto a slide. E) fixation using methanol or formalin. 33) The Gram stain works due to differences in the of bacteria. 33) A) cell walls B) antigens C) cell membranes D) capsules E) genetic characteristics 34) In the Linnaean system of taxonomy, an order is a subset of a larger taxonomic group called the 34) A) genus. B) kingdom. C) class. D) family. E) phylum. 35) Why are modern light microscopes better than the ones Leeuwenhoek used? 35) A) Modern microscopes are compound instead of simple. B) Modern microscopes have a fivefold better resolution. C) Modern microscopes have lenses with smaller numerical apertures. D) Both A and B are correct. E) A, B, and C are correct. MATCHING. Choose the item in column 2 that best matches each item in column 1. Match the names of the objective lenses on the left with the appropriate power of magnification on the right: 36) Low-power objective lens A) 10X 36) 5
6 37) Oil immersion objective lens 38) Scanning objective lens 39) High, dry objective lens A) 100X B) 40X C) 4X 37) 38) 39) Match the reagent on the left with the staining procedure in which it is used on the right: 40) Osmium tetraoxide 41) Eosin 42) Crystal violet 43) Carbolfuchsin 44) Malachite green 45) Pararosanaline A) Negative stain B) Gram stain C) Endospore stain D) Flagellar stain E) Electron microscopy stain F) Acid-fast stain 40) 41) 42) 43) 44) 45) TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 46) A resolution of 1 µm would be better than a resolution of 0.5 µm. 46) 47) Bacterial cells are so similar to each other that physical characteristics cannot be used in identification of organisms. 47) 48) The three domains proposed by Carl Woese are the Archaea, the Eukarya, and the Bacteria. 48) 49) Linnaeus proposed the system of binomial nomenclature that we use today. 49) 50) A negative stain leaves cells colorless while staining the background of the smear. 50) 51) Members of the genera Bacillus and Clostridium can be identified using the endospore stain. 51) 52) Acid-fast cells such as Mycobacterium lose the color of the primary stain in the presence of hydrochloric acid. 52) 53) In the presence of a decolorizing agent, Gram-negative cells lose the color of the counterstain. 53) 54) Light rays that are in phase reinforce each other and produce a brighter image. 54) 55) Light rays that pass through the edge of a curved lens will be refracted more than those that pass through the center. 55) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 56) A(n) microscope has a single ocular lens. 56) 6
7 57) A(n) molecule is one that absorbs invisible radiation and emits visible light. 57) 58) The total magnification using a 10X ocular and a 40X objective would be. 58) 59) A(n) is a substance that binds to a dye and makes it less soluble. 59) 60) In taxonomy, organisms in similar classes can be classified in larger groups called. 60) 61) An agglutination test is an example of a(n) type of classification test. 61) 62) Robert Whitaker first proposed a taxonomic approach that is based on kingdoms. 62) 63) Carl Woese and his colleagues proposed the, a taxon that replaces the kingdom. 63) 64) The definitive reference work for the identification of bacteria is known as. 64) 65) Bacterial viruses that can be used to help classify different groups of bacteria are called. 65) 66) A(n) is a clear area on a bacterial lawn that is evidence of virus growth. 66) 67) An integral part of serological testing is the use of a solution called that contains antibodies. 67) 68) In a compound microscope, the lens that directs light through the specimen is the lens. 68) 69) is the process of immobilizing organisms on a glass slide through the application of either heat or chemicals. 69) 70) A staining procedure that uses more than one dye is called a(n) stain. 70) ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 71) Discuss the ways in which light rays can be manipulated in order to increase resolution and/or contrast. 72) Compare and contrast the light microscope with the electron microscope. 73) Discuss the role of the decolorizing agent in differential staining procedures. 74) Compare and contrast the three domains identified by Woese Eukarya, Bacteria, and Archaea. 75) List and explain five types of techniques that can be used to identify unknown microorganisms. 7
8 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED4 1) C 2) B 3) B 4) B 5) B 6) D 7) B 8) E 9) C 10) E 11) B 12) C 13) D 14) D 15) D 16) E 17) D 18) D 19) A 20) D 21) E 22) A 23) E 24) B 25) A 26) C 27) B 28) B 29) E 30) A 31) A 32) B 33) A 34) D 35) D 36) A 37) A 38) C 39) B 40) E 41) A 42) B 43) F 44) C 45) D 46) FALSE 47) FALSE 48) TRUE 49) TRUE 50) TRUE 8
9 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED4 51) TRUE 52) FALSE 53) FALSE 54) TRUE 55) TRUE 56) monocular 57) fluorescent 58) 400X 59) mordant 60) phyla 61) serological 62) five 63) domain 64) Bergey's Manual 65) bacteriophages 66) plaque 67) antiserum 68) condenser 69) Fixation 70) differential 71) There are a variety of ways that light rays can be manipulated in order to increase the resolution and contrast of a specimen. In bright-field microscopes, immersion oil is used to capture light rays that would otherwise be refracted and lost, thereby increasing the resolution of the image. Dark-field microscopes purposely scatter light rays in such a way as to improve the contrast of the specimen. Phase microscopes alter the wavelengths of light rays by making them in and out of phase with each other, thereby increasing contrast. Finally, fluorescent microscopes use UV light, which produces increased resolution because of its shorter wavelength, and the fluorescent dyes that are used emit a variety of colors, increasing contrast. 72) Both the light microscope and the electron microscope depend on the wavelength of radiation in order to achieve the resolution necessary to see fine details of specimens. Light microscopes use light rays, which, because of their relatively long wavelengths, limit the magnification of these microscopes to 2000X or less. Electron beams, on the other hand, have such a short wavelength that the resolution is greatly increased, to the point that magnification of 100,000X or more is possible. Both microscopes are capable of modulating and focusing their radiation sources in such a way as to increase the quality of the magnification; however, in a light microscope, the light rays are focused using glass lenses, whereas in an electron microscope, the electron beam is focused with magnetic fields. Because of their higher levels of magnification and extreme resolving power, electron microscopes are capable of seeing the finest details of the cell's ultrastructure, even to the point of being able to visualize molecules and atoms; light microscopes are capable of seeing only the larger cellular structures such as organelles. 73) All differential stains involve a series of reagents applied to a smear in such a way that different cells will have a different microscopic appearance or color. For example, the Gram stain produces two outcomes: some cells stain purple and are labeled Gram-positive, while other cells stain pink (Gram-negative). In the Gram stain and in other differential stains, the role of the decolorizing agent is to wash the primary stain out of some cells, while being unable to remove it from others. The decolorizing agent in the Gram stain is ethanol-acetone, and removes the primary stain only from Gram-negative cells. The acid-fast stain uses hydrochloric acid to remove the primary stain from non-acid-fast cells. The endospore stain uses water to wash the primary stain out of the vegetative cells. In each case, the decolorizing agent leaves these cells colorless, so that a counterstain is necessary to give a color to them. 9
10 Answer Key Testname: UNTITLED4 74) With respect to cell type, organisms in Eukarya have eukaryotic cells and the characteristics that go with this cell type, such as a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria and Archaea both have prokaryotic cells lacking nuclei and membrane-bound organelles. All three have different rrna sequences found in the small subunit of their ribosomes that are characteristic of the domain, which is an important tool for categorizing organisms. All three have cell membranes; however, they differ in the lipids found in the cell membrane. Eukaryotes belong to one of four kingdoms: plant, animal, protista, or fungi. Archaea have only three kingdoms and Bacteria have over fifty. 75) There are five major types of identification techniques used in the microbiology lab. One method is simply observation and classification of the physical characteristics of an organism, which includes both cellular morphology and colony morphology. A second method is the use of biochemical tests such as fermentation of carbohydrates or production of metabolic by-products to place microbes in different groups. A third type of identification technique is serological testing, in which antibodies are used to detect particular antigens on the surfaces of different microbes, in an effort to distinguish between closely related species or strains of microbes. Phage typing is the fourth technique, which is the use of bacteriophages to infect bacterial cells; because bacteriophages are highly specific in their infection of cells, the patterns of infected and uninfected cells can be used to differentiate between bacterial strains and species. Finally, a fifth method involves the analysis of the genetic material of microbes, such as the percentage of G and C bases in a cell's DNA, as a way of demonstrating possible relationships between species. 10
Ch 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
 Ch 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope SLOs Review the metric units of measurement Define total magnification and resolution Explain how electron and light microscopy differ Differentiate
Ch 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope SLOs Review the metric units of measurement Define total magnification and resolution Explain how electron and light microscopy differ Differentiate
Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use
 Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use 2 Abstract We will introduce bright-field microscope use, practice Gram staining with foodborne pathogens, and practice endospore staining with Bacillus
Staining Technology and Bright- Field Microscope Use 2 Abstract We will introduce bright-field microscope use, practice Gram staining with foodborne pathogens, and practice endospore staining with Bacillus
chapter one: the history of microbiology
 chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 8/29/2016 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 8/29/2016 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE/FUNCTION. 2. The uses the visible light to illuminate cell. 3. How is the magnification of a compound microscope calculated?
 CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE/FUNCTION 1. Define magnification and the term resolution. 2. The uses the visible light to illuminate cell. 3. How is the magnification of a compound microscope calculated? 4.
CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE/FUNCTION 1. Define magnification and the term resolution. 2. The uses the visible light to illuminate cell. 3. How is the magnification of a compound microscope calculated? 4.
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS YUSRON SUGIARTO
 IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS YUSRON SUGIARTO BACKGROUND One of the most fundamental tasks that someone working with micro-organisms must perform is to identify microorganisms. There are a number of
IDENTIFICATION OF MICROORGANISMS YUSRON SUGIARTO BACKGROUND One of the most fundamental tasks that someone working with micro-organisms must perform is to identify microorganisms. There are a number of
Medical Microbiology. Microscopic Techniques :
 ! Lecture 2 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Microscopic Techniques : Several types of microscopes are used in study of microbiology one of the most important tools for studying microorganisms
! Lecture 2 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Microscopic Techniques : Several types of microscopes are used in study of microbiology one of the most important tools for studying microorganisms
Bacterial Structure and Function
 Bacterial Structure and Function Charles Okolie, PhD. Room 311 (on level 4), First College Building, Landmark University okolie.charles@lmu.edu.ng Tel: Ext: Mobile: 08060241166 Structure of Bacteria The
Bacterial Structure and Function Charles Okolie, PhD. Room 311 (on level 4), First College Building, Landmark University okolie.charles@lmu.edu.ng Tel: Ext: Mobile: 08060241166 Structure of Bacteria The
Microscopy Text book Chapter 3
 Lab 2 Goals and Objectives: Microscopy lecture: Text Chapter 3 (supplement pg 39) Exercise 1: Brightfield Microscopy Learn how to use the microscope (guide in supplement pg 41) Diopter and interocular
Lab 2 Goals and Objectives: Microscopy lecture: Text Chapter 3 (supplement pg 39) Exercise 1: Brightfield Microscopy Learn how to use the microscope (guide in supplement pg 41) Diopter and interocular
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Starch grains - excess sugars
 (a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
(a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
BIOLOGY. A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL. Robert Hooke (1665) Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1674) Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 6 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Robert Hooke (1665) Figure 1.1 The structure
6 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Robert Hooke (1665) Figure 1.1 The structure
Fig. LPS in Gram negative bacteria
 Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
2) In what two ways do Archaea differ from true bacteria?
 STATION 1: 1) Explain the benefit of saprotrophic bacteria/fungi. 2) In what two ways do Archaea differ from true bacteria? 3) When transitioning from a low power to a higher power on a microscope, describe
STATION 1: 1) Explain the benefit of saprotrophic bacteria/fungi. 2) In what two ways do Archaea differ from true bacteria? 3) When transitioning from a low power to a higher power on a microscope, describe
CH 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Characteristics DNA not enclosed in membrane. No histone proteins associated with DNA. Lack membrane-bound organelles
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Characteristics DNA not enclosed in membrane. No histone proteins associated with DNA. Lack membrane-bound organelles
Cell Structure and Function D R. B E R T O L O T T I
 Cell Structure and Function D R. B E R T O L O T T I Essential Question How are cell structures adapted to their functions? Light Microscopes Most microscopes use lenses to magnify the image of an object
Cell Structure and Function D R. B E R T O L O T T I Essential Question How are cell structures adapted to their functions? Light Microscopes Most microscopes use lenses to magnify the image of an object
BIOSC 041. v Today s lecture. v Today s lab. v Note- Monday is a holiday good time to do some reading!
 BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function. Section Objectives: Relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells and cell structure.
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Section Objectives: Relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells and cell structure. Compare the operation of a microscope with that of an electron
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Section Objectives: Relate advances in microscope technology to discoveries about cells and cell structure. Compare the operation of a microscope with that of an electron
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell. 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells Concepts of Microscopy MAGNIFICATION factor by which the image
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells Concepts of Microscopy MAGNIFICATION factor by which the image
1. Studying Cells. Concepts of Microscopy 11/7/2016. Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Electron microscope Light microscope Unaided eye 11/7/2016 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells
Electron microscope Light microscope Unaided eye 11/7/2016 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Classification of Infectious Agents. Dr W. D. Colby
 Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
Ch 4. Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses
 Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Basic Microscopy Laboratory Exercises
 Basic Microscopy Laboratory Exercises Laboratory Exercise After you have completed the Basic Microscopy elearning course, it is strongly recommended that you complete the following laboratory exercises
Basic Microscopy Laboratory Exercises Laboratory Exercise After you have completed the Basic Microscopy elearning course, it is strongly recommended that you complete the following laboratory exercises
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Bacteria. Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles)
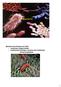 Bacteria Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles) 1 Grouped by their need for oxygen obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen
Bacteria Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles) 1 Grouped by their need for oxygen obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen
General Biology. The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell. All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 3. A Tour of the Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 3. A Tour of the Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of
Explain how the genetic information in the nucleus is used to direct the production of proteins in the cytoplasm.
 Cells: The building blocks of life Study Guide Compare the following pairs of terms, noting the most significant differences: prokaryotic cells versus eukaryotic cells, plant cells versus animal cells.
Cells: The building blocks of life Study Guide Compare the following pairs of terms, noting the most significant differences: prokaryotic cells versus eukaryotic cells, plant cells versus animal cells.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam 3 BIOL 1406, Fall 2012 HCC Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When biologists wish to study the internal ultrastructure
Exam 3 BIOL 1406, Fall 2012 HCC Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When biologists wish to study the internal ultrastructure
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3)
 Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Lab 2: Investigating Variation Across Spatial Scales
 Lab 2: Investigating Variation Across Spatial Scales What are scales and variation in a biological context? The world around us displays incredible diversity across many scales. Today s lab investigates
Lab 2: Investigating Variation Across Spatial Scales What are scales and variation in a biological context? The world around us displays incredible diversity across many scales. Today s lab investigates
Mahon: Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 4 th Edition
 Mahon: Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 4 th Edition Chapter 01: Bacterial Cell Structure, Physiology, Metabolism, and Genetics Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. To survive, microbial inhabitants have learned
Mahon: Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 4 th Edition Chapter 01: Bacterial Cell Structure, Physiology, Metabolism, and Genetics Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. To survive, microbial inhabitants have learned
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
CELL THEORY- EQ: What are the 3 facts of the cell theory? - pp191. EQ- Which Scientists are connected to cell discovery?
 UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
UNIT 3 - CELLS Cell theory Types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic,plant and animal) Homeostasis in cells Enzymes Biomolecules Cell structure and function and processes Transport across cellular membranes
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
3. When he discovered enzymes in 1897, Eduard Buchner was investigating the causes of. disease antisepsis spontaneous generation fermentation
 Chapter 2 1. Which of the following elements forms the backbone of organic molecules? carbon fluorine chlorine sodium carbon 2. The smallest chemical unit of matter is the. neutron element atom proton
Chapter 2 1. Which of the following elements forms the backbone of organic molecules? carbon fluorine chlorine sodium carbon 2. The smallest chemical unit of matter is the. neutron element atom proton
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Dako IT S ABOUT TIME. Interpretation Guide. Agilent Pathology Solutions. ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis)
 INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral sizes and structures. Workbook Lesson 1.4
 Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Biology EOC Review. Saturday Session
 Biology EOC Review Saturday Session Cells DNA Ribosome Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryotic Bacteria Flagellum Cell Membrane (Plasma) Cell Wall Eukaryotic Animal Mitochondria Ribosome
Biology EOC Review Saturday Session Cells DNA Ribosome Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryotic Bacteria Flagellum Cell Membrane (Plasma) Cell Wall Eukaryotic Animal Mitochondria Ribosome
Bio10 Lab 2: Cells. Using your text and the cell models and posters in the lab, sketch an animal cell and a plant cell on the group results sheet.
 Bio10 Lab 2: Cells Cells are the smallest living things and all living things are composed of cells. They are able to perform all necessary metabolic functions as well as specialized tasks such as moving,
Bio10 Lab 2: Cells Cells are the smallest living things and all living things are composed of cells. They are able to perform all necessary metabolic functions as well as specialized tasks such as moving,
I. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells
 科目 : 生命科學概論教材單元 : A Tour of the Cell 共 8 頁第 1 頁 I. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells 1. A were first isolated from mold in 1928 2. The widespread use of a drastically
科目 : 生命科學概論教材單元 : A Tour of the Cell 共 8 頁第 1 頁 I. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells 1. A were first isolated from mold in 1928 2. The widespread use of a drastically
How we see cells Hooke saw cork cells (plant cell) underneath a microscope and described them as cells
 Biology How we see cells Hooke saw cork cells (plant cell) underneath a microscope and described them as cells a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination Because
Biology How we see cells Hooke saw cork cells (plant cell) underneath a microscope and described them as cells a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination Because
NAME: ADM NO: DATE: BIOLOGY FORM ONE END OF TERM 3 EXAMS. Instructions to candidates:
 NAME: ADM NO: DATE: BIOLOGY FORM ONE END OF TERM 3 EXAMS Instructions to candidates: a) Write your Name and Admission number in the spaces provided b) Write the date of examination in the space provided
NAME: ADM NO: DATE: BIOLOGY FORM ONE END OF TERM 3 EXAMS Instructions to candidates: a) Write your Name and Admission number in the spaces provided b) Write the date of examination in the space provided
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Chapter 3. Cell Structure
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
Chapter 4-5. Prokaryotic Cells and Membranes
 Chapter 4-5 Prokaryotic Cells and Membranes Four Important People Anton Von Leeuwenheok Inventing microscopes and first observing unicellular living organisms Robert Hooke Discovered and coined the term
Chapter 4-5 Prokaryotic Cells and Membranes Four Important People Anton Von Leeuwenheok Inventing microscopes and first observing unicellular living organisms Robert Hooke Discovered and coined the term
Bacterial Structures. Capsule or Glycocalyx TYPES OF FLAGELLA FLAGELLA. Average size: µm 2-8 µm Basic shapes:
 PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi
 number Done by Corrected by 46 2017/9/20 Doctor Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 2 nd year Medical Students JU Bacterial Structure and
number Done by Corrected by 46 2017/9/20 Doctor Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 66 /8486535 مركز الرائد للخدمات الطالبية 2 nd year Medical Students JU Bacterial Structure and
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Levels of Organization. Anatomical Position
 Levels of Organization Anatomical Position A stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor, arms at the sides, and the palms, face, and eyes facing forward. The body standing erect,
Levels of Organization Anatomical Position A stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor, arms at the sides, and the palms, face, and eyes facing forward. The body standing erect,
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
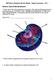 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Biology Multiple Choice, 2 pt each.
 Biology 3340 Spring 2007 Name Exam 1, Version A Write your name on both the exam booklet and the mark sense sheet. On the upper left corner of the mark sense sheet in the Key ID box, mark the version letter
Biology 3340 Spring 2007 Name Exam 1, Version A Write your name on both the exam booklet and the mark sense sheet. On the upper left corner of the mark sense sheet in the Key ID box, mark the version letter
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
The City School. PAF Chapter. Comprehensive Worksheet DEC Science. Class 8. Candidate Name: Index Number: Section: Branch/Campus: Date:
 The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet DEC 2018 Science Class 8 Candidate Name: Index Number: Section: Branch/Campus: Date: INSTRUCTIONS: Write your name, index number, section, branch/campus
The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet DEC 2018 Science Class 8 Candidate Name: Index Number: Section: Branch/Campus: Date: INSTRUCTIONS: Write your name, index number, section, branch/campus
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers. EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3
 Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
year 7 REVISION Spring Assessment - Biology
 year 7 REVISION Spring Assessment - Biology year 7 REVISION Microscope and Cells THE MICROSCOPE Used to view things too small for the naked eye. Consists of lenses of different magnification to make things
year 7 REVISION Spring Assessment - Biology year 7 REVISION Microscope and Cells THE MICROSCOPE Used to view things too small for the naked eye. Consists of lenses of different magnification to make things
A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7
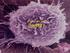 A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7 CELL THEORY Before microscopes, people thought diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits They had no idea microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses existed
A View of the Cell CHAPTER 7 CELL THEORY Before microscopes, people thought diseases were caused by curses and supernatural spirits They had no idea microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses existed
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. RPTSE Biology Fall 2015, Dr. Jong B. Lee 1. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
Chapter 1: Studying Life
 Chapter 1: Studying Life 1. Most living organisms share key characteristics: consist of one or more cells, contain genetic information, reproduce themselves, have evolved, and carry out metabolism. 2.
Chapter 1: Studying Life 1. Most living organisms share key characteristics: consist of one or more cells, contain genetic information, reproduce themselves, have evolved, and carry out metabolism. 2.
On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging. On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging. Wavelength Specific Imaging
 On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, FOPS, OCT-C Penn State Hershey Eye Center Hershey, PA On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Wavelengths
On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, FOPS, OCT-C Penn State Hershey Eye Center Hershey, PA On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Wavelengths
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
What does your body do to protect itself from invading microbes?
 46 Disease Fighters i n v e s t i g at i o n What does your body do to protect itself from invading microbes? Even before an organism can enter your body, your skin provides a protective barrier. But foreign
46 Disease Fighters i n v e s t i g at i o n What does your body do to protect itself from invading microbes? Even before an organism can enter your body, your skin provides a protective barrier. But foreign
Biodiversity: prokaryotes & viruses
 Biodiversity: prokaryotes & viruses All three domains contain microscopic organisms. Focus now: Prokaryotes Prokaryotes in general Asexual, single-celled, no nucleus or organelles, circular DNA Can live
Biodiversity: prokaryotes & viruses All three domains contain microscopic organisms. Focus now: Prokaryotes Prokaryotes in general Asexual, single-celled, no nucleus or organelles, circular DNA Can live
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Weds. Date. Aug. 26. Sept. 2
 Mt.SanAntonioCollege Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Fall 2015 Mon./ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk. Mon. 1 Aug. 24 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations 2 Aug. 31 Exercise #1: The Microscope
Mt.SanAntonioCollege Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Fall 2015 Mon./ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk. Mon. 1 Aug. 24 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations 2 Aug. 31 Exercise #1: The Microscope
PMT. Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 µm
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
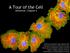 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES
 EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES The lectures and reading assignments of BIS 2A are designed to convey a large number of facts and concepts that have evolved from modern studies of living organisms. In order to
EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES The lectures and reading assignments of BIS 2A are designed to convey a large number of facts and concepts that have evolved from modern studies of living organisms. In order to
INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE
 Name: INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Introduction: If you missed the microscope lab we did in class, you will need to make it up by using a "virtual microscope" which can be accessed on the internet.
Name: INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Introduction: If you missed the microscope lab we did in class, you will need to make it up by using a "virtual microscope" which can be accessed on the internet.
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/Thurs. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/Weds. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Exam 2 spring 2016 Page 1
 xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
MicroLife Review Sheet
 Name: KEY Due Date: MicroLife Review Sheet Directions: Complete the review sheet to help study for the unit test. This is only a guide of what will be on the test. Be sure to use this, notes, lab booklet,
Name: KEY Due Date: MicroLife Review Sheet Directions: Complete the review sheet to help study for the unit test. This is only a guide of what will be on the test. Be sure to use this, notes, lab booklet,
Phases of the bacterial growth:
 L3: Physiology of Bacteria: Bacterial growth Growth is the orderly increase in the sum of all the components of an organism. Cell multiplication is a consequence of growth, in unicellular organism, growth
L3: Physiology of Bacteria: Bacterial growth Growth is the orderly increase in the sum of all the components of an organism. Cell multiplication is a consequence of growth, in unicellular organism, growth
Made by :aseel al-waked corrected by : sarah awaisheh
 Microbiology sheet (2) Made by :aseel al-waked corrected by : sarah awaisheh DATE :25-9-2016 "Anatomy" and Function of Prokaryotes: Last lecture we talked about the shape of the bacteria. Now the shape
Microbiology sheet (2) Made by :aseel al-waked corrected by : sarah awaisheh DATE :25-9-2016 "Anatomy" and Function of Prokaryotes: Last lecture we talked about the shape of the bacteria. Now the shape
Exam 1 SC135 spring 2011 Page 1
 xam 1 S135 spring 2011 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 Which other item is worth the same (has the same weight) as your lecture exams toward your final grade? quizzes writing assignments participation presentation
xam 1 S135 spring 2011 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 Which other item is worth the same (has the same weight) as your lecture exams toward your final grade? quizzes writing assignments participation presentation
All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction
 Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
LECTURER: WILLIAM GARIBA AKANWARIWIAK Senior Lecturer, Biological Sciences
 BIOL 151 CELL STRUCTURE LECTURER: WILLIAM GARIBA AKANWARIWIAK Senior Lecturer, Biological Sciences 7/1/2017 1 ATTENDANCE AT LECTURES Attendance at lectures is an integral part of the requirements of assessment
BIOL 151 CELL STRUCTURE LECTURER: WILLIAM GARIBA AKANWARIWIAK Senior Lecturer, Biological Sciences 7/1/2017 1 ATTENDANCE AT LECTURES Attendance at lectures is an integral part of the requirements of assessment
