Rationale for co-targeting IGF-1R and ALK in ALK fusion positive lung cancer
|
|
|
- Laurence Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figures and Legends Rationale for co-targeting IGF-1R and ALK in ALK fusion positive lung cancer Christine M. Lovly 1,2, Nerina T. McDonald 1, Heidi Chen 2, Sandra Ortiz-Cuaran 3, Lukas C. Heukamp 4,5, Yingjun Yan 1, Alexandra Florin 4, Luka Ozretić 4, Diana Lim 6, Lu Wang 6, Zhao Chen 7, Xi Chen 2, Pengcheng Lu 2, Paul K. Paik 8, Ronglai Shen 9, Hailing Jin 1, Reinhard Buettner 4, Sascha Ansén 1, Sven Perner 11, Michael Brockmann 12, Marc Bos 3,1, Jürgen Wolf 1, Masyar Gardizi 1, Gavin M. Wright 13, Benjamin Solomon 14, Prudence A. Russell 15, Toni-Maree Rogers 16, Yoshiyuki Suehara 6, Monica Red-Brewer 1, Rudy Tieu 17, Elisa de Stanchina 17, Qingguo Wang 18, Zhongming Zhao 18, David H. Johnson 19, Leora Horn 1, Kwok-Kin Wong 7, Roman K. Thomas 3,4, Marc Ladanyi 6, William Pao 1 Departments of 1 Medicine, 2 Biostatistics, and 18 Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, 3 Department of Translational Genomics, Center of Integrated Oncology Köln Bonn, University Hospital Cologne, Cologne, Germany; Departments of 4 Pathology and 1 Internal Medicine (Department I), Center for Integrated Oncology Köln-Bonn, University Hospital Cologne, Cologne, Germany; 5 New Oncology, Cologne, Germany; Departments of 6 Pathology, 8 Medicine, 9 Epidemiology and Biostatistics and 17 Anti-tumor Assessment Core Facility, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York; 7 Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA; 11 Department of Prostate Cancer Research, Institute of Pathology, Center of Integrated Oncology Köln Bonn, University Hospital of Bonn, Bonn, Germany; 12 Department of Pathology, Hospital Merheim, Cologne, Germany; 13 University of Melbourne, Department of Surgery, St Vincent's Hospital, Melbourne, Australia; 14 Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, Australia; 15 Department of Anatomical Pathology, St Vincent's Hospital, Melbourne, Australia; 16 Department of Pathology, Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, Melbourne, Australia; 19 Department of Medicine, UT Southwestern School of Medicine, Dallas, TX; 2 Corresponding author: Vanderbilt University Medical Center and Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center, 222 Pierce Avenue, 777 Preston Research Building, Nashville, TN Phone ; Fax: ; christine.lovly@vanderbilt.edu
2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: EGFR inhibition does not sensitize ALK+ lung cancer cells to the effects of ALK inhibitors or IGF-1R inhibitors. (a) H3122 cells were treated with erlotinib or erlotinib + MAb391. Soft agar assays were performed using hextuplicate biological replicates. (b) H3122 cells were treated with erlotinib, OSI-96, or the combination. Cell titer blue assays were performed using hextuplicate biological replicates. (c) STE-1 cells were treated with crizotinib or crizotinib + MAb391. Soft agar assays were performed using hextuplicate biological replicates. (d) H3122 cells were treated with crizotinib and OSI-96 as described in Fig. 2b. Data from this experiment were analyzed as previously described 1. The Loewe index provides a measure of drug interaction. A Loewe index < 1 is indicative of a synergistic drug-drug interaction. The blue line in the figure represents a Loewe index of 1. The dashed red lines represent the upper and lower 95% confidence intervals. (e) SUDHL-1 cells were treated with crizotinib, OSI-96, or the combination. Cell titer blue assays were performed using hextuplicate biological replicates. (f) Quantification of H3122 xenograft tumor volumes after treatment with the indicated inhibitors. *P =.41 by the Wilcoxon rank sum test. (g) H3122 cells were treated crizotinib, erlotinib, or the combination. Cell titer blue assays were performed using hextuplicate biological replicates. (h) H3122 cells were treated crizotinib, lapatinib, or the combination. Cell titer blue assays were performed using hextuplicate biological replicates. (i) Quantification of AKT phosphorylation from the western blot shown in Fig. 2f. Supplementary Figure 2: IGF-1 ligand stimulates phosphorylation of IGF-1R but not ALK. (a) H3122 cells were serum starved overnight, treated with vehicle or OSI-96, and then stimulated with IGF-1 for 1min, 5min, or 1min prior to harvest. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies specific for the indicated proteins. (b) Quantification of AKT phosphorylation from the western blot shown in Fig. 3b.
3 Supplementary Figure 3: IRS-1 knock-down impedes the growth of H2228 ALK+ lung cancer cells. (a) H2228 cells were transfected with the indicated sirnas and treated with 5nM crizotinib for 72h.Triplicate biological replicates for each sample were counted on Coulter Counter. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (b) Western blot confirming IRS-1 knockdown in the experiment shown in Supplementary Fig. 3a. Supplementary Figure 4: Characterization of ALK TKI resistant cells. (a) Results from ALK FISH using the ALK Break Apart FISH probe in H3122 CR cells. (b) H3122 parental and isogenic H3122 CR cells were treated with 5nM crizotinib. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (c) Results from ALK FISH using the Vysis ALK Break Apart FISH probe in H3122 XR cells. (d) Lysates from H3122 parental and isogenic H3122 XR cells subjected to phospho-rtk arrays according to the manufacturer s instructions. (e) H3122 CR cells were treated with increasing amounts of crizotinib, OSI-96, or the combination crizotinib + OSI-96 at the indicated concentrations for 72h. Cell titer blue assays were performed to assess growth inhibition. Each point represents hextuplicate replicates. Data are presented as the percentage of viable cells compared to control. (f) Conditioned supernatant from H3122 parental, H3122 CR, and H3122 XR cells were subjected to ELISA assays for IGF-1 according to the manufacturer s instructions. Data are presented as fold change in IGF-1 level compared to H3122 parental cells. Supplementary Figure 5: Efficacy of IGF-1R TKIs in EGFR mutant lung cancer cell lines. Four different isogenic pairs of EGFR TKI sensitive and EGFR TKI resistant cell lines were used in these experiments, including PC-9 parental (TKI sensitive cells) and PC-9 ERc1 (Erlotinib Resistant clone 1) (a), HCC827 parental (TKI sensitive cells) and HCC827 ER (Erlotinib Resistant) (b), HCC2279 parental (TKI sensitive cells) and HCC2279 ER (Erlotinib Resistant)
4 (c), and HCC46 parental (TKI sensitive cells) and HCC46 ER (Erlotinib Resistant) (d). Please see Supplementary Table 1 for a summary of these cell lines. Cell were treated with increasing amounts of erlotinib alone, OSI-96 alone, or the combination of erlotinib + 1µM OSI- 96 for 72h. Cell Titer Blue Assays were performed as previously described. Each point represents hextuplicate biological replicates. Data are representative of two independent experiments. The x-axis indicates the concentration of erlotinib or OSI-96 when these inhibitors were used as single treatment agents. (e) Lysates from the four different isogenic pairs of EGFR TKI sensitive (S) and TKI resistant (R) cell lines described above were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Supplementary Figure 6: Representative pigf-1r py1161 immunohistochemistry and Nanostring data from patients with EGFR mutant lung cancer pre- and post-egfr TKI therapy. (a c) Representative pigf-1r py1161 immunohistochemistry showing low (a), medium (b), and high (c) pigf-1r staining on lung tumor biopsies. Scalebars are shown and represent 5 µm. All images viewed correspond to a magnification of 4x. (d f) RNA was extracted from 11 different matched pairs of snap-frozen tumor biopsy samples from patients with EGFR mutant lung cancer pre- and post-egfr TKI therapy. Panel (d) shows aggregate data. 6 pairs of matched tumor samples were from patients who underwent biopsy prior to and 2 days post initiation of an EGFR TKI (e). 5 pairs of matched tumor samples were from patients who underwent biopsy prior to and at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI (f). P values were determined with the paired T-test. Supplementary Figure 7: Effects of LDK-378 in ALK+/TKI sensitive and ALK+/TKI resistant cell lines. (a) STE-1 cells were treated with increasing amounts of crizotinib, LDK- 378, or TAE-684 at the indicated concentrations for 72h. Cell titer blue assays were performed
5 to assess growth inhibition. Each point represents hextuplicate replicates. Data are presented as the percentage of viable cells compared to control (vehicle only treated) cells and are representative of two independent experiments. (b) H3122 XR cells were treated with increasing amounts of X-376 or LDK-378 at the indicated concentrations for 72h. Cell titer blue assays were performed to assess growth inhibition. Each point represents hextuplicate replicates. Data are presented as the percentage of viable cells compared to control (vehicle only treated) cells and are representative of two independent experiments. (c) H3122 cells were treated with crizotinib or LDK-378 for 72 hours prior to harvest. Cells were stained with propidium iodide (PI) and counted on a FACSCalibur machine. Apoptosis was defined by the percentage of cells harboring a sub-2n DNA content. This experiment was repeated two times. Representative results are shown. Supplementary Figure 8: Characterization of novel STE 1 ALK+ lung cancer cell line. (a) Results from ALK FISH using the Vysis ALK Break Apart FISH probe in STE-1 cells. (b) cdna sequencing of ALK from STE-1 cells reveals the presence of an EML4-ALK E13;A2 (variant 1) fusion.
6 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE LEGENDS Supplementary Table 1: Isogenic pairs of EGFR TKI sensitive and EGFR TKI resistant cell lines. Summary of the isogenic pairs of EGFR TKI sensitive and EGFR TKI resistant cell lines used in these studies. These cell lines have been previously described 2,3. Supplementary Table 2: Microarray data for crizotinib resistant cell lines. Summary of the top 2 downregulated genes in the H3122 crizotinib resistant (CR) cells versus isogenic H3122 crizotinib sensitive parental cells as assessed by microarray analysis. Each value shown for a specific gene represents a unique probe. Changes in IGFBP3 are noted in bold. Supplementary Table 3: Microarray data for X-376 resistant cell lines. Summary of the top 2 downregulated genes in the H3122 X-376 resistant (XR) cells versus isogenic H3122 crizotinib sensitive parental cells as assessed by microarray analysis. Each value shown for a specific gene represents a unique probe. Changes in IGFBP3 are noted in bold. Supplementary Table 4: Summary of the mechanisms of crizotinib resistance evaluated for in the study cohort. a PCR/Direct sequencing; b Whole exome sequencing; c RNA sequencing; d Whole genome sequencing. Supplementary Table 5: Index patient s clinical genotyping results. Results from SNaPshot clinical genotyping of the index patient's tumor. Prior to enrollment in the Profile 17 study of
7 crizotinib vs. pemetrexed or docetaxel for patients with advanced ALK fusion positive lung cancer, the patient s tumor sample was sent for ALK FISH (as part of the study enrollment) and also for our institutional SNaPshot lung cancer panel 4. ALK FISH testing was positive at the central laboratory (Esoterix). No other mutations were found based on the SNaPshot results.
8 SUPPLEMENTAL REFERENCES 1. Boik, J.C., Newman, R.A. & Boik, R.J. Quantifying synergism/antagonism using nonlinear mixed-effects modeling: a simulation study. Stat Med 27, (28). 2. Chmielecki, J., et al. Optimization of dosing for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with evolutionary cancer modeling. Sci Transl Med 3, 9ra59 (211). 3. Ohashi, K., et al. Lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors occasionally harbor BRAF gene mutations but lack mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or MEK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 19, E (212). 4. Su, Z., et al. A platform for rapid detection of multiple oncogenic mutations with relevance to targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Mol Diagn 13, (211).
9 Supplementary Fig. 1 (Lovly et al 214) a. 1 9 % growth relative to control b. MAB391 1nM erlotinib 5nM erlotinib 1,nM erlotinib 1nM erlotinib + MAb391 5nM erlotinib + MAb391 1,nM erlotinib + MAB391 % growth relative to control Erlotinib OSI-96 Erlotinib + OSI-96 Erlotinib (µm) OSI-96 (µm)
10 Supplementary Fig. 1 (Lovly et al 214) c. d. % growth relative to control MAb391 1nM crizotinib 1nM crizotinib + MAb391 Loewe Index > 1: Drug combination is antagonistic Loewe Index = 1: Drug combination is additive Loewe Index < 1: Drug combination is synergistic
11 Supplementary Fig. 1 (Lovly et al 214) e. 16 f. 7 % growth relative to control Crizotinib OSI-96 Crizotinib + OSI-96 Tumor volume (mm 3 ) * * Vehicle Crizotinib MAb391 Crizotinib + MAb Crizotinib (μm) OSI-96 (μm) Time (days) g. 12 h % growth relative to control Crizotinib Erlotinib Crizotinib + erlotinib % growth relative to control Crizotinib Lapatinib Crizotinib + lapatinib Crizotinib (µm) Crizotinib (µm) Erlotinib (µm) Lapatinib (µm)
12 Supplementary Fig. 1 (Lovly et al 214) i. Pixel intensity compared to control Control IGF-1 Crizotinib OSI-96 IGF-1 + crizotinib IGF-1 + OSI-96 IGF-1 + crizotinib + OSI-96
13 Supplementary Fig. 2 (Lovly et al 214) a. IGF OSI-96 + pigf-1r Y1131 IGF-1R palk Y164 ALK Actin b Control IGF-1 Crizotinib OSI-96 IGF-1 + crizotinib Pixel intensity compared to control IGF-1 + OSI-96 IGF-1 + crizotinib + OSI-96
14 Supplementary Fig. 3 (Lovly et al 214) a % cell number relative to control NT sirna: DMSO NT sirna: Crizotinib IRS-1 sirna (pool #1): DMSO IRS-1 sirna (pool #1): crizotinib IRS-1 sirna (pool #2): DMSO IRS-1 sirna (pool #2): crizotinib b. NT sirna IRS-1 sirna (pool #1) IRS-1 sirna (pool #2) Crizotinib IRS palk Y164 Actin
15 Supplementary Fig. 4 (Lovly et al 214) a. b. Blot: ALK H3122 Parental H3122 CR Crizotinib + + c. d. IGF-1R H3122 Parental H3122 XR
16 Supplementary Fig. 4 (Lovly et al 214) e. f. % growth relative to control Crizotinib OSI-96 Crizotinib + OSI-96 Crizotinib (μm) OSI-96 (μm) Fold change in IGF H3122 parental H3122 CR H3122 XR
17 Supplementary Fig. 5 (Lovly et al 214) a. b. % growth relative to control , Erlotinib (nm) PC-9 parental: erlotinib PC-9 parental: OSI- 96 PC-9 parental: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM) PC-9 ER: erlotinib PC-9 ER: OSI-96 PC-9 ER: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM) % growth relative to control , Erlotinib (nm) HCC827 parental: erlotinib HCC827 parental: OSI-96 HCC827 parental: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM) HCC827 ER: erlotinib HCC827 ER: OSI-96 HCC827 ER: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM) c. d. % growth relative to control , Erlotinib (nm) HCC2279 parental: erlotinib HCC2279 parental: OSI-96 HCC2279 parental: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM) HCC2279 ER: erlotinib HCC2279 ER: OSI-96 HCC2279 ER: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM) % growth relative to control , Erlotinib (nm) HCC46 parental: erlotinib HCC46 parental: OSI-96 HCC46 parental: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM) HCC46 ER: erlotinib HCC46 ER: OSI- 96 HCC46 ER: erlotinib + OSI-96 (1μM)
18 Supplementary Fig. 5 (Lovly et al 214) e. HCC- 46 HCC HCC- 827 PC-9 S R S R S R S R IGF-1R pigf-1r Y1131 IRS-1 EGFR Actin
19 5µM Supplementary Fig. 6 (Lovly et al 214) a. b. c.
20 Supplementary Fig. 6 (Lovly et al 214) d. e. Rebiopsy 2 days f. Aggregate data (n=11) post initiation of EGFR TKI therapy (n=6) P =.56 P =.51 Rebiopsy at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI therapy (n=5) P =.84 Log (intensity) Log (intensity) Log (intensity) Pre-EGFR TKI Post-EGFR TKI Pre-EGFR TKI Post-EGFR TKI Pre-EGFR TKI Post-EGFR TKI
21 Supplementary Fig. 7 (Lovly et al 214) a. b. % growth relative to control c Crizotinib 8 7 LDK TAE , Drug concentration(nm) % growth relative to control , Drug Concentration (nm) X-376 LDK Fold change in sub-2n DNA content compared to control Crizotinib LDK-378
22 Supplementary Fig. 8 (Lovly et al 214) a. b. ALK EML4
23 Variant KRAS c. 34G>A (G12S) KRAS c. 34G>C (G12R) KRAS c. 34G>T (G12C) KRAS c. 35G>A (G12D) KRAS c. 35G>C (G12A) KRAS c. 35G>T (G12V) KRAS c. 37G>T (G13C) KRAS c. 37G>A (G13S) KRAS c. 37G>C (G13R) KRAS c. 38G>A (G13D) KRAS c. 38G>C (G13A) KRAS c. 181C>A (Q61K) KRAS c. 182A>G (Q61R) KRAS c. 182A>T (Q61L) KRAS c. 183A>T (Q61H) KRAS c. 183A>C (Q61H) BRAF c.1397 G>T (G466V) BRAF c.146 G>C (G469A) BRAF c.1789 C>G (L597V) BRAF c.1799 T>A (V6E) NRAS c.182 A>T (Q61L) NRAS c.181 C>A (Q61K) NRAS c.182 A>G (Q61R) PIK3CA c.314 A>G (H147R) PIK3CA c.314 A>T (H147L) PIK3CA c.1624 G>A (E542K) PIK3CA c.1633 G>A (E545K) PIK3CA c.1633 G>A (E545Q) MEK1 c.167 A>C (Q56P) MEK1 c.171 G>T (K57N) MEK1 c.199 G>A (D67N) AKT1 c. 49 G>A (E17K) PTEN c.697 C>T (R233X) EGFR c G>T (G719C) EGFR c G>A (G719S) EGFR c G>C (G719A) EGFR c C>T (T79M) EGFR c T>G (L858R) EGFR c T>A (L861Q) EGFR exon 19 deletion EGFR exon 2 insertion ERBB2 exon 2 insertion Result Supplementary Table 1: Results from SNaPshot clinical genotyping from the Index patient's tumor. Prior to enrollment in the Profile 17 study of crizotinib vs. pemetrexed or docetaxel for patients with advanced ALK fusion positive lung cancer, the patient s tumor sample was sent for ALK FISH (as part of the study enrollment) and also for our institutional SNaPshot lung cancer panel. ALK FISH testing was positive at the central laboratory (Esoterix), but no other mutations were found based on the SNaPshot results shown above.
24 PROBE_ID SYMBOL Log Fold Change Adj. p value (H3122 CR vs. H3122 Parental) ILMN_ SERPINE e-7 ILMN_ SERPINA e-6 ILMN_ MAT2A e-7 ILMN_ PRSS e-7 ILMN_ IGFBP e-7 ILMN_ IGFBP e-5 ILMN_ PHLDA e-6 ILMN_ ODC e-7 ILMN_ STMN e-6 ILMN_ ERRFI e-7 ILMN_ ITGB e-7 ILMN_ ITGB e-8 ILMN_ HMGA e-7 ILMN_ FHL e-6 ILMN_ FHL e-7 ILMN_ CYBA e-6 ILMN_ MUC e-6 ILMN_ DUSP e-6 ILMN_ LOC e-5 ILMN_ TRIB e-5 Supplementary Table 2: Summary of the top 2 downregulated genes in the H3122 crizotinib resistant (CR) cells versus isogenic H3122 crizotinib sensitive parental cells as assessed by microarray analysis. Each value shown for a specific gene represents a unique probe. Changes in IGFBP3 are noted in bold.
25 PROBE_ID SYMBOL Log Fold Change adj.p.val (H3122 XR vs. H3122 Parental) ILMN_ TFF e-1 ILMN_ TFF e-8 ILMN_ PLUNC e-8 ILMN_17163 ALPL e-8 ILMN_ CYBA e-8 ILMN_ SLPI e-8 ILMN_ HMGA e-9 ILMN_ CLDN e-9 ILMN_ FCGBP e-9 ILMN_ IGFBP e-7 ILMN_ GDF e-8 ILMN_ DUSP e-8 ILMN_ CFB e-8 ILMN_ PHLDA e-8 ILMN_ CLDN e-8 ILMN_ MUC5AC e-1 ILMN_ SERPINA e-7 ILMN_ C2orf e-8 ILMN_ IGFBP e-8 ILMN_ MUC e-7 Supplementary Table 3: Summary of the top 2 downregulated genes in the H3122 X-376 resistant (XR) cells versus isogenic H3122 crizotinib sensitive parental cells as assessed by microarray analysis. Each value shown for a specific gene represents a unique probe. Changes in IGFBP3 are noted in bold.
26 Established Cell line PC-9 HCC827 HCC2279 HCC46 Summary of isogenic pairs of EGFR TKI sensitive and TKI resistant cell lines Primary Resistance Mechanism EGFR + Resistant EGFR derived of acquired IGF-1R TKIs Cell Line mutation against resistance synergistic? Exon 19 deletion Exon 19 deletion Exon 19 deletion Exon 19 deletion PC-9 ERc1 HCC827 ER HCC2279 ER HCC46 ER Erlotinib EGFR T79M No 2 Erlotinib EGFR T79M No 3 Erlotinib EMT No 3 Erlotinib EMT No 3 Reference (cited in supplemental referenes) Supplementary Table 4: Summary of the isogenic pairs of EGFR TKI sensitive and EGFR TKI resistant cell lines used in these studies. These cell lines have been previously described 2,3.
27 Mechanisms of acquired resistance to crizotinib ALK Patient # pigf-1r IRS-1 ALK mutation amplification 1 + N/A WT a Negative a WT a,b Negative b WT c N/A 4 + N/A G122R d Negative d 5 - N/A WT d Negative d Supplementary Table 5: Summary of the mechanisms of crizotinib resistance evaluated for in the study cohort. a PCR/Direct sequencing; b Whole exome sequencing; c RNA sequencing; d Whole genome sequencing.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Kris MG, Johnson BE, Berry LD, et al. Using Multiplexed Assays of Oncogenic Drivers in Lung Cancers to Select Targeted Drugs. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3741 etable 1. Trials
Supplementary Online Content Kris MG, Johnson BE, Berry LD, et al. Using Multiplexed Assays of Oncogenic Drivers in Lung Cancers to Select Targeted Drugs. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3741 etable 1. Trials
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Nat Med. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 March 01.
 HHS Public Access Author manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2014 September ; 20(9): 1027 1034. doi:10.1038/nm.3667. Rationale for co-targeting IGF-1R and ALK in ALK fusion positive
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. 2014 September ; 20(9): 1027 1034. doi:10.1038/nm.3667. Rationale for co-targeting IGF-1R and ALK in ALK fusion positive
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. Relative cell viability. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng SCR shyap1-1 shyap
 Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, China; 5 Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China; 6 Department of Pathology, University of Michigan
 Overexpression of FAM83H-AS1 indicates poor patient survival and knockdown impairs cell proliferation and invasion via MET/EGFR signaling in lung cancer Jie Zhang 1,2, Shumei Feng 3, Wenmei Su 4, Shengbin
Overexpression of FAM83H-AS1 indicates poor patient survival and knockdown impairs cell proliferation and invasion via MET/EGFR signaling in lung cancer Jie Zhang 1,2, Shumei Feng 3, Wenmei Su 4, Shengbin
Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis
 5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
Frequency(%) KRAS G12 KRAS G13 KRAS A146 KRAS Q61 KRAS K117N PIK3CA H1047 PIK3CA E545 PIK3CA E542K PIK3CA Q546. EGFR exon19 NFS-indel EGFR L858R
 Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL-
 Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
Supplementary Material for mtor Inhibition Specifically Sensitizes Colorectal Cancers with KRAS or BRAF Mutations to BCL-2/BCL- XL Inhibition by Suppressing MCL-1 Anthony C. Faber 1,2 *, Erin M. Coffee
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy
 Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San
 Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Lung Cancer Genetics: Common Mutations and How to Treat Them David J. Kwiatkowski, MD, PhD. Mount Carrigain 2/4/17
 Lung Cancer Genetics: Common Mutations and How to Treat Them David J. Kwiatkowski, MD, PhD Mount Carrigain 2/4/17 Histology Adenocarcinoma: Mixed subtype, acinar, papillary, solid, micropapillary, lepidic
Lung Cancer Genetics: Common Mutations and How to Treat Them David J. Kwiatkowski, MD, PhD Mount Carrigain 2/4/17 Histology Adenocarcinoma: Mixed subtype, acinar, papillary, solid, micropapillary, lepidic
Next Generation Sequencing in Clinical Practice: Impact on Therapeutic Decision Making
 Next Generation Sequencing in Clinical Practice: Impact on Therapeutic Decision Making November 20, 2014 Capturing Value in Next Generation Sequencing Symposium Douglas Johnson MD, MSCI Vanderbilt-Ingram
Next Generation Sequencing in Clinical Practice: Impact on Therapeutic Decision Making November 20, 2014 Capturing Value in Next Generation Sequencing Symposium Douglas Johnson MD, MSCI Vanderbilt-Ingram
Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer
 Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer Pimpin Incharoen, M.D. Assistant Professor, Thoracic Pathology Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital Genetic alterations in lung cancer Source: Khono et al, Trans
Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer Pimpin Incharoen, M.D. Assistant Professor, Thoracic Pathology Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital Genetic alterations in lung cancer Source: Khono et al, Trans
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor
 Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer
 Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer No disclosures Objectives Understand how FISH and NGS provide complementary data for the evaluation of lung cancer Recognize the challenges of performing testing
Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer No disclosures Objectives Understand how FISH and NGS provide complementary data for the evaluation of lung cancer Recognize the challenges of performing testing
PIK3CA mutations are found in approximately 7% of
 Original Article Impact of Concurrent PIK3CA Mutations on Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers and on Prognosis in Oncogene-Driven Lung Adenocarcinomas Juliana Eng, MD,*
Original Article Impact of Concurrent PIK3CA Mutations on Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers and on Prognosis in Oncogene-Driven Lung Adenocarcinomas Juliana Eng, MD,*
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
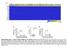 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
ALCHEMIST. Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification And Sequencing Trials
 ALCHEMIST Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification And Sequencing Trials What is ALCHEMIST? ALCHEMIST is 3 integrated trials testing targeted therapy in early stage lung cancer: l A151216:
ALCHEMIST Adjuvant Lung Cancer Enrichment Marker Identification And Sequencing Trials What is ALCHEMIST? ALCHEMIST is 3 integrated trials testing targeted therapy in early stage lung cancer: l A151216:
K-Ras signalling in NSCLC
 Targeting the Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk pathway Egbert F. Smit MD PhD Dept. Pulmonary Diseases Vrije Universiteit VU Medical Centre Amsterdam, The Netherlands K-Ras signalling in NSCLC Sun et al. Nature Rev. Cancer
Targeting the Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk pathway Egbert F. Smit MD PhD Dept. Pulmonary Diseases Vrije Universiteit VU Medical Centre Amsterdam, The Netherlands K-Ras signalling in NSCLC Sun et al. Nature Rev. Cancer
Personalized Healthcare Update
 Dr. Kai - Oliver Wesche Market Development Manager, Personalized Healthcare QIAGEN Personalized Healthcare Update Pioneering Personalized Medicine through Partnering TOMTOVOK BKM120 Zelboraf QIAGEN partners:
Dr. Kai - Oliver Wesche Market Development Manager, Personalized Healthcare QIAGEN Personalized Healthcare Update Pioneering Personalized Medicine through Partnering TOMTOVOK BKM120 Zelboraf QIAGEN partners:
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER: 70% PRESENT IN ADVANCED STAGE
 MORPHOLOGY AND MOLECULAR TESTING IN NON-SMALL CELL OF LUNG NEW FRONTIEIRS IN CYTOPATHOLOGY PRACTICE American Society for Cytopathology San Antonio, Texas Sunday March 5, 2017 Disclosure of Relevant Financial
MORPHOLOGY AND MOLECULAR TESTING IN NON-SMALL CELL OF LUNG NEW FRONTIEIRS IN CYTOPATHOLOGY PRACTICE American Society for Cytopathology San Antonio, Texas Sunday March 5, 2017 Disclosure of Relevant Financial
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
PRECISION INSIGHTS. Liquid GPS. Blood-based tumor profiling and quantitative monitoring. Reveal more with cfdna + cfrna.
 PRECISION INSIGHTS Liquid GPS Blood-based tumor profiling and quantitative monitoring Reveal more with cfdna + cfrna www.nanthealth.com Why Blood-Based Tumor Profiling? Although tissue-based molecular
PRECISION INSIGHTS Liquid GPS Blood-based tumor profiling and quantitative monitoring Reveal more with cfdna + cfrna www.nanthealth.com Why Blood-Based Tumor Profiling? Although tissue-based molecular
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
ras Multikinase Inhibitor Multikinase Inhibitor 0.1
 a ras ** * ** * ** ** ** ** un in et m lu Se ib SL G 32 W 7 So 50 ra 74 fe ni b LY W 294 or 0 tm 02 R an ap n a in Ev my er cin ol im BE us Z2 3 En P 5 za I13 st 0 au rin D as SP ati 60 nib C 012 is 5
a ras ** * ** * ** ** ** ** un in et m lu Se ib SL G 32 W 7 So 50 ra 74 fe ni b LY W 294 or 0 tm 02 R an ap n a in Ev my er cin ol im BE us Z2 3 En P 5 za I13 st 0 au rin D as SP ati 60 nib C 012 is 5
Characterisation of structural variation in breast. cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on. the Illumina Genome Analyser
 Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
MET skipping mutation, EGFR
 New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research: detection of MET skipping mutation, EGFR T790M, and other important biomarkers Fernando López-Ríos Laboratorio de Dianas Terapéuticas Hospital Universitario HM
New NSCLC biomarkers in clinical research: detection of MET skipping mutation, EGFR T790M, and other important biomarkers Fernando López-Ríos Laboratorio de Dianas Terapéuticas Hospital Universitario HM
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
KEY FINDINGS 1. Potential Clinical Benefit in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Gefitinib, Erlotinib, Afatinib due to EGFR E746_A750del. 2. Potential Cl
 PATIENT INFO SAMPLE REFERING PHYSICIAN COPY TO (if different from ordering) Name: John Smith Date Collected: 10/23/2016 Name: Oncologist, M.D. Name: Pathologist, M.D. DOB: 04/22/1937 Date Received: 10/24/2016
PATIENT INFO SAMPLE REFERING PHYSICIAN COPY TO (if different from ordering) Name: John Smith Date Collected: 10/23/2016 Name: Oncologist, M.D. Name: Pathologist, M.D. DOB: 04/22/1937 Date Received: 10/24/2016
Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know
 Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know Stephen P. Ethier, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, MUSC Director, MUSC Center for Genomic Medicine Genomics and
Genomic Medicine: What every pathologist needs to know Stephen P. Ethier, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, MUSC Director, MUSC Center for Genomic Medicine Genomics and
Lung Cancer Case. Since the patient was symptomatic, a targeted panel was sent. ALK FISH returned in 2 days and was positive.
 Lung Cancer Case Jonathan Riess, M.D. M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California Davis School of Medicine UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center 63 year-old woman, never smoker, presents
Lung Cancer Case Jonathan Riess, M.D. M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California Davis School of Medicine UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center 63 year-old woman, never smoker, presents
1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance. 13/10/2017 Sara Redaelli
 Dott.ssa Sara Redaelli 13/10/2017 1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance Tumor Heterogeneity: Oncogenic Drivers in NSCLC The Promise of Genotype-Directed Therapy
Dott.ssa Sara Redaelli 13/10/2017 1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance Tumor Heterogeneity: Oncogenic Drivers in NSCLC The Promise of Genotype-Directed Therapy
Transform genomic data into real-life results
 CLINICAL SUMMARY Transform genomic data into real-life results Biomarker testing and targeted therapies can drive improved outcomes in clinical practice New FDA-Approved Broad Companion Diagnostic for
CLINICAL SUMMARY Transform genomic data into real-life results Biomarker testing and targeted therapies can drive improved outcomes in clinical practice New FDA-Approved Broad Companion Diagnostic for
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Next generation diagnostics Bringing high-throughput sequencing into clinical application
 Next generation diagnostics Bringing high-throughput sequencing into clinical application Leonardo A. Meza-Zepeda, PhD Translational Genomics Group Institute for Cancer Research Leonardo.Meza-Zepeda@rr-research.no
Next generation diagnostics Bringing high-throughput sequencing into clinical application Leonardo A. Meza-Zepeda, PhD Translational Genomics Group Institute for Cancer Research Leonardo.Meza-Zepeda@rr-research.no
GENETIC TESTING FOR TARGETED THERAPY FOR NON-SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER (NSCLC)
 CANCER (NSCLC) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
CANCER (NSCLC) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
and management of lung cancer Maureen F. Zakowski, M.D. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
 The new role of cytology in the diagnosis and management of lung cancer Maureen F. Zakowski, M.D. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Outline Role of cytology in the diagnosis of lung cancer Non-small
The new role of cytology in the diagnosis and management of lung cancer Maureen F. Zakowski, M.D. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Outline Role of cytology in the diagnosis of lung cancer Non-small
EXAMPLE. - Potentially responsive to PI3K/mTOR and MEK combination therapy or mtor/mek and PKC combination therapy. ratio (%)
 Dr Kate Goodhealth Goodhealth Medical Clinic 123 Address Road SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Melanie Citizen Referring Doctor Your ref Address Dr John Medico 123 Main Street, SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Phone 02 9999 9999
Dr Kate Goodhealth Goodhealth Medical Clinic 123 Address Road SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Melanie Citizen Referring Doctor Your ref Address Dr John Medico 123 Main Street, SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Phone 02 9999 9999
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4078
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers
 Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers from genomics to clinical application Aldo Scarpa ARC-NET Applied Research on Cancer Department of Pathology and Diagnostics
Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers from genomics to clinical application Aldo Scarpa ARC-NET Applied Research on Cancer Department of Pathology and Diagnostics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Select analysis on the next pages. Sample request and sending address see last page. Institut für Pathologie und Molekularpathologie
 Diagnostic Tumor Genome Analysis Schmelzbergstrasse 12 8091 Zürich Tel.: (+41) 044 255 3929 Fax.: (+41) 044 255 4416 Client (address, telephone number): ngs.pathologie@usz.ch www.pathologie.usz.ch Sample-Nr:
Diagnostic Tumor Genome Analysis Schmelzbergstrasse 12 8091 Zürich Tel.: (+41) 044 255 3929 Fax.: (+41) 044 255 4416 Client (address, telephone number): ngs.pathologie@usz.ch www.pathologie.usz.ch Sample-Nr:
TITLE: Deficient BIM Expression as a Mechanism of Intrinsic and Acquired Resistance to Targeted Therapies in EGFR-Mutant and ALK-Positive Lung Cancers
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0227 TITLE: Deficient BIM Expression as a Mechanism of Intrinsic and Acquired Resistance to Targeted Therapies in EGFR-Mutant and ALK-Positive Lung Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0227 TITLE: Deficient BIM Expression as a Mechanism of Intrinsic and Acquired Resistance to Targeted Therapies in EGFR-Mutant and ALK-Positive Lung Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR:
Rob Ross, MD. Infinity Pharmaceuticals March 9 th, 2011
 Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) Inhibition as a Potential Novel Approach to the Treatment of Patients with ALK Mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Rob Ross, MD Infinity Pharmaceuticals March 9 th,
Heat Shock Protein 90 (Hsp90) Inhibition as a Potential Novel Approach to the Treatment of Patients with ALK Mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Rob Ross, MD Infinity Pharmaceuticals March 9 th,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/3/75/75ra26/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Genotypic and Histological Evolution of Lung Cancers Acquiring Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors Lecia V. Sequist,*
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/3/75/75ra26/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Genotypic and Histological Evolution of Lung Cancers Acquiring Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors Lecia V. Sequist,*
MUTATION TEST CE IVD. ctnras-braf FEATURES
 ctnras-braf CE IVD TECHNICAL SHEET IDYLLA ctnras-braf MUTATION TEST The Idylla ctnras-braf Mutation Test, performed on the Biocartis Idylla System, is an in vitro diagnostic test for the qualitative detection
ctnras-braf CE IVD TECHNICAL SHEET IDYLLA ctnras-braf MUTATION TEST The Idylla ctnras-braf Mutation Test, performed on the Biocartis Idylla System, is an in vitro diagnostic test for the qualitative detection
AACR 101st Annual Meeting 2010, Washington D.C. Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics Section 29; Abstract #3855
 Investigation of the Growth Inhibitory Activity of the MEK Inhibitor ARRY-162 in Combination with Everolimus in a Variety of KRas and PI3K Pathway Mutant Cancers Brian Tunquist, Tyler Risom, Debbie Anderson,
Investigation of the Growth Inhibitory Activity of the MEK Inhibitor ARRY-162 in Combination with Everolimus in a Variety of KRas and PI3K Pathway Mutant Cancers Brian Tunquist, Tyler Risom, Debbie Anderson,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Individualized Cancer Therapy: Chemotherapy Resistance Testing before Therapy
 Individualized Cancer Therapy: Chemotherapy Resistance Testing before Therapy 1 st st International Oncological Conference Wrocław, October 6 th, 2012 Dr. Frank Kischkel Individualized Cancer Therapy:
Individualized Cancer Therapy: Chemotherapy Resistance Testing before Therapy 1 st st International Oncological Conference Wrocław, October 6 th, 2012 Dr. Frank Kischkel Individualized Cancer Therapy:
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1. Int6 gene silencing efficiency. (A) Western Blot analysis of Int6 expression at different times after sirna transfection. Int6 expression is strongly silenced in Int6
Supplementary Information Figure S1. Int6 gene silencing efficiency. (A) Western Blot analysis of Int6 expression at different times after sirna transfection. Int6 expression is strongly silenced in Int6
State of the Art in Tumor Profiling
 State of the Art in Tumor Profiling Dora Dias-Santagata, PhD, FACMG ddiassantagata@partners.org Translational Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Disclosures
State of the Art in Tumor Profiling Dora Dias-Santagata, PhD, FACMG ddiassantagata@partners.org Translational Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Disclosures
Supplementary Data Cyclophilin B Supports Myc and Mutant p53 Dependent Survival of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells
 Supplementary Data Cyclophilin B Supports Myc and Mutant p53 Dependent Survival of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells Jae Won Choi, Mark A. Schroeder, Jann N. Sarkaria, and Richard J. Bram 1 Figure S1. Pharmacological
Supplementary Data Cyclophilin B Supports Myc and Mutant p53 Dependent Survival of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells Jae Won Choi, Mark A. Schroeder, Jann N. Sarkaria, and Richard J. Bram 1 Figure S1. Pharmacological
Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer
 S1 of S6 Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer Shang-Gin Wu, Tzu-Hua Chang, Meng-Feng Tsai, Yi-Nan Liu, Chia-Lang
S1 of S6 Supplementary Methods: IGFBP7 Drives Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Lung Cancer Shang-Gin Wu, Tzu-Hua Chang, Meng-Feng Tsai, Yi-Nan Liu, Chia-Lang
Daniele Santini University Campus Bio-Medico Rome, Italy
 Daniele Santini University Campus Bio-Medico Rome, Italy Anti EGFR therapy and colorectal cancer Cetuximab or Panitumumab Adapted from Ciardiello F. and Tortora G. NEJM 2008;358:1160-74 Who will benefit
Daniele Santini University Campus Bio-Medico Rome, Italy Anti EGFR therapy and colorectal cancer Cetuximab or Panitumumab Adapted from Ciardiello F. and Tortora G. NEJM 2008;358:1160-74 Who will benefit
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples
 A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. IDH1 and IDH2 mutation site sequences on WHO grade III
 Supplementary Materials: Supplementary Figure 1. IDH1 and IDH2 mutation site sequences on WHO grade III patient samples. Genomic DNA samples extracted from punch biopsies from either FFPE or frozen tumor
Supplementary Materials: Supplementary Figure 1. IDH1 and IDH2 mutation site sequences on WHO grade III patient samples. Genomic DNA samples extracted from punch biopsies from either FFPE or frozen tumor
The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine
 The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine Ignacio I. Wistuba, M.D. Jay and Lori Eissenberg Professor in Lung Cancer Director of the Thoracic Molecular Pathology Lab Departments
The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine Ignacio I. Wistuba, M.D. Jay and Lori Eissenberg Professor in Lung Cancer Director of the Thoracic Molecular Pathology Lab Departments
Comprehensive Genomic Profiling, in record time. Accurate. Clinically Proven. Fast.
 Comprehensive Genomic Profiling, in record time Accurate. ly Proven. Fast. PCDx advantages Comprehensive genomic profiling, in record time PCDx Comprehensive Genomic Profiling (CGP) provides precise information
Comprehensive Genomic Profiling, in record time Accurate. ly Proven. Fast. PCDx advantages Comprehensive genomic profiling, in record time PCDx Comprehensive Genomic Profiling (CGP) provides precise information
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Conflict of Interest. The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine. NSCLC Landscape Change
 Slide 1 The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine Ignacio I. Wistuba, M.D. Jay and Lori Eissenberg Professor in Lung Cancer Director of the Thoracic Molecular Pathology Lab Departments
Slide 1 The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine Ignacio I. Wistuba, M.D. Jay and Lori Eissenberg Professor in Lung Cancer Director of the Thoracic Molecular Pathology Lab Departments
Solange Peters, MD-PhD Cancer Center, Lausanne Switzerland EGFR AND NSCLC
 Solange Peters, MD-PhD Cancer Center, Lausanne Switzerland EGFR AND NSCLC Interactive Clinical Case History Maria José 1963 Since end 2010, progressive dyspnea Attends Emergency Room 02.01.2011 after 3
Solange Peters, MD-PhD Cancer Center, Lausanne Switzerland EGFR AND NSCLC Interactive Clinical Case History Maria José 1963 Since end 2010, progressive dyspnea Attends Emergency Room 02.01.2011 after 3
The Pathology of Neoplasia Part II
 The Pathology of Neoplasia Part II February 2018 PAUL BOGNER, MD A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R O F O N C O L O G Y P A T H O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O L O G Y Clinical goals of cancer pathology
The Pathology of Neoplasia Part II February 2018 PAUL BOGNER, MD A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R O F O N C O L O G Y P A T H O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O L O G Y Clinical goals of cancer pathology
Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma
 Supplementary information for: Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma Rintaro Hashizume 1, Noemi Andor 2, Yuichiro Ihara 2, Robin Lerner 2, Haiyun
Supplementary information for: Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma Rintaro Hashizume 1, Noemi Andor 2, Yuichiro Ihara 2, Robin Lerner 2, Haiyun
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
BCR-ABL uncouples canonical JAK2-STAT5 signaling in chronic myeloid
 Supplementary Results BCR-ABL uncouples canonical JAK2-STAT5 signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia Oliver Hantschel*, Wolfgang Warsch*, Eva Eckelhart*, Ines Kaupe, Florian Grebien, Kay-Uwe Wagner, Giulio
Supplementary Results BCR-ABL uncouples canonical JAK2-STAT5 signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia Oliver Hantschel*, Wolfgang Warsch*, Eva Eckelhart*, Ines Kaupe, Florian Grebien, Kay-Uwe Wagner, Giulio
Figure S1 A. MGH092-1 (Biopsy) MGH092-1B (Cell Line)
 a/f3 G1del ell viability (% control) a/f3 G1R ell viability (% control) Figure S1 MGH9-1 (iopsy) MGH9-1 (ell Line) G1del LK G1del (c.33_35delggg) Reference MGH9-1 D 5 rizotinib I 5 = 5. nm eritinb I 5
a/f3 G1del ell viability (% control) a/f3 G1R ell viability (% control) Figure S1 MGH9-1 (iopsy) MGH9-1 (ell Line) G1del LK G1del (c.33_35delggg) Reference MGH9-1 D 5 rizotinib I 5 = 5. nm eritinb I 5
Multi-Center Phase III Clinical Trials and NCI Cooperative Groups. Dr. John E. Niederhuber Director, National Cancer Institute July 1, 2008
 Multi-Center Phase III Clinical Trials and NCI Cooperative Groups Dr. John E. Niederhuber Director, National Cancer Institute July 1, 2008 Phase II Trial of Paclitaxel by 96-Hour Continuous Infusion Plus
Multi-Center Phase III Clinical Trials and NCI Cooperative Groups Dr. John E. Niederhuber Director, National Cancer Institute July 1, 2008 Phase II Trial of Paclitaxel by 96-Hour Continuous Infusion Plus
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Montagut C, Argilés G, Ciardiello F, et al. Efficacy of Sym4 in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to anti-egfr therapy and molecularly selected
Supplementary Online Content Montagut C, Argilés G, Ciardiello F, et al. Efficacy of Sym4 in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to anti-egfr therapy and molecularly selected
Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each mutated gene and the panel of 125 cancer-driving genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each mutated gene and the panel of 125 cancer-driving genes
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma. Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
 Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays
 SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays Detect all cancer-relevant variants in a single SureSelect assay SNV Indel TL SNV Indel TL Single DNA input Single AIO assay Single data analysis
SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays Detect all cancer-relevant variants in a single SureSelect assay SNV Indel TL SNV Indel TL Single DNA input Single AIO assay Single data analysis
Liquid biopsy in lung cancer: The EGFR paradigm
 Liquid biopsy in lung cancer: The EGFR paradigm Lynette M. Sholl, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana Farber Cancer Institute Department of Pathology Boston, MA Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
Liquid biopsy in lung cancer: The EGFR paradigm Lynette M. Sholl, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana Farber Cancer Institute Department of Pathology Boston, MA Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
Distinguishing Second Primary Cancers From Metastases: Statistical Challenges in Testing Clonal Relatedness of Tumors
 Distinguishing Second Primary Cancers From Metastases: Statistical Challenges in Testing Clonal Relatedness of Tumors Colin Begg Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer
Distinguishing Second Primary Cancers From Metastases: Statistical Challenges in Testing Clonal Relatedness of Tumors Colin Begg Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Vertical Magnetic Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells and Somatic Genomic-Alteration Analysis in Lung Cancer Patients
 Vertical Magnetic Separation of Circulating Cells and Somatic Genomic-Alteration Analysis in Lung Cancer Patients Chang Eun Yoo 1,2#, Jong-Myeon Park 3#, Hui-Sung Moon 1,2, Je-Gun Joung 2, Dae-Soon Son
Vertical Magnetic Separation of Circulating Cells and Somatic Genomic-Alteration Analysis in Lung Cancer Patients Chang Eun Yoo 1,2#, Jong-Myeon Park 3#, Hui-Sung Moon 1,2, Je-Gun Joung 2, Dae-Soon Son
The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine
 The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine Ignacio I. Wistuba, M.D. Jay and Lori Eissenberg Professor in Lung Cancer Director of the Thoracic Molecular Pathology Lab Departments
The Role of Pathology/Molecular Diagnostics in Personalized Medicine Ignacio I. Wistuba, M.D. Jay and Lori Eissenberg Professor in Lung Cancer Director of the Thoracic Molecular Pathology Lab Departments
EGFR ctdna Testing. Andrew Wallace 21/09/2015 Genomic Diagnostics Laboratory St. Mary s Hospital, Manchester
 EGFR ctdna Testing Andrew Wallace 21/09/2015 Genomic Diagnostics Laboratory St. Mary s Hospital, Manchester ctdna & EGFR Testing in NSCLC EGFR ctdna testing Non-invasive - patients too sick/biopsy or cytology
EGFR ctdna Testing Andrew Wallace 21/09/2015 Genomic Diagnostics Laboratory St. Mary s Hospital, Manchester ctdna & EGFR Testing in NSCLC EGFR ctdna testing Non-invasive - patients too sick/biopsy or cytology
Joachim Aerts Erasmus MC Rotterdam, Netherlands. Drawing the map: molecular characterization of NSCLC
 Joachim Aerts Erasmus MC Rotterdam, Netherlands Drawing the map: molecular characterization of NSCLC Disclosures Honoraria for advisory board/consultancy/speakers fee Eli Lilly Roche Boehringer Ingelheim
Joachim Aerts Erasmus MC Rotterdam, Netherlands Drawing the map: molecular characterization of NSCLC Disclosures Honoraria for advisory board/consultancy/speakers fee Eli Lilly Roche Boehringer Ingelheim
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Inhibidores de EGFR Noemi Reguart, MD, PhD Hospital Clínic Barcelona IDIPAPS
 Inhibidores de EGFR Noemi Reguart, MD, PhD Hospital Clínic Barcelona IDIPAPS Driver Mutations to Classify Lung Cancer Unknown 36% KRAS 25% EGFR 15% ALK 4% HER2 2% Double Mut 2% BRAF 2% PIK3CA
Inhibidores de EGFR Noemi Reguart, MD, PhD Hospital Clínic Barcelona IDIPAPS Driver Mutations to Classify Lung Cancer Unknown 36% KRAS 25% EGFR 15% ALK 4% HER2 2% Double Mut 2% BRAF 2% PIK3CA
Targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: a focus on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations
 Review Article Page 1 of 5 Targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: a focus on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations Gérard A. Milano Oncopharmacology Unit, EA 3836 UNS, Centre Antoine Lacassagne,
Review Article Page 1 of 5 Targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: a focus on epidermal growth factor receptor mutations Gérard A. Milano Oncopharmacology Unit, EA 3836 UNS, Centre Antoine Lacassagne,
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
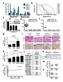 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Targeted therapies for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Tom Stinchcombe Duke Cancer Insitute
 Targeted therapies for advanced non-small cell lung cancer Tom Stinchcombe Duke Cancer Insitute Topics ALK rearranged NSCLC ROS1 rearranged NSCLC EGFR mutation: exon 19/exon 21 L858R and uncommon mutations
Targeted therapies for advanced non-small cell lung cancer Tom Stinchcombe Duke Cancer Insitute Topics ALK rearranged NSCLC ROS1 rearranged NSCLC EGFR mutation: exon 19/exon 21 L858R and uncommon mutations
Utility of liquid biopsies EQA Program Naples, IT Sidney A. Scudder, MD Director, Clinical Science 13 May, 2017
 Utility of liquid biopsies EQA Program Naples, IT Sidney A. Scudder, MD Director, Clinical Science 13 May, 2017 picture placeholder Agenda cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2 Ring Trial SQI Semi Quantitative Index
Utility of liquid biopsies EQA Program Naples, IT Sidney A. Scudder, MD Director, Clinical Science 13 May, 2017 picture placeholder Agenda cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2 Ring Trial SQI Semi Quantitative Index
