VEGF-C ShRNA Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Growth and Lymphangiogenesis in an Orthotopic Fluorescent Nude Mouse Model
|
|
|
- Jemima Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VEGF-C ShRNA Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Growth and Lymphangiogenesis in an Orthotopic Fluorescent Nude Mouse Model YUZHEN SHI 1,2, MINGMIN TONG 3, YUEFEI WU 1, ZHIJIAN YANG 4, ROBERT M. HOFFMAN 7,8, YONG ZHANG 7, YING TIAN 5, MINGMEI QI 6, YANFEI LIN 1, YONGKANG LIU 1, LINGLING DAI 1, YU SUN 4 and ZHONGQIU WANG 1 1 Department of Radiology, East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai , P.R. China; 2 Department of Medical Imaging, Huai an First People s Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Huai an, Jiangsu, P. R. China; 3 Department of Radiology, Suzhou Municipal Hospital (East Area), Suzhou, Jiangsu, P. R. China; 4 Origin Biosciences Inc., Nanjing, Jiangsu, P.R. China; 5 Department of Medical Imaging, Jinling Hospital, Clinical School of Medical College, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, P. R. China; 6 Molecular Medicine and Cancer Research Centre, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, P. R. China; 7 AntiCancer, Inc., San Diego, CA, U.S.A.; 8 Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego, San Diego, CA, U.S.A. Abstract. The aim of this study was to assess the inhibitory efficacy of short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) targeting vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) in an orthotopic pancreatic cancer mouse model. BxPC-3 human pancreatic cancer cells expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) were orthotopically implanted onto the pancreas of nude mice. All mice were randomly divided into four groups when the average tumor size had reached 100 mm 3 and were treated with either vehicle or gemcitabine at 150 mg/kg; or intravenous VEGF-C ShRNA at 150 mg/kg; or intratumoral VEGF-C ShRNA at 150 μg/kg. In vivo fluorescence imaging was performed to monitor tumor growth and metastasis during the study. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were performed to determine the mrna and protein level of VEGF-C in tumor tissues. Lymphatic vessel marker D2-40, blood vessel marker CD31 and proliferation marker Ki67 expression of the tumor tissues were analyzed by immunohistochemistry staining. Intravenous and intratumoral VEGF-C ShRNA treatment significantly inhibited tumor Correspondence to: Zhongqiu Wang, MD, Ph.D., Department of Radiology, East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine. 150 Jimo Road, Shanghai , P.R. China. Tel: , zhq2001us@yahoo.com Key Words: VEGF-C, ShRNA, pancreatic cancer, nude mice, orthotopic, GFP. growth, downregulated the expression of VEGF-C mrna, reduced tumor microlymphatic vessel density (MLVD), and inhibited cancer cell proliferation. Gemcitabine, as the standard treatment for pancreatic cancer, demonstrated a stronger inhibitory effect on tumor growth, with less inhibition of MLVD and more inhibition of microvessel density (MVD) and proliferation than VEGF-C ShRNA. These results indicate that different mechanisms are associated with the efficacy of gemcitabine and VEGF-C ShRNA. Pancreatic cancer is a highly treatment-resistant disease. Realistic orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic cancer have been developed (1, 2) for this disease. These models are enhanced by fluorescent protein expression to image the disease in real time and to visualize the efficacy of therapeutics, including gemcitabine, first-line therapy for this disease (3, 4). Treatment of the orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer with metronomic gemcitabine and sunitinib significantly prolonged median overall survival compared with control and with either regimen alone (5). However, improved therapeutics for pancreatic cancer are still urgently needed. Lymph node metastasis is the most common metastatic pathway of pancreatic cancer and often occurs earlier than hematogenous metastasis (6, 7). Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) expression stimulates lymph node metastasis in pancreatic cancer (8-10). Interfering with the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling pathway suppresses lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastases (11-13). Blocking VEGF- C inhibits tumor growth and metastasis (14, 15) /2013 $
2 Short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) expression vector systems (16-18) induce targeted gene silencing in mammalian cells. Lentivirus vectors encoding ShRNAs are capable of efficient transfection into human cells, including non-dividing cells, resulting in long-term and stable expression of the ShRNAs (19). In this study, we examined the antitumor and antimetastasis effects of a lentivirus vector encoding VEGF-C ShRNA in an orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP). In vivo fluorescence imaging was used to visualize and quantify tumor growth and metastasis development, thereby allowing real-time efficacy evaluation. Materials and Methods Cell culture. The human pancreatic cancer cell line BxPC-3 GFP was obtained from AntiCancer, Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA). The cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 (GIBCO Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) at 37 C in 5% CO 2 in saturated air. All media were supplemented with penicillin/streptomycin (GIBCO/BRL, Grand Island, NY, USA) Animal care. BALB/C male nu/nu nude mice, aged 4-6 weeks and weighing g, were purchased from the Beijing Kelihua laboratory animal center (Beijing, PRC). The mice were maintained in a HEPA-filtered environment at C and with 50-60% humidity. The animals were fed an autoclaved laboratory rodent diet. Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Committee of Origin Biosciences Inc. (Nanjing, PRC). Surgical orthotopic implantation (SOI). BxPC-3-GFP tumor stock was established by subcutaneously (s.c.) by injecting BxPC-3-GFP cells ( ) in the flank of nude mice. Pancreatic tumors grown s.c. in nude mice were harvested at the exponential growth phase and resected under aseptic conditions. Strong GFP expression of the BxPC-3-GFP tumor tissue was confirmed by fluorescence microscopy. Necrotic tissues were removed and viable tissues were cut with scissors and minced into 1-mm 3 pieces. For SOI, the animals were anesthetized by injection of 0.02 ml of solution of 50% ketamine, 38% xylazine, and 12% acepromazine maleate. The abdomen was sterilized using iodine solution and alcohol and an incision was made through the left upper abdominal pararectal line and peritoneum. The pancreas was exposed, and the capsule of the pancreatic body and tail was stripped. Then one piece of tumor fragment was transplanted to the pancreatic tail with 8-0 surgical sutures and this segment of the pancreas was fixed on the anterior peritoneum. The pancreas was then returned to the peritoneal cavity and the abdomen was closed with sterile 5-0 surgical sutures (1-3). All surgical procedures and animal manipulations were conducted under HEPA-filtered laminar-flow hoods with a 8 surgical microscope (YZ20P5; Alltion (Wuzhou) Co. Ltd., Wuzhou, Guangxi, PRC). VEGF-C ShRNA. Lentiviral vector plasmids encoding VEGF-C ShRNA were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). VEGF-C ShRNA plasmid is a pool of three targetspecific lentiviral vector plasmids each encoding nt (plus hairpin) ShRNAs designed to knock-down gene expression. Each plasmid contains a puromycin resistance gene for the selection of cells stably expressing ShRNA. Drug treatment. Gemcitabine (Jiangsu Hansoh Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Jiangsu, PRC) was reconstituted in saline and administered intraperitoneally. VEGF-C ShRNA plasmid was diluted in saline and administered by intravenous or intratumoral injection. Mice were randomly divided into four groups of eight mice per group for treatment when the average tumor size had reached 100 mm 3 at day 16 after orthotopic implantation. Group 1 served as the vehicle control and received saline in the same volume of drug as the treated animals. Group 2 was treated weekly i.p. with gemcitabine at 150 mg/kg. Group 3 received intravenous (i.v.) VEGF-C ShRNA treatment every three days at 150 μg/kg. Group 4 received intratumoral (i.t.) VEGF-C ShRNA treatment every three days at 150 μg/kg. The treatment duration was two weeks. Clinical signs and body weights for each tumor-bearing mouse were observed daily or measured twice per week, respectively, during the course of the treatment. In vivo fluorescence imaging. Real-time, quantitative measurements of tumor volume were carried out twice per week by whole-body fluorescence imaging during the study. Tumor volume was calculated using the formula (L W 2 ) 0.5, where W and L represent the perpendicular minor and major dimensions of the tumor, respectively. At the end of the study, all mice were sacrificed and open fluorescence imaging was performed (3). Primary tumors and all metastases to distant organs, including the mesentery lymph nodes, lung, liver, abdominal cavity and thoracic cavity were imaged. The primary tumor was removed and weighed after open-body imaging. A fluorescence stereo microscope model (MZ650; Nanjing Optic Instrument Inc., Nanjing, PRC) equipped with D510 long-pass and HQ600/50 band-pass emission filters (Chroma Technology, Brattleboro, VT) and a cooled color charge-coupled device camera (Qimaging, Surrey, BC, Canada) was used. Selective excitation of GFP was produced through an illuminator equipped with HQ470/40 and HQ540/40 excitation band-pass filters (Chroma Technology, Brattleboro, VT). Images were processed and analyzed with the use of IMAGE PRO PLUS 6.0 software (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD). Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Frozen tumor tissues were homogenized in a pre-cooled tissue homogenizer. Total RNA was extracted from the homogenate using a Trizol kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and reverse-transcribed to cdna using a First-Strand cdna synthesis kit (Fermentas, Vilnius, Lithuania) according to the manufacturer s instructions. RT-qPCR was performed using SYBR Green Real-Time PCR Master Mix (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan). The PCR primers were as follows: VEGF-C, sense: 5 -AGCACGAGCTACCTCAGCAAGA-3, antisense: 5 -GGGAAC GTCTAATAATGGAATG-3. β-action, sense: 5 -GCAGAAGGAG ATCACTGCCCT-3, antisense: 5 -GCTGATCCACATCTGCTGG AA-3. Reactions were analyzed on a DA7600 real-time PCR machine (Zhongshan Bio-Tech Co., Ltd., Zhongshan, PRC) using the following cycle conditions: 5 minutes pre-denaturation at 95 C, followed by 40 cycles of 15 s denaturation at 95 C, 20 s annealing at 60 C and 40 s extension at 72 C. Results were normalized against β- action mrna expression. 410
3 Shi et al: VEGF-C ShRNA Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Figure 1. Longitudinal in vivo whole-body fluorescence imaging of tumor progression over time in the mice treated with vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF- C) short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) and gemcitabine in the orthotopic BxPC-3-GFP pancreatic cancer mouse model. Tumor-bearing animals were treated either with VEGF-C ShRNA or gemcitabine when orthotopic tumors had reached 100 mm 3 as described in the Materials and Methods. Whole-body fluorescence imaging was performed at day 16, day 25 and day 30 after orthotopic implantation, as described in the Materials and Methods. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). VEGF-C production in the tumors was measured in tumor homogenates by ELISA using a human VEGF-C ELISA kit (Invitrogen). ELISA was performed according to the manufacturer s instruction. Briefly, the flat-bottom 96-well microtiter plates were coated with antibodies to VEGF-C and incubated overnight at 4 C, then blocked with bovine serum albumin buffer at 37 C for 3 h. The blank wells were then loaded with diluted sample (supernatant of tumor homogenates) or standard, and the remaining wells were loaded with sample or standard at different concentrations (100 μl/well) and incubated at 37 C for 2 h. The plates were washed five times and incubated with biotinylated antibody to VEGF-C at 37 C for 1 h. After washing five times, the plates were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-labeled avidin at 37 C for 30 min. After washing again five times, the plates were incubated with substrate tetramethyl benzidine (100 μl/well) at 37 C for 30 min. The color reaction was stopped by addition of H 2 SO 4 (2 mol/l, 50 μl/well), and the optical density was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (ELx800uv; Bio-Tec Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA). A standard curve was constructed and the protein level of VEGF-C was calculated on the basis of the standard curve. Immunohistochemistry. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor tissue sections (4 μm) were deparaffinized in xylene, rehydrated in graded ethanol solutions, and rehydrated in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; ph 7.2). To enhance antigen retrieval, sections were microwaved for 5 min. Each slice was treated with two drops of 3% H 2 O 2 -methanol solution for 15 min at 37 C and washed with PBS. Monoclonal antibodies to D2-40, CD31 and Ki67 (Biocare Medical Co., Concord, CA, USA) were used as a lymphatic vessel marker, a blood vessel marker, and a proliferating cell marker, respectively. Tissue sections were incubated overnight at 4 C with diluted primary antibodies (1:100 D2-40; 1:100 CD31; and 1:50 Ki67). After washing in PBS, the slices were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody (1:200, Maixin Bio-Tech Co., Ltd, Fuzhou, PRC) for 30 min at room temperature. After color development using diaminobenzidine (Maixin 411
4 Figure 2. Tumor growth curves after treatment with vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) or gemcitabine in the orthotopic BxPC-3-GFP pancreatic cancer mouse model. Whole-body fluorescence imaging was performed and tumor volumes were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Data are the means ± SD from eight mice in each group at each time point. Figure 3. Efficacy of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) and gemcitabine on tumor weights in the orthotopic BxPC-3-GFP pancreatic cancer mouse model. Primary tumors were excised and tumor weights were determined for each animal at autopsy. Data are the means ± SD from eight mice in each group. Bio-Tech Co., Ltd), the slices were counterstained in hematoxylin and mounted with a neutral resin medium. The microlymphatic vessel density (MLVD) and microvessel density (MVD) were quantified as described previously (20, 21). Briefly, a scanning slice was first examined at 100 magnification for a hot spot representing the area of the highest vessel density. Then the field was switched to 400 magnification for clear depiction and better counting. For each slice, the MLVD or MVD was calculated as the average of vessels in four fields. Proliferation was calculated as the average ratio of Ki67-positive cells to 100 total cells in four fields (at 400 magnification). 412
5 Shi et al: VEGF-C ShRNA Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Figure 4. Representative open-body images of mice with orthotopic BxPC-3-GFP pancreatic cancer from each group at autopsy. A: Saline control. B: Gemcitabine treatment. C: vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) i.v. treatment. D: VEGF-C ShRNA i.t. treatment. Arrow heads, primary tumor; arrows, abdominal lymph node metastases. Statistical analysis. Data are expressed as means ± SD, and were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), using SPSS software version 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA), where p<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Results Effect of VEGF-C ShRNA on the growth of orthotopic pancreatic tumors. Tumor growth was monitored and measured by whole-body fluorescence imaging during the course of the treatment (Figure 1). Gemcitabine (i.p.)-, VEGF-C ShRNA (i.v.)-, and VEGF-C ShRNA (i.t.)- treated mice started showing tumor-growth inhibition beginning from day 20 after orthotopic implantation. The tumor size was significantly reduced in all three treated groups compared to control group (p<0.01) at the end of the study (Figure 2). At autopsy, tumors were excised and tumor weights were determined for each animal. The mean tumor weights for each group are presented in Figure 3. Tumor weights were significantly reduced by gemcitabine (i.p.), VEGF-C ShRNA (i.v.), and VEGF-C ShRNA (i.t.) as compared to the control (p<0.01). The tumor-bearing animals treated with gemcitabine (i.p.), VEGF-C ShRNA (i.v.) and VEGF-C ShRNA (i.t.) demonstrated a 67.1% (1.7 ± 0.3; p<0.01); a 35.1% (3.3 ± 0.8; p<0.01); and a 40.7% (3.0 ± 0.5; p<0.01) decrease, respectively, in tumor weight as compared with control animals. Efficacy of VEGF-C ShRNA on lymph node metastasis. At the end of the study, all animals were sacrificed and openbody imaging was conducted for metastasis evaluation. The metastasis incidence, especially for lymph node metastasis, was determined and analyzed. Gemcitabine (i.p.), VEGF-C ShRNA (i.v.), and VEGF-C ShRNA (i.t.) groups showed a reduced incidence of metastasis compared with the control group. However, no statistically-significant difference was found between three treated groups and the control group (p>0.05) (Figure 4). 413
6 Figure 5. Efficacy of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) and gemcitabine on the expression of VEGF-C in the BxPC-3-GFP pancreatic orthotopic tumor mouse model. A: Relative VEGF-C mrna levels were determined by real- time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis. Data are the means ± SD of triplicate determinations from four tumors per group. *p<0.01 when compared with control; # p<0.01 when compared with gemcitabine; B: VEGF-C protein content was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis. Data are the means ± SD from four tumors per group. *p>0.05 when compared with control. Effect of VEGF-C ShRNA on VEGF-C production in tumors. RT-qPCR and ELISA were performed to determine the mrna and protein level of VEGF-C in tumor tissues from all three treated and control groups. VEGF-C ShRNA and gemcitabine treatment significantly down-regulated the expression of VEGF-C mrna compared with the control (p<0.01). Both VEGF-C ShRNA (i.v.) and VEGF-C ShRNA (i.t.) groups had significantly lower levels of VEGF-C mrna expression than the gemcitabine group (p<0.01) (Figure 5A). A lower level of VEGF-C protein was found in VEGF-C ShRNA and gemcitabine-treated animals, although statistical difference was not achieved (Figure 5B). Effects of VEGF-C ShRNA on expression of lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis and a proliferation marker. Expression of lymphatic vessel (MLVD) marker D2-40, blood vessel (MVD) marker CD31, and a proliferation marker Ki67 in the tumor tissues was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Significant reduction in the MLVD was found in the gemcitabine- and VEGF-C ShRNA-treated groups compared with the control group (p<0.01). MLVD was significantly more reduced by VEGF-C ShRNA than by gemcitabine (p<0.01) (Figure 6). No significant difference of MVD was found between the VEGF-C ShRNA-treated and untreated control groups (p>0.05), although a significant reduction in MVD was 414
7 Shi et al: VEGF-C ShRNA Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Figure 6. Efficacy of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) and gemcitabine on lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis and proliferation in the orthotopic BxPC-3-GFP pancreatic cancer mouse model. A: Representative immunostaining for D2-40, CD31, and Ki-67 in BxPC-3 tumors that were treated with saline control, gemcitabine, i.v. VEGF- C ShRNA or i.t.vegf-c ShRNA, respectively. Original magnification, 400. B: Quantitative morphometry for D2-40, CD31 and Ki-67 immunoreactivity from the tumors shown in (A). Data are the means ± SD from four tumors per group, with four fields analyzed for each tumor. *p<0.05 when compared with controls; # p<0.05 when compared with gemcitabine; & P>0.05 when compared with control. 415
8 Figure 7. Toxicity of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) short hairpin RNA (ShRNA) and gemcitabine on mouse body weight in the orthotopic BxPC-3-GFP pancreatic cancer mouse model. Data are the means ± SD from eight mice in each group at each time point. observed in the gemcitabine group as compared with the control group (p<0.01) (Figure 6). Ki67 expression was significantly inhibited by VEGF-C ShRNA and gemcitabine as compared with the untreated control (p<0.01). Gemcitabine treatment resulted in a more significant reduction of Ki67 expression level than did VEGF-C ShRNA treatment (p<0.01) (Figure 6). Body weight and toxicity. The body weights of mice were measured to evaluate the toxic side-effects of all treatments. The body weights of VEGF-C ShRNA-treated groups were not significantly different from the untreated control group (p>0.05). However, a significant decline on body weight was noticed in the gemcitabine-treated group as compared with the untreated control (p<0.05) and the VEGF-C ShRNAtreated groups (p<0.05), beginning from day 20 after orthotopic implantation (Figure 7). No other physical or behavioral signs that indicated adverse effects due to the treatments were observed in any group. Discussion In the present study, we demonstrated that i.v. and i.t. VEGF- C ShRNA treatment significantly inhibited growth of the human pancreatic BxPC-3 tumor in an orthotopic mouse tumor model. VEGF-C ShRNA treatment significantly downregulated the expression of VEGF-C mrna, reduced tumor MLVD and inhibited tumor cell proliferation. However, tumor MVD was not significantly affected by VEGF-C ShRNA. The result indicates that inhibition of VEGF-C expression and lymphangiogenesis contributes to the anticancer efficacy of VEGF-C ShRNA. To investigate if the inhibitory effects of VEGF-C ShRNA on VEGF-C expression and lymphangiogenesis may result in reduction of regional lymph node metastases, metastasis incidence was evaluated in this study with the orthotopic pancreatic cancer mouse model. The VEGF-C ShRNA-treated groups showed a decreased incidence of metastasis compared with the control group, however, the difference was not significant. This may be attributable to the fact that lymph node metastasis is regulated by factors beside VEGF-C (13, 22). Gemcitabine, the treatment standard for pancreatic cancer, was selected for comparison and showed more inhibitory efficacy on tumor growth than did VEGF-C ShRNA treatment. However, gemcitabine induced less inhibition of MLVD and more inhibition of MVD and proliferation than did VEGF-C ShRNA, indicating a different mechanism was associated with efficacy of gemcitabine and VEGF-C ShRNA. GFP- and red fluorescent protein-expressing orthotopic pancreatic tumor models have been shown to be useful for the evaluation of novel treatment strategies for pancreatic cancer (3-5, 23-25). Such strategies are needed to combat this highly lethal tumor. RNA interference as a new emerging therapy is still under development. Treatment conditions need to be further investigated and optimized to increase the anticancer therapeutic potential of this modality. 416
9 Shi et al: VEGF-C ShRNA Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Conflicts of Interest None of the Authors have a conflict of interest regarding this study. Acknowledgements This study was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation in China (numbers , and ). References 1 Fu X, Guadagni F and Hoffman RM: A metastatic nude-mouse model of human pancreatic cancer constructed orthotopically with histologically intact patient specimens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: , Furukawa T, Kubota T, Watanabe M, Kitajima M and Hoffman RM: A novel patient-like treatment model of human pancreatic cancer constructed using orthotopic transplantation of histologically intact human tumor tissue in nude mice. Cancer Res 53: , Bouvet M, Wang J, Nardin SR, Nassirpour R, Yang M, Baranov E, Jiang P, Moossa AR and Hoffman RM: Real-time optical imaging of primary tumor growth and multiple metastatic events in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic model. Cancer Res 62: , Katz MH, Takimoto S, Spivack D, Moossa AR, Hoffman RM and Bouvet M: A novel red fluorescent protein orthotopic pancreatic cancer model for the preclinical evaluation of chemotherapeutics. J Surg Res 113: , Tran Cao HS, Bouvet M, Kaushal S, Keleman A, Romney E, Kim G, Fruehauf J, Imagawa DK, Hoffman RM and Katz MH: Metronomic gemcitabine in combination with sunitinib inhibits multisite metastasis and increases survival in an orthotopic model of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 9: , Achen MG, Mann GB and Stacker SA: Targeting lymphangiogenesis to prevent tumour metastasis. Br J Cancer 94: , Schneider M, Buchler P, Giese N, Giese T, Wilting J, Buchler MW and Friess H: Role of lymphangiogenesis and lymphangiogenic factors during pancreatic cancer progression and lymphatic spread. Int J Oncol 28: , Huang C, Huang R, Chang W, Jiang T, Huang K, Cao J, Sun X and Qiu Z: The expression and clinical significance of pstat3, VEGF and VEGF-C in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Neoplasma 59: 52-61, Li K, Li MJ, He T, Zheng Z, Zheng XL, Qu BH, Wang Y, Duan X and Zheng YJ: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C in pancreatic cancer and its effect upon lymph node metastasis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 89: , Ochi N, Matsuo Y, Sawai H, Yasuda A, Takahashi H, Sato M, Funahashi H, Okada Y and Manabe T: Vascular endothelial growth factor-c secreted by pancreatic cancer cell line promotes lymphatic endothelial cell migration in an in vitro model of tumor lymphangiogenesis. Pancreas 34: , He Y, Karpanen T and Alitalo K: Role of lymphangiogenic factors in tumor metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1654: 3-12, Chen Z, Varney ML, Backora MW, Cowan K, Solheim JC, Talmadge JE and Singh RK: Down-regulation of vascular endothelial cell growth factor-c expression using small interfering RNA vectors in mammary tumors inhibits tumor lymphangiogenesis and spontaneous metastasis and enhances survival. Cancer Res 65: , Roberts N, Kloos B, Cassella M, Podgrabinska S, Persaud K, Wu Y, Pytowski B and Skobe M: Inhibition of VEGFR-3 activation with the antagonistic antibody more potently suppresses lymph node and distant metastases than inactivation of VEGFR-2. Cancer Res 66: , Chaudary N, Milosevic M and Hill RP: Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR3) and vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) inhibits hypoxia-induced lymph node metastases in cervix cancer. Gynecol Oncol 123: , Karpanen T, Egeblad M, Karkkainen MJ, Kubo H, Yla-Herttuala S, Jaattela M and Alitalo K: Vascular endothelial growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and intralymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res 61: , Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R and Agami R: Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell 2: , Xia H, Mao Q, Paulson HL and Davidson BL: sirna-mediated gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 20: , Qin XF, An DS, Chen IS and Baltimore D: Inhibiting HIV-1 infection in human T-cells by lentiviral-mediated delivery of small interfering RNA against CCR5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: , Nishitsuji H, Ikeda T, Miyoshi H, Ohashi T, Kannagi M and Masuda T: Expression of small hairpin RNA by lentivirus-based vector confers efficient and stable gene-suppression of HIV-1 on human cells including primary non-dividing cells. Microbes Infect 6: 76-85, Weidner N: Intratumor microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol 147: 9-19, Li K, Tao J, Li T, Yu Z, Yang Z, Wu H, Xiong J and Wang C: Effect of antisense oligodeoxynucleotide of vascular endothelial growth factor C on lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 27: 51-53, He Y, Kozaki K, Karpanen T, Koshikawa K, Yla-Herttuala S, Takahashi T and Alitalo K: Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J Natl Cancer Inst 94: , Hoffman RM and Yang M: Subcellular imaging in the live mouse. Nat Protoc 1: , Hoffman RM and Yang M: Color-coded fluorescence imaging of tumor-host interactions. Nat Protoc 1: , Hoffman RM and Yang M: Whole-body imaging with fluorescent proteins. Nat Protoc 1: , Received November 6, 2012 Revised December 17, 2012 Accepted December 18,
Tumor-educated Macrophages Promote Tumor Growth and Peritoneal Metastasis in an Orthotopic Nude Mouse Model of Human Pancreatic Cancer
 Tumor-educated Macrophages Promote Tumor Growth and Peritoneal Metastasis in an Orthotopic Nude Mouse Model of Human Pancreatic Cancer RHIANA S. MENEN 1,2,3*, MOHAMED K. HASSANEIN 1,2*, MASASHI MOMIYAMA
Tumor-educated Macrophages Promote Tumor Growth and Peritoneal Metastasis in an Orthotopic Nude Mouse Model of Human Pancreatic Cancer RHIANA S. MENEN 1,2,3*, MOHAMED K. HASSANEIN 1,2*, MASASHI MOMIYAMA
Antimetastatic efficacy of adjuvant gemcitabine in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic model
 Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 379 384, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 379 Antimetastatic efficacy of adjuvant gemcitabine in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 379 384, 2001. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 379 Antimetastatic efficacy of adjuvant gemcitabine in a pancreatic cancer orthotopic
MELANOMA CANCER TEST
 MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 35: (2015)
 Complementarity of Variable-magnification and Spectralseparation Fluorescence Imaging Systems for Noninvasive Detection of Metastasis and Intravital Detection of Single Cancer Cells in Mouse Models YONG
Complementarity of Variable-magnification and Spectralseparation Fluorescence Imaging Systems for Noninvasive Detection of Metastasis and Intravital Detection of Single Cancer Cells in Mouse Models YONG
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Chronologically-specific metastatic targeting of human pancreatic tumors in orthotopic models
 Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 213 218, 2000. 2000 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 213 Chronologically-specific metastatic targeting of human pancreatic tumors in orthotopic
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis 18: 213 218, 2000. 2000 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 213 Chronologically-specific metastatic targeting of human pancreatic tumors in orthotopic
Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long. Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE
 92 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 11(2): 92 --96, 1999 ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE LI Peiyu z}~r~]~-,1 YUAN Mei 3~'J~,
92 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 11(2): 92 --96, 1999 ANTITUMOR EFFECT OF AN ANTI-ENDOTHELIAL CELL MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY BVE-1 ON SOLID TUMOR XENOGRAFT IN NUDE MICE LI Peiyu z}~r~]~-,1 YUAN Mei 3~'J~,
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
this mutation. However, VEM was not effective. The PDOX model thus helped identify
 /, Vol. 7, No. 44 Vemurafenib-resistant BRAF-V600E-mutated melanoma is regressed by MEK-targeting drug trametinib, but not cobimetinib in a patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) mouse model Kei Kawaguchi
/, Vol. 7, No. 44 Vemurafenib-resistant BRAF-V600E-mutated melanoma is regressed by MEK-targeting drug trametinib, but not cobimetinib in a patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) mouse model Kei Kawaguchi
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Simultaneous blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 induces synergistic. Short title: Synergistic antitumour effect by dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2
 carticle Simultaneous blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 induces synergistic antitumour effect in vivo 1 Short title: Synergistic antitumour effect by dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 S. Yasuda 1, M. Sho 1, I.
carticle Simultaneous blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 induces synergistic antitumour effect in vivo 1 Short title: Synergistic antitumour effect by dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGFR2 S. Yasuda 1, M. Sho 1, I.
Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3*
 A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS. (A) Workflow for tumor cell line derivation and orthotopic implantation.
 SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulating the expression of VEGF-C through MAPK signal pathways in breast cancer MCF-7 cell
 Zhang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2016) 14:51 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-0797-5 RESEARCH Open Access Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulating the expression of VEGF-C through MAPK signal
Zhang et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2016) 14:51 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-0797-5 RESEARCH Open Access Macrophage migration inhibitory factor regulating the expression of VEGF-C through MAPK signal
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
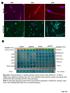 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
Supporting information. Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers
 Supporting information Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers Yulei Chang 1, Xiaodan Li 1,3, Li zhang 1,3, Lu Xia 1, Xiaomin
Supporting information Precise Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer via Subcellular Dynamic Tracing of Dual-loaded Upconversion Nanophotosensitizers Yulei Chang 1, Xiaodan Li 1,3, Li zhang 1,3, Lu Xia 1, Xiaomin
INTRODUCTION. Journal of Surgical Research 132, (2006) doi: /j.jss
 Journal of Surgical Research 132, 164 169 (2006) doi:10.1016/j.jss.2005.12.028 Dual-Color Imaging of Nascent Blood Vessels Vascularizing Pancreatic Cancer in an Orthotopic Model Demonstrates Antiangiogenesis
Journal of Surgical Research 132, 164 169 (2006) doi:10.1016/j.jss.2005.12.028 Dual-Color Imaging of Nascent Blood Vessels Vascularizing Pancreatic Cancer in an Orthotopic Model Demonstrates Antiangiogenesis
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
COVER STORIES. Hoffman, R.M. Visualization of GFP-expressing tumors and metastasis in vivo. BioTechniques 30, , 2001.
 COVER STORIES Hoffman, R.M. Three-dimensional histoculture: origins and applications in cancer research. Cancer Cells 3, 86-92, 1991. Hoffman, R.M. Visualization of GFP-expressing tumors and metastasis
COVER STORIES Hoffman, R.M. Three-dimensional histoculture: origins and applications in cancer research. Cancer Cells 3, 86-92, 1991. Hoffman, R.M. Visualization of GFP-expressing tumors and metastasis
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3726-3731 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0077355 Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma Minhua
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3726-3731 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0077355 Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma Minhua
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model
 CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
Page 1 09/10/2013 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0453 TITLE: The cytoplasm translocation of the androgen receptor cofactor p44 as a target for prostate cancer treatment PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Zhengxin Wang
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176
 human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors
 ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD. Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China. Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine
 GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis
 Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis
 The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 32: (2012)
 Inhibition of Metastasis of Circulating Human Prostate Cancer Cells in the Chick Embryo by an Extracellular Matrix Produced by Foreskin Fibroblasts in Culture RHIANA MENEN 1,4,5, EMMETT PINNEY 2, MOHAMED
Inhibition of Metastasis of Circulating Human Prostate Cancer Cells in the Chick Embryo by an Extracellular Matrix Produced by Foreskin Fibroblasts in Culture RHIANA MENEN 1,4,5, EMMETT PINNEY 2, MOHAMED
Hopkins University, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, USA) (27). Cells were maintained in DMEM
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell Culture HCT116 (TP53 +/+ and TP53 -/- ) cells were provided by Dr. Bert Vogelstein (Johns Hopkins University, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, USA) (27). Cells
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell Culture HCT116 (TP53 +/+ and TP53 -/- ) cells were provided by Dr. Bert Vogelstein (Johns Hopkins University, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, USA) (27). Cells
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel
 KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
For personal use only
 ASX and Media release 6 April 211 Circadian s Inhibits Tumour Growth in Models of Lung, Ovarian and Prostate Cancer Data demonstrates efficacy of with other therapeutic agents in mouse models of lung,
ASX and Media release 6 April 211 Circadian s Inhibits Tumour Growth in Models of Lung, Ovarian and Prostate Cancer Data demonstrates efficacy of with other therapeutic agents in mouse models of lung,
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002
![Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002](/thumbs/79/80181511.jpg) Data Sheet PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 DESCRIPTION: The PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit is designed for screening and profiling purposes. PCSK9 is known to function
Data Sheet PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 DESCRIPTION: The PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit is designed for screening and profiling purposes. PCSK9 is known to function
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA
 YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
Shangqiu Medical College, Shangqiu, China 2. Corresponding author: M.Z. Zhang
 Comparison of the expression of human equilibrative nucleotide transporter 1 (hent1) and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 (RRM1) genes in seven non-hodgkin lymphoma cell lines H.B. Zhao 1,2, X.F. Zhang
Comparison of the expression of human equilibrative nucleotide transporter 1 (hent1) and ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 (RRM1) genes in seven non-hodgkin lymphoma cell lines H.B. Zhao 1,2, X.F. Zhang
Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 2671-2676, 2015 Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer JIE CHEN *, JUNKAI WANG *, XINGANG CUI, YUSHAN LIU, LEI YIN, YAO LI,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 2671-2676, 2015 Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer JIE CHEN *, JUNKAI WANG *, XINGANG CUI, YUSHAN LIU, LEI YIN, YAO LI,
Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on
 Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Supplemental Methods Immunohistochemical Analyses Immunostaining was performed on tumor biopsy samples arranged in a tissue-microarray format or on prostatectomy sections obtained post-study. Briefly,
Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma. patients. Supplemental data. First author: Baojun Wang
 Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma patients Supplemental data First author: Baojun Wang Patients and tumor samples A total of 87 patients with
Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma patients Supplemental data First author: Baojun Wang Patients and tumor samples A total of 87 patients with
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Molecular Imaging for Cancer Visualization
 Molecular Imaging for Cancer Visualization American College of Surgeons Surgical Simulation Summit Chicago, IL March 16-17, 2018 Michael Bouvet, MD Professor of Surgery University of California San Diego
Molecular Imaging for Cancer Visualization American College of Surgeons Surgical Simulation Summit Chicago, IL March 16-17, 2018 Michael Bouvet, MD Professor of Surgery University of California San Diego
Reason for Dissection. Pleomorphic adenoma. Tongue base adenocarcinoma
 Supplementary Table S1 Human Patients Patient Sample No. Gender Age Additional Medication Treatment 1 Reason for Dissection Total Irradiation Dose Estimated Irradiation Dose to SG Gland Time of Resection
Supplementary Table S1 Human Patients Patient Sample No. Gender Age Additional Medication Treatment 1 Reason for Dissection Total Irradiation Dose Estimated Irradiation Dose to SG Gland Time of Resection
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Serum vascular endothelial growth factor C levels predict lymph node metastasis and prognosis of patients with gallbladder cancer
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS Serum vascular endothelial growth factor C levels predict lymph node metastasis and prognosis of patients with gallbladder cancer LEI JIANG 1,2*, MINCHAO LIU 1,3*, XINRAN CAI 1,2, LIJUN
ONCOLOGY LETTERS Serum vascular endothelial growth factor C levels predict lymph node metastasis and prognosis of patients with gallbladder cancer LEI JIANG 1,2*, MINCHAO LIU 1,3*, XINRAN CAI 1,2, LIJUN
Effects of AFP gene silencing on Survivin mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells
 mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
Lymphangiogenesis and biological behavior in pancreatic carcinoma and other pancreatic tumors
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 5: 959-963, 2012 Lymphangiogenesis and biological behavior in pancreatic carcinoma and other pancreatic tumors ZHONGQIU WANG 1*, JIANG WU 1*, GUOJUN LI 3, XINHUA ZHANG 2, MINGMIN
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 5: 959-963, 2012 Lymphangiogenesis and biological behavior in pancreatic carcinoma and other pancreatic tumors ZHONGQIU WANG 1*, JIANG WU 1*, GUOJUN LI 3, XINHUA ZHANG 2, MINGMIN
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells
 CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Argininosuccinate synthetase 1 suppression and arginine restriction inhibit cell
 Argininosuccinate synthetase 1 suppression and arginine restriction inhibit cell migration in gastric cancer cell lines Yan-Shen Shan 1, Hui-Ping Hsu 1, Ming-Derg Lai 2,3, Meng-Chi Yen 2,4, Wei-Ching Chen
Argininosuccinate synthetase 1 suppression and arginine restriction inhibit cell migration in gastric cancer cell lines Yan-Shen Shan 1, Hui-Ping Hsu 1, Ming-Derg Lai 2,3, Meng-Chi Yen 2,4, Wei-Ching Chen
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis
 Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit
 ab136955 Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the sensitive and accurate measurement of Glucose uptake in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab136955 Glucose Uptake Colorimetric Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the sensitive and accurate measurement of Glucose uptake in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended
Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION 60611, USA
 Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION G.R. Scott Budinger 1,2 *, Gökhan M. Mutlu 1 *, Daniela Urich 2, Saul Soberanes 1, Leonard
Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION G.R. Scott Budinger 1,2 *, Gökhan M. Mutlu 1 *, Daniela Urich 2, Saul Soberanes 1, Leonard
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Differential expression of the Na + /I symporter protein in thyroid cancer and adjacent normal and nodular goiter tissues
 368 Differential expression of the Na + /I symporter protein in thyroid cancer and adjacent normal and nodular goiter tissues SHASHA WANG 1, JUN LIANG 1, YANSONG LIN 2 and RUYONG YAO 3 1 Department of
368 Differential expression of the Na + /I symporter protein in thyroid cancer and adjacent normal and nodular goiter tissues SHASHA WANG 1, JUN LIANG 1, YANSONG LIN 2 and RUYONG YAO 3 1 Department of
Approved for Public Release; Distribution Unlimited
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0186 TITLE: A Novel Therapeutic System for the Treatment of Occult Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Shongyun Dong, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0186 TITLE: A Novel Therapeutic System for the Treatment of Occult Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Shongyun Dong, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Díaz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201209151/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Hypoxia induces invadopodia formation in different epithelial
Supplemental material Díaz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201209151/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Hypoxia induces invadopodia formation in different epithelial
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
