Influence of Flaxseed on Lipid Profiles and Expression of LXRα, in Intestine of Diabetic Rat
|
|
|
- Buck Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Biology; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2013 ISSN E-ISSN X Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Influence of Flaxseed on Lipid Profiles and Expression of LXRα, in Intestine of Diabetic Rat Abbas Mohammadi 1,2, Fateme Mirzaei 3, Mohammad Jamshidi 4, Reza Yari 5, Solmaz Pak 5, Parham Norouzian 6, Vahideh Abdolkarimi 7 & Ebrahim Abbasi Oshaghi 4 1 Department of Biochemistry, Afzalipour School of Medicine, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran 2 Physiology Research Centre, Afzalipour School of Medicine, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran 3 Department of Anatomy, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran 4 Department of Biochemistry, Medical School, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran 5 Department of Biology, Islamic Azad University, Boroūjerd Branch, Boroūjerd, Iran 6 Department of Pharmacy, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences International Branch, Shiraz, Iran 7 Tehran Daru Co, Tehran, Iran Correspondence: Ebrahim Abbasi Oshaghi, Department of Biochemistry, Medical School, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran. 7abbasi@gmail.com Received: June 17, 2013 Accepted: July 2, 2013 Online Published: September 3, 2013 doi: /ijb.v5n4p23 URL: Abstract The aim of this study is to examine the effect of flaxseed on lipid profiles in diabetic rats, focusing on intestinal LXR α. Animals were randomly divided into 3 groups of 8 rats each. group1: rats + chow diet (control), group 2: diabetic rats + chow diet (diabetic control), and group3: diabetic rats + chow diet + 4% flaxseed (w/w) (flaxseed group). After one-month rats were sacrificed, blood was collected; lipid profiles were determined enzymatically as well as mrna and protein levels of SR-BI were determined by RT-PCR and westernblot respectively. Compared with diabetic control (group 2), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides, and very low density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C) (all of them P < 0.01) significantly decreased in flaxseed group (group 3). Intestinal LXR α mrna was significantly increased (P < 0.001) in flaxseed group treatment compared with diabetic animals (group 2). Levels of intestinal regulatory protein of LXR α significantly increased in flaxseed group (P < 0.05). In conclusion, flaxseedsignificantly reduced TC, LDL-C, TG, VLDL-C and atherogenic index, as compared with the diabetic rats (group 2). On the other hand flaxseed led to up-regulation of LXR α in the intestine of rats. Keyword: flaxseed, cholesterol, LXR α, diabetes, Iran 1. Introduction Dyslipidaemia is a major forecaster of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events and diabetic patient s mortality. High plasma concentration of total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol are major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (Vafa, 2012; Manhas, 2004). Therefore, attentive control of lipid profiles is vital. Diabetic patient have two-four fold higher risk of developing coronary heart disease than people without diabetes, and CVDaccounts for percent of diabetic patient deaths (Mohammed, 2010). The restriction of nutritional cholesterol has been used as the principal primary therapeutic modality for the prevention and also treatment of dyslipidemia. Consequently, investigating nutritional components that can markedly improve dyslipidemia is important. The livers X receptors (LXRα and LXRβ) are vital regulators of lipid and carbohydrate homeostasis that belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily. Two isotypes of LXR have been known in mammals including LXRα that is mainly expressed in the liver, intestine, spleen, kidney and adrenals, and LXRβ thatis expressed universally 23
2 (Kruit, 2006). LXRα by regulating of cholesterol transporters in the intestine plays important role in whole blood cholesterol. Flaxseed is recognized as a richest source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), lignans, phytoestrogen, and soluble fiber. Studies showed that flaxseed markedly reduced plasma cholesterol and suggested as a useful plant in prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease (Pellizzon, 2007). We have evaluated the hypolipidemic effects of flaxseed in diabetic rats. We also have measured expression of LXRαin rat intestine. 2. Method 2.1 Animals Male Wistar rats of same age with mean body weight of g were used for this experiment. The animals were bred and kept in the animal house. The animal house was maintained under standard hygienic condition, at a room temperature of 25 ± 1 C and relative humidity 55 ± 5% with 12 h light/dark cycle (Hajianfar, 2013). After one week of acclimation, rats were randomly divided into 3 groups of 8 rats each. Group1: rats + chow diet (control), group2: diabetic rats + chow diet (diabetic control), and group3: diabetic rats + chow diet + 4% flaxseed (w/w) (flaxseed group). The procedure of this study has been approved by the Animal Research Ethic Committee of Tehran Payamenoor University (Tehran, Iran). 2.2 Diabetic Rats After an overnight fast, diabetes was induced in animals by a single intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of streptozotoc in (70 mg/kg in 10 mm citrate buffer, ph 4.5). Diabetes was recognized by polyuria, polydipsia and by evaluate of non-fasting serum glucose levels after one week. Rats with blood glucose levels greater than 300 mg/dl were considered diabetic (Abbasi-Oshaghi, 2012). 2.3 Preparing Samples After one month, the rats were anesthetized with diethyl ether and killed by decapitation. Blood samples of each rat were collected by cardiac puncture into glass tubes and afterward centrifuged at 3000 rpm, for 15 min at 4 C. The serum was conveyed to a clean glass tube and stored at -20 C (Mohammadi, 2012; Esfahani, 2013). 2.4 Biochemical Analysis Amount of TG, TC and HDL-C were measured enzematicaly using kits (Pars Azmoon, Iran). Levels of LDL-C and VLDL-C were calculated according to the Friedewald formula. Non-HDL-cholesterol concentration was calculated by subtracting HDL-C from total cholesterol (Ghamar-Chehreh, 2012). 2.5 Semiquantitative RT-PCR RNA from intestine was extracted with Accuzol Reagent (Bioneer, Korea) according to the manufacturers protocol. Synthesis of cdna was performed according to the manufacturer s protocol (Fermentas, Lithuania). For semiquantitative RT-PCR reaction 13 µl PCR Master Mix (Cinnagen, Iran), 1 µl forward primer (P mol/µl), 1 µl reverse primer (P mol/µl), 2 µl cdna and 8 µl deionized water were added into a sterile tube on ice, and centrifuged for a short time. Thirty five cycles of PCR amplification were achieved with denaturation at 95 ºC for 30 s, annealing at 63 ºC for 30 s, and extension at 72 ºC for 30 s using a PCR machine. All reactions were completed with a single additional cycle at 72 ºC for 5 minutes. The samples were electrophoresed on a 2% agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. The primers that used in this studywere fallowing:βactin : upper, 5 -TGG AAT CCT GTG GCA TCC ATG AAA C-3 lower primer, 5 -TAA AAC GCA GCT CAG TAA CAG TCC G-3 LXR alpha : pper primer, F: 5'-GCG TCC ATT CAG AGC AAG TGT-3', lower primer, 5'-TCA CTC GTG GAC ATC CCA GAT-3' (Mohammadi, 2012). 2.6 Western Blotting About 50 mgofintestine samplewas homogenized in 500 µl of RIPA buffer which containing 1% protein inhibitor cocktail (Santa Cruz, USA) and 1 µm PMSF. The homogenate then was centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 15 min at 4 ºC. Fifty microgram of protein was separated on a 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to a Polyvinylidenedifluoride (PVDF) membrane (Roche Applied Science). The PVDF membrane was blocked (2 hr) with 3% non-fat dried milk in Tris-buffered saline with Tween 20 (TBS-T, Roche Applied Science) at room temperature. The membrane then was probed with rabbit anti-lxr alpha antibody (1:300 dilutions, Santa Cruz), and rabbit polyclonal β-actin antibody (1:2000 dilutions, Novus Biological) for 1.5 hr at room temperature. After washing in TBS-T (three times, 15 min), the blots were incubated for 1.5 hr sat room temperature with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:10000, Roche Applied Science). The complexes of 24
3 antibody and antigen were exposed to ECL western blotting detection reagents (Roche Applied Science) for 30 s and the film was developed. Lab Work analyzing software (UVP, UK) was used to analyze Band densities. Data are expressed as the percent ratio of the LXR to β-actin (Abbasi-Oshaghi, 2012; Mohammadi, 2012; Chen, 2009). 2.7 Statistical Analysis The data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance with ANOVA followed by Tukey. Results were expressed as mean values ± SD. The differences between groups were considered significant when P < Results 3.1 Effect of Flaxseed Treatment on Blood Lipid Levels The effect of flaxseed treatment on the blood lipid profiles of the tested rat groups is given in Table 1. The levels of TG (P < 0.001), VLDL-C (P < 0.001), TC (P < 0.01) and LDL-C (P < 0.01) significantly reduced in the flaxseed treatment rats compared with diabetic control. The high levels of TC, LDL-C and TG were brought down markedly after one month treatment period. A fall of 36% in TC, 63% in LDL-C and 55% in TG was observed in flaxseed treated group and there was also an increase of 7% HDL-C in the treated group compared with diabetic control. Table 1. Lipid profiles in different treatment groups Biochemical factors diabetic rat+ Flaxseed diabetic rat ( diabetic control) chow diet (Control) TC ± 5.29 b ± ± 4.03 b TG 62.93± 5.53 c ± ± 6.82 c LDL-C ± 2.06 b ± ± 1.08 b HDL-C ± ± ± 5.60 VLDL-C ± 0.35 c ± ± 0.45 c TC: Total cholesterol, TG: Triglyceride, LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, VLDL-C: Very low-density lipoprotein Cholesterol, Data represent as mean ± SD (n = 8). a P< 0.05, b P < 0.01 and c P < Considered as significant compared with diabetic control (diabetic rats + chow diet). 3.2 Protein and mrna Levels Intestinal LXRα protein significantly increased in flaxseed treated group in comparison with diabetic rats (P < 0.05) (Figure 1). LXRα mrna significantly increased (P < 0.05) in flaxseed group in comparison with diabetic rats (Figure 2). 25
4 Figure 1. Expression of LXR protein in intestine of flaxseed, diabetic and control rats (n = 8) LXR protein expression significantly increased in flaxseed group. *p < 0.05 considered as significant compared with diabetic rats. Data are presented as means ± SD. LXR alpha band from left to right; lane 1: flaxseed group (diabetic rats + chow diet + 4% flaxseed), 2: control (rats + chow diet), 3: diabetic control (diabetic rats + chow ). Figure 2. Expression of LXR mrna in intestine of flaxseed, diabetic and control rats (n = 8) LXR mrna expression significantly increased in flaxseed group. ***p < considered as significant compared with diabetic rats. Data are presented as means ± SD. LXR alpha band from left to right; lane 1: flaxseed group (diabetic rats + chow diet + 4% flaxseed), 2: control (rats + chow diet), 3: diabetic control (diabetic rats + chow ). 4. Discussion 4.1 Biochemical Markers Prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular disease are growing quickly in the world. Optimal control of lipid profiles in diabetic patient is very important to prevention of cardiovascular diseaseand also growing health is a matter in the world (Manhas, 2004). Diabetic patients frequently have higher total cholesterol, TG and LDL-C. 26
5 This combination participates markedly to their cardiovascular risk.in the diabetic patients, and LDL-C is a powerful risk factor for cardiovascular (Brown, 2008). In this study LDL-C significantly reduced by flaxseed. Studies have shown that rate of cardiovascular event is reduced by nearly 1% for every 1% decrease in LDL-C, and by at least 1% for every 1% raise in HDL-C (Brown, 2008). We observed that the diabetic animals which fed flaxseed had the lowest plasma cholesterol concentration compared with the diabetic animals. However, high plasma cholesterol levels are related to coronary artery disease (CAD) (Manhas, 2004; Brown, 2008). 4.2 Gene Expression Homeostasis of plasma cholesterol is controlled by a complex interaction of intestinal absorption, biliary clearance, faecal excretion and denovo synthesis. Absorption of cholesterol from intestinal has been established to be a main determinant of plasma lipid profiles. Theliver X receptor (LXR) is a part of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors liver X receptors (LXRs) are vital regulators of cholesterol, triglyceride, and glucose metabolism. Two isoforms of LXR have been recognized including LXRα and LXRβ. LXRα expression is limited to liver, intestine, adipose tissue, kidney, lung, macrophages and spleen, while LXRβ is expressed in approximately all tissues. LXRα by regulating expression of many genes such as Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 (NPC1L1) and heterodimer of ATPbinding cassette transporter G5 and G8 (ABCG5 andabcg8) leads to reduction of intestinal cholesterol absorption (Kruit, 2006; Zhoa & Dahlman-Wright, 2010). Activation of LXR increases both ABCG5 and ABCG8 expression, which transfer absorbed cholesterol back to the intestinal lumen. Studies have shown that administration of LXR agonists significantly decreases intestinal net cholesterol absorption in animals (Zhoa & Dahlman-Wright, 2010). NPC1L1 (Neimanna Pick C1 Like 1) has been recognized as a main cholesterol transporter which have important role in the cholesterol absorption. This protein is expressed in the brush border of enterocytes (Altmann, 2004). It was recently suggested that activation of LXR downregulates NPC1L1 expression. Elevation of plasma cholesterol is related to atherosclerotic coronary heart disease. By reducing plasma cholesterol levels, NPC1L1 inhibition and activation of ABCG5 and ABCG8 should have useful effects on atherosclerosis (Davis, 2001). Treatment with flaxseed significantly reduces lowers total cholesterol probably with inhibition of cholesterol absorption, and also may inhibit the development and progression of atherosclerosis in diabetic rats. Flaxseed is rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), lignans, phytoestrogen, soluble fiber, and these substances are likely antioxidant and hypolipidemic effects. Thus, intake of flaxseed in diabetic rats enhanced antioxidant free radical scavenging capacity and significantly reduced lipid profiles. On the other hand, flaxseed with reduction of NPC1L1 and raise of ABCG5, ABCG8 and LXR α significantly reduced plasma LDL-C and total cholesterol. This research provides a rationale to examine these effects in diabetic patient. Acknowledgements We are thankful to Rezaii A, from Tehran Payeme Noor University for preparation of diabetic rats and safety of blood samples. We also would like to thanks professor Gholamhosseinian from Kerman Razi laboratory for analysis of biochemical factors and Borūjerd Azad University for gene expression help. References Abbasi-Oshaghi, E., Noori-Sorkhani, A., & Rezaei, A. (2012). Effects of Walnut on Lipid Profile as Well as the Expression of Sterol-Regulatory Element Binding Protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors α (PPARα) in Diabetic Rat. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 3(2), Altmann, S. W., Davis, H.R., Zhu, L. J., Yao, X., Hoos, L. M., Tetzloff, G., Zeng, M. (2004). Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science, 303, Brown, W. V. (2008). Optimal management of lipids in diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Journal of Clinical Lipidology, 2, Chen, Y., & Chen, K. (2009). Characterization and Prokaryotic expression of Glucuronyltransferase-S Gene in Silkworm Bombyxmori. International Journal of Biology, 1(1),
6 Davis, J., Compton, H. R., Hoos, D. S., & Tetzloff, G. (2001). Ezetimibe, a potent cholesterol absorption inhibitor, inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 21, Esfahani, A. S., Gharakhanlou, R., Karimian, J., Khazaei, M., Feizi, A., & Safarzade, A. (2013). Effect of Resistance Training on Plasma Nitric Oxide and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Concentrations in Type I Diabetic Rats. Int J Prev Med, 4, Ghamar-Chehreh, M. E., Amini, M., Khedmat, H., Daraei, F., Mohtashami, R., & Karbasi, A. (2012). Comparative Effectiveness of Ezetimibe in Improving Lipid Profile in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Statins Still Rule. International Journal of Biology, 4(2), Hajianfar, H., Paknahad, Z., & Bahonar, A. (2013). The Effect of Omega-3 Supplements on Antioxidant Capacity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J Prev Med, 2, Kruit, J. K., Groen, A. K., Berkel, T. J., & Kuipers, F. (2006). Emerging roles of the intestine in control of cholesterol metabolism. World J Gastroenterol, 12(40), Manhas, A., & Farmer, J. A. (2004). Hypolipidemic therapy and cholesterol absorption. Current Atherosclerosis Reports, 6(2), Mohammadi, A., Abbasi-Oshaghi, E., Noori-Sorkhani, A., Oubari, F., Kia, R., & Rezaei, A. (2012). Effect of Opium on Lipid Profile and Expression of Liver X Receptor Alpha (LXRα) in Normolipidemic Mouse. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 3(2), Mohammed, K., Ali, K. M., Narayan, V., & Tandon, N. (2010). Diabetes & coronary heart disease: Current perspectives. Indian J Med Res, 132, Pellizzon, M. A., Billheimer, J. T., Bloedon, L. T., Philippe, R. D., Szapary, O., & Rader, D. J. (2007). Flaxseed Reduces Plasma Cholesterol Levels in Hypercholesterolemic Mouse Models. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 26(1), Vafa, M., Mohammadi, F., Shidfar, F., Sormaghi, M., Heidari, I., & Golestan, B. (2012). Effects of Cinnamon Consumption on Glycemic Status, Lipid Profle and BodyComposition in Type 2. J Prev Med, 3, Zhoa, C., & Dahlman-Wright, K. (2010). Liver X receptor in cholesterol metabolism. J Endocrinol, 204(3), Copyrights Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( 28
Ebrahim Abbasi Oshaghi 1,2
 1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
1 2 Flaxseed normalized antioxidant status and also changed ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes expression in diabetic rat Fatemeh Mirzaei 1,Mona Pourjafarr 1, Seyyed Alireza Vafaei 1, Rezvan Mostoli 1, Ebrahim Abbasi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Supplementary Table 2. Conserved regulatory elements in the promoters of CD36.
 Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
CD31 5'-AGA GAC GGT CTT GTC GCA GT-3' 5 ' -TAC TGG GCT TCG AGA GCA GT-3'
 Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr Gene PRDM16 UCP1 PGC1α Dio2 Elovl3 Cidea Cox8b PPARγ AP2 mttfam CyCs Nampt NRF1 16s-rRNA Hexokinase 2, intron 9 β-actin Primer Sequences 5'-CCA CCA GCG
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for qrt-pcr Gene PRDM16 UCP1 PGC1α Dio2 Elovl3 Cidea Cox8b PPARγ AP2 mttfam CyCs Nampt NRF1 16s-rRNA Hexokinase 2, intron 9 β-actin Primer Sequences 5'-CCA CCA GCG
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
c Tuj1(-) apoptotic live 1 DIV 2 DIV 1 DIV 2 DIV Tuj1(+) Tuj1/GFP/DAPI Tuj1 DAPI GFP
 Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Supplementary Table 3. 3 UTR primer sequences. Primer sequences used to amplify and clone the 3 UTR of each indicated gene are listed.
 Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards
 Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Plasmids Western blot analysis and immunostaining Flow Cytometry Cell surface biotinylation RNA isolation and cdna synthesis
 Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
BHP 2-7 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cells were grown in RPMI1640 medium (Hyclone) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 2mM L-glutamine, and 100 U/mL
 1 2 3 4 Materials and Methods Cell culture BHP 2-7 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cells were grown in RPMI1640 medium (Hyclone) 5 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 2mM L-glutamine, and 100 U/mL 6 penicillin-streptomycin.
1 2 3 4 Materials and Methods Cell culture BHP 2-7 and Nthy-ori 3-1 cells were grown in RPMI1640 medium (Hyclone) 5 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco), 2mM L-glutamine, and 100 U/mL 6 penicillin-streptomycin.
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
B. Patient has not reached the percentage reduction goal with statin therapy
 Managing Cardiovascular Risk: The Importance of Lowering LDL Cholesterol and Reaching Treatment Goals for LDL Cholesterol The Role of the Pharmacist Learning Objectives 1. Review the role of lipid levels
Managing Cardiovascular Risk: The Importance of Lowering LDL Cholesterol and Reaching Treatment Goals for LDL Cholesterol The Role of the Pharmacist Learning Objectives 1. Review the role of lipid levels
a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
Supplementary Information. Bamboo shoot fiber prevents obesity in mice by. modulating the gut microbiota
 Supplementary Information Bamboo shoot fiber prevents obesity in mice by modulating the gut microbiota Xiufen Li 1,2, Juan Guo 1, Kailong Ji 1,2, and Ping Zhang 1,* 1 Key Laboratory of Tropical Plant Resources
Supplementary Information Bamboo shoot fiber prevents obesity in mice by modulating the gut microbiota Xiufen Li 1,2, Juan Guo 1, Kailong Ji 1,2, and Ping Zhang 1,* 1 Key Laboratory of Tropical Plant Resources
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Regulating Hepatic Cellular Cholesterol
 Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and cdna sequences of the targeted regions in WT-KI and
 Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at
 Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Lipoprotein Particle Profile
 Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
Lipoprotein Particle Profile 50% of people at risk for HEART DISEASE are not identified by routine testing. Why is LPP Testing The Most Comprehensive Risk Assessment? u Provides much more accurate cardiovascular
By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
 Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc YFP N
 MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Lifestyle, Transport, Genes and Health
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Biology Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Lifestyle, Transport, Genes and Health Thursday 8 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCE Centre Number Candidate Number Biology Advanced Subsidiary Unit 1: Lifestyle, Transport, Genes and Health Thursday 8 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most
 Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences. Research Article
 International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com February - March, 214, Vol. 3, No.2, pp 943-948 ISSN: 2278-238 Research Article
International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Available online at http//www.ijrdpl.com February - March, 214, Vol. 3, No.2, pp 943-948 ISSN: 2278-238 Research Article
ZL ZDF ZDF + E2 *** Visceral (g) ZDF
 Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Comparative Effectiveness of Ezetimibe in Improving Lipid Profile in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Statins Still Rule
 Comparative Effectiveness of Ezetimibe in Improving Lipid Profile in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Statins Still Rule Mohammad Ebrahim Ghamar-Chehreh, Mohsen Amini, Hossein Khedmat (Corresponding
Comparative Effectiveness of Ezetimibe in Improving Lipid Profile in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Statins Still Rule Mohammad Ebrahim Ghamar-Chehreh, Mohsen Amini, Hossein Khedmat (Corresponding
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
BCH 447. Triglyceride Determination in Serum
 BCH 447 Triglyceride Determination in Serum Introduction: Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed by lipase to glycerol and free fatty acids. Triglyceride determinations when performed
BCH 447 Triglyceride Determination in Serum Introduction: Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed by lipase to glycerol and free fatty acids. Triglyceride determinations when performed
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice.
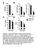 Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Lipids digestion and absorption, Biochemistry II
 Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Information. MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Table I - Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR and RT-PCR
 Supplement Supplementary Table I - Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR and RT-PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse primer (5-3 ) Reference Human ST2 CTTGATTGATAAACAGAATG CTGATCCAGATACTGTTGAA
Supplement Supplementary Table I - Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR and RT-PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse primer (5-3 ) Reference Human ST2 CTTGATTGATAAACAGAATG CTGATCCAGATACTGTTGAA
Supporting Information. Supporting Tables. S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Product size. Gene Primer pairs
 Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the. Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
Citation for published version (APA): Oosterveer, M. H. (2009). Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Oosterveer, Maaike IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Oosterveer, Maaike IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
13/09/2012. Dietary fatty acids. Triglyceride. Phospholipids:
 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
LDL (Human) ELISA Kit
 LDL (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3864 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This immunoassay kit allows for the specific measurement of human low density lipoprotein, LDL concentrations in cell culture supernates,
LDL (Human) ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA3864 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This immunoassay kit allows for the specific measurement of human low density lipoprotein, LDL concentrations in cell culture supernates,
Gender: M Chart No: Fasting: Yes. Boston Heart HDL Map TM Test 1 ApoA-I (mg/dl) levels in HDL particles. α Range > <14 mg/dl. α-2 50.
 Pro vider: Ordering Provider 123 Main Street Anytown, ST 12345 Account No: DOB: 00/00/1950 Framingham Risk Score: Patient Info: FAMILY HIST CVD Lipid, Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein Tests Total Cholesterol
Pro vider: Ordering Provider 123 Main Street Anytown, ST 12345 Account No: DOB: 00/00/1950 Framingham Risk Score: Patient Info: FAMILY HIST CVD Lipid, Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein Tests Total Cholesterol
Triglyceride determination
 Triglyceride determination Introduction: - Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed to glycerol and free fatty acids (by lipase) - Triglyceride determinations when performed in conjunction
Triglyceride determination Introduction: - Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed to glycerol and free fatty acids (by lipase) - Triglyceride determinations when performed in conjunction
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins
 Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
control kda ATGL ATGLi HSL 82 GAPDH * ** *** WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi iwat gwat ibat
 body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
EFFECT OF LYCOPENE IN TOMATO SOUP AND TOMATO JUICE ON THE LIPID PROFILE OF HYPERLIPIDEMIC SUBJECTS
 EFFECT OF LYCOPENE IN TOMATO SOUP AND TOMATO JUICE ON THE LIPID PROFILE OF HYPERLIPIDEMIC SUBJECTS Nora Vigasini, Assistant Professor, Department of Home Science, Women s Christian College, Chennai, noravigas@gmail.com
EFFECT OF LYCOPENE IN TOMATO SOUP AND TOMATO JUICE ON THE LIPID PROFILE OF HYPERLIPIDEMIC SUBJECTS Nora Vigasini, Assistant Professor, Department of Home Science, Women s Christian College, Chennai, noravigas@gmail.com
New opportunities for targeting. multiple lipid pathways. Michel FARNIER, DIJON, FRANCE
 New opportunities for targeting multiple lipid pathways Michel FARNIER, DIJN, FRANCE Lipid lowering drug therapy 60s and 70s - nicotinic acid -resins 70s to 90s - fibrates the 90s - statins Coronary heart
New opportunities for targeting multiple lipid pathways Michel FARNIER, DIJN, FRANCE Lipid lowering drug therapy 60s and 70s - nicotinic acid -resins 70s to 90s - fibrates the 90s - statins Coronary heart
Maintain Cholesterol
 Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Estimation of glucose in blood serum
 Estimation of glucose in blood serum Enzymatic estimation of glucose uses a reagent containing two enzymes and a chromogen. Glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconolactone with the
Estimation of glucose in blood serum Enzymatic estimation of glucose uses a reagent containing two enzymes and a chromogen. Glucose oxidase catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconolactone with the
 http://noodlemaz.wordpress.com/category/science/cancer/ Outline Introduction Serious nature of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) How to prevent CVD? The disease process Damage and plaque development Current
http://noodlemaz.wordpress.com/category/science/cancer/ Outline Introduction Serious nature of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) How to prevent CVD? The disease process Damage and plaque development Current
Weight control and satiety effects of flaxseed A Review. Kelley Fitzpatrick, M.Sc. NutriScience Solutions Flaxresearch.com
 Weight control and satiety effects of flaxseed A Review Kelley Fitzpatrick, M.Sc. NutriScience Solutions Flaxresearch.com Global Childhood Obesity 2000 2010 2013 2025 Number and proportion estimated to
Weight control and satiety effects of flaxseed A Review Kelley Fitzpatrick, M.Sc. NutriScience Solutions Flaxresearch.com Global Childhood Obesity 2000 2010 2013 2025 Number and proportion estimated to
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Cell culture RNA extraction and analysis Immunohistochemical analysis and laser capture microdissection (LCM)
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Cell culture Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from healthy donors by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation. Monocyte differentiation to resting macrophages ()
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Cell culture Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from healthy donors by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation. Monocyte differentiation to resting macrophages ()
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Cholesterol Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels
 Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
RayBio Human PPAR-alpha Transcription Factor Activity Assay Kit
 RayBio Human PPAR-alpha Transcription Factor Activity Assay Kit Catalog #: TFEH-PPARa User Manual Jan 5, 2018 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 200 Norcross, GA 30092 Tel: 1-888-494-8555 (Toll Free) or 770-729-2992,
RayBio Human PPAR-alpha Transcription Factor Activity Assay Kit Catalog #: TFEH-PPARa User Manual Jan 5, 2018 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 200 Norcross, GA 30092 Tel: 1-888-494-8555 (Toll Free) or 770-729-2992,
Ezetimibe: a selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2001) 3 (Supplement E), E6 E10 Ezetimibe: a selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption Dipartimento di Scienze Farmacologiche, Universita degli Studi di Milano, Milano,
European Heart Journal Supplements (2001) 3 (Supplement E), E6 E10 Ezetimibe: a selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption Dipartimento di Scienze Farmacologiche, Universita degli Studi di Milano, Milano,
Ezetimibe: a selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2001) 3 (Supplement E), E6 E10 Ezetimibe: a selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption Dipartimento di Scienze Farmacologiche, Universita degli Studi di Milano, Milano,
European Heart Journal Supplements (2001) 3 (Supplement E), E6 E10 Ezetimibe: a selective inhibitor of cholesterol absorption Dipartimento di Scienze Farmacologiche, Universita degli Studi di Milano, Milano,
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Therapeutic effect of flavonoid rich extract of apricots on high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rabbits
 Therapeutic effect of flavonoid rich extract of apricots on high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rabbits in rabbits TOOBA LATEEF Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry Jinnah University for
Therapeutic effect of flavonoid rich extract of apricots on high-fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in rabbits in rabbits TOOBA LATEEF Assistant Professor Department of Biochemistry Jinnah University for
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
Cardiovascular disease, studies at the cellular and molecular level. Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century September 23, 2009
 Cardiovascular disease, studies at the cellular and molecular level Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century September 23, 2009 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics
Cardiovascular disease, studies at the cellular and molecular level Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century September 23, 2009 Content Introduction The number 1 killer in America Some statistics
Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
 Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Supplementary Fig. 1 No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
Attenuating Effect of Curcumin on Diet-induced Hypercholesterolemia in Mice
 International Journal of Medical Laboratory 2017;4(4):299-306. Original Article Attenuating Effect of Curcumin on Diet-induced Hypercholesterolemia in Mice Sahar Farzaneh 1 M.Sc., Masoud Salehipour 1*
International Journal of Medical Laboratory 2017;4(4):299-306. Original Article Attenuating Effect of Curcumin on Diet-induced Hypercholesterolemia in Mice Sahar Farzaneh 1 M.Sc., Masoud Salehipour 1*
Formylpeptide receptor2 contributes to colon epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis
 Supplementary Data Formylpeptide receptor2 contributes to colon epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis Keqiang Chen, Mingyong Liu, Ying Liu, Teizo Yoshimura, Wei Shen, Yingying Le, Scott
Supplementary Data Formylpeptide receptor2 contributes to colon epithelial homeostasis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis Keqiang Chen, Mingyong Liu, Ying Liu, Teizo Yoshimura, Wei Shen, Yingying Le, Scott
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
III. Results and Discussion
 III. Results and Discussion 1. Histological findings in the coronary artery Twenty-four swine had surgical treatments performed in two of the coronary arteries, LAD as well as either the LCX or RCA. A
III. Results and Discussion 1. Histological findings in the coronary artery Twenty-four swine had surgical treatments performed in two of the coronary arteries, LAD as well as either the LCX or RCA. A
Drug regulation of serum lipids
 Drug regulation of serum lipids Foundations of Biomedical Science MEDS90001 Dr Michelle Hansen Pharmacology & Therapeutics mjhansen@unimelb.edu.au References Katzung, Basic & Clinical Pharmacology Ch 35
Drug regulation of serum lipids Foundations of Biomedical Science MEDS90001 Dr Michelle Hansen Pharmacology & Therapeutics mjhansen@unimelb.edu.au References Katzung, Basic & Clinical Pharmacology Ch 35
Is it really that simple? Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics
 Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Why we care about hepatic lipogenesis Control of lipid synthesis What can go wrong in humans Animal models dlto study lipoprotein
Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Why we care about hepatic lipogenesis Control of lipid synthesis What can go wrong in humans Animal models dlto study lipoprotein
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27
 Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats
 J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
Zuhier Awan, MD, PhD, FRCPC
 Metabolism, Atherogenic Properties and Agents to Reduce Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins (TRL) The Fifth IAS-OSLA Course on Lipid Metabolism and Cardiovascular Risk Muscat, Oman, February 8-11, 2019 Zuhier
Metabolism, Atherogenic Properties and Agents to Reduce Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins (TRL) The Fifth IAS-OSLA Course on Lipid Metabolism and Cardiovascular Risk Muscat, Oman, February 8-11, 2019 Zuhier
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
Lipid Metabolism Prof. Dr. rer physiol. Dr.h.c. Ulrike Beisiegel
 Lipid Metabolism Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology II Medical Center Hamburg-ppendorf 1 Lipids. visceral fat. nutritional lipids 0 1.5 3 4.5 9 h. serum lipids. lipid accumulation in the
Lipid Metabolism Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology II Medical Center Hamburg-ppendorf 1 Lipids. visceral fat. nutritional lipids 0 1.5 3 4.5 9 h. serum lipids. lipid accumulation in the
Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and. steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E
 Supplementary Information Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E Yinhua Ni, 1,2 Mayumi Nagashimada, 1 Fen Zhuge, 1 Lili
Supplementary Information Astaxanthin prevents and reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and steatohepatitis in mice: A comparison with vitamin E Yinhua Ni, 1,2 Mayumi Nagashimada, 1 Fen Zhuge, 1 Lili
