Susceptibility of human primary neuronal cells to Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-related (XMRV) virus infection.
|
|
|
- Earl Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Virology Journal This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Susceptibility of human primary neuronal cells to Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-related (XMRV) virus infection. Virology Journal 2011, 8:443 doi: / x Veerasamy Ravichandran Eugen O Major (Majorg@ninds.nih.gov) Carol Ibe (ibec@mail.nih.gov) Maria Chiara Monaco (monaco@ninds.nih.gov) Mohan Kumar Haleyur Girisetty (mohan.haleyurgirisetty@fda.hhs.gov) Indira K Hewlett (indira.hewlett@fda.hhs.gov) ISSN X Article type Short report Submission date 1 August 2011 Acceptance date 20 September 2011 Publication date 20 September 2011 Article URL This peer-reviewed article was published immediately upon acceptance. It can be downloaded, printed and distributed freely for any purposes (see copyright notice below). Articles in Virology Journal are listed in PubMed and archived at PubMed Central. For information about publishing your research in Virology Journal or any BioMed Central journal, go to For information about other BioMed Central publications go to Ravichandran et al. ; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Susceptibility of human primary neuronal cells to Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-related (XMRV) virus infection. Veerasamy Ravichandran 1, Eugen O Major 2, Carol Ibe 2, Maria Chiara Monaco 2, Mohan Kumar Haleyur Girisetty 1, Indira K Hewlett 1* 1 Laboratory of Molecular Virology, Division of Emerging and Transfusion Transmitted Diseases, Office of Blood Research and Review, Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA; 2 Laboratory of Molecular Medicine and Neuroscience, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD , USA. VR: veerasamy.ravichandran@fda.hhs.gov EOM: Majorg@ninds.nih.gov CI: ibec@mail.nih.gov MCM: monaco@ninds.nih.gov MKHG: mohan.haleyurgirisetty@fda.hhs.gov IKH: indira.hewlett@fda.hhs.gov *Corresponding Author: Dr. Indira Hewlett Bld. 29B, Room. 4NN16, Laboratory of Molecular Virology, DETTD, OBRR, CBER, FDA, Bethesda, MD Phone: (301) Fax: (301) indira.hewlett@fda.hhs.gov
3 ABSTRACT Background: Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-related (XMRV) virus is a recently identified mouse gammaretrovirus that has the ability to infect certain human cells. In this study, we investigated the susceptibility of primary neuronal cell types to infection with XMRV. Findings: We observed that the human primary progenitors, progenitor-derived neurons, and progenitor-derived astrocytes supported XMRV multiplication. Interestingly, both progenitors and progenitor-derived neurons were more susceptible compared with progenitor-derived astrocytes. In addition, XMRV-infected Jurkat cells were able to transmit infection to neuronal cells. Conclusions: These data suggest that neuronal cells are susceptible for XMRV infection. Keywords: XMRV infection, Primary neuronal cells, Non-neuronal cells, Nuclear factors.
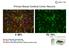
4 Findings: XMRV has been associated with prostate cancer and CFS [1, 2]. Although CFS patients show many symptoms for inflammation in brain, there is no report about the presence of XMRV in the brain of CFS patients. In an effort to determine the susceptibility of neuronal cells to XMRV in-vitro, we used human primary Progenitors, Progenitor-Derived Neurons (PDN), and Progenitor-Derived Astrocytes (PDA). Human central nervous system progenitor cells were isolated from an 8-week-gestation fetal brain according to National Institutes of Health guidelines. The isolation and culture conditions of the progenitor cells and subsequent selective differentiation into neurons were previously reported [3]. Progenitor cultures stained positive for nestin staining (Fig 1A). Differentiation of progenitors into an astrocytic lineage PDA was initiated by growing the cells in Eagle minimal essential medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Quality Biologicals, Gaithersburg, MD) (Fig. 1B). Progenitors were differentiated into a neuronal phenotype (MAP-2+, ßIII-tubulin+, and negative for nestin) by culturing in 10 ng/ml brain-derived neurotrophic factor and 10 ng/ml platelet-derived growth factor A/B (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.) (Fig. 1C). XMRV (10 8 copies/ml) was used to infect progenitors, PDN, and PDA for two hours, and then washed, replenished with appropriate fresh neuronal media. Four days after the infection, cells were washed four times, and harvested for total RNA isolation. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed with Master Mix (Quantitect Probe RT-PCR, Qiagen) using forward and reverse primers encoding gag region of XMRV, probe, RTmix, and 1 ug of RNA in a total volume of 25 ul. The mixture was incubated at 50 C for 20 min, at 95 C for 10 min, and then cycled at 95 C for 15 sec and 60 C for 60 sec 40
5 times, using the Applied Biosystems 7500 sequence detection system. XMRV levels were quantitated using the XMRV clone VP62-pcDNA3.1 (GenBank accession no. EF185282; obtained through NIH AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Program) as a standard. Expression levels of XMRV were normalized against glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) RNA expression. As shown in Fig.2A., four days post-infection, PDN showed higher susceptibility to XMRV infection, having about 90 pg of XMRV RNA/ug of total cellular RNA. The infected progenitors contained about 50 pg of XMRV RNA/ug of total cellular RNA. Interestingly, infected PDA had levels around 7 pg of XMRV RNA/ug of total cellular RNA. We also measured XMRV levels in the culture media, and found a similar trend (results not shown). To compare the infectivity of XMRV in neuronal cells with non-neuronal cell types, the average XMRV levels measured four days post-xmrv infection in various cell types are presented in Table.1. Of many cell types tested for the XMRV infectivity, we observed maximal infectivity in LNCaP cells. This is in agreement with reported studies that the human prostate adenocarcinoma cell line LNCaP which provides optimal environment for the XMRV multiplication. Interestingly, the neuronal cells showed high susceptibility to XMRV compared with another human prostate carcinoma cell line DU145. T-cell traffic into the central nervous system is thought to occur when activated T- cells cross the blood-brain barrier [4]. The T-cells presumably act as a Trojan horse to store and transport infectious materials across the blood-brain barrier. This Trojan horse hypothesis has been well established in the pathogenesis of many viruses that
6 infect the central nervous system [5, 6, 7]. Based on the assumption that XMRV infected lymphocytes could infiltrate and infect the neuronal cells, we conducted an in-vitro coinfection/co-culture study using XMRV-infected Jurkat cells with neuronal cells. To produce XMRV-infected Jurkat cells, Jurkat cells were exposed with XMRV (1.0 X 10 8 copies of XMRV/mL) for two hours, washed and replenished with fresh media. Four weeks after the infection, cells were washed four times, and harvested for total RNA isolation. The XMRV levels were measured using Real-time PCR method as described above. The XMRV-infected Jurkat cells had levels around 500 pg of XMRV per ug of total RNA. For the co-infection/co-culture experiment, 1.0 X 10 6 XMRVinfected Jurkat cells (XMRV equivalent of 500 pg) were pelleted, treated with trypsin for 3 min at room temperature, washed and suspended in progenitor/pdn/pda media; and added on to the appropriate adherent neuronal cell types (progenitors, PDN, or PDA) grown in 24 well plate (2.5 X 10 5 cells/well). Four hours after co-infection/co-culture, XMRV-infected Jurkat cells were removed, and the adherent neuronal cells were washed with appropriate neuronal media. To remove any adhered Jurkat cells from neuronal cells, each culture well was treated with trypsin, and just before the cells were ready to detach (after about 3 min), fresh neuronal media were added and washed three times using neuronal media. The resulting adherent neuronal cells were free from Jurkat cells, and continued to grow with appropriate neuronal media. After four days, the neuronal cells were harvested for total RNA isolation, and XMRV levels were quantified. As in the neuronal infection study (Fig 2A), the co-culture/co-infection of XMRV-infected Jurkat (XMRV equivalent of 500 pg) with neuronal cells resulted in proportionate XMRV infection in neuronal cells (Fig. 2B). In a separate co-culture/co-
7 infection experiment, the XMRV-infected Jurkats (XMRV equivalent of 4.8 pg) were added with individual neuronal cells (progenitor, PDN, or PDA) as described above, continued for four days. We observed that even the small amount of XMRV in the XMRV-infected Jurkats could release virus and infect the neuronal cells (results not shown). Interestingly, in the co-cultures/co-infection study, we co-culture the XMRVinfected Jurkats with neuronal cells only for four hours. The released virus during this time was able to infect the bystander neuronal cells. These observations support the possibility that the infiltrated XMRV-infected T-cells could infect neuronal cells. Brain cells are protected from pathogens by the blood-brain barrier. Even though neuronal cells are susceptible for XMRV infection, this virus should first cross the bloodbrain barrier to inflict any damage to the brain cells in vivo. After XMRV is transported to neuronal cells, the virus needs favorable multiplication environment for its multiplication. For example, we have observed the requirement of nuclear factor I-A (NF-IA) for the XMRV multiplication in Jurkat cells (unpublished observation). Interestingly, both progenitors and neurons express higher levels of NF-IA [8], and this could account for the optimal XMRV multiplication in these cells. In addition, PDA, which is shown to express low NF-IA level compared to progenitor and PDN [8], showed lower susceptibility to XMRV. In a recent animal study, XMRV was administered to rhesus macaques through intravenous inoculation [9]. Interestingly, 291 days post-infection, infected cells were detectable by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) in brain, showing the possibility of XMRV infection in the brain. This study further substantiates our speculation that
8 XMRV could infect brain cells. Further in-vitro and in-vivo studies are warranted to identify and characterize the XMRV, and its role if any, in the brain cells. Competing interests: There are no potential conflicts of financial or personal conflicts of interest related to the results communicated in this paper. Author Contributions: All authors read and approved the final manuscript. V.R., C.I., M.C.M., M.K.H.G. performed experiments; V.R., I.K.H. contributed to designing research, analyzing data, discussing findings, and writing the manuscript; E.O.G., I.K.H supervised the work. Acknowledgements: We thank Dr. Xue Wang, Dr. Mingjie Zhang, Dr. Robin Biswas, and Dr. Chintamani D. Atreya for critical review of the article. The findings and conclusions in this paper have not been formally disseminated by the Food and Drug Administration and should not be construed to represent any Agency determination or policy.
9 Table.1. Comparison of XMRV infection. Cell Type XMRV level (pg/ug total RNA) Progenitor Primary neuronal 50.0 Progenitor-derived Neuron Primary neuronal 90.0 Progenitor-derived Astrocyte Primary neuronal 7.2 Jurkat Immortalized T-cell 4.8 DU145 Human prostate carcinoma 3.8 LNCaP Human prostate adenocarcinoma T Human embryonic kidney Table legend: Neuronal and non-neuronal cells were exposed with XMRV (10 7 copies/ml) for two hours. Four days post-infection, XMRV levels were measured from the total RNA.
10 REFERENCES 1. Lombardi, V. C., F. W. Ruscetti, J. Das Gupta, M. A. Pfost, K. S. Hagen, D. L. Peterson, S. K. Ruscetti, R. K. Bagni, C. Petrow-Sadowski, B. Gold, M. Dean, R. H. Silverman, and J. A. Mikovits Detection of an infectious retrovirus, XMRV, in blood cells of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Science 326: Urisman, A., R. J. Molinaro, N. Fischer, S. J. Plummer, G. Casey, E. A. Klein, K. Malathi, C. Magi-Galluzzi, R. R. Tubbs, D. Ganem, R. H. Silverman, and J. L. DeRisi Identification of a novel Gammaretrovirus in prostate tumors of patients homozygous for R462Q RNASEL variant. Plos Pathogens 2:e Messam, C. A., J. Hou, R. M. Gronostajski, and E. O. Major Lineage pathway of human brain progenitor cells identified by JC virus susceptability. Annals of Neurology 53: Galea, I., M. Bernardes-Silva, P. A. Forse, N. van Rooijen, R. S. Liblau, and V. H. Perry An antigen-specific pathway for CD8 T cells across the bloodbrain barrier. J Exp Med 204: Houff, S. A., and J. R. Berger The bone marrow, B cells, and JC virus. Journal of Neurovirology 14: Houff, S. A., E. O. Major, D. A. Katz, C. V. Kufta, J. L. Sever, S. Pittaluga, J. R. Roberts, J. Gitt, N. Saini, and W. Lux Involvement of JC virus-infected mononuclear cells from the bone marrow and spleen in the pathogenesis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med 318: Monaco, M. C. G., W. J. Atwood, M. Gravell, C. S. Tornatore, and E. O. Major JC virus infection of hematopoietic progenitor cells, primary B lymphocytes, and tonsillar stromal cells: Implications for viral latency. Journal of Virology 70: Ravichandran, V., and E. O. Major DNA-binding transcription factor NF- 1A negatively regulates JC virus multiplication. Journal of General Virology 89: Onlamoon, N., J. Das Gupta, P. Sharma, K. Rogers, S. Suppiah, J. Rhea, R. J. Molinaro, C. Gaughan, B. Dong, E. A. Klein, X. Qiu, S. Devare, G. Schochetman, J. Hackett, Jr., R. H. Silverman, and F. Villinger Infection, Viral Dissemination, and Antibody Responses of Rhesus Macaques Exposed to the Human Gammaretrovirus XMRV. J Virol 85:
11 FIGURE LEGENDS Figure 1. Human neuronal cells used for the XMRV infection study: A. Human neural progenitor cells (NPCs) generated from a human fetal brain. Progenitor cells were labeled with human nestin-specific goat anti-mouse FITC (green) monoclonal antibody (Invitrogen, A10530). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. B. Progenitor-derived Astrocyte (PDA). PDAs express GFAP. Cells were stained using donkey anti-rabbit IgG-TRITC (orange) secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoRes, ). Nuclei are shown in blue (DAPI). C. Progenitor-derived neurons (PDN). PDNs express the neuron-specific class III β- tubulin (TUJ1) marker. Cells were stained using goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 647 (Red) secondary antibody (Invitrogen: A21241). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Figure 2. Infection of XMRV in Primary Neuronal cell types. A. Progenitors, PDNs, or PDAs are plated on 24-well poly d-lysine coated plates (2.5 X 10 5 cells/well). XMRV (10 7 copies/ml) was exposed these cells for two hours. Four days post-infection, XMRV levels were measured from the total RNA. Results are from three independent experiments. B. Infection of XMRV on Neuronal Cells Co-cultured with XMRV-infected Jurkat cells. XMRV-infected Jurkat cells are exposed on the adherent neuronal cells for four hours. The Jurkat cells were washed and the XMRV from the neuronal cells were measured. Results are from three independent experiments.
12 A B C Figure 1
13 XMRV Level (pg/ug total RNA) A Progenitor Progenitor-derived Neuron (PDN) Progenitor-derived Astrocyte (PDA) XMRV Level (pg/ug total RNA) B Figure 2 0 Progenitor + XMRVinfected Jurkat PDN + XMRV-infected Jurkat PDA + XMRV-infected Jurkat
TITLE: Examination of a Newly Discovered Human Retrovirus, XMRV, in Breast Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0464 TITLE: Examination of a Newly Discovered Human Retrovirus, XMRV, in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Wayne State
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0464 TITLE: Examination of a Newly Discovered Human Retrovirus, XMRV, in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Wayne State
*To whom correspondence should be addressed. This PDF file includes:
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1212182/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partial Retraction to Detection of an Infectious Retrovirus, XMRV, in Blood Cells of Patients with Chronic Fatigue
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1212182/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partial Retraction to Detection of an Infectious Retrovirus, XMRV, in Blood Cells of Patients with Chronic Fatigue
Dong, B. and Silverman, R.H.
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 November 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01763-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 November 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01763-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Picture of cell art Picture of cell under a microscope Daniel L. Peterson, MD Whittemore Peterson Institute
 XMRV, A New Human Pathogenic Retrovirus: Detection In Chronic Diseases Picture of cell art Picture of cell under a microscope Daniel L. Peterson, MD Whittemore Peterson Institute Daniel L. Peterson, MD
XMRV, A New Human Pathogenic Retrovirus: Detection In Chronic Diseases Picture of cell art Picture of cell under a microscope Daniel L. Peterson, MD Whittemore Peterson Institute Daniel L. Peterson, MD
Paper Title: Sexual transmission of XMRV: a potential infection route
 Paper Title: Sexual transmission of XMRV: a potential infection route Authors: Prachi Sharma 1, @ (psharm9@emory.edu) Kenneth A. Rogers 1, (kroger3@emory.edu) Suganthi Suppiah 2 (ssuppi2@emory.edu) Ross
Paper Title: Sexual transmission of XMRV: a potential infection route Authors: Prachi Sharma 1, @ (psharm9@emory.edu) Kenneth A. Rogers 1, (kroger3@emory.edu) Suganthi Suppiah 2 (ssuppi2@emory.edu) Ross
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Infect Dis. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 November 15.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Infect Dis. 2010 November 15; 202(10): 1478 1481. doi:10.1086/657168. XMRV Prevalence in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Infect Dis. 2010 November 15; 202(10): 1478 1481. doi:10.1086/657168. XMRV Prevalence in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Detecting Retroviral Sequences in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Viruses 2010, 2, 2404-2408; doi:10.3390/v2112404 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Detecting Retroviral Sequences in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Ila R. Singh Department
Viruses 2010, 2, 2404-2408; doi:10.3390/v2112404 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Detecting Retroviral Sequences in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Ila R. Singh Department
Research Article Lack of Detection of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in HIV-1 Lymphoma Patients
 Advances in Virology Volume 2011, Article ID 797820, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/797820 Research Article Lack of Detection of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in HIV-1 Lymphoma Patients Krista
Advances in Virology Volume 2011, Article ID 797820, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/797820 Research Article Lack of Detection of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in HIV-1 Lymphoma Patients Krista
Research Article Sexual Transmission of XMRV: A Potential Infection Route
 Advances in Virology Volume 2011, Article ID 965689, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/965689 Research Article Sexual Transmission of XMRV: A Potential Infection Route Prachi Sharma, 1 Kenneth A. Rogers, 1 Suganthi
Advances in Virology Volume 2011, Article ID 965689, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/965689 Research Article Sexual Transmission of XMRV: A Potential Infection Route Prachi Sharma, 1 Kenneth A. Rogers, 1 Suganthi
Tsukasa; Sakai, Hideki; Kubo, Yoshi. Biophysical Research Communications
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Androgen-independent proliferation infected by xenotropic murine leuke Kakoki, Katsura; Kamiyama, Haruka; Hayashi, Hideki; Yamamoto, Naoki; M
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Androgen-independent proliferation infected by xenotropic murine leuke Kakoki, Katsura; Kamiyama, Haruka; Hayashi, Hideki; Yamamoto, Naoki; M
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Modulation of HIV replication by steroid hormones in monocyte derived macrophages
 Modulation of HIV replication by steroid hormones in monocyte derived macrophages Krishnakumar Devadas, Ph.D. Laboratory of Molecular Virology Division of Emerging and Transfusion Transmitted Diseases
Modulation of HIV replication by steroid hormones in monocyte derived macrophages Krishnakumar Devadas, Ph.D. Laboratory of Molecular Virology Division of Emerging and Transfusion Transmitted Diseases
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India
 Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India Pankaj Seth, Ph.D Associate Professor, Molecular & Cellular Neuroscience National Brain Research Centre (NBRC) Manesar, INDIA pseth@nbrc.res.in NeuroAIDS
Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India Pankaj Seth, Ph.D Associate Professor, Molecular & Cellular Neuroscience National Brain Research Centre (NBRC) Manesar, INDIA pseth@nbrc.res.in NeuroAIDS
No Evidence of Murine-Like Gammaretroviruses in CFS Patients Previously Identified as XMRV-Infected
 No Evidence of Murine-Like Gammaretroviruses in CFS Patients Previously Identified as XMRV-Infected Konstance Knox, 1,2 Donald Carrigan, 1,2 Graham Simmons, 3,4 Fernando Teque, 5 Yanchen Zhou, 3,4 John
No Evidence of Murine-Like Gammaretroviruses in CFS Patients Previously Identified as XMRV-Infected Konstance Knox, 1,2 Donald Carrigan, 1,2 Graham Simmons, 3,4 Fernando Teque, 5 Yanchen Zhou, 3,4 John
No Evidence for XMRV Nucleic Acids, Infectious Virus or Anti-XMRV Antibodies in Canadian Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 No Evidence for XMRV Nucleic Acids, Infectious Virus or Anti-XMRV Antibodies in Canadian Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Imke Steffen 1,2, D. Lorne Tyrrell 3, Eleanor Stein 4, Leilani Montalvo 1,
No Evidence for XMRV Nucleic Acids, Infectious Virus or Anti-XMRV Antibodies in Canadian Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Imke Steffen 1,2, D. Lorne Tyrrell 3, Eleanor Stein 4, Leilani Montalvo 1,
Healing After Plague: Lessons Applied. Emerging Concepts
 Healing After Plague: Lessons Applied Emerging Concepts Recombination events in animal and human cells can generate families of infectious related gamma retroviruses Greatest concern is that they have
Healing After Plague: Lessons Applied Emerging Concepts Recombination events in animal and human cells can generate families of infectious related gamma retroviruses Greatest concern is that they have
Situation of XMRV and Blood Transfusion. Celso Bianco, MD ISBT Working Party on TTID Lisbon, June 19, 2011
 Situation of XMRV and Blood Transfusion Celso Bianco, MD ISBT Working Party on TTID Lisbon, June 19, 2011 Lombardi et al. Science 326, 585 (2009) Conclusions: CFS and XMRV XMRV found in 67% of CFS patients
Situation of XMRV and Blood Transfusion Celso Bianco, MD ISBT Working Party on TTID Lisbon, June 19, 2011 Lombardi et al. Science 326, 585 (2009) Conclusions: CFS and XMRV XMRV found in 67% of CFS patients
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Generation of molecular standard for quantitative PCR
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
 Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) By Jamie Meier Introduction: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) occurs when change in an individual s immune status triggers reactivation
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) By Jamie Meier Introduction: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) occurs when change in an individual s immune status triggers reactivation
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
XMRV among Prostate Cancer Patients from the Southern United States and Analysis of Possible Correlates of Infection
 XMRV among Prostate Cancer Patients from the Southern United States and Analysis of Possible Correlates of Infection Bryan Danielson Baylor College of Medicine Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology
XMRV among Prostate Cancer Patients from the Southern United States and Analysis of Possible Correlates of Infection Bryan Danielson Baylor College of Medicine Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology
Assays to Address Emerging Threats to Blood Safety
 Assays to Address Emerging Threats to Blood Safety Jeffrey M. Linnen, Ph.D. Director, Product Development Gen-Probe Incorporated San Diego, CA The IPFA/PEI 17th Workshop on Surveillance and Screening of
Assays to Address Emerging Threats to Blood Safety Jeffrey M. Linnen, Ph.D. Director, Product Development Gen-Probe Incorporated San Diego, CA The IPFA/PEI 17th Workshop on Surveillance and Screening of
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Screening for Complex Phenotypes
 Screening for Complex Phenotypes Michael Hemann hemann@mit.edu Screening for cancer phenotypes in mice How do we typically model cancer in mice? Tumor Suppressor KO Oncogene transgenesis Problems with
Screening for Complex Phenotypes Michael Hemann hemann@mit.edu Screening for cancer phenotypes in mice How do we typically model cancer in mice? Tumor Suppressor KO Oncogene transgenesis Problems with
Lipid Droplets Fluorescence Assay Kit
 Lipid Droplets Fluorescence Assay Kit Item No. 500001 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Lipid Droplets Fluorescence Assay Kit Item No. 500001 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Journal of Negative Results in BioMedicine 2011, 10:5
 Journal of Negative Results in BioMedicine This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon.
Journal of Negative Results in BioMedicine This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon.
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum...1. Trademarks: HiLyte Fluor (AnaSpec, Inc.)
 Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
TITLE: The Role of XMRV, a Novel Xenotropic Murine Retrovirus, in Human Prostate Cancers
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0387 TITLE: The Role of XMRV, a Novel Xenotropic Murine Retrovirus, in Human Prostate Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Stephen P. Goff CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0387 TITLE: The Role of XMRV, a Novel Xenotropic Murine Retrovirus, in Human Prostate Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Stephen P. Goff CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson, MS 39216
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0201 TITLE: Role of long non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yin-Yuan Mo CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0201 TITLE: Role of long non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yin-Yuan Mo CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical Center Jackson,
Supplemental Figure 1. Isolation and characterization of CD133+ neurosphere-like
 SUPPLEMENTL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Isolation and characterization of CD133+ neurosphere-like spheroids from a human brain tumor sample or glioma xenograft. () CD133+ tumor cells isolated
SUPPLEMENTL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Isolation and characterization of CD133+ neurosphere-like spheroids from a human brain tumor sample or glioma xenograft. () CD133+ tumor cells isolated
Severe Restriction of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus Replication and Spread in Cultured Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May, p. 4888 4897 Vol. 85, No. -538X//$. doi:.8/jvi.46- Copyright, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Severe Restriction of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May, p. 4888 4897 Vol. 85, No. -538X//$. doi:.8/jvi.46- Copyright, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Severe Restriction of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL
 DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
viruses ISSN
 Viruses 2011, 3, 1312-1319; doi:10.3390/v3081312 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Origin of XMRV and its Demise as a Human Pathogen Associated with Chronic Fatigue
Viruses 2011, 3, 1312-1319; doi:10.3390/v3081312 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Origin of XMRV and its Demise as a Human Pathogen Associated with Chronic Fatigue
A Report from the 9th Hemispherx Biopharma Investigators Meeting
 XMRV & AMPLIGEN A Report from the 9th Hemispherx Biopharma Investigators Meeting HUNTER HOPKINS CENTER Hunter-Hopkins ME-letter March 2011 http://www.drlapp.net/melettermar2011.htm Hunter-Hopkins Center,
XMRV & AMPLIGEN A Report from the 9th Hemispherx Biopharma Investigators Meeting HUNTER HOPKINS CENTER Hunter-Hopkins ME-letter March 2011 http://www.drlapp.net/melettermar2011.htm Hunter-Hopkins Center,
VIRUSES AND CANCER Michael Lea
 VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT
 Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Large Scale Infection for Pooled Screens of shrna libraries
 Last modified 01/11/09 Large Scale Infection for Pooled Screens of shrna libraries Biao Luo, Glenn Cowley, Michael Okamoto, Tanaz Sharifnia This protocol can be further optimized if cells being used are
Last modified 01/11/09 Large Scale Infection for Pooled Screens of shrna libraries Biao Luo, Glenn Cowley, Michael Okamoto, Tanaz Sharifnia This protocol can be further optimized if cells being used are
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN No Treatment. EZN-3920, 2 μm. Time, h
 Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
Next generation sequencing of prostate tumours provides independent evidence of XMRV contamination
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 December 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06170-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 December 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06170-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Development of sero-assays to screen for XMRV antibodies in clinical samples
 National Cancer Institute Development of sero-assays to screen for XMRV antibodies in clinical samples Rachel K. Bagni, Ph.D. September 8, 2010 Xentropic murine leukaemia virus-related virus - XMRV The
National Cancer Institute Development of sero-assays to screen for XMRV antibodies in clinical samples Rachel K. Bagni, Ph.D. September 8, 2010 Xentropic murine leukaemia virus-related virus - XMRV The
CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc.
 CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc. Copyright (c) 2018 Cellecta, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents 1. CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator
CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator Assay Kit v1 Last update: 2018/07/04 Cellecta, Inc. Copyright (c) 2018 Cellecta, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Table of Contents 1. CRISPRaTest Functional dcas9-activator
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Human Polyomavirus JC (JCV) Infection of Human B Lymphocytes: A Possible Mechanism for JCV Transmigration across the Blood-Brain Barrier
 MAJOR ARTICLE Human Polyomavirus JC (JCV) Infection of Human B Lymphocytes: A Possible Mechanism for JCV Transmigration across the Blood-Brain Barrier Moti L. Chapagain and Vivek R. Nerurkar Retrovirology
MAJOR ARTICLE Human Polyomavirus JC (JCV) Infection of Human B Lymphocytes: A Possible Mechanism for JCV Transmigration across the Blood-Brain Barrier Moti L. Chapagain and Vivek R. Nerurkar Retrovirology
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Received 4 December 2001/Accepted 29 April 2002
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 2002, p. 8433 8445 Vol. 76, No. 16 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.16.8433 8445.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Relationship
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 2002, p. 8433 8445 Vol. 76, No. 16 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.16.8433 8445.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Relationship
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening
 Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Virology 420 (2011) Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Virology. journal homepage:
 Virology 420 (2011) 66 72 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro No detectable XMRV in subjects with chronic fatigue syndrome from Quebec
Virology 420 (2011) 66 72 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro No detectable XMRV in subjects with chronic fatigue syndrome from Quebec
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
DATA SHEET. Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter calf thymus DNA.
 Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections
 Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
Diagnostic Methods of HBV and HDV infections Zohreh Sharifi,ph.D Blood Transfusion Research Center, High Institute for Research and Education in Transfusion Medicine Hepatitis B-laboratory diagnosis Detection
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Restricted VZV transcription in human trigeminal ganglia
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 June 2012 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01331-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Restricted VZV transcription
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 June 2012 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01331-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Restricted VZV transcription
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Exosome ELISA Complete Kits
 Exosome ELISA Complete Kits EXOEL-CD9A-1, EXOEL-CD63A-1, EXOEL-CD81A-1 User Manual See PAC for Storage Conditions for Individual Components Version 12 4/17/2017 A limited-use label license covers this
Exosome ELISA Complete Kits EXOEL-CD9A-1, EXOEL-CD63A-1, EXOEL-CD81A-1 User Manual See PAC for Storage Conditions for Individual Components Version 12 4/17/2017 A limited-use label license covers this
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
ExoQuick PLUS Exosome Purification Kit for Serum & Plasma
 ExoQuick PLUS Exosome Purification Kit for Serum & Plasma Cat# EQPL10A-1 User Manual Store kit at +4 0 C Version 2 2/22/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product. By use of this product, you
ExoQuick PLUS Exosome Purification Kit for Serum & Plasma Cat# EQPL10A-1 User Manual Store kit at +4 0 C Version 2 2/22/2017 A limited-use label license covers this product. By use of this product, you
Supplementary Materials for
 immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
EML Erythroid and Neutrophil Differentiation Protocols Cristina Pina 1*, Cristina Fugazza 2 and Tariq Enver 3
 EML Erythroid and Neutrophil Differentiation Protocols Cristina Pina 1*, Cristina Fugazza 2 and Tariq Enver 3 1 Department of Haematology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK; 2 Dipartimento de Biotecnologie
EML Erythroid and Neutrophil Differentiation Protocols Cristina Pina 1*, Cristina Fugazza 2 and Tariq Enver 3 1 Department of Haematology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK; 2 Dipartimento de Biotecnologie
ROS Activity Assay Kit
 ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Micropathology Ltd. University of Warwick Science Park, Venture Centre, Sir William Lyons Road, Coventry CV4 7EZ
 www.micropathology.com info@micropathology.com Micropathology Ltd Tel 24hrs: +44 (0) 24-76 323222 Fax / Ans: +44 (0) 24-76 - 323333 University of Warwick Science Park, Venture Centre, Sir William Lyons
www.micropathology.com info@micropathology.com Micropathology Ltd Tel 24hrs: +44 (0) 24-76 323222 Fax / Ans: +44 (0) 24-76 - 323333 University of Warwick Science Park, Venture Centre, Sir William Lyons
Multiple Sources of Contamination in Samples from Patients Reported to Have XMRV Infection
 Multiple Sources of Contamination in Samples from Patients Reported to Have XMRV Infection Mary F. Kearney 1 *, Jonathan Spindler 1, Ann Wiegand 1, Wei Shao 2, Elizabeth M. Anderson 1, Frank Maldarelli
Multiple Sources of Contamination in Samples from Patients Reported to Have XMRV Infection Mary F. Kearney 1 *, Jonathan Spindler 1, Ann Wiegand 1, Wei Shao 2, Elizabeth M. Anderson 1, Frank Maldarelli
A metagenomic approach to investigate the microbial causes of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome: moving beyond XMRV
 Fatigue: Biomedicine, Health & Behavior, 2013 Vol. 1, No. 4, 185 189, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/21641846.2013.812831 EDITORIAL A metagenomic approach to investigate the microbial causes of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic
Fatigue: Biomedicine, Health & Behavior, 2013 Vol. 1, No. 4, 185 189, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/21641846.2013.812831 EDITORIAL A metagenomic approach to investigate the microbial causes of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Guanhan Li. Section of Infections of the Nervous System National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD
 Towards an HIV Cure Pre-Conference Symposium 20 & 21 July 2012 Guanhan Li Section of Infections of the Nervous System National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD Viral Reservoir in Astrocytes Ranki et
Towards an HIV Cure Pre-Conference Symposium 20 & 21 July 2012 Guanhan Li Section of Infections of the Nervous System National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD Viral Reservoir in Astrocytes Ranki et
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
HIV-1 Viral Load Real Time (RG)
 -1 Viral Load Real Time (RG) Real Time RT-PCR type 1 RNA quantification assay MSP Reg. pending Valdense 3616. 11700. Montevideo. Uruguay. phone (598) 2 336 83 01. Fax (598) 2 336 71 60. Info@atgen.com.uy
-1 Viral Load Real Time (RG) Real Time RT-PCR type 1 RNA quantification assay MSP Reg. pending Valdense 3616. 11700. Montevideo. Uruguay. phone (598) 2 336 83 01. Fax (598) 2 336 71 60. Info@atgen.com.uy
Human Cytomegalovirus Infection of Human Embryonic Stem Cell- Derived Primitive Neural Stem Cells is Restricted at Several Steps but
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 22 January 2014 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.03492-13 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 22 January 2014 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.03492-13 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based
 APPrU MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1972, p. 138-142 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based on Enumeration of Inclusion-Containing
APPrU MICROBIOLOGY, JUly 1972, p. 138-142 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 24, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Quantitative Assay of Paravaccinia Virus Based on Enumeration of Inclusion-Containing
OIE Reference Laboratory Reports Activities
 OIE Reference Laboratory Reports Activities Activities in 2017 This report has been submitted : 2018-01-09 09:49:33 Name of disease (or topic) for which you are a designated OIE Reference Laboratory: Classical
OIE Reference Laboratory Reports Activities Activities in 2017 This report has been submitted : 2018-01-09 09:49:33 Name of disease (or topic) for which you are a designated OIE Reference Laboratory: Classical
Fluorescence Microscopy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
hemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes (RNA/recombinant viruses/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis/genetics)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 6, pp. 242-246, June 976 Microbiology Mapping of the influenza virus genome: Identification of the hemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes (RNA/recombinant viruses/polyacrylamide
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 73, No. 6, pp. 242-246, June 976 Microbiology Mapping of the influenza virus genome: Identification of the hemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes (RNA/recombinant viruses/polyacrylamide
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research
 Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research Current Activities Future Directions Washington, DC January 25, 2010 Karen Midthun, MD Acting Director, CBER CBER Our Mission To ensure the safety, purity,
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research Current Activities Future Directions Washington, DC January 25, 2010 Karen Midthun, MD Acting Director, CBER CBER Our Mission To ensure the safety, purity,
Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Prostate Cancer
 DOI 10.1007/s11882-010-0106-2 Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Prostate Cancer James N. Baraniuk # Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2010 Abstract Xenotropic
DOI 10.1007/s11882-010-0106-2 Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Prostate Cancer James N. Baraniuk # Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2010 Abstract Xenotropic
