Dong, B. and Silverman, R.H.
|
|
|
- Gwen Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 November 2009 J. Virol. doi: /jvi Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved. Dong, B. and Silverman, R.H. Androgen Stimulates Transcription and Replication of XMRV (Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus) Beihua Dong and Robert H. Silverman* Department of Cancer Biology, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, 9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44195: Running title: Hormonal control of XMRV growth * Corresponding author: Robert H. Silverman, Cleveland Clinic, 9500 Euclid Avenue NB40, Cleveland, OH Telephone: , Fax: , silverr@ccf.org 1
2 ABSTRACT XMRV is a gammaretrovirus originally identified in a subset of prostate cancer patients. Because androgens stimulate prostate tumors and some retroviruses, we investigated effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on XMRV transcription and replication. Transcription from the XMRV U3 region was stimulated up to 2-fold by DHT, but only in cells containing a functional androgen receptor. Mutations in the glucocorticoid response element (GRE) of XMRV impaired basal transcription and androgen responsiveness. Furthermore, DHT stimulated XMRV replication by 3-fold, whereas androgen inhibitors (casodex and flutamide) suppressed viral growth up to 3-fold. Findings suggest that integration of the XMRV LTR into host DNA could impart androgen stimulation on cellular genes. Downloaded from on October 17, 2018 by guest 2
3 Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV) is an infectious gammaretrovirus identified in tumor-bearing prostates of men homozygous for a reduced activity variant of the antiviral enzyme RNase L(8, 19). More recently, XMRV has also been detected in 67% of chronic fatigue syndrome patients and 3.7% of normal health control individuals(13). A genome-wide analysis of XMRV integration sites in a prostate cancer cell line and in human prostate cancer tissues revealed a preference for transcription start sites, CpG islands, DNase-hypersensitive sites and high gene density regions(10). Furthermore, XMRV integration sites in human prostate DNA showed a preference for cancer-related genes and breakpoints, common fragile sites, and microrna genes. Those findings suggested that XMRV integration might cause dysregulation of select host genes possibly contributing to oncogenesis. In addition, multiple XMRV proviruses were recently identified in human 22Rv1 prostate carcinoma cells, suggesting a role for viral integration in carcinogenesis(11). Transcription of the XMRV genome is mediated by elements in the U3 region of the 5 -long terminal repeat (LTR), a 390 nt segment that includes the core promoter and enhancers (Fig. 1A). Many retroviruses contain glucocorticoid response element(s) (GRE) in the U3 region, including XMRV and other gammaretroviruses such as Moloney MLV (Mo-MLV) and Friend murine leukemia (F-MLV) as well as the betaretrovirus mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV)(2, 3, 17, 19)(Fig. 1B). Viral GREs are stimulated in response to various steroids, including glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, progesterone and androgen(1, 4, 5, 7, 14). Viral GREs often have homology to the classical androgen response element (ARE), a binding site for dimers of the androgen receptor (AR) that consists of an inverted 6 bp repeat separated by a 3 bp spacer (Fig. 1B)(16). There is homology between these viral GREs and AREs in some mammalian 3
4 genes. For example, the first inverted repeat, positions -7 to -2 (AGAACA), in the XMRV GRE is identical to the prostate specific antigen (PSA) ARE1(6). To determine if the XMRV U3 region of the 5 -LTR contains a functional ARE, experiments were performed in human prostate cancer cell line LNCaP which express a functional androgen receptor(12) (Fig. 1C). The reporter plasmid, pgl4.26-xmrv_u3, was constructed by digesting pgl4.26 vector containing firefly luciferase cdna (Promega, Madison, WI) and XMRV clone Vp62-pcDNA3.1(-)(GenBank accession EF185282)(8) with NheI and HindIII and inserting nts 7748 to the end of XMRV into pgl4.26. This segment of the XMRV genome includes all of the U3 region (except for 28 nts at the 5 end) and the R region. Two mutations were generated in the putative ARE: (1) an A to G transition mutation at position -2(agaacA to agaacg) in the GRE(3); and (2) a deletion of the 5 half of the GRE ( AGAACA) (Fig. 1B). QuikChange XL Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit from Stratagene (La Jolla, CA) was used to generate the point mutation with a pair of primers containing sequences producing an A7913 to G mutation and the deletion mutation was generated with primers including a deletion of the sequence AGAACA from nts 7908 to All mutations were confirmed by sequencing. Cells in 12 well plates cultured in hormone-depleted media (phenol red-free RPMI medium 1640 plus 2% charcoal stripped FBS) (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) were cotransfected using lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) with 1.0 µg of WT or mutant pgl4.26- XMRV_U3 and 0.1 µg of prl-pk (encoding Renilla luciferase) for 24 h followed by treating cells with 4,5a-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) in fresh hormone-depleted media. Cells were lysed after 24 h and luciferase assays were performed with Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System kit (Promega, Madison, WI). Firefly luciferase activity from pgl4.26-xmrv_u3 was normalized with Renilla luciferase activity and expressed as relative light units (RLU). Results using LNCaP cells showed 4
5 that induced transcriptional activity from the WT U3 by 100 nm of DHT was %of the control (untreated) activity level, whereas the mutated U3 regions had reduced basal activities (to 56 to 60% of WT U3 activity) and were unresponsive to DHT (Fig. 1D). The Mo-MLV U3 contains a sequence that is highly similar to the GRE in XMRV U3 except for a one nt difference (Fig. 1B). To compare the U3 regions of XMRV with that of Mo-MLV an additional promoter construct was made. The Mo-MLV U3 (nts 7846 to 8332) was prepared by PCR from plasmid p63-2 of Mo-MLV (a gift from H. Fan, University of California, Irvine, CA)(9) and was inserted into pgl4.26 after digestion with NheI and HindIII. The relative activities of the XMRV and Mo-MLV U3 regions were directly compared in human prostate cancer cell lines that express (LNCaP) or lack (DU145) androgen receptor(12)(fig. 2A&B, respectively) in the absence or presence of DHT as determined by luciferase activity. In the LNCaP cells DHT stimulated transcription from both the XMRV U3 and Mo-MLV U3 regions by about 2.0- and 1.8- fold, respectively(fig. 2A). However, the XMRV U3 was 1.6- and 1.8-fold more active than the Mo-MLV promoter in the absence and presence of DHT, respectively. In contrast, neither the XMRV U3 nor the Mo-MLV U3 was stimulated by DHT in the DU145 cells which lack androgen receptor(fig. 2B). These findings are consistent with the our prior observation that XMRV replicates to 4-fold higher levels in LNCaP cells than in DU145 cells(8). To compare the androgen effect on XMRV transcription with that of another steroid hormone, DU145 and LNCaP cells which have a glucocorticoid receptor (Fig. 1C) were plated in hormone-depleted media and transfected with XMRV-U3-pGL4 for 24 h prior to treatment with the glucocorticoid, dexamethasone, for 24 h. Dexamethasone increased the transcription from the XMRV U3 region in both LNCaP and DU145 cells by 1.3- and 1.5-fold, respectively(fig.2c). To investigate the effect of androgen on viral replication, LNCaP cells were cultured in triplicate in 24-well plates in hormone-depleted media for 2 days until cells were fully 5
6 confluent to minimize the effect of DHT on cell numbers. Cells were infected with XMRV in serum- and phenol red-free RPMI with 8 µg/ml polybrene(8). After 3 h incubation, cells were washed once with PBS and treated with DHT in fresh hormone-depleted media for 2 days. Cell numbers were determined and conditioned cell media was collected for RT assays performed with poly(ra) as template and oligo(dt) as primer(18). Relative RT activities of radiolabeled reaction products were determined with a Storm 840 phosphor imager (Sunnyvale, CA). DHT treatment stimulated XMRV replication to % of the control (Fig. 3A). To verify androgen regulation of XMRV replication, the LNCaP cells acutely infected with XMRV in regular RPMI media containing 10% FBS were treated with different concentrations of an anti-androgen, either casodex or flutamide (Fig. 3B&C, respectively). The anti-androgens (at 10 µm) inhibited viral replication as measured by RT activity to % (casodex) and % % (flutamide) of the control. In comparison, DHT slightly increased cell numbers (111+10% of the control) while casodex and flutamide had no effect on cell numbers. In addition to these acute infection experiments, viral expression of RT activity in LNCaP cells chronically-infected with XMRV was stimulated by DHT by more than 3-fold and similarly inhibited by casodex or flutamide (data not shown). Virus replication in DU145 cells was not affected by DHT due to the absence of the androgen receptor in these cells (data not shown). To determine if the XMRV GRE/ARE imparts androgen responsiveness on intact virus, we mutated A to G at position -2 (Figs. 1B&3D) in plasmid encoding full-length XMRV strain VP62. WT and mutant viral stocks were prepared in LNCaP cells as described previously(8). LNCaP cells were infected with either WT or mutant XMRV with polybrene in hormone-depleted media and cultured 3 days in the absence or presence of DHT. Treatment with DHT stimulated WT XMRV replication to % of the control as determined by measuring RT activity in the conditioned media. However, 6
7 DHT had no effect on the replication of XMRV with the single-base mutation (A->G) at position -2 in the GRE/ARE (Fig. 3D). Our findings show the presence of a functional androgen response element (ARE) in the U3 region of the XMRV LTR. The XMRV ARE sequence (AGAACAGATGGTCCT) is conserved among different XMRV strains(19). Inhibition of XMRV replication by antiandrogens suggests that viral growth could also be suppressed in XMRV-infected prostate cancer patients during androgen ablation therapy. Recently, we reported that XMRV integration sites in human prostate tumors include many cancer-related genes(8, 10). XMRV has a strong preference for integrating near transcriptional start sites possibly imposing androgen responsiveness on host genes. XMRV has been observed in both prostatic stromal (19) and epithelial carcinoma cells(11, 15). Therefore, XMRV integration into stromal and epithelial cells could cause androgen-stimulation of proinflammatory genes and proto-oncogenes leading to cancer. In addition, because the androgen receptor is expressed in prostatic cells these findings could also help to explain why XMRV infections localize to prostate. 7
8 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thank Dr. Hung Fan (Irvine, CA) for the gift of Mo-MLV cdna. This study was supported by grants CA from the NCI/NIH, Charlotte Geyer Foundation, V Foundation for Cancer Research and the Mal and Lea Bank Chair fund. Downloaded from on October 17, 2018 by guest 8
9 FIGURE LEGENDS FIG. 1. Functional analysis of the XMRV GRE in LNCaP cells. (A) Map of the XMRV 5 - LTR and promoter-luciferase construct. (B) Comparison of classical ARE with viral GREs, mutant XMRV GREs, and human PSA ARE1 ( *, indicates deleted nts). (C) Western blot for androgen receptor (AR) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in DU145 and LNCaP cells. Cell extracts (60 µg) were used and the blot was probed with rabbit antiandrogen receptor antibody and followed by reprobing with rabbit anti-glucocorticoid receptor antibody (both from Santa Cruz, Inc.) after stripping. Antibody against β actin (Sigma-Aldrich) was used. (D) LNCaP cells were transfected with either wild type (WT) or mutant XMRV U3 (as indicated) fused with firefly luciferase cdna in combination with Renilla luciferase cdna for normalization of data. Relative light units (RLU) were determined by dividing firefly luciferase activity by Renilla luciferase activity after culturing in the absence or presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) for 24 h in hormonedepleted media with 2% charcoal-stripped FBS. Experiments were reproduced two times and analyses were performed in triplicate and standard deviations (SD) were calculated. *, p value< 0.05 as determined by two-tailed, paired Student s t test. FIG. 2. Androgen stimulates transcription from the XMRV and Mo-MLV U3 regions in (A) LNCaP but not in (B) DU145 cells and (C) dexamethasone stimulates transcription of XMRV-U3 in both cell types. Cells were transfected with either the XMRV U3 or Mo- MLV U3 each fused to firefly luciferase cdna. (A & B) DHT and (C) dexamethasone treatments were for 24 h at the concentration indicated (x axis) in hormone-depleted media with 2% charcoal-stripped FBS. RLUs were determined by normalizing with 9
10 Renilla luciferase activity expressed from plasmid prl. Experiments were reproduced two times. Error bars represent SD. *, p < 0.05 and **, p < 0.01 as determined by twotailed, paired Student s t test. FIG. 3. XMRV replication is stimulated by androgen and suppressed by anti-androgens. LNCaP cells were cultured in 24 well plates with RPMI media + 10% FBS for 2 days until cells were fully confluent. Cells were infected with XMRV in the presence of 8 µg polybrene/ml for 3 h followed by washing the cells with PBS and treatment with (A) DHT (0.01 to 100 nm) in hormone-depleted media for 2 days, (B) casodex (0.1 to 10 µm) or (C) flutamide (0.1 to 10 µm) in RPMI media + 10% FBS for 4 days. (D) Comparison of effects of DHT on acute infections with WT XMRV and A G GRE mutant XMRV in LNCaP cells. Experiments were done as described for panel (A) except infections were for 3 days. Experiments were repeated two or three times and each individual experiment was done in triplicate. RT activities were determined with conditioned cell media. Cell numbers shown are per well. Error bars represent SD. *, p < 0.05 and **,p value < 0.01 as determined by two-tailed, paired Student s t test.. 10
11 REFERENCES 1. Arriza, J. L., C. Weinberger, G. Cerelli, T. M. Glaser, B. L. Handelin, D. E. Housman, and R. M. Evans Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science 237: Belikov, S., C. Astrand, and O. Wrange Mechanism of histone H1- stimulated glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 27: Bruland, T., L. A. Lavik, H. Y. Dai, and A. Dalen A glucocorticoid response element in the LTR U3 region of Friend murine leukaemia virus variant FIS-2 enhances virus production in vitro and is a major determinant for sex differences in susceptibility to FIS-2 infection in vivo. J Gen Virol 84: Cato, A. C., D. Henderson, and H. Ponta The hormone response element of the mouse mammary tumour virus DNA mediates the progestin and androgen induction of transcription in the proviral long terminal repeat region. EMBO J 6: Cato, A. C., R. Miksicek, G. Schutz, J. Arnemann, and M. Beato The hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumour virus mediates progesterone induction. EMBO J 5: Cleutjens, K. B., C. C. van Eekelen, H. A. van der Korput, A. O. Brinkmann, and J. Trapman Two androgen response regions cooperate in steroid hormone regulated activity of the prostate-specific antigen promoter. J Biol Chem 271: Darbre, P., M. Page, and R. J. King Androgen regulation by the long terminal repeat of mouse mammary tumor virus. Mol Cell Biol 6:
12 8. Dong, B., S. Kim, S. Hong, J. Das Gupta, K. Malathi, E. A. Klein, D. Ganem, J. L. Derisi, S. A. Chow, and R. H. Silverman An infectious retrovirus susceptible to an IFN antiviral pathway from human prostate tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: Feuerman, M. H., B. R. Davis, P. K. Pattengale, and H. Fan Generation of a recombinant Moloney murine leukemia virus carrying the v-src gene of avian sarcoma virus: transformation in vitro and pathogenesis in vivo. J Virol 54: Kim, S., N. Kim, B. Dong, D. Boren, S. A. Lee, J. Das Gupta, C. Gaughan, E. A. Klein, C. Lee, R. H. Silverman, and S. A. Chow Integration site preference of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus, a new human retrovirus associated with prostate cancer. J Virol 82: Knouf, E. C., M. J. Metzger, P. S. Mitchell, J. D. Arroyo, J. R. Chevillet, M. Tewari, and A. D. Miller Multiple Integrated Copies and High-Level Production of the Human Retrovirus XMRV from 22Rv1 Prostate Carcinoma Cells. J Virol. 12. Litvinov, I. V., L. Antony, S. L. Dalrymple, R. Becker, L. Cheng, and J. T. Isaacs PC3, but not DU145, human prostate cancer cells retain the coregulators required for tumor suppressor ability of androgen receptor. Prostate 66: Lombardi, V. C., F. W. Ruscetti, J. Das Gupta, M. A. Pfost, K. S. Hagen, D. L. Peterson, S. K. Ruscetti, R. K. Bagni, C. Petrow-Sadowski, B. Gold, M. Dean, R. H. Silverman, and J. A. Mikovits Detection of an Infectious Retrovirus, XMRV, in Blood Cells of Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Science. 12
13 14. Miksicek, R., A. Heber, W. Schmid, U. Danesch, G. Posseckert, M. Beato, and G. Schutz Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell 46: Schlaberg, R., D. J. Choe, K. R. Brown, H. M. Thaker, and I. R. Singh XMRV is present in malignant prostatic epithelium and is associated with prostate cancer, especially high-grade tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: Shaffer, P. L., A. Jivan, D. E. Dollins, F. Claessens, and D. T. Gewirth Structural basis of androgen receptor binding to selective androgen response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: Shinnick, T. M., R. A. Lerner, and J. G. Sutcliffe Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature 293: Telesnitsky, A., S. Blain, and S. P. Goff Assays for retroviral reverse transcriptase. Methods Enzymol 262: Urisman, A., R. J. Molinaro, N. Fischer, S. J. Plummer, G. Casey, E. A. Klein, K. Malathi, C. Magi-Galluzzi, R. R. Tubbs, D. Ganem, R. H. Silverman, and J. L. Derisi Identification of a Novel Gammaretrovirus in Prostate Tumors of Patients Homozygous for R462Q RNASEL Variant. PLoS Pathog 2:e25. 13
14
15
16
TITLE: Examination of a Newly Discovered Human Retrovirus, XMRV, in Breast Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0464 TITLE: Examination of a Newly Discovered Human Retrovirus, XMRV, in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Wayne State
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0464 TITLE: Examination of a Newly Discovered Human Retrovirus, XMRV, in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Wayne State
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
VIRUSES AND CANCER Michael Lea
 VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
*To whom correspondence should be addressed. This PDF file includes:
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1212182/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partial Retraction to Detection of an Infectious Retrovirus, XMRV, in Blood Cells of Patients with Chronic Fatigue
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1212182/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Partial Retraction to Detection of an Infectious Retrovirus, XMRV, in Blood Cells of Patients with Chronic Fatigue
XMRV among Prostate Cancer Patients from the Southern United States and Analysis of Possible Correlates of Infection
 XMRV among Prostate Cancer Patients from the Southern United States and Analysis of Possible Correlates of Infection Bryan Danielson Baylor College of Medicine Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology
XMRV among Prostate Cancer Patients from the Southern United States and Analysis of Possible Correlates of Infection Bryan Danielson Baylor College of Medicine Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology
TITLE: The Role of XMRV, a Novel Xenotropic Murine Retrovirus, in Human Prostate Cancers
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0387 TITLE: The Role of XMRV, a Novel Xenotropic Murine Retrovirus, in Human Prostate Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Stephen P. Goff CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0387 TITLE: The Role of XMRV, a Novel Xenotropic Murine Retrovirus, in Human Prostate Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Stephen P. Goff CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Susceptibility of human primary neuronal cells to Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-related (XMRV) virus infection.
 Virology Journal This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Susceptibility of human primary
Virology Journal This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Susceptibility of human primary
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Tsukasa; Sakai, Hideki; Kubo, Yoshi. Biophysical Research Communications
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Androgen-independent proliferation infected by xenotropic murine leuke Kakoki, Katsura; Kamiyama, Haruka; Hayashi, Hideki; Yamamoto, Naoki; M
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Androgen-independent proliferation infected by xenotropic murine leuke Kakoki, Katsura; Kamiyama, Haruka; Hayashi, Hideki; Yamamoto, Naoki; M
Detecting Retroviral Sequences in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Viruses 2010, 2, 2404-2408; doi:10.3390/v2112404 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Detecting Retroviral Sequences in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Ila R. Singh Department
Viruses 2010, 2, 2404-2408; doi:10.3390/v2112404 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Detecting Retroviral Sequences in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Ila R. Singh Department
Research Article Lack of Detection of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in HIV-1 Lymphoma Patients
 Advances in Virology Volume 2011, Article ID 797820, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/797820 Research Article Lack of Detection of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in HIV-1 Lymphoma Patients Krista
Advances in Virology Volume 2011, Article ID 797820, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/797820 Research Article Lack of Detection of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in HIV-1 Lymphoma Patients Krista
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Picture of cell art Picture of cell under a microscope Daniel L. Peterson, MD Whittemore Peterson Institute
 XMRV, A New Human Pathogenic Retrovirus: Detection In Chronic Diseases Picture of cell art Picture of cell under a microscope Daniel L. Peterson, MD Whittemore Peterson Institute Daniel L. Peterson, MD
XMRV, A New Human Pathogenic Retrovirus: Detection In Chronic Diseases Picture of cell art Picture of cell under a microscope Daniel L. Peterson, MD Whittemore Peterson Institute Daniel L. Peterson, MD
CANCER. Inherited Cancer Syndromes. Affects 25% of US population. Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease)
 CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
CANCER Affects 25% of US population Kills 19% of US population (2nd largest killer after heart disease) NOT one disease but 200-300 different defects Etiologic Factors In Cancer: Relative contributions
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
The prostate cancer-associated human retrovirus XMRV lacks. direct transforming activity but can induce low rates. of transformation in cultured cells
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 December 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01941-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 December 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01941-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
Retroviruses. ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase.
 Retroviruses ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase. ---Reverse transcriptase (RT) converts the RNA genome present in the virus particle into DNA. ---RT discovered in 1970.
Retroviruses ---The name retrovirus comes from the enzyme, reverse transcriptase. ---Reverse transcriptase (RT) converts the RNA genome present in the virus particle into DNA. ---RT discovered in 1970.
The Prostate Cancer-Associated Human Retrovirus XMRV Lacks Direct Transforming Activity but Can Induce Low Rates of Transformation in Cultured Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2010, p. 1874 1880 Vol. 84, No. 4 0022-538X/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.01941-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Prostate Cancer-Associated
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2010, p. 1874 1880 Vol. 84, No. 4 0022-538X/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.01941-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Prostate Cancer-Associated
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Infect Dis. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 November 15.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Infect Dis. 2010 November 15; 202(10): 1478 1481. doi:10.1086/657168. XMRV Prevalence in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Infect Dis. 2010 November 15; 202(10): 1478 1481. doi:10.1086/657168. XMRV Prevalence in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
VIROLOGY. Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors
 VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay
 Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes ~ 4.6 -
 Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Severe Restriction of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus Replication and Spread in Cultured Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May, p. 4888 4897 Vol. 85, No. -538X//$. doi:.8/jvi.46- Copyright, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Severe Restriction of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May, p. 4888 4897 Vol. 85, No. -538X//$. doi:.8/jvi.46- Copyright, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Severe Restriction of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen
 Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
/06/$15.00/0 Molecular Endocrinology 20(9): Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: /me
 0888-8809/06/$15.00/0 Molecular Endocrinology 20(9):2062 2079 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0316 Androgens, Progestins, and Glucocorticoids Induce Follicle-Stimulating
0888-8809/06/$15.00/0 Molecular Endocrinology 20(9):2062 2079 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0316 Androgens, Progestins, and Glucocorticoids Induce Follicle-Stimulating
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Insertional Oncogenesis by Non-Acute Retroviruses: Implications for Gene Therapy
 Viruses 2011, 3, 398-422; doi:10.3390/v3040398 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Review Insertional Oncogenesis by Non-Acute Retroviruses: Implications for Gene Therapy Hung
Viruses 2011, 3, 398-422; doi:10.3390/v3040398 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Review Insertional Oncogenesis by Non-Acute Retroviruses: Implications for Gene Therapy Hung
DATA SHEET. Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter calf thymus DNA.
 Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
No Evidence of Murine-Like Gammaretroviruses in CFS Patients Previously Identified as XMRV-Infected
 No Evidence of Murine-Like Gammaretroviruses in CFS Patients Previously Identified as XMRV-Infected Konstance Knox, 1,2 Donald Carrigan, 1,2 Graham Simmons, 3,4 Fernando Teque, 5 Yanchen Zhou, 3,4 John
No Evidence of Murine-Like Gammaretroviruses in CFS Patients Previously Identified as XMRV-Infected Konstance Knox, 1,2 Donald Carrigan, 1,2 Graham Simmons, 3,4 Fernando Teque, 5 Yanchen Zhou, 3,4 John
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 RETROVIRUSES. 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
 1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
Integration Site Preference of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus, a New Human Retrovirus Associated with Prostate Cancer
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2008, p. 9964 9977 Vol. 82, No. 20 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01299-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Integration Site Preference
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2008, p. 9964 9977 Vol. 82, No. 20 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01299-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Integration Site Preference
TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Audrey van Drogen, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Sidney
AD Award Number: TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Audrey van Drogen, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Sidney
Suppression of 5 -androstenediol-induced androgen receptor transactivation by selective steroids in human prostate cancer cells
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 11173 11177, September 1999 Biochemistry Suppression of 5 -androstenediol-induced androgen receptor transactivation by selective steroids in human prostate cancer
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 11173 11177, September 1999 Biochemistry Suppression of 5 -androstenediol-induced androgen receptor transactivation by selective steroids in human prostate cancer
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplemental Data. Short Article. ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1. Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival. under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 7 Supplemental Data Short Article ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1 Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Suguru Yamaguchi, Hisamitsu Ishihara,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 7 Supplemental Data Short Article ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1 Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Suguru Yamaguchi, Hisamitsu Ishihara,
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Generation of molecular standard for quantitative PCR
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
TITLE: Investigating the Role of TBX2 in the Inhibition of Senescence in Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0155 TITLE: Investigating the Role of TBX2 in the Inhibition of Senescence in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Srinivas Nandana CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0155 TITLE: Investigating the Role of TBX2 in the Inhibition of Senescence in Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Srinivas Nandana CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Vanderbilt
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of
 Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Paper Title: Sexual transmission of XMRV: a potential infection route
 Paper Title: Sexual transmission of XMRV: a potential infection route Authors: Prachi Sharma 1, @ (psharm9@emory.edu) Kenneth A. Rogers 1, (kroger3@emory.edu) Suganthi Suppiah 2 (ssuppi2@emory.edu) Ross
Paper Title: Sexual transmission of XMRV: a potential infection route Authors: Prachi Sharma 1, @ (psharm9@emory.edu) Kenneth A. Rogers 1, (kroger3@emory.edu) Suganthi Suppiah 2 (ssuppi2@emory.edu) Ross
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Activation of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Transcription in T Cells Revisited: NF- B p65 Stimulates Transcriptional Elongation
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2001, p. 8524 8537 Vol. 75, No. 18 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.18.8524 8537.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activation
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2001, p. 8524 8537 Vol. 75, No. 18 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.18.8524 8537.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activation
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
NF-κB Activation Stimulates Transcription and Replication of. Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus in Human B-lineage
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 26 January 2011 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.02333-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 26 January 2011 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.02333-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
viruses ISSN
 Viruses 2011, 3, 1312-1319; doi:10.3390/v3081312 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Origin of XMRV and its Demise as a Human Pathogen Associated with Chronic Fatigue
Viruses 2011, 3, 1312-1319; doi:10.3390/v3081312 OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses Commentary Origin of XMRV and its Demise as a Human Pathogen Associated with Chronic Fatigue
Complementation of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Replication by Intracellular Selection of Escherichia coli trna 3 Lys Supplied in trans
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9641 9650 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00709-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Complementation of Human
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2006, p. 9641 9650 Vol. 80, No. 19 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00709-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Complementation of Human
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
Name Section Problem Set 6
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed of lipids
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed of lipids
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described
 Supplemental Methods In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described previously 1 2 using 32P-labeled 211 bp fragment from 3 HS1. Footprinting reaction mixes contained
Supplemental Methods In vitro DNase I foot printing. In vitro DNase I footprinting was performed as described previously 1 2 using 32P-labeled 211 bp fragment from 3 HS1. Footprinting reaction mixes contained
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Bhatnagar et al, 2010 Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS T
 Bhatnagar et al, Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS--98-T Supplemental Materials. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure (A) WPE-NA and WPE-NB6 cells were treated with 4 nm of Docetaxel
Bhatnagar et al, Cell Death and Disease Manuscript # CDDIS--98-T Supplemental Materials. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure (A) WPE-NA and WPE-NB6 cells were treated with 4 nm of Docetaxel
~Lentivirus production~
 ~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
Retroviruses: Endogenous MLV and XMRV
 Retroviruses: Endogenous MLV and XMRV John M. Coffin Tufts University Tufts University The Retrovirus Family Tree Virus Genus bel1, bel2 tat, rev orfa, orfb, orfc HFV MLV FeLV HERV-C WDS HIV-1 HIV-2 EIAV
Retroviruses: Endogenous MLV and XMRV John M. Coffin Tufts University Tufts University The Retrovirus Family Tree Virus Genus bel1, bel2 tat, rev orfa, orfb, orfc HFV MLV FeLV HERV-C WDS HIV-1 HIV-2 EIAV
Activation of Gene Expression by Human Herpes Virus 6
 Activation of Gene Expression by Human Herpes Virus 6 M. E. M. Campbell and S. McCorkindale 1 Introduction Human herpes virus type 6 (HHV-6) was first detected by Salahuddin et al. [6] and has been isolated
Activation of Gene Expression by Human Herpes Virus 6 M. E. M. Campbell and S. McCorkindale 1 Introduction Human herpes virus type 6 (HHV-6) was first detected by Salahuddin et al. [6] and has been isolated
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Inhibition of Xenotropic Murine Leukemia Virus-Related Virus by APOBEC3 Proteins and Antiviral Drugs
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2010, p. 5719 5729 Vol. 84, No. 11 0022-538X/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00134-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Inhibition of Xenotropic
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2010, p. 5719 5729 Vol. 84, No. 11 0022-538X/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00134-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Inhibition of Xenotropic
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems
 ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems Jumpstart your research with ViraPower Lentiviral Expression Systems With ViraPower Lentiviral Systems you can: Efficiently transduce both dividing and non-dividing
Supplemental Figure 1
 1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
Qin Yu and Casey D. Morrow 1. Department of Microbiology, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama 35294
 Virology 254, 160 168 (1999) Article ID viro.1998.9542, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Complementarity between 3 Terminal Nucleotides of trna and Primer Binding Site Is a Major Determinant
Virology 254, 160 168 (1999) Article ID viro.1998.9542, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Complementarity between 3 Terminal Nucleotides of trna and Primer Binding Site Is a Major Determinant
Multiple Sources of Contamination in Samples from Patients Reported to Have XMRV Infection
 Multiple Sources of Contamination in Samples from Patients Reported to Have XMRV Infection Mary F. Kearney 1 *, Jonathan Spindler 1, Ann Wiegand 1, Wei Shao 2, Elizabeth M. Anderson 1, Frank Maldarelli
Multiple Sources of Contamination in Samples from Patients Reported to Have XMRV Infection Mary F. Kearney 1 *, Jonathan Spindler 1, Ann Wiegand 1, Wei Shao 2, Elizabeth M. Anderson 1, Frank Maldarelli
Materials and Methods , The two-hybrid principle.
 The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Data Sheet IL-2-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog # 60481
 642 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Tel: 1.858.829.382 Data Sheet IL-2-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog # 6481 Description Human IL-2 reporter construct is stably integrated into the genome
642 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Tel: 1.858.829.382 Data Sheet IL-2-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog # 6481 Description Human IL-2 reporter construct is stably integrated into the genome
Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus: current research, disease associations and therapeutic opportunities
 Perspective Review Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus: current research, disease associations and therapeutic opportunities Despite the fact that xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus
Perspective Review Xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus: current research, disease associations and therapeutic opportunities Despite the fact that xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Certificate of Analysis
 Certificate of Analysis plvx-ef1α-ires-puro Vector Table of Contents Product Information... 1 Description... 2 Location of Features... 3 Additional Information... 3 Quality Control Data... 4 Catalog No.
Certificate of Analysis plvx-ef1α-ires-puro Vector Table of Contents Product Information... 1 Description... 2 Location of Features... 3 Additional Information... 3 Quality Control Data... 4 Catalog No.
Construction and Characterization of a Hybrid Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus/Murine Leukemia Virus-Based Retroviral Vector
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 1998, p. 1699 1703 Vol. 72, No. 2 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Construction and Characterization of a Hybrid Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus/Murine
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 1998, p. 1699 1703 Vol. 72, No. 2 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Construction and Characterization of a Hybrid Mouse Mammary Tumor Virus/Murine
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0392 TITLE: The Role of Notch Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Annapoorni Rangarajan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indian Institute
AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0392 TITLE: The Role of Notch Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Annapoorni Rangarajan, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Indian Institute
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the
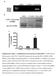 Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN No Treatment. EZN-3920, 2 μm. Time, h
 Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
A Report from the 9th Hemispherx Biopharma Investigators Meeting
 XMRV & AMPLIGEN A Report from the 9th Hemispherx Biopharma Investigators Meeting HUNTER HOPKINS CENTER Hunter-Hopkins ME-letter March 2011 http://www.drlapp.net/melettermar2011.htm Hunter-Hopkins Center,
XMRV & AMPLIGEN A Report from the 9th Hemispherx Biopharma Investigators Meeting HUNTER HOPKINS CENTER Hunter-Hopkins ME-letter March 2011 http://www.drlapp.net/melettermar2011.htm Hunter-Hopkins Center,
Next generation sequencing of prostate tumours provides independent evidence of XMRV contamination
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 December 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06170-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 December 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06170-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
