A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
|
|
|
- Willis Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: DOI /s REVIEW ARTICLE A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis Jayanta M. Barua 1,2 & Ignacio Arance 3 & Javier C. Angulo 3 & Claus R. Riedl 4 Received: 24 June 2015 /Accepted: 2 November 2015 /Published online: 20 November 2015 # The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Abstract Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/ IC) is a chronic disease characterised by persistent irritating micturition symptoms and pain. The objective was to compare the clinical efficacy of currently available products for intravesical therapy of BPS/IC and to assess their pharmacoeconomic impact. A Pubmed/Medline database search was performed for articles on intravesical therapy for BPS/IC. A total of 345 publications were identified, from which 326 were excluded. Statistical evaluation was performed with effect size (ES) assessment of symptom reduction and response rates. The final set of 19 articles on intravesical BPS/IC therapy included 5 prospective controlled trials (CTs), the remaining were classified as uncontrolled clinical studies. The total number of patients included was 801, 228 of whom had been evaluated in a CT. For CTs, the largest ES for symptom reduction as well as response rate was observed for high molecular weight hyaluronic acid (HMW-HA), with similar findings in two uncontrolled studies with HMW-HA. The number needed to treat to achieve a response to intravesical therapy was 2.67 for intravesical pentosan polysulphate and 1.31 for HMW-HA which were superior to all other instillates. * Claus R. Riedl riedlc@compuserve.com King George Hospital (BHRUT), Ilford, UK Barts and the London School of Medicine & Dentistry, QMUL, London, UK Servicio de Urología, Hospital Universitario de Getafe, Universidad Europea de Madrid, Madrid, Spain Department of Urology, Landesklinikum Thermenregion, Wimmergasse 19, 2500 Baden, Austria HMW-HA was significantly superior in cost effectiveness and cost efficacy to all other instillation regimes. The present meta-analysis combined medical and pharmacoeconomic aspects and demonstrated an advantage of HMW-HA over other instillation agents; however, direct comparisons between the different products have not been performed to date in properly designed controlled studies. Keywords Bladder pain syndrome. Interstitial cystitis. Intravesical instillation. Hyaluronic acid Abbreviations BPS/IC Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis ChS Chondroitin sulphate CT Controlled trial DMSO Dimethyl sulfoxide ES Effect size ESSIC International Society for the Study of BPS FDA Food and drug administration GAG Glycosaminoglycans HA Hyaluronic acid HMW High molecular weight LMW Low molecular weight MW Molecular weight NIDDK National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NNT Number needed to treat PPS Pentosan polysulphate PST Potassium sensitivity test RR Response rate UCT Uncontrolled trial VAS Visual analogue scale
2 1138 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Introduction Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is a chronic disease characterised by persistent irritating micturition symptoms and pain [1]. While there is no general agreement on the precise pathophysiology of this disease, a disorder at the level of the urine tissue barrier of the bladder seems to be the underlying mechanism behind the functional, anatomical and symptomatic manifestations in a considerable number of cases. Even if study results are not entirely consistent and, therefore, the subject is not closed, a defect in the protective bladder s mucous lining of glycosaminoglycans (GAG) and, thus, the urine tissue barrier, has been documented in a subset of BPS/IC patients [2], mainly demonstrated by a positive potassium sensitivity test (PST) [3 6] and the favourable response to GAG-restoring agents. Glycosaminoglycans are classified in four structural families [7] (heparin and heparan sulphates; chondroitin and dermatan sulphates; hyaluronan; and keratan sulphate) and have been used during the last few decades as intravesical instillations for GAG substitution therapy with the benefit of delivering high concentrations of the therapeutic agent at the target tissue with a low risk of systemic side effects [8]. The diversity of available therapeutic agents for GAG substitution may make it difficult for physicians to choose the optimal treatment for their patients [9, 10]; therefore, the selection of a particular therapeutic regimen should be based on its capacity for symptom improvement, its impact on the patient s quality of life, and its costs [10]. Heparin has commonly been used off-label for BPS/IC therapy. Pentosan polysulphate (PPS), a semisynthetic heparin-like GAG of low molecular weight (MW) classically used for oral therapy of BPS/IC, is also available for intravesical instillation. Today, hyaluronan, the salt of hyaluronic acid (HA), and chondroitin sulphate (ChS) are the two most commonly used GAGs for intravesical treatment, alone or in combination. Other intravesical instillations containing anaesthetic solutions, such as lidocaine and bupivacaine, are also used in combination with sodium bicarbonate to control bladder pain [11], while dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), which has a putative effect on the sensory peripheral nerves of the bladder [12], is the only intravesical therapy approved by the FDA. At present, eight agents for intravesical BPS/IC therapy are commercially available in Europe (Table 1) Despite the widespread clinical use of each of these substances, the research-based evidence regarding therapeutic efficacy is limited and mainly based on uncontrolled trials. Levels of evidence for the use of these agents have been rated 1b for PPS and heparin, and 2b for HA and ChS in their different concentrations [13]. Table 1 Intravesical agents for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) therapy, their registered trade names and pharmacological composition Intravesical agent Registered trade name The aim of this meta-analytical review is to directly compare the data on the clinical efficacy of products currently available for intravesical BPS/IC therapy and to assess their pharmacoeconomic impact to assist in therapeutic decisionmaking. Materials and methods Literature search Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta- Analyses (PRISMA) [14] guidelines were used to perform a comprehensive search for literature on intravesical therapy for BPS/IC and published in the PubMed/Medline database from 1996 to The Medical Subject Heading (MESH) search terms used were: interstitial cystitis, bladder pain syndrome, intravesical treatment, intravesical chondroitin sulphate, intravesical hyaluronan, intravesical PPS, intravesical DMSO, and intravesical lidocaine. Selection criteria Composition HA Cystistat 40 mg HMW-HA (0.08 %) in 50 ml Hyacyst 40/120 mg HA (0.08/0.24 %) in 50 ml (MW unknown) Uromac 100 mg LMW HA (0.2 %) in 50 ml CS Gepan instill 80 mg CS (0.2 %) in 40 ml Uracyst 400 mg CS (2 %) in 20 ml HA/CS Ialuril 800 mg LMW-HA (1.6 %) / 1 g CS (2 %) in 50 ml PPS a Cyst-u-ron 300 mg PPS (1 %) in 30 ml DMSO Rimso g DMSO (5.4 %) in 50 ml HA hyaluronan, CS chondroitin sulphate, PPS pentosan polysulphate sodium, DMSO dimethyl sulfoxide, HMW high molecular weight, MW molecular weight, LMW low molecular weight a Elmiron is the oral form of pentosan polysulphate sodium (100 mg) The PubMed/Medline search allowed us to identify publications regarding intravesical treatment for BPS/IC. From these, only studies in English or Spanish reporting clinical results were reviewed. Further analysis included only studies with a single compound or a fixed commercially available combination. Studies were excluded if they: 1. Were performed using intravesical Bcocktails^ 2. Did not evaluate intravesical treatment for BPS/IC
3 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Assessed other related topics, but did not evaluate treatment efficacy (case reports, conference reports etc.) 4. Were defined as review or meta-analysis papers Data extraction and statistical analysis Data were extracted from each publication by two independent reviewers (CLL and AMG) and included: type of study according to the presence of a control arm (controlled or uncontrolled clinical trials), randomisation (randomised or nonrandomised controlled trials) and observational studies (prospective or retrospective), type of intravesical solution, total of patients at baseline (intention-to-treat analysis), total patients treated (per protocol analysis), number of patients lost to follow-up, therapy regimen (total number of instillations/ frequency of application), instruments/scales used for evaluation of symptoms before and after treatment, and response rates (RR), considered as the percentage of patients with symptom reduction after therapy out of the total study sample [15]. In the absence of an explicitly cited definition for RR, and according previous publications [16, 17], a reduction of 2 on a visual analogue scale (VAS) was considered to be a response to treatment; the percentage of responders was inferred by calculating the z value, defined as the proportion of responders within confidence intervals at 95 % (CI 95 %). The different products were compared with regard to the average reduction of bladder symptoms on the VAS and the overall response rates by calculation of BCohen s d^ [18], a statistical value for effect size (ES) based on differences between mean values and the average difference in the proportion of patients with a response to treatment and allows the difference between the two groups to be quantified using the standard deviation. While the broadly accepted and cited p value informs whether an effect from the investigated measure exists, it does not reveal the size of the effect. For Cohen s d,a low value<0.5 shows a small ES, d values>1 are regarded as large ES. From the CTs, a post-hoc calculation of a composite VAS/ RR odds ratio (OR) allowed the comparison of results of different intravesical agents with the placebo/control-treated arms. These values were also used to calculate the number of patients needed to treat (NNT) to obtain a response. Finally, the pharmacoeconomic assessment was performed by multiplying the unit costs by the number of instillations administered in each CT. Costs per unit and frequency of instillation (one per week) are very similar for HA and ChS products; thus, a cost factor of 1 has been assigned for these two therapies. PPS is less expensive (instillation units cost 40 % of HA/ChS, oral therapy 20 %), but has to be administered two or three times per week and may be accompanied by oral therapy, Thus, a cost factor of 0.4 for intravesical/0.6 for intravesical and oral therapy has been assumed for PPS trials. Results The Medline search led to a total of 345 hits. Initially, all titles and abstracts were reviewed to identify studies not directly reporting on BPS/IC or intravesical treatment for BPS/IC, reviews, and other type of publications not suitable for this analysis. From the 33 studies selected according to the outlined criteria, 11 (33.33 %) assessed intravesical therapy with HMW-HA 0.08 % (of which one paper also evaluated intravesical heparin), 7 studies presented the results of ChS 0.2 % therapy (21.21 %), and 3 studies evaluated treatment with ChS 2.0 % (9.09 %). Results of the combined formulation of LMW-HA + ChS 2.0 % were presented in 4 publications (12.12 %), 3 papers assessed the results of intravesical treatment with PPS (9.09 %), 2 with lidocaine (6.06 %), and another 3 articles reported results with DMSO (9.09 %). No publications on LMW-HA alone for the treatment of BPS/IC were retrieved from the search. The main criteria for the exclusion of studies were reports on combination therapies with non-gag substances, duplicity of results (same sample of patients), and results not comparable in a standardised way because of the different instruments used for outcome evaluation. Thus, 2 of the articles on HMW-HA therapy were excluded from further analysis because they involved combination with alkalised lidocaine [19] or oral PPS [20]. Similarly, 2 publications on DMSO were excluded because of combination therapies (DMSO + hydrocortisone + heparin sulphate [21] and DMSO + triamcinolone [22]). One study with the combination of LMW-HA 1.6 % + ChS 2.0 % [23] was excluded owing to obvious coincidences with another publication [24]. The majority of the selected publications referred to BPS/ IC therapy, except for 2 papers on ChS 0.2 %, which evaluated the product in patients with overactive bladder [25, 26] and for the prophylaxis of radiation cystitis [27]; 2 of the excluded articles reported on the efficacy of a combination of heparin and lidocaine as an acute analgesic intervention for severe pain [28, 29]. Two publications on HMW-HA 0.08 % therapy were excluded because they evaluated symptoms with different nonstandardised scales [30, 31], and in one study in which patients received intravesical instillations with LMW-HA 1.6 % + ChS 2.0 % data on VAS pain scores were missing [32]. The full text version of one publication for ChS 0.2 % [33] could not be found after searching several databases. In summary, 14 publications were excluded (Fig. 1). The final set of 19 articles on intravesical BPS/IC therapy was further qualitatively and quantitatively analysed: 5 studies were prospective controlled trials [34 38], 1 compared different intravesical products [39], 1 paper was designed as a retrospective study [40],andanother1compared two different regimens of the same product [41]. The
4 1140 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: procedure-related discomfort and to improve the retention of the subsequently instilled PPS [38]. Evaluation of efficacy Fig. 1 Selection process of the studies included for analysis rest of the trials were classified as uncontrolled clinical studies (Table 2). Patients characteristics The final sample of 19 trials corresponds to a total of 801 patients, with 228 patients evaluated in a CT. Only 4 trials included male and female patients [15, 35, 44, 45], while the rest of the studies exclusively included women. Diagnosis of BPS/IC has been made according to NIDDK/ National Institutes of Health criteria in most studies (one including cystoscopic examination [42]), except for three publications (ESSIC criteria [40], the East Asian guidelines [41] or clinical perception plus cystoscopy [38]). Other relevant differences were also detected: six of the studies included Btreatment-refractory patients^, considered to be cases with an inadequate response to previous BPS/IC treatments such as intravesical DMSO [15], heparin and/or PPS [15, 41] and/or oral drug therapy [24, 43, 47]. One study only included Bnaïve patients^ (no previous disease-specific treatment) with a positive PST and a reduction of 2pointsin symptom score after the first instillation of ChS 0.2 % [44]. Instillation regimen Initial instillation therapy was performed weekly in 73.7 % of the studies, but with different follow-up schedules (Table 2). The instillation procedure was similar in most studies, with the exception of one trial, where a solution of lidocaine and sodium bicarbonate was instilled before the PPS to reduce the In most studies a first symptom evaluation was performed at week 12; however, different scales/scores were used. Among them, the most commonly used were the O Leary Sant Symptom and Problem Index (ICSI/ICPI), the VAS pain assessment and the Pain, Urgency and Frequency (PUF) score. According to their design, studies were classified as controlled (Table 3) and uncontrolled (Table 4) trials. All the studies reviewed reported reductions of VAS pain scores after treatment, including those controlled using placebo/inactive controls (Table 3). The ES of VAS reduction was calculated for each CT and showed significant differences between active and control groups in all but one study, which compared ChS 2 % with a placebo arm [36]. The largest ES in all CT studies was observed for HMW-HA in the study by Shao et al. (Fig. 2) [34], with similar findings in two UCT studies with HMW-HA [16, 40] by a superior Bd^ for average VAS difference. Closest to this VAS reduction were the results obtained using 300 mg of intravesical PPS [47]. Response rates were compared between intervention arms by ES assessment only in the trial by Shao et al. [34] with HMW-HA (d=2.68 [IC95%: ] vs d=0.88 [IC95%: ]) for patients without intravesical therapy (Fig. 3). In CTs, studies with HMW-HA and with ChS 0.2 % reported superior response rates, with both rates (HMW-HA vs ChS 0.2 %) not being statistically different. The post-hoc calculation of composite ES based on VAS improvement plus RR revealed distinct differences among studies and products as shown in Fig. 4.ORvaluewashighest for HMW-HA in the Shao et al. study [34], followed by the intravesical application of 300 mg of PPS described by Bade et al. [37]. Pharmacoeconomic evaluation/cost-effectiveness The NNT for a response to intravesical therapy ranged between 1.33 (HMW-HA) and (ChS 2 %), with a negative value for the PPS combination therapy (Table 5). With this low NNT, HMW-HA was also significantly superior with regard to cost-effectiveness and cost efficacy to all other instillation regimes. Discussion The present meta-analysis on intravesical BPS/IC therapy clearly demonstrates the dilemma of the poor scientific evidence currently available for this disease. Owing to the different associations regarding the aetiology of the disease and its
5 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Table 2 All studies included for comparison Study (reference) Treatment Type of study Total sample Instillation protocol Follow-up Evaluation scale Morales et al. [15] 0.8 % HMW-HA UCT 25 Weekly for 4 weeks and monthly for 12 months VAS for pain (Cystistat ) 12 months Kallestrup et al. [42] UCT 48 Weekly for 4 weeks and monthly for 3 years VAS for pain 2 months Gupta et al. [43] UCT 38 Weekly for 6 weeks 6 weeks ICSI-ICSP Riedl et al. [16] UCT 121 Weekly and in response to symptoms 6.5 months VAS for pain Engelhardt et al. [40] UCT 70 Weekly for 10 weeks 4.9 years VAS for pain Shao et al. [34] CT 31 After hydrodistention, weekly for 9 months VAS for pain 4 weeks and monthly for 2 months Lai et al. protocol A a [41] UCT 30 Weekly for 4 weeks and monthly for 6 months VAS for pain/icsi-icpi 5 months Lai et al. protocol B a [41] UCT 30 Every 2 weeks 6 months VAS for pain/icsi-icpi Steinhoff [44] 0.2 % CS (Gepan UCT 18 Weekly for 4 weeks and monthly for 12 months ICSI-ICPI instill ) 12 months Nordling and van UCT 165 Weekly for 4 to 6 weeks and one 3 months VAS for pain Ophoven [45] monthly Nickel et al. [46] 2 % CS (Uracyst / UCT 53 Weekly for 6 weeks and monthly for 6 months VAS for pain/icsi-icpi Uropol S ) 4 months Nickel et al. [35] CT 65 Weekly for 6 weeks 3 months VAS for pain/icsi-icpi Nickel et al. [35] CT 98 Weekly for 7 weeks 3 months VAS for pain/icsi-icpi Porru et al. [24] 1.6 % LMW-HA + 2 % UCT Weekly for 12 weeks and biweekly 6 months VAS for pain/icsi-icpi CS (Ialuril ) for 6 months Porru et al. [47] UCT 22 Weekly for 8 weeks and biweekly for 6 months VAS for pain/icsi-icpi 6 months Bade et al. [48] i-pps 300 mg b UCT 20 Every 2 weeks for 3 months 3 months Not available Bade et al. [37] (Elmiron ) CT 9 Twice weekly for 3 months 3 months ICSI/ICPI Daha et al.[17] UCT 29 Twice weekly for 10 weeks; monthly 12 months ICSI/ICPI for 6 months Davis et al. [38] i-pps 200 mg c +daily CT 41 Twice a week for 18 weeks 18 weeks VAS for pain/ ICSI-ICPI o-pps 400 mg (Elmiron ) Sairanen et al. [39] DMSO UCT 37 Weekly for 6 weeks 3 months VAS for pain CT controlled trials, UCT uncontrolled trials, VAS visual analogue scale, ICSI/ICPI O Leary Sant symptom index and problem index, i-pps intravesical PPS, o-pps oral PPS a Lai et al. corresponds to two effective protocols with HMW-HA evaluated in the same publication b Intravesical instillation with 300 mg (three capsules) of Elmiron + mixed with 50 ml of 0.9 % sodium chloride c 200 mg or two capsules mixed with 30 ml sterile normal buffered saline rather low prevalence, most published studies cohorts are heterogeneous. The lack of globally accepted instruments for the evaluation of treatment success resulted in the exclusion of some trials from this meta-analytical review because the reported outcomes were not comparable. Even after a careful selection of 19 studies, we still found a heterogeneous population of 801 patients (mostly women) who were considered to have BPS/IC according to four different diagnostic criteria and typified as Btreatment-refractory^ (a concept that is not further defined) in 6 studies or as Btreatment-naïve^ patients in 1 study. Differences in design are also of particular relevance as only 5 studies (26 %) compared the intravesical formulas against placebo or non-active controls, while the remainder corresponded to uncontrolled and observational trials. Length of treatment and frequency of instillations also differed: weekly instillations were initially performed in 15 studies, biweekly or twice weekly instillations were reported for 2 studies each, while the duration of instillation therapy varied from 6 weeks to 12 months. Similarly, the time period of follow-up for final evaluation varied from 3 months to 5 years. All the instruments/scales used for outcome evaluation (O Leary Sant Score, the PUF and VAS for pain) can potentially measure treatment effects, but they are not readily comparable with each other. There is also no globally accepted definition as to the percentage of symptom regression that is regarded as treatment response. In addition, relatively small differences in VAS scores before and after treatment may be statistically but probably not clinically significant. With the intention to improve the balance between investigational and
6 1142 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Table 3 Effect size of the average reduction on the VAS pain (12 weeks) and the response rates for controlled trials (CT) Study Treatment Total patients Total instillations at week 12 VAS BT VAS AT VAS RR (%) VAS effect size RR effect size Mean SD Mean SD d Minimum Maximum d Minimum Maximum Shao et al. [34] Control Cystistat Laietal.[41] Cystistat Cystistat Nickel et al. [35] Placebo Uracyst Nickel et al. [36] Placebo Uracyst Bade et al. [37] Placebo i-pps 300 mg b Davis et al. [38] a Placebo daily o-pps 400 mg i-pps 200 mg c daily o- 400 mg Sairanen et al. [39] DMSO BCG VAS visual analogue pain score, BT before treatment, AT after treatment, RR response rate, d Cohen s d, i-pps intravesical PPS, o-pps oral PPS, DMOS dimethyl sulfoxide, BCG intravesical Bacillus Calmette Guérin a Results at 24 weeks b Intravesical instillation with 300 mg (three capsules) of Elmiron +mixed with 50 ml of 0.9 % sodium chloride c 200 mg or two capsules mixed with 30 ml of sterile normal buffered saline
7 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Table 4 Effect size results for uncontrolled trials (UCT) Study Treatment Total patients Number of instillations (12 weeks) VAS BT VAS AT VAS RR (%) VAS effect size RR effect size Mean SD Mean SD d Min Max d Min Max Morales et al. [15] 0,8 % HMW-HA Kallestrup et al. [42] (Cystistat ) Gupta et al. a [43] Riedl et al. [16] Engelhardt et al. [40] Steinhoff b [44] 0.2 % CS Nordling and van (Gepan instill ) Ophoven [45] Nickel et al. [46] 2 % CS (Uracyst / Uropol S ) Porru et al. [24] 1,6 % HA+ 2 % Porru et al. [47] CS (Ialuril ) Bade et al. [48] i-pps 300 mg Daha et al. [17] VAS visual analogue pain score, BT before treatment, AT after treatment, RR response rate, d=cohen s d, i-pps intravesical instillation with 300 mg (three capsules) of Elmiron + mixed with 50 ml of 0.9 % sodium chloride a 6weeks b 24 weeks clinical outcomes, and to extract the maximal information from the selected set of evaluable studies on intravesical BPS/IC therapy, refined statistical techniques such as Cohen s d along with confidence intervals have been used in this meta-analytical review to be able to compare the selected set of evaluable studies. Interestingly, symptom improvement was observed in all cases, including those from the placebo/non-active treatment arms. By far the largest effect sizes (d>2) for symptom reduction were found in 3 studies performed with HMW-HA [16, 34, 40]. With respect to response rates, effect size measurements showed similar results for HMW-HA and 0.2 % ChS, and Fig. 2 Randomised controlled trials: effect size of average VAS reduction. 95%CI 95 % confidence intervals, HMW-HA high molecular weight hyaluronic acid 0.08 %, ChS 2%chondroitin sulphate 2 %, o-pps oral dose of pentosan polysulphate, i- PPS intravesical instillation with pentosan polysulphate
8 1144 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Fig. 3 Randomised controlled trials: effect size of the response rates. 95%CI 95 % confidence intervals, HMW-HA high molecular weight hyaluronic acid 0.08 %, ChS 2% chondroitin sulphate 2 %, o-pps oral dose of pentosan polysulphate, i- PPS intravesical instillation with pentosan polysulphate for PPS. If only CTs were included in the analysis, HMW-HA was significantly superior to all other instillates (Table 3). The closest results on efficacy were observed with intravesical PPS [37] and a combination of intravesical plus oral PPS [38]; this last combined strategy reported by Davis et al. [38], however, showed a higher RR in patients who received oral PPS alone (90 vs 85.7 %). In the pharmacoeconomic approach of CTs, a clear advantage for HMW-HA was observed: the NNT for a treatment response was 1.31 for HMW-HA vs 2.74 for intravesical PPS and 5.51 for ChS 2 %. Cost efficacy (treatment costs * NNT) and cost effectiveness (treatment costs/responders) were higher for HMW-HA. Cost effectiveness was less than half for ChS and only about a third for PPS compared with HMW-HA, and cost efficacy was less than 25 % for ChS compared with HMW-HA. However, these results are based on a small number of studies with final analysis. Fig. 4 Composite effect size of response rates and VAS reduction: active treatments versus placebo (OR 95%CI). 95%CI 95 % confidence intervals, VAS visual analogue scale of pain, OR odds ratio
9 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Table 5 Pharmacoeconomic evaluation Product HMW-HA 0.08 % (Cystistat ) 2 % CS (Uracyst -Uropol S ) i-pps 300 mg (Elmiron ) i-pps 200 mg + o-pps 400 mg (Elmiron ) Study Shao et al. [34] Nickel et al. [35] Nickel et al. [36] Badeet al. [37] Davis et al.[38] Cost per instillation Number of instillations Cost of treatment (CT) %Responders placebo/control %Responders active treatment Odds ratio (95%IC) 76.5 (6.08; ) 2.33 (0.76; 7.17) 1.35 (0.58; 3.11) 3.19 (0.42; 24.38) 0.67 (0.10; 4.48) Absolute risk reduction (95%CI) 0.75 ( 1 0; 0.50) 0.18 ( 2.88; 0.18) 0.07 ( 0.26; 0.12) 0.20 ( 0.59; 0.19) 0.04 ( 0.16; 0.24) NNT (95%CI) 1.33 (1.0; 2.0) 5.51 (2.4; 18.84) (3.92; 8.31) 2.67 (0.36; 19.71) ( 4.13; 6.40) Cost-effectiveness (CT/%responders) Cost efficacy (CT a NNTs) HMW-HA high molecular weight hyaluronic acid, CS chondroitin sulphate, i-pps intravesical pentosan polysulphate, o-pps oral pentosan polysulphate, NNT number needed to treat to obtain a response a Response rates correspond to those presented in the articles [29, 30, 31, 33] and/or calculated by total of responders/total patients with per protocol results [32] The present meta-analytical analysis adds important information to the body of published evidence and is partly contradictory to systematic reviews that have been published in the past. In particular, ES assessment of outcome parameters facilitates the comparison of results with different GAG products for BPS/IC. Madersbacher et al. [7] searched the literature for all forms of chronic cystitis, including radiation cystitis and also OAB (which is not considered a form of chronic cystitis) and excluded all but 27 publications for further analysis. They concluded that ChS is superior to other intravesical GAG substitutes. However, in their review, 368 patients who were treated with ChS had a diagnosis of OAB, 20 patients a diagnosis of radiation cystitis [27], and only 118 patients were Bexclusively^ diagnosed with BPS/IC. The authors also state that no significant superiority versus controls was observed in the single controlled studyonchs2%thatwasreviewed[35]. Giannantoni et al. [49] evaluated CTs and UCTs on a multitude of therapies for BPS/IC, including behavioural, dietary, interventional, pharmacological and surgical therapies. In their systematic review not a single study on HA therapy was included. Given the high number of publications on HA in BPS/IC reporting superiority to other intravesical agents, this review is presumably incomplete. The authors conclude that evidence of BPS/IC therapy is limited, and that only the oral drugs cyclosporine A and amitriptyline showed significant ES on the classical BPS/IC symptoms of pain and frequency/urgency. Fall et al. [13] reviewed the literature to find an evidence base for treatment decisions in BPS/IC. Their conclusions were: level of evidence (LE) 1b/grade of recommendation (GR) A for intravesical PPS, LE 2b/GR B for HA and for ChS, and LE 3/GR C for intravesical heparin. The review performed by Matsuoka et al. [50] included four treatment modalities for BPS/IC: resiniferatoxin, Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG), oxybutynin and alkalinised lidocaine; as no GAG substitutes were evaluated, their results are not comparable with our analysis. In conclusion, this meta-analytical review provides evidence of the positive effects of intravesical GAG therapy for BPS/IC and that this treatment may significantly improve patients symptoms. Single reports even suggest that complete and permanent remission is possible in a subgroup of patients that has not yet been well defined [40, 42]. If medical and pharmacoeconomic aspects are combined, HMW-HA seems to have some advantage over other instillation agents. Despite these findings, direct comparisons between the different products have not been performed to date in properly designed controlled studies. The present meta-analysis suffers from the limited number of controlled accessible studies on intravesical therapies for BPS/IC and non-standardised response criteria. Many studies had to be excluded because of noncomparable inclusion criteria, treatment combinations and evaluation instruments. However, it gives a complete summary of all the data currently available and, by assessing the effect size, makes it possible to compare the relevance of the individual studies. Acknowledgements Dr Agustí Martí Gil and Dr Cindy L. Larios from the Medical Department of Clever Instruments S.L. (Barcelona, Spain) collaborated as independent reviewers.
10 1146 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Compliance with ethical standards Conflicts of interest J.M. Barua: consultancy and speaker s honoraria for/from Mylan; I. Arance: none; J.C. Angulo: none; C.R. Riedl: consultancy and speaker s honoraria for/from Mylan. Funding Data and statistical analysis were funded by an unrestricted grant by Mylan. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. References 1. Hanno P, Dmochowski R (2009) Status of international consensus on interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: 2008 snapshot. Neurourol Urodyn 28: Hurst RE, Roy JB, Min KW, Veltri RW, Marley G, Patton K, Shackelford DL, Stein P, Parsons CL (1996) A deficit of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans on the bladder uroepithelium in interstitial cystitis. Urology 48: Parsons CL, Lilly JD, Stein P (1991) Epithelial dysfunction in nonbacterial cystitis (interstitial cystitis). J Urol 145: Parsons CL (1996) Potassium sensitivity test. Tech Urol 2: Daha LK, Riedl CR, Hohlbrugger G, Knoll M, Engelhardt PF, Pflüger H (2003) Comparative assessment of maximal bladder capacity, 0.9% NaCl vs. 0.2 M KCl, for the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: a prospective controlled study. J Urol 170: Daha KL, Riedl CR, Lazar D, Simak R, Pflüger H (2008) Effect of intravesical glycosaminoglycan substitution therapy on bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis, bladder capacity and potassium sensitivity. Scand J Urol 8: Madersbacher H, van Ophoven A, van Kerrebroeck PEVA (2013) GAG layer replenishment therapy for chronic forms of cystitis with intravesical glycosaminoglycans a review. Neurourol Urodyn 32: Von Heyden B, Schmid HP (2000) Intravesical therapy of interstitial cystitis. Urologe A 39: Rovner E, Propert KJ, Bresinger C, Wein AJ, Foy M, Kirkemo A et al (2000) Treatment used in women with interstitial cystitis: the interstitial cystitis data base (ICDB) study experience. The Interstitial Cystitis Data Base Study Group. Urology 26: Burkman RT (2004) Chronic pelvic pain of bladder origin: epidemiology, pathogenesis and quality of life. J Reprod Med 49: Nickel JC, Moldwin R, Lee S, Davis EL, Henry RA, Wyllie MG (2009) Intravesical alkalinized lidocaine (PSD597) offers sustained relief from symptoms of interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int 103: Parkin J, Shea C, Sant GR (1997) Intravesical dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for interstitial cystitis a practical approach. Urology 49: Fall M, Oberpenning F, Peeker R (2008) Treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis 2008: can we make evidence-based decisions? Eur Urol 54: Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and metaanalyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e Morales A, Emerson L, Nickel J, Lundie M (1996) Intravesical hyaluronic acid in the treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis. J Urol 156: Riedl C, Engelhardt P, Daha K, Moraskis N, Pfluger H (2008) Hyaluronan treatment of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Int Urogynecol J 19: Daha LK, Lazar D, Simak R, Pfluger H (2008) The effects of intravesical pentosanpolysulfate treatment on the symptoms of patients with BPS/IC: preliminary results. Int Urogynecol J 19: Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences, 2nd edn. Erlbaum, Hillsdale 19. Lv YS, Zhou HL, Mao HP, Gao R, Wang YD, Xue XY (2012) Intravesical hyaluronic acid and alkalinized lidocaine for the treatment of severe painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J 23: Daha LK, Riedl CR, Lazar D, Hohlbrugger G, Pfluger H (2005) Do cystometric findings predict the results of Intravesical hyaluronic acid in women with interstitial cystitis? Eur Urol 47: Hung MJ, Chen YT, Shen PS, Hsu ST, Chen GD, Ho ESC (2012) Risk factors that affect the treatment of interstitial cystitis using intravesical therapy with a dimethyl sulfoxide cocktail. Int Urogynecol J 23: Gafni-Kane A, Botros SM, Du H (2013) Measuring the success of combined intravesical dimethylsulfoxide and triamcinolone for treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J 24: Cervigni M, Natale F, Nasta L, Padoa A, Lo Voi R, Porru D (2008) A combined intravesical therapy with hyaluronic acid and chondroitin for refractory painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J 19: Porru D, Cervigni M, Nasta L, Natale F, Lo Voi R, Tinelli C et al (2008) Results of endovesical hyaluronic acid/chondroitin sulfate in the treatment of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Rev Recent Clin Trials 3: Gauruder-Burmester A, Wildt B, Tunn R (2006) Treatment of overactive bladder with sodium chondroitin sulphate. Zentralbl Gynakol 128: Gauruder-Burmester A, Popken G (2009) Follow-up at 24 months after treatment of overactive bladder with 0.2% sodium chondroitin sulfate. Aktuelle Urol 40: Hazewinkel MH, Stalpers LJA, Dijkgraaf MG, Roovers JWR (2011) Prophylactic vesical instillations with 0.2% chondroitin sulfate may reduce symptoms of acute radiation cystitis in patients undergoing radiotherapy for gynecological malignancies. Int Urogynecol J 22: Parsons CL (2005) Successful downregulation of bladder sensory nerves with combination of heparin and alkalinized lidocaine in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology 65: Parsons CL, Zupkas P, Proctor J, Koziol J, Franklin A, Giesing D et al (2012) Alkalinized lidocaine and heparin provide immediate relief of pain and urgency in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Sex Med 9: Porru D, Campus G, Tudino D, Valdes E, Vespa A, Scarpa R, Usai E (1997) Results of treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis with intravesical hyaluronic acid. Urol Int 59: Figuereido AB, Palma P, Riccetto C, Hermann V, Dambros M, Capmartin R (2011) Clinical and urodynamic experience with intravesical hyaluronic acid in painful bladder syndrome associated with interstitial cystitis. Actas Urol Esp 35: Cervigni M, Natale F, Nasta L, Mako A (2012) Intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulphate for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: long-term treatment results. Int Urogynecol J 23:
11 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27: Sorensen RB (1996) Chondroitin sulphate in the treatment of interstitial cystitis and chronic inflammatory disease of the urinary bladder. Eur Urol 2: Shao Y, Shen ZJ, Rui WB, Zhou WL (2010) Intravesical instillation of hyaluronic acid prolonged the effect of bladder hydrodistention in patients with severe interstitial cystitis. Urology 75: Nickel JC, Egerdie B, Steinhoff G, Palmer B, Hanno P (2010) A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, and parallel groups: pilot evaluation of the efficacy and safety of intravesical sodium chondroitin sulfate versus vehicle control in patients with IC/PBS. Urology 76: Nickel JC, Hanno P, Kumar K, Thomas H (2012) Effectiveness and safety of intravesical sodium chondroitin sulfate compared with inactive vehicle control in subjects with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Urology 79: Bade JJ, Laseur M, Nieuwenburg A, van der Weele LT, Mensink HJA (1997) A placebo-controlled study of intravesical pentosan polysulphate for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. Br J Urol 79: Davis EL, El Khoudary SR, Talbott EO, Davis J, Regan LJ (2008) Safety and efficacy of the use of intravesical and oral pentosan polysulfate sodium for interstitial cystitis: a randomized doubleblind clinical trial. J Urol 179: Sairanen J, Leppilahti M, Tammela TLJ, Paananen I, Aaltomaa S, Taari K, Ruutu M (2009) Evaluation of health-related quality of life in patients with painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis and the impact of four treatments on interstitial cystitis? Scand J Urol Nephrol 43: Engelhardt PF, Morakis N, Daha LK, Esterbauer B, Riedl CR (2011) Long-term results of intravesical hyaluronan therapy in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J 22: Lai MC, Kuo YC, Kuo HC (2013) Intravesical hyaluronic acid for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. A comparative randomized assessment of different regimens. Int J Urol 20: Kallestrup E, Jorgensen S, Nordling J, Hald H (2005) Treatment of interstitial cystitis with Cystistat : a hyaluronic acid product. Scand J Urol Nephrol 39: Gupta SK, Pidcock L, Parr NJ (2005) The potassium sensitivity test: a predictor of treatment response in interstitial cystitis. BJU Int 96: Steinhoff G (2003) The efficacy of chondroitin sulphate in treating interstitial cystitis. Eur Urol Suppl 2: Nordling J, van Ophoven A (2008) Intravesical glycosaminoglycan replenishment with chondroitin sulphate in chronic forms of cystitis. A multi-national, multi-centre, prospective observational clinical trial. Arzneitmittelforschung 58: Nickel J, Egerdie B, Downey J, Singh R, Skehan A, Carr L, Irvine- Bird K (2008) A real-life multicenter clinical practice study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravesical chondroitin sulphate for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. BJU Int 103: Porru D, Leva F, Parmigiani A, Barletta D, Choussos D, Gardella B et al (2011) Impact of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate on bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J 23: Bade JJ, Mensink HJ, Laseur M (1995) Intravesical treatment of interstitial cystitis with a heparin analogue. Br J Urol 75: Giannantoni A, Bini V, Dmochowski R, Hanno P, Nickel JC, Proietti S, Wyndaele JJ (2012) Contemporary management of the painful bladder: a systematic review. Eur Urol 61: Matsuoka PK, Hadda JM, Pacetta AM, Baracat EC (2012) Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urogynecol J 23:
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
 Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_
 207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
Introduction. For further information please contact:
 Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis
 Review Article Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis Kristina Cvach 1, Anna Rosamilia 2 1 Mercy Hospital for Women, Melbourne, Australia; 2 Monash Medical Centre,
Review Article Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis Kristina Cvach 1, Anna Rosamilia 2 1 Mercy Hospital for Women, Melbourne, Australia; 2 Monash Medical Centre,
Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Original Article - Infection/Inflammation. Ömer Gülpınar, Ahmet Hakan Haliloğlu 1, Mehmet İlker Gökce, Nihat Arıkan
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354 Original Article - Infection/Inflammation http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-05-16
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354 Original Article - Infection/Inflammation http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-05-16
BJU International EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME
 EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW?
 NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT
 USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT Ivanov D.D., M.D., Professor Dombrowski Ya.A. National Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupik, Kiev, Kyiv City
USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT Ivanov D.D., M.D., Professor Dombrowski Ya.A. National Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupik, Kiev, Kyiv City
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 645 651 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Infections Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections by Intravesical Administration
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 645 651 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Infections Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections by Intravesical Administration
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O. Talbott,* Josephine Davis and Lisa J. Regan
 Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
UroToday International Journal. Volume 2 - October 2009
 UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA
 PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Treatment effectiveness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines?
 original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines
 Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
Davide De Vita, Henrik Antell & Salvatore Giordano
 Effectiveness of intravesical hyaluronic acid with or without chondroitin sulfate for recurrent bacterial cystitis in adult women: a meta-analysis Davide De Vita, Henrik Antell & Salvatore Giordano International
Effectiveness of intravesical hyaluronic acid with or without chondroitin sulfate for recurrent bacterial cystitis in adult women: a meta-analysis Davide De Vita, Henrik Antell & Salvatore Giordano International
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2
 Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
4/30/2008. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Menke H. Hazewinkel & Lukas J. A. Stalpers & Marcel G. Dijkgraaf & Jan-Paul W. R. Roovers
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:725 730 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1357-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prophylactic vesical instillations with 0.2% chondroitin sulfate may reduce symptoms of acute radiation cystitis in patients
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:725 730 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1357-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prophylactic vesical instillations with 0.2% chondroitin sulfate may reduce symptoms of acute radiation cystitis in patients
2/9/2008. Men Women. Prevalence of OAB. Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence (%) < Age (years)
 Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS?
 Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Interstitial cystitis
 Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
C. Lowell Parsons UC San Diego Medical Center, Department of Surgery/Urology, La Jolla, CA, USA
 ; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
CYSTISTAT. Hyaluronan Training
 CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS)
 Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
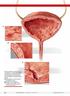 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA Injections for Refractory Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Toxins 2015, 7, 2860-2871; doi:10.3390/toxins7082860 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA
Toxins 2015, 7, 2860-2871; doi:10.3390/toxins7082860 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN OF BLADDER ORIGIN:
 ACCREDITATION This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship
ACCREDITATION This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship
Results of Omalizumab in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis (BPS/IC)
 Article ID: WMC002428 ISSN 2046-1690 Results of Omalizumab in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis (BPS/IC) Corresponding Author: Dr. Daniele Porru, Consultant Urologist, Divisione Urologia, IRCCS
Article ID: WMC002428 ISSN 2046-1690 Results of Omalizumab in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis (BPS/IC) Corresponding Author: Dr. Daniele Porru, Consultant Urologist, Divisione Urologia, IRCCS
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond
 Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review
 eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
Introduction. Original Article
 Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, FEBRUARY 2012
 REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, March 2008, Milan, Italy
 A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations
 EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 179 186 Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations Jørgen Nordling* Department of Urology, Herlev Hospital, University
EAU Update Series EAU Update Series 2 (2004) 179 186 Pelvic Pain and Interstitial Cystitis: Therapeutic Strategies, Results and Limitations Jørgen Nordling* Department of Urology, Herlev Hospital, University
Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
 Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mini-Reviews. Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review
 J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Bladder Pain Syndrome Jørgen Nordling Jean-Jacques Wyndaele Joop P. van de Merwe Pierre Bouchelouche Mauro Cervigni Magnus Fall Editors Bladder Pain Syndrome A Guide for Clinicians Editors Jørgen Nordling
Bladder Pain Syndrome Jørgen Nordling Jean-Jacques Wyndaele Joop P. van de Merwe Pierre Bouchelouche Mauro Cervigni Magnus Fall Editors Bladder Pain Syndrome A Guide for Clinicians Editors Jørgen Nordling
The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical Study
 Pain Physician 2016; 19:E581-E587 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Evaluation The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical
Pain Physician 2016; 19:E581-E587 ISSN 2150-1149 Prospective Evaluation The Role of Immunoglobulin E in the Pathogenesis of Ketamine Related Cystitis and Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis: An Immunohistochemical
Infection/Inflammation. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis
 Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores
 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
CAnnually, about 3 million patient visits to doctors in the
 UDC 1.2 002.2:15.032.2 ACTUAL TOPICS The modern approach to intravesical therapy of chronic cystitis O.D. Nikitin Bogomolets National Medical University Kyiv The difficulty of treating patients with chronic
UDC 1.2 002.2:15.032.2 ACTUAL TOPICS The modern approach to intravesical therapy of chronic cystitis O.D. Nikitin Bogomolets National Medical University Kyiv The difficulty of treating patients with chronic
IAUN Conference Dublin, January Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist
 IAUN Conference Dublin, January 2014 Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Theoretical component Observation Supervised practice Assessment
IAUN Conference Dublin, January 2014 Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Theoretical component Observation Supervised practice Assessment
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder
 Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Comparison of Intravesical Application of Chondroitin Sulphate and Colchicine in Rat Protamine/Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cystitis Model
 Comparison of Intravesical Application of Chondroitin Sulphate and Colchicine in Rat Protamine/Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cystitis Model Orhun Sinanoglu, 1 Isin Dogan Ekici, 2 Sinan Ekici 1 MISCELLANEOUS
Comparison of Intravesical Application of Chondroitin Sulphate and Colchicine in Rat Protamine/Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cystitis Model Orhun Sinanoglu, 1 Isin Dogan Ekici, 2 Sinan Ekici 1 MISCELLANEOUS
Long-term efficacy and tolerability of pentosan polysulphate sodium in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome
 Original research Long-term efficacy and tolerability of pentosan polysulphate sodium in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome Ali A. Al-Zahrani, MD; Jerzy B. Gajewski, MD, FRCSC See related article on
Original research Long-term efficacy and tolerability of pentosan polysulphate sodium in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome Ali A. Al-Zahrani, MD; Jerzy B. Gajewski, MD, FRCSC See related article on
Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
 Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis Hong-Chen Qu 1, Wei Zhang 2, Shi Yan 3, Yi-Li Liu 1, Ping Wang 1 * 1 Department of Urological
Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis Hong-Chen Qu 1, Wei Zhang 2, Shi Yan 3, Yi-Li Liu 1, Ping Wang 1 * 1 Department of Urological
Program and Abstracts
 Program and Abstracts summary INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR THE STUDY OF BPS ESSIC Annual Meeting Philadelphia (USA) 13-15 June 2014 Venue Geary Hall Hahnemann Hospital, Drexel University 230 North Broad Street
Program and Abstracts summary INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR THE STUDY OF BPS ESSIC Annual Meeting Philadelphia (USA) 13-15 June 2014 Venue Geary Hall Hahnemann Hospital, Drexel University 230 North Broad Street
The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence?
 Rev Article CHRONIC PROSTATITIS THERAPY NICKEL The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence? J. CURTIS NICKEL Department of Urology,
Rev Article CHRONIC PROSTATITIS THERAPY NICKEL The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence? J. CURTIS NICKEL Department of Urology,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
A REVIEW OF THE ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS), AUGUST 2013, BARCELONA, SPAIN
 A REVIEW OF THE ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS), 26-30 AUGUST 2013, BARCELONA, SPAIN Jane Meijlink It was perhaps not so surprising to find that this year s ICS
A REVIEW OF THE ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL CONTINENCE SOCIETY (ICS), 26-30 AUGUST 2013, BARCELONA, SPAIN Jane Meijlink It was perhaps not so surprising to find that this year s ICS
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome and Male Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: How Are They Related?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
From bladder to systemic syndrome: concept and treatment evolution of interstitial cystitis
 International Journal of Women s Health open access to scientific and medical research Open Access Full Text Article From bladder to systemic syndrome: concept and treatment evolution of interstitial cystitis
International Journal of Women s Health open access to scientific and medical research Open Access Full Text Article From bladder to systemic syndrome: concept and treatment evolution of interstitial cystitis
Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial cystitis
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
Problem solving therapy
 Introduction People with severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia may show impairments in problem-solving ability. Remediation interventions such as problem solving skills training can help people
Introduction People with severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia may show impairments in problem-solving ability. Remediation interventions such as problem solving skills training can help people
REVIEW. International Journal of Surgery
 International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive Bladder
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Comparison of Symptom Severity and Treatment Response in Patients with Incontinent and Continent Overactive Bladder
 European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 110 115 Female UrologyöIncontinence Comparison of Symptom Severity and Treatment Response in Patients with Incontinent and Continent Overactive Bladder Martin
European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 110 115 Female UrologyöIncontinence Comparison of Symptom Severity and Treatment Response in Patients with Incontinent and Continent Overactive Bladder Martin
Functional Bladder Problems
 european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
Intravesical OnabotulinumtoxinA Injections for Refractory Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Pain Physician 2012; 15:197-202 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Evaluation Intravesical OnabotulinumtoxinA Injections for Refractory Painful Bladder Syndrome Shiu-Dong Chung, MD 1,2, Yuh-Chen Kuo, MD 2, and
Pain Physician 2012; 15:197-202 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Evaluation Intravesical OnabotulinumtoxinA Injections for Refractory Painful Bladder Syndrome Shiu-Dong Chung, MD 1,2, Yuh-Chen Kuo, MD 2, and
Urinary tract disorders
 Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
 Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Inflammation Pathways
 Inflammation Pathways Siam Oottamasathien, MD FAAP FACS Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatric Urology Research Associate Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Director of Pediatric Urology Basic Science
Inflammation Pathways Siam Oottamasathien, MD FAAP FACS Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatric Urology Research Associate Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Director of Pediatric Urology Basic Science
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis
 Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
