1. Introduction. Volume 6 Issue 9, September Dr. Baydaa H. Mutlak 1, Dr. Intidhar M. Mnati 2, Dr. Iman S.
|
|
|
- Adela Chandler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
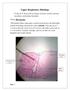
1 The Morphological Description and Histological Study of Lingual Papillae in the Tongue Bat Pipistrillus kuhli Dr. Baydaa H. Mutlak 1, Dr. Intidhar M. Mnati 2, Dr. Iman S. AL-Jumaily 3 Department ofbiology, College of Education for Pure Science (Ibn Al-Haitham), University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq Abstract: The present study was carried out to investigate the morphological and histological structure as well as some histochemical aspects oftongue bat Pipistrillus kuhli.the dorsal surface of the tongue has lateral oblique grooves connected with inter median groove, while the ventral surface, contain long process with deep fissure on its free end. Histologically, the dorsal surface was covered by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, while the ventral surface covered with non- keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Three types of lingual papillae (filiform, fungiform and circumvallate) were project and distributed on the dorsal surface. The filiform papillae are the most abundant and characterized by a slender sharp pointed structure, while the fungiform papillae like the mashroom, the wall contain taste buds, but the circumvallate papillae circular in shape and embedded in the epithelium and surrounded by circle grooves which contain taste buds. The lamina propria is consisted of dense connective tissue which is rich in blood vessels and striated muscle fibers that have arranged in different directions. The results of histochemical examination of lingual glands showed positive reaction for PAS stain in this species. Key words: lingual papillae, tongue, histology, bat. 1. Introduction Tongue as taste organ has important role in digestion of food in all vertebrates. [1] examined the fundamental importance of morphology in the evolution of the vertebrate tongue, focusing on the origin of the tongue and on the relationship between morphology and environmental conditions. The author examined the tongues of various extant vertebrates, including those of amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals. Bats with nearly 1250 species are the second largest group of mammals and play ecological and economic role in our community[2]. The study of the histological and the histochemical aspects on the tongues of the species in different classes of vertebrates, and specifically bats, has attracted the attention of certain investigators. Earlier anatomical and microscopic on insectivorous species from families of Vespertilionidae and Molossidae [3], Hipposideridae, Rhinolophidae and fruit eating bats such as Pterpus vampyrus [4]. There are various types oflingual papillae on the dorsal surface of tongue. These papillae are divided into mechanical(filiform and conical) and gustatory papillae(fungiform, circumvallate). Shape, position and distribution of these lingual papillae play important role in eating habits[5]. [6]study the anatomical differences in the tongue of rat, bat and pangolin, the results showed non papillae of the keratinized stratified epithelium of pangolin tongue unlike the papillae seen in the tongue of the rat and bat, while the filiform papillae seen in the rat was bristle like, the filiform papillae in the bat were crown-like. The structure of the tongue in the Millivera capenesiswas studied by [7], five types (filiform, conical, fungiform, circumvallate and foliate) papillae were project and distributed on dorsal and lateral surface. The filiform was similarly to threads or like hairs, while conical was cylindrical shaped.the fungiform papillae like the mashroum, the wall contain taste buds, but the circumvallate papillae circular in shape and embedded in the epithelium, the foliate papillae was similar ridges, both circumvallate and foliate papillae were contain taste buds. The morphological characteristics and histological structure of the tongue and lingual papillae has been study in the Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettusaegyptiacus). This study showed that elongated and movable tongue and tine keratinized epithelium especially on ventral surface of tongue, numerous and different types(4 types) of papillae on the dorsal surface of tongue in different locations and orientation were seen in this species, hyaline cartilage was observed in tip of tongue [2]. In the Egyptian bat Pipistrillus kuhli the tongue is characterized by the presence of numerous filiform papillae at its dorsal and a small number of circumvallate, while in the Syrian Pipistrillus kuhli, the circumvallate papillae absent [8]. The available literature indicated that few studies have carried on the histology and histochemistry of the tongue of this species in Iraq. So, the present study was performed to investigate the histological structure and the histochemical characteristics of the lingual glands. 827
2 2. Materials and Methods which is covered with thinkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium (Fig.3,4), while the ventral surface were lack the Tongue fromfive Pipistrillus kuhli was used is this study.the lingual papillae which is covered by non keratinized stratified animals were collected from different agriculture regions epithelium (Fig.5). around Baghdad. Each bat was dissected, tissue samples of the tongues were immediately excised, cut into small pieces, fixed rapidly in 10% neutral formalin solution for hours and then dehydrated in ascending series of ethyl alcohol, cleared in xylene and embedded in paraffin wax. Sections of 4-6µm thick were stained with heamatoxylin and eosin. For histochemistry processing, sections were stained with Periodic Acid Shaiff(PAS) for polysaccharides of the glands and the muscle of the tongue [9]. Histological examination carried out using light microscope Kruss and photographed by using Sony digital camera. 3. Results Tongue was long, muscular and movable, it is lies in the floor of the buccal cavity and is connected posteriorly by means of the frenulum linguae, it was divided into three areas: apex, body and root. The dorsal surface has lateral oblique grooves connected with inter median groove (Fig.1), but inthe ventral surface of the tongue there is a long process with deep fissure on its free end (Fig.2). Figure 3: Transverse section of the tongue showing types of lingual papillae, filiform (Fi), fungiform (Fu) and circumvallate papillae(ci). ( 10X)(H&E) Figure 4: Transverse section of the tongue showing thin keratinized epitheliu on the dorsal Surface (40X)(H&E) Figure 5: Transverse section of the tongue showing the non keratinized epithelium on thesurface (40X)(H&E). The filiform papillae are most numerous and distributed over the dorsal anterior portionof the tongue and consists of conical mass(process) of stratified squamous epithelial cells it is a Three types of lingual papillae (filiform, fungiform and slender sharp pointed structureand vascular core of connective circumvallate) were found on the dorsal surface of the tongue, tissue(fig.6). 828
3 circumvallate papillae are flattened structure, exhibit a thin keratinized epithelium (Fig.9, 10, 11). Fungiform papillae are relatively few in number and are interspersed among the filiform papillae, they were observed on all of surface especially at the tip and lateral margins of tongue. They are large,mushroom form andbroader than the base with many taste buds and has a core of connective tissue, it is covered by keratinized epithelium (Fig.7, 8). Figure 10: Circumvallate papilla(ci) showing circular groove(cg),lamina propria(lp)and muscle fibers(mf)(10x)(h&e). Figure 7: Transverse section of the tongue showing filiform (Fi), fungiform papilla(fu),lining epithelium(le) and lamina propria (Lp) (10X)(H&E). Figure 11: Circumvallate papilla showing circular groove (Cg) and taste buds (Tb) (40X) (H&E) Figure 8: Fungiform papilla showing lining epithelium (Le), connective tissue cone(cc) and taste buds (Tb)(40X)(H&E). The circumvallate papillae were less in number, they were located on the behind of mid region of tongue and surrounded by circle grooves which contain many taste buds. The The lamina propria is built up of connective tissue rich with blood vessels, longitudinal and transverse bundles of muscle fibers were surrounded by collagenous fibers below the connective tissue (Fig.12). 829
4 4. Discussion The morphological and histological features of mammalian tongues reflect the differences among the life styles of mammals [1]. The results of the present study showed three parts distinguished in the dorsal surface of the tongue, apex, body and root. This design appeared also in most vertebrates species [10;11; 12]. Figure 12: Transverse section of the tongue showing lamina propria(lp),blood vessels(bv)and muscle fibers (Mf) (10X) (H&E) The histochemical examination showed, the lingual glands are stained with red color with PAS method indicating the presence of mucopolysacchride secretion. The mucous glandular cells are irregular in shape with basely flattened nuclei (Fig.13,14). On the dorsal surface of the tongue of mammals, there are various kinds of lingual papillae including filiform, fungiform, circumvallate and foliate papillae,each having different morphological structure and shape [7].Distribution of these lingual papillae has been considered to be related to species eating habits [13]. The epithelium of the anterior half is more extensively keratinized than that of the posterior ones which provide the tongue with greater rigidity to be efficient for feeding [14]. In the present study the keratin is less in the anterior half, this may be due to the difference of feeding habits, this is similar to the adult Egyptian bats and Syrian bats[8]. In mammals there are some variation in the shape and number of papillae on the dorsal surface of the tongue [6]. Histological observations of insectivorous batof the present study showed that the dorsal surface of the tongue is rough due to the presence of three types of lingual papillae (filiform,fungiform and circumvallate papillae), these observations provided similar results to those of[15; 8],while in the Syrian bat Pipistrillus kuhli the circumvallate papillae absent [8], whereas there are four types of lingual papillae (filiform, fungiform conical and circumvallate papillae) in the tongue of fruit eater bats [2]. Figure 13: Transverse section of the tongue showing mucous lingual glands (MlG)(40X) (H&E) In the insectivorous bat (Rhinopama hardwickie), [16] showed that the filiform papillae are most numerous and distributed over the dorsal anterior portion of the tongue and consists of a slender vascular core of connective tissue covered with cornified stratified squamous epithelium, this finding is contradicting that reported in the present study, and in the study of Egyptian bat (Pipistrillus kuhli) and Syrian bat (Pipistrillus kuhli) [8] but in the Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegytiacus) were reviewed by [2], the authors postulated that the filiform papillae were distributed on the dorsal surface and were divided into three types with different size and position which are: small, giant and bifid filiform papillae. Fungiform papillae in some mammals such as buffalo[17]hasn t taste buds but in the current study, the fungiform papillae are large,mushroom form with many taste buds were observed. Figure 14: Lingual glands showing positive reaction for PAS stain (10X)(H&E) Fungiform and circumvallate papillae were covered by a thin keratinized layer becausethey have taste buds [18],the food particles were exposed to the taste buds and facilitate 830
5 absorption of food, this finding is agreement with previous helvm) and pangolin (Manis tricuspis), investigators [7; 16]. Int.J.Morphol.,27(4): , [7] Ali,T.G., Some histological description of lingual The circumvallate papillae were circular shape surrounded papillae in the Millivora capeneries tongue,biol.j.alby circular groove and embedded in the lingual epithelium Kufa Uni.,4(1): , these our observations were similar to previous work which [8] Selim,A.;Nahla,N.E. and Shelfeh,M., Comparative and done on rodents and ferret [1; 19]. anatomical and histological studies of the tongue between the Egyptian bat Pipistrillus kuli and the Syrian bat The number of circumvallate papillae in different species of Pipistrillus kuli, bats was reported by several authors, there are two papillae in [9] Bancroft,J. and Stevens,A.,Theory and practice of the Japanese long-fringed bat [20; 21] and four papillae in the histological techniques, Churchill Living stone, long-nosed bat [21].The present observations could not detect London,2 nd : 622pp+XIV, or arrived to the exact number of the circumvallate papillae in [10] Mutlak, B.H.; Dauood, H.A. and ALlDoori,T.Y., A study this species of bats. of the anatomy and histology of the tongue of fresh water turtle Clemmys caspica caspica.,j.diyalla,8(1): , The bundle of skeletal muscle fibers was occupied the core of Pipistrilluskuhli tongue arranged in all direction, these [11] Nasr,E.S.; Gamal,A.M. andelsheikh,e.h., Light and observation came to correspond the previous study on the scanning electron microscopic study of the dorsal lingual other vertebrate tongue [1;22].[2] reported for the first time the papillae of the rat Arvicanthis niloticus (Muridae, presence of cartilage in the front part of the tongue of Radentia), J.Amer.Sci.,8(4): , Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus) which is important [12] Taha, A.M., Comparative anatomical, histological and for movement, the results of the present study not agreement histochemical study of tongue in two species of with previous study. insectivorous vertebrates Aust. J.Bas.Appl.Sci.,7(1): , Histochemical examination results of the present study [13] Fawcett,D.W., A text book of histology, W.B.Sanuders showed that the lingual glands are positive with PAS reaction company,(cited by Taha,2013), for mucopolysacharides, this was indicates a considerable [14] Selim,A., Comparative histological, histochemical and activity of this glands in the production of mucous secretion. physiological studies on the digestive system of the two This observation agree with that of Egyptian bat [16]. insectivorous bats Rhinopoma herdweickei and Ase lliatridens, MSc.Zoology department faculty of science, In conclusion, the present study showed that the shape and the Tanta Univ. Tanta Egypt (cited by Selim et al., 2008), distribution of lingual papillae depend on the type of diet and location of these papillae on the tongue, in addition [15] Pastor,J.F.;Moro,J.A.;Verona,J.A.;Gato,A.;Represa,J. and histological structure are appropriate to their function. Barbosae,A., Morphological study by scanning electron microscopy bat Pipistrellus References pipistrellus,arch.oral.biol.,38(7): , [16] Taki El-Deen, F.M.A.; Samia,M.I. and [1] Iwasaki,S., Evolution of the structure and function of the Shahin,M.A., Comparative histological studies on the vertebrate tongue, J.Anat.,201:1-13, tongue of three species of Egyptian bats, Life Sci.J., [2] Ghassemi,F.,Jahromi,H.K. and Ahmadi,N., Macroscopic 10(2): , and light microscopic study of the tongue of the Egyptian [17] Khaksary, M.; Mahababy,H.; Morovvati, K. and Khazaeil, fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus), L., A microscopic study of lingual papillae in Iranian [3] Azzali,G.;Gabbi,C.;Graandi,D. and buffalo (Bubalus bubalus), Asi. J. Ani., 5(2): , Bonomini,D. Morphological and ultrastructural features of the non sensory papillae,in tongue of hibernating [18] Emura, S., SEM study on the lingual papillae and their bats,archital.anat.embryol.,96: , connective tissue cores of the Japanese common pipstrelle [4] Emura,S.;Hayakawa,D.;Chen,H;Shoumura,S.;Atoji,Y. (Pipistrelle abramus), Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., and Wijayanto, H., SEM study on the dorsal lingual 153:56-62, surface of the large flying fox, Pteropus vamypy.okajimas [19] Mohammed, A., Salih,K. and Dala, K. Some Folia, Anat.Jpn., 79: , microscopic and morphologic aspects of the lingual [5] Hanna,J.;Trzcielinska-Lorych,J. and Gadynicki,S., The papillae in the tongue of ferret (Mustela putrious), microstructureof lingual papillae in the Egyptian fruit Scient. conf., 11: , bat(rousettus aegyptiacus) as observed by light [20] Kobayashi, K. and Shimamura,S., Comparative microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, anatomical observations of the tongue of Japanese longfingered bat, Miniopterus schreibersi fuliginosus, Arch.Histol.Cytol.,72:13-21, [6] Abayomi,T.A.;Ofusori,D.A.;Ayoka,O.A.;Odukoya,S.A.; Okajimas Folia Anatomica Japan 58: , Omotoso,E.;Amegor,F.O.; Ajaayi,S.A.;Ojo,G.B. and [21] Greenbaum,I.F. and Phillips, C.J., Comparative anatomy Oluwayginka,O.P., A comparative histological study of and general histology of the tongues of long-nosed bats the tongue of the rat (Rattus norvegicus), Bat (Eidolon 831
6 (Leptonycteris sanboni) and (L. nivalis) with reference infestation of oral mites, J.Mammal., 55: , [22] Igbokwe,C.O. and Okolie,C., The morphological observations of some lingual papillae in the prenatal and prepuberal stages of red sokoto goats (Capra hircus) Int. J. Morphol.,27(1): ,
Dorsum of the tongue. Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types. Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove
 Histology of TONGUE Figure 22.13 Dorsum of the tongue Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types a. filiform papillae,
Histology of TONGUE Figure 22.13 Dorsum of the tongue Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types a. filiform papillae,
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Advances in Bioresearch
 Advances in Bioresearch Adv. Biores., Vol 5 (1) March 2014: 70-74 Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3 ICV 7.20 [Poland] Advances in Bioresearch
Advances in Bioresearch Adv. Biores., Vol 5 (1) March 2014: 70-74 Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3 ICV 7.20 [Poland] Advances in Bioresearch
HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES. At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions:
 HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES CHAPTER ONE The Special Senses Learning objectives At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions: 1. What is the gross and histological
HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES CHAPTER ONE The Special Senses Learning objectives At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions: 1. What is the gross and histological
HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN ROUSETTUS AEGYPTIACUS IN THE SOUTHWEST OF IRAN (JAHROM)
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Applied, Natural and Social Sciences (IMPACT: IJRANSS) ISSN(E): 2321-8851; ISSN(P): 2347-4580 Vol. 1, Issue 6, Nov 2013, 43-50 Impact Journals HISTOLOGICAL
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Applied, Natural and Social Sciences (IMPACT: IJRANSS) ISSN(E): 2321-8851; ISSN(P): 2347-4580 Vol. 1, Issue 6, Nov 2013, 43-50 Impact Journals HISTOLOGICAL
COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN TWO SPECIES OF RAT (RATTUS NORVEGICUS & RATTUS WISTAR)
 COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN TWO SPECIES OF RAT (RATTUS NORVEGICUS & RATTUS WISTAR) *Farangis Ghassemi & Ghazale Cheshmi Department of Biology, Jahrom branch, Islamic Azad University, Jahrom,
COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN TWO SPECIES OF RAT (RATTUS NORVEGICUS & RATTUS WISTAR) *Farangis Ghassemi & Ghazale Cheshmi Department of Biology, Jahrom branch, Islamic Azad University, Jahrom,
Morphology of the lingual papillae of the eland (Taurotragus oryx)
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 93(3): Lingual 99 103, papillae November, of eland 2016 99 Morphology of the lingual papillae of the eland (Taurotragus oryx) By Shoichi EMURA Heisei College of Health Sciences,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 93(3): Lingual 99 103, papillae November, of eland 2016 99 Morphology of the lingual papillae of the eland (Taurotragus oryx) By Shoichi EMURA Heisei College of Health Sciences,
Scanning electron microscopic study of the tongue in the rainbow lorikeet (Trichoglossus haematodus)
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 88(1): 17 21, May, 2011 Scanning electron microscopic study of the tongue in the rainbow lorikeet (Trichoglossus haematodus) By Shoichi EMURA 1, Toshihiko OKUMURA 2 and Huayue
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 88(1): 17 21, May, 2011 Scanning electron microscopic study of the tongue in the rainbow lorikeet (Trichoglossus haematodus) By Shoichi EMURA 1, Toshihiko OKUMURA 2 and Huayue
Oral cavity Lab exercises
 Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI
 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 LEVEL I MID-SEMESTER II EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (BScN) AND BACHELOR OF PHARMACY (B.PHARM) MARKING SCHEME HNS101/UPC106:
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 LEVEL I MID-SEMESTER II EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (BScN) AND BACHELOR OF PHARMACY (B.PHARM) MARKING SCHEME HNS101/UPC106:
abstract Key words: Hard palate, Tongue, Buccal floor, Sambar deer, Gross anatomy
 Gross anatomical studies on the hard palate, tongue and buccal floor in sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) a.r sreeranjini 1, c.v rajani 2 and n. ashok 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology College
Gross anatomical studies on the hard palate, tongue and buccal floor in sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) a.r sreeranjini 1, c.v rajani 2 and n. ashok 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology College
A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove.
 By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
Objectives. Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract
 GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
GI Histology Lab 1. Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji
 GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Lingual Dorsal Surface of the Beagle Dog. Shin-ichi IWASAKI and Koichi SAKATA
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 62 (1) : 1-14, May 1985 Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Lingual Dorsal Surface of the Beagle Dog By Shin-ichi IWASAKI and Koichi SAKATA Department of Oral Anatomy, Nippon
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 62 (1) : 1-14, May 1985 Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Lingual Dorsal Surface of the Beagle Dog By Shin-ichi IWASAKI and Koichi SAKATA Department of Oral Anatomy, Nippon
The distribution and structure of the lingual papillae on the tongue of the bank vole Clethrionomys glareolus
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 326 333 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The distribution and structure of the lingual papillae on the tongue
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 326 333 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The distribution and structure of the lingual papillae on the tongue
Morphohistological study of the tongue in local mice species by using special stain
 Morphohistological study of the tongue in local mice species by using special stain Dr. Shrmean Abdulla Abd AL-Rhman 1, Azhaar Raheem AL-Fartwsy 1, Entikhab Hameed AL- Shuaily 1 1 Department of biology,
Morphohistological study of the tongue in local mice species by using special stain Dr. Shrmean Abdulla Abd AL-Rhman 1, Azhaar Raheem AL-Fartwsy 1, Entikhab Hameed AL- Shuaily 1 1 Department of biology,
口腔生理學 ( 含顎咬合 ) Oral physiology (occlusion included) 學習目標. Oral moucosa 參考資料. Classification. Mucosa
 口腔生理學 ( 含顎咬合 ) Oral physiology (occlusion included) Mucosa 臺北醫學大學牙醫學系張維仁老師 E-mail cweijen1@tmu.edu.tw 學習目標 1. let the student to understand the base knolwedge of oral physisology. 2.The student can firsther
口腔生理學 ( 含顎咬合 ) Oral physiology (occlusion included) Mucosa 臺北醫學大學牙醫學系張維仁老師 E-mail cweijen1@tmu.edu.tw 學習目標 1. let the student to understand the base knolwedge of oral physisology. 2.The student can firsther
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 56(5) : 309-316, December 1979 Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle By IKUO YOSHIOKA, MICHIKO IIDA and HIROSHI MUTO
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 56(5) : 309-316, December 1979 Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle By IKUO YOSHIOKA, MICHIKO IIDA and HIROSHI MUTO
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems
 Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians. with Marnie Hayward
 Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
Prepared By Student. Dania Abed Al-majeed. Rahma Raad Hanna. Balqees Mohammed Aasim. Dania Hisham. Rasha Rafiee
 Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Taste. Alexis, Emma, Maureen
 Taste Alexis, Emma, Maureen There will be essential vocabulary throughout the presentation. We will define them then. Anatomy 3 Cranial Nerves Facial Glossopharyngeal* Vagus Tongue Brain Papillae Tastebuds
Taste Alexis, Emma, Maureen There will be essential vocabulary throughout the presentation. We will define them then. Anatomy 3 Cranial Nerves Facial Glossopharyngeal* Vagus Tongue Brain Papillae Tastebuds
Morphology of the Lingual Papillae in the Least Weasel (Mustela nivalis)
 Int. J. Morphol., Morphology of the Lingual Papillae in the Least Weasel (Mustela nivalis) Morfología de las Papilas Linguales en la Comadreja Común (Mustela nivalis) Neveen E. R. El Bakary * & Shoichi
Int. J. Morphol., Morphology of the Lingual Papillae in the Least Weasel (Mustela nivalis) Morfología de las Papilas Linguales en la Comadreja Común (Mustela nivalis) Neveen E. R. El Bakary * & Shoichi
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
The Digestive System. Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1
 The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Reformation of Taste Buds by Crossed Sensory Nerves in the Rat s Tongue
 Acta physiol. scand. 1970. 79. 88-94 From the Department of Physiology, Veterinarhogskolan, Stockholm, Sweden and the Department of Zoology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, U.S.A. Reformation
Acta physiol. scand. 1970. 79. 88-94 From the Department of Physiology, Veterinarhogskolan, Stockholm, Sweden and the Department of Zoology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, U.S.A. Reformation
TISSUES. Objectives. Tissues
 TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
BI 121 LAB. WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System
 BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
The Tissue Level of Organization
 Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN:
 Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Cytological and Histological Study of Adult and Neonate Epidermis in Thick and Thin Skin of Various Anatomical Sites
 Available online on www.ijpqa.com International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance 218; 9(2); 174-179 doi: 1.25258/ijpqa.v9i2.13642 ISSN 975 956 Research Article Cytological and Histological Study
Available online on www.ijpqa.com International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance 218; 9(2); 174-179 doi: 1.25258/ijpqa.v9i2.13642 ISSN 975 956 Research Article Cytological and Histological Study
The Special Senses. Chapter 17
 The Special Senses Chapter 17 Objective Describe the structure of vertebrate sensory organs and relate structure to function in vertebrate sensory systems. The 5 Special Senses 1. Olfaction 2. Gustation
The Special Senses Chapter 17 Objective Describe the structure of vertebrate sensory organs and relate structure to function in vertebrate sensory systems. The 5 Special Senses 1. Olfaction 2. Gustation
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
Microscopic Study on the Tongue of Male Ostrich
 European Journal of Biological Sciences 2 (2): 24-31, 2010 ISSN 2079-2085 IDOSI Publications, 2010 Microscopic Study on the Tongue of Male Ostrich 1 2 2 Aghdas Poost Pasand, Mina Tadjalli and Hadi Mansouri
European Journal of Biological Sciences 2 (2): 24-31, 2010 ISSN 2079-2085 IDOSI Publications, 2010 Microscopic Study on the Tongue of Male Ostrich 1 2 2 Aghdas Poost Pasand, Mina Tadjalli and Hadi Mansouri
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
Morphological differences in epithelial papillae and microvascular architecture according to site in cat filiform papillae
 J Osaka Dent Univ 2015 (April) ; 49 (1) : 35 48. Morphological differences in epithelial papillae and microvascular architecture according to site in cat filiform papillae Masaya Hikida, Akimichi Takemura
J Osaka Dent Univ 2015 (April) ; 49 (1) : 35 48. Morphological differences in epithelial papillae and microvascular architecture according to site in cat filiform papillae Masaya Hikida, Akimichi Takemura
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Upper Respiratory Histology
 Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF DORSAL LINGUAL PAPILLAE OF THE GREEN TOAD (BUFO BUFO)
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2016 ONLINE FIRST ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.1030 Short communication MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF DORSAL LINGUAL PAPILLAE OF THE GREEN TOAD (BUFO BUFO) N. GOODARZI¹,
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2016 ONLINE FIRST ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.1030 Short communication MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF DORSAL LINGUAL PAPILLAE OF THE GREEN TOAD (BUFO BUFO) N. GOODARZI¹,
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation
 Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Descriptive Histology
 Atlas of Descriptive Histology Michael H. Ross University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Wojciech Pawlina Mayo Medical School College of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota
Atlas of Descriptive Histology Michael H. Ross University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Wojciech Pawlina Mayo Medical School College of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet
 Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. One of the present authors, KIKUCHI, has reported in detail on the innervation
 Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 19, n. 3 (May 1960). P. 437-446. Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku Univ., Sendai. On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. Mizuho KIKUCHI, Shunsaku HATAKEYAMA,
Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 19, n. 3 (May 1960). P. 437-446. Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku Univ., Sendai. On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. Mizuho KIKUCHI, Shunsaku HATAKEYAMA,
Learning Objectives (1&2)
 Learning Objectives (1&2) By the end of the session, students should be able to: 1) Identify anatomical position seated, standing, prone, supine. 2) Pronounce, define and be able to use directional and
Learning Objectives (1&2) By the end of the session, students should be able to: 1) Identify anatomical position seated, standing, prone, supine. 2) Pronounce, define and be able to use directional and
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
14 Taste. 14 Taste versus Flavor. Chapter 14
 14 Taste Chapter 14 14 Taste Taste versus Flavor Anatomy and Physiology The Four Basic Tastes Coding of Taste Quality Genetic Variation in Taste Experience The Pleasures of Taste 14 Taste versus Flavor
14 Taste Chapter 14 14 Taste Taste versus Flavor Anatomy and Physiology The Four Basic Tastes Coding of Taste Quality Genetic Variation in Taste Experience The Pleasures of Taste 14 Taste versus Flavor
B. Classification of epithelium: by number of cell layers present and by shape of the superficial cell layers.
 I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Classification of Tissues
 6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Topic and Aims. Contractile cells. Nervous system. Muscle tissue is one of the four basic tissue types.
 Topic and Aims Contractile cells Muscle tissue is one of the four basic tissue types. You should be able to: 1. Describe and identify the types of contractile cells, and summarise similarities and differences.
Topic and Aims Contractile cells Muscle tissue is one of the four basic tissue types. You should be able to: 1. Describe and identify the types of contractile cells, and summarise similarities and differences.
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep
 DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
Mohamed M. A. Abumandour *
 Int. J. Morphol., 32(4):1407-1417, 2014. Morphological Comparison of the Filiform Papillae of New Zealand White Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) as Domestic Mammals and Egyptian Fruit Bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus)
Int. J. Morphol., 32(4):1407-1417, 2014. Morphological Comparison of the Filiform Papillae of New Zealand White Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) as Domestic Mammals and Egyptian Fruit Bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus)
Surface Structures of the Tongue, Palate and Buccal Mucosa of the Rat. (Scanning Electron Microscopic Studies on the Oral Mucosa 3) Introduction
 Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 52: 297-312, 1976 Surface Structures of the Tongue, Palate and Buccal Mucosa of the Rat (Scanning Electron Microscopic Studies on the Oral Mucosa 3) By Ikuo Yoshioka and Hiroshi
Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 52: 297-312, 1976 Surface Structures of the Tongue, Palate and Buccal Mucosa of the Rat (Scanning Electron Microscopic Studies on the Oral Mucosa 3) By Ikuo Yoshioka and Hiroshi
LM and SEM Studies on Tongue and Lingual Papillae in the Donkey (Equus asinus)
 LM and SEM Studies on Tongue and Lingual Papillae in the Donkey (Equus asinus) Hanna Jackowiak 1, Hassen Jerbi 2, Kinga Skieresz-Szewczyk 1 and Ewelina Prozorowska 1 1 Department of Histology and Embryology,
LM and SEM Studies on Tongue and Lingual Papillae in the Donkey (Equus asinus) Hanna Jackowiak 1, Hassen Jerbi 2, Kinga Skieresz-Szewczyk 1 and Ewelina Prozorowska 1 1 Department of Histology and Embryology,
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE
 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
