Advances in Bioresearch
|
|
|
- Roy Jennings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Bioresearch Adv. Biores., Vol 5 (1) March 2014: Print ISSN ; Online ISSN Journal s URL: CODEN: ABRDC3 ICV 7.20 [Poland] Advances in Bioresearch ORIGINAL ARTICLE Macroscopic and microscopic study of tongue in Wistar rats Ghazale Cheshmi 1, Frangis Ghassemi 2 1- Department of Biology, Jahrom branch, Islamic Azad University, Jahrom, Iran *2- Faculty of Biology Department, Jahrom branch, Islamic Azad University, Jahrom, Iran ABSTRACT The aim of the present study was to investigate the structure of the tongue in rat since tongue is an important organ in taking food. For this purpose, the tongue of 8 adult male and 8female rats (wistar) was dissected from the root. Their weight, length and wide were measured. Then, they were fixed in formalin (10%) and prepared by tissue processing (fixation, dehydrated, clearing and impregnation). The serial sections (5 μ) were obtained and subjected to Haematoxylin and Eosin stains. The morphology and morphometric study of the tongue were studied by light microscope and progress capture soft ware. The results showed that the epithelium of muscular tongue in male and females were keratinized stratified squamous. It's length and in both sexes were similar approximately with 2.67± 0.02cm and of its apex, body and root were and 1.2 cm respectively. Deep median sulcus was seen on midline of tongue and four types of lingual papillae with different distribution and density were observed on its dorsal surface. Filiform papillae with the highest density and distribution were whole of tongue, a few fungiform. p with taste buds were on midlateral and two circumvallate with many taste buds were on posterior of tongue mucous and serous glands were in ventral surface of tongue. The results showed that the morphology and structure of tongue in both sexes are similar and related to diet pattern. Key words: Papillae, Taste bud, Diet Received 19/01/2014 Accepted 12/02/2014 How to cite this article: Ghazale C., Frangis G.Macroscopic and microscopic study of tongue in Wistar rats. Adv. Biores., Vol 5 [1] March 2014: DOI: /abr INTRODUCTION The morphology and microscopic structure of the tongue was investigated in vertebrates [1,2] and many rodents as mouse [3, 4], rat [3,5], mice [6,3] and rabbit [7,8]. The tongue is muscular organ with three layers including mucosa, submocosa and muscularis. Mucosa is covered by psudostratified squamous epithelium with variation in the keratinization. Six types of the lingual papillae with different density and distribution were known in mammals [9, 10]. These papillae are divided to mechanical (filiform.p, fugiform.p, conical.p) and gustatory papillae (vallate. P, foliate. P, lentiform. P). Filiform papillae are needle shape and they were oriented to pharynx. They were divided to three distinct types as type I which are needle like and covered with thin keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and they were located on apex and anterior of body [11]. The bifid or trifled filiform papillae (type II, III) were shorter and thicker than type 1, and placed on posterior area [5]. Fungiform. P less than filiform. P and are on the apex of the tongue [1]. These papillae In addition mechanical function, are gustatory duo to have a taste bud which is on their conical surface. Lamina propria like to many mammals is thin in filliform. P and very thick in fungiform. P [12]. The purpose of this study was to determine anatomy of tongue especially lingual papillae on light microscopy in female and male rat (wistar) and compared in both sexes. MATERIALS AND METHOD The tongue of 8 adult male and female rats (Wistar) was dissected from the root. Their weight, length and wide were measured. Then, they were fixed in neutral buffered formalin (10%) for 48 hours and prepared by tissue processing (dehydrated with alcohol %, clearing by xylol and paraffin impregnation. The serial sections (5 μm) were obtained by microtome and subjected to Haematoxylin and ABR Vol 5 [1] March P a g e
2 Eosin stains. The morphology and morphometric study of the tongue were studied by light microscope and progress capture soft ware. RESULTS The tongue of wistar rat in both sexes was composed of three layers as follows: Mucosa was covered by stratified squamous epithelium and thick keratin, thick submocosa with blood vessels and glands (almost serouse) and thick muscularis layer (Fig. 1). The tip of the tongue is flat with a deep median sulcus on dorsum and three parts (apex, body and root) were distinguished (Fig. 2). Length and of these pares were different (Table 1). Frenulum was from apex to posterior of body. Three types of papillae include filiform, fungiform, and circumvallate papillae were observed on the dorsum [1]. The density and distribution of papillae were different and decreased from the apex to root of tongue (Table 2). Filiform papillae have a pointed needle shape with high density were placed in the anteriolateral of the tongue and their orientation forward to pharynx (Fig. 1, 3).Fungiform papillae less than filiform papillae and were on the tongue apex (Fig. 4). These papillae has mechanical and gustatory function because they have one taste bud which is on their conical surface. In this study, foliate papillae were not observed on the contrary [13]. The one circumvallate papillae is suited on front of root. This was observed without microscope and was seen as papillae which surrounded by narrow canal in cross section (Fig 5). Epithelium and keratin in ventral surface were thiner than dorsal surface. Many glands (serous and mucous gland), thick lamina propria and more muscular mass (circular and longitudinal) was observed in this surface. The most of muscle were transverse bundle and longitudinal bundle were between them (Fig 6). Colagenous fiber was in front and many lymphoid cells in posterior of tongue. Table1. Comparatives characteristic of tongue in female and male of rat (wistar ) Parameter mean of length mean of (Apex) Width (Body) mean of (Root) mean of Female 2.65 Cm.0.58 Cm 0.69 Cm 1.00 Cm Male 2.69 Cm.0.58 Cm 0.64 Cm 1.20 Cm Table2. Comparatives characteristic of lingual papillae in female and male of rat (wistar) Female /83 Male /20 mm(size) Density low High 1 number Distribution Apex, midlateral Whole of dorsum Posterior of body Papillae Fungiform. P Filiform. P Vallate.P Fig1. Apex of tongue in male Rat (wistar) Stratified squmose epithelium (S.S.E); lamina propria (L.P); muscle bundle (M); keratin (K); mucosa (mu); submucosa (S.m); vessel (V); filiform papilla (Fi.P1, 2); adipose gland (A.g), Fig 2. Apex of tongue in female Rat (wistar) stratified squamous; filiform papilla (Fi.P); lamina propria (L.P); mucosa (m) ; submucosa(s.m); muscle bundle (M) ABR Vol 5 [1] March P a g e
3 Cheshmi and Ghassemi Fig 3. Body of tongue in male Rat (wistar) Fig 4. Apex of tongue in Female Rat (wistar) Keratinized stratified squmose epithelium (K.S.S.E); lamina propria(l.p); fungiform papillae (Fu.P); taste buds (T.B); muscle fibres (M); keratin (K); filiform. papillae (Fi.P); mucus gland (M.g); serouse gland (S.g) Fig 5. posterior of tongue in male Rat (wistar) Fig 6. posterior of tongue in male Rat (wistar) Circumvallate papillae (ci,p); taste buds ( t.b); blood vessel (B); Cleft( Cl); pseudostratified squamose epithelium (Ps.sS.E) stratified squamose epithelium (S.S.E); lamina proprian(l.p); circular muscle (C.M); longitudinal muscle (L.M); keratin (K); collagenous fiber (col); serous gland (S.g) lamina propria(l.p); fungiform papillae (Fu.P); taste buds (T.B); muscle fibres (M); keratin (K); vessel (V); mucus gland (M.g); serouse gland (S.g) Discussion In present study, anatomy of tongue especially lingual papillae was observed with light microscope and compared in female and male rat (wistar). According previous study [3, 8], stratified squamous epithelium and thick keratin on filiform.p was necessary for protection against damage due to taking hard food. ABR Vol 5 [1] March P a g e
4 Observation of different types of papillae on dorsal surface of tongue in male and female rat (wistar) suggests that their tongue is specialized for digestion. Filiform.P have a similar structure and localization as those of rats and mice [6,12]. Since rat (wistar) and mice are similar in food source, this result is expected. Long and biforked filiform.p which were placed in the apex, aid to take food particles and orientation of them (toward to posterior) facilitate swallowing [10]. The distribution, structure and morphology of these papillae were adapted to gallinaceous diet. Although these papillae were on the whole of dorsal surface of tongue but high density of them was on apex and decrease to posterior are. This finding was unlike previous finding about mice's tongue [13]. Although foliate papillae were observed on tongue in some vertebrates [14, 15] and were seen on the lateral surface of the rat's tongue [13] but in this survey, it wasn t seen. Further research is suggested about this papillae Gustatory papillae include fungiform and circumvallate papillae because they have taste bud. Despite fungiform.p have mechanical role in some vertebrates [16] but obtained results showed that they have both roles (gustatory and mechanical ) in this species. Presence obvious keratin on the surface and a few taste bud (one) in these papillae showed that their mechanical role is preferable (Fig.3, 4). The number of taste bud is vary in mammals and placed on conical surface [16]. The one circumvallate papillae is suited front of root [6]. This papillae have many taste buds in lateral walls epithelium and tubular canal is around it [17]. The serous and mucous glands which were in submocusa and related to taste buds via its canal and aid to gustatory (Fig.5). This papillae is oval and big as seen without microscope (Fig.6). Thick epithelium and keratin in dorsal surface especially on apx and filliform papillae are useful for contacting hard food. Although the oral epithelium covered by keratin in all of mammals but keratinization is variable and related to their diets [6]. Thick lamina propria with blood vessel and collagenous fiber supported mucosa well. (Fig 6). Density of muscle and collagen aid to movement of tongue and mastication. A few vessel in lamina propria This may be relate to low absorption in oral cavity. Because food consumed by rat is hard and is not digested in the mouth [18]. On the other presence of taste buds in fungiform and vallate papillae confirm to begging of food digestion. Presence of fungiform.p on epithelium of apex aid to take food whereas this papillae almost pleased on middle or posterior of tongue [7, 19]. Its taste bud (one) were exposed to food, masticated and facilitated to swallow food particles [13]. CONCLUSION Obtained results showed that morphology and microscopic anatomy of tongue are similar in both sexes of rat (Wistar). Their structural specifications are taxonomic and adaptations to their feeding patterns. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We would like to thank authorities of Islamic Azad University, Jahrom branch, to assist this project. REFERENCES 1. Igbokwe, C. O. and Okolie, C. (2009). The Morphological Observations of Some Lingual Papillae in the Prenatal and Prepuberal Stages of Red Sokoto Goats (Capra hircus). Int. J. Morphol. 27(1): , Ebru K. S, MelekK. H, Ismail S. H. (2010). Characteristics of dorsal lingual papillae of Zavot cattle. J. Anim. Vet. Adv 9: Iwasaki, S., Yoshizawa, H., Kawahara,I. (1999). Ultra structure study of the relationship between the morphogenesis of filiform papillae and the keratinization of the lingual epithelium in the rat. J. Anat., 195: Carrard VC, Pires AS, Badauy CM, et al. (2008). Effects of aging on mouse tongue epithelium focusing on cell proliferation rate and morphological aspects, Bull Tokyo Dent Coll.;49(4): Nasr, E. S; Gamal, A.M. and Elsheikh, E.H. (2012). Light and scanning electron microscopic study of the dorsal lingual papillae of the rat Arvicanthis niloticus (Muridae, Rodentia). Journal of American Science. 8(4). 6. Kobayashi K, Kumakura M, Yoshimura K, Takahashi et al. (2004): Comparative morphological studies on the stereo structure of the lingual papillae of selected primates using scanning electron microscopy. Ann. Anat.,186 : Silva Mcp, Watanabe I, Kronka Mc. (2002). Three-Dimensional Architec-Ture Of The Connective Tissue Core And Surface Structure Of The Lingual Papillae In The Rabbit. Histol Histopathol. 17: Nonaka K, Zheng J, Kobayashi K. (2008). Comparative morphological study on the lingual papillae and their connective tissue cores in rabbits. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn 85: Agungpriyono S, Yamada J, Kitamura N, et al. (1995).Morphology of the dorsal lingual papillae in the lesser mouse deer, Tragulus javanicus. J. Anat. 187: ABR Vol 5 [1] March P a g e
5 10. Jackowiak H and Godynicki S. (2007). Thescanning electron observations on the structure of the lingual papillae of the feathertail glider (Acrobates pygmeus, Burramyidae). Anat Histol Embryol 35(1): Jwasakis A. (2002). Evolution of the structure and function of the vertebrate tongue. J. Anat 201 (1), Toprak B, (2006). Light and scanning microscopic structure of filiform papillae in mice. Veterinarski Arhiv.76: Taiwo, A, Abayomi D, Ofusorti O, Ayoka A (2009). A comparative histological Study of the tongue of Rat, Bat and pangolin. Int J Morphol 27: Jackowiak, H. (2006). Scanning electron microscopy study of the lingual papillae in the European Mole (Talpa europea,l., Talpidae). Anat. Histol. Embryol., 35: Emura S, Hayakawa D, Chen H, et al. (2004). Morphology of the lingual papillae in the tiger.okajimas Folia Anat Jpn.;81: Benetti E.J, Pícoli L.C, Guimarães J.P, Motoyama, et al.(2009). Characteristics of filiform, fungiform and vallate papillae and surface of interface epithelium-connective tissue of the maned sloth tongue mucosa (Bradypus torquatus, Iliger, 1811): Light and Scanning Electron Microscopy Study. Anat Histol Embryol 38(1): Mistretta, C.M.and Baum, J.B. (1984). Quantitive study of taste buds in fungiform and circumvallate papillae of young and aged rats. J. Anatomy, 138(2) Ofusori, D. A, Enaibe, B. U,Falana, B. A, Adeeyo, O. A, Yusuf, U. A. & Ajayi, S. A. A. (2008). comparative morphometric analysis of the stomach in Rat Rattus norvegicus, Bat Eidolon helvum and Pangolin Manis tricuspis. J. Cell. Anim. Biol., 2(3): Yoshimura, K, Hama, N, Shindo, j, Kobayashi, K and Kageyama, N.( 2008).. Light and scanning electron microscopic study on the lingual papillae and their connective tissue cores of the Cape hyrax Procavia capensis, J Anat. November, 213(5): ABR Vol 5 [1] March P a g e
COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN TWO SPECIES OF RAT (RATTUS NORVEGICUS & RATTUS WISTAR)
 COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN TWO SPECIES OF RAT (RATTUS NORVEGICUS & RATTUS WISTAR) *Farangis Ghassemi & Ghazale Cheshmi Department of Biology, Jahrom branch, Islamic Azad University, Jahrom,
COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN TWO SPECIES OF RAT (RATTUS NORVEGICUS & RATTUS WISTAR) *Farangis Ghassemi & Ghazale Cheshmi Department of Biology, Jahrom branch, Islamic Azad University, Jahrom,
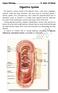
Dorsum of the tongue. Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types. Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove
 Histology of TONGUE Figure 22.13 Dorsum of the tongue Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types a. filiform papillae,
Histology of TONGUE Figure 22.13 Dorsum of the tongue Oral Part of Tongue divided into Left & right halves by shallow median groove Oral Part exhibit lingual papillae of the 4 types a. filiform papillae,
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF TONGUE IN ROUSETTUS AEGYPTIACUS IN THE SOUTHWEST OF IRAN (JAHROM)
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Applied, Natural and Social Sciences (IMPACT: IJRANSS) ISSN(E): 2321-8851; ISSN(P): 2347-4580 Vol. 1, Issue 6, Nov 2013, 43-50 Impact Journals HISTOLOGICAL
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Applied, Natural and Social Sciences (IMPACT: IJRANSS) ISSN(E): 2321-8851; ISSN(P): 2347-4580 Vol. 1, Issue 6, Nov 2013, 43-50 Impact Journals HISTOLOGICAL
Morphology of the lingual papillae of the eland (Taurotragus oryx)
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 93(3): Lingual 99 103, papillae November, of eland 2016 99 Morphology of the lingual papillae of the eland (Taurotragus oryx) By Shoichi EMURA Heisei College of Health Sciences,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 93(3): Lingual 99 103, papillae November, of eland 2016 99 Morphology of the lingual papillae of the eland (Taurotragus oryx) By Shoichi EMURA Heisei College of Health Sciences,
HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES. At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions:
 HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES CHAPTER ONE The Special Senses Learning objectives At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions: 1. What is the gross and histological
HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES CHAPTER ONE The Special Senses Learning objectives At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions: 1. What is the gross and histological
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
MICROSTRUCTURES LIPS TOOTH TONGUE OESOPHAGUS STOMACH, CARDIAC, PYLORIC FUNDIC GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES, FORM, FUNCTION, MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE: A hollow
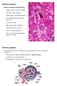
A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove.
 By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
1. Introduction. Volume 6 Issue 9, September Dr. Baydaa H. Mutlak 1, Dr. Intidhar M. Mnati 2, Dr. Iman S.
 The Morphological Description and Histological Study of Lingual Papillae in the Tongue Bat Pipistrillus kuhli Dr. Baydaa H. Mutlak 1, Dr. Intidhar M. Mnati 2, Dr. Iman S. AL-Jumaily 3 Department ofbiology,
The Morphological Description and Histological Study of Lingual Papillae in the Tongue Bat Pipistrillus kuhli Dr. Baydaa H. Mutlak 1, Dr. Intidhar M. Mnati 2, Dr. Iman S. AL-Jumaily 3 Department ofbiology,
The distribution and structure of the lingual papillae on the tongue of the bank vole Clethrionomys glareolus
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 326 333 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The distribution and structure of the lingual papillae on the tongue
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 326 333 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The distribution and structure of the lingual papillae on the tongue
Morphohistological study of the tongue in local mice species by using special stain
 Morphohistological study of the tongue in local mice species by using special stain Dr. Shrmean Abdulla Abd AL-Rhman 1, Azhaar Raheem AL-Fartwsy 1, Entikhab Hameed AL- Shuaily 1 1 Department of biology,
Morphohistological study of the tongue in local mice species by using special stain Dr. Shrmean Abdulla Abd AL-Rhman 1, Azhaar Raheem AL-Fartwsy 1, Entikhab Hameed AL- Shuaily 1 1 Department of biology,
Ultramorphological studies on the lingual papillae of Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in relation to its feeding habits
 Proc. 7 th Int. Con. Biol. Sci. (Zool) Ultramorphological studies on the lingual papillae of Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in relation to its feeding habits Gamal Ali Mohammed Departments of Zoology,
Proc. 7 th Int. Con. Biol. Sci. (Zool) Ultramorphological studies on the lingual papillae of Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in relation to its feeding habits Gamal Ali Mohammed Departments of Zoology,
LM and SEM Studies on Tongue and Lingual Papillae in the Donkey (Equus asinus)
 LM and SEM Studies on Tongue and Lingual Papillae in the Donkey (Equus asinus) Hanna Jackowiak 1, Hassen Jerbi 2, Kinga Skieresz-Szewczyk 1 and Ewelina Prozorowska 1 1 Department of Histology and Embryology,
LM and SEM Studies on Tongue and Lingual Papillae in the Donkey (Equus asinus) Hanna Jackowiak 1, Hassen Jerbi 2, Kinga Skieresz-Szewczyk 1 and Ewelina Prozorowska 1 1 Department of Histology and Embryology,
GI Histology Lab 1. Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji
 GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
Oral cavity Lab exercises
 Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
Scanning electron microscopic study of the tongue in the rainbow lorikeet (Trichoglossus haematodus)
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 88(1): 17 21, May, 2011 Scanning electron microscopic study of the tongue in the rainbow lorikeet (Trichoglossus haematodus) By Shoichi EMURA 1, Toshihiko OKUMURA 2 and Huayue
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 88(1): 17 21, May, 2011 Scanning electron microscopic study of the tongue in the rainbow lorikeet (Trichoglossus haematodus) By Shoichi EMURA 1, Toshihiko OKUMURA 2 and Huayue
Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 56(5) : 309-316, December 1979 Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle By IKUO YOSHIOKA, MICHIKO IIDA and HIROSHI MUTO
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 56(5) : 309-316, December 1979 Morphology of the Tongue Muscles of the Mouse with Special Reference to the Genioglossus Muscle By IKUO YOSHIOKA, MICHIKO IIDA and HIROSHI MUTO
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
Objectives. Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract
 GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
abstract Key words: Hard palate, Tongue, Buccal floor, Sambar deer, Gross anatomy
 Gross anatomical studies on the hard palate, tongue and buccal floor in sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) a.r sreeranjini 1, c.v rajani 2 and n. ashok 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology College
Gross anatomical studies on the hard palate, tongue and buccal floor in sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) a.r sreeranjini 1, c.v rajani 2 and n. ashok 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology College
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Processes of DIGESTION Mechanical
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians. with Marnie Hayward
 Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Histologic developmental horizons of the prenatal dromedary tongue
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Sokoto Journal of Veterinary Sciences (P-ISSN 1595-093X/ E-ISSN 2315-6201) Jaji et al/sokoto Journal of Veterinary Sciences (2016) 14(1): 28-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/sokjvs.v14i1.5
RESEARCH ARTICLE Sokoto Journal of Veterinary Sciences (P-ISSN 1595-093X/ E-ISSN 2315-6201) Jaji et al/sokoto Journal of Veterinary Sciences (2016) 14(1): 28-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/sokjvs.v14i1.5
Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep
 DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today, we will leave all hormones and start with another topic which is GI system This lecture is talking about general histology of Gastrointestinal system.. The gastrointestinal
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Today, we will leave all hormones and start with another topic which is GI system This lecture is talking about general histology of Gastrointestinal system.. The gastrointestinal
Morphology of the dorsal lingual papillae in the lesser mouse deer, Tragulus javanicus
 J. Anat. (1995) 187, pp. 635-640, with 5 figures Printed in Great Britain 635 Morphology of the dorsal lingual papillae in the lesser mouse deer, Tragulus javanicus SRIHADI AGUNGPRIYONO",2, JUNZO YAMADA',
J. Anat. (1995) 187, pp. 635-640, with 5 figures Printed in Great Britain 635 Morphology of the dorsal lingual papillae in the lesser mouse deer, Tragulus javanicus SRIHADI AGUNGPRIYONO",2, JUNZO YAMADA',
Surface Morphological Structure Of The Tongue Of The Hedgehog,HemiechinusAuritus (Insectivora:Erinaceidae) Nasr, E.S.
 Surface Morphological Structure Of The Tongue Of The Hedgehog,HemiechinusAuritus (Insectivora:Erinaceidae) Nasr, E.S. Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Zagazig University Nasriraky1970@yahoo.com
Surface Morphological Structure Of The Tongue Of The Hedgehog,HemiechinusAuritus (Insectivora:Erinaceidae) Nasr, E.S. Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Zagazig University Nasriraky1970@yahoo.com
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Lingual Dorsal Surface of the Beagle Dog. Shin-ichi IWASAKI and Koichi SAKATA
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 62 (1) : 1-14, May 1985 Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Lingual Dorsal Surface of the Beagle Dog By Shin-ichi IWASAKI and Koichi SAKATA Department of Oral Anatomy, Nippon
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 62 (1) : 1-14, May 1985 Scanning Electron Microscopy of the Lingual Dorsal Surface of the Beagle Dog By Shin-ichi IWASAKI and Koichi SAKATA Department of Oral Anatomy, Nippon
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI
 UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 LEVEL I MID-SEMESTER II EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (BScN) AND BACHELOR OF PHARMACY (B.PHARM) MARKING SCHEME HNS101/UPC106:
UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 LEVEL I MID-SEMESTER II EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING (BScN) AND BACHELOR OF PHARMACY (B.PHARM) MARKING SCHEME HNS101/UPC106:
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Histology Lab. looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira book and you can use BlueHistolgy website
 Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Digestive System
 Digestive System The digestive system consists of the digestive tract oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and anus and its associated glands salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
Digestive System The digestive system consists of the digestive tract oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and anus and its associated glands salivary glands, liver, and pancreas.
Connective tissue The Digestive System
 Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Morphological adaptations of yak (Bos grunniens) tongue to the foraging environment of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau 1
 Published December 4, 2014 Morphological adaptations of yak (Bos grunniens) tongue to the foraging environment of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau 1 B. Shao,* R. Long,* 2 Y. Ding, J. Wang, L. Ding,* and H.
Published December 4, 2014 Morphological adaptations of yak (Bos grunniens) tongue to the foraging environment of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau 1 B. Shao,* R. Long,* 2 Y. Ding, J. Wang, L. Ding,* and H.
Microscopic Study on the Tongue of Male Ostrich
 European Journal of Biological Sciences 2 (2): 24-31, 2010 ISSN 2079-2085 IDOSI Publications, 2010 Microscopic Study on the Tongue of Male Ostrich 1 2 2 Aghdas Poost Pasand, Mina Tadjalli and Hadi Mansouri
European Journal of Biological Sciences 2 (2): 24-31, 2010 ISSN 2079-2085 IDOSI Publications, 2010 Microscopic Study on the Tongue of Male Ostrich 1 2 2 Aghdas Poost Pasand, Mina Tadjalli and Hadi Mansouri
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
TASTE BUDS IN THE PITS AT THE POSTERIOR DORSUM OF THE TONGUE OF
 TASTE BUDS IN THE PITS AT THE POSTERIOR DORSUM OF THE TONGUE OF STENELLA COERULEOALBA FUSAO YAMASAKI, SHUNRO KOMATSU Department of Biology, Sapporo Medical College, Sapporo AND TOSHIRO KAMIYA Department
TASTE BUDS IN THE PITS AT THE POSTERIOR DORSUM OF THE TONGUE OF STENELLA COERULEOALBA FUSAO YAMASAKI, SHUNRO KOMATSU Department of Biology, Sapporo Medical College, Sapporo AND TOSHIRO KAMIYA Department
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Morphology of the Lingual Papillae in the Least Weasel (Mustela nivalis)
 Int. J. Morphol., Morphology of the Lingual Papillae in the Least Weasel (Mustela nivalis) Morfología de las Papilas Linguales en la Comadreja Común (Mustela nivalis) Neveen E. R. El Bakary * & Shoichi
Int. J. Morphol., Morphology of the Lingual Papillae in the Least Weasel (Mustela nivalis) Morfología de las Papilas Linguales en la Comadreja Común (Mustela nivalis) Neveen E. R. El Bakary * & Shoichi
口腔生理學 ( 含顎咬合 ) Oral physiology (occlusion included) 學習目標. Oral moucosa 參考資料. Classification. Mucosa
 口腔生理學 ( 含顎咬合 ) Oral physiology (occlusion included) Mucosa 臺北醫學大學牙醫學系張維仁老師 E-mail cweijen1@tmu.edu.tw 學習目標 1. let the student to understand the base knolwedge of oral physisology. 2.The student can firsther
口腔生理學 ( 含顎咬合 ) Oral physiology (occlusion included) Mucosa 臺北醫學大學牙醫學系張維仁老師 E-mail cweijen1@tmu.edu.tw 學習目標 1. let the student to understand the base knolwedge of oral physisology. 2.The student can firsther
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa!
 A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN:
 Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
From the Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku University, Innervation of Radical Part of Tongue of Hedgehog.
 From the Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku University, Sendai. Innervation of Radical Part of Tongue of Hedgehog. Many histological studies on the innervation, especially on the sensory innervation,
From the Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku University, Sendai. Innervation of Radical Part of Tongue of Hedgehog. Many histological studies on the innervation, especially on the sensory innervation,
Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA)
 Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA) Original article Anatomical and histological studies of esophagus of one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) Adel Jabbar Hussein 1 ;Muntdhur
Mirror of Research in Veterinary Sciences and Animals (MRVSA) Original article Anatomical and histological studies of esophagus of one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) Adel Jabbar Hussein 1 ;Muntdhur
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud
 Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud The oral cavity has 2 parts: 1. Oral vestibule: outer part that consists of outside the teeth, between the teeth, the cheeks and
Anatomy Sheet: Oral cavity Done by: rasha Rakan edited by: khansaa Mahmoud The oral cavity has 2 parts: 1. Oral vestibule: outer part that consists of outside the teeth, between the teeth, the cheeks and
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Urinary system. Urinary system
 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Connective tissue The Digestive System
 Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
Connective tissue The Digestive System Part 1 Structure of digestive system Functions Basic Structure of the Alimentary Canal Wall Tube is made up of four layers: 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
Morphological differences in epithelial papillae and microvascular architecture according to site in cat filiform papillae
 J Osaka Dent Univ 2015 (April) ; 49 (1) : 35 48. Morphological differences in epithelial papillae and microvascular architecture according to site in cat filiform papillae Masaya Hikida, Akimichi Takemura
J Osaka Dent Univ 2015 (April) ; 49 (1) : 35 48. Morphological differences in epithelial papillae and microvascular architecture according to site in cat filiform papillae Masaya Hikida, Akimichi Takemura
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
The Digestive System. Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1
 The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System. Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences
 Digestive System Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences Today we will discuss: Histological layers of alimentary canal Oral cavity Lip
Digestive System Presented by: Dr M. Arianmanesh PhD in Reproductive and Developmental Biology Dept. of Anatomical Sciences Today we will discuss: Histological layers of alimentary canal Oral cavity Lip
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Digestive System. The group of organs which performs the function of digestion constitute digestive system.
 Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Digestive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Digestive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 24 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Digestive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 24 For this lab you will use
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion?
 Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 78(2-3): 49-54, August. 2001 Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve By Hiromitsu EZURE, Noboru GOTO, Naoko NONAKA, Jun GOTO and Hiroaki TANI Department of Anatomy,
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 78(2-3): 49-54, August. 2001 Morphometric Analysis of the Human Trigeminal Nerve By Hiromitsu EZURE, Noboru GOTO, Naoko NONAKA, Jun GOTO and Hiroaki TANI Department of Anatomy,
Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation
 Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
Supplementary Information Intravital Microscopic Interrogation of Peripheral Taste Sensation Myunghwan Choi 1, Woei Ming Lee 1,2, and Seok-Hyun Yun 1 * 1 Harvard Medical School and Wellman Center for Photomedicine,
On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. One of the present authors, KIKUCHI, has reported in detail on the innervation
 Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 19, n. 3 (May 1960). P. 437-446. Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku Univ., Sendai. On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. Mizuho KIKUCHI, Shunsaku HATAKEYAMA,
Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 19, n. 3 (May 1960). P. 437-446. Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku Univ., Sendai. On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. Mizuho KIKUCHI, Shunsaku HATAKEYAMA,
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human;
 Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Lips and labial mucosa
 Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Reformation of Taste Buds by Crossed Sensory Nerves in the Rat s Tongue
 Acta physiol. scand. 1970. 79. 88-94 From the Department of Physiology, Veterinarhogskolan, Stockholm, Sweden and the Department of Zoology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, U.S.A. Reformation
Acta physiol. scand. 1970. 79. 88-94 From the Department of Physiology, Veterinarhogskolan, Stockholm, Sweden and the Department of Zoology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, U.S.A. Reformation
by authors and SVSBT.
 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
Taste. Alexis, Emma, Maureen
 Taste Alexis, Emma, Maureen There will be essential vocabulary throughout the presentation. We will define them then. Anatomy 3 Cranial Nerves Facial Glossopharyngeal* Vagus Tongue Brain Papillae Tastebuds
Taste Alexis, Emma, Maureen There will be essential vocabulary throughout the presentation. We will define them then. Anatomy 3 Cranial Nerves Facial Glossopharyngeal* Vagus Tongue Brain Papillae Tastebuds
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Lab activity manual Histology of the digestive system
 Lab activity manual Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from the
Lab activity manual Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from the
