Instant download and all chapter: Test Bank for Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition By Stanfield CLICK HERE Chapter 1
|
|
|
- Harold Leo Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Instant download and all chapter: Test Bank for Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition By Stanfield CLICK HERE Chapter 1 1) The smallest living units capable of carrying out their own basic life functions are called A) cells. B) organelles. C) organs. D) organ systems. E) tissues. 2) Cells are classified into which of the following four broad categories? A) squamous, cubodial, columnar, and basement membranes B) endocrine, nervous, integumentary, and reproductive C) atoms, tissues, organs, and organ systems D) neurons, muscle, epithelial, and connective tissue E) skeletal, cardiac, endocrine, and nervous 3) Epithelial cells are associated with a noncellular material called a(n) A) muscle fiber. B) endocrine gland. C) basement membrane. D) connective tissue. E) fibroblast. 4) are found in the linings of hollow organs where they separate fluids in the interior cavity from the surrounding body fluids. The interior cavity of a hollow organ or vessel is known as a. A) Epithelial : lumen B) Endocrine cells : lumen C) Elastin cells : cavity D) Smooth muscle cells : cavity E) Connective tissues : basement membrane 5) The tissue type that generates mechanical force and movement, and whose activity is controlled both on a voluntary and involuntary level, is tissue. A) nervous B) epithelial C) skeletal D) muscle E) connective 6) Glands are derived from what type of tissue? A) connective B) reticular C) nerve D) muscle E) epithelial 7) The cell types blood, bone, fat, and lymph would be categorized into which of the following major cell classes? A) muscle cells B) epithelial cells 1
2 C) endocrine cells D) neurons E) connective tissue cells 8) Which tissue type includes cells contained in an extracellular matrix composed of collagen and elastin? A) muscle tissue B) nervous tissue C) endocrine tissue D) epithelial tissue E) connective tissue 9) What is a general name for the noncellular material that holds the widely scattered cells of connective tissue together? A) intracellular matrix B) extracellular matrix C) basement membrane D) elastin E) collagen 10) Which of the following is a protein found in connective tissue that provides the tensile strength to resist stretching? A) erythropoietin B) elastin C) vimentin D) collagen E) basement membrane 11) What are the structures that attach bone to muscle? A) aponeuroses B) intracellular matrix proteins C) ligaments D) extracellular matrix proteins E) tendons 12) Organs of the body are defined as A) a collection of cells that function independently of one another. B) a collection of cells that perform similar functions. C) a collection of tissues that function independently of one another. D) two or more tissues combined to form a structure that allows each tissue to function independently. E) a combination of two or more tissues that make up a structure which performs a specific function. 13) Which of the following accurately represents the order of complexity for the components of the body, from least to most complex? A) cells, tissues, organ systems, organs B) cells, tissues, organs, organ systems C) organ systems, organs, tissues, cells D) tissues, cells, organs, organ systems E) organ systems, cells, tissues, organs 2
3 14) The uptake of nutrients across the epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract and into the bloodstream is called A) secretion. B) filtration. C) reabsorption. D) absorption. E) excretion. 15) What organ system includes the pituitary gland, adrenal gland, and thyroid gland? A) nervous B) immune C) endocrine D) integumentary E) cardiovascular 16) The lumen of which of the following systems is part of the internal environment? A) respiratory system B) gastrointestinal system C) urinary system D) cardiovascular system E) gastrointestinal and urinary systems 17) The process whereby fluid from the bloodstream enters the tubules of the kidneys is called A) excretion. B) absorption. C) filtration. D) secretion. E) reabsorption. 18) The process whereby fluid in the kidneys is transported from the tubules back into the bloodstream is called A) absorption. B) reabsorption. C) secretion. D) excretion. E) filtration. 19) Referring to a membrane as "selectively permeable" describes its ability to A) allow the movement of particular molecules across a membrane. B) restrict only the movement of sodium across a membrane. C) restrict only the movement of potassium across the membrane. D) provide a barrier that restricts the movement of all molecules across a membrane. E) provide a minimal barrier that allows almost any molecule to move across a membrane. 20) Extracellular fluid is composed of A) plasma and intracellular fluid. B) intracellular fluid only. C) interstitial fluid and plasma. D) plasma only. E) interstitial fluid only. 3
4 21) Total body water is composed of A) extracellular fluid only. B) intracellular and interstitial fluid. C) intracellular and extracellular fluid. D) intracellular fluid only. E) plasma and intracellular fluid. 22) Where is most of our total body water located? A) in the lumen of the kidneys B) surrounding the cells C) in blood D) inside cells E) in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract 23) Which of the following compartments contain most of the water found in the human body? A) plasma B) intracellular fluid C) interstitial fluid D) lumen of the intestinal tract E) extracellular fluid 24) What are the two extracellular fluid compartments of the body? A) intracellular fluid and blood B) intracellular fluid and interstitial fluid C) intracellular fluid and plasma D) interstitial fluid and blood E) interstitial fluid and plasma 25) The portion of body water outside of cells that bathes most cells of the body is called A) interstitial fluid. B) extracellular fluid. C) intracellular fluid. D) plasma. E) intercellular fluid. 26) The fluid compartment with a high sodium and protein concentration is called A) intracellular and extracellular fluids. B) intracellular fluid. C) extracellular fluid. D) interstitial fluid. E) plasma. 27) Which of the following best describes intracellular fluid? A) rich in sodium, potassium, and chloride B) rich in potassium and chloride C) rich in proteins and chloride D) rich in proteins and potassium E) rich in sodium and chloride 28) The fluid compartment with a high sodium concentration that contains only trace amounts of protein is called A) interstitial fluid. 4
5 B) intracellular and extracellular fluids. C) extracellular fluid. D) plasma. E) intracellular fluid. 29) For a person weighing 150 pounds, how many liters of water are contained in all of the body's compartments? A) 11 B) 42 C) 50 D) 14 E) 70 30) Homeostasis is a term which describes the process whereby the body A) maintains a variable internal environment. B) affects the external environment. C) maintains a constant external environment. D) maintains a constant internal and external environment. E) maintains a constant internal environment. 31) Of the following conditions associated with excess heat, which is the most serious condition? A) excessive sweating B) dehydration C) dizziness D) heat exhaustion E) heat stroke 32) The maintenance of a stable internal environment compatible for life is called A) biochemistry. B) anatomy. C) microbiology. D) physiology. E) homeostasis. 33) What is the primary mechanism for maintaining homeostasis? A) intrinsic control B) extrinsic control C) inherent control D) negative feedback E) positive feedback 34) Which of the following statements about homeostasis is FALSE? A) Homeostasis is the maintenance of the internal environment. B) The organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis. C) The extracellular fluid is maintained in a state compatible for life. D) The primary mechanism to maintain homeostasis is positive feedback. E) Illness can result if homeostasis is disrupted. 35) Changes in the external environment alter the, which is detected by the, and that information is sent to the integrator. A) sensor : regulated variable B) set point : regulated variable C) error signal : regulated variable D) regulated variable : set point E) regulated variable : sensor 5
6 36) Lisinopril is a medication that lowers high blood pressure back to within a desired range of function. The action of this medication is similar to that of a(n) in the human body. A) negative feedback response B) regulated variable C) positive feedback response D) set point E) integrating center 37) If you were to take the temperature of everyone in class, assuming no one is sick, you would find that not everyone has a temperature of 98.6 F. Which statement below best explains your findings? A) If the subject is not at 98.6 F then he or she is in a disease state B) An error signal has occurred and a positive feedback response has put the persons in question out of the normal range of function. C) The measuring instrument is not working properly; everyone has a set point of 98.6 F. D) Their temperature is no doubt higher than 98.6 F because a positive feedback loop has increased the subjects' metabolism. E) Most regulated variables, such as temperature, fluctuate continuously and oscillate about the set point due to negative feedback control. 38) When people cut themselves, they have clotting factors in their blood that will be released continuously in a cascade until their blood clots and terminates the bleeding. What mechanism caused their blood to clot? A) secretion B) reabsorption C) negative feedback control D) positive feedback control E) homeostasis 39) A detects a change in a regulated variable and sends that information to a(n) which relays signals to a(n), usually a muscle or a gland. A) receptor : stimulus : regulated variable B) stimulus : receptor : organ system C) sensor : integrating center : effector D) sensor : effector : integrating center E) receptor : integrating center : negative feedback control 40) Vinnie has high blood glucose and must take insulin shots to control his blood sugar. Why must he override his normal homeostatic mechanisms by taking medication? A) Vinnie's set point has changed telling him he needs more sugar. B) Vinnie's positive feedback controls are not functioning properly. C) Vinnie's negative feedback controls are not functioning properly. D) Vinnie's sensors are detecting high levels of glucose and therefore are not secreting insulin due to positive feedback control. E) An error signal has been sent to Vinnie's integrating center, which is not functioning properly. 41) A patient has a high salt or sodium intake which draws fluid out of his cells to dilute the sodium. This process occurs as a result of A) excretion. B) negative feedback control. C) absorption. D) positive feedback control. 6
7 E) reabsorption. 42) The process of maintaining the internal environment in a state compatible for life is called, and it occurs primarily through. A) homeostasis : negative feedback B) negative feedback : intrinsic control C) positive feedback : intrinsic control D) intrinsic control : negative feedback E) intrinsic control : homeostasis 43) Which of the following is an example of negative feedback? A) At the time of birth, uterine contractions push the baby toward the cervix. Receptors in the cervix detect the pressure caused by the baby and cause the release of a hormone called oxytocin. This hormone stimulates stronger uterine contractions, which push more on the baby, causing an increase in pressure and another increase in oxytocin. The cycle continues until the baby is delivered from the mother. B) During a blood clot, platelets release ADP, which stimulates platelet aggregation, causing platelets to release more ADP. C) During an infection, the body temperature set point is increased. The hypothalamus communicates to skeletal muscles to shiver and to blood vessels to decrease blood flow to the skin, causing a rise in body temperature. D) Consumption of caffeine increases urine output, causing dehydration. E) If blood pressure increases above normal, baroreceptors in major arteries detect the change and send signals to the brain. Certain areas of the brain then send signals to the nerves that control the heart and blood vessels to make the heart beat slower and the blood vessels increase in diameter, which in turn reduce the blood pressure. 44) Luteinizing hormone-mediated regulation of estrogen during ovulation in women is an example of A) a quasi-positive feedback loop. B) a quasi-negative feedback loop. C) both a positive and a negative feedback loop. D) a negative feedback loop. E) a positive feedback loop. 45) The feedback loop involving luteinizing hormone and estrogen is terminated by A) ovulation, which directly inhibits luteinizing hormone secretion. B) ovulation, which decreases estrogen secretion. C) pregnancy. D) nothing; the cycle cannot be terminated. E) birth. 46) Which of the following is a normal blood glucose level? A) 100 mg/dl B) 200 mmolar C) 50 mg/dl D) 50 mmolar E) 100 gm/ml 47) What is the difference between diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus? A) One is a lack of insulin secretion; the other a resistance to insulin. B) One causes diarrhea; the other causes diuresis. C) One is a deficit in insulin activity; the other a deficit in ADH activity. D) One causes increased fluid loss; the other causes increased thirst. 7
8 E) One is a lack of ADH secretion; the other a resistance to ADH. 48) What cells secrete insulin? A) several cells located throughout the body B) alpha cells of the pancreas C) beta cells of the pancreas D) I cells of the adrenal cortex E) G cells of the adrenal cortex 49) Approximately what percentage of people living in the United States suffers from diabetes mellitus? A) 0.1% B) 8% C) 0.5% D) 15% E) 1% 50) Which of the following people would be more prone to develop diabetes mellitus type II? A) an obese Hispanic adult B) an obese white adult C) a thin white adult D) a thin, malnourished, African American child E) an obese Hispanic child 51) What percentage of adults in the United States is obese? A) 15% B) 35% C) 25% D) 10% E) 20% 52) Which of the following types of diabetes mellitus was formerly referred to as insulin-dependent or juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus? A) type 1 B) prediabetes C) type 2 D) gestational diabetes E) diabetes insipidus 53) What are the two major consequences for those who suffer from diabetes mellitus? A) high blood glucose and excessive urination B) low blood sugar and fainting C) high blood glucose and glucose in the urine D) high blood glucose and cells that cannot utilize that glucose for energy E) high blood glucose and excessive thirst 54) Although diabetes mellitus has many symptoms, the primary diagnostic symptoms of the disease are and. A) dizziness : dehydration B) lethargy : dizziness C) elevated blood glucose : glucose in the urine D) elevated blood glucose : lethargy E) elevated blood glucose : poor healing 8
9 55) What lab test, often deemed the "lie detector test" by health care workers, measures the average blood glucose levels for the past 2-3 months? A) fasting blood glucose test B) random blood glucose test C) siphon test D) hemoglobin A1c test E) glucose tolerance test 56) Obesity is identified using what measurement? A) body mass index (BMI) B) body type index C) ethnicity scale D) CDC disease scale E) waist circumference scale 57) What percentage of women will develop type 2 diabetes after developing gestational diabetes? A) 5-10% B) 1-2% C) 25-30% D) 3-4% E) 12-15% 58) What is the primary reason the prevalence of diabetes is increasing in the U.S. population? A) the U.S. diet B) an aging population C) sedentary lifestyles D) lack of physical activity E) obesity 59) Prediabetics have a fasting blood glucose level of and, according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), approximately million Americans are prediabetic. A) mg/dl : 80 B) mg/dl : 300 C) mg/dl : 10 D) mg/dl : 100 E) mg/dl : 50 60) John has type 2 diabetes. He has a sedentary lifestyle, is overweight, and recently went to the doctor who gave him a hemoglobin A1c test which came back at 7%. What is the best course of treatment for John? A) a strict diet, frequent monitoring of his blood glucose, exercise, and oral glucose medication B) frequent monitoring of his blood glucose levels with insulin shots C) measure his BMI, continued monitoring of his blood glucose levels with a hemoglobin A1c test, and changes in lifestyle D) insulin shots and exercise E) insulin shots and a healthy diet 61) Which tissue below is specialized for lining the lumen of vessels material? A) epithelial tissue 9
10 B) connective tissue C) nervous tissue D) muscle tissue E) reticular tissue 62) Which tissue below conducts signals primarily via electrical impulses? A) epithelial tissue B) connective tissue C) nervous tissue D) muscle tissue E) reticular tissue 63) Which tissue below provides structural support? A) epithelial tissue B) connective tissue C) nervous tissue D) muscle tissue E) reticular tissue 64) Which tissue below contracts to generate force? A) epithelial tissue B) connective tissue C) nervous tissue D) muscle tissue E) reticular tissue 65) The elimination of unabsorbed materials from the body refers to which of the processes below? A) filtration B) secretion C) excretion D) reabsorption E) absorption 66) Movement from the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract to the blood would represent which of the following processes? A) absorption B) reabsorption C) excretion D) filtration E) secretion 67) Movement from the blood into the kidney tubules would represent which of the following processes? A) excretion B) absorption C) secretion D) reabsorption E) filtration 68) Which of the following is/are associated with the endocrine system? A) bronchi B) adrenal gland C) blood vessels D) pancreas 10
11 E) esophagus 69) Which of the following is/are associated with the nervous system? A) bronchi B) brain C) esophagus D) adrenal cortex E) blood vessels 70) Which of the following is/are a component of the cardiovascular system? A) esophagus B) adrenal gland C) brain D) bronchi E) blood vessels 71) Which of the following is/are associated with the respiratory system? A) adrenal gland B) brain C) bronchi D) blood vessels E) esophagus 72) Which of the following is/are associated with the gastrointestinal system? A) esophagus B) adrenal gland C) bronchi D) brain E) blood vessels 73) The smallest living units, capable of carrying out their own basic life processes, are A) organs. B) atoms. C) tissues. D) cells. E) molecules. 74) Cells that carry oxygen in the bloodstream are called A) hemoglobin. B) leukocytes. C) karyocytes. D) lymphocytes. E) erythrocytes. 75) What tissue is specialized for separating fluids? A) epithelial B) connective C) nervous 76) What tissue is a major component of bone, ligaments, and blood? A) epithelial B) connective C) nervous D) muscle E) endocrine D) muscle E) endocrine 77) What tissue is specialized for generating electrical signals? 11
12 A) epithelial B) connective C) nervous 78) What tissue is specialized to contract? A) epithelial B) connective C) nervous 79) The specific structures that attach bone to bone are called A) sheathing. B) skeletal muscle. C) tendons. D) smooth muscle. E) ligaments. 80) The is the interior compartment of a hollow organ or vessel. A) lumen B) epithelium C) cavity D) intracellular matrix E) basement membrane D) muscle E) endocrine D) muscle E) endocrine 81) The process whereby enzymes are moved into the gastrointestinal tract to digest nutrients is called A) filtration. B) excretion. C) reabsorption. D) absorption. E) secretion. 82) The process whereby fluid and ions that have not been reabsorbed by the kidneys exit the body as urine is called A) filtration. B) secretion. C) reabsorption. D) excretion. E) absorption. 83) The fluid (non-cellular) portion of blood is called A) plasma. B) the internal environment. C) intracellular matrix. D) intracellular fluid. E) interstitial fluid. 84) The fluid compartment with a high protein and potassium concentration is called A) interstitial fluid. B) intracellular fluid. C) the internal environment. D) total body water. E) extracellular fluid. 85) Where is most of the water in the body found? A) in the lumen of the stomach B) in the plasma C) in the extracellular fluid D) in the intracellular fluid 12
13 E) in the interstitial fluid 86) Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels. It is released when glucose levels increase above normal. Based on the concept of negative feedback, what effect will insulin have on blood glucose levels? A) It will increase them. B) Insulin does not regulate blood glucose levels. C) It will decrease them. D) Insulin will not affect glucose levels. E) It makes them go both up and down. 87) What cells secrete insulin? A) collagen cells B) exocrine cells C) neurons D) beta cells E) alpha cells 88) Body mass index is a measure of weight in kilograms relative to A) gender. B) weight (in kilograms in water). C) arm length. D) waste circumference. E) height in meters (squared). 89) Pre-diabetics have fasting blood glucose levels of A) mg/dl B) mg/dl C) mg/dl D) mg/dl E) mg/dl 90) What type of ductless gland secretes hormones into the bloodstream? A) endocrine B) exocrine C) sweat D) matrix E) salivary 91) Which statement below best defines homeostasis? A) Homeostasis is the process whereby the body maintains the internal environment in a state compatible for life. B) Homeostasis is maintained through positive feedback loops. C) Homeostasis refers to the regulation of temperature in the human body. D) Homeostasis means all regulated variables are at the set point. E) Homeostasis is the process whereby the body changes with the external environment. 92) Which statement below lists the essential components of a feedback loop and describes their function? A) Integrator interprets the information; set point is the value of the regulated variable; effector alters the regulated variable. B) Set point is the value of the regulated variable; integrator interprets the information and sends it to the appropriate effector; effector alters the regulated variable; set point is the point the variable must always return to. C) Set point detects the regulated variable; integrator interprets the information and sends it to the appropriate effector; effector decides if it will react or not to the signal. D) Sensor detects a regulated variable; integrator interprets the information and sends it to the appropriate effector; effector alters the regulated variable; organ system returns the body back to normal 13
14 E) Sensor detects a regulated variable; set point is the value of the regulated variable; integrator interprets the information and sends it to the appropriate effector; effector alters the regulated variable. 93) Physiology is the study of function and can come in many forms, including plant physiology. 94) Pathophysiology is what happens when normal body functions are disrupted. 95) Connective tissue forms both endocrine and exocrine glands. 96) Exocrine glands secrete hormones. 97) The immune system protects the body from invading microorganisms. 98) Most of the cells of the body are able to directly exchange materials with the external environment. 99) The internal and external environments are separated by the selectively permeable membranes of epithelial cells. 100) The most abundant substance in the body is carbon. 101) Intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid are of the same ion composition. 102) The homeostatic mechanisms of the body are unlimited in their ability to respond to changes in the external environment. 103) Blood glucose is a regulated variable. 104) Effectors bring about a final response in a negative feedback loop. 105) Positive feedback loops are impossible to stop once they have begun. 106) All forms of diabetes involve a decrease in plasma levels of insulin. 107) Diabetes mellitus requires insulin injections for maintenance. 14
15 108) Once a woman develops gestational diabetes, she will have diabetes for life. 109) People with a body mass index (BMI) less than 25 are most prone to develop type 2 diabetes mellitus. 110) Cases of diabetes mellitus are increasing throughout the world, not just in the United States. 111) Obesity predisposes a person to develop type 1 diabetes mellitus. 112) Diabetes mellitus causes hyperglycemia. 113) Describe the four general groups of cells (tissues) that are found in the body, outlining the important characteristics of each group and their functions. Answer: Nervous tissue - Neurons are specialized for the transmission of information in the form of electrical signals. They typically possess a number of branches that function to receive or transmit those electrical signals. Some are even capable of detecting sensory information. Muscle tissue - Muscle cells are involved in force development and movement. They tend to be elongated in shape and can be under either voluntary or involuntary control. Epithelial tissue - Epithelial cells are arranged as a sheet-like layer of cells connected to a thin, non-cellular basement membrane. These cells are found in many shapes, sizes, and layer thicknesses. They are closely associated with their neighbors, providing a barrier separating body fluids from the external environment. Certain epithelial cells are specialized to transport specific molecules from one compartment to another. Connective tissue - This tissue encompasses many cell types including blood cells, bone cells, and many others. In a narrow sense, these cells provide physical support for other structures like tendons and ligaments. In a broader sense, the term connective tissue encompasses fluids like blood and lymph that "connect" parts of the body by providing an avenue for communication. 114) Water is the most abundant molecule in the human body. Identify both the amount of water and its location within the body. Answer: TBW represents the total volume of fluid within the body and is approximately 42 liters for an ideal human subject of 150 pounds. Most of the water in the body (28 liters) is found in intracellular fluid or the fluid found inside of cells. Extracellular fluid (14 liters of TBW), the fluid outside of cells, is composed of two compartments. One is the fluid component of blood (plasma), which is approximately 3 liters. The second is the fluid that bathes cells (interstitial fluid), which makes up 11 liters of TBW. 115) Blood glucose is a regulated variable controlled by a negative feedback loop. Explain what is meant by the term negative feedback and discuss how this mechanism would work in the case of high blood glucose. Answer: Negative feedback systems reverse the response of an increasing variable back to the set point for that variable. In this case, the rising blood glucose levels are detected by the sensors or beta cells within the pancreas. The beta cells also act as the integrating center and release the hormone insulin into the blood stream. Insulin causes glucose to move from the plasma of the blood into the cells of the body or effectors therefore driving down the levels of glucose back to within normal ranges. 116) Compare and contrast the different forms of diabetes. Answer: There are several types of diabetes, including diabetes mellitus type 1, diabetes mellitus type 2, diabetes insipidus, and gestational diabetes. Diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2 are associated with insufficient actions of insulin causing hyperglycemia and a number of other symptoms. 15
16 Diabetes mellitus type 1 is caused by decreased secretion of insulin. Without sufficient insulin, cells do not uptake glucose to meet their metabolic needs. Liver and muscle cells do not uptake insulin to store energy for later needs. Thus hyperglycemia and fatigue are common symptoms. In diabetes mellitus type 2, beta cells of the pancreas secrete insulin, but effector cells do not respond to the insulin. Thus symptoms are similar to that of diabetes mellitus type 1. Diabetes insipidus is a disease affecting the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). ADH promotes water reabsorption from the kidneys, and in its absence (or a decrease in tissue responsiveness to it), excessive water is lost in the urine causing dehydration. Gestational diabetes develops in some pregnant women. It is similar to type 2 diabetes mellitus, with hormones of pregnancy thought to induce the insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes often reverses following delivery of the baby. 16
Instant download and all chapter: Test Bank for Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition By Stanfield
 Instant download and all chapter: Test Bank for Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition By Stanfield http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-principles-of-human-physiology-5th-editionby-stanfield/
Instant download and all chapter: Test Bank for Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition By Stanfield http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-principles-of-human-physiology-5th-editionby-stanfield/
download instant at
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The smallest living units capable of carrying out their own basic life functions are
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The smallest living units capable of carrying out their own basic life functions are
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is/are associated with the gastrointestinal system? 1) A) blood
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is/are associated with the gastrointestinal system? 1) A) blood
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The smallest living units capable of carrying out their own basic life functions are
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The smallest living units capable of carrying out their own basic life functions are
download instant at
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The smallest living units capable of carrying out their own basic life functions are
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The smallest living units capable of carrying out their own basic life functions are
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which research field below employs a variety of tools from other fields, including engineering,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which research field below employs a variety of tools from other fields, including engineering,
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Select the incorrect association. a. anatomy/function b. human body/multicellular. c. carbon dioxide/cell waste product. d. physiology/body
Chapter 1 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Select the incorrect association. a. anatomy/function b. human body/multicellular. c. carbon dioxide/cell waste product. d. physiology/body
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
Anatomy & Homeostasis. Unit 5
 Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Anatomy & Homeostasis Unit 5 Main Ideas discuss with a buddy 2 What is Homeostasis? How is homeostasis different in single-celled organisms vs. multicellular organisms? What unique challenges to maintaining
Chapter 8 Human Organization
 Biology 12 Name: KY Human Organization Per: Date: hapter 8 Human Organization omplete using B Biology 12, pages 236 255 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 539) 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. c
Biology 12 Name: KY Human Organization Per: Date: hapter 8 Human Organization omplete using B Biology 12, pages 236 255 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 539) 1. b 2. a 3. c 4. c
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Chapter 8 Human Organization
 Biology 12 Name: Human Organization Per: Date: Chapter 8 Human Organization Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 236 255 8.1 Types of Tissues pages 240-243 1. The tissues in the human body can be categorized
Biology 12 Name: Human Organization Per: Date: Chapter 8 Human Organization Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 236 255 8.1 Types of Tissues pages 240-243 1. The tissues in the human body can be categorized
Unit 4 Homeostasis. The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt. Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment -
 Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
INTRODUCTION TO ANIMALS
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS ACTIVITY #1 NAME DATE HOUR INTRODUCTION TO ANIMALS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Animals Activity #1 page 1 HOMEOSTASIS: DEFINITION IMPORTANCE MECHANISMS FOR MAINTAINING HOMEOSTASIS: Animals
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS ACTIVITY #1 NAME DATE HOUR INTRODUCTION TO ANIMALS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Animals Activity #1 page 1 HOMEOSTASIS: DEFINITION IMPORTANCE MECHANISMS FOR MAINTAINING HOMEOSTASIS: Animals
5. Maintaining the internal environment. Homeostasis
 5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
Biology Anatomy and Physiology I. Learn and Understand. What is Biology? bios = life -ology = study of
 Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
Introduction to Organ Systems & Homeostasis. Packet #2
 Introduction to Organ Systems & Homeostasis Packet #2 Properties of Life Order All living things maintain a high degree of order and complexity Even the smallest living thing a cell Regulate Use of Energy
Introduction to Organ Systems & Homeostasis Packet #2 Properties of Life Order All living things maintain a high degree of order and complexity Even the smallest living thing a cell Regulate Use of Energy
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion
 Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Tissues. groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types. epithelium connective muscle nervous
 Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Connexons: hollow connective tubes
 Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
Chapter 3 1. tight junctions: like a zipper, these junctions hold the cells tightly together making them impermeable to the extracellular fluid that surrounds them. 2. desmosomes: like buttons, these
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Interactions Among Animal Systems. Biology 10(A)
 Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
Homeostasis. OpenStax College. 1 Negative Feedback
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45989 1 Homeostasis OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m45989 1 Homeostasis OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
Tissues. Group of cells that are similar in structure and function. 4 primary types. Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control)
 Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissues. Definition. A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function.
 Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals
 Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Classification of Tissues
 6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
6 R e v i e w S h e e t Exercise Classification of Tissues NAME LAB TIME/DATE Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group of cells similar to one another in structure that perform
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
A Single Neuron from the Brain
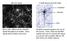 Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE
 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review. 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,,
 Name Period PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,, 2. Put the following pictures below in the correct
Name Period PAP Animal Body Systems Test Review 1. List the levels of organization from largest to smallest. (Organ-Organism-Cell-Organ System-Tissue),,,, 2. Put the following pictures below in the correct
Excretion and Waste Management. Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski
 Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Activity Booklet Name: Per: #: Label the following diagram with the levels of structural organization and the examples of each: 1 Identify the following body systems and
The Human Body: An Orientation Activity Booklet Name: Per: #: Label the following diagram with the levels of structural organization and the examples of each: 1 Identify the following body systems and
They cells can not function death.
 Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
HOMEOSTASIS 37 C. ph of % blood sugar
 HOMEOSTASIS ph of 7.35 37 C 0.1% blood sugar Homeostasis an equilibrium (steady state) between an organism s various physiological functions, and between the organism and the environment. This is a balance
HOMEOSTASIS ph of 7.35 37 C 0.1% blood sugar Homeostasis an equilibrium (steady state) between an organism s various physiological functions, and between the organism and the environment. This is a balance
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8vp5jeap3k4 27 2012 2012 Welcome back! Please write a response to the following: Imagine a time that you have been stressed, please describe the physical sensations that
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8vp5jeap3k4 27 2012 2012 Welcome back! Please write a response to the following: Imagine a time that you have been stressed, please describe the physical sensations that
Endocrine System. Regulating Blood Sugar. Thursday, December 14, 17
 Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
TISSUES. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Tissues. How do cells form tissues?
 Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
What is histology? HISTOLOGY
 Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Tissues. Definition. A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function.
 Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
TISSUE. A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS
 TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
ANIMAL ORGANIZATION, HOMEOSTASIS, AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Chapter 31
 ANIMAL ORGANIZATION, HOMEOSTASIS, AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Chapter 31 Tissue Tissues are groups of similar cells performing similar functions Organs are groups of tissues performing a specialized function
ANIMAL ORGANIZATION, HOMEOSTASIS, AND THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Chapter 31 Tissue Tissues are groups of similar cells performing similar functions Organs are groups of tissues performing a specialized function
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types:
 Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues. Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below:
 Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below: A. Connective B. Epithelium C. Muscle D. Nervous 1. B Lines body cavities and covers the body s external
Name: Test Date: Chapter 4- Tissues Use the choices to identify the major tissue types found below: A. Connective B. Epithelium C. Muscle D. Nervous 1. B Lines body cavities and covers the body s external
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1. Fill in the Blanks.
 Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Cells & Tissues. Chapter 3
 Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Classification of Tissues
 M06_MARI0000_00_SE_CH06.qxd 3/28/11 4:37 PM Page 35 NAME LAB TIME/DATE R E V I E W S H E E T EXERCISE 6 Classification of Tissues Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group
M06_MARI0000_00_SE_CH06.qxd 3/28/11 4:37 PM Page 35 NAME LAB TIME/DATE R E V I E W S H E E T EXERCISE 6 Classification of Tissues Tissue Structure and Function General Review 1. Define tissue. A group
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
4. A phospholipid is an example of organization at the level.
 1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
1. Physiology is the study of a. the structures of anatomical features. b. cellular metabolism. c. processes that allow organisms to function. d. how organ systems develop from the embryo. 2. Mary spends
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Pages
 NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Homeostasis Enlightenment
 Anatomy/Physiology Homeostasis Quick and Dirty Big Picture: We carry around inside us an environment (an internal environment ) that bathes our cells. It can t change too much or the cells and organs are
Anatomy/Physiology Homeostasis Quick and Dirty Big Picture: We carry around inside us an environment (an internal environment ) that bathes our cells. It can t change too much or the cells and organs are
n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y
 n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS
n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS
THE HUMAN BODY. study of the structure of living organisms. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: studying the structure of the heart.
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Anatomythe study of the structure of living organisms. Ex: studying the structure of the heart. Physiologythe study of how the body works. Ex: how the heart works to pump blood, etc.
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic
 Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
