Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
|
|
|
- Donna White
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cover Page The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ellenbroek, Johanne Hendrike (Rianne) Title: Pancreatic β- and α-cell adaptation in response to metabolic changes Issue Date:
2 Chapter 7 A high-throughput screening platform using primary human islets to assess β-cell function Johanne H. Ellenbroek 1, Carianne N. Langerijs 2, Michela A. Tessari 2, Blandine Mille-Baker 3, Marten A. Engelse 1, Ton J. Rabelink 1, Françoise Carlotti 1, Richard A. J. Janssen 2, Eelco J. P. de Koning 1,4,5 1 Department of Nephrology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; 2 Galapagos BV, Leiden, The Netherlands; 3 BioFocus, a Charles River company, Leiden, The Netherlands; 4 Department of Endocrinology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; and 5 Hubrecht Institute, Utrecht, The Netherlands Submitted
3 Abstract Aims β-cell dysfunction plays a crucial role in all types of diabetes mellitus. Therapies that restore β-cell mass and/or function are needed. High-throughput platforms using primary human β-cells can be a powerful tool for the screening of viral-delivered shrna or small compound libraries to identify new mechanisms involved in β-cell dysfunction and to identify possible starting points for therapeutic interventions. We developed a high-throughput culture platform for primary human islets to assess β-cell function. Methods Three culture systems were established in microwell plates format and compared: intact human islets, and islet cells cultured either in monolayer on ECM or reaggregated into isletcell clusters. β-cell function was determined by measuring glucose-induced insulin secretion and responsiveness to known insulin secretagogues. In addition, we assessed the efficiency of adeno- or lentivirus mediated transduction of the cells. Results All three culture platforms were set up successfully over a period of 3 days. Glucose-induced insulin secretion of islet cell aggregates was similar to intact islets, whereas the response of islet cells in monolayer was reduced. Exposure to glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists did not enhance insulin secretion, independent of the culture platform used. Activation of camp/epac-2 signal transduction and inhibition of K-channels enhanced glucose-induced insulin secretion in intact islets and islet cell aggregates, but not in monolayer culture. In contrast to intact islets, dispersed islet cells were efficiently transduced with adeno- or lentivirus. Conclusions We present three culture platforms in microwell format using primary human islet cells in which β-cell function can be assessed. Dispersed islet cells can be efficiently transduced using adeno- or lentivirus. Intact islets and islet cell aggregates did respond to insulin secretagogues, while islet cells in monolayer did not. These platforms can be used for highthroughput screening of viral-delivered shrna or small compound libraries to identify new mechanisms involved in β-cell function and survival. 104 Chapter 7
4 Introduction Diabetes mellitus affects 382 million people worldwide and by 2035 this is expected to increase to 592 million people (1). β-cell dysfunction plays a crucial role in all types of diabetes. Despite intensive treatment with diets and/or current antihyperglycemic agents, normalization of glycemic control can often not be achieved and patients are at risk to develop long-term microand macrovascular complications (2). Therefore, novel therapies are needed that restore β-cell function. High-throughput screenings of viral-delivered shrna or small compound libraries can be used to identify novel mechanisms involved in the regulation of glucose-induced insulin secretion. However, the development of robust high-throughput assay platforms of intact islets is challenging because islet sizes are heterogeneous and the virus transduction efficiency of these three-dimensional cell clusters is low (3). Currently no assay platforms are present in which human islet function is assessed. Existing assay platforms are mostly using rodent-derived cell lines and are set up to assess insulin gene expression or protein content (4 7). Following glucose stimulation only a fraction of the total insulin content is secreted from β-cells, which makes these existing read-outs poor indicators of secretory function (8). Therefore, the aim of this study is to set up a high-throughput culture system using primary human islets in which β-cell function can be assessed. Three different culture systems were compared: intact human islets, and cells from dispersed human islets cultured either in monolayer or reaggregated into islet-cell clusters. Materials and Methods Human islet isolation and cell culture Human pancreata were procured through a multiorgan donor program. Islet isolation was performed in the Good Manufacturing Practice facility of our institute according to the method described by Ricordi et al. (9). Isolated islets could be used for scientific research if the number and/or quality of the islets were insufficient for clinical islet transplantation, in accordance with national laws, and if research consent was available. Alternatively islets were obtained from Asterand (Detroit, MI, USA) or Tissue Solutions (Glasgow, UK). Islet purity was determined by dithizone staining. Only islet fractions with a purity of >70% were used in the studies. Islets were cultured in CMRL 1066 medium (Cellgro; Mediatech, Manassas, VA, USA) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 2 mmol/l L-glutamine, 10 mmol/l HEPES, 1.2 mg/ml nicotinamide, 50 μg/ml Gentamycin and penicillin/streptomycin (50 U/ml and 50 ug/ml respectively). A screening platform to assess human β-cell function 105
5 Islet dissociation and culture Islets were dispersed into single cells by incubation with TrypLE Express (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 37 C while gently pipetting up and down for 8 12 minutes. For monolayer culture 384-wells plates (Greiner Bio-One, Frickenhausen, Germany) were coated with a mixture (referred to as ECM) of 50% (vol/vol) ECM (final concentration 0.5 mg/ml; Sigma- Aldrich, St Louis, CA, USA), 37.5% PureCol (final concentration 1.12 mg/ml; Inamed, Gauting, Germany), 5% DMEM 10x (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific), 5% NaCO 3 (37 g/l), 2.5% Hepes (1 M), ph 7.4. Coated plates were incubated at 37 C for at least 30 minutes. Per 384-well 10,000 islet cells were plated. For the aggregate culture 20,000 cells were seeded in 96-wells U-shaped ultra-low binding plates (Costar, Corning, New York, USA). In parallel, intact islets were cultured at a density of 20 islets per well in 96-wells U-shaped ultra-low binding plates (Costar). Virus transduction Virus transduction was performed 2 hours after seeding the cells. Adenoviruses expressing the cdna of the Zsgreen fluorescent protein, or the shrna adenoviral construct expressing an shrna sequence with no significant homology to any known mammalian genes (egfp) or an empty virus vector were produced as described before (10). Islet cells cultured in monolayer and islet cell aggregates were transduced by the addition of adenovirus suspension resulting in a final MOI of 2 infectious particles per cell. Lentivirus transductions of islet cells were performed using vectors derived from prrl cppt-cmv-gfp-pre. Third generation self-activating lentivirus vectors were produced as described before (11). Islet cells cultured in monolayer and islet cell aggregates were transduced by the addition of lentivirus resulting in a final MOI of 2 (3). After 24 hours, the proteins Zsgreen protein was visualised using fluorescence microscopy and the transduction efficiency was determined by estimating the percentage of cells expressing the fluorescent protein of at least 3 wells per donor. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion Three days after seeding the cells or islets a glucose-induced insulin secretion test was performed. Intact islets and islet cell aggregates were transferred to a 96-wells transwell plate (Corning). Cells were washed two times with a modified Krebs-Ringer Bicarbonate HEPES (KRBH) buffer containing 115 mm NaCl, 5 mm KCl, 24 mm NaHCO 3, 2.2 mm CaCl 2, 1 mm MgCl 2, 20 mm HEPES and 2 g/l human serum albumin, ph 7.4 (incubation buffer). Cells were primed for 1.5 h at 37 C in incubation buffer supplemented with 2 mm glucose (low glucose). Subsequently, the cells were incubated in fresh incubation buffer supplemented with 2 mm glucose for 1 h to measure the basal insulin secretion levels. The cells were then incubated for 1 h in incubation buffer supplemented with 16.7 mm glucose (high glucose) in the presence or absence of insulin secretagogues. Insulin secretagogues tested were liraglutide (Novo Nordisk, Bagsvaerd, Denmark), exendin-4 (Sigma-Aldrich), the EPAC-2 agonist Reh3 (kindly provided by H. Rehmann), 106 Chapter 7
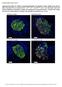
6 forskolin (Sigma-Aldrich) and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX; Calbiochem, Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA), and tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA; Sigma-Aldrich). Insulin concentrations were determined by ELISA (Mercodia, Uppsala, Sweden) in the supernatants that were collected after low and high glucose incubation. For each donor n=4 wells per condition were tested, from which the average was calculated. The stimulation index of insulin was expressed as the ratio of insulin secreted during high glucose over low glucose. The stimulation index of insulin secretagogues was expressed as the ratio of insulin secreted during high glucose in the presence of the insulin secretagogue over high glucose. Immunofluorescence staining Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 minutes and washed in PBS. Intact islets or islet cell aggregates were spun down at high speed in fluid agar. Agar-containing cell pellets were embedded in paraffin blocks and sliced into 4 µm sections. For identification of β-cells, sections were incubated with guinea-pig-anti-insulin IgG (1:200, Millipore) and for the identification of α-cells with rabbit-anti-glucagon IgG (1:200, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) for 1 hour, followed by secondary antibodies TRITC-anti-guinea pig (1:400, Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, West Grove, PA, USA) and goat-anti-rabbit Alexa-488 (1:500, Molecular Probes; Thermo Fisher Scientific) and Dapi (Vector Laboratories) was used as a nuclear staining. For islet cells cultured in monolayer, cells were permeabilized with 0.5% Triton for 10 minutes after which the cells were incubated with mouse-anti-c-peptide IgG (1:1000, Millipore) and rabbit-antiglucagon IgG (1:100, Vector Laboratories) overnight. Hoechst was used as nuclear staining and secondary antibodies were goat-anti-mouse Alexa-568 (1:1000, Molecular Probes) and goat-antirabbit Alexa-488 (1:500, Molecular Probes). Statistical analysis Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Statistical calculations were carried out using GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). The statistical significance of differences was determined by Mann-Whitney test or Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn s multiple comparison test, as appropriate. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results Cellular composition of human islet cells cultured either in monolayer or in 3D aggregates is similar to intact islets Human islets were obtained from pancreas of 20 organ donors (13 M / 7 F, age 47.8±2.5 years, Body Mass Index 25.9±0.7 kg/m 2 ). The purity of the islets was 85.6+/-1.3% (range 80-95%) as determined by dithizone staining (Fig. 1A). Intact human islets were dispersed into single A screening platform to assess human β-cell function 107
7 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 R9 R10 R11 R12 R13 R14 R15 R16 R17 R18 R19 R20 R21 R22 R23 R24 R25 R26 R27 R28 R29 R30 R31 R32 R33 R34 R35 R36 R37 R38 R39 cells which were cultured either in monolayer on a matrix of ECM (Fig. 1B) or reaggregated islet cell clusters (Fig. 1C). For the monolayer culture different matrices were tested (gelatin, poly-llysin, methylcellulose, collagen-i, laminin, ECM (data not shown). Using ECM, cells were firmly attached to the matrix, which was essential for the multiple washing steps that are required for the glucose-induced insulin secretion tests. For islet cell aggregates, spontaneous reaggregation of 20,000 islet cells resulted in one islet cell cluster without affecting cell viability (data not shown) that could be easily transferred to trans-well membrane plates for the glucose-induced insulin secretion test. To determine the percentage of β- or α-cells present in the three culture platforms, the presence of insulin or glucagon immunostaining was examined in 324±73 (islets), 265±5 (monolayer) and 371±50 (aggregates) cells per donor. After 3 days of culture the percentage of β- or α-cells present in islet cells cultured either in monolayer or in islet cell aggregates was similar to intact human islets (Fig. 1D-G). Figure 1. Morphologic appearance and cellular composition of intact human islets, islet cells in monolayer and islet cell aggregates. A. Purified human islets after isolation stained for insulin using dithizone (red), 40x magnification. B. Islet cells cultured in monolayer on ECM, 40x magnification. C. Re-aggregated islet cells, 40x magnification. D-F. Representative pictures of an intact human islet (D), islet cells in monolayer (E) and aggregated islet cells (F), immunostained for insulin (red) and glucagon (green) to identify β-cells and α-cells, respectively. Cell nuclei are stained using DAPI/Hoechst (blue), scale bar = 20 μm. G. Percentage of β-cells and α-cells of total cell number of intact human islets (n=5 donors), islet cells in monolayer (n=2 donors) or islet cell aggregates (n=5 donors). 108 Chapter 7
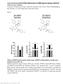
8 Efficient virus transduction in human islet cells in monolayer or islet cell aggregates The transduction efficiency of cells from dispersed human islets was assessed by expression of adenoviral-transduced Zsgreen. Zaldumbide et al. (3) have shown that in intact human islets, primarily the outer layer of islet cells is transduced by virus. For islet cells in monolayer a transduction efficiency of >80% was reached using adenovirus with MOI 2 (Fig 2A). Also, after transduction of single cells in suspension, islet cells were able to cluster together into islet cell aggregates resulting in a transduction efficiency with adenovirus of >80% with MOI 2 (Fig 2B). Similar results were obtained using lentivirus (data not shown). Figure 2. Transduction efficiency of islet cells in monolayer and islet cell aggregates. A. Representative pictures of islet cells in monolayer and B. aggregated islet cells, transduced with adenovirus expressing Zsgreen (MOI 2) imaged 24 hours post-transduction, 40x magnification. Cultured intact islets and islet cell aggregates maintain glucose-induced insulin secretory response Next we assessed the insulin secretory response of human islet cells in the different culture platforms. Intact human islets cultured in a 96-well plate preserved their glucose-induced insulin secretory response after 3 days (Fig. 3A). High glucose stimulation of intact islets resulted in a ~8x increase of insulin secretion compared to low glucose (Fig. 3B, E). Although glucose stimulation resulted in increased insulin secretion from islet cells cultured in monolayer, this response was significantly lower than in intact islets (Fig. 3C, E). In contrast, the stimulation index of islet cells cultured in aggregates was similar to intact human islets (Fig. 3D, E). The stimulation index was not significantly affected by adenovirus transduction of islet cells cultured either in monolayer or aggregates after 3 days (Fig. 3F). Similar results were obtained using lentivirus (data not shown and (3)). A screening platform to assess human β-cell function 109
9 Figure 3. Glucose-induced insulin secretory response of intact islets, islet cells in monolayer and islet cell aggregates. A. Insulin release expressed as ratio of the insulin secretory response during high (16.7 mmol/l) glucose and low (2 mmol/l) glucose stimulation (stimulation index) of intact human islets after culture for 0 or 3 days in 96-well plates (n=4 donors). B-D. Insulin secretion from intact islets (B, n=8 donors), islet cells in monolayer (C, n=3 donors) and aggregated islet cells (D, n=4 donors) in response to 16.7 mmol/l glucose (High glucose). E. Stimulation index of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Intact islets: n=14 donors, islet cells in monolayer: n=5 donors, and aggregated islet cells: n=8 donors. F. Stimulation index of glucoseinduced insulin secretion in monolayer (n=2 donors) and aggregated islet cells (n=3-4 donors) untransduced or transduced with an empty adenovirus vector or an adenovirus expressing shrna against egfp as a negative control (MOI = 2), 3 days post-transduction. *p<0.05, ***p< In vitro exposure of human islet cells to GLP-1R agonists does not significantly enhance glucose-induced insulin secretion The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonism on enhancement of glucoseinduced insulin secretion was assessed for the three culture platforms. When intact human islets were exposed to glucose and different concentrations of the GLP-1R agonist exendin-4 or liraglutide, only a minor enhancement of insulin secretion by 100 nm liraglutide was observed (Fig. 4A). Furthermore, there was no significant enhancement of glucose-induced insulin secretion by GLP-1R agonist treatment in islet cells in monolayer or islet cell aggregates (Fig. 4B, Fig. 5A-C). 110 Chapter 7
10 Figure 4. Insulin secretory responses of intact human islets, human islet cells in monolayer and islet cell aggregates to GLP-1R agonist treatment. A. Insulin secretion from intact islets (n=2-5 donors) in response to 2 mm glucose (low) and 16.7 mmol/l glucose (high) alone and in combination with different concentrations of exendin-4 or liraglutide. B. Stimulation index of liraglutide (100 nm)-induced enhancement of insulin secretion in intact human islets (n=11 donors), human islet cells in monolayer (n=2 donors) and islet cell aggregates (n=4 donors). **p<0.01 vs. low glucose. Activation of camp/epac-2 signal transduction and inhibition of K-channels enhances glucose-induced insulin secretion in intact human islets and islet cell aggregates To evaluate whether the signaling pathway activated after GLP-1 receptor activation was functional, we assessed the effect of camp/epac-2 signal transduction on insulin secretion in our culture systems. Increasing camp levels by forskolin and IBMX resulted in ~2.5x enhancement of glucose-induced insulin secretion compared to control in intact human islets (Fig. 5A). A similar induction of insulin secretion was reached with an EPAC-2 agonist in intact islets. However, neither forskolin and IBMX, nor EPAC-2 agonism significantly enhanced insulin secretion from islet cells in monolayer (Fig. 5B). In contrast, reaggregated islet cells showed increased glucoseinduced insulin secretion upon stimulation with forksolin and IBMX or the EPAC-2 agonist (Fig. 5C). K-channel inhibition of intact human islets using TEA resulted in ~2x potentiation of insulin secretion and a similar response was observed in islet cell aggregates (Fig. 5A, C). Conversely, exposure of islet cells in monolayer to TEA did not result in enhancement of glucose-induced insulin secretion (Fig. 5B). Finally, the stimulation indices for the insulin secretagogues forskolin and IBMX, EPAC-2 agonist and TEA were reproducible in different donors and similar between intact islets and islet cell aggregates derived from the same donor (Fig. 5D-F). A screening platform to assess human β-cell function 111
11 Figure 5. Insulin secretory responses to elevation of camp, EPAC-2 agonism and K-channel inhibition of intact islets. A-C. Stimulation index of high glucose (16.7 mm) in the presence of liraglutide (100 nm), forskolin (10 µm) and IBMX (100 µm), EPAC-2 agonist (100 µm), or TEA (100 µm) over high glucose alone in (A) intact human islets (n=2-7 donors), (B) human islet cells in monolayer (n=2 donors) and (C) islet cell aggregates (n=3-5 donors). D-F. Stimulation index of forskolin and IBMX (D), EPAC-2 agonist (E) and TEA (F) in intact islets or aggregates expressed per donor. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 vs. DMSO control. The use of intact human islets, islet cells in monolayer or islet cell aggregates for highthroughput screening purposes We evaluated the use of three different culture platforms in microwell plates using primary human islets. Table 1 summarizes the main characteristics of the three culture platforms that were compared in this study. These platforms can ultimately be used for medium to high-throughput screening of viral-delivered shrna or small compound libraries to identify hits that can enhance insulin secretion in human islets. We therefore calculated the number of compounds that can be tested on 10,000 human islets (in quadruplicates) per set-up showing their ability to serve as a platform for medium to high-throughput screening purposes. 112 Chapter 7
12 Intact islets Monolayer Aggregates Glucose responsiveness yes yes (reduced) yes Insulin secretagogues responsiveness yes no yes Transduction efficiency low high high No of compounds tested per islets (quadruplicates)* Table 1. Culture platform characteristics. *Calculations were done based on the assumption that 1 islet consists of ~1.500 islet cells. Discussion In this study, we present a high-throughput culture platform in which the insulin secretory response of human islets is used as readout. In previous studies using rodent-derived cell lines, platforms were used in which ATP-levels were used as a proxy indicator for islet function (12), insulin protein content (6) or insulin gene expression (7). However, the biology of islets from rodents is very different from humans (13). One of the few culture systems using human islet cells is the multiparameter high-throughput screening by Hill et al. (4). However, in this platform gene expression was assessed as indicator for the ability of natural compounds to modulate insulin and Pdx1. Also, Kiselyuk et al. (5) who used a cell line derived from human islets, used insulin promoter activity as readout. Following glucose stimulation only a fraction of the total insulin content is secreted from β-cells, which makes these readouts poor indicators of secretory function. Since insulin gene expression and protein content do not directly correlate to β-cell function (8), measurement of insulin secretion is a more accurate reflection of islet function. In this study we show that human islet cells cultured in monolayer show reduced glucoseresponsiveness compared to intact islets. In the platform set up by Walpita et al. (14) human islet cells were also cultured in monolayer on ECM to screen for compounds that could enhance β-cell proliferation. The magnitude of the glucose-responsiveness of this study and our results for the monolayer culture are similar. Interestingly, in our study the insulin secretory function of human islet cell aggregates was comparable to intact human islets. This is in line with the observation that mouse MIN6 pseudoislets show improved insulin secretion compared to a monolayer culture of MIN6 cells (15). Also, Wojtusciszyn et al. (16) showed that insulin secretion from human β-cells improved when β-cells were paired with another β- or α-cell. Altogether these results show that the glucose-induced insulin secretory response of reaggregated islet cells is more in line with secretory capacity of intact human islets than of islet cells cultured in a monolayer. From rodent studies it is known that activation of the GLP-1 receptor, which is expressed on β-cells, can potently enhance glucose-induced insulin secretion in vitro (17). In our study GLP-1 receptor activation did not significantly increase insulin secretion from human islet cells in any of the culture platforms. Recently, Hodson et al. (18) showed that loss of cell-cell communication results in decreased incretin-stimulated insulin secretion in human islets, which may explain A screening platform to assess human β-cell function 113
13 the low responsiveness in our monolayer culture. Furthermore, Hansen et al. (19) failed to see the expected increment in insulin release by exposing intact human islets to exogenous GLP-1. Also, α-cells within intact islets may already secrete GLP-1 locally, which may prevent further enhancement of insulin secretion by exogenously provided GLP-1R agonists (19, 20). Since α-cells are present in all three culture platforms, this may have interfered with the insulin secretory response of β-cells to exogenous GLP-1 analogues. Nevertheless, direct stimulation of camp/epac-2 signal transduction, one of the main signaling pathways activated by GLP-1 receptor activation, resulted in enhancement of insulin secretion in intact islets and islet cell aggregates. This response was absent in islet cells in monolayer. In addition, closure of K-channels in β-cells resulted in increased insulin secretion from intact islets and islet cells in aggregates, but not from islet cells in monolayer. Together these results show that the aggregation of human islet cells is necessary to remain responsive to several insulin secretagogues. Whether this is also attributed to the loss of cell-cell communication as described for incretin-stimulated insulin secretion remains an open question (18). For screening platforms in which efficient virus transduction is required, reaggregation of cells into islet cell aggregates is therefore preferred over monolayer culture. The culture platforms presented in this study show that human islets can be used for highthroughput screening assays to identify targets or compounds that enhance human islet function. Also, these systems can be applied to study other aspects of islet cell biology, such as β-cell proliferation and apoptosis. This could lead to the identification of novel mechanisms involved in β-cell function and survival. 114 Chapter 7
14 References 1. Guariguata L et al. (2014) Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for Diabetes Res Clin Pract 103: Forbes JM, Cooper ME (2013) Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev 93: Zaldumbide A et al. (2013) Genetically engineered human islets protected from CD8-mediated autoimmune destruction in vivo. Mol Ther 21: Hill JA et al. (2010) A multi-parameter, high-content, high-throughput screening platform to identify natural compounds that modulate insulin and Pdx1 expression. PLoS One 5:e Kiselyuk A et al. (2010) Phenothiazine neuroleptics signal to the human insulin promoter as revealed by a novel high-throughput screen. J Biomol Screen 15: Codd EE et al. (2010) Diabetogenic effect of a series of tricyclic delta opioid agonists structurally related to cyproheptadine. Toxicol Sci 117: Fomina-Yadlin D et al. (2010) Small-molecule inducers of insulin expression in pancreatic alpha-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: Fu Z, Gilbert ER, Liu D (2013) Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev 9: Ricordi C, Lacy PE, Finke EH, Olack BJ, Scharp DW (1988) Automated method for isolation of human pancreatic islets. Diabetes 37: Arts G-J et al. (2003) Adenoviral vectors expressing sirnas for discovery and validation of gene function. Genome Res 13: Carlotti F et al. (2004) Lentiviral vectors efficiently transduce quiescent mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Ther 9: Chou DHC et al. (2010) Small-molecule suppressors of cytokine-induced beta-cell apoptosis. ACS Chem Biol 5: Carlotti F et al. (2011) β-cell Generation: Can Rodent Studies Be Translated to Humans? J Transplant 2011: Walpita D et al. (2012) A human islet cell culture system for high-throughput screening. J Biomol Screen 17: Chowdhury a, Dyachok O, Tengholm a, Sandler S, Bergsten P (2013) Functional differences between aggregated and dispersed insulin-producing cells. Diabetologia 56: Wojtusciszyn A, Armanet M, Morel P, Berney T, Bosco D (2008) Insulin secretion from human beta cells is heterogeneous and dependent on cell-to-cell contacts. Diabetologia 51: Farilla L et al. (2003) Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibits cell apoptosis and improves glucose responsiveness of freshly isolated human islets. Endocrinology 144: Hodson DJ et al. (2013) Lipotoxicity disrupts incretin-regulated human β cell connectivity Hansen AMK et al. (2011) Upregulation of alpha cell glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in Psammomys obesus - An adaptive response to hyperglycaemia? Diabetologia 54: Marchetti P et al. (2012) A local glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) system in human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 55: A screening platform to assess human β-cell function 115
15
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32608 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ellenbroek, Johanne Hendrike (Rianne) Title: Pancreatic β- and α-cell adaptation
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32608 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ellenbroek, Johanne Hendrike (Rianne) Title: Pancreatic β- and α-cell adaptation
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
Avrahami et al., Suppression of p57kip2 allows successful replication of adult human -cells
 Avrahami et al., Suppression of p57kip2 allows successful replication of adult human -cells Legends to Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. A. Suppression of p57 Kip2 in human islets does not
Avrahami et al., Suppression of p57kip2 allows successful replication of adult human -cells Legends to Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. A. Suppression of p57 Kip2 in human islets does not
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets. A.N.Balamurugan
 Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Identification of GLP1R agonists using a novel high throughput screening assay Wan Namkung, Ph.D.
 Identification of GLP1R agonists using a novel high throughput screening assay Wan Namkung, Ph.D. College of Pharmacy, Yonsei University Contents High-throughput screening (HTS) HTS assays for identification
Identification of GLP1R agonists using a novel high throughput screening assay Wan Namkung, Ph.D. College of Pharmacy, Yonsei University Contents High-throughput screening (HTS) HTS assays for identification
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins
 Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins www.vectalys.com/products/ Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Catalog Number referring to this User Manual: 0008VCT; 0009VCT;
Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins www.vectalys.com/products/ Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Catalog Number referring to this User Manual: 0008VCT; 0009VCT;
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis
 icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for NF-κB Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
PROTOCOL: OPTIMIZATION OF LENTIVIRAL TRANSDUCTION USING SPINFECTION
 Last Modified: April 2018 Last Review: October 2018 PROTOCOL: OPTIMIZATION OF LENTIVIRAL TRANSDUCTION USING SPINFECTION Table of Contents 1. Brief Description 1 2. Materials and Reagents.1 3. Optimization
Last Modified: April 2018 Last Review: October 2018 PROTOCOL: OPTIMIZATION OF LENTIVIRAL TRANSDUCTION USING SPINFECTION Table of Contents 1. Brief Description 1 2. Materials and Reagents.1 3. Optimization
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
Transplantation of Human Pancreatic Endoderm Cells Reverses Diabetes. Post Transplantation in a Prevascularized Subcutaneous Site
 Stem Cell Reports, Volume 8 Supplemental Information Transplantation of Human Pancreatic Endoderm Cells Reverses Diabetes Post Transplantation in a Prevascularized Subcutaneous Site Andrew R. Pepper, Rena
Stem Cell Reports, Volume 8 Supplemental Information Transplantation of Human Pancreatic Endoderm Cells Reverses Diabetes Post Transplantation in a Prevascularized Subcutaneous Site Andrew R. Pepper, Rena
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins
 Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Introduction Kit Components Cat. # # of vials Reagent Quantity Storage
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue
 Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name
 Supplementary Table. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name ccession Number Fwd Rev Type of PCR Cre NC_8 GGCGTCTTCCGC GTGCCCCTCGTTTG Standard PCR LoUcp CCGGGCTGTCTCCGCGG GGCTGTTCGCCCGGCC Standard PCR
Supplementary Table. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name ccession Number Fwd Rev Type of PCR Cre NC_8 GGCGTCTTCCGC GTGCCCCTCGTTTG Standard PCR LoUcp CCGGGCTGTCTCCGCGG GGCTGTTCGCCCGGCC Standard PCR
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Institute of Experimental Diabetes Research, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
 Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 2309630, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2309630 Research Article Dynamics of Insulin Secretion from EndoC-βH1 β-cell Pseudoislets in Response to
Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 2309630, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2309630 Research Article Dynamics of Insulin Secretion from EndoC-βH1 β-cell Pseudoislets in Response to
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Product Use HPSC-CC are for research use only. It is not approved for human or animal use, or for application in in vitro diagnostic procedures.
 HPSC-derived Cardiomyocyte Cells (HPSC-CC) Catalog #6240 Cell Specification Human primary cardiomyocytes and cardiac tissue are superior modeling systems for heart disease studies, drug discovery and toxicity
HPSC-derived Cardiomyocyte Cells (HPSC-CC) Catalog #6240 Cell Specification Human primary cardiomyocytes and cardiac tissue are superior modeling systems for heart disease studies, drug discovery and toxicity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Imaging of glycolytic metabolism in primary glioblastoma cells with
 63 Chapter 5 Imaging of glycolytic metabolism in primary glioblastoma cells with RIMChip 5.1. Introduction Glioblastoma(GBM) is one of the most common brain tumors 1. It is composed of heterogeneous subpopulations
63 Chapter 5 Imaging of glycolytic metabolism in primary glioblastoma cells with RIMChip 5.1. Introduction Glioblastoma(GBM) is one of the most common brain tumors 1. It is composed of heterogeneous subpopulations
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate. bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic
 COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Glucose Homeostasis. Liver. Glucose. Muscle, Fat. Pancreatic Islet. Glucose utilization. Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon
 Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Last updated Glycogen synthesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis in primary mouse hepatocytes
 Last updated 2011-03-02 Glycogen synthesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis in primary mouse hepatocytes Media Formulations A. Media for glycogen synthesis: Culture medium base: DMEM-Low (Mediatech/Cellgro
Last updated 2011-03-02 Glycogen synthesis, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis in primary mouse hepatocytes Media Formulations A. Media for glycogen synthesis: Culture medium base: DMEM-Low (Mediatech/Cellgro
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
2-Deoxyglucose Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3753 100 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Metabolic Disease drug discovery at Evotec
 Metabolic Disease drug discovery at Evotec Evotec, Metabolic Disease Drug Discovery, 2016 Evotec, an ideal partner in metabolic disease drug discovery The different ways to work with us On your specific
Metabolic Disease drug discovery at Evotec Evotec, Metabolic Disease Drug Discovery, 2016 Evotec, an ideal partner in metabolic disease drug discovery The different ways to work with us On your specific
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Soltani et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102715108 SI Experimental Procedures Evaluation of Mice and Drug Administration. IPGTT, insulin tolerance test, and glucagon tolerance test were performed
Supporting Information Soltani et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102715108 SI Experimental Procedures Evaluation of Mice and Drug Administration. IPGTT, insulin tolerance test, and glucagon tolerance test were performed
Supplementary Material and Methods
 Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug
 1 Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug 6 2009 XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached
1 Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug 6 2009 XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Burford et al. 1.173/pnas.1339311 SI Materials and Methods β-arrestin Recruitment Assay. PathHunter human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) expressing either μ-opioid receptors (U2OS- OPRM1)
Supporting Information Burford et al. 1.173/pnas.1339311 SI Materials and Methods β-arrestin Recruitment Assay. PathHunter human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) expressing either μ-opioid receptors (U2OS- OPRM1)
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
*Corresponding author:
 LIPID DROPLETS HYPERTROPHY: A CRUCIAL DETERMINING FACTOR IN INSULIN REGULATION BY ADIPOCYTES 1 Bahram Sanjabi #, 2,3 Monireh Dashty #, 4 Behiye. Özcan, 5 Vishtaseb Akbarkhanzadeh, 3 Mehran Rahimi, 7,8
LIPID DROPLETS HYPERTROPHY: A CRUCIAL DETERMINING FACTOR IN INSULIN REGULATION BY ADIPOCYTES 1 Bahram Sanjabi #, 2,3 Monireh Dashty #, 4 Behiye. Özcan, 5 Vishtaseb Akbarkhanzadeh, 3 Mehran Rahimi, 7,8
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
-51mV 30s 3mV. n=14 n=4 p=0.4. Depolarization (mv) 3
 Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Acid-Resistant Mesoporous Metal Organic Framework Toward Oral Insulin Delivery: Protein Encapsulation, Protection & Release Yijing Chen, Peng Li, Justin A. Modica, Riki J.
Supplementary Information for Acid-Resistant Mesoporous Metal Organic Framework Toward Oral Insulin Delivery: Protein Encapsulation, Protection & Release Yijing Chen, Peng Li, Justin A. Modica, Riki J.
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate
 Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol
 L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
Mouse primary keratinocytes preparation
 Mouse primary keratinocytes preparation 1. Fill a 150 X 25 mm petri dish with ice. Put newborn mice (2 3 days old) in the petri dish and insert it in an ice bucket. Leave the mice in the ice bucket for
Mouse primary keratinocytes preparation 1. Fill a 150 X 25 mm petri dish with ice. Put newborn mice (2 3 days old) in the petri dish and insert it in an ice bucket. Leave the mice in the ice bucket for
Conversion of mature human β-cells into glucagon-producing α-cells. Running title: Conversion of human β-cells into α-cells
 Page 1 of 34 Diabetes Conversion of mature human β-cells into glucagon-producing α-cells Running title: Conversion of human β-cells into α-cells H. Siebe Spijker 1, Raimond B.G. Ravelli 2, A. Mieke Mommaas-Kienhuis
Page 1 of 34 Diabetes Conversion of mature human β-cells into glucagon-producing α-cells Running title: Conversion of human β-cells into α-cells H. Siebe Spijker 1, Raimond B.G. Ravelli 2, A. Mieke Mommaas-Kienhuis
Ready-to-use Lentiviral Particles for intracelular labeling
 Ready-to-use Lentiviral Particles for intracelular labeling (LocLight TM Living cell imaging lentivirus for sub-cellular localization) LocLight TM cell organelle labeling lentivirus are provided as 200ul/per
Ready-to-use Lentiviral Particles for intracelular labeling (LocLight TM Living cell imaging lentivirus for sub-cellular localization) LocLight TM cell organelle labeling lentivirus are provided as 200ul/per
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies
 2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium Martin C, Coolen N, Wu YZ, Thévenot G, Touqui L, PrulièreEscabasse V, Papon JF, Coste
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium Martin C, Coolen N, Wu YZ, Thévenot G, Touqui L, PrulièreEscabasse V, Papon JF, Coste
Immature organoids appear after hours.
 THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED Allison Ruchinskas, B.S., and James Clinton, Ph.D. ATCC Cell Systems, Gaithersburg, MD INTRODUCTION Figure 1. Mouse small intestinal organoid
THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED Allison Ruchinskas, B.S., and James Clinton, Ph.D. ATCC Cell Systems, Gaithersburg, MD INTRODUCTION Figure 1. Mouse small intestinal organoid
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well
 Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO
 COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery
 Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery Presenter: April 12, 2017 Ed Davis, Ph.D. Senior Application Scientist GeneCopoeia, Inc. Outline Introduction to GeneCopoeia Lentiviral
Choosing Between Lentivirus and Adeno-associated Virus For DNA Delivery Presenter: April 12, 2017 Ed Davis, Ph.D. Senior Application Scientist GeneCopoeia, Inc. Outline Introduction to GeneCopoeia Lentiviral
Figure S1 (A) Comparison of body weight and blood glucose levels in male wild-type (WT) and Cre littermates. Mice were maintained on a normal chow
 Figure S1 (A) Comparison of body weight and blood glucose levels in male wild-type (WT) and Cre littermates. Mice were maintained on a normal chow diet (n = 7 per genotype). Body weight and fed blood glucose
Figure S1 (A) Comparison of body weight and blood glucose levels in male wild-type (WT) and Cre littermates. Mice were maintained on a normal chow diet (n = 7 per genotype). Body weight and fed blood glucose
Supplemental Materials, Nishimura et al, Page1 of 22 1
 Supplemental Materials, Nishimura et al, Page of 5 Quantitative assessment of Pdx promoter activity in vivo using a secreted luciferase reporter system 6 7 8 9 Wataru Nishimura, Koki Eto, Atsushi Miki,
Supplemental Materials, Nishimura et al, Page of 5 Quantitative assessment of Pdx promoter activity in vivo using a secreted luciferase reporter system 6 7 8 9 Wataru Nishimura, Koki Eto, Atsushi Miki,
Determination of serum insulin level by ELISA
 Practical course: Basic biochemical methods and ischemic heart models Determination of serum insulin level by ELISA A practical manual Tamas Csont, MD, PhD Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 1 BACKGROUND
Practical course: Basic biochemical methods and ischemic heart models Determination of serum insulin level by ELISA A practical manual Tamas Csont, MD, PhD Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 1 BACKGROUND
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
Supplemental Information. b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous. Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 25 Supplemental Information b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato, Mark van Haaren, Magdalena Mruk,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 25 Supplemental Information b Cell Aging Markers Have Heterogeneous Distribution and Are Induced by Insulin Resistance Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato, Mark van Haaren, Magdalena Mruk,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32608 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ellenbroek, Johanne Hendrike (Rianne) Title: Pancreatic β- and α-cell adaptation
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32608 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ellenbroek, Johanne Hendrike (Rianne) Title: Pancreatic β- and α-cell adaptation
Hormones. BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8
 Hormones BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8 Hormones Regulatory molecules Affect all areas of metabolism Endocrine- hormones travel via the bloodstream to its target cell: true hormone Modern definition- any regulatory
Hormones BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8 Hormones Regulatory molecules Affect all areas of metabolism Endocrine- hormones travel via the bloodstream to its target cell: true hormone Modern definition- any regulatory
