Building The Retina Company
|
|
|
- Ellen Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Building The Retina Company
2 Optos devices produce ultra-widefield (UWF ), high resolution images (optomap ) of approximately 82% (200 ) of the retina. A single optomap can document the retina from the central pole through the vortex vessels; no other technology can capture this view in a single image. optomap images provide more clinical information which facilitates early detection and more effective management of retinal diseases. Retinal imaging can also uncover systemic diseases such as hypertension and certain cancers. optomap color images consist of two channels of information, a red channel (635nm) which visualizes the choroidal layer and a green channel (532nm) which visualizes the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). optomap af images are captured using the green wavelength (532nm) and visualize the function of the RPE. optomap fa images uses the blue wavelength (488nm) to capture the circulation of the retina. A fluorescein angiogram is used to analyze the integrity of the retinal vascular system, looking for leakages, blockages, neovascularization and vascular abnormalities. The optomap : is designed to illustrate how different pathologies are visualized on UWF fluorescein angiogram. Reference for Definitions Dictionary of Eye Terminology. Sixth Edition Barbara Cassin and Melvin L. Rubin, MD. Triad Communications, Inc. Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green Angiography: Technique and Interpretation. Second Edition Joseph W. Berkow, MD; Robert W. Flower; David H. Orth, MD; James S. Kelley, MD American Academy of Ophthalmology The Retinal Atlas. Second Edition Bailey Freund, MD; David Sarraf, MD; Wiliam F. Mieler, MD; Lawrence A. Yannuzzi, MD Elsevier
3
4 Fluorescein Angiography optomap color composite images provide a structural image of the retina. optomap consist of two channels of information, a red channel (635nm) which visualizes the choroidal layer and a green channel (532nm) which visualizes the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). optomap af images are captured using the green wavelength (532nm) and visualize the health and function of the RPE. optomap fa images are captured using the blue wavelength (488nm) to visualize the circulation of the retina vasculature. Fluorescein sodium (C20H10Na2O5), resorcinolphthalein sodium, is injected intravenously into a patient s arm. When the dye is injected and the retina is illuminated with blue light, the dye fluoresces and exciter and barrier filters are put in place to allow only the fluorescent light to be imaged. The dye absorbs the blue light with an excitation at nm (blue) and the dye emits the yellow-green wavelength from nm (yellow-green). Upon injection, images are captured and each image has a timestamp to track the circulation time of the retinal vessels. 2
5 Fluorescein Angiography Phases Phase Choroidal Flush/ Pre-Arterial Phase Arterial Arterial-Venous Phase Venous Phase Recirculation Phase Timing seconds choroid fills 1 second before the dye enters the retinal circulation second seconds 2-4 minutes Description Choroid and choriocapillaris fill. Choroidal retinal arteries fill with the choroid at the same time. Arteries begin to fill. Complete filling of the arteries and capillaries. Laminar flow seen in the veins. Veins are completely filled. Veins and arteries are equally bright. Choroidal 10 Seconds Arterial-Venous 19 Seconds Arterial 15 Seconds Venous 33 Seconds Fluorescein Angiography Late Phase 5-10 minutes Staining around the optic disc. Recirculation 3:11 Minutes Late 7:51 Minutes 3
6 Retinal Anatomy The Retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue that lines the inside of the eye and sends visual messages through the optic nerve to the brain. The Choroid is the vascular (major blood vessel) layer of the eye lying between the retina and the sclera. It provides nourishment to outer layers of the retina. Vein is any of the tubes forming part of the blood circulation system of the body, carrying in most cases oxygen-depleted blood toward the heart. Macula is a small central area of the retina surrounding the fovea; area of acute central vision. Fovea is the central pit in the macula that produces sharpest vision. It contains a high concentration of cones and no retinal blood vessels. Artery is any of the muscular-walled tubes forming part of the circulation system by which blood (mainly that which has been oxygenated) is conveyed from the heart to all parts of the body. Optic Disc, Optic Nerve Head (ONH) is the ocular end of the optic nerve. Denotes the exit of retinal nerve fibers from the eye and entrance of blood vessels to the eye. 4
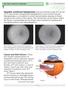
7 Fluorescein Angiogram of a Healthy Retina Arteriovenous Crossings are areas where the artery and vein meet within the retina these however can result in occlusions which can be observed on an FA. Vein will fill after the arteries and will appear bright once the dye enters. Macula will appear dark on a normal FA as this is an avascular zone. Artery will fill first and will appear bright once the dye enters. Optic Disc, Optic Nerve Head will appear uniformly bright once the dye circulates. Uneven brightness may indicate edema, neovascularization or the presence of drusen. Retinal Anatomy 5
8 Hyperfluorescence Hyperfluorescence is an increase in the level of fluorescence caused by an abnormality in the RPE. A structural abnormality may allow either the fluorescein dye to pass from the choroid into or under the retina or the fluorescent light from the dye to shine through the pigment epithelium. Autofluorescence Occurs when tissue fluoresces without the assistance of a fluorescent dye. Window/Transmission - An area of the RPE that no longer has sufficient melanin to block fluorescence from the underlying choriocapillaris (ie. pigment epithelial window defect, atrophy or drusen). Leakage - The passage of fluorescein dye through a membrane that normally cannot be penetrated (ie capillary leakage, aneurysm or neovascularization). Chorioretinal Atrophy Window defect from Atrophy Optic Nerve Head Drusen Autofluorescence without Fluorescein Dye Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Leakage from Neovascularization Pooling - The accumulation of fluorescein dye in what is typically tissue space (ie. cystoid macular edema, sensory retinal detachment or pigment epithelial detachment). Staining - The accumulation of fluorescein within tissue substance. Central Serous Retinopathy Pooling from a serous detachment Stargardts Disease Staining of Lesions and Optic Disc 6
9 Hypofluorescence is a lower level of fluorescence (seen as darker patches) caused by either the blockage of light from normally fluorescing structures or inadequate circulation in an area of the retina or choroid. Filling defect An area of poor fluorescence caused by a abnormal circulation. This can be non-perfusion or ischemia. Retinal Vein Occlusion Filling defect from non-perfusion Hypofluorescence Blocking defect An absence or marked decrease of fluorescence observed in an area that would normally show fluorescence. This can be caused by the presence of opaque material such as blood or pigment in a nevus. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Blocking defect from hemorrhage 7
10 Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Diabetic Retinopathy is a series of progressive retinal changes that can result from long-standing diabetes mellitus. Early stage DR is non-proliferative (NPDR). It may advance to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), which includes neovascularization and fibrous tissue which can be visualized on FA. Peripheral non-perfusion Neovascularization Recent research has established the importance of monitoring the retinal periphery (area outside of ETDRS) for early signs of DR. optomap imaging has demonstrated that diabetic lesions occur in the retinal periphery in up to 50% of eyes and these lesions result in a more severe grade of retinopathy in 10% of eyes and a 4.7 fold increased risk of progression to PDR. 2 Peripheral non-perfusion The gold standard for classification of diabetic retinopathy is stereoscopic color fundus photographs in 7 standard fields, as defined by the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) group (area captured shown in circles above). optomap images have been found equivalent in quality and may be used in place of ETDRS in managing DR Silva et al. Nonmydriatic Ultrawide Field Retinal Imaging Compared with Dilated Standard 7-Field 35-mm Photography and Retinal Specialist Examination for Evaluation of Diabetic Retinopathy. American Journal Of Ophthalmology, Silva et al Peripheral Lesions Identified on Ultrawide Field Imaging Predict Increased Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy Progression over 4 Years. Ophthalmology, 2015
11 Retinal Hemorrhage is the abnormal bleeding or leakage of the blood vessels in the retina often seen in conditions such as diabetic retinopathy. Retinal hemorrhage can be caused by injury or disease resulting in temporary or permanent loss of vision. Dot and blot hemorrhages are tiny round hemorrhages in the retina, usually in the outer plexiform layer. Retinal hemorrhages Spokes of cortical cataract will create shadows NVD Diabetic Retinopathy Vitreous hemorrhage Hypofluorescent blocking from hemorrhages Vitreous Hemorrhage is blood in the vitreous that may result from blunt eye trauma, blood leakage from neovascularization, vitreous detachment or a retinal tear. It is also called a vitreal bleed and typically associated with diabetes. A vitreous hemorrhage will hypofluoresce on a fluorescein angiogram and will appear as blockage. Blocking from a vitreous hemorrhage 9
12 Diabetic Retinopathy Neovascularization is the abnormal formation of new blood vessels, usually in or under the retina or on the iris surface. Neovascularization of the optic disc (NVD) are new vessels growths at the optic disc and neovascularization elsewhere (NVE) occurs outside of the optic disc. Neovascularization will cause hyperfluoresce on a optomap fa and will appear similar to leakage. NVD NVD Zoomed in view NVE NVE NVD NVD 10 Previous laser spots
13 Microaneurysms are focal dilation of the venous end of retinal capillaries. These appear in the retinal vessels as a small round red spot resembling a tiny, deep hemorrhage. PDR Microaneurysms Zoomed in view PDR NVE NVD Diabetic Retinopathy Venous Beading is a pattern of nodular irregularity in the retinal venous blood Microaneurysms vessel walls that are typically next to areas of non-perfusion. This can be found in Coats disease and diabetic retinopathy. Microaneurysms Microaneurysms NVD Previous laser spots Venous beading Non-perfusion Venous beading 11
14 Ischemia, Non-Perfusion Diabetic Retinopathy is caused by inadequate blood supply to a body part caused by partial blockage of a blood vessel. If not reversed, surrounding tissue may die from lack of nutrients. It may result in retinal edema, cotton-wool spots, microaneurysms, venous engorgement and neovascularization. NVE Zoomed in view Non-perfusion Neovascular fronds optomap fa has been demonstrated to show 3.9 times more non-perfusion than traditional ETDRS. 1 Another study concluded that non-perfusion in DR begins in the midperipheral retina and ischemia, thus accounting for the increased risk of progression Kiss et al. Ultra Wide Field Angiography Improves the Detection and Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy. Retina Aiello et al. Diabetic Retinopathy Severity and Peripheral Lesions Are Associated with Non-perfusion on Ultrawide Field Angiography. Ophthalmology, 2015.
15 Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) is retinal swelling and cyst formation in the macular area. It usually results in temporary decreased or permanent vision loss. DME will hyperfluoresce as pooling on a fluorescein angiogram. DME Exudates point to an area of leakage on a fluorescein angiogram such as DME Exudates optomap fa findings have been correlated to traditional FA imaging methods macular edema and signs of macular ischemia on SD-OCT. 1 Diabetic Retinopathy Exudates are proteins or lipids that leak from blood vessels into the surrounded tissue or space. No DME Early FA phase may show no edema DME Edema appears in the late phase of an FA as hyperfluorescent pooling 42 seconds 4 minutes 1. Tsui et al. Ultra Wide Field Fluorescein Angiography Can Detect Macular Pathology in Central Retinal Vein. OSLI
16 Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormalities (IRMA) Diabetic Retinopathy is a development of abnormal blood vessels with tiny aneurysms along with connections (shunts) from arterioles to venules. They occur in hypertensive and diabetic retinopathy, when blood is unable to flow through the normal capillaries, resulting in retinal anoxia and possible edema. PDR IRMA PDR Cotton wool spots Hard exudates Hemorrhages Non-perfusion Pan-Retinal Photocoagulation (PRP) is used to treat the vascular abnormalities associated with diabetic retinopathy. Laser photocoagulation uses the heat from a laser to seal or destroy abnormal, leaking blood vessels in the retina. optomap imaging can be used to help determine areas that need laser treatment. PDR treated with PRP Leakage Non-perfusion 14
17 Retinal Artery Occlusion occurs when there is an obstruction to the blood flow in the arteries. It is found in elderly patients who have arteriorsclerotic disease or younger patient whom have an embolic obstruction of the artery or its branches. 19 seconds 27 seconds Retinal Artery Occlusion 44 seconds 2:26 5:42 optomap fa images show delayed filling in Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion in a fluorescein angiography series. 15
18 Retinal Vein Occlusion Retinal Vein Occlusion is a retinal vascular disorder that can involve the central retinal vein, a major branch of the central vein, or any part of a branch. Fluorescein circulation is delayed showing areas of non-perfusion and the point of the occlusion can usually be seen with angiography. Vessel leakage and staining can occur in the vessels extending off the region of occlusion. Cystoid macular edema (CME) can also be present and visual acuity is greatly decreased. Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) CRVO with cystoid macular edema Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) 16
19 Ocular Ischemic Syndrome Retinal Vein Occlusion is a retinal vascular disorder, which is a result of carotid artery insufficiency. Delayed perfusion of the retina and choroidal circulation, macular edema and disc staining are seen with fluorescein angiography. Hemi-Retinal Vein Occlusion (HRVO) Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) Flame shaped hemorrhages and hypofluorescence from non-perfusion due to delayed filling in the retina. Ocular Ischemic Syndrome Non-perfusion is across the entire retina. Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) Hypofluorescence in the periphery due to delayed filling. 17
20 Sickle Cell Retinopathy Sickle Cell Retinopathy is a hereditary blood disorder that causes systemic problems relating to localized clumping of blood cells. In the eye, retinal changes occur such as: neovascularization, sea-fans, arterial blockage, capillary closure, angioid streaks, and retinal deposits. optomap fa is used to show extent of peripheral vascular changes. Sea-fan neovascularization Non-perfusion Peripheral non-perfusion observed on optomap fa is greater in those with sickle cell disease and proliferative retinopathy and has been correlated with macular vessel density on OCTA Han et al. Correlation of ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography and OCT angiography in sickle cell retinopathy. Ophthalmology Retina
21 Central Serous (Chorio) Retinopathy (CSR, CSCR) is a blister-like elevation of sensory retina in the macula (area of central vision), with localized detachment from the pigment epithelium. Results in reduction and/or distortion of vision that usually recovers within a few months. Area of hyperfluorescence where fluid leakage originates. optomap fa is used to identify the source of leakage and whether it is from a single or multiple sources. Color imaging alone can be challenging to pinpoint the area of leakage from CSR. Central Serous Retinopathy Area of hyperfluorescence where fluid-filled gutters appear. 19
22 Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD, ARMD) Age-Related Macular Degeneration is a group of conditions that include deterioration of the macula, resulting in loss of sharp central vision. Two general types: dry and wet. Dry is usually evident as a disturbance of macular pigmentation and deposits of yellowish material under the pigment epithelial layer in the central retinal zone. Wet AMD is abnormal new blood vessel growth under the retina which leaks fluid and blood, further disturbing macular function. optomap fa is used to rule out progression to wet AMD. Wet AMD Drusen in the periphery appear as hyperfluorescence due to staining Age-related macular degeneration is best managed with multimodal imaging and may be more than a macular condition but one that involves the entire retina. 1 Hypofluorescent blockage from hemorrhage Friberg. Peripheral Retinal Changes Associated with Age-Related Macular Degeneration in the Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2. Ophthalmology
23 Choroidal Neovascular Membrane (CNV, CNVM) is associated with AMD and there are two types: classic and occult. Classic will appear in the early phase with a well-defined area of hyperfluorescence. Occult may be poorly defined and areas of neovascularization are fuzzy, bright hyperfluorescent regions. Age-Related Macular Degeneration A recent study, looked at AMD subjects using UWF fluorescein angiography and found that 84.59% had hyperfluorescent characteristics in the periphery of which the main contributors were drusen, paving stone, and atrophic areas. 2 optomap fa imaging has been validated to have equivalent resolution in the central pole to traditional imaging methods and ETDRS Friberg. Morphologic and Angiographic Peripheral Retinal Changes in Patients with Age-related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology Tsui. Ultra Wide Field Fluorescein Angiography Can Detect Macular Pathology in Central Retnal Vein Occlusion
24 Uveitis Inflammatory Disease is inflammation of any of the structures of the uvea: iris, ciliary body or choroid. optomap fa is used to look for localized and diffuse leakage throughout the retina. Images may appear slightly blurry due to inflammatory cells in the vitreous, called vitreous haze. optomap fa shows hyperfluorescent staining of the peripheral lesions seen in uveitis. One study showed combined ultra-widefield color and optomap fa altered management in 48% of patients Campbell et al. Wide-field Retinal Imaging in the Management of Noninfectious Posterior Uveitis American Journal of Ophthalmology 2012
25 Vasculitis is the inflammation of a blood or lymph vessel. Fluorescein angiography is used to identify these areas of leakage or vessel staining. optomap fa is used to identify the level of activity pre and post-treatment. Inflammatory Disease Leakage of the vessels Vessel staining optomap fa has been found to detect up to 59% more changes associated with vasculitis than conventional imaging and exam. It has also been reported that the changes seen on optomap fa has impacted treatment decisions up to 65% of the time. 1,2 Retinitis and choroiditis 1. Leder et al. Ultra-wide-field retinal imaging in the management of non-infectious retinal vasculitis. Journal of Ocular Inflammation, Stanga et al. Ultra-widefield fundus fluorescein angiography in the diagnosis and management of retinal vasculitis. Eye
26 Coats Disease Pediatric Disease is a chronic, progressive retinal disorder characterized by massive white exudates under the retina, with eventual detachment and glaucoma. This disorder is associated with malformed, tortuous retinal blood vessels and aneurysmal dilatations. Coat s Disease Aneurysmal changes, telangiectatic vasculature, and peripheral non-perfusion in the far temporal periphery. Coat s Disease Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy (FEVR) is a hereditary condition characterized by fluid leakage from the retina, and vitreo-retinal membrane formation with new blood vessels. FEVR FEVR Extensive peripheral leakage which is correlated with central retinal vascular changes. 24
27 ROP Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) is a retinal vasculature disorder that affects severely premature babies, resulting from incomplete peripheral vascularization at birth followed by abnormal vascularization. optomap fa is used to determine the extent of vasculature present to grade the level of ROP and monitor response to treatment. ROP Pediatric Disease optomap can obtain high-quality images in babies with retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) down to 34 weeks. 1 optomap has been shown to capture up to 75% more abnormal peripheral pathology in pediatric patients unseen by conventional imaging methods in ROP. 1,2 Best Disease is a juvenile disease and vitelliform macular degeneration is an inherited eye condition. Best disease can start to cause changes at the back of the eye between the ages of 3 to 15 although it does not usually affect vision until later on in life. Best Disease Best Disease 1. Patel et al. Non-contact Ultra-widefield imaging of Retinopathy of Prematurity Using the Optos dual Wavelength scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope. Eye Kang et al. Ultra-widefield imaging for the management of pediatric retinal diseases. Journal of Pediatric Ophthalmology and strabismus
28 Choroidal Melanoma Tumors is a form of malignant tumor derived from pigment cells initiated in the choroid. If an ocular tumor is suspected, optomap fa can aid in determining the characteristics of the retinal circulation at or around the tumor mass as well as establishing if the tumor is leaking dye or blocking fluorescence. Multi-modal optomap fa imaging allows for documentation and monitoring of the extensive retinal changes and patterns of vascular damage that can be associated with choroidal tumors and their treatment McCannel et al. New Ultra-Wide-Field Angiographic Grading Scheme for Radiation Retinopathy after Iodine-125 Brachytherapy for Uveal Melanoma. Retina
29 Tumors 27
30 Image Acknowledgements David Brown, MD Netan Choudhry, MD Mandar Joshi, MD George Ko, MD Rahul Mandinga, MD Charles Newell, MD Quan Nguyen, MD Jeffrey Rubin, MD Srinivas Sadda, MD Michael Singer, MD Paulo Stanga, MD Yoshihiro Yonekawa, MD The optomap : was created by the Optos Clinical Team and reviewed by Rishi Singh, MD Contact clinical@optos.com for any additional educational questions.
31
32 Optos is a leading provider of devices that enable eye care professionals to enhance their patient care. Our ultra-widefield (UWF ) retinal imaging devices image 82% or 200 of the retina in a single capture something no other retinal imaging device is capable of doing. optomap images facilitate the early detection, management, and effective treatment of disorders and diseases evidenced in the retina. Additionally, optomap is the only clinically-validated ultra-widefield retinal image with more than 500 published studies incorporating optomap imaging for diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient engagement. Optos is committed to continue to deliver new products and software that supports optomap as a standard of care, helping eye care professionals around the world save sight and save lives. Building The Retina Company Optos plc Queensferry House Carnegie Campus Enterprise Way Dunfermline, Fife Scotland KY11 8GR Tel: +44 (0) ics@optos.com Optos, Inc. 500 Nickerson Road Suite 201 Marlborough, MA USA Call Toll-free (US & Canada): Outside of the US: usinfo@optos.com Optos Australia 10 Myer Court Beverley South Australia 5009 Tel: auinfo@optos.com 2018 Optos. All rights reserved. Optos, optos and optomap are registered trademarks of Optos plc. Registered in Scotland Number: SC Registered Office: Queensferry House, Carnegie Campus, Dunfermline, Fife KY11 8GR, UK PN GA / 1
af Diagnostic Atlas A Retinal Reference Guide Building The Retina Company
 af Diagnostic Atlas A Retinal Reference Guide Building The Retina Company af Diagnostic Atlas A Retinal Reference Guide Optos core devices produce ultra-widefield (UWF ), high resolution digital images
af Diagnostic Atlas A Retinal Reference Guide Building The Retina Company af Diagnostic Atlas A Retinal Reference Guide Optos core devices produce ultra-widefield (UWF ), high resolution digital images
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY
 PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care
 OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care An Image Interpretation Primer Julie Rodman, OD, MS, FAAO and Nadia Waheed, MD, MPH Table of Contents Diabetic Retinopathy 3-6 Choroidal Neovascularization 7-9 Central
OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care An Image Interpretation Primer Julie Rodman, OD, MS, FAAO and Nadia Waheed, MD, MPH Table of Contents Diabetic Retinopathy 3-6 Choroidal Neovascularization 7-9 Central
ZEISS AngioPlex OCT Angiography. Clinical Case Reports
 Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS /16/2018. Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases???
 When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
Leo Semes, OD, FAAO UAB Optometry
 Leo Semes, OD, FAAO UAB Optometry Safe; inert Has long track record - over 45 years Mixes with plasma and highlights blood vessel compromise Using specific exciting (490 nm)and absorption (510 nm) filters
Leo Semes, OD, FAAO UAB Optometry Safe; inert Has long track record - over 45 years Mixes with plasma and highlights blood vessel compromise Using specific exciting (490 nm)and absorption (510 nm) filters
Widefield Retinal Imaging with Auto Fluorescence Technology in the Optometric Practice
 Widefield Retinal Imaging with Auto Fluorescence Technology in the Optometric Practice This course will define ultra-widefield retinal imaging and autofluorescence for the attendee. Will show how it is
Widefield Retinal Imaging with Auto Fluorescence Technology in the Optometric Practice This course will define ultra-widefield retinal imaging and autofluorescence for the attendee. Will show how it is
Diabetic Retinopathy. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
The Human Eye. Cornea Iris. Pupil. Lens. Retina
 The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography
 Ruth E. Picchiottino, CRA Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography 15 Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography Recommendations for tailoring retinal fluorescein angiography to diabetic retinopathy, macular
Ruth E. Picchiottino, CRA Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography 15 Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography Recommendations for tailoring retinal fluorescein angiography to diabetic retinopathy, macular
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetes & Your Eyes
 Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
Michael P. Blair, MD Retina Consultants, Ltd Libertyville/Des Plaines, Illinois Clinical Associate University of Chicago 17 October 2015
 Michael P. Blair, MD Retina Consultants, Ltd Libertyville/Des Plaines, Illinois Clinical Associate University of Chicago 17 October 2015 So What Parts of the Eye Retina are Affected by VHL Neural tissue
Michael P. Blair, MD Retina Consultants, Ltd Libertyville/Des Plaines, Illinois Clinical Associate University of Chicago 17 October 2015 So What Parts of the Eye Retina are Affected by VHL Neural tissue
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City
 Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion
 EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina
EyePACS Grading System (Part 2): Detecting Presence and Severity of Background (Non-Proliferative) Diabetic Retinopathy Lesion George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy. Reviewed & ratified by: Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Incorporating OCT Angiography Into Patient Care
 Incorporating OCT Angiography Into Patient Care Beth A. Steele, OD, FAAO OCT A: Introduction Isolates microvascular circulation from OCT image data Axial resolution = 5 microns (i.e. fine capillaries visible)
Incorporating OCT Angiography Into Patient Care Beth A. Steele, OD, FAAO OCT A: Introduction Isolates microvascular circulation from OCT image data Axial resolution = 5 microns (i.e. fine capillaries visible)
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
OCT Angiography The Next Frontier
 Choroid Retina avascular 5/13/2017 OCT Angiography The Next Frontier Pierce Kenworthy OD, FAAO June 9, 2017 OCT Angiography (OCTA) 2016 Non-invasive, motion contrast imaging Represents erythrocyte movement
Choroid Retina avascular 5/13/2017 OCT Angiography The Next Frontier Pierce Kenworthy OD, FAAO June 9, 2017 OCT Angiography (OCTA) 2016 Non-invasive, motion contrast imaging Represents erythrocyte movement
Fluorescein Angiography
 Last revision: October 2011 by Luis Arias Fluorescein Angiography Authors: Luis Arias, MD Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge - University of Barcelona. Spain Jordi Monés, MD Institut de la Màcula i de
Last revision: October 2011 by Luis Arias Fluorescein Angiography Authors: Luis Arias, MD Hospital Universitari de Bellvitge - University of Barcelona. Spain Jordi Monés, MD Institut de la Màcula i de
FRANZCO, MD, MBBS. Royal Darwin Hospital
 Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Your eyes are. a window to your health. Take a closer look with optomap.
 Your eyes are a window to your health. Take a closer look with optomap. Protect your vision. Bringing the most advanced technology to our patients, we recommend optomap ultra-wide digital retinal imaging
Your eyes are a window to your health. Take a closer look with optomap. Protect your vision. Bringing the most advanced technology to our patients, we recommend optomap ultra-wide digital retinal imaging
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
 Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY. <Your Hospital Name> <Your Logo>
 MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
What Is O.C.T. and Why Should I Give A Rip? OCT & Me How Optical Coherence Tomography Changed the Life of a Small Town Optometrist 5/19/2014
 OCT & Me How Optical Coherence Tomography Changed the Life of a Small Town Optometrist Email: myoder@wcoil.com Mark A. Yoder, O.D. 107 N. Main Street PO Box 123 Bluffton, OH 45817 @yoderod 115.02 Histoplasma
OCT & Me How Optical Coherence Tomography Changed the Life of a Small Town Optometrist Email: myoder@wcoil.com Mark A. Yoder, O.D. 107 N. Main Street PO Box 123 Bluffton, OH 45817 @yoderod 115.02 Histoplasma
OCT Interpretation in Retinal Disease
 OCT Interpretation in Retinal Disease Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Advanced Ocular
OCT Interpretation in Retinal Disease Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Advanced Ocular
THE ROLE OF anti-vegf IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AND AGE RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION
 THE ROLE OF anti-vegf IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AND AGE RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION MOESTIDJAB DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AIRLANGGA UNIVERSITY DR SOETOMO HOSPITAL SURABAYA INTRODUCTION
THE ROLE OF anti-vegf IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AND AGE RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION MOESTIDJAB DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AIRLANGGA UNIVERSITY DR SOETOMO HOSPITAL SURABAYA INTRODUCTION
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
Mild NPDR. Moderate NPDR. Severe NPDR
 Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Fundus Autofluorescence
 Brittany Bateman, BS Fundus autofluorescence imaging is used to record fluorescence that may occur naturally in ocular structures or as a byproduct of a disease process. This technique allows the topographic
Brittany Bateman, BS Fundus autofluorescence imaging is used to record fluorescence that may occur naturally in ocular structures or as a byproduct of a disease process. This technique allows the topographic
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP
 Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient
 Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy. George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD
 EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
Amber Priority. Image Library
 Amber Priority Image Library Amber flag Diabetic Maculopathy (M1) Pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (R2) Old, treated and now inactive DR (R1/M0/P1or R0/M0/P1) Where only partial or incomplete images
Amber Priority Image Library Amber flag Diabetic Maculopathy (M1) Pre-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (R2) Old, treated and now inactive DR (R1/M0/P1or R0/M0/P1) Where only partial or incomplete images
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease
 Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS
 GENERAL INFORMATION RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS WHAT ARE RETINAL CONDITIONS? Retinal conditions affect the light-sensitive tissue at the back of eye known as the retina. They include diseases
GENERAL INFORMATION RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS WHAT ARE RETINAL CONDITIONS? Retinal conditions affect the light-sensitive tissue at the back of eye known as the retina. They include diseases
Role of Fluorescein angiography in evaluation of posterior segment disorders
 Original Article Role of Fluorescein angiography in evaluation of posterior segment disorders Arvind R, Surendar S 2, Ch. Jagan Mohan Rao 3 Associate Professor, 2 Postgraduate student, 3 Senior resident,
Original Article Role of Fluorescein angiography in evaluation of posterior segment disorders Arvind R, Surendar S 2, Ch. Jagan Mohan Rao 3 Associate Professor, 2 Postgraduate student, 3 Senior resident,
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema
 Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
The Quick Guide to OCT Mastery 50 Real Cases with Expert Analysis
 OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY The Quick Guide to OCT Mastery 50 Real Cases with Expert Analysis VOL 1 Sanjay Sharma, MD, FRCS, MSc (Epid), MBA Ophthalmologist, Epidemiologist Queen s University, Canada
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY The Quick Guide to OCT Mastery 50 Real Cases with Expert Analysis VOL 1 Sanjay Sharma, MD, FRCS, MSc (Epid), MBA Ophthalmologist, Epidemiologist Queen s University, Canada
FA vs. OCTA? The status of OCTA, today. Fukuoka, JSOS 2016 Gerd Klose. Korobelnik J Fr Ophthalmol (2015)
 FA vs. OCTA? The status of OCTA, today Korobelnik J Fr Ophthalmol (2015) Fukuoka, JSOS 2016 Gerd Klose 1 2 FA / ICGA a well-founded Gold standard! Benefits Useful for many pathologies High contrast, detailed
FA vs. OCTA? The status of OCTA, today Korobelnik J Fr Ophthalmol (2015) Fukuoka, JSOS 2016 Gerd Klose 1 2 FA / ICGA a well-founded Gold standard! Benefits Useful for many pathologies High contrast, detailed
10/17/2017. FDA Approved. Zeiss AngioPlex TM Optovue AngioVue TM
 Images retinal microvasculature without dye injection Displays structure and function from a single imaging system Standard of Care-2011 DFE, Fundus Photos, VF 10-2, SD-OCT, FAF, or mferg 2016-AAO Baseline
Images retinal microvasculature without dye injection Displays structure and function from a single imaging system Standard of Care-2011 DFE, Fundus Photos, VF 10-2, SD-OCT, FAF, or mferg 2016-AAO Baseline
Posterior Segment Update
 Posterior Segment Update Featured Speaker: Dr. Kyle Cheatham, FAAO, DIP ABO DISCLOSURE STATEMENT We have no direct financial or proprietary interest in any companies, products or services mentioned in
Posterior Segment Update Featured Speaker: Dr. Kyle Cheatham, FAAO, DIP ABO DISCLOSURE STATEMENT We have no direct financial or proprietary interest in any companies, products or services mentioned in
MAGNITUDE OF DIABETIC EYE DISEASE IN INDIA
 Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
 Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) What is the Macula? What is Dry AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration)? Dry AMD is an aging process that causes accumulation of waste product under the macula leading
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) What is the Macula? What is Dry AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration)? Dry AMD is an aging process that causes accumulation of waste product under the macula leading
The College of Optometrists - Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina
 Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
Brampton Hurontario Street Brampton, ON L6Y 0P6
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Hiroki Fujita, Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, Soh Futagami and Takashi Tokoro Department of Visual Science, Tokyo Medical
Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Hiroki Fujita, Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, Soh Futagami and Takashi Tokoro Department of Visual Science, Tokyo Medical
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
World Sight Day Case Studies. Mark Frost Screening Manager South East London DESP
 World Sight Day 2015 Case Studies Mark Frost Screening Manager South East London DESP Introduction All of the following cases have been identified in our screening programme over the last 3 years. The
World Sight Day 2015 Case Studies Mark Frost Screening Manager South East London DESP Introduction All of the following cases have been identified in our screening programme over the last 3 years. The
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Ophthalmology Retinal Imaging Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: OPXRET_D.XPT December 2008 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component:
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Ophthalmology Retinal Imaging Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: OPXRET_D.XPT December 2008 NHANES 2005 2006 Data Documentation Exam Component:
Patient AB. Born in 1961 PED
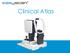 Clinical Atlas Patient AB Born in 1961 PED Autofluorescence Dilated 45 EasyScan Zero-dilation IR 45 Fundus Dilated 45 In the fundus photos (Canon CX1) the PED is not able to be seen. However, the extent
Clinical Atlas Patient AB Born in 1961 PED Autofluorescence Dilated 45 EasyScan Zero-dilation IR 45 Fundus Dilated 45 In the fundus photos (Canon CX1) the PED is not able to be seen. However, the extent
The Foundation WHAT IS THE RETINA?
 Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a deterioration of the retina and choroid that leads to a substantial loss in visual acuity (sharpness of vision). AMD is the leading cause of significant visual
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a deterioration of the retina and choroid that leads to a substantial loss in visual acuity (sharpness of vision). AMD is the leading cause of significant visual
Five Things You re Missing with Your Fundus Camera
 ebook Five Things You re Missing with Your Fundus Camera By Donald J. Siegel, OD, Sun City West Eye Care Sponsored by: Before I began incorporating EIDON true-color imaging into my practice, my retinal
ebook Five Things You re Missing with Your Fundus Camera By Donald J. Siegel, OD, Sun City West Eye Care Sponsored by: Before I began incorporating EIDON true-color imaging into my practice, my retinal
Ocular Pathology. I. Congenital and/or developmental. A. Trisomy 21. Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea)
 I. Congenital and/or developmental Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6 th Ed. A. Trisomy 21 Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea) Focal hypoplasia of iris Cataracts frequently
I. Congenital and/or developmental Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6 th Ed. A. Trisomy 21 Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea) Focal hypoplasia of iris Cataracts frequently
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
Stabilization of visual acuity with photodynamic therapy in eyes with chorioretinal anastomoses
 Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2004) 242:368 376 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-003-0844-0 Rufino M. Silva José R. Faria de Abreu António Travassos José G. Cunha-Vaz Stabilization of visual
Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2004) 242:368 376 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-003-0844-0 Rufino M. Silva José R. Faria de Abreu António Travassos José G. Cunha-Vaz Stabilization of visual
OPTIC DISC PIT Pathogenesis and Management OPTIC DISC PIT
 OPTIC DISC PIT Pathogenesis and Management Abdel-Latif Siam Ain Shams University Cairo Egypt OPTIC DISC PIT Congenital pit is an atypical coloboma usually located on the temporal edge of the disc, associated
OPTIC DISC PIT Pathogenesis and Management Abdel-Latif Siam Ain Shams University Cairo Egypt OPTIC DISC PIT Congenital pit is an atypical coloboma usually located on the temporal edge of the disc, associated
Contractor Information. LCD Information. Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Ophthalmic Angiography (Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green) (L34426)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Ophthalmic Angiography (Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green) (L34426) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Ophthalmic Angiography (Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green) (L34426) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE
 GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Cataract clouding of the eye s lens. Cataracts develop at an earlier age in people
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Outline. Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness. Eye Care Center Doctors. Justin Kanoff, MD. Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado
 Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
The Foundation. continued next page. RETINA HEALTH SERIES Facts from the ASRS
 The Foundation American Society of Retina Specialists Committed to improving the quality of life of all people with retinal disease. Idiopathic Juxtafoveal Telangiectasis (pronounced tell an gee ACT te
The Foundation American Society of Retina Specialists Committed to improving the quality of life of all people with retinal disease. Idiopathic Juxtafoveal Telangiectasis (pronounced tell an gee ACT te
4/19/2018 FUNDUS AUTOFLUORESCENCE. Fluorescence Imaging. Fundus Autofluorescence (FAF) Fluorescence. Fluorescence
 I have no financial or proprietary interest in the subject matter of this presentation. FUNDUS AUTOFLUORESCENCE Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, OCT-C, FOPS Penn State Eye Center Hershey, PA Fluorescence Imaging
I have no financial or proprietary interest in the subject matter of this presentation. FUNDUS AUTOFLUORESCENCE Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, OCT-C, FOPS Penn State Eye Center Hershey, PA Fluorescence Imaging
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 Age-Related Macular Degeneration Age-Related Macular Degeneration Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the most common causes of poor vision after age 60. AMD is a deterioration or breakdown
Age-Related Macular Degeneration Age-Related Macular Degeneration Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the most common causes of poor vision after age 60. AMD is a deterioration or breakdown
2009 REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE, VISUCAM and VISUCAM NM/FA
 2009 REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE FF 450 PLUS PRO NM, VISUCAM and VISUCAM NM/FA Zeiss Fundus Cameras INTRODUCTION The following guide provides an overview of billing and reimbursement for procedures performed with
2009 REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE FF 450 PLUS PRO NM, VISUCAM and VISUCAM NM/FA Zeiss Fundus Cameras INTRODUCTION The following guide provides an overview of billing and reimbursement for procedures performed with
Spontaneous Large Serous Retinal Pigment Epithelial Tear
 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
Visualize. Analyze. Personalize. OCT + OCTA
 Visualize. Analyze. Personalize. OCT + OCTA A New Approach to Protecting Vision AngioVue OCT Angiography brings valuable new information to clinical practice. Non-invasive visualization of retinal vasculature.
Visualize. Analyze. Personalize. OCT + OCTA A New Approach to Protecting Vision AngioVue OCT Angiography brings valuable new information to clinical practice. Non-invasive visualization of retinal vasculature.
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT CAUSES DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT ARE THE STAGES OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY?
 Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
Misdiagnosed Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease and atypical central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC)
 HPTER 12 Misdiagnosed Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease and atypical central serous chorioretinopathy (S) linical Features VKH disease is a bilateral granulomatous panuveitis often associated with exudative
HPTER 12 Misdiagnosed Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) disease and atypical central serous chorioretinopathy (S) linical Features VKH disease is a bilateral granulomatous panuveitis often associated with exudative
Jay M. Haynie, O.D.; F.A.A.O. Olympia Tacoma Renton Kennewick Washington
 Jay M. Haynie, O.D.; F.A.A.O. Olympia Tacoma Renton Kennewick Washington I Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO have received honoraria from the following companies: Reichert Technologies Notal Vision Carl Zeiss Meditec
Jay M. Haynie, O.D.; F.A.A.O. Olympia Tacoma Renton Kennewick Washington I Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO have received honoraria from the following companies: Reichert Technologies Notal Vision Carl Zeiss Meditec
Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist
 Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
FROM OUTDATED TO UPDATED Eminence-Based Medicine
 FROM OUTDATED TO UPDATED Eminence-Based Medicine Evidence-Based Medicine A REVIEW OF KEY CLINICAL TRIALS Anthony DeWilde, OD FAAO 1 EMINENCE BASED MEDICINE 2 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE 3 4 CLINICAL TRIALS
FROM OUTDATED TO UPDATED Eminence-Based Medicine Evidence-Based Medicine A REVIEW OF KEY CLINICAL TRIALS Anthony DeWilde, OD FAAO 1 EMINENCE BASED MEDICINE 2 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE 3 4 CLINICAL TRIALS
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy #
 RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
Vascular Disease Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Hypertension
 Vascular Disease Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Hypertension Maynard L. Pohl, OD, FAAO Pacific Cataract & Laser Institute 10500 NE 8 th Street, Suite 1650 Bellevue, WA 98004 USA 425-462-7664 Cerebrovascular
Vascular Disease Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Hypertension Maynard L. Pohl, OD, FAAO Pacific Cataract & Laser Institute 10500 NE 8 th Street, Suite 1650 Bellevue, WA 98004 USA 425-462-7664 Cerebrovascular
연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과
 연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과 40 Table. Clinical characteristics and results of patients undergoing photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation Patients No. Age/ sex Eye
연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과 40 Table. Clinical characteristics and results of patients undergoing photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation Patients No. Age/ sex Eye
Contractor Information. LCD Information. Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Ophthalmic Angiography (Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green) (L34426)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Ophthalmic Angiography (Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green) (L34426) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Ophthalmic Angiography (Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green) (L34426) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong. Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong
 Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Neuropathy (NAION) and Avastin. Clinical Assembly of the AOCOO-HNS Foundation May 9, 2013
 Non Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) and Avastin Shalom Kelman, MD Clinical Assembly of the AOCOO-HNS Foundation May 9, 2013 Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Acute, painless, visual loss,
Non Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) and Avastin Shalom Kelman, MD Clinical Assembly of the AOCOO-HNS Foundation May 9, 2013 Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Acute, painless, visual loss,
Scrub In. What is the function of vitreous humor? What does the pupil do when exposed to bright light? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision
 Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction
 Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
OCT Angiography. SriniVas Sadda, MD
 OCT Angiography SriniVas Sadda, MD Professor of Ophthalmology Director, Medical Retina Unit Ophthalmic Imaging Unit University of Southern California Los Angeles, California, USA Disclosure Consulting
OCT Angiography SriniVas Sadda, MD Professor of Ophthalmology Director, Medical Retina Unit Ophthalmic Imaging Unit University of Southern California Los Angeles, California, USA Disclosure Consulting
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network
 Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Peripheral Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Lesions on Ultrawide-field Fundus Images and Risk of DR Worsening Over Time Version 4.0 July 21, 2017 peripheral dr lesions
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Peripheral Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Lesions on Ultrawide-field Fundus Images and Risk of DR Worsening Over Time Version 4.0 July 21, 2017 peripheral dr lesions
Diabetic Management beyond traditional risk factors and LDL-C control: Can we improve macro and microvascular risks?
 Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE RETINA AND OPTIC NERVE. Lindsay B. Howse, OD
 OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE RETINA AND OPTIC NERVE Lindsay B. Howse, OD drlindsayhowse@gmail.com None. FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES OUTLINE Introduction/How OCTA works OCTA Analysis Advantages
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE RETINA AND OPTIC NERVE Lindsay B. Howse, OD drlindsayhowse@gmail.com None. FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES OUTLINE Introduction/How OCTA works OCTA Analysis Advantages
ATLAS OF OCT. Retinal Anatomy in Health & Pathology by Neal A. Adams, MD. Provided to you by:
 ATLAS OF OCT Retinal Anatomy in Health & Pathology by Neal A. Adams, MD Provided to you by: Atlas of OCT The OCT Atlas is written by Neal A. Adams, MD, and produced by Heidelberg Engineering, Inc. to help
ATLAS OF OCT Retinal Anatomy in Health & Pathology by Neal A. Adams, MD Provided to you by: Atlas of OCT The OCT Atlas is written by Neal A. Adams, MD, and produced by Heidelberg Engineering, Inc. to help
OCULAR HEMORRHAGES. ROSCOE J. KENNEDY, M.D. Department of Ophthalmology
 OCULAR HEMORRHAGES ROSCOE J. KENNEDY, M.D. Department of Ophthalmology Ocular hemorrhages are important not only because they produce visual loss but also because they usually indicate a disorder elsewhere
OCULAR HEMORRHAGES ROSCOE J. KENNEDY, M.D. Department of Ophthalmology Ocular hemorrhages are important not only because they produce visual loss but also because they usually indicate a disorder elsewhere
DIABETES AND YOUR EYES. Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler
 DIABETES AND YOUR EYES Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler Tahlequah, OK Forest Grove, OR Brief Review of Diabetes The body s endocrine system is responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and tissue
DIABETES AND YOUR EYES Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler Tahlequah, OK Forest Grove, OR Brief Review of Diabetes The body s endocrine system is responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and tissue
On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging. On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging. Wavelength Specific Imaging
 On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, FOPS, OCT-C Penn State Hershey Eye Center Hershey, PA On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Wavelengths
On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Timothy J. Bennett, CRA, FOPS, OCT-C Penn State Hershey Eye Center Hershey, PA On Different Wavelengths: The Spectrum of Retinal Imaging Wavelengths
OCT Image Analysis System for Grading and Diagnosis of Retinal Diseases and its Integration in i-hospital
 Progress Report for1 st Quarter, May-July 2017 OCT Image Analysis System for Grading and Diagnosis of Retinal Diseases and its Integration in i-hospital Milestone 1: Designing Annotation tool extraction
Progress Report for1 st Quarter, May-July 2017 OCT Image Analysis System for Grading and Diagnosis of Retinal Diseases and its Integration in i-hospital Milestone 1: Designing Annotation tool extraction
Fluorescein and Indocyanine Green Videoangiography of Choroidal Melanomas
 luorescein and Indocyanine Green Videoangiography of Choroidal Melanomas Leyla S. Atmaca, igen Batioğlu and Pelin Atmaca Eye Clinic, Ankara University Medical School, Ankara, Turkey Purpose: This study
luorescein and Indocyanine Green Videoangiography of Choroidal Melanomas Leyla S. Atmaca, igen Batioğlu and Pelin Atmaca Eye Clinic, Ankara University Medical School, Ankara, Turkey Purpose: This study
Diabetic Retinopatathy
 Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Central venous occlusion
 Central venous occlusion Central venous occlusion (right eye) There are dark haemorrhages at the macula and all over the retina. Choroidal haemangioma A choroidal haemangioma has salmon pink colour. There
Central venous occlusion Central venous occlusion (right eye) There are dark haemorrhages at the macula and all over the retina. Choroidal haemangioma A choroidal haemangioma has salmon pink colour. There
The Foundation WHAT IS THE RETINA?
 The Foundation American Society of Retina Specialists Committed to improving the quality of life of all people with retinal disease. Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Retinal vein occlusions occur when there
The Foundation American Society of Retina Specialists Committed to improving the quality of life of all people with retinal disease. Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Retinal vein occlusions occur when there
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Scanning Computerized Ophthalmic Diagnostic Imaging (SCODI) (L34431)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Scanning Computerized Ophthalmic Diagnostic Imaging (SCODI) (L34431) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Scanning Computerized Ophthalmic Diagnostic Imaging (SCODI) (L34431) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
