1- Arteries include conducting and resistance vessels
|
|
|
- Brandon Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Structure of Blood Vessels (general considerations) 1- Arteries include conducting and resistance vessels The vascular portion of the circulatory system is composed of a variety of blood vessel compartments that are categorized by size, structure and function. These include arteries, which are conducting and resistance vessels; capillaries; and veins * Elastic Arteries The largest blood vessels in the body, the aorta and the elastic arteries, are conduits for blood flow to smaller arterial branches and are composed of three layers: a- Tunica intima: This consists of a single layer of endothelial cells, a subendothelial compartment containing a few smooth muscle cells and connective tissue extending to the luminal side of the internal elastic lamina. The aortic intima is thicker than the other elastic arteries and contains matrix proteins including collagen, proteoglycans and small amounts of elastin. b- Tunica media: The next layer outward is the tunica media, the thickest tunica. It is bounded by internal and external elastic laminae and itself displays numerous elastic laminae and smooth muscle cells within an extracellular connective tissue matrix. c- Tunica adventitia: The most external vessel wall layer contains fibroblasts, connective tissue, nerves and small vessels that give rise to the vasa vasorum. *Muscular Arteries Blood conducted by the elastic arteries is distributed to individual organs through large muscular arteries (resistance vessels), The tunica media of a muscular artery consists of layers of smooth muscle cells without prominent bands of elastin, although a prominent internal elastic lamina and usually an external elastic lamina are present. The small muscular arteries are important regulators of blood flow and maintain systemic pressure by regulating total peripheral resistance. * Arterioles Arterioles are the smallest elements of the arterial system. They have an endothelial lining surrounded by one or two layers of smooth muscle cells. No elastic layers are evident. The smallest arterioles provide dynamic regulation of blood flow by vasomotion (change in the caliber of an artery), thus controlling the distribution of blood in the capillary tree. 1
3 Subdivisions and histologic structure of the vascular system. Normal blood pressures in the different portions of the circulatory system when a person is lying in the horizontal position. 2 Distribution of blood (in percentage of total blood) in the different parts of the circulatory system.
4 2- Capillaries Permit Transport From the Blood to the Interstitium In these smallest blood vessels, the endothelium is supported only by sparse smooth muscle cells. The capillary endothelium provides for exchange of solutes and cells between blood and extracellular fluid. The capillary endothelium is a semipermeable membrane, in which exchange of plasma solutes with extracellular fluid is controlled by molecular size and charge. The permeability of capillaries depends on their endothelial cells. Structure of the mesenteric capillary bed. Structure of the capillary wall. Note especially the intercellular cleft at the junction between adjacent endothelial cells; it is believed that most water-soluble substances diffuse through the capillary membrane along the clefts. 3- Veins Return Blood to the Heart Venules are the first vessels to collect blood from capillaries. Their thin media is appropriate for a vessel that does not face high intraluminal pressures. Venules merge into small and medium-sized veins, which in turn converge into large veins. Many veins, particularly in the extremities, have valves, made of endothelial- lined folds of the tunica intima, that prevent backflow and help to move blood under the low pressure of the venous circulation 4- Lymphatics Drain Interstitial Fluid Lymphatic circulation is composed of blind-ended lymphatic capillaries, consisting of (1) endothelium with no pericytes; (2) precollecting lymphatics; and (3) collecting lymphatics, which pump lymph toward the lymph nodes, lymphatic trunks and finally thoracic and right lymphatic ducts, which return lymph back to the blood. Diffusion of fluid molecules and dissolved substances between. the capillary and interstitial fluid spaces. 3 Special structure of the lymphatic capillaries that permits passage of substances of high molecular weight into the lymph
5 Cells of the Blood Vessel Wall (general considerations) 1-A Single Layer of Endothelial Cells Comprises a Confluent Macromolecular Barrier It had several biological functions, including coagulation, platelet regulation, fibrinolysis, inflammation, immunoregulation and repair. They also modulate vascular smooth muscle cell function through paracrine pathways. Endothelium integrity depends on several types of adhesion complexes *Cell substrate adhesion molecules attach endothelial cells to their substratum (e.g., basal lamina). (For example, integrins bind endothelial cells to extracellular matrix adhesive molecules, including laminin, fibronectin, fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor and thrombospondin). *Cell cell adhesion molecules attach one endothelial cell to its neighbor (The cadherins are linked to the actin cytoskeleton by catenins). 2- Smooth Muscle Cells Maintain Blood Vessel Integrity like endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells proliferate in response to injury, and are important in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic plaques. Smooth muscle cells are major producers of the growth factors, cytokines and chemokines involved in atherogenesis. Smooth muscle cells maintain blood vessel integrity and provide support for endothelium. They control blood flow by contracting or dilating in response to specific stimuli. 3-Leukocytes Enter Vessel Walls and Are Important in Atherosclerosis 4-Pericytes Are Modified Smooth Muscle Cells That Surround Capillaries They are in close contact with endothelial cells, and both share the same basement membrane contractile or regulate the function and proliferation of adjacent endothelial cells. 5-Vacular Progenitor/Stem Cells Regulate Vasculogenesis Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are bone marrow derived cells arising from perinatal hemangioblasts, and are present in adult bone marrow and peripheral circulation. They are multipotent immature cells that can proliferate, migrate and differentiate into endothelial cells. The presence of circulating EPCs in adults suggests that new blood vessel growth in adults occurs by vasculogenesis, not only by angiogenesis as previously thought (angiogenesis refers to the sprouting of new capillaries from existing blood vessels, whereas vasculogenesis is the differentiation of angioblasts [precursor cells] into endothelial cells that form a vascular network de novo). 4
6 Atherosclerosis:- In atherosclerosis, inflammatory and immune cells, smooth muscle cells, lipid and connective tissue progressively accumulate in the intima of large and medium-sized elastic and muscular arteries. The classic atherosclerotic lesion is best described as a fibroinflammatory lipid plaque (atheroma). These plaques develop over several decades Their continued growth encroaches on the media of the arterial wall and into the lumen of the vessel, narrowing the lumen. Atherosclerotic lesions are also called atherosclerotic plaques, atheromas, fibrous plaques or fibrofatty lesions. The life of a plaque can be divided into three stages: (1) Initiation and formation Stage (a. sites that appear to be predisposed to lesion formation b. Lipid accumulation, c. Mononuclear macrophages factors, d. mural thrombi formation, e. ischemic necrosis of deeper thickened intima, f. fibroinflammatory lipid plaque is formed, g. immune system participates) (2) Adaptation Stage (plaque protrudes into the lumen and the wall of the artery remodels to maintain lumen size.) (3) Clinical stage (hemorrhage occurs when fragile new vessels are formed in the plaques, which may rupture locally. Macrophages clean up the hemorrhagic material and Complications develop surface ulceration, fissure formation, calcification). Complicated lesions of atherosclerosis. The luminal surface of the abdominal aorta and the common iliac arteries shows numerous fibrous plaques and raised, ulcerated lesions containing friable, atheromatous debris. The distal portion of the aorta displays a small aneurysmal dilation. A unifying hypothesis for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis 5
7 Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis 1- Hypertension: High blood pressure is consistently associated with greater risk of myocardial infarction. 2- Blood cholesterol level: Serum cholesterol levels correlate directly with development of ischemic heart disease 3- Cigarette smoking: Coronary and aortic atherosclerosis are more severe and extensive in cigarette smokers than in nonsmokers, 4- Diabetes: Diabetics are at greater risk for occlusive atherosclerotic vascular disease in many organs. 5- Increasing age and male sex: These factors are strongly correlated with risk of myocardial infarction 6- Physical inactivity and stressful life patterns 7- Homocysteine: Homocystinuria is a rare autosomal recessive disease caused by mutations in the gene encoding cystathionine synthase. 8- C-reactive protein: CRP is an acute phase reactant mainly produced by hepatocytes. It is a serum marker for systemic inflammation, and has been linked to increased risk of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke. Hypertensive Vascular Disease Blood pressure is the product of cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance to blood flow. Both systolic and diastolic pressures are important in determining the risk of cardiovascular disease, especially atherosclerosis. Over the course of the day, blood pressure varies widely, depending on exertion, emotional state and other poorly understood factors. It also exhibits a circadian rhythm falling at night or during sleep, as sympathetic nervous system tone declines. Blood pressure also varies with age. The most widespread hypothesis holds that primary hypertension results from an imbalance in the interactions between these mechanisms, Frequency of hypertension increases as the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) falls even with mild renal dysfunction. Reduced GFR in renal dysfunction causes sodium retention and volume expansion, which should be compensated by reduced tubular sodium reabsorption, the end result of autoregulation is always increased peripheral resistance due to smooth muscle cells contraction in vessel wall 6
8 Factors contributing to hypertension and the counterregulatory factors that lower blood pressure. An imbalance in these factors results in the increased peripheral resistance that is responsible for most cases of essential (primary) hypertension. Note the central role of peripheral resistance. 7
9 Monckeberg Medial Sclerosis Monckeberg medial sclerosis refers to degenerative calcification of the media of large and medium sized muscular arteries. The disorder occurs principally in older persons and most often involves arteries of the upper and lower extremities. It is also common in advanced chronic kidney disease. Raynaud Phenomenon Raynaud phenomenon refers to intermittent, bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes the ears or nose. It is characterized by severe pallor and is often accompanied by paresthesias and pain. Symptoms are precipitated by cold or emotional stimuli and relieved by heat. Fibromuscular Dysplasia Fibromuscular dysplasia is a rare, noninflammatory thickening of large and medium-sized muscular arteries, which is distinct from atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. Vasculitis Vasculitis is inflammation and necrosis of blood vessels. It may affect arteries, veins and capillaries Model of the pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) vasculitis Famous examples of vaculitis:- 1-Serum sickness: immune complexes and complement are found in local tissue reaction 2-Viral antigens: viral antigen antibody complexes circulate and are deposited in the vascular lesions. 3-Hypersensitivity Angiitis: Is a Response to Exogenous Substances 4-Giant Cell Arteritis (Temporal Arteritis, Granulomatous Arteritis) Is a Focal, Chronic, Granulomatous Inflammation, Mainly of the Temporal Arteries 5-Wegener Granulomatosis Is a Vasculitis of the Respiratory Tract and Kidney 6-Allergic Granulomatosis and Angiitis (Churg- Strauss Syndrome) Is a Systemic Vasculitis of Young Patients with Asthma 7-Kawasaki Disease (Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome) Is a Childhood Vasculitis That Targets Coronary Arteries 8-Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger Disease) Is a Peripheral Vascular Disease of Smokers 8
10 Aneurysms Arterial aneurysms are localized dilations of blood vesselsncaused by a congenital or acquired weakness of the media. Veins Varicose Veins Are Enlarged, Tortuous Veins: Superficial varicosities of leg veins are usually in the saphenous system, and are very common. The principal symptoms are aching in the legs, aggravated by standing and relieved by elevation, Factors are Age, Sex, Heredity, Posture, Obesity. Lymphatic Vessels Transport of infectious material to regional lymph nodes incites lymphadenitis. The periphery of a focus of inflammation reveals dilated lymphatics filled with fluid exudate, cells, cellular debris and bacteria B-hemolytic streptococci (pyogenes). Lymphatic obstruction causes Lymphedema Benign Tumors of Blood Vessels Hemangiomas Are Common Benign Tumors of Vascular Channels Glomus Tumor (Glomangioma) Is a PainfulTumor of the Glomus Body: Glomus bodies are normal neuromyoarterial receptors that are sensitive to temperature and regulate arteriolar flow. Glomus tumors are widely distributed in the skin, mostly in the distal regions of fingers and toes. This pattern is reflected in the location of glomus tumors at these sites, typically in a subungual location. Hemangioendothelioma Is a Vascular Tumor of Endothelial Cells That is Intermediate Between Benign Hemangiomas and Frankly Malignant Angiosarcomas Malignant Tumors of Blood Vessels Angiosarcoma Is a Rare, Highly Malignant Tumor of Endothelial Cells Hemangiopericytoma is a rare neoplasm previously thought to arise from pericytes, modified smooth muscle cells outside the walls of capillaries and arterioles. Kaposi sarcoma is a malignant angioproliferative tumor derived from endothelial cells. It Is a Common Complication of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Tumors of the Lymphatic System Capillary Lymphangioma: Sometimes called simple lymphangiomas, these benign tumors are small, circumscribed, grayish pink, fleshy nodules which can be single or multiple. Cystic Lymphangioma (Cystic Hygroma, Cavernous Lymphangioma) These benign lesions are most common in the neck and axilla Lymphangiosarcoma May Occur Following Lymphedema or Radiation These are rare malignant tumors 9
Vascular pathology. dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA
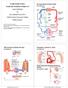
 Vascular pathology dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA DEPARTMENT of ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY FACULTY of MEDICINE UNIVERSITY of INDONESIA Center of Anatomic Pathology Studies Vascular Pathology Normal blood vessels.
Vascular pathology dr. Budiana Tanurahardja.,SpPA DEPARTMENT of ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY FACULTY of MEDICINE UNIVERSITY of INDONESIA Center of Anatomic Pathology Studies Vascular Pathology Normal blood vessels.
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS
 UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
The Peripheral Vascular System
 The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System
 Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
 HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
Functional vascular disorders
 Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Heart. Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node. Lymphatic. system Arteriovenous anastomosis. (exchange vessels)
 Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Venous system Large veins (capacitance vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Postcapillary venule Thoroughfare channel Heart Large lymphatic vessels Lymph node Lymphatic system Arteriovenous anastomosis
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology. Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta )
 Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
Extra notes for lab- 1 histology Slide 1 : cross section in the elastic artery ( aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta ) - twin of ascending aorta is the pulmonary trunk. Ascending aorta represents
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
CVS HISTOLOGY. Dr. Nabil Khouri.
 CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel
 Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel Now we will take about A granulocytes : Lymphocyte Monocytes 1- Lymphocyte - The second major type of presence
Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel Now we will take about A granulocytes : Lymphocyte Monocytes 1- Lymphocyte - The second major type of presence
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Microcirculation. Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton)
 Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton) Elements of Arterioles, capillaries, venules Structure and function: transport Fluid balance Lymph system Vessels of the Circulatory System Diameter Aorta
Lecture Block 11 (contributions from Brett Burton) Elements of Arterioles, capillaries, venules Structure and function: transport Fluid balance Lymph system Vessels of the Circulatory System Diameter Aorta
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
Histology of the Cardiac System. Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department
 Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. 12/8/2005 1 PHYSIOLOGY OF CIRCULATION BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE CAPILLARIES LYMPHATIC SYSTEM BLOOD PRESSURE 12/8/2005 2 1 Fig.21.08 12/8/2005 3 The Blood Pressure
Physiology of Circulation Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. 12/8/2005 1 PHYSIOLOGY OF CIRCULATION BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE CAPILLARIES LYMPHATIC SYSTEM BLOOD PRESSURE 12/8/2005 2 1 Fig.21.08 12/8/2005 3 The Blood Pressure
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation
 Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation Lecture Objectives Compare and contrast the structure of an artery, arteriole, vein, venule, and capillary Discuss the structure and function
Chapter 21 (1) An Introduction to Blood Vessels and Circulation Lecture Objectives Compare and contrast the structure of an artery, arteriole, vein, venule, and capillary Discuss the structure and function
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
The Cardiovascular System. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Blood Vessels. Blood Vessel Review
 The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation
 Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
Chapter 21 Peripheral circulation and Regulation I. Blood vessel structure A. Blood flows from large arteries to small capillaries 1. Large arteries contain large amounts of elastic tissue and little smooth
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
MI Acute occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery is the cause of 40% to 50% of all MIs. *
 MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well
 Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
Any of these questions could be asked as open question or lab question, thus study them well describe the factors which regulate cardiac output describe the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of heart
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes. Pulmonary Circulation H E A R T. Systemic Circulation
 The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
Six main classes of blood vessels (on handout) Wall structure of arteries and veins (on handout) Comparison: Arteries vs. Veins (on handout)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
Introduction. Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level.
 Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels on the basis of their structure and function.
 Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
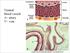 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Physiology of Circulation. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018 Overview of the circulation The function of the circulation is to: 1. transport nutrients to the body tissues 2. transport waste products away 3. conduct
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 16/12/2018 Overview of the circulation The function of the circulation is to: 1. transport nutrients to the body tissues 2. transport waste products away 3. conduct
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Vascular System Part One
 Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
Vascular System Part One Objectives Trace the route taken by blood as it leaves, and then returns to the heart. Describe the structure of the walls of arteries and veins. Discuss the structure and function
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Ischemic heart disease
 Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Blood Vessel Disorders
 Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
Blood Vessel Disorders Objectives: Hyperlipidemia Arterioschlerosis Disorders associated with arteries Disorders associated with veins Hypertension and hypotension Part 1: Diseases Associated with Arterial
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
Chapter 21. Blood Vessels and Circulation
 Chapter 21 Openstax: Chapter 20 Blood Vessels and Circulation Chapter 21 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 21, you will be able to: 1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels based on their
Chapter 21 Openstax: Chapter 20 Blood Vessels and Circulation Chapter 21 Learning Outcomes After completing Chapter 21, you will be able to: 1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels based on their
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation
 Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation I. General Features of Blood Vessel Structure A. General Pattern of Circulation 1. Ventricles pump blood into 2. These arteries
Chapter 21: Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Regulation I. General Features of Blood Vessel Structure A. General Pattern of Circulation 1. Ventricles pump blood into 2. These arteries
Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44806 1 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m44806 1 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Regulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Cardiovascular Physiology Lecture 1 objectives Explain the basic anatomy of the heart and its arrangement into 4 chambers. Appreciate that blood flows in series through the systemic and pulmonary circulations.
Cardiac Pathology 1: Blood Vessels. Kris6ne Kra8s, M.D.
 Cardiac Pathology 1: Blood Vessels Kris6ne Kra8s, M.D. Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels Heart I Heart II Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels Atherosclerosis Hypertension Aneurysms Vasculi6s
Cardiac Pathology 1: Blood Vessels Kris6ne Kra8s, M.D. Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels Heart I Heart II Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels Atherosclerosis Hypertension Aneurysms Vasculi6s
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
SCPA602 Cardiovascular System
 SCPA602 Cardiovascular System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCPA602 Cardiovascular System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Hemo Dynamics and Blood Vessels I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 721 through 734. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Hemo Dynamics and Blood Vessels I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 721 through 734. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh)
 Chapter 21 Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh) By: Alejandra & Lindsay I. Cardiac Ischemia =the most common cause of death in Western Culture ~35% of deaths. -Suddenly from acute coronary occlusion or fibrillation
Chapter 21 Cardiac Ischemia (is-kē-mē-uh) By: Alejandra & Lindsay I. Cardiac Ischemia =the most common cause of death in Western Culture ~35% of deaths. -Suddenly from acute coronary occlusion or fibrillation
Veins. VENOUS RETURN = PRELOAD = End Diastolic Volume= Blood returning to heart per cardiac cycle (EDV) or per minute (Venous Return)
 Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Biology 232 Final. 7. Which of the following lists the elements of the heart s conduction system in the correct order? Name
 Biology 232 Final Name 1. The heart is located within the: a) mediastinum b) pleural cavity c) pericardial cavity 2. Which of the following is not part of cardiac muscle histology: a) striations b) intercalated
Biology 232 Final Name 1. The heart is located within the: a) mediastinum b) pleural cavity c) pericardial cavity 2. Which of the following is not part of cardiac muscle histology: a) striations b) intercalated
