1. is used to decrease the effect of friction force between the internal moving parts of machines.
|
|
|
- Steven Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1) Complete the following sentences : 1. is used to decrease the effect of friction force between the internal moving parts of machines. 2. Friction force has its effect in the direction of the objects movement. 3. The force that slows down the objects is 4. The value of between two surfaces depends on the type of material of both surfaces. 5. Friction force has its effect in the opposite direction of 6. The friction force between the air & the object that moves through is called 7. The friction force between the water & the object that moves through is called 8. increases by the increase of the surface area of a moving object. 9. The force of acts in the direction of an objects motion. 1
2 2) Write scientific terms : 1. A force that slows down the moving object and has its effect in the opposite direction of the object's movement. (.) 2. A set of small balls with smooth surfaces are put together between the internal surfaces of the moving objects of machines. (.) 3. A friction force between air and the moving object through. (.) 4. A friction force between water and the moving object through. (.) 5. Materials used to decrease the effect of friction force between the internal moving parts of machines. (.) 3) Give reason: 1. Lubricants & oil are used in machines. 2. * Ball bearing are put between the surfaces of moving parts of machines. * Using ball bearing in machines. 3. Ball bearing is designed to reduce the friction force. 4. Rockets & air crafts have stream line shape. 5. Bodies of birds have stream line shape. 6. Birds stretch their wings on landing. 7. Parachutist opens his parachute on landing. 2
3 8. The friction depends on type of material surface. 9. The rise in temperature of internal parts of machines. 10. Friction force causes an economical loss. 11. Car drivers shouldn't increase the car speed up to a certain limit. 12. Car tries should be replaced when their grooves disappear. 13. Car tires have grooves. 14. Car movement needs friction. 15. The fish has a stream line shape. 16. Friction force slows down the object motion. 4) Put ( ) or ( ) & correct the wrong answer : 1. The friction force is always in the same direction of the object's movement. ( ) 2. The friction force between 2 surfaces is greater while moving than stopping. ( ) 3. The moving car is affected by air resistance in the same direction of its movement. ( ) 4. The relationship between the area of the object surfaces exposed to the air and the air resistance of its movement is an inverse relation. ( ) 5. The air resistance decreases when the car moves so fast. ( ) 6. When the parachutist opens his parachute, the friction force decreases. ( ) 3
4 7. The friction force affects in an opposite direction to the direction of motion. ( ) 8. The friction force depends on the shape of the surface of two touching objects. ( ) 9. Ball bearing are used to increase the friction force. ( ) 10. The pushing of an object forward is opposed by a friction force at the backward direction. ( ) 11. Oil is used to decrease the friction force. ( ) 12. Air resistance to the objects move in high speeds cannot observe. ( ) 13. The consumption of fuel increases as the car's speed increases. ( ) 4
5 5) Answer the following question :- 1. Mention the disadvantages of the friction force. 2. Mention the most important ways that can be used to decrease the disadvantages of friction force. 3. What happens if we drop two similar sheets of paper, one of them is folded & the other is unfolded which one reaches the ground first? Give reason. 4. Why are road partitions made of cement? 5. If you push a marble on a glass surface & another similar one on a metal surface, which one will move for a longer distance? Why? 6. Write a brief account about each of the following:- (1) Friction (2) Water resistance 5
6 1) Complete the following sentences : 1. Heart is located within the chest cavity between the 2. Heart beats cause to all body parts. 3. Heart consists of 4 chambers filled with and connected with 4. Blood flows inside a network of pipelines called 5. The blood vessels that emerge from the heart are called 6. blood cells carry O 2 & Co 2 inside the body. 7. keep body temperature constant. 8. Blood platelets form which help in healing wounds. 9. Left ventricles pushes the blood into the 10. atrium receives blood from all body parts except the lungs. 11. The vessels that carry blood to the heart are called 12. There are a between atrium & ventricle on each side of the heart. 13. The tube, which extends from the bladder & opens out the body is called 14. When the left atrium contracts, it pushes the blood to the 6
7 15. All the arteries carry blood rich in oxygen except 16. is a balloon like sac. 17. Blood consists of red blood cells & white blood cells, and 18. When the blood is exposed to the air, a bloody is formed. 19. Urine consists of water containing excess salt and 20...are main organs of urinary system. 21. The kidney excretes the wastes dissolved in water in form of 22. is connected with kidney and carries the urine into.. 2) Write scientific terms : 1. A muscular organ, about the fist in size and located within the chest. (. ) 2. The two upper chambers in the heart. (. ) 3. The two lower chambers of the heart. (. ) 4. The network of pipelines that extend all over the human body. (. ) 5. The artery that carries blood rich in carbon dioxide. (. ) 6. The blood vessels that collect blood from all body parts and pour it into heart. (. ) 7
8 7. The small bodies that play a role in blood coagulation when the body is wounded. (. ) 8. A yellow watery fluid in which blood cells float. (. ) 9. The flow of blood to the lungs and its returning back again to the heart. (. ) 10. Blood circulation between the heart and all body parts except the two lungs. (. ) 11. The cells which carry oxygen. (. ) 12. The artery that carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. (. ) 13. The group of organs that clarifies the body from wastes and harmful substances. (. ) 14. The system that clarifies blood from excess salts, urea and uric acid. (. ) 15. The two organs which excrete carbon dioxide and excess water in the form of a vapor. (. ) 16. The fluid which the kidneys produces and contains harmful substance. (. ) 17. The narrow tube which connects with the kidney and urine passes through it. (. ) 18. Tube extends from the urinary bladder and opens outside the body. (. ) 8
9 3) Give reason: 1. The two sides of heart are separated. 2. The heart contains valves. 3. Blood flows in one direction between atrium & ventricle inside the heart. 4. The wall of left ventricle is thicker than that of right one. 5. The blood is in a liquid form. 6. Blood capillaries have thin walls. 7. Red blood cells have great importance. 8. Blood platelets have a role in healing wounds. 9. White blood cells are called the defense cells. 10. Aorta is the largest artery in the body. 11. Blood is a very important fluid. 12. It is necessary to keep exercising. 13. Smoking must be avoided. 14. It is necessary to avoid exposure to infection & accidents. 15. The human body must get rid of excretory material. 16. The body cells release their wastes into the blood. 17. The skin is one of excretory organs. 18. The urinary system is very important. 19. The urinary system contains urinary bladder. 20. There are two ureters in the urinary system. 9
10 21. If the 2 kidneys are damaged, the person will die. 22. The 2 kidneys protect us from poisoning. 23. Man urinates less in summer than in winter. 24. Sweat has salty taste. 25. The presence of sweat glands inside the skin. 26. * You must not keep urine for a long periods. * You must eat food low in salts. 27. You must not urinate or wash in irrigation canals. 4) Put ( ) or ( ) & correct the wrong answer : 1. There are valves within the heart cavity. ( ) 2. The aorta delivers blood to the lungs. ( ) 3. White blood cells defend the body against microbes. ( ) 4. Eating meals rich in fats and salt activate the circulatory system. ( ) 5. Keeping the urine and delaying getting rid of it, benefits urinary bladder. ( ) 6. The kidney filters excess water and salts from the human body. ( ) 7. Ureters is a tube that extends from the bladder to open outside of the body. ( ) 8. Eating diets rich in fats & salts activate the circulatory system. ( ) 10
11 5.Choose the correct answer :- 1- Carbon dioxide & water vapor are released by the 1) kidneys 2) lungs 3) heart 2- Urea is expelled by the 1) heart 2) kidney 3) lungs 3- The heart is a muscular pump in a size of your 1) fingers 2) foot 3) fist 4- Blood vessels which carry blood from the heart are the 1) arteries 2) veins 3) blood capillaries 5- Blood components which are responsible for attacking the microbes causing diseases to man are the 1) red blood corpuscles 2) white blood corpuscles 3) blood platelets 11
12 6- How can you keep your excretory system healthy? 7. State the function of the following :- The kidney Urinary bladder Ureter. 8. Write a brief account about each of the following :- (1) Plasma (2) Aorta (3) Sweat 9. What's meant by:- a. Excretory materials. b. minor blood circulation. c. major (systemic) blood circulation. 12
13 1) Complete : 1. Soil is a thin layer covers 2. The main soil components are,, 3. add nutrients to the soil. 4. Water and break down rocks into small pieces. 5. The main types of soil are,, 6. soil is highly fertile because it contains large amount of 7. Clay soil's color is while soil is yellow. 8. The compactness of clay soil is while in sand soil is 9. soil holds less water while soil holds more water. 10. The size of particles in sand soil is while in clay soil is & in silt are 11. is considered the most suitable soil for cultivation because it contains 12. The aeration in sand soil is and in clay soil is while in silt soil is 13. soil drains water more than other two types of soil. 14., plants grow in clay soil while sand soil is suit for cultivating tubers such as, 13
14 15. Cactus plant are seen in soil. 16. Silt soil is suit for cultivating, 17. The soil pollutants are,, 18. The origin of agricultural soil is Egypt in the rocks from the plateau. 19. The region in Egypt is considered as the best region for rice cultivation 20. The fertility of sand soil is & in silt soil is 21. The drainage of water in sand soil is but in clay soil is 22. In sand soil, the water absorption is but in clay soil is 23. The clay soil is mainly consists of & but silt soil is a mixture of,,,, 24. Humus is consists of, 25. Soil salinity increases by the effect of & 26. increase the soil acidity. 27. dissolves in the water rains forming that increase the soil 28. is the decayed remains of animals & plants mixed with soil components. 14
15 2) Write scientific terms : 1. A thin loose layer covering the earth's crust. ( ) 2. The remains of the decayed organisms. ( ) 3. A highly fertile soil because it contains suitable dissolved salts and humus. ( ) 4. The most aerated soil. ( ) 5. The soil which rich with humus. ( ) 6. The remains of fragmented small rocks which was deposited on the earth's surface. ( ) 7. It's any change in the environment that disturbs its natural balance. ( ) 8. It's any change in the soil that disturbs its natural balance and harms it's living organisms. ( ) 9. A soil which is mainly composed of clay and silt particles. ( ) 10. A soil which is rarely contains humus. ( ) 11. The suitable soil for cultivation of plants that produce tubers. ( ) 12. Chemical substance used to compensate the poor of soil with element required for plant growth. ( ) 13. Materials that increase the soil acidity. ( ) 14. Rains formed when the industrial wastes dissolved in its water. ( ) 15
16 15. Chemical substances that eradicate the pests of agricultural crops. ( ) 16. Materials that disturbs the natural balance of the soil. ( ) 17. Used to protect soil from pollution instead of pesticides. ( ) 3) Give reason for : 1. The soil is the main component of the environment. 2. The color of soil is dark brown or black. 3. Roots of plants are important for soil. 4. The microorganisms that live inside the soil have great importance. 5. Soil differs in compactness according to their type. 6. The sand soil is well aerated. 7. The level of water in the clay soil is higher than the level of water in both sand and silt soil. 8. Silt soil fertility is the highest. 9. Clay soil has poor aeration. 10. Sand soil has good aeration. 11. Soil pollution are harmful. 12. Chemical pesticides are harmful. 13. The acidic rains have bad effect. 14. Increase soil salinity. 16
17 15. It is preferable to depend on natural enemies of insects inslead of pesticides. 4) Put ( ) or ( ) & correct the wrong answer : 1. Wheat plant grows in sand soil. ( ) 2. The spaces between the particles of clay soil are large. ( ) 3. Cactus plants are seen in sand soil. ( ) 4. Silt soil contains gravel, clay, sand, silt and humus. ( ) 5. Sand soil is more compacted than silt one. ( ) 6. Adding natural fertilizes leads to soil pollution. ( ) 7. Using insecticides to control agricultural pests protects the soil from pollution. ( ) 8. Spacing periods of irrigation leads to increase the validity of soil. ( ) 9. The pollution is any change in the environment that disturbs its natural balance. ( ) 10. The sand soil is strongly compact, has poor ventilation and fertile. ( ) 11. Clay soil has poor ventilation. ( ) 12. Humus is the remains of fragmented small rocks and was deposited on the earth's surface. ( ) 13. Cactus plant grows in clay soil. ( ) 14. Clay soil suits cultivation of cotton and rice. ( ) 17
18 1) Complete the following sentences : 1-oil&lubricant 2-opposite 3-friction force 4-friction force 5-The movement 6-air resistance 7-water resistance 8- friction force 9-motion (movement) force. 2) Write scientific terms : 1. friction force 2. Ball bearing 3. air resistance 4. Water resistance. 5. oil & lubricants. 3) Give reason : 1. Lubricants & oil are used in machines. To decrease the friction force. 2. * Ball bearing are put between the surfaces of moving parts of machines. * Using ball bearing in machines. To decrease the friction force. 3. Ball bearing are designed to reduce the friction force. Because they are formed of small metallic balls with smooth surfaces so the friction between them is almost not found. 18
19 4. Rockets & air crafts have stream line shape. To decrease air resistance by decreasing surface area. 5. Bodies of birds have streamline shape. To decrease air resistance by decreasing surface area. 6. Birds stretch their wings on landing. To increase surface area and air resistance, so speed decreases and land safely. 7. Parachutist opens his parachute on landing. To increase surface area and air resistance, so speed decreases and land safely. 8. The friction depends on type of material surface. Because friction increases between rough surfaces & decrease between smooth surfaces. 9. The rise in temperature of internal parts of machines. Due to friction force. 10. Friction force causes great economical loss. Because it causes damage for most of machines so a lot of money is wasted. 11. Car drivers shouldn't increase the car speed up to a certain limit. To decrease air resistance & also reduce the consumption of fuel. 19
20 12. Car tires should be replaced when their grooves disappear. Because grooves are necessary to squeeze water out as water decrease the friction force & makes the control of car very hard. 13. Car tires have inscriptions (grooves). To squeeze water out. 14. Car movement needs friction. To control its speed and change its direction. 15. The fish has a stream line shape. To decrease water resistance by decreasing surface area. 16. Friction force slows down the object motion. Because friction force act in opposite direction of movement. 4) Put ( ) or ( ) & correct the wrong answer : 1- opposite 2- smaller 3- opposite 4- direct 5- slow 6- increases 7-8- type 9- decrease low 13-5) Answer the following question :- 1- Dis advantages of friction force:- a. Rise in the temperature of internal parts of machines. b. Damage of machines. c. A lot of money wasted. 20
21 2- Ways to decrease friction force:- a. Using lubricants & oils. b. Using ball bearing. 3- The folded paper reaches ground first. - Because by decreasing surface area, the air resistance decreases. 4- To decrease air resistance. 5- The glass surface. - Because glass smooth, so it has less friction force. 6. Write a brief account about each of the following:- 1- Friction: It is the force which exists between two surfaces when they touch each other and it affects in the opposite direction of movement. 2- Water resistance: It is a type of friction force resulting from object movement in water. 1-Complete:- 1-2 lungs 2-pumping the blood 3-blood-blood vessels 4-blood vessels 5-arteries 6- red 7-blood 8-blood clot 9-aorta 10-right 11-veins 12-valve 13-urethra 14-left ventricle 15-pulmonary artery 16- urinary bladder 21
22 17-plasma-blood platelets 18-clot 19-urea-uric acid 20- Two kidneys 21- urine 22- Ureter urinary bladder. 2) Write scientific terms : 1. Heart 2. Atria 3. ventricles 4. Blood capillaries [blood vessels] 5. pulmonary artry 6. Veins (vena cava) 7. blood platelets 8. Plasma 9. minor blood circulation (pulmonary) 10. Systemic circulation (major) 11. Red blood cell 12. Aorta artery 13. execretory system 14. Urinary system 15. two lungs 16. Urine 17. Ureter 18. urethra 3) Give reason:- 1. The two sides of heart are separated. To prevent mixing of blood found in both sides. 2. The heart contains valves. To allow blood to pass in one direction only, from atrium to ventricle and prevent its returning back. 3. Blood flows in one direction between atrium & ventricle inside the heart. Due to the presence of valve between each atrium & ventricle. 22
23 4. The wall of left ventricle is thicker than that of right one. Because left ventricle pushes the blood to all body parts, while the right ventricle pushes the blood to the 2 lungs only. 5. The blood is in a liquid form. Due to presence of plasma. 6. Blood capillaries have thin walls. To Exchange between food, oxygen to all body cells and wastes, Co 2 gas from them. 7. Red blood cells have great importance. Because they carry oxygen from the lungs to all body cells & Co 2 from the cells to the lungs. 8. Blood platelets have a role in healing wounds. Because they form blood clot to stop bleeding. 9. White blood cells are called the defense cells. Because they attack microbes. 10. Aorta is the largest artery in the body. Because it carries blood from heart to all body parts. 11. Blood is a very important fluid. Because it is necessary for : * The transfer of materials to all body cells. * The defence & protection of the body. * keep temperature of body constant. 23
24 12. It is necessary to keep exercising. To activate the blood circulation & to keep your circulatory system healthy. 13. Smoking must be avoided. To keep your circulatory system healthy. 14. It is necessary to avoid exposure to infection & accidents. To keep your circulatory system healthy. 15. The human body must get rid of excretory material. Because excretory material contain harmful poisonous materials and other harmless materials that the body can't use them. 16. The body cells release their wastes into the blood. Because the blood carries these wastes to special organs to get rid of them. 17. The skin is one of excretory organs. Because skin gets rid of some excess salts & excess water in the form of sweat. 18. The urinary system is very important. Because : * It filters the blood from some excess salts, urea & uric acid & other waste material. * It expels these wastes outside the body in the form of urine. 24
25 19. The urinary system contains urinary bladder. To store urine until it is released outside the body. 20. There are two ureters in the urinary system. To transfer the excretory materials ( urine ) from the two kidneys to The urinary bladder. 21. If the 2 kidneys are damaged, the person will die. Because kidneys filter the blood from excretory materials which contain poisonous materials. 22. The 2 kidneys protect us from poisoning. Because they filter the blood from (excretory materials) which contains poisonous materials. 23. Man urinates less in summer than in winter. Because we get rid of more sweat in summer due to high temperature. 24. Sweat has salty taste. Because it consists of some excess salts & excess water. 25. The presence of sweat glands inside the skin. To get rid of some excess salts & excess water. 26. * You must not keep urine for long periods. * You must eat food low in salts. To keep your urinary system healthy. 25
26 27. You must not urinate or wash in irrigation canals. To avoid infection with schistosomiasis disease. 4) Put ( ) or ( ) & correct the wrong answer : 1-2- all the body cells 3-4- low 5- harms 6-7- urethra 8- harm 5) Choose: 1- Lungs 2- kidney 3- fist 4- arteries 5- white blood corpuscles 6-How can you keep your excretory system healthy? 1. Drink enough amounts of clean water daily, especially in the summer. 2. Eat healthy and balanced food, low in salt. 3. Avoid schistosomiasis disease (Bloody urine) by keeping away and not urinating in irrigation canals. 4. Don t keep urine for a long period of time. 7) State the function of the following:- 1- The kidney : 1. Filter the blood from some wastes as ( urea, uric acid, excess salts ). 2. Getting rid of wastes in the form of urine. 26
27 2- Urinary bladder : stores the urine temporarly until it is released outside the body through urethra. 3-Ureter: transfer urine from the two kidneys to the urinary bladder. 8.Write a brief account about each of the following:- 1- Plasma : It is a yellow watery fluid in which all the blood components are suspended carry digested food & wastes. 2- Aorta : It is a large artery that carry oxygenated blood from left ventricle to all the body parts. 3- Sweat : It consists of some excess salts & water get out through sweat glands in the skin. 9.What's meant by:- a. Excretory materials:- * They are waste materials that produced inside the body cells (cell wastes). b. minor blood circulation. *It is the blood circulation between the heart and the all the parts of the body. c. major (systemic) blood circulation. * It is the blood circulation between the heart and the two lungs 27
28 1) Complete : 1. non compacted superficial - Earth's crust 2. humus - mud (clay) - sand 3. humus 4. wind, heat 5. sand - clay - silt 6. silt - humus 7. dark - sand 8. strong - weak 9. sand - clay 10. large - small - medium 11. silt - more humus 12. good - poor - medium 13. sand 14. rice, wheat - potato, sweet potato 15. sand 16. lemon, orange 17. chemical pesticides, chemical fertilizers, industrial wastes 18. Ethiopian 19. delta 28
29 20. less fertile - high fertile 21. fast - slow 22. low - high 23. (clay & silt) - gravel - humus - sand - clay - silt 24. decayed remains of animal & plants 25. spacing period of irrigation, raising the level of ground water 26. acidic rain 27. acids - acidic rain - acidity 28. humus 2) Write scientific terms : 1. soil 2. Humus 3. silt soil 4. Sand soil 5. silt soil 6. soil 7. Pollution 8. soil pollution 9. Clay soil 10. sand soil 11. sand soil 12. chemical fertilizers 13. Acids 14. acidic rains 15. Chemical pesticides 16. soil pollutants 17. Natural enemies 29
30 3) Give reason for : 1. The soil is the main component of the environment. Because it is necessary for: - plant growth - animals and human that eat these plants - some animals as they make their homes in soil 2. The color of soil is dark brown or black. Due to the color of humus. 3. Roots of plants are important for soil. Because : 1- roots hold the soil in its place (make soil cohesive) 2- they add nutrients to soil as they convert into Humus after death 3- prevent soil erosion 4. The micro-organisms that live inside the soil have great importance. Because : 1- they dig tunnels, so this allow air and water to pass easily through soil 2- when they die their bodies decay forming Humus 5. Soil differ in compactness according to their type. A ccording to the difference in their components & ability to the hold water. 30
31 6. The sand soil is well aerated. Because it has weakly compacted particles. 7. The level of water in the clay soil is higher than the level of water in both sand and silt soil. Because clay soil has the highest absorption of water than silt and sand soil since particles of clay soil are highly compacted. 8. Silt soil fertility is the highest. Because it is rich in humus. 9. Clay soil has poor aeration. Because its particles are highly compacted. 10. Sand soil has good aeration. Because it is weakly compacted. 11. Soil pollution are harmful. Because they : 1- reduce the ability of the agricultural soil for cultivation 2- cause the death of plants 3- harm the human and animals health 12. Chemical pesticides are harmful. Because they contaminate plants as they leak in the soil and harm human and animals health. 31
32 13. The acidic rains have bad effect. Because they increase the soil acidity and deprive plants from the soil salts that are necessary for plant growth. 14. Increase soil salinity. Due to increasing the periods between the irrigation times and rising of ground water. 15. It is preferable to depend on natural enemies of insects instead of pesticides. To avoid using of soil pesticides which cause soil pollution. 4) Put ( ) or ( ) & correct the wrong answer : 1. ( ) clay 2. ( ) sand 3. ( ) 4. ( ) 5. ( ) less 6. ( ) chemical 7. ( ) natural enemies 8. ( ) decrease 9. ( ) 10. ( ) clay 11. ( ) 12. ( ) soil 13. ( ) sand 14. ( ) 32
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
5 th Primary. Science
 Final revision sheet A-Complete the following: 1. two lungs. 2. Kidney 3. Soil 4. friction. 5. cancelled 6. silt soil, clay soil,sand soil. 7. avoid mixing of the blood. 8. Silt - yellow. 9. Clay - sand.
Final revision sheet A-Complete the following: 1. two lungs. 2. Kidney 3. Soil 4. friction. 5. cancelled 6. silt soil, clay soil,sand soil. 7. avoid mixing of the blood. 8. Silt - yellow. 9. Clay - sand.
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Circulatory System. The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Blood Vessels. veins. valve. to the heart. capillaries from the heart. arteries. Visual 25-1
 Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
By Semih. The first system is about the respiratory system. It provides our body with the oxygen it needs and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
 By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System
 Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Topic Page: Circulatory system
 Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Cardiovascular System Facts The average person has nearly 100,000 km of blood vessels running through them. The larger the organism, the slower the heart beats (a woman s heart will
The Circulatory System Cardiovascular System Facts The average person has nearly 100,000 km of blood vessels running through them. The larger the organism, the slower the heart beats (a woman s heart will
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
OB16 Demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse and breathing rate and appreciate that a balance of each promotes good health
 Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
 The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
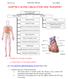 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed.
 They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
The Cardiovascular. Parts and Functions
 The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
MESA DAY CONTEST RULES
 FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
1 Food and its use by the body (pp )
 Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL
 1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review
 Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
The Excretory System. Functions of the Excretory System. The Urinary System. Figure 9 The excretory system includes other body systems.
 The Excretory System Functions of the Excretory System It s your turn to take out the trash. You carry the bag outside and put it in the trash can. The next day, you bring out another bag of trash, but
The Excretory System Functions of the Excretory System It s your turn to take out the trash. You carry the bag outside and put it in the trash can. The next day, you bring out another bag of trash, but
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
One system involved in exercising is the respiratory system. The respiratory system includes three main parts breathing, lungs and blood.
 By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
Circulatory Systems AP Biology
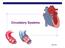 Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
Circulatory Systems 2006-2007 Exchange of materials Animal cells exchange material across their cell membrane fuels for energy nutrients oxygen waste (urea, CO 2 ) If you are a 1-cell organism that s
Chapter 15. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
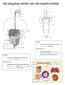 THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Location: The location of the Excretory System Is the body. Major Function: Location: The Excretory System the toxic build up of wastes, such as ammonia or
THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM AND THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Location: The location of the Excretory System Is the body. Major Function: Location: The Excretory System the toxic build up of wastes, such as ammonia or
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
RESPIRATION- Life function. Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems
 Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Functions of the Circulatory System
 Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
BIO 2 GO! 3211b, 3212b Circulation and Excretion in Plants and Animals
 BIO 2 GO! 3211b, 3212b Circulation and Excretion in Plants and Animals The circulatory system, vascular system, and excretory system work together to feed and clean the body of multicellular organisms.
BIO 2 GO! 3211b, 3212b Circulation and Excretion in Plants and Animals The circulatory system, vascular system, and excretory system work together to feed and clean the body of multicellular organisms.
Thanks. Connect. You Might Also Like. Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback.
 Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
HOMEOSTASIS. Regulating the Body to Maintain Homeostasis
 HOMEOSTASIS Regulating the Body to Maintain Homeostasis As in all systems in nature, animal systems must maintain balance. We call this homeostasis. How do ecosystems maintain balance? In animal systems,
HOMEOSTASIS Regulating the Body to Maintain Homeostasis As in all systems in nature, animal systems must maintain balance. We call this homeostasis. How do ecosystems maintain balance? In animal systems,
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body
 The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
Toxic Waste?! So now we ve eaten we have to get rid of the waste!
 Toxic Waste?! So now we ve eaten we have to get rid of the waste! Excretory/Urinary System Notes Continuation of digestion food is transferred into nutrients and passes through the body as waste 7.7B transformation
Toxic Waste?! So now we ve eaten we have to get rid of the waste! Excretory/Urinary System Notes Continuation of digestion food is transferred into nutrients and passes through the body as waste 7.7B transformation
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM VOCABULARY blood vessel - arteries veins capillaries blood plasma white blood cells red blood cells platelets WHAT IS CIRCULATION? What messenger makes trillions
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM VOCABULARY blood vessel - arteries veins capillaries blood plasma white blood cells red blood cells platelets WHAT IS CIRCULATION? What messenger makes trillions
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular
 transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
