January Here it is boys and girls, an exam is coming and you are no doubt studying hard and getting your brain in gear for the big day!
|
|
|
- Sylvia Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exam Review January 2019 Grade 11 Biology Student Here it is boys and girls, an exam is coming and you are no doubt studying hard and getting your brain in gear for the big day! First of all, you should spend some time reviewing the following: 1. Unit Tests these are good examples of the kind of multiple choice and written questions that you may see on the exam 2. Quiz Cards Use these valuable tools to sharpen your knowledge of details. 3. Notes Hey, they have lots of information! Could be useful? 4. Assignments and Assorted Practice Activities Also a good source of practice questions Use this review sheet to help guide you through your studying. Listed below are some summaries and tasks that you can do in preparation for your exam. If you encounter difficulties or have any questions about the material in this review package, ask a question in class or via at AskMrLloyd@shaw.ca
2 Unit One: Wellness and Homeostasis / Cellular Biology Text References: Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 9 (p ) Labs / Assignments: Microscope Investigation Art of Biology Histology Investigation Passive Transport Investigation Tasks to be Successful: Calculate the total magnification under scanning (4X), low power (10X) and high power (43X) using an eyepiece of 10X magnification Review the parts and functions of the compound microscope Review the Homeostatic Conditions of the Human Body Review Tissue Types: Be able to identify tissue types and describe their function Identify and explain methods of Passive Transport Identify and explain methods of Active Transport Diagram a negative feedback system including the receptor / sensor, coordinating centre and effector Be able to diagram the feedback system that regulates blood sugar levels. Include the pancreas, liver, insulin, glucagons and blood sugar levels Additional Questions to Consider: 1. What are the 5 characteristics of life? 2. What is a cell? 3. What is a prokaryotic cell? 4. What is a eukaryotic cell? 5. What are the differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? 6. What is an organelle? 7. What is a tissue? 8. What are different types of tissue and their functions? 9. What is a solute? 10. What is a solvent? 11. What does it mean to be Hypertonic, Hypotonic or Isotonic? 12. What is a Concentration Gradient?
3 Unit Two: Digestion and Nutrition Text References: Chapter 11 (p ) Labs / Assignments: Biochemistry Crash Course Pathology Project Digestion Assignment You Make the Call Tasks to be Successful: Diagram and explain the lock and key theory of enzyme action State the function of the mouth, salivary glands, tongue, teeth, uvula, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus, liver, pancreas and gall bladder Structure of Teeth Where does protein digestion take place? What chemicals are required Where does fat digestion take place? What chemicals are required? What are 3 groups of carbohydrates? Diagram and label the formation of a polysaccharide (dehydration synthesis) Describe how we use Benedict s Solution, Iodine, Nitric Acid, Litmus, Solubility test, brown paper test in a lab What are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, nucleic acids? What are their nutritional value (why do we need them? Where do we get them? What do they look like?) Trace a piece of cheese from mouth to anus Write a brief description of the symptoms and treatments for Anorexia, Acid Reflux, Appendicitis, Hemmeroids, Cirrhosis, Lactose Intolerance, Ulcers Explain the role of the liver, pancreas, insulin, glucagons, glycogen and glucose in the regulation of blood sugar. Use a diagram to support your answer
4 Label a diagram of the digestive system Additional Questions to Consider: 1. Trace the path of food through the alimentary canal. 3. Define mechanical digestion. 4. Define chemical digestion. 5. List the structures of the human digestive system that perform mechanical digestion. 6. List the structures of the human digestive system that perform chemical digestion. 7. What is the food mass called after it has left the mouth? 8. Name the movements of the esophagus that move the food along to the stomach. 9. What is the name of the ring of muscles that controls food entry into the stomach? 10. What other function does this ring of muscle have? 11. What enzyme is active in the stomach? 12. What stimulates the production of this enzyme? 13. Which structures release this enzyme? 14. What other secretions are present in this stomach? What are their functions? 15. What is the name of the ring of muscles that controls the movement of food into the small intestine? 16. What is the food mass called after it leaves the stomach? 17. List, in order, the three parts of the small intestine. 18. Which is the most important of these? 19. What secretions are active in the small intestine? 20. Where do these secretions come from? 21. What is the function of bile? 22. Where is bile made? 23. Where is bile stored before it enters the duodenum? 24. Why is it important for the secretions found in the duodenum to be basic? 25. What enzymes are active in the small intestine? What do they do? 26. What are two structural features of the small intestine that make it well adapted for absorption of nutrients? 27. What is the function of the cuboidal cells of the villi? 28. What is the function of the capillaries of the villi? 29. What is the function of the lacteals of the villi? 30. What is the function of the Krypts of Leiberkuhn?
5 31. What are 4 functions of the liver? 32. What is insulin? What does it do? 33. What is glucagon? What does it do? 34. What are the 4 functions of peristalsis in the small intestine? 35. What is the name of the valve that connects the small and large intestine? 36. List, in order, the 6 parts of the large intestine. 37. What are the functions of the large intestine? 38. What is the function of the bacteria that live in the large intestine? 39. What is the name of this bacterium? 40. What is the function of the rectum? 41. What happens if not enough water is reabsorbed? 42. What happens if too much water is reabsorbed? 43. What is the function of carbohydrates in a healthy diet? 44. What is the function of proteins in a healthy diet? 45. What is the function of fat in a healthy diet? 46. What type of information can be found on a nutrition label? 47. What foods contain Vitamin D? Vitamin C? Vitamin A? Vitamin B12? Vitamin E? Don t forget about Biochemistry! 1. Define organic. 2. Define inorganic. 3. What element is found in every organic molecule? 4. How many bonds does this element form? 5. What other elements are commonly found in organic molecules? 6. Draw a monosaccharide. What is the name of this monosaccharide? 7. Draw a disaccharide. Name one dissacharide. 8. What is the name of the process that bonds two monosaccharides together? 9. What is else is created through this process? 10. What is the name for 10 monosaccharides bonded together? 11. Name one polysaccharide. 12. Draw a fat molecule. 13. What are the 4 components of a fat molecule? 14. Draw each component of a fat molecule. 15. What are the names of the three components? 16. Draw an unsaturated fatty acid. 17. What makes this unsaturated? 18. Draw a saturated fatty acid. 19. What makes this saturated? 20. What types of foods contain saturated fats? 21. What types of foods contain unsaturated fats? 22. What are proteins made up of? 23. What is the name of the process that binds these together? 24. Draw an amino acid. 25. Circle the amino group, carboxyl group and R group. 26. What is the name of the bond that holds two amino acids together? 27. How many different types of amino acids are there? 28. What test did we use to identify glucose in the lab? What is a positive result for this test? 29. What test did we use to identify protein in the lab? What is a positive result for this test? 30. What did test did we use to identify salt in the lab? What is a positive result for this test? 31. What test did we use to identify vitamin C in the lab? What is a positive result for this test? 32. What test did we use to identify starch in the lab? What is a positive result for this test?
6 Unit Three: Transportation and Respiration Text References: Chapter 9 (p ) Chapter 10 Labs / Assignments: Pathologies of the Circulatory System Pathologies of the Respiratory System Heart Dissection Blood Typing Investigation Tasks to be Successful: Explain how transport mechanisms are used to supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues and how they remove carbon dioxide and other wastes Compare and contrast capillaries, veins and arteries Label the parts of the heart, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, chambers of the heart, valves, SA node, AV node, Purkinje Fibres, Bundle of His, Septum Describe systemic and pulmonary circulation Draw and label a RBC, WBC, platelets and state their functions Create a chart of blood types including antigen, antibody, universal donor and universal recipient, Rh factors Trace a RBC from the right atrium to the big toe and back What is blood pressure? Define systolic and diastolic pressure What factors increase blood pressure (state 4) What is a heart attack Distinguish between internal and external respiration
7 Identify nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, vocal cords, trachea, bronchi, lungs, pleura, diaphragm, ribs, intercostals muscles How is respiration controlled? Describe the measurement of rate, tidal volume, vital capacity, exhaling reserve Describe the signs and symptoms of COPD, Emphysema, Chronic Bronchitis and Acute Bronchitis Explain the relationship between pressure and volume Describe the changes in the chest volumes in inhalation and exhalation Additional Questions to Consider: 1. Be able to define: a. Arteries b. Veins c. Capillaries d. Pericardium e. Atria f. Ventricles g. Septum h. Tricuspid Valve i. Bicuspid Valve j. Semilunar Valves k. Pulmonary Veins l. Pulmonary Arteries m. Superior Vena Cava n. Aorta o. Diastole p. Systole q. Sinoatrial Node r. Atrioventricular Node s. Noradrenaline t. Acetylcholine u. Cardiac Output v. Heart Rate w. Stroke Volume x. Erythrocytes y. Leukocytes z. Neutrophils aa. Eosinophils
8 bb. Basophils cc. Monocytes dd. Lymphocytes ee. Platelets ff. Plasma gg. Antigens hh. Antibodies 2. Describe the structure and function of arteries and arterioles 3. Describe the structure and function of veins and venules 4. Describe the structure and function of capillaries. 5. Compare and contrast the structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries 6. What is the function of the pericardium? 7. Describe the path of a drop of blood through the heart starting at the vena cava. 8. What is the function of the pulmonary artery? 9. What is the function of the pulmonary vein? 10. What is the function of the aorta? 11. Explain the function of the heart valves. 12. Describe the function of each of the four chambers of the heart. 13. What makes the pulmonary artery different from all other arteries? 14. What makes the pulmonary vein different from all other veins? 15. Where does the carbon dioxide in the blood come from? 16. What is the name of the respiratory pigment in humans? 17. What are the three primary cycles of blood in the human body? 18. What are the three main elements of a circulatory system? 19. What is the function of erythrocytes? 20. What are the 2 factors that play a major role in the determining when oxygen is picked up and when it is released? 21. What is the resting heart rate of the average person? 22. How is your heart rate sped up when you exercise? 23. How is your heart rate slowed down after exercise? 24. What is the relationship between cardiac output and fitness? 25. What is the relationship between stroke volume and fitness? 26. What are 2 factors that affect stroke volume? 27. What is the relationship between maximum heart rate and fitness? 28. What is the blood pressure of the average person? 29. What are the 4 blood types? 30. How are they determined? 31. Which blood type is the universal donor? Why? 32. Which blood type is the universal recipient? Why? 33. Compare and contrast AB and O blood types. 34. Why is it dangerous to have a transfusion from the wrong blood type? 35. What is Rh factor? 36. How does the Rh factor affect blood type? 37. What are the structures and the role of the Lymphatic System?
9 Unit Four: Waste and Excretion Text References: Chapter 11 (p ) Labs / Assignments:, Excretion Assignment Urinalysis Lab Tasks to be Successful: State the function of the skin, lung, liver and large intestine in excretion Diagram and label the Urinary System and Kidney Describe techniques and substances tested in Urinalysis Differentiate between blood plasma and filtrate Draw and label a nephron Diagram and explain secretion, absorption and filtration Describe the role of ADH and Aldosterone in maintaining water balance What does sugar, protein and excess salt in urine indicate? Trace the formation of urine from the nephron to the outside of the body Compare and contrast the 3 nitrogenous wastes; urea, ammonia and uric acid
10 Unit Five: Protection and Control Text References: Chapter 11 (p ) Chapter 12 Labs / Assignments: Tasks to be Successful: define and specific and non-specific defense mechanisms, the inflammatory response, the immune response compare the Nervous System and Endocrine Systems describe the organization of the Nervous System identify the functional regions of the brain diagram and label a neuron explain a nerve impulse (depolarization, repolarization and synapses) describe the components of a reflex arc
SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL
 Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Title: Series Title (if applicable): Format: Copyright Date: ISBN:
 MANITOBA CALL FOR BIOLOGY CURRICULUM CORRELATION FORM Resource ID #(s) Title: Series Title (if applicable): Format: Copyright Date: ISBN: Student Resource Teacher Resource Indicate in the boxes below the
MANITOBA CALL FOR BIOLOGY CURRICULUM CORRELATION FORM Resource ID #(s) Title: Series Title (if applicable): Format: Copyright Date: ISBN: Student Resource Teacher Resource Indicate in the boxes below the
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Chapter 24. Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill.
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
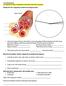 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Chapter 15. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: RESULTS/SCORES FROM LEARNING ASSESSMENTS
 MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
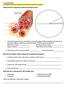 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Animal Structure and Function
 Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Biology 2201 Unit III: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I
 Intended Learning Outcomes Circulatory System: Biology 2201 Unit III: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I 1. Explain the concept of homeostasis and its critical nature of living things. 2. Explain the importance
Intended Learning Outcomes Circulatory System: Biology 2201 Unit III: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I 1. Explain the concept of homeostasis and its critical nature of living things. 2. Explain the importance
Reason Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress. Differentiate between negative and positive mechanisms
 Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
WAEC -Biology 11 (BIOR3S) Course Outline
 WAEC -Biology 11 (BIOR3S) Course Outline Mr. M. Hegel Blog site: http://blogs.winnipegsd.ca/mhegel/ My email: mhegel@wsd1.org Grading Program: Jupiter Ed http://www.jupitered.com Welcome to Biology 11!
WAEC -Biology 11 (BIOR3S) Course Outline Mr. M. Hegel Blog site: http://blogs.winnipegsd.ca/mhegel/ My email: mhegel@wsd1.org Grading Program: Jupiter Ed http://www.jupitered.com Welcome to Biology 11!
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Travel Brochure of the Body System
 Travel Brochure of the Body System By: Hector Capo, Mater Gardens Middle School, Miami Lakes, FL Name: Your team at the (create a name for your ad agency) has been hired as a travel consultant to design
Travel Brochure of the Body System By: Hector Capo, Mater Gardens Middle School, Miami Lakes, FL Name: Your team at the (create a name for your ad agency) has been hired as a travel consultant to design
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16
 Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
TEST 5. Module 9 & 10
 TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Big Idea/Questions/Notes:
 Ch 38: Digestive and Excrery Systems 38-1 Food and Nutrition A. Food and Energy 1. One calorie is equal the amount of energy needed raise the temperature of. 2. The energy in food is measured. 3. One Calorie
Ch 38: Digestive and Excrery Systems 38-1 Food and Nutrition A. Food and Energy 1. One calorie is equal the amount of energy needed raise the temperature of. 2. The energy in food is measured. 3. One Calorie
WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus
 )ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
)ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview
 Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
Anatomy and Physiology Content Overview D Block Final = Tuesday May 23, 2017 The format of the exam is fill-ins, matching, and multiple choice. You will have an alphabetical word banks for the fill-in
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
1 Food and its use by the body (pp )
 Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38
 Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 1 st SEMESTER FINAL EXAM:
 TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 1 st SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 1 and 2 Will assess your
TIPS TO PREPARE FOR THE BIOLOGY 1 st SEMESTER FINAL EXAM: FINAL EXAM DETAILS: 80 questions Multiple choice Will assess your mastery of the biological concepts covered in Units 1 and 2 Will assess your
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Biology 11 Exam Review. Study of the Human Body
 Biology 11 Exam Review Study of the Human Body Fine Print: This comprehensive review contains information that will be valuable for the preparation of the final exam. However, this review should not be
Biology 11 Exam Review Study of the Human Body Fine Print: This comprehensive review contains information that will be valuable for the preparation of the final exam. However, this review should not be
Mouth. Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion. breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces.
 Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
3. Because of homeostasis, large external changes cause internal changes.
 Biology 30S Page 1 I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. In a negative feedback mechanism, an effector is a A) muscle. B) gland. C) answers A) and B) D) none of the above 2. Which of the following is an example
Biology 30S Page 1 I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. In a negative feedback mechanism, an effector is a A) muscle. B) gland. C) answers A) and B) D) none of the above 2. Which of the following is an example
Class XI Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Biology
 Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Station A: YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament. Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5.
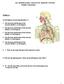 YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes
 Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes 1. What is the model for cell membrane structure called? Why is it called this? 2. What is the function of plasma membrane? 3. Draw one phospholipid, label
Quick Quiz Revision Questions Cell Membranes 1. What is the model for cell membrane structure called? Why is it called this? 2. What is the function of plasma membrane? 3. Draw one phospholipid, label
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I
 Adult Basic Education Science Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A Biology 2101B Biology 3101A Biology 3101B Biology
Adult Basic Education Science Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I Prerequisites: Biology 2101A Credit Value: 1 Biology Concentration Biology 1101 Biology 2101A Biology 2101B Biology 3101A Biology 3101B Biology
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science
 CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets
 The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a
The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
9 Transport in animals
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Science 3105 From Life to Lifestyle Study Guide
 Adult Basic Education Science From Life to Lifestyle Study Guide Credit Value: 1 Prerequisites: None Text: science.connect1; Colbourne, Fernandez, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson; 2002. Science Courses [General
Adult Basic Education Science From Life to Lifestyle Study Guide Credit Value: 1 Prerequisites: None Text: science.connect1; Colbourne, Fernandez, et al; McGraw-Hill Ryerson; 2002. Science Courses [General
Subsection 21.1 Review Quiz
 ate Subsection 21.1 Review Quiz p. 518 pp. 518 19 p. 517 1. The space between the vocal cords is the. palate.. glottis.. uvula.. pleura. 2. Which is the correct pathway of air as it enters the body?. nose,
ate Subsection 21.1 Review Quiz p. 518 pp. 518 19 p. 517 1. The space between the vocal cords is the. palate.. glottis.. uvula.. pleura. 2. Which is the correct pathway of air as it enters the body?. nose,
6. The diagram below represents an interaction between parts of an organism.
 Endocrine Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary
Endocrine Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary
LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER
 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
