Department of Physiology Teaching Schedule: First Semester, M.B.B.S. July - December, 2013
|
|
|
- Thomasina Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Physiology Teaching Schedule: First Semester, M.B.B.S. July - December, 2013 VENUE: s: LT-II (, and ) s: Demonstration room, Department of Physiology s: Undergraduate Laboratory, Department of Physiology Date & Day Time Teaching - learning methodology Topic Introduction to department of Physiology Faculty/ Tutors Prof.R Mathur 10-5 pm (Each practical is for half day and then batches interchange Batch A: Recording of biological phenomena following electrical stimulation (Inner UG laboratory) Prof. HN Mallick Dr Geetanjali Dr Kumar Dr Anita Dr Sankanika Dr Avinash Dr Bhupender Dr. Navdeep Dr. Manju Dr. Pankaj Dr. Priyanka Dr. Komal Batch B: Use of microscope, counting chambers and pipettes in hematology (Main UG laboratory) Dr KK Deepak Dr Gaurav Dr Nishanth Dr Manpreet Dr Suneeta Dr Suriya Dr Neha Dr. Shival Dr. Jojo Dr. Sivaraj Dr. Arjun Dr. Bhvya 1
2 Principles of physiological control and Homeostasis Physicochemical properties of cell membrane Physiology of the cell Rationale and ethics in animal experimentation Dr Nalin Mehta 10-5 pm (Each practical is for half day and then students interchange) Batch A: Expt 1 and 2 Expt. 1: Total red blood cells in peripheral blood sample Expt. 2: Preparation of blood film and identification of cells in peripheral blood sample Dr RK Yadav Dr Geetanjali Dr Shival Dr Jojo Dr. Anita Dr Bhupender Dr. Sivraj Dr. Bhvya Dr. Pankaj Batch B: Expt. 3 and 4 Expt. 3: To study the excitable and contractile properties in an amphibian nerve muscle preparation and demonstration of isotonic contraction (inner UG Lab) Dr Gaurav Dr Manpreet Dr Neha Dr Manju Expt. 4: Estimation of hemoglobin concentration in peripheral blood sample. Determination of osmotic fragility of erythrocytes. (Inner UG Lab) Dr A Talwar Dr Nishanth Dr Suriya Dr Avinash Dr Priynaka Batch C: Expt. 5 and 6 Expt. 5: Determination of Dr Kumar 2
3 eosinophil count. Dr Navdeep Dr Komal Expt. 6: Total white blood cells in peripheral blood sample Dr S Jain Dr Suneetha Dr Sankanika Dr Arjun Molecular building blocks of cell and their function Cell membrane: permeability and transport Intercellular connections and communication Body fluids: intercellular, intracellular and blood: Principles of methods for determination of body fluid Batch A: Expt. 3 and 4 Batch B: Expt. 5 and 6 Batch C: Expt. 1 and 2 Principles of bioelectricity: Genesis of resting membrane potential Introduction to blood and functions of plasma proteins Film show Principles of hemopoiesis Action potential Dr. S Jain Dr. Kumar Nerve- muscle Physiology 3
4 Properties of nerve fibre Batch A: Expt. 5and 6 Batch B: Expt. 1and 2 Batch C: Expt. 3 and Regulation of erythropoeisis Neuromuscular transmission Haematology Contractile and tubular elements of skeletal muscle: Physiology of contraction Functions of RBC / Applied aspects of neuromuscular transmission: Myasthenia gravis and botulinism toxicity Hemoglobin and Hemoglobinopathies Batch A: Expt. 7and 8 Expt. 7: Differential leucocyte count (Main UG lab) Dr Suneetha Dr Suriya Dr Priyanka Expt. 8: To study the excitable and contractile properties in an amphibian nerve muscle preparation: (a)effect of threshold, subthreshold and suprathreshold stimuli (b)effect of two or more successive stimuli (Inner UG lab) Dr S Jain Dr Kumar Dr Nishanth Dr Neha Dr Jojo Batch B: Expt. 9 and 10 Expt. 9 (a) Recording of isometric Dr N Mehta Dr Geetanjali 4
5 contraction.* (b)length tension relationship* (* Demonstraiton experiments) (Inner UG Lab) Dr Avinash Dr Komal Dr Arjun Expt. 10: Platelet count (Main UG lab) Dr KP Kochhar Dr Gaurav Dr Shival Dr Manju Batch C: Expt. 11 and 12 Expt. 11: Determination of ESR and PCV. Calculation of absolute values Determination of prothrombin time, bleeding time, clotting time and blood groups. (PG Lab) Dr Anita Dr Bhupender Dr Navdeep Dr Sivraj Expt. 12: Determination of reticulocyte count. Examination of bone marrow smears. Dr H N Mallick Dr Manpreet Dr Sankanika Dr Pankaj Dr Bhvya Destruction of red blood cell: Physiological basis of jaundice Excitation-contraction coupling / Iron metabolism Physiology of smooth muscle-i Classification and physiological basis of anaemia Physiological basis of investigations for anaemia and jaundice Physiology of smooth muscle-ii Batch A: Expt. 9and 10 Batch B: Expt. 11 and 12 Batch C: Expt. 7 and 8 5
6 Granulopoiesis: Principles and regulation Injury and repair in nerve and muscle Energetics of nerve and muscle: Work physiology Functions and fate of white blood cells Development, functions and fate of platelets Mini PBL: Nerve- muscle Physiology Cultural Week 16 th to 22 th September, Hemostasis and coagulation Batch A: Expt. 11 and 12 Batch B: Expt. 7 and 8 Batch C: Expt. 9 and 10 Physiology of immune system: innate immunity Physiology of immune system: Adaptive immunity Introduction to cardiovascular system and functional anatomy of heart Thrombosis and thrombolysis Blood groups; physiological basis of blood transfusion and its reactions Dr A Patil Properties of cardiac muscle Dr A Patil 6
7 Introduction to respiratory system and functional anatomy of respiratory system Revision practical Mid Semester Examination: 1 st -11 th october 2013 Dr S Jain and all residents Composition of respired air and pulmonary ventilation Dr A K Jaryal Batch A: Expt. 13and 14 Expt. 13 : Study of the factors controlling ionotropic and chronotropic functions in isolated and perfused amphibian heart preparation (Inner UG lab) Dr Gaurav Dr Suneetha Dr Avinash Dr Shival Expt. 14: Study of human fatigue using: (a) Mosso s ergograph (b) Hand grip dynamometer Dr KP Kochhar Dr Geetanjali Dr Bhupender Dr Sivraj Dr. Bhvya Batch B: Expt. 15 and 16 Expt. 15: # a) Recording and analysis of compound action potential in amphibian nerve muscle preparation b) Recording of strength- duration curve in amphibian nerve muscle preparation c) Recording of conduction velocity in human ulnar nerve (# Demonstration experiment) (Inner UG Lab) Expt. 16: Clinical examination of respiratory system. (PG lab) 7 Dr Ratna Sharma Dr Kumar Dr Suriya Dr Sankanika Dr Arjun Dr RK Yadav Dr Nishanth Dr Navdeep
8 Dr Pankaj Batch C: Expt. 17 and 18 Expt. 17: Determination of blood pressure in a human subject. (Main UG lab) Dr A Patil Dr Manpreet Dr Neha Dr Jojo Dr Priyanka Expt. 18: Clinical examination of CVS (PG lab) Dr Nalin Mehta Dr Anita Dr Manju Dr Komal Properties of cardiac muscle Mechanics of respiration-i Action potential and spread of impulse in the heart Excitation-contraction coupling in myocardium Mechanics of respiration-ii Cardiac physiology: comparison of action potentials of various types of muscle fibers Pressure changes in the heart and cardiac cycle Batch A: Expt. 15 and 16 Batch B: Expt. 17 and 18 Batch C: Expt. 13 and Exchange of gases in the lungs Neural regulation of cardiac activity and cardiac reflexes Lung volumes, capacities and artificial 8
9 respiration Functional basis of heart sounds and murmurs Ventilation- perfusion ratio 1 st Mid semester feedback Dr Suman Jain and all senior residents Intrinsic regulation of cardiac activity Batch A: Expt. 15 and 16 Batch B: Expt. 17 and 18 Batch C: Expt. 13 and 14 Oxygen carriage and oxygen dissociation curve Electrocardiography Respiratory Physiology Cardiovascular reflex Carbon dioxide carriage Cardiac Physiology Cardiac output: measurement and regulation Revision practical General principles of hemodynamics Nutrition and metabolism of the heart O Pulmonary function tests and assisted ventialtion Neural and local control of circulation Chemical regulation of respiration Exercise physiology 9
10 Regulation of blood pressure, Hypertension Batch A: Expt. 19 Expt. 17 $ a: Study of neuromuscular transmission in an amphibian nerve muscle preparation: (a) phenomenon of fatigue (b) site of fatigue* (c) neuromuscular blocking* (* demonstration experiments) b: Study of work performed by skeletal muscle using amphibian nerve muscle preparation under (a) free loading and (b) after loading conditions ( $ Full Day Experiment) (Inner UG lab) Dr A K Jaryal Dr Manpreet Dr Suneetha Dr Bhupendra Dr Shival Dr Jojo Dr Komal Dr Arjun Batch B: Expt. 20 Expt. 20: Electrocardiography $ ( $ Full day experiment) (Demonstration room) Batch C: Expt. 21and 22 Dr K K Deepak Dr Nishanth Dr Anita Dr Suriya Dr Avinash Dr Sivraj Expt. 21: Spirometry: Determination of various lung volumes; capacities, timed vital capacity and maximum voluntary ventilation. Expt. 22: Effect of posture on blood pressure. (PG lab) Neural regulation of respiration Hypoxia, cyanosis and dyspnoea Dr Gaurav Dr Sankanika Dr Manju Dr Pankaj Dr A Talwar Dr Geetanjali Dr Neha Dr Navdeep Dr Bhvya 10
11 UG seminar: How to assess vascular function Physiology of capillaries and lymphatics Batch A: Expt. 20 Batch B: Expt. 21 and 22 Batch C: Expt. 19 Special features of coronary circulation Special features of circulation in skeletal muscle, skin and mesentery Respiratory Physiology Special features of pulmonary circulation Introduction to nutrition and energy metabolism Dr K P Kochhar Vascular system Macronutrients : functions and sources Dr K P Kochhar Batch A: Expt. 21 and 22 Batch B: Expt.19 Batch C: Expt. 20 Special features of cerebral circulation Micronutrients and functional food: functions and sources Dr K P Kochhar Special features of circulation in foetus and neonate Recommended dietary allowances, food guide pyramids Dr K P Kochhar Dietary requirements in health and disease Dr K P Kochhar Applied aspects: Pathophysiology of 11
12 circulatory shock and cardiac failure End Semester Examination:2 nd -12 th December
UNIVERSITY DEVELOPMENT CENTER. Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Medical Physiology (first year)
 Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Medical Physiology (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Medical Physiology Course Specification: Programme(s) on which the course is given : Department offering
Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Medical Physiology (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Medical Physiology Course Specification: Programme(s) on which the course is given : Department offering
Physiology PHY 302. Physiology. First year
 Physiology PHY 302 Basic Information Program(s) Title Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery; MB,BCh Department offering the course Physiology Academic year / Level First year Date of specification approval
Physiology PHY 302 Basic Information Program(s) Title Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery; MB,BCh Department offering the course Physiology Academic year / Level First year Date of specification approval
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Department of Physiology.
 Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Department of Physiology. Course Specifications Course title: Physiology. Code: MED 0703 Academic Year (2010 2011) Department offering the course: Physiology. Academic
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Department of Physiology. Course Specifications Course title: Physiology. Code: MED 0703 Academic Year (2010 2011) Department offering the course: Physiology. Academic
TEACHING SCHEDULE FOR 1 st SEMESTER MBBS STUDENTS (BATCH 2015) FROM AUGUST TO DECEMBER 2015
 TEACHING SCHEDULE FOR 1 st SEMESTER MBBS STUDENTS (BATCH 2015) FROM AUGUST TO DECEMBER 2015 Date Day 08-09 AM 09-10 AM 10-11 AM 11AM 12PM 12-1 PM 24.08.2015 Mon Introduction Practical : to Physiology :
TEACHING SCHEDULE FOR 1 st SEMESTER MBBS STUDENTS (BATCH 2015) FROM AUGUST TO DECEMBER 2015 Date Day 08-09 AM 09-10 AM 10-11 AM 11AM 12PM 12-1 PM 24.08.2015 Mon Introduction Practical : to Physiology :
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY. 1. Explain the normal functioning of all the organ systems and their interactions for well coordinated
 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY A) GOAL The broad goal of teaching undergraduate students Human Physiology is to provide the student comprehensive knowledge of the normal functions of the organ systems of the body to
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY A) GOAL The broad goal of teaching undergraduate students Human Physiology is to provide the student comprehensive knowledge of the normal functions of the organ systems of the body to
PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours)
 PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours) COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is an introduction to the anatomy and physiology of the human body. Learners will explore the structure and function of the major
PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours) COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is an introduction to the anatomy and physiology of the human body. Learners will explore the structure and function of the major
M.D.PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY J.N. MEDICAL COLLEGE, AMU, ALIGARH. Physiology: Theory & Practical. Themes and Topics 1 ANNEXURE II
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY J.N. MEDICAL COLLEGE, AMU, ALIGARH 1 ANNEXURE II M.D.PHYSIOLOGY Physiology: Theory & Practical I. a. General & Cellular Physiology b. Haematology c. Renal Physiology & Fluid Balance
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY J.N. MEDICAL COLLEGE, AMU, ALIGARH 1 ANNEXURE II M.D.PHYSIOLOGY Physiology: Theory & Practical I. a. General & Cellular Physiology b. Haematology c. Renal Physiology & Fluid Balance
Blood and Circulation Module
 Blood and Circulation Module 1 Module coordinator Prof. NS Kalupahana Module code CONCEPT Objectives 3/1 3/2 Students should be able to understand the Overview clinical relevance to structure and function
Blood and Circulation Module 1 Module coordinator Prof. NS Kalupahana Module code CONCEPT Objectives 3/1 3/2 Students should be able to understand the Overview clinical relevance to structure and function
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Introductory Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 KNES 200 Kinesiology Program/University Studies. Course Outline
 Introductory Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 KNES 200 Kinesiology Program/University Studies Course Outline COURSE IMPLEMENTATION DATE: Pre 1998 OUTLINE EFFECTIVE DATE: September 2018 COURSE OUTLINE REVIEW
Introductory Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 KNES 200 Kinesiology Program/University Studies Course Outline COURSE IMPLEMENTATION DATE: Pre 1998 OUTLINE EFFECTIVE DATE: September 2018 COURSE OUTLINE REVIEW
Semester. Numbers of credits Total number of Total number of hours from. Total number of individual hours per curriculum
 SYLLABUS Total number of hours (per semester) from curriculum (84) Name of discipline PHYSIOLOGY Year of study I Semester Type of final evaluation (E / V / II * C) Discipline regime (Co compulsory, Op
SYLLABUS Total number of hours (per semester) from curriculum (84) Name of discipline PHYSIOLOGY Year of study I Semester Type of final evaluation (E / V / II * C) Discipline regime (Co compulsory, Op
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite
 Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
BIOL 230 Human Physiology Common Course Outline
 South Central College BIOL 230 Human Physiology Common Course Outline Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Types of Instruction Instruction Type This course provides an in-depth
South Central College BIOL 230 Human Physiology Common Course Outline Course Information Description Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Types of Instruction Instruction Type This course provides an in-depth
Reason Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress. Differentiate between negative and positive mechanisms
 Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
15 hours of seminars. 45 hours of exercises. 2nd year, 4th semester
 Program of Study : GENERAL MEDICINE Course : Physiology Abbreviation : FYZ/VAB12 Schedule : 45 hours of lectures 15 hours of seminars 45 hours of exercises Course Distribution : 2nd year, 4th semester
Program of Study : GENERAL MEDICINE Course : Physiology Abbreviation : FYZ/VAB12 Schedule : 45 hours of lectures 15 hours of seminars 45 hours of exercises Course Distribution : 2nd year, 4th semester
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science. Learning Outcomes
 IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Learning Outcomes 1 TOPIC 1: ANATOMY 1.1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1.1.1 Distinguish anatomically between the axial and appendicular skeleton. 1.1.2 Distinguish between
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Learning Outcomes 1 TOPIC 1: ANATOMY 1.1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1.1.1 Distinguish anatomically between the axial and appendicular skeleton. 1.1.2 Distinguish between
DAYANAND MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, LUDHIANA Teaching Schedule of MBBS First Prof. Month: November, 2016.
 Day Date 8.30 am to 9.30 am 9.30 am to 10.30 am 10.30 am to 11.30 11.30 am to 12.30 12.30 pm to 1.30 pm 2.30 pm to 3.30 pm 3.30 pm to 4.30 pm Tuesday 1 Demonstration ESR & PCV Dr. Manpreet Kaur compt.
Day Date 8.30 am to 9.30 am 9.30 am to 10.30 am 10.30 am to 11.30 11.30 am to 12.30 12.30 pm to 1.30 pm 2.30 pm to 3.30 pm 3.30 pm to 4.30 pm Tuesday 1 Demonstration ESR & PCV Dr. Manpreet Kaur compt.
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
Cardiovascular System
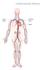 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Advanced Anatomy and Physiology
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Advanced Anatomy
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806179 Advanced Anatomy and Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Advanced Anatomy
Langara College Spring archived
 COURSE DETAILS Department of Human Kinetics and Recreation Human Kinetics 1191 Anatomy & Physiology II Term: 2007-10 Sections: 001, 002, 003 Lecture/Seminar/Lab Hrs: 2: 0: 2 Credits: 3 Schedule: Section
COURSE DETAILS Department of Human Kinetics and Recreation Human Kinetics 1191 Anatomy & Physiology II Term: 2007-10 Sections: 001, 002, 003 Lecture/Seminar/Lab Hrs: 2: 0: 2 Credits: 3 Schedule: Section
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
THEMATIC PLAN OF LECTURES (NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY)
 THEMATIC PLAN OF LECTURES (NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY) 1 st semester 018/019 ed.y. Subject hr 1 Introduction. The subject, task and purpose of physiology..0 Homeostatic control mechanisms. Blood physiology. Functions,
THEMATIC PLAN OF LECTURES (NORMAL PHYSIOLOGY) 1 st semester 018/019 ed.y. Subject hr 1 Introduction. The subject, task and purpose of physiology..0 Homeostatic control mechanisms. Blood physiology. Functions,
CURRICULUM OF HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY INCLUDING BIO-PHYSICS FOR UNDERGRADUATE MEDICAL STUDENTS. At the end of the course the learner shall be able to:
 CURRICULUM OF HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY INCLUDING BIO-PHYSICS FOR UNDERGRADUATE MEDICAL STUDENTS I. PHYSIOLOGY A. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Physiology aims at providing the
CURRICULUM OF HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY INCLUDING BIO-PHYSICS FOR UNDERGRADUATE MEDICAL STUDENTS I. PHYSIOLOGY A. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Physiology aims at providing the
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Cardiovascular System: Blood and Blood Vessels. Formed Elements of Blood
 Cardiovascular System: Blood and Blood Vessels Formed Elements of Blood 1 Whole Blood and the Hematocrit What is the likely cause of a WBC count of 34K, in which most of the WBCs are lymphocytes? How much
Cardiovascular System: Blood and Blood Vessels Formed Elements of Blood 1 Whole Blood and the Hematocrit What is the likely cause of a WBC count of 34K, in which most of the WBCs are lymphocytes? How much
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Physiology including Biochemistry Question bank (New pattern )
 Physiology including Biochemistry Question bank (New pattern ) Q.1.Write appropriate answers (any ten out of fifteen) 10X2= 20 System:- (Blood, CVS, Respiratory, Excretory System, Special Senses, Body
Physiology including Biochemistry Question bank (New pattern ) Q.1.Write appropriate answers (any ten out of fifteen) 10X2= 20 System:- (Blood, CVS, Respiratory, Excretory System, Special Senses, Body
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Bone (A) Dr Pushpa NB. Transport across the Cell membrane (B) Dr.AkilaPrashant. General Anatomy. Muscular Tissue (A) Dr Malar D LUNCH BREAK
 I st MBBS INTEGRATED TEACHING TIME TABLE FOR THE MONTH OF SEPTEMBER 2017 WEEK 1 Time Day 1 04.09.2017 8 9 Structure of cell, organelle and cell junction(a) Dr. N M Shasundar 9 10 Introduction Homeostasis
I st MBBS INTEGRATED TEACHING TIME TABLE FOR THE MONTH OF SEPTEMBER 2017 WEEK 1 Time Day 1 04.09.2017 8 9 Structure of cell, organelle and cell junction(a) Dr. N M Shasundar 9 10 Introduction Homeostasis
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
The goal of these lectures is to discuss
 Cardiovascular (#2) The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology of the cardiovascular system (heart, vessels, blood pressure, control, hemostasis). This second lecture will discuss blood
Cardiovascular (#2) The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic physiology of the cardiovascular system (heart, vessels, blood pressure, control, hemostasis). This second lecture will discuss blood
Anatomy and Physiology by Central Council of Homeopathy India
 Anatomy and Physiology by Central Council of Homeopathy India Study of Normal Man in Pre-Clinical Period Human economy is the most difficult of all sciences to study. Man is a conscious mentalised, living
Anatomy and Physiology by Central Council of Homeopathy India Study of Normal Man in Pre-Clinical Period Human economy is the most difficult of all sciences to study. Man is a conscious mentalised, living
BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. Chapter 11
 BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 11 BLOOD 5 L of blood 55% fluid 45% blood cells Blood cells produced in bone marrow Hematocrit-percentage of red blood cells PLASMA Plasma-fluid portion of blood(90%
BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 11 BLOOD 5 L of blood 55% fluid 45% blood cells Blood cells produced in bone marrow Hematocrit-percentage of red blood cells PLASMA Plasma-fluid portion of blood(90%
Circulation and Gas Exchange
 Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Circulation and Gas Exchange Sponges (porifera) Flat worms (platyhelminthes) Round worms (nematoda) Segmented worms (annelida) Stinging celled (cnidaria) Squishy (mollusca) Hard shelled (arthropods) Spiny
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 1: Human Structure and Function
 SUNY Downstate College of Medicine Integrated Pathways Curriculum, Class of 2019 Unit 1: Human Structure and Function Calendar August 10 October 2, 2015 Corresponds to V-21 of Master Calendar 1 UNIT 1
SUNY Downstate College of Medicine Integrated Pathways Curriculum, Class of 2019 Unit 1: Human Structure and Function Calendar August 10 October 2, 2015 Corresponds to V-21 of Master Calendar 1 UNIT 1
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science
 Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science Mission Statement The Mission of Science Education Is: 1) To nurture an active interest in science that continues throughout life.
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science Mission Statement The Mission of Science Education Is: 1) To nurture an active interest in science that continues throughout life.
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS. October 21, 2016
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS October 21, 2016 Review AGENDA Questions Activity Notes HEART HEART = A BIG, WET, MUSCLY PUMP Body temperature ph levels Volume of body fluid REGULATES HEART TRANSPORTS
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS October 21, 2016 Review AGENDA Questions Activity Notes HEART HEART = A BIG, WET, MUSCLY PUMP Body temperature ph levels Volume of body fluid REGULATES HEART TRANSPORTS
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD
 PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD FUNCTION OF BLOOD... Oxygen is carried to tissues Carbon dioxide is carried fro m tissues to lungs Glucose is carried from
PLASMA, ERYTHROCYTES, LEUKOCYTES AND PLATELETS COMPOSITION AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD FUNCTION OF BLOOD... Oxygen is carried to tissues Carbon dioxide is carried fro m tissues to lungs Glucose is carried from
Circulatory System. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted. Circulatory System 1
 Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Chapter 34 Active Reading Guide Circulation and Gas Exchange
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 34 Active Reading Guide Circulation and Gas Exchange Section 1 1. Gaining O 2 and nutrients while shedding CO 2 and other waste products occurs with every cell in the
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 34 Active Reading Guide Circulation and Gas Exchange Section 1 1. Gaining O 2 and nutrients while shedding CO 2 and other waste products occurs with every cell in the
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education
 Date Adopted: July 1, 1980 Date Reviewed: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY
Date Adopted: July 1, 1980 Date Reviewed: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002, 2011 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY
Introduction. Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level.
 Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
What is the composition of blood, including blood cells? What organs and structures control the flow of blood throughout the body?
 3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange. d = t 2
 Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
Chapter 42: Circulation / Gas Exchange Transport systems connect organs of exchange with body cells Diffusion Lung Blood 100 m 1 s 1 mm 100 s 1 cm 10000 s d = t 2 Bulk Flow (Pressure) Blood Cells Methods
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Required Syllabus Information all must be included in the course syllabus
 Effective Implementation date: Summer 2018, 201910 Required Syllabus Information all must be included in the course syllabus BIO 202 Course Title: Human Anatomy and Physiology II with Lab:GT-SC1 Course
Effective Implementation date: Summer 2018, 201910 Required Syllabus Information all must be included in the course syllabus BIO 202 Course Title: Human Anatomy and Physiology II with Lab:GT-SC1 Course
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review. 3 weeks A&P1, A&P2
 Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
Unit 1: Introduction and Biochemistry / Cells Review A&P1, A&P2 Does the study of anatomy at the molecular and cellular level support a creationist theory about our origins? List and describe the major
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070, Honors Human Physiology MSNBIO 2070, Human Physiology Fall Semester, 2018
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070, Honors Human Physiology MSNBIO 2070, Human Physiology Fall Semester, 2018 Classroom: Scaife Hall Lecture Room 3 Class Meetings: Lectures:, 5:30-6:45 PM PBLs and Exams: 3:00-5:00 PM Grading:
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070, Honors Human Physiology MSNBIO 2070, Human Physiology Fall Semester, 2018 Classroom: Scaife Hall Lecture Room 3 Class Meetings: Lectures:, 5:30-6:45 PM PBLs and Exams: 3:00-5:00 PM Grading:
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated)
 Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Students will identify factors that affect blood flow and/or describe how these factors affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system.
 Students will identify factors that affect blood flow and/or describe how these factors affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system. Content Limits Items may address factors such as blood pressure,
Students will identify factors that affect blood flow and/or describe how these factors affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system. Content Limits Items may address factors such as blood pressure,
Chapter 23 Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: How Does Gravity Affect
Chapter 23 Circulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction: How Does Gravity Affect
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Human Biological Science 2
 SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Human Biological Science 2 SECTION 1 GENERAL INFORMATION Subject Code: BIOH122 Award/s: Total course credit points: Level: Bachelor of Health Science (Naturopathy) 128 1 st
SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Human Biological Science 2 SECTION 1 GENERAL INFORMATION Subject Code: BIOH122 Award/s: Total course credit points: Level: Bachelor of Health Science (Naturopathy) 128 1 st
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) All the following statements related to blood volume are correct except for: 5 A. Blood volume is about 5 litres. B.
 PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
PHYSIOLOGY MeQ'S (Morgan) Chapter 5 All the following statements related to capillary Starling's forces are correct except for: 1 A. Hydrostatic pressure at arterial end is greater than at venous end.
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
BIO 202 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II with LAB
 BIO 202 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) PRESENTED AND APPROVED: JANUARY 12, 2012 EFFECTIVE: FA 2012-13 Prefix & Number BIO 202 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
BIO 202 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) PRESENTED AND APPROVED: JANUARY 12, 2012 EFFECTIVE: FA 2012-13 Prefix & Number BIO 202 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Blood
 Chapter 13 The Blood Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms agglutination erythrocyte lymphocyte albumin fibrin megakaryocyte anemia hematocrit monocyte antigen
Chapter 13 The Blood Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms agglutination erythrocyte lymphocyte albumin fibrin megakaryocyte anemia hematocrit monocyte antigen
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Objectives. Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 7 Body Systems. Define term connective tissue. Identify five body cavities
 Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Circulatory System. The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
CHAPTER 26. Circulation and Gas Exchange
 CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
CHAPTER 26 Circulation and Gas Exchange CO INTRODUCTION Every organism must exchange materials with its environment Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level In unicellular organisms, these exchanges
Unit 1: Human Structure and Function
 SUNY Downstate College of Medicine Integrated Pathways Curriculum, Class of 2021 Unit 1: Human Structure and Function August 14 October 6, Corresponds to V-6a of Master Calendar 1 UNIT 1 Human Structure
SUNY Downstate College of Medicine Integrated Pathways Curriculum, Class of 2021 Unit 1: Human Structure and Function August 14 October 6, Corresponds to V-6a of Master Calendar 1 UNIT 1 Human Structure
Muscles and Muscle Tissue
 1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
1 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Chapter 9 2 Overview of Muscle Tissues Compare and Contrast the three basic types of muscle tissue List four important functions of muscle tissue 3 Muscle Terminology Muscle
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION
 Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
Chapter 9 GAS EXCHANGE & CIRCULATION MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Respiration Taking up O 2 and giving up CO 2 2 3 MECHANISMS OF GAS EXCHANGE Three phases of gas exchange Breathing Transport of oxygen and
General Anatomy & Physiology
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Unit 1: Human Structure and Function
 SUNY Downstate College of Medicine Integrated Pathways Curriculum, Class of 2022 Unit 1: Human Structure and Function August 13 October 5, Corresponds to V-7a of Master Calendar 1 UNIT 1: Human Structure
SUNY Downstate College of Medicine Integrated Pathways Curriculum, Class of 2022 Unit 1: Human Structure and Function August 13 October 5, Corresponds to V-7a of Master Calendar 1 UNIT 1: Human Structure
Class XI Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Biology
 Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Introduction The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, is an organ system that allows blood to flow to all the cells in
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Introduction The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, is an organ system that allows blood to flow to all the cells in
Energy sources in skeletal muscle
 Energy sources in skeletal muscle Pathway Rate Extent ATP/glucose 1. Direct phosphorylation Extremely fast Very limited - 2. Glycolisis Very fast limited 2-3 3. Oxidative phosphorylation Slow Unlimited
Energy sources in skeletal muscle Pathway Rate Extent ATP/glucose 1. Direct phosphorylation Extremely fast Very limited - 2. Glycolisis Very fast limited 2-3 3. Oxidative phosphorylation Slow Unlimited
Circulation. Invertebrates on Land: such as insects, and such as earthworms also do not have a gastrovascular cavity.
 Circulation A. Invertebrates in Water: Organisms that are a cells thick. Diffusion alone is sufficient for single-celled (amoeba and paramecium) and simple, multi-cellular animals such as (hydra, jellies,
Circulation A. Invertebrates in Water: Organisms that are a cells thick. Diffusion alone is sufficient for single-celled (amoeba and paramecium) and simple, multi-cellular animals such as (hydra, jellies,
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp , , , I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System
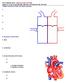 P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
Cardiovascular Physiology. Heart Physiology. Introduction. The heart. Electrophysiology of the heart
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
