Disclosures. Imaging in the NICU. Neonatal Imaging. Objectives. Lines and Tubes. Endotracheal tube 4/18/2017. I have no disclosures
|
|
|
- Marjory Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Disclosures I have no disclosures Imaging in the NICU Adina Alazraki, FAAP, MD Special thanks to Sarah Sarvis Milla, FAAP, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Objectives Neonatal Imaging Identify normal and malpositioning of lines/tubes Discuss neonatal congenital and acquired lung and abdominal pathology Briefly review normal and abnormal cranial sonography Lines and Tubes Chest Airway Bones Cardiac Diaphragms Effusions Free Air Abdominal Gas Pattern Free air Pneumatosis Portal venous gas Mass Bones Stones/calcs Cranial Sonograms Anatomy Pathology Endotracheal tube Orogastric tube Central lines Umbilical arterial Umbilical venous Lines and Tubes Endotracheal tube Optimal position Mid thoracic trachea ~T2-4 1
2 C5 C6 C7 Orogastric Tube Optimal position Left upper quadrant Abnormal location Trachea or bronchi High in the proximal esophagus Esophageal atresia Mid esophagus or esophagogastric junction At risk for reflux and aspiration during OG feeds 2
3 Umbilical Venous Catheter Normal course Umbilical vein left portal vein ductus venosus middle hepatic vein IVC Optimal location IVC just at/below the right hemidiaphragm Abnormal Overlying the liver Hyperosmolar substances (TPN) can damage the liver parenchyma Requires removal and new catheter placement 3
4 Umbilical Arterial Line Normal course Umbilical artery internal iliac artery aorta Optimal location Aorta (between the T6- T10 vertebral bodies) Aorta (below L3) Abnormal Above T6 Near the ostia of the subclavian and carotid arteries Below T10 Near the ostia of the renal, celiac and superior mesenteric arteries Peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) Upper and lower extremities Need to document tip location and course of catheter Beware of curls (particularly Left Inguinal) Complications Thrombosis Embolic phenomena Leakage if malposition 4
5 Neonatal Chest Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema (PIE) Transient Tachypnea of Newborn (TTN) Meconium aspiration Pneumothorax Pneumomediastinum Neonatal Chest Neonatal Chest Congen Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) Congen Lobar Emphysema/Hyperinfla tion (CLE/CLH) Sequestration Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation (CPAM) Normal thymus PREMATURE BABY Respiratory distress syndrome Surfactant deficiency Alveolar instability and collapse Impaired oxygenation» Metabolic acidosis» Increased pulmonary vascular resistance right to left shunting through ductus Hyaline membrane disease Microscopic appearance of RDS» Homogeneous, eosinophilic membranes that line terminal bronchioles and alveolar ducts PREMATURE BABY RDS RDS Radiologic features reflect acinar collapse Hypoaeration Homogeneous reticulogranular appearance or groundglass opacity summation of collapsed alveoli transudation of fluid into the interstitium from capillary leak distension by air of innumerable bronchioles 5
6 PREMATURE BABY RDS Management Prenatal administration of corticosteroids Accelerates structural and biochemical lung maturity Antenatal administration of exogenous surfactant Delivered into the tracheobronchial tree as a liquid bolus» Uneven or asymmetric distribution PREMATURE BABY Profoundly premature babies Initial radiograph appears relatively normal Subtle haziness or interstitial thickening Structurally immature lungs Paucity of alveoli Over several days to weeks radiographic changes manifest to diffuse haziness coarse, irregular pattern PREMATURE BABY Bronchopulmonary dyspasia (BPD) Term introduced by Northway et al in 1967 Chronic lung disease Prolonged positive-pressure mechanical ventilation and supplemental oxygen Etiology Combination of barotrauma and oxygen toxicity (due to inadequate concentrations of antioxidant enzymes) Introduction of surfactant replacement therapy BPD in very premature neonates Due to the inhibition of acinar and vascular growth during a vulnerable stage of lung development (rather than barotrauma and oxygen toxicity) PREMATURE BABY Bronchopulmonary dyspasia (BPD) Radiologic features Northway 4 developmental stages» Stage I: (2-3 days after birth); typical granular opacities of RDS» Stage II: (4-19 days); nearly complete opacification of the lungs» Stage III: (10-20 days); small round cystic lucencies alternating with regions of irregular opacity» Stage IV: (beyond 1 month); bubbly lungs Surfactant replacement era coarse interstitial opacities without cystic lucencies 6
7 BPD PREMATURE BABY Air leak phenomena Pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) Rupture of terminal airways or alveoli Predisposes to pneumothorax Imaging findings Linear and serpentine lucencies radiating out from hila Treatment Reduce ventilatory pressures High-frequency ventilation (oscillator) Selective intubation away from affected side Decubitus position with affected side down PIE PREMATURE BABY Pulmonary hemorrhage Usually secondary to severe hypoxia or capillary damage, as can be seen in RDS, meconium aspiration, patent ductus arteriosus or neonatal pneumonia Typically manifests clinically as blood within ET tube Radiographic findings Acute onset of large areas of airspace consolidation 7
8 6 hours later PREMATURE BABY Patent ductus arteriosus Ductus closes within 24 hrs triggered by high oxygen tensions Hypoxia prevents closure of the ductus Radiographic findings Hyperaerated lungs Cardiomegaly Increased perihilar pulmonary vascularity Bilateral consolidation secondary to edema RDS FULL TERM NEONATES Amniotic fluid aspiration Transient tachypnea Neonatal pneumonia/sepsis Meconium aspiration RDS Severe systemic abnormalities Congenital heart disease RDS-PDA 8
9 FULL TERM NEONATES Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) Secondary to delayed clearance of fetal pulmonary fluid C-section babies and precipitous deliveries Maternal sedation or diabetes Respiratory distress evidenced by tachypnea, retractions and nasal flaring Begins ~6 hrs of life, peaks 1 day, resolves 2-3 days Radiographic findings Hyperaeration Airspace opacification Increased interstitial markings Prominent/indistinct pulmonary vascularity Pleural effusion FULL TERM NEONATES Amniotic fluid aspiration Occurs during or just prior to birth Usually related to stress No meconium present Radiographic findings Hyperaeration Mildly coarse increased markings FULL TERM NEONATES Meconium aspiration If released in utero into the amniotic fluid Often aspirated during fetal respirations Usually occurs in full-term or post-term newborns Aspirated meconium causes Obstruction of small airways Chemical pneumonitis Radiographic findings Hyperaeration- asymmetric and patchy Asymmetric coarse, nodular lung densities Pleural effusions may be present Pneumothorax in 20 40% of cases 9
10 FULL TERM/PRETERM NEONATES Neonatal pneumonia (sepsis) Often associated with maternal rupture of membranes Infection can occur in utero, during passage through birth canal or shortly after birth Usual bacteria E. coli Group B Streptococcus Radiographic findings are variable Hyperinflated, hypoinflated or normally aerated lungs Coarse patchy asymmetric infiltrates Fine, reticular changes Mimicking edema or RDS Group B Strep FULL TERM NEONATES Chylothorax Most common cause of large pleural effusion in the newborn Due to traumatic tear of thoracic duct during delivery Right sided chylothorax tear below T7 Left sided chylothorax tear above T7 Radiographic findings Pleural effusion ranging from small to complete opacification of the hemithorax with contralateral shift of mediastinal structures Treatment Thoracentesis Chest tube placement 10
11 PNEUMOMEDIASTINUM Can occur spontaneously in both premature and full-term neonates Radiographic signs Elevation of the thymus ( spinnaker sign ) Radiolucency outlining superior mediastinum, sometimes cardiac silhouette Pneumopericardium Air outlines the heart on the AP and lateral views Retropharyngeal air Subcutaneous emphysema in the neck Continuous diaphragm sign Air in the mediastinum beneath the heart Spontaneously resolve PNEUMOTHORAX Common in both premature and full-term neonates Spontaneous or secondary to barotrauma Radiographic findings Hyperlucency adjacent to the heart borders or diaphragms In the supine position, pleural air tends to accumulate anteriorly and medially Relative hyperlucency of the entire hemithorax May see faint lungs markings Air collects anteriorly Cross-table lateral Look for displacement of the ventral surface of the lung 11
12 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS HYPOAERATION HYPERAERATION FINE INCREASED MARKINGS COARSE INCREASED MARKINGS RDS TRANSIENT TACHYPNEA RDS TRANSIENT TACHYPNEA SEPSIS (Group B Strep) AMNIOTIC FLUID ASPIRATON SEPSIS AMNIOTIC FLUID ASPIRATON MECONIUM ASPIRATION MECONIUM ASPIRATION NEONATAL PNEUMONIA SEPSIS CONGENITAL LYMPHANGIECTASIA 28 wk preemie- RDS Neonatal Pneumothorax Look for neonatal pneumo along mediastinal border 12
13 Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema Fullterm infant with respiratory distress- Meconium aspiration Congenital diapragmatic hernia Incidental Morgagni hernia Often diagnosed prenatally; Liver (left lobe) position and lung volume help predict outcome Follow stomach and small bowel to help make diagnosis Congenital lobar hyperinflation Chronic left lower lobe PNA or prenatally diagnosed chest masssequestration Look for aortic feeder to lung and note drainage: intralobar is into pulmonary venous drainage 13
14 Hyperinflation from Pulmonary sling Shunt vascularity Common Left-right shunts: ASD, VSD, PDA Remember this appearance on UGI Neonatal Abdomen (Bowel) Be familiar with normal appearances of the thymus NEC/pneumoperitoneum Esophageal atresia (TE fistula) Pyloric stenosis Malrotation (+/- volvulus) Duodenal atresia/stenosis/web Jejunal atresia Meconium ileus/peritonitis Colonic atresia Small left colon/immature colon/mec plug Hirschsprung If you think pneumatosis, look for portal venous gas and free air 14
15 Pneumoperitoneum Beneath the diaphragm Outlining the liver Anteriorly over the abdomen/falciform (football) Outlining bowel (Rigler s sign) 86 Esophageal atresia Prenatal diagnosis or newborn with feeding intolerance Look for distal gas to suggest presence of distal TE fistula (most common form) Double bubble of duodenal atresia- no distal bowel gas Newborn with bilious emesis Complete obstruction from volvulus Malrotation with midgut volvulustruly life threatening 15
16 Malrotation and midgut volvulus Malrotation, no volvulus Gastroschisis Omphalocele Lower bowel obstruction Meconium ileus Colonic atresia Small left colon syndrome (aka meconium plug) Hirschsprung Water soluble contrast enema Omphalocele is often associated with chromosomal and associated congenital anomalies Hirschsprung Rectum should be bigger than sigmoid Functional immaturity of colon risk factors: diabetic moms, mag sulfate 16
17 Microcolon--Meconium ileus test for CF Meconium peritonitis and periorchitis in utero bowel perforation and patent processus Neonatal CNS Imaging Neonatal sono Anatomy Germinal Matrix hemorrhage Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) Macrocephaly Congenital malformation Tethered cord Preterm infants Screen/follow IC Hemorrhage (< g, <30 wk) PVL Hydrocephalus Extra-axial fluid collections Symptoms Seizures CNS infection Who gets head US? Near term/term Too sick to be moved for head CT or MRI Macrocephaly On ECMO Follow finding detected in utero/syndromic Screening Standard views and anatomy < 32 weeks, 1500 g Majority of bleeding identified within the first week < 28 weeks, < 1000 g Most at risk 1 st screen in asymptomatic infant Between 7 and 14 days If normal, follow-up at term (36-40 w) If abnormal, tailor follow-up individually 17
18 Corpus callosum Cingulate gyrus Frontal white matter Frontal White Matter Circle of Willis Cavum septum pellucidum Cerebellar vermis Belly of Pons Cerebral peduncles Quadrigeminal plate 4V Cisterna magna Quadrigeminal plate cistern Choroid plexus Centrum semiovale Intracranial hemorrhage Premature Term Choroid in atrium of LV Caudothalamic groove Centrum semiovale GMH IVH Intraparenchymal Venous infarct periventricular Hypoxic-ischemic PVL Intracerebellar Subarachnoid IVH Intraparenchymal Subdural Intracranial hemorrhage Grade I: subependymal (GMH) 75% of total Grade II: intraventricular (IVH) without ventricular dilatation 25% develop Post hemorrhagic hydrocephalus (PHH) Grade III: IVH with ventricular dilatation 50% PHH 20% mortality Grade IV: parenchymal hemorrhage 5% of total with gestational age > 50% mortality 90% major motor deficits 70% cognitive dysfunction Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage Germinal matrix Cellular region of caudate Source of neuronal and glial precursors Involutes by 36 weeks Fetus has poor autoregulation of CBF Immature, complex vascular feeders of GM Poor response to changes in cerebral blood flow Hypo/hypertension Elevated cerebral venous pressure Bleeds on caudate Extension into ventricles IVH 18
19 Periventricular infarct ICH Grade IV GMH venous congestion and back pressure Causes venous hemorrhagic infarct Not bleeding from GM leaking into brain Sequelae PH Hydrocephalus Acute obstruction by clot Obliterative arachnoiditis Malfunction of pacchionian granulation Clot in cisterna magna increases risk Mastoid view Motor defect Developmental delay Acquired subependymal cyst from evolving hemorrhage ICH grade 2 Lateral ventricles full of blood without dilatation Grade 2 IVH 3 day follow up Dilated ventricles, clot Post hemorrhagic hydrocephalus NOT evolution to grade 3 Prognostically important L R L R ICH Grade 3 ICH grade 4 Dilated, clot filled ventricle Wedge of echogenicity Venous infarct Evolves to small cyst IVH 3 on left and 4 on right 19
20 Porencephalic cyst Cystic resolution of venous infarct Here has wide communication with lateral ventricle Periventricular Leukomalacia Periventricular Leukomalacia Acute Echogenic region of necrosis 1-3 weeks WM cysts End stage Ventriculomegally Loss of PVWM GM impingement on vents Lobulated ventricular walls US relatively insensitive Detects 30-50% MRI Diffusion images show extent Need image early in course CT not sensitive Grade 1 increased PV echogenicity > 7 days Asymmetric, coarse, globular or more hyperechoic than the choroid plexus Normal periventricular halo Hyperechoic 'blush' posterosuperior to the ventricular trigones Grade 2 small PV cysts Grade 3 extensive occipital and frontoparietal PV cysts Grade 4 deep WM subcortical cysts Grade 1 PVL vs. flaring PVL grade 2 Normal flaring of PV white matter Not more echogenic than choroid Grade 1 PVL Resolves on follow up 20
21 PVL grade 3 PVL grade 2 PVL grade 4 21
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation
 CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph
 Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph Poster No.: C-1008 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad ; Hyderabad/IN, 1 2 1 1 2 HYDERABAD, ANDHRA PRADESH/IN
Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph Poster No.: C-1008 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad ; Hyderabad/IN, 1 2 1 1 2 HYDERABAD, ANDHRA PRADESH/IN
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
SUMPh N. Testemitanu Radiology and Medical imaging department PEDIATRIC IMAGING. M. Crivceanschii, assistant professor
 SUMPh N. Testemitanu Radiology and Medical imaging department PEDIATRIC IMAGING M. Crivceanschii, assistant professor GOALS AND OBJECTIVES to be aware of the role of modern diagnostic imaging modalities
SUMPh N. Testemitanu Radiology and Medical imaging department PEDIATRIC IMAGING M. Crivceanschii, assistant professor GOALS AND OBJECTIVES to be aware of the role of modern diagnostic imaging modalities
disease, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, pulmonary hypoplasia and congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
 Neonatal Chest Imaging - What the Nurse Should Know Expires Monday, April 30, 2018 Nursing Michael J. Diament, M.D. Objectives 1. Describe a good technique for positioning a neonate for the purpose of
Neonatal Chest Imaging - What the Nurse Should Know Expires Monday, April 30, 2018 Nursing Michael J. Diament, M.D. Objectives 1. Describe a good technique for positioning a neonate for the purpose of
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by
 24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Hyaline membrane disease. By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg
 Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017
 Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Hirschprung s. Meconium plug R/S >1 R/S <1
 NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome
 Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
Radiological evaluation of neonatal lesions in 118 neonates
 Original Research Article ISSN: 394-006 (P) Radiological evaluation of neonatal thoracic lesions in 8 neonates Konark Sarvaiya *, Himanshu Singla, Nirav Patel, Jai Inder Dhillon, Babubhai Patel 3 nd year
Original Research Article ISSN: 394-006 (P) Radiological evaluation of neonatal thoracic lesions in 8 neonates Konark Sarvaiya *, Himanshu Singla, Nirav Patel, Jai Inder Dhillon, Babubhai Patel 3 nd year
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool.
 Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals
 Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영
 When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
Case Report Coexistent Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Extrapulmonary Sequestration
 Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 1460480, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1460480 Case Report Coexistent Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Extrapulmonary Sequestration Nao
Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 1460480, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1460480 Case Report Coexistent Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Extrapulmonary Sequestration Nao
The Blue Baby. Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin
 The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
Neonatology ICD-10 documentation
 Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous structures - Significant thoracic inj
 PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management
 Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline.
 Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Pediatric radiology. Endre Szabó
 Pediatric radiology Endre Szabó A child is not a small adult! Water content of a baby s body is higher than that of an adult, there are more free radicals and bigger damage due to radiation! Baby s chest
Pediatric radiology Endre Szabó A child is not a small adult! Water content of a baby s body is higher than that of an adult, there are more free radicals and bigger damage due to radiation! Baby s chest
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes
 Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Imaging of the Lung in Children
 Imaging of the Lung in Children Imaging methods X-Ray of the Lung (Anteroposterior, ) CT, HRCT MRI USG Congenital developmental defects of the lungs Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia Tension pulmonary anomalies
Imaging of the Lung in Children Imaging methods X-Ray of the Lung (Anteroposterior, ) CT, HRCT MRI USG Congenital developmental defects of the lungs Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia Tension pulmonary anomalies
Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children
 Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children David A. Mong, MD SUNDAY Andrew Mong MD Beyond the interstitium (path includes airways/airspace) Radiographic diffuse disease Adult Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial Lung Disease in Infants and Children David A. Mong, MD SUNDAY Andrew Mong MD Beyond the interstitium (path includes airways/airspace) Radiographic diffuse disease Adult Interstitial Lung Disease
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia information for parents. David M Notrica MD FACS FAAP Pediatric Surgeons of Phoenix
 Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia information for parents David M Notrica MD FACS FAAP Pediatric Surgeons of Phoenix CDH Congenital absence of a portion of the diaphragm allowing abdominal contents to migrate
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia information for parents David M Notrica MD FACS FAAP Pediatric Surgeons of Phoenix CDH Congenital absence of a portion of the diaphragm allowing abdominal contents to migrate
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 3 rd Week Discussion with Dr. Muna Al-Jufairi (Part 2)
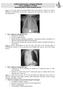 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 3 rd Week Discussion with Dr. Muna Al-Jufairi (Part 2) - Case 1: a 32 weeks preterm developed RDS 4 hours after delivery. Chest X-ray shows:
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 3 rd Week Discussion with Dr. Muna Al-Jufairi (Part 2) - Case 1: a 32 weeks preterm developed RDS 4 hours after delivery. Chest X-ray shows:
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe
 Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
Case Based Fetal Lung Masses
 Case Based Fetal Lung Masses Advances in Fetal and Neonatal Imaging Course Orlando, Florida, January 28, 2017 Leann E. Linam, MD Associate Professor Radiology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences/
Case Based Fetal Lung Masses Advances in Fetal and Neonatal Imaging Course Orlando, Florida, January 28, 2017 Leann E. Linam, MD Associate Professor Radiology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences/
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
Interpretation of Neonatal Chest Radiography 신생아흉부촬영의판독
 Review Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.5.279 Interpretation of Neonatal Chest Radiography 신생아흉부촬영의판독 Hye-Kyung Yoon, MD* Department of Radiology, Kangwon
Review Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.5.279 Interpretation of Neonatal Chest Radiography 신생아흉부촬영의판독 Hye-Kyung Yoon, MD* Department of Radiology, Kangwon
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP. October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18
 Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Survival Radiology: neonatal chest X-ray for residents.
 Survival Radiology: neonatal chest X-ray for residents. Poster No.: C-2351 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Uceda, A. Moreno, R. Llorens, M. A. Meseguer, S. P. G. 1 2 2 2 2 1 2
Survival Radiology: neonatal chest X-ray for residents. Poster No.: C-2351 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Uceda, A. Moreno, R. Llorens, M. A. Meseguer, S. P. G. 1 2 2 2 2 1 2
Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma
 Baltic Congress of Radiology, Riga 2010 Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General
Baltic Congress of Radiology, Riga 2010 Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis?
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE
 PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
BASIC TRAINING Knowledge Guide Neonatal and Perinatal Medicine
 COMMON PRESENTATIONS AND CONDITIONS Basic Trainees will require a sufficient depth of knowledge of these presentations and conditions. Antenatal conditions such as cerebral ventricular dilatation, choroid
COMMON PRESENTATIONS AND CONDITIONS Basic Trainees will require a sufficient depth of knowledge of these presentations and conditions. Antenatal conditions such as cerebral ventricular dilatation, choroid
Lecture 3. Inflammatory Processes
 Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Pulmonary Sequestration
 July 26, 2004 Pulmonary Sequestration Jonathan Shaw, Harvard Medical School Year IV What do these two patients have in common? Patient 1: 50 y.o. non-smoking female with several months cough and hemoptysis;
July 26, 2004 Pulmonary Sequestration Jonathan Shaw, Harvard Medical School Year IV What do these two patients have in common? Patient 1: 50 y.o. non-smoking female with several months cough and hemoptysis;
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn
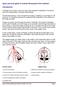 Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Gastrointestinal tract
 Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate. Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA
 Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
The neonatal chest X-ray
 PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY REVIEWS (2001) 2, 311 323 doi:10.1053/prrv.2001.0169, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on SERIES: IMAGING The neonatal chest X-ray R. Arthur X-ray and Ultrasound Department,
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY REVIEWS (2001) 2, 311 323 doi:10.1053/prrv.2001.0169, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on SERIES: IMAGING The neonatal chest X-ray R. Arthur X-ray and Ultrasound Department,
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy
 An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
HFOV IN THE NON-RECRUITABLE LUNG
 HFOV IN THE NON-RECRUITABLE LUNG HFOV IN THE NON-RECRUITABLE LUNG PPHN Pulmonary hypoplasia after PPROM Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Pulmonary interstitial emphysema / cystic lung disease 1 30 Mean
HFOV IN THE NON-RECRUITABLE LUNG HFOV IN THE NON-RECRUITABLE LUNG PPHN Pulmonary hypoplasia after PPROM Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Pulmonary interstitial emphysema / cystic lung disease 1 30 Mean
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connections: Anatomy and Diagnostic Imaging
 Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connections: Anatomy and Diagnostic Imaging Timothy Slesnick, MD March 12, 2015 Congenital Cardiac Anesthesia Society Annual Meeting Disclosures I will discuss the use
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connections: Anatomy and Diagnostic Imaging Timothy Slesnick, MD March 12, 2015 Congenital Cardiac Anesthesia Society Annual Meeting Disclosures I will discuss the use
-Tamara Wahbeh. -Razan Abu Rumman. Dr. Mohammed Al-Muhtaseb
 -2 -Tamara Wahbeh -Razan Abu Rumman Dr. Mohammed Al-Muhtaseb I tried to include everything the doctor mentioned in both the lecture and his slides in the simplest way possible, so hopefully there would
-2 -Tamara Wahbeh -Razan Abu Rumman Dr. Mohammed Al-Muhtaseb I tried to include everything the doctor mentioned in both the lecture and his slides in the simplest way possible, so hopefully there would
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System
 The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
Neonatal Chest X-Ray Introduction Indications Interpretation
 43 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Introduction The chest X-ray is the most frequently ordered radiological investigation in NICUs. It should ideally be performed in the ICU using a portable X-ray equipment. In most
43 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Introduction The chest X-ray is the most frequently ordered radiological investigation in NICUs. It should ideally be performed in the ICU using a portable X-ray equipment. In most
QUESTIONS IN SURGERY General Surgery (3rd year) Surgery nr.1 (4th year)
 QUESTIONS IN SURGERY General Surgery (3 rd year) 1. Bleeding: definition, classification. Physiological mechanisms of compensation and pathological mechanisms of decompensation in case of hemorrhage. Physiologic
QUESTIONS IN SURGERY General Surgery (3 rd year) 1. Bleeding: definition, classification. Physiological mechanisms of compensation and pathological mechanisms of decompensation in case of hemorrhage. Physiologic
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care. Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN. Other. Other Diseases
 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Topics for discussion. Pediatric General Surgery. Physiology. Surgical Newborns. Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction
 Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Extralobar lung sequestration associated with fatal
 Thorax (1971), 26, 125. Extralobar lung sequestration associated with fatal neonatal respiratory distress A. J. BLIEK and D. J. MULHOLLAND The Departments of Radiology and Pathology, Royal Alexandra Hospital,
Thorax (1971), 26, 125. Extralobar lung sequestration associated with fatal neonatal respiratory distress A. J. BLIEK and D. J. MULHOLLAND The Departments of Radiology and Pathology, Royal Alexandra Hospital,
Pediatric Imaging Studies: Congenital and Acquired Diagnoses
 Pediatric Imaging Studies: Congenital and Acquired Diagnoses Robin Foster MD FAAP FACEP Division Chief Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at Virginia Commonwealth University Health
Pediatric Imaging Studies: Congenital and Acquired Diagnoses Robin Foster MD FAAP FACEP Division Chief Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at Virginia Commonwealth University Health
3/30/18. Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery. Disclosure Information. Objectives
 Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery A Scenario Based Approach to Interpretation for the Pediatric Nurse and Provider presented by Elizabeth A. Paton, DNP, RN-BC, PNP-A, PPCNP-BC, CPEN, FAEN Disclosure
Common Radiology Studies in Pediatric Surgery A Scenario Based Approach to Interpretation for the Pediatric Nurse and Provider presented by Elizabeth A. Paton, DNP, RN-BC, PNP-A, PPCNP-BC, CPEN, FAEN Disclosure
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
ADMISSION/DISCHARGE FORM FOR INFANTS BORN IN 2019 DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
!"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.
 !"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.!"#$%&'()$*+&,--#&$.//,0'1232'!-#0'45 *6 '7849!!"#$%&'"(&)*+),$-.*/*01) 2$34/&1)*+)5"-.3.(") 6%.(3")*+)7*(08/$)9(.:"%;.&1)) )?
!"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.!"#$%&'()$*+&,--#&$.//,0'1232'!-#0'45 *6 '7849!!"#$%&'"(&)*+),$-.*/*01) 2$34/&1)*+)5"-.3.(") 6%.(3")*+)7*(08/$)9(.:"%;.&1)) )?
Diagnostic Imaging
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Cantrell s pentalogy: an unusual midline defect October 2004 2 Cevey-Macherel MN, Meijboom EJ, Di Bernardo S, Truttmann AC, Division of Neonatology and Division of Pediatric
HOW TO IMAGE AND DESCRIBE CONGENITAL LUNG MALFORMATIONS
 HOW TO IMAGE AND DESCRIBE CONGENITAL LUNG MALFORMATIONS Paul Thacker, MD Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology and Pediatrics Medical University of South Carolina DISCLOSURES I have no relevant
HOW TO IMAGE AND DESCRIBE CONGENITAL LUNG MALFORMATIONS Paul Thacker, MD Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology and Pediatrics Medical University of South Carolina DISCLOSURES I have no relevant
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy. Basic Training
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
Cardiac CT in Infants with Congenital heart disease Sunrise Session. LaDonna Malone, MD May 17, 2018
 Cardiac CT in Infants with Congenital heart disease Sunrise Session LaDonna Malone, MD May 17, 2018 None Disclosures Objectives Describe cardiac CT techniques used in infants with congenital heart disease.
Cardiac CT in Infants with Congenital heart disease Sunrise Session LaDonna Malone, MD May 17, 2018 None Disclosures Objectives Describe cardiac CT techniques used in infants with congenital heart disease.
Exam 2 Respiratory Disorders
 Exam 2 Respiratory Disorders Common Cold Common Cold Pathology Common Cold Consequences Rhinosinusitis Rhinosinusitis Pathology Rhinosinusitis ostia can close due to Influenza (Flu) Influenza Pathology
Exam 2 Respiratory Disorders Common Cold Common Cold Pathology Common Cold Consequences Rhinosinusitis Rhinosinusitis Pathology Rhinosinusitis ostia can close due to Influenza (Flu) Influenza Pathology
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
There are four general types of congenital lung disorders:
 Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
Lung- and airway emergencies
 Lung- and airway emergencies Charlotte de Lange,MD,PhD Pediatric Radiology unit, Oslo University Hospital, Norway 5th Nordic course - Emergency Radiology Oslo 18-21.5.2015 clange@ous-hf.no How come pediatric
Lung- and airway emergencies Charlotte de Lange,MD,PhD Pediatric Radiology unit, Oslo University Hospital, Norway 5th Nordic course - Emergency Radiology Oslo 18-21.5.2015 clange@ous-hf.no How come pediatric
